Reliability of Cutting Edge Radius Estimator Based on Chip Production Rate for Micro End Milling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Previous Research
2.1. Cutting Edge Radius
2.2. Previous Experiment
3. Calibration
3.1. Size Filtering Threshold for Simulation Data
3.2. Size Filtering Threshold for Experimental Data
3.3. Drop Detection Threshold
4. Cutting Edge Radius Estimation
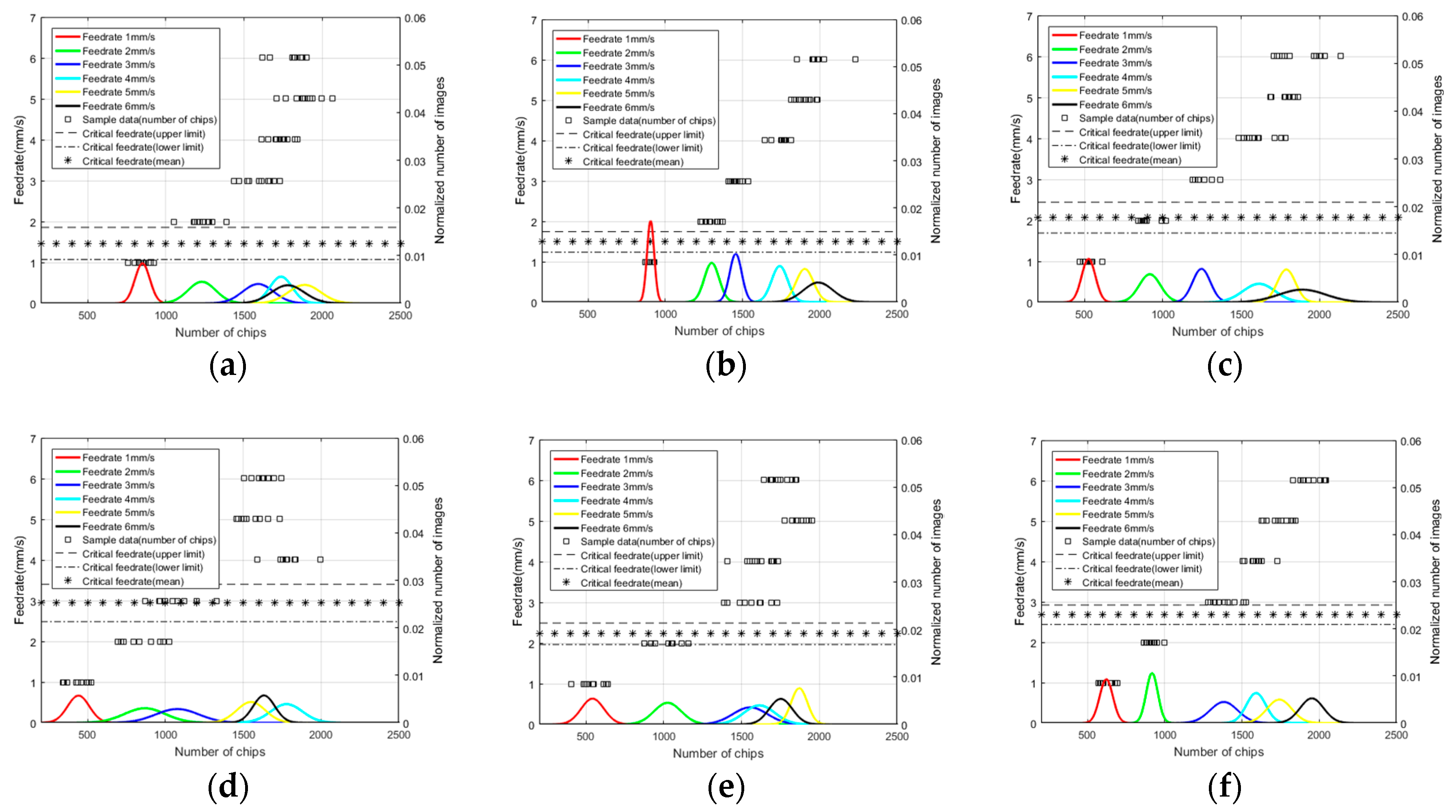
5. Result
6. Conclusions
- The average value of the probabilities of correct estimation from the experiments is 84.05%. The probabilities of correct estimation from the experiments are more than 70% except in Exp. 3 with 64.91%. Exps. 2, 5, and 6 show probabilities of correct estimation above 90%.
