Virtual Sensor for Accuracy Monitoring in CNC Machines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
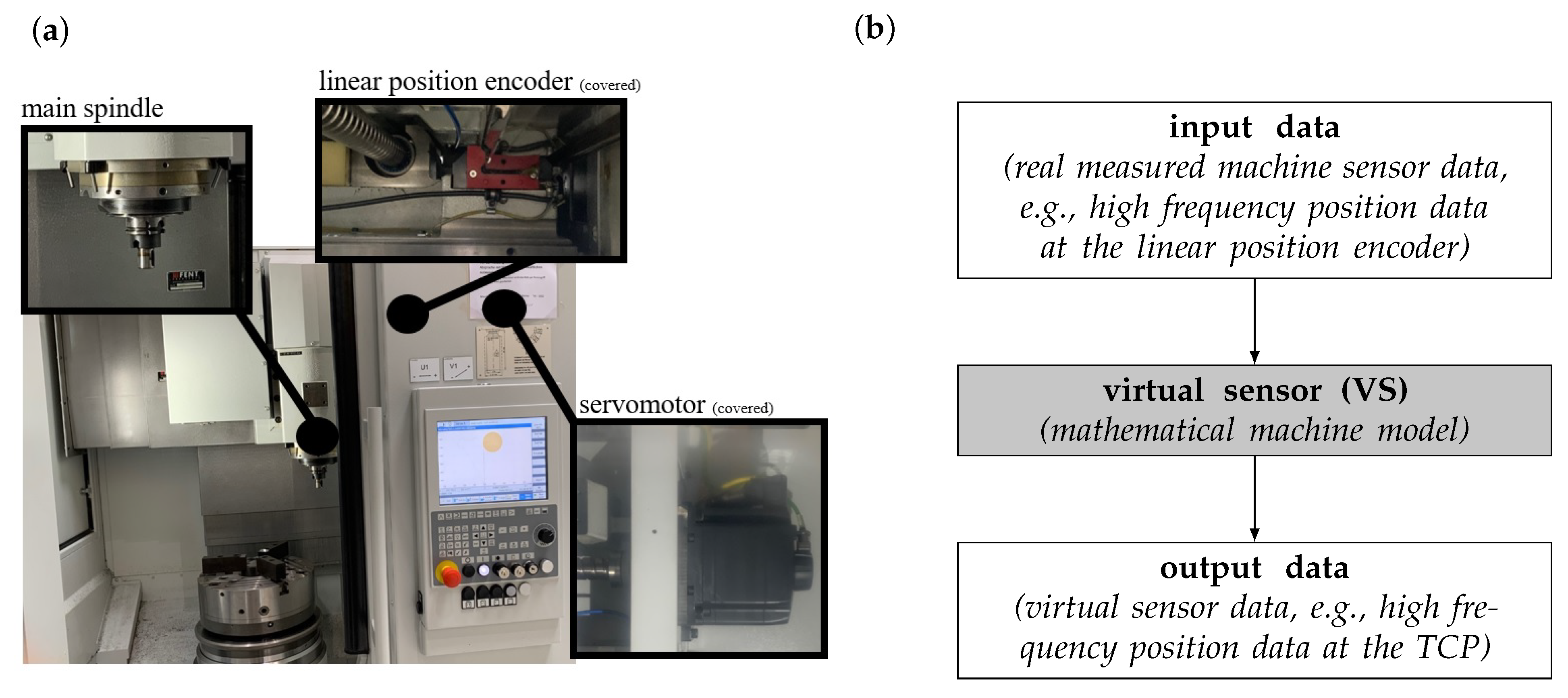
2.1. Concept of Virtual Sensor in Machine Tools
2.2. Modeling
2.3. Implementation
2.4. Strategies for Model Identification
3. Results
3.1. Measured Transmissibility Functions
3.2. Position Depending Dynamic Behaviour of Machine Tools
3.3. Modal Fitting
3.4. Verification of the Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altintas, Y.; Brecher, C.; Weck, M.; Witt, S. Virtual Machine Tool. CIRP Ann. 2005, 54, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecher, C.; Wellmann, F.; Epple, A. Quality-predictive CAM Simulation for NC Milling. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenel, A.; Seidel, A.; Friess, U.; Teicher, U.; Wiemer, H.; Wang, D.; Wenkler, E.; Penter, L.; Hellmich, A.; Ihlenfeldt, S. Digital Twins for High-Tech Machining Applications—A Model-Based Analytics-Ready Approach. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Kersting, P.; Biermann, D.; Budak, E.; Denkena, B.; Lazoglu, I. Virtual process systems for part machining operations. CIRP Ann. 2014, 63, 585–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, D.; Surmann, T.; Kersting, P. Oscillator-based approach for modeling process dynamics in NC milling with position- and time-dependent modal parameters. Prod. Eng. 2013, 7, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großmann, K.; Loeser, M. Einflussgroessen auf die Stabilitaet von Zerspanprozessen eine vergleichende Untersuchung. ZWF 2011, 106, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A.; Rauh, S.; Kolouch, M.; Radons, G. Extension of Tlustys law for the identification of chatter stability lobes in multi-dimensional cutting processes. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2014, 82, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, W. Review of tool condition monitoring methods in milling processes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 2509–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, T.; Shankar, S.; Rajasekar, R.; Pramatik, A. Tool condition monitoring techniques in milling process—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, D.; Federhen, J.; Fleischer, J. Retrofittable vibration-based monitoring of milling processes using wavelet packet transform. Procedia CIRP 2021, 96, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudana, C.K.; Kumar, H.; Narendranath, S. Condition monitoring of face milling tool using K-star algorithm and histogram features of vibration signal. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Liang, S.Y. Analytical modeling of acoustic emission for monitoring of peripheral milling process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1991, 31, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.; Krause, D. Softsensorsysteme - Mathematik als Bindeglied zum Prozessgeschehen. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2010, 82, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dementjev, A.; Hensel, B.; Kabitzsch, K.; Kauschinger, B.; Schroeder, S. Virtual Sensor for Calibration of Thermal Models of Machine Tools. Adv. Artif. Neural Syst. 2014, 2014, 347062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erwinski, K.; Paprocki, M.; Wawrzak, A.; Grzesiak, L.M. Neural network contour error predictor in CNC control systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 21st International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 29 August–1 September 2016; pp. 