The Influence of Servo Drive Control on the NC Vertical Milling Machine Dynamic Compliance
Abstract
1. Introduction
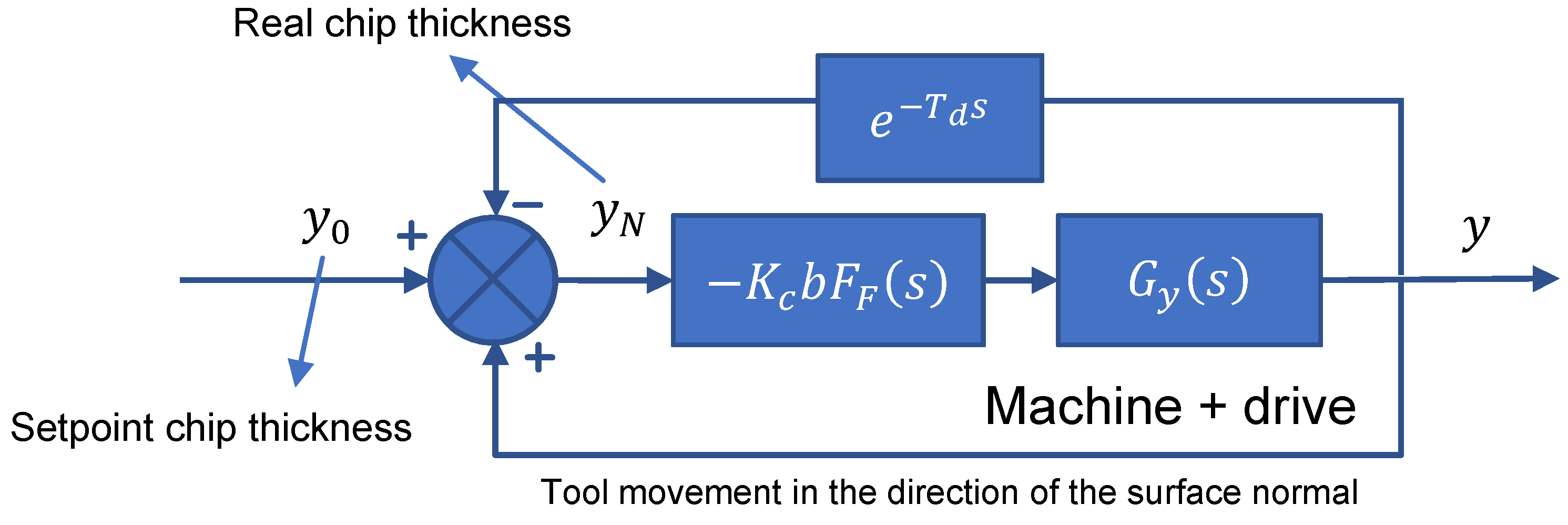
2. Proposed Methodology
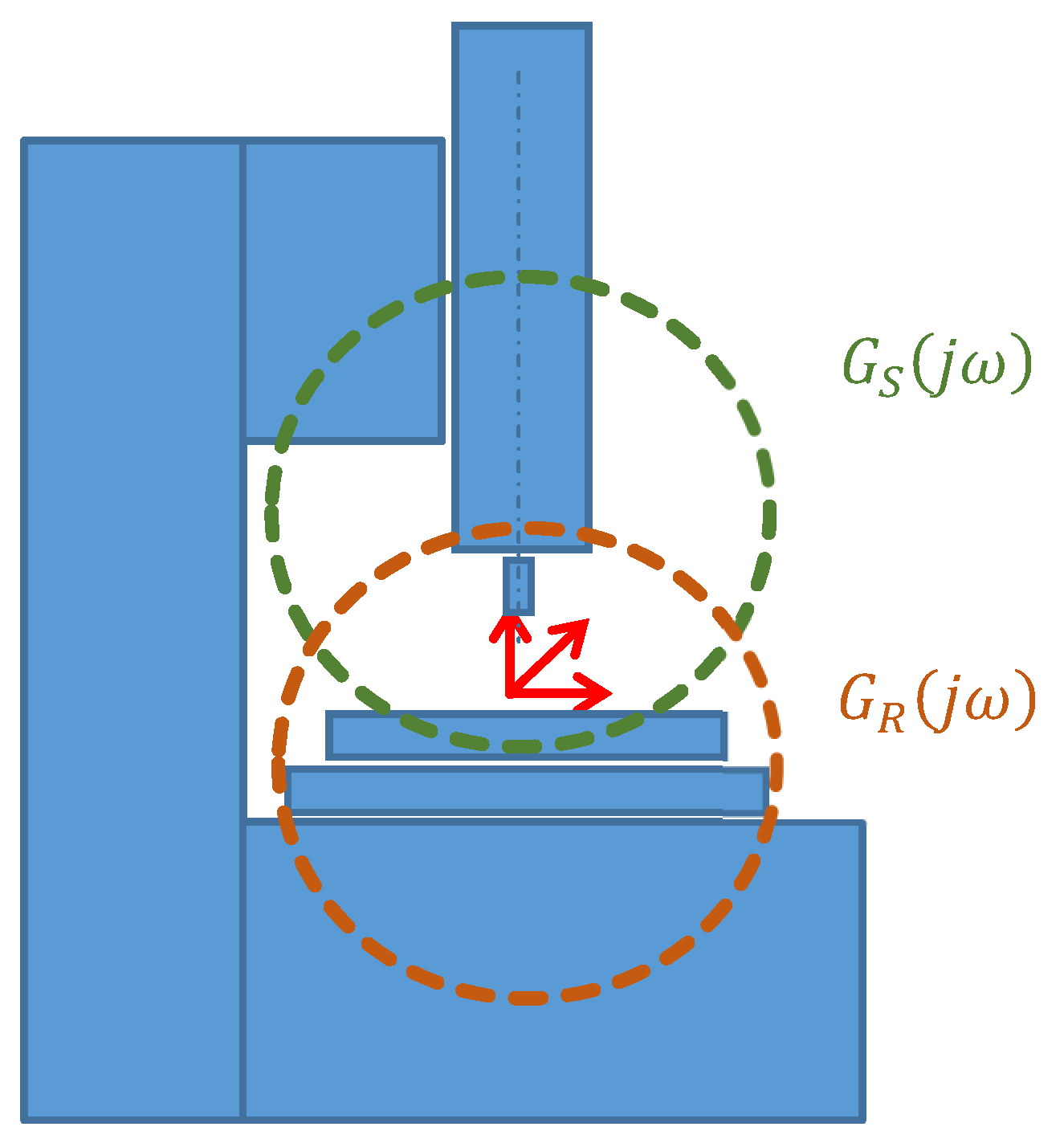
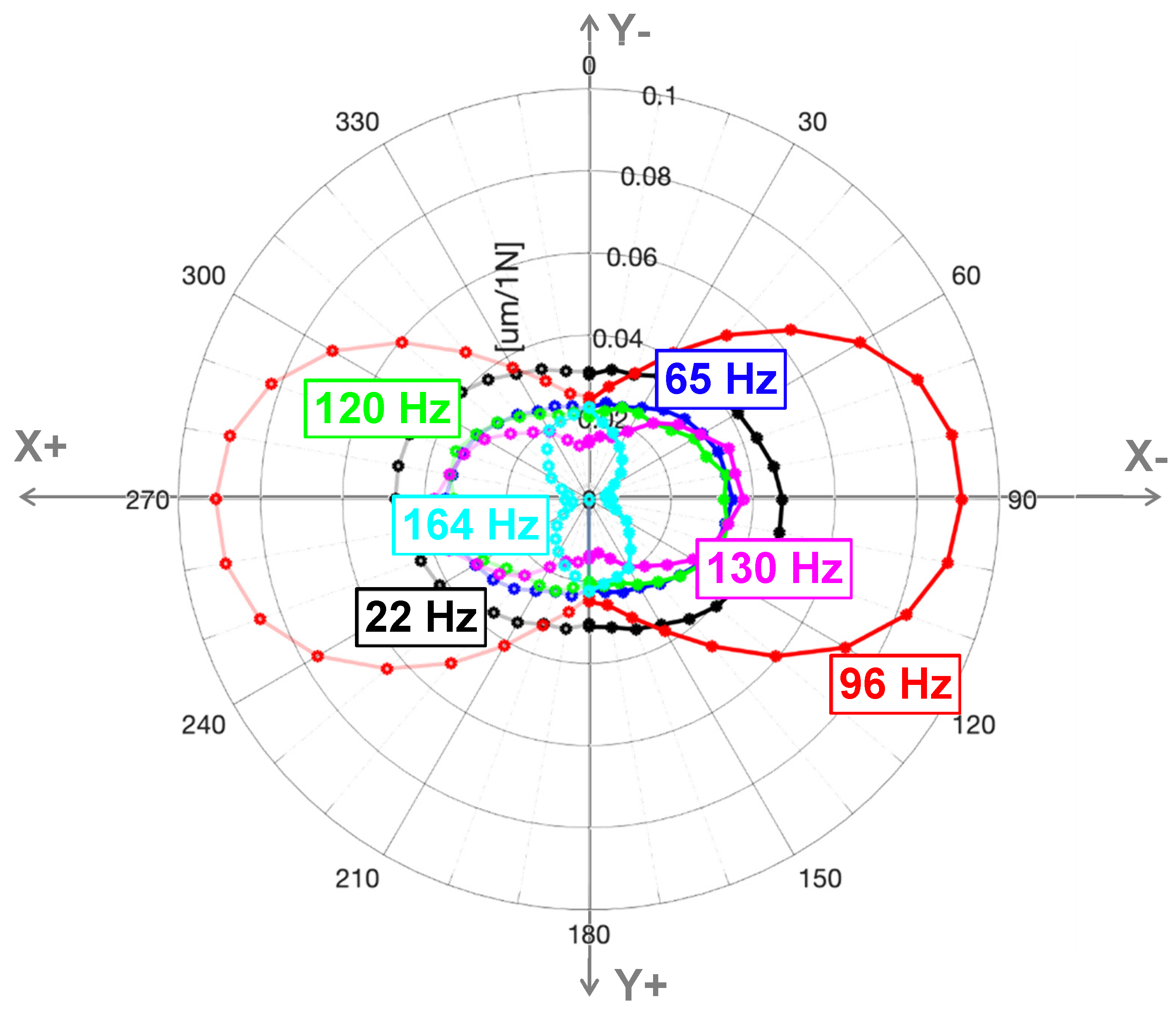