- In Exps. 1, 3, and 4, the standard deviation values of the actual critical feedrates are larger than the standard deviation values from the other experiments. As a result, the probabilities of wrong estimation are larger in Exps. 1, 3, and 4 than in Exps. 2, 5, and 6, due to the influence of the standard deviation on the estimation.
- The critical feedrate in this experiment can be only approximated to within 1mm/s. Since the feedrate increment in the experiment is 1 mm/s, it is only possible to estimate what feedrate range the critical feedrate is within. Further experiments are needed to determine if a higher precision of estimation is possible by using a feedrate increment smaller than 1 mm/s.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alting, L.; Kimura, F.; Hansen, H.N.; Bissacco, G. Micro Engineering. CIRP Ann. 2003, 52, 635–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T. State of the Art of Micromachining. CIRP Ann. 2000, 49, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornfeld, D.; Min, S.; Takeuchi, Y. Recent advances in mechanical micromachining. CIRP Ann. 2006, 55, 745–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussul, E.M.; Rachkovskij, D.A.; Baidyk, T.N.; Talayev, S.A. Micromechanical engineering: A basis for the low-cost manufacturing of mechanical microdevices using microequipment. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1996, 6, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-J.; Mayor, J.R.; Ni, J. A Static Model of Chip Formation in Microscale Milling. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2005, 126, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, A.; Li, M.; Mayor, R.; Forest, C.R. Micromilling of molds for microfluidic blood diagnostic devices. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Precision Engineering, Monterey, CA, USA, 4–9 October 2009; pp. 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guckenberger, D.J.; de Groot, T.E.; Wan, A.M.D.; Beebe, D.J.; Young, E.W.K. Micromilling: A method for ultra-rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2364–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owens, C.E.; Hart, A.J. High-precision modular microfluidics by micromilling of interlocking injection-molded blocks. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramcharoen, A.; Mativenga, P.T. Size effect and tool geometry in micromilling of tool steel. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanqiang, L.; Zhenyu, S.; Yi, W. Definition and determination of the minimum uncut chip thickness of microcutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; DeVor, R.E.; Kapoor, S.G. An analytical model for the prediction of minimum chip thickness in micromachining. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2006, 128, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegert, J.C.; Pathak, J.P.; Jokiel, B. An Ultra-high Speed Spindle for Micro-milling. In Proceedings of the ASPE, Portland, OR, USA, 26–31 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Jia, Z.; Liang, S.Y. The flank wear prediction in micro-milling Inconel 718. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2018, 70, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, J.R.; Sodemann, A.A. Intelligent tool-path segmentation for improved stability and reduced machining time in micromilling. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2008, 130, 031121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przestacki, D.; Chwalczuk, T.; Wojciechowski, S. The study on minimum uncut chip thickness and cutting forces during laser-assisted turning of WC/NiCr clad layers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3887–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducobu, F.; Filippi, E.; Rivière-Lorphèvre, E. Chip formation and minimum chip thickness in micro-milling. In Proceedings of the 12th CIRP Conference on Modeling of Machining Operations, Donostia-San Sebastian, Spain, 7–8 May 2009; pp. 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Oliaei, S.N.B.; Karpat, Y. Influence of tool wear on machining forces and tool deflections during micro milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 84, 1963–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, S.; Conley, C.M.; Wasserman, M.B.; Ozdoganlar, O.B. An experimental investigation of micro-machinability of copper 101 using tungsten carbide micro-endmills. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, L.; Azcárate, S.; Herrero, A.; Lopez de Lacalle, L.N.; Lamikiz, A. Mechanistic modelling of the micro end milling operation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2008, 222, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadeff, L.L.; Marshall, M.B.; Curtis, D.T.; Slatter, T. Protocol for tool wear measurement in micro-milling. Wear 2019, 420–421, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Melkote, S.N.; Rahman, M.; Kumar, A.S. Experimental study of micro- and nano-scale cutting of aluminum 7075-T6. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weule, H.; Hüntrup, V.; Tritschler, H. Micro-Cutting of Steel to Meet New Requirements in Miniaturization. CIRP Ann. 2001, 50, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissacco, G.; Hansen, H.N.; De Chiffre, L. Size Effects on Surface Generation in Micro Milling of Hardened Tool Steel. CIRP Ann. 2006, 55, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehorn, A.G.; Jiang, J.; Orban, P.E.; Bordatchev, E.V. State-of-the-art methods and results in tool condition monitoring: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2004, 26, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepsonthi, T.; Özel, T. Experimental and finite element simulation based investigations on micro-milling Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy: Effects of cBN coating on tool wear. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucun, İ.; Aslantas, K.; Bedir, F. An experimental investigation of the effect of coating material on tool wear in micro milling of Inconel 718 super alloy. Wear 2013, 300, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Peng, F.Y.; Yan, R.; Yao, P.F.; Yang, C.C.; Li, B. Analytical modeling and experimental validation of micro end-milling cutting forces considering edge radius and material strengthening effects. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2015, 97, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, I.N.; Bao, W.Y.; Reen, N.S.; Kropas-Hughes, C.V. Genetic tool monitor (GTM) for micro-end-milling operations. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Chiou, S.-J. Application of backpropagation neural network for spindle vibration-based tool wear monitoring in micro-milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Balazinski, M.; Baron, L.; Jemielniak, K.; Botez, R.; Achiche, S. Type-2 fuzzy tool condition monitoring system based on acoustic emission in micromilling. Inf. Sci. 2014, 255, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Mei, T.; Ye, D. Online Condition Monitoring in Micromilling: A Force Waveform Shape Analysis Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3806–3813. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Sodemann, A.A.; Bajaj, A.K. Experimental Validation of Chip Production Rate as a Tool Wear Identification in Micro-EndMilling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. (accepted).
- Lee, J.-H.; Sodemann, A.A. Geometrical Simulation of Chip Production Rate in Micro-EndMilling. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Sodemann, A.A. Digital Image Processing for Counting Chips in Micro-End-Milling. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Vision, Image and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–29 August 2018; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Sodemann, A.A. Simulation of Cutting Edge Wear Model based on Chip Production Rate in Micro-endmilling. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 14th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference (MSEC2019), Erie, PA, USA, 10–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]







| Exp. | Experimental Size Filtering Threshold | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimum Filtering Threshold | Maximum r-Squared | Slope | Y-Intercept (Offset) | |
| 1 | 47 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 63.76 |
| 2 | 126 | 0.80 | 0.24 | –132.23 |
| 3 | 124 | 0.88 | 0.15 | 10.46 |
| 4 | 150 | 0.85 | 0.13 | 9.46 |
| 5 | 172 | 0.94 | 0.14 | –14.48 |
| 6 | 116 | 0.91 | 0.23 | –36.81 |
| Exp. | Probability of Estimation and Threshold (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Optimum Threshold (%) | Max. Probability (%) | |
| 1 | 27 | 78 |
| 2 | 23 | 99 |
| 3 | 25 | 62 |
| 4 | 31 | 77 |
| 5 | 25 | 92 |
| 6 | 25 | 97 |
| Exp. | Actual Critical Feedrate (mm/s) (Mean (±Std.)) | Probability of Estimation (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Critical Feedrate | ||||||
| 1–2 mm/s | 2–3 mm/s | 3–4 mm/s | 4–5 mm/s | None | ||
| 1 | ) | 76.95 | 13.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 10.05 |
| 2 | 98.81 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.69 | |
| 3 | 17.29 | 64.91 | 17.05 | 0.75 | 0.75 | |
| 4 | 7.27 | 74.29 | 18.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 5 | 4.92 | 92.67 | 0.32 | 2.10 | 2.10 | |
| 6 | 2.01 | 96.66 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 0.11 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Sodemann, A.A. Reliability of Cutting Edge Radius Estimator Based on Chip Production Rate for Micro End Milling. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3010025
Lee J-H, Sodemann AA. Reliability of Cutting Edge Radius Estimator Based on Chip Production Rate for Micro End Milling. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2019; 3(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jue-Hyun, and Angela A. Sodemann. 2019. "Reliability of Cutting Edge Radius Estimator Based on Chip Production Rate for Micro End Milling" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 3, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3010025
APA StyleLee, J.-H., & Sodemann, A. A. (2019). Reliability of Cutting Edge Radius Estimator Based on Chip Production Rate for Micro End Milling. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 3(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3010025