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieng, H.; Yang, H.C.; Hung, M.H.; Cheng, F.T. A novel virtual metrology scheme for predicting machining precision of machine tools. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Kakinuma, Y. Sensorless cutting force estimation for full-closed controlled ball-screw-driven stage. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, D.; Altintas, Y. Prediction of Cutting Forces in Five-Axis Milling Using Feed Drive Current Measurements. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2018, 23, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamar, A.; Le, T.P.; Gagnol, V.; Sabourin, L. Modal identification of a machine tool structure during machining operations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, J.; Kolouch, M.; Wittstock, V.; Putz, M. Identification of modal parameters of machine tools during cutting by operational modal analysis. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, J.; Kolouch, M.; Regel, J.; Putz, M. Investigation of the dynamic behavior of machine tools during cutting by operational modal analysis. MM SJ (MM Sci. J.) 2019, 2019, 3078–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghbani, I.; Songmene, V. Estimation of machine-tool dynamic parameters during machining operation through operational modal analysis. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Harmann, J.; Wiegaertner, G. Elektrische Vorschubantriebe in der Automatisierungstechnik: Grundlagen, Berechnung, Bemessung; Publicis: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Law, M.; Ihlenfeldt, S.; Wabner, M.; Altintas, Y.; Neugebauer, R. Position-dependent dynamics and stability of serial-parallel kinematic machines. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecher, C.; Altstädter, H.; Daniels, M. Axis Position Dependent Dynamics of Multi-axis Milling Machines. Procedia CIRP 2015, 31, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natke, H. Einführung in Theorie und Praxis der Zeitreihen- und Modalanalyse Schwingungsfähiger Elastomechanischer Systeme; Vieweg: Braunschweig, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doerrer, F.; Otto, A.; Kolouch, M.; Ihlenfeldt, S. Virtual Sensor for Accuracy Monitoring in CNC Machines. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2022, 6, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6060137
Doerrer F, Otto A, Kolouch M, Ihlenfeldt S. Virtual Sensor for Accuracy Monitoring in CNC Machines. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2022; 6(6):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6060137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoerrer, Felix, Andreas Otto, Martin Kolouch, and Steffen Ihlenfeldt. 2022. "Virtual Sensor for Accuracy Monitoring in CNC Machines" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 6, no. 6: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6060137
APA StyleDoerrer, F., Otto, A., Kolouch, M., & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2022). Virtual Sensor for Accuracy Monitoring in CNC Machines. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 6(6), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6060137