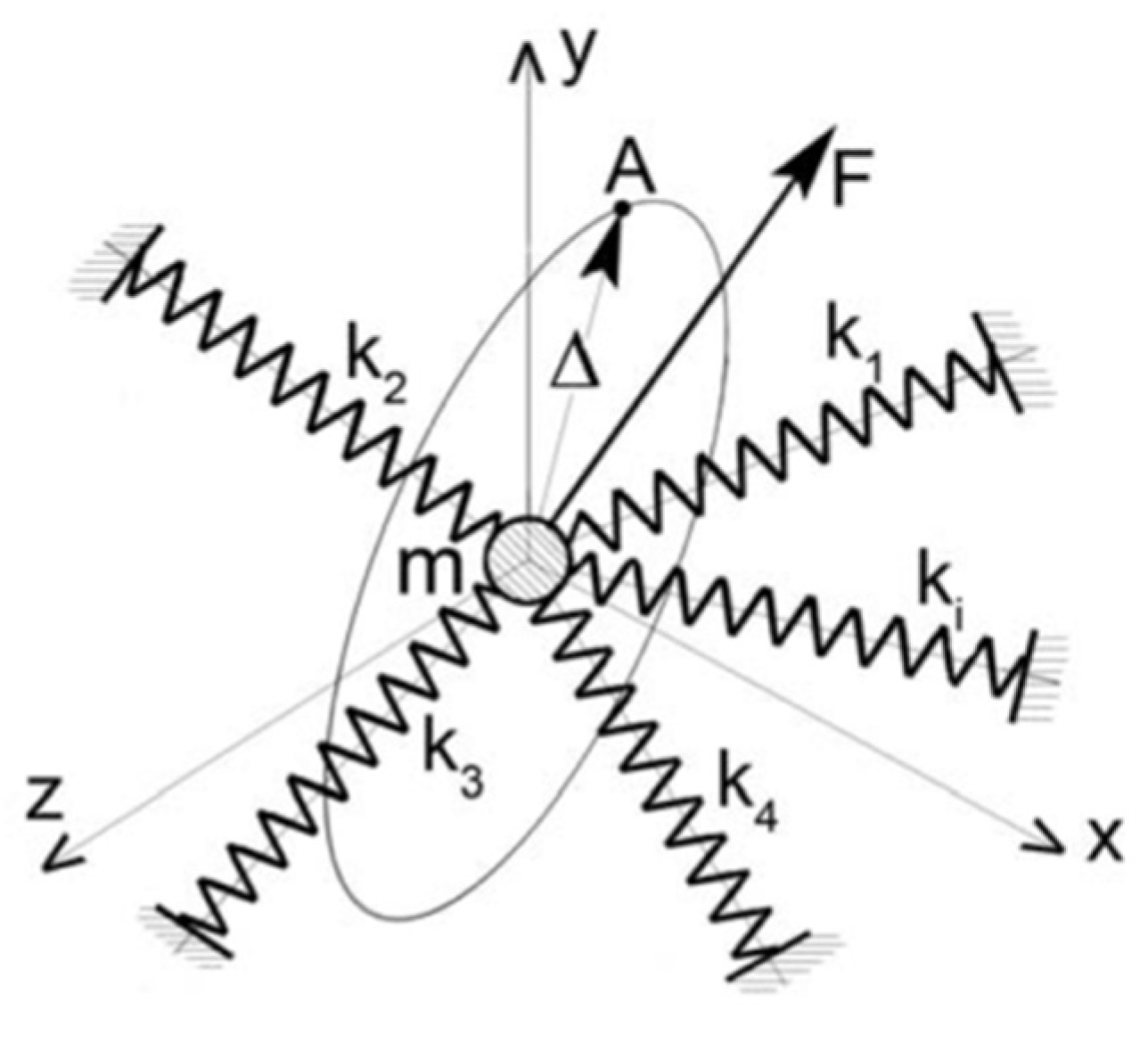
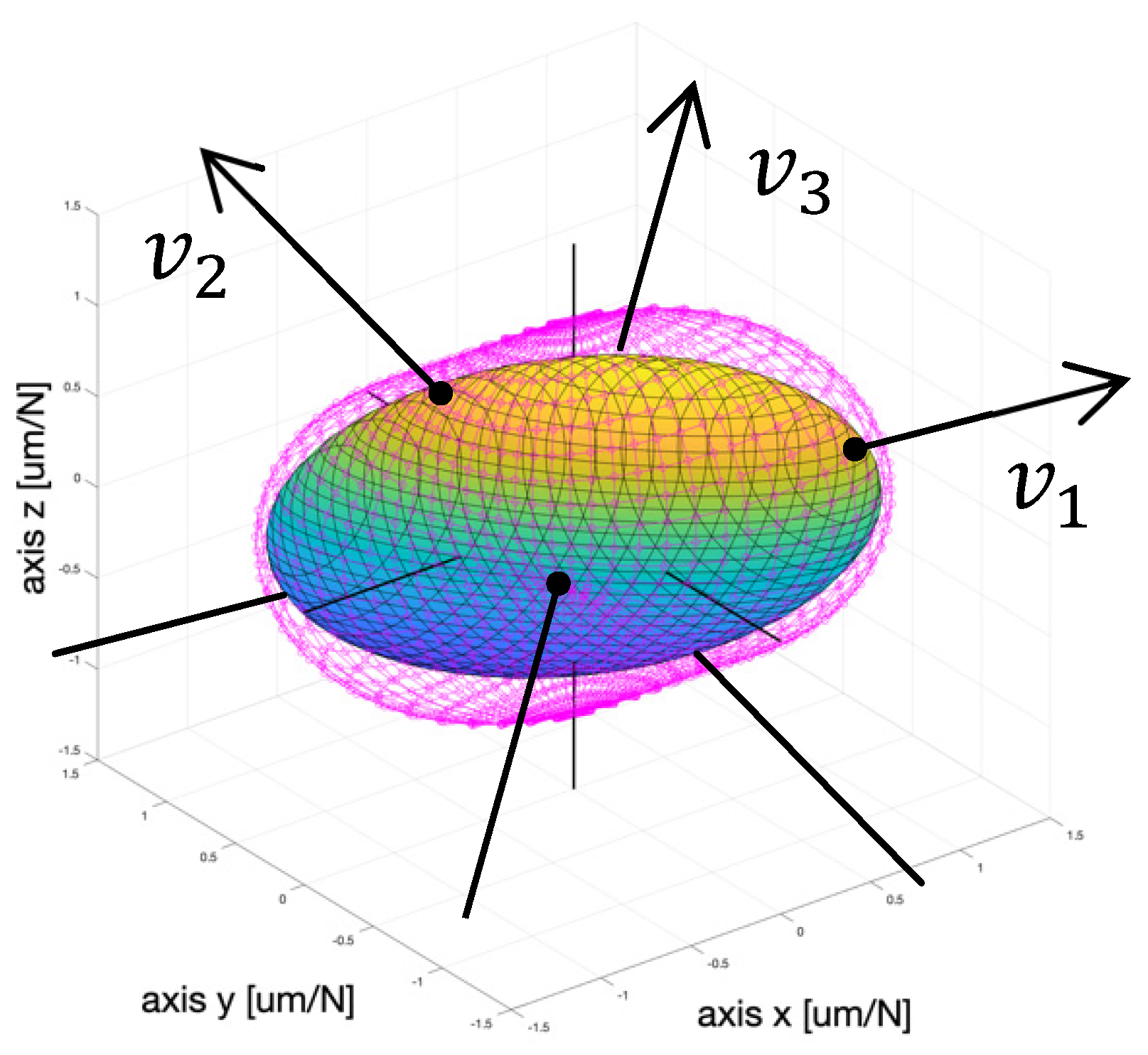
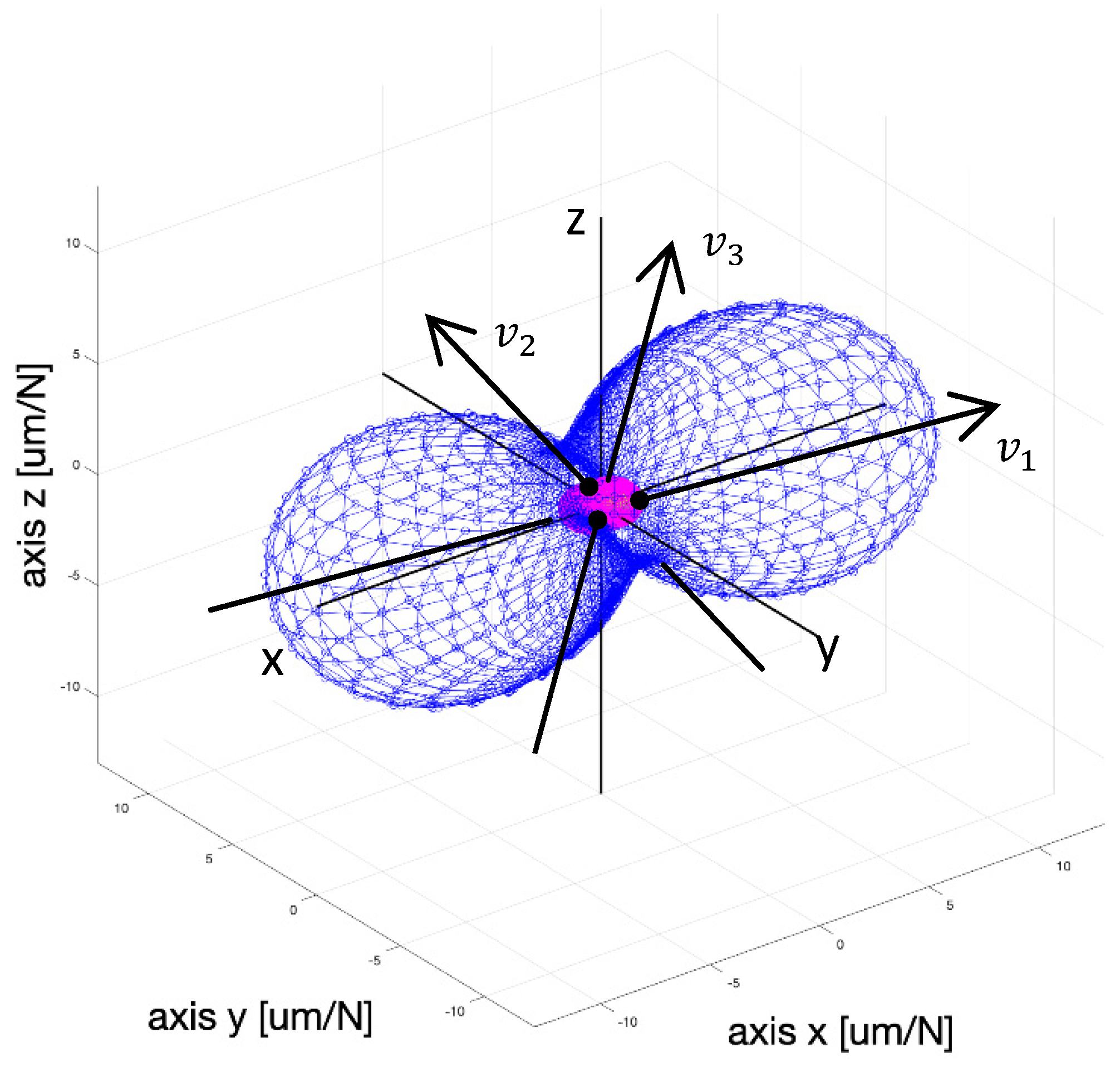
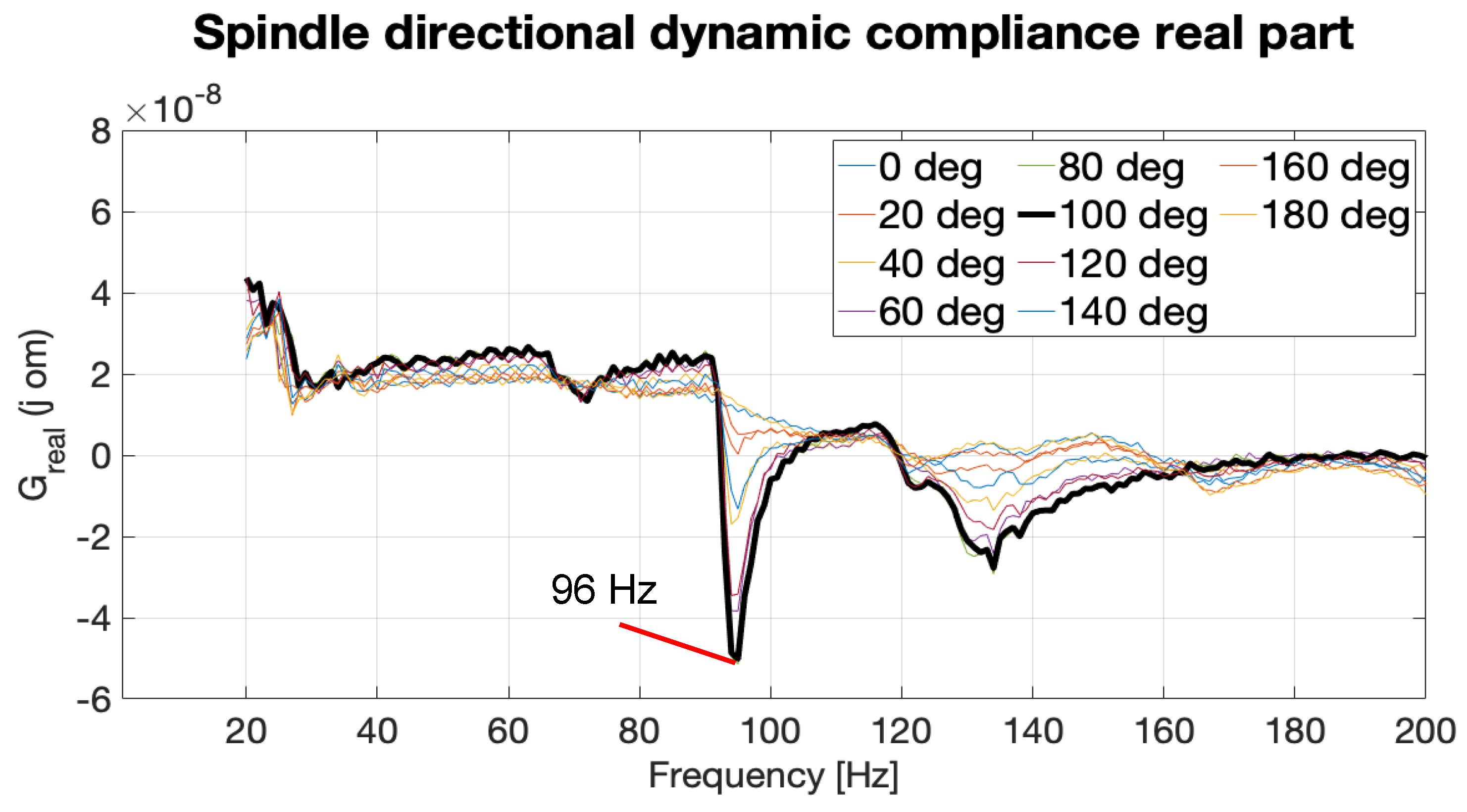
3. Spindle Dynamic Compliance
- Displacement in the force direction
- Natural frequency
- Modal damping
- Eigenvectors
- Directional force cosine vector
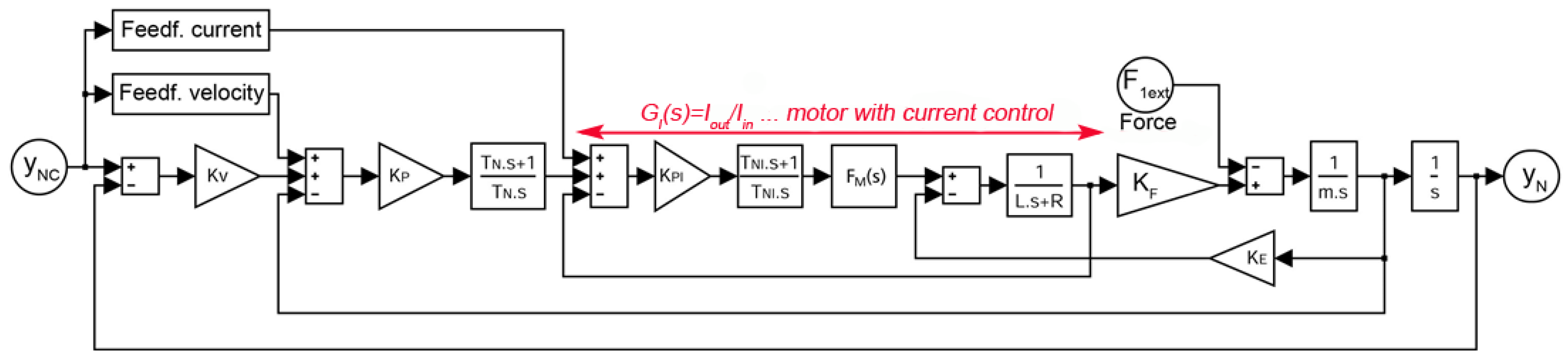
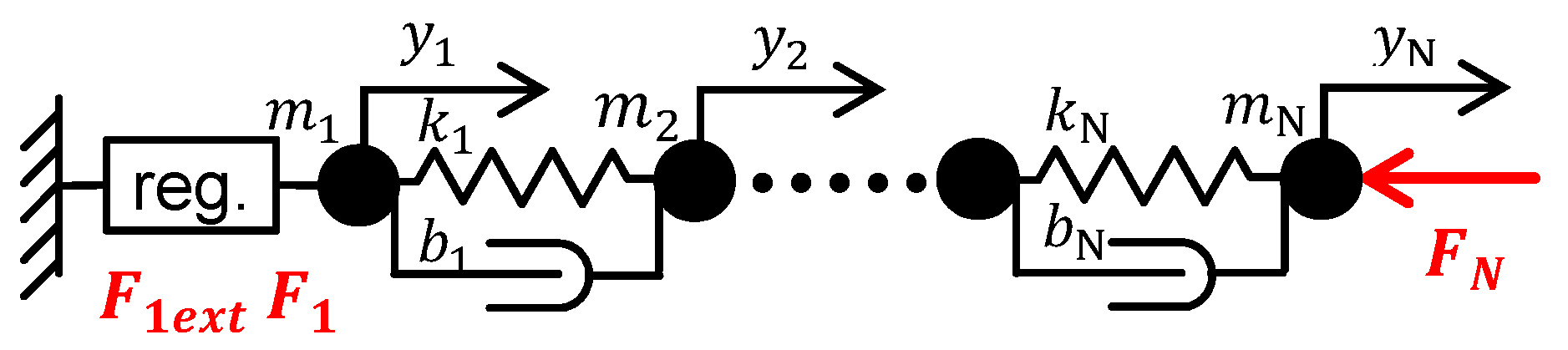
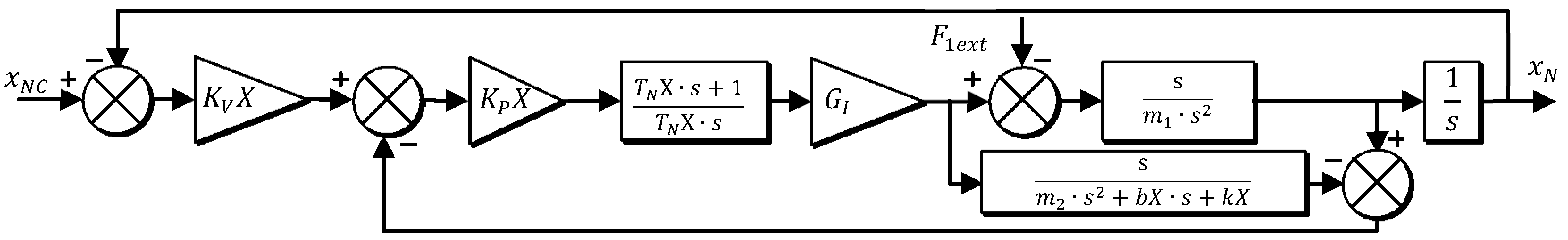
4. Structural Model of Feed Drive Axis
4.1. One-Mass Model of Linear Motor Feed Drive
4.2. N-Mass Model of Linear Motor Feed Drive
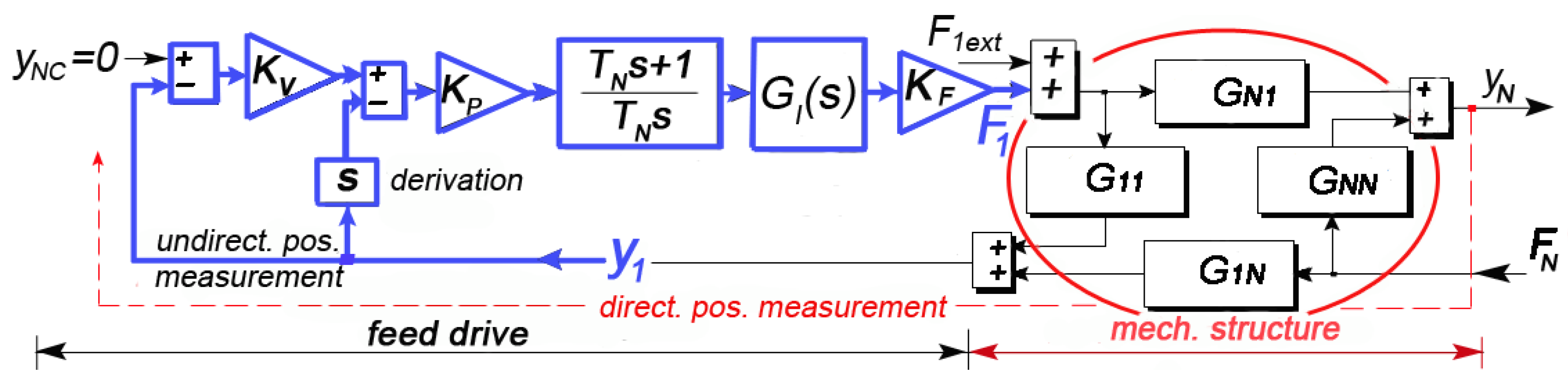
4.3. General Dynamic Compliance Matrix of Mechanic Structure and Feed Drive Control
- can be obtained from the motor current commutation position sensors.
- motor force can be simulated by the additional current source.
5. Feed Drive Coupled Model of the Machining Center
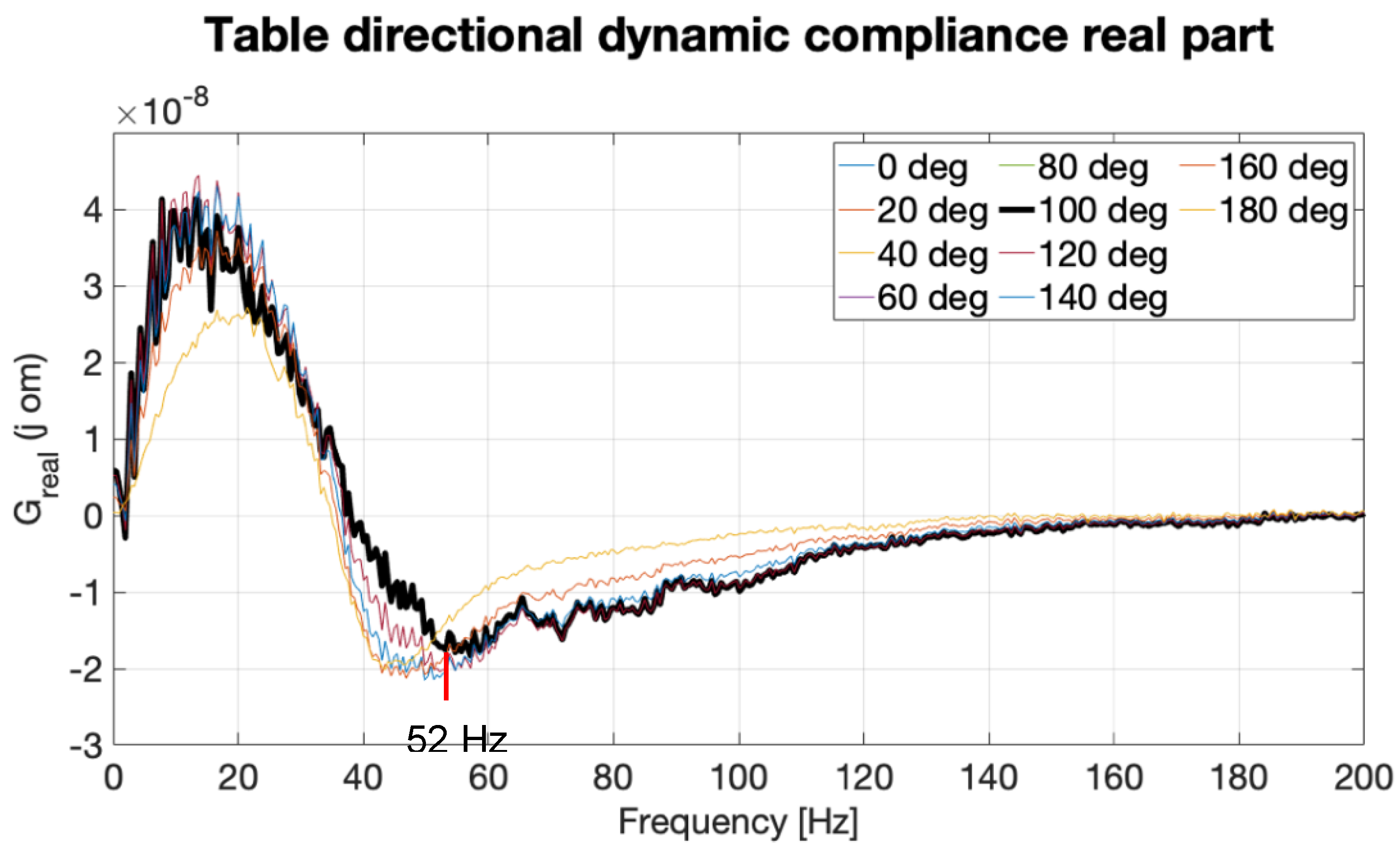
5.1. Machine Tool Spindle
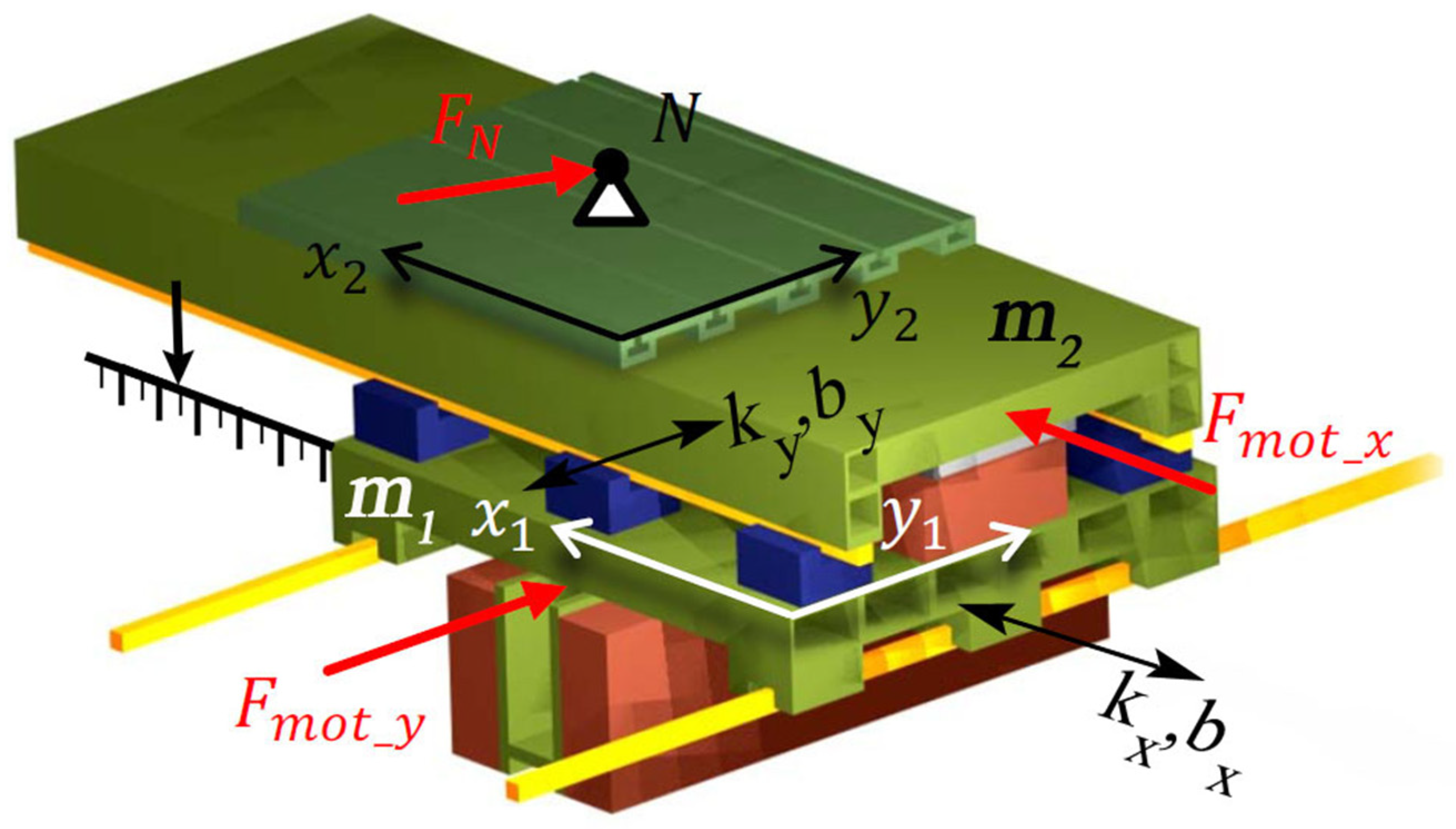
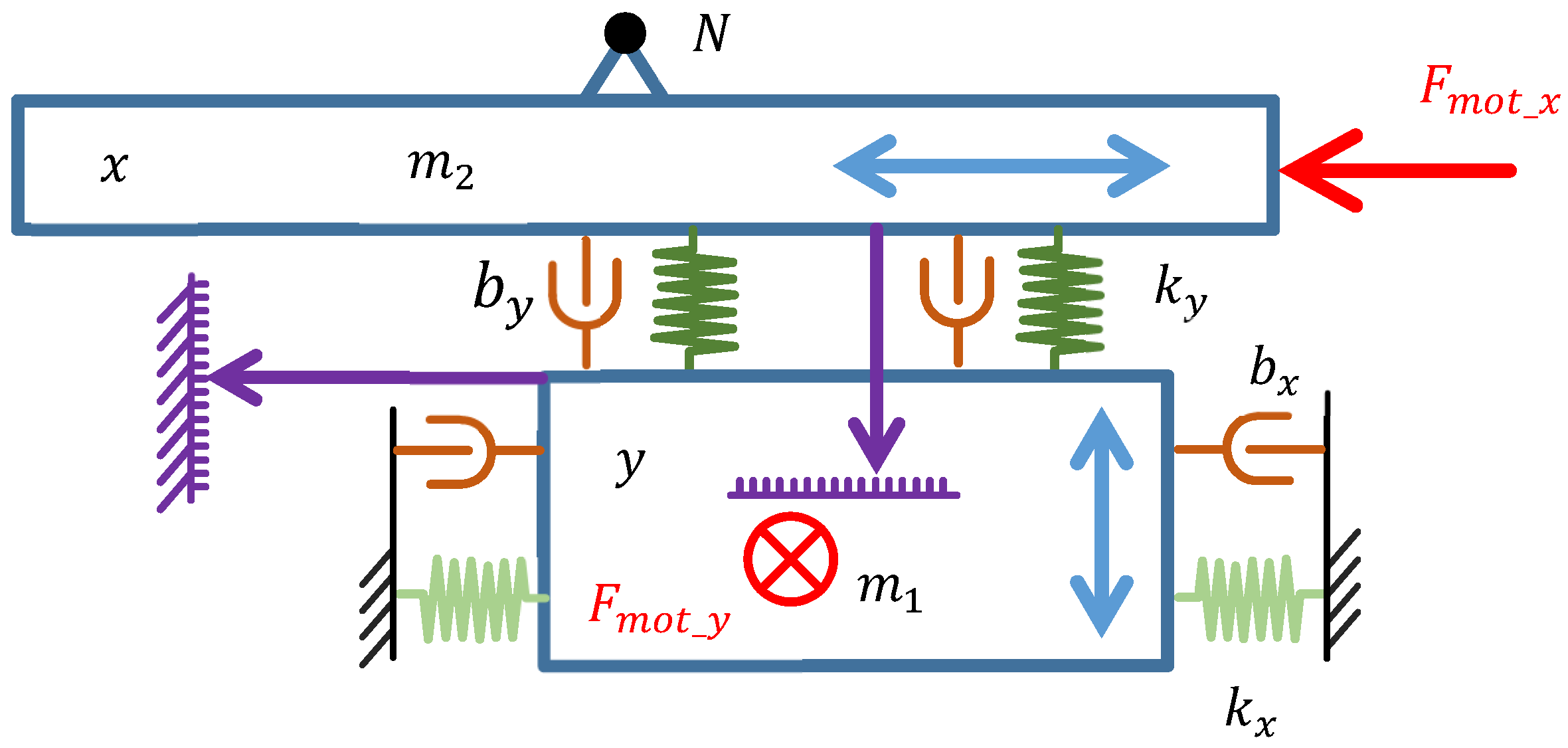
5.2. Machine Tool XY Cross Table
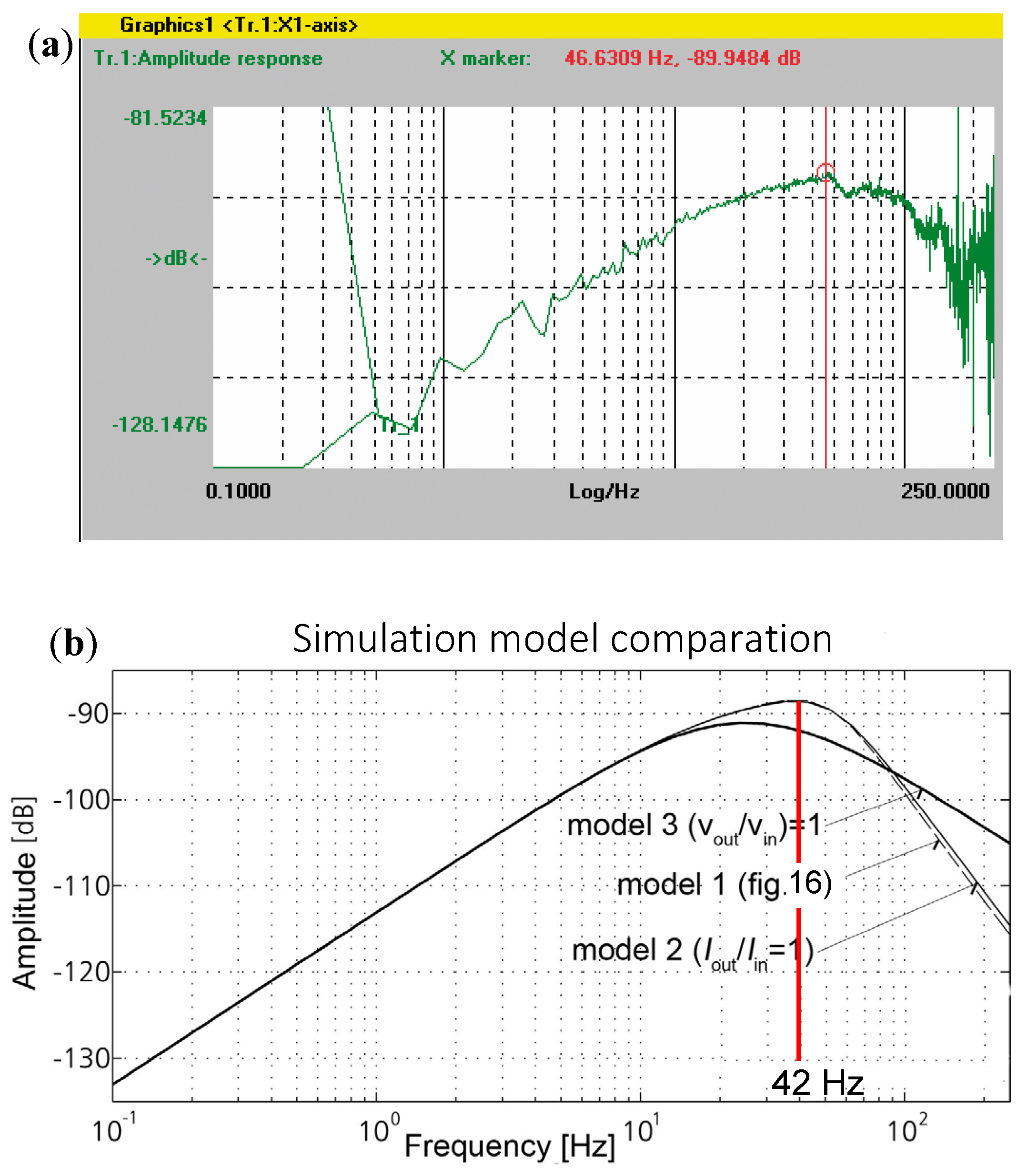
5.2.1. X Axis
- Model —represents the complete system shown in Figure 16 including inner ;
- Model —represents the system where the current transfer function is simplified: and is accepted for further modelling;
- Model —represents the system where the velocity transfer function is simplified: .
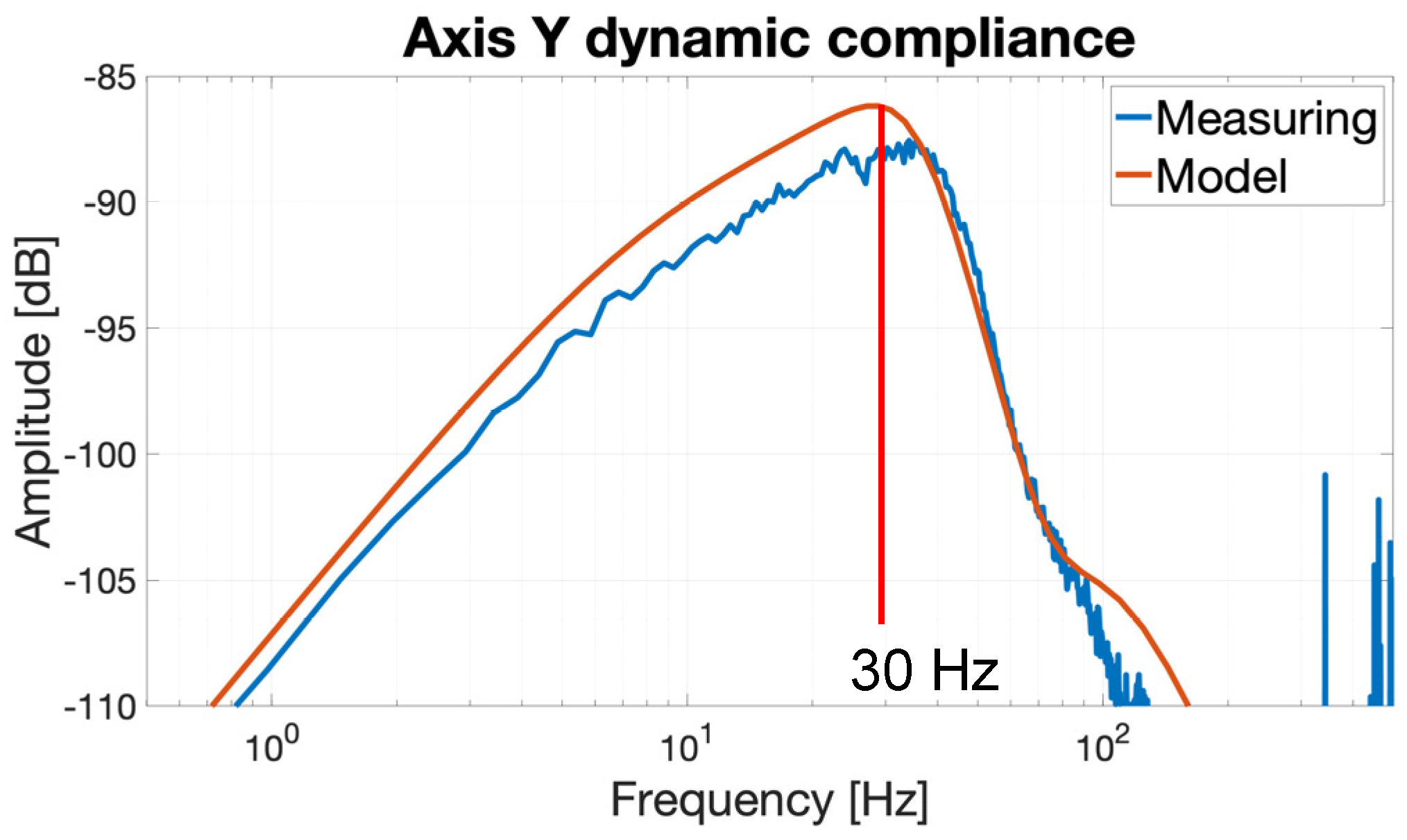
5.2.2. Y Axis
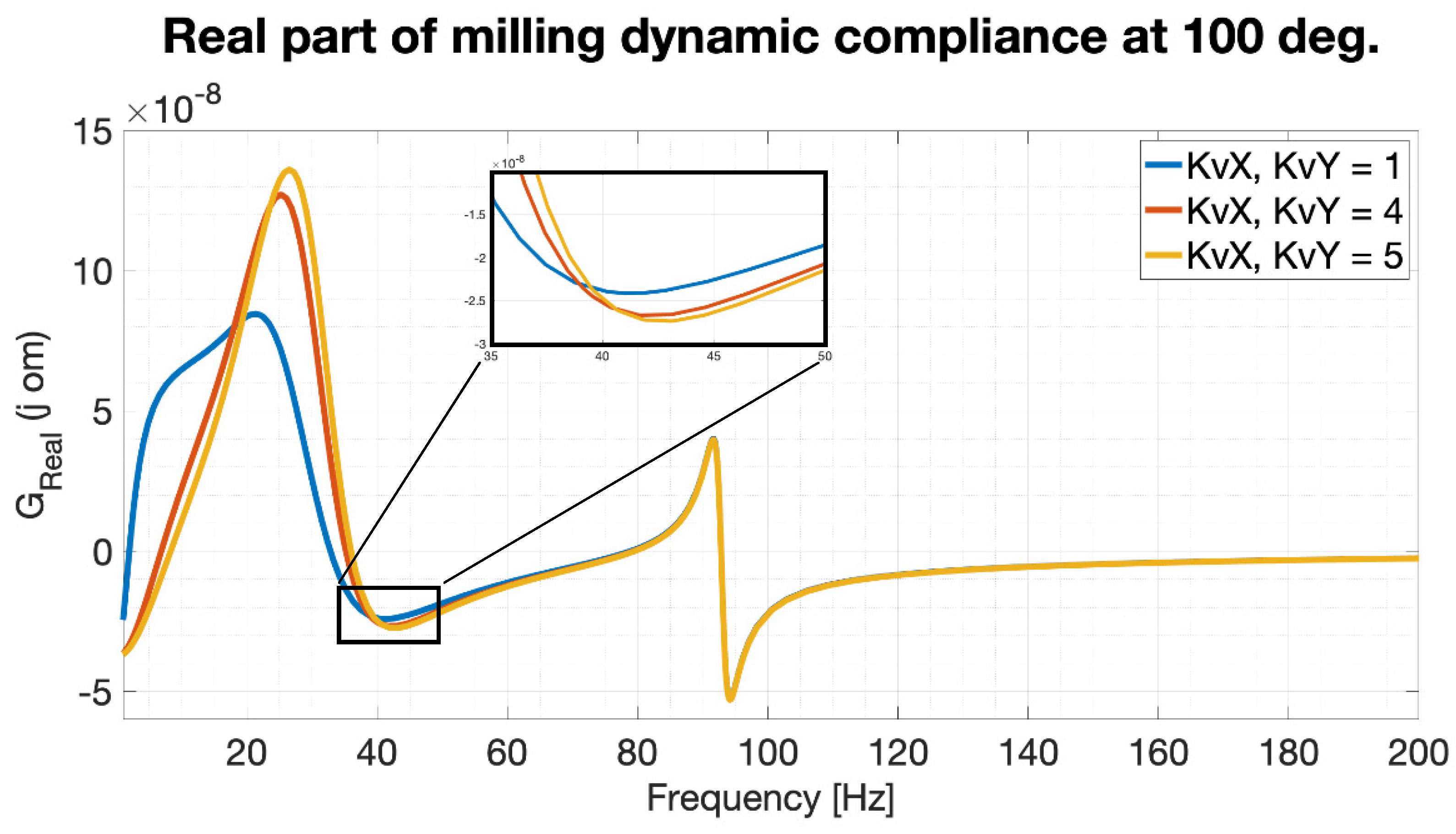
6. Impact of Feed Drive Control Parameters on Machining Stability Prediction
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Controller dynamic transfer function | ||
| Damping coefficient | ||
| Critical depth of cut | ||
| Local limit depth of cut | ||
| Directional force cosine vector | ||
| Additional force transfer function | ||
| Mechanical model dynamic compliance matrix entries | ||
| Current transfer function | ||
| Mechanical part transfer function | ||
| Mechanical model dynamic compliance matrix | ||
| Cross table transfer function | ||
| General dynamic compliance matrix | ||
| General dynamic compliance matrix entries | ||
| Real part of G transfer function | ||
| Feed drive transfer function | ||
| Spindle transfer function | ||
| Velocity transfer function | ||
| Machine and drive transfer function | ||
| Current input signal | ||
| Current output signal | ||
| Stiffness | ||
| Cutting force coefficient | ||
| Force constant | ||
| Proportional velocity loop gain | ||
| Proportional current loop gain | ||
| Proportional position loop gain | ||
| Time delay | ||
| Velocity integration constant | ||
| Current integration constant | ||
| Displacement in the force direction | ||
| Eigenvectors | ||
| Velocity input signal | ||
| Velocity output signal | ||
| Linear scale | ||
| Requested chip thickness | ||
| Linear scale | ||
| Real cutting depth | ||
| Damping ratio | ||
| Modal damping | ||
| Natural frequencies | ||
| Chip width | ||
| Damping coefficients matrix | ||
| Acting forces vector | ||
| Acting forces | ||
| Finite Element Method | ||
| Stiffness matrix | ||
| Inductance | ||
| Mass matrix | ||
| Mass | ||
| Resistance | ||
| Rounds per second | ||
| Laplace operator | ||
| Stability lobe diagram | ||
| Axis direction | ||
| Actual position | ||
| Linear scale vector | ||
| [°] | Angle of measurement | |
| Frequency |
References
- Tlustý, J.; Poláček, M. The stability of machine tools against self-excited vibrations in machining, International Research in Production Engineering. Proc. ASME Int. 1963, 1, 465–474. [Google Scholar]
- Tobias, S.A.; Fishwick, W. Theory of regenerative machine tool chatter. Engineer 1958, 205, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana, G.; Ciurana, J. Chatter in machining processes: A review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2011, 51, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, J.; Sulitka, M.; Souček, P. Influence of linear feed drive controller setting in CNC turning lathe on the stability of machining. J. Mach. Eng. 2019, 19, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Verl, A.; Brecher, C.; Uriarte, L.; Pritschow, G. Machine tool feed drives. CIRP Ann. 2011, 60, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertelli, P.; Cau, N.; Bianchi, G.; Monno, M. The effects of dynamic interaction between machine tool subsystems on cutting process stability. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 58, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotzky, D.; Turi, J.; Insperger, T. Stabilizability diagram for turning processes subjected to digital PD control. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2014, 2, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beudaert, X.; Mancisidor, I.; Ruiz, L.M.; Barrios, A.; Erkorkmaz, K.; Munoa, J. Analysis of the feed drives control parameters on structural chatter vibrations. In Proceedings of the XIIIth International Conference on High Speed Machining, Metz, France, 4–5 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, O.; Bedauert, X.; Erkorkmaz, K.; Barrios, A.; Munoa, J. Machining chatter stability limit improvement by means of feed drive control parameters. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Virtual Machining Process Technology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–25 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, O.; Bedauert, X.; Erkorkmaz, K. Effect of Rack and Pinion Feed Drive Control Parameters on Machine Tool Dynamics. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beudaert, X.; Franco, O.; Erkorkmaz, K.; Zatarain, M. Feed drive control tuning considering machine dynamics and chatter stability. CIRP Ann. 2020, 69, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, H. Regeneration Theory. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1932, 11, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y. Manufacturing automation: Metal cutting mechanics, machine tool vibrations, and CNC design. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, B84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, T.L.; Smith, K.S. Machining Dynamics: Frequency Response to Improved Productivity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Altintas, Y.; Budak, E. Analytical Prediction of Stability Lobes in Milling. CIRP Ann. 1995, 44, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weck, M.; Brecher, C. Werkzeugmaschinen 5: Messtechnische Untersuchung und Beurteilung, dynamische Stabilität; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Drobilek, J.; Polacek, M.; Bach, P.; Janota, M. Improved dynamic cutting force model with complex coefficients at orthogonal turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souček, P.; Bubák, A. Vybrané Statě Z Kmitání V Pohonech Výrobních Strojů (The Chatter in Feed Drives of Production Machines: Summary); České vysoké učení technické: Praze, Czech Republic, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Smolík, J.; Houša, J. Křížový Stůl S Lineárními Pohony Z Nekonvenčních Materiálů (Linear Feed Drive Cross Table Made of Unconventional Materials); Společnost pro obráběcí stroje: Praha, Czech Republic, 2000. [Google Scholar]




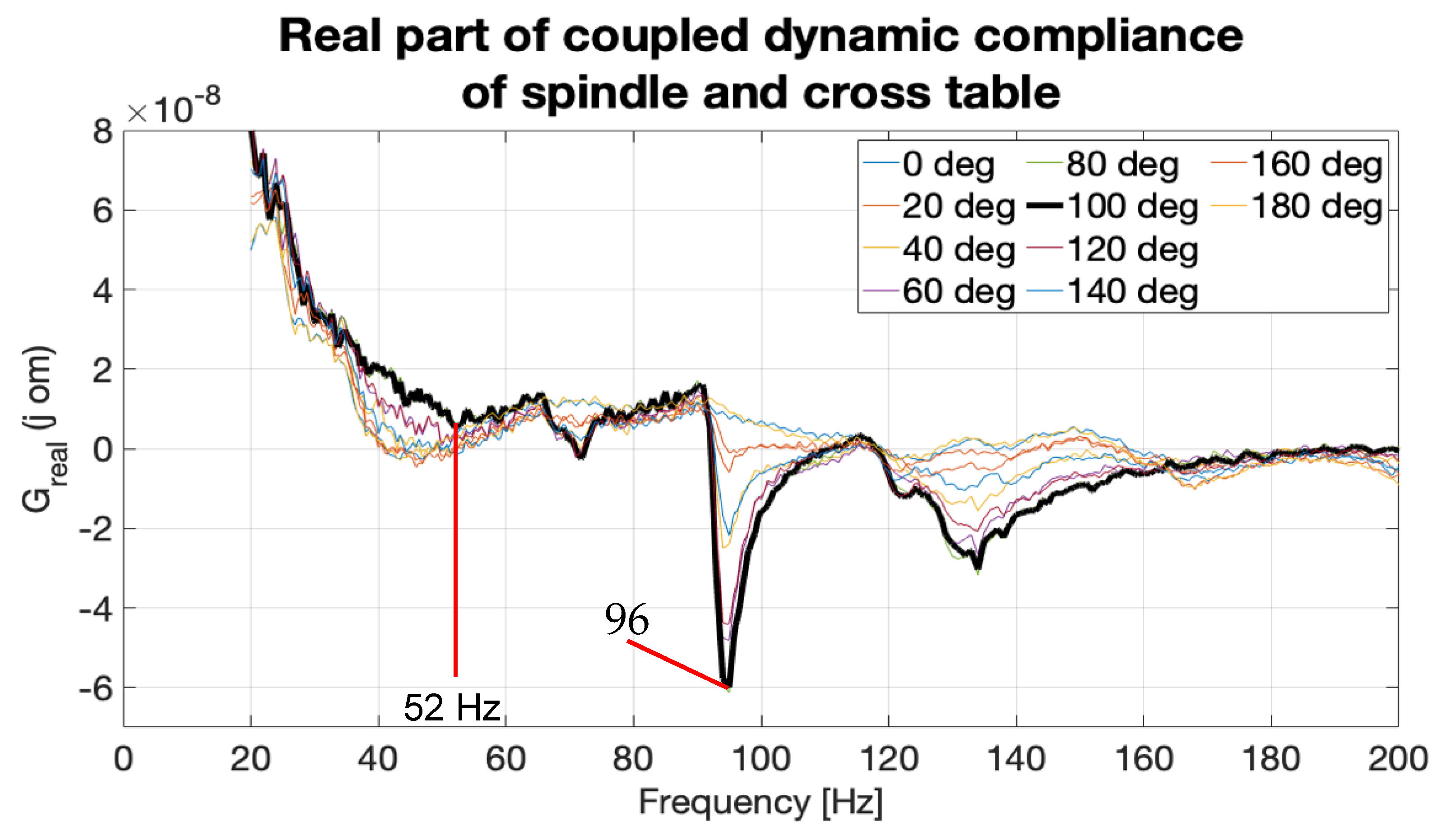


| Symbol | Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass 1 | kg | ||
| Mass 2 | |||
| Stiffness | |||
| Damping ratio | – |
| Symbol | Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass 1 | |||
| Mass 2 | m2 | ||
| Stiffness | |||
| Damping ratio | – |
| Symbol | Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | |||
| Stiffness one direction | |||
| Stiffness in perpendicular direction | |||
| Damping ratio one direction | |||
| Damping ratio in perpendicular direction |
| KvX, KvY [(m/min)/mm] | blim [mm] | Ratio [%] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.2 | 109.5 |
| 4 | 8.4 | 100 |
| 5 | 8.25 | 98.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grau, J.; Souček, P.; Sulitka, M. The Influence of Servo Drive Control on the NC Vertical Milling Machine Dynamic Compliance. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp4040111
Grau J, Souček P, Sulitka M. The Influence of Servo Drive Control on the NC Vertical Milling Machine Dynamic Compliance. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2020; 4(4):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp4040111
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrau, Jan, Pavel Souček, and Matěj Sulitka. 2020. "The Influence of Servo Drive Control on the NC Vertical Milling Machine Dynamic Compliance" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 4, no. 4: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp4040111
APA StyleGrau, J., Souček, P., & Sulitka, M. (2020). The Influence of Servo Drive Control on the NC Vertical Milling Machine Dynamic Compliance. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 4(4), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp4040111






