Exploring the Effects of Laser Surface Modification on AISI 301LN Steel: A Micro-Mechanical Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Experiments
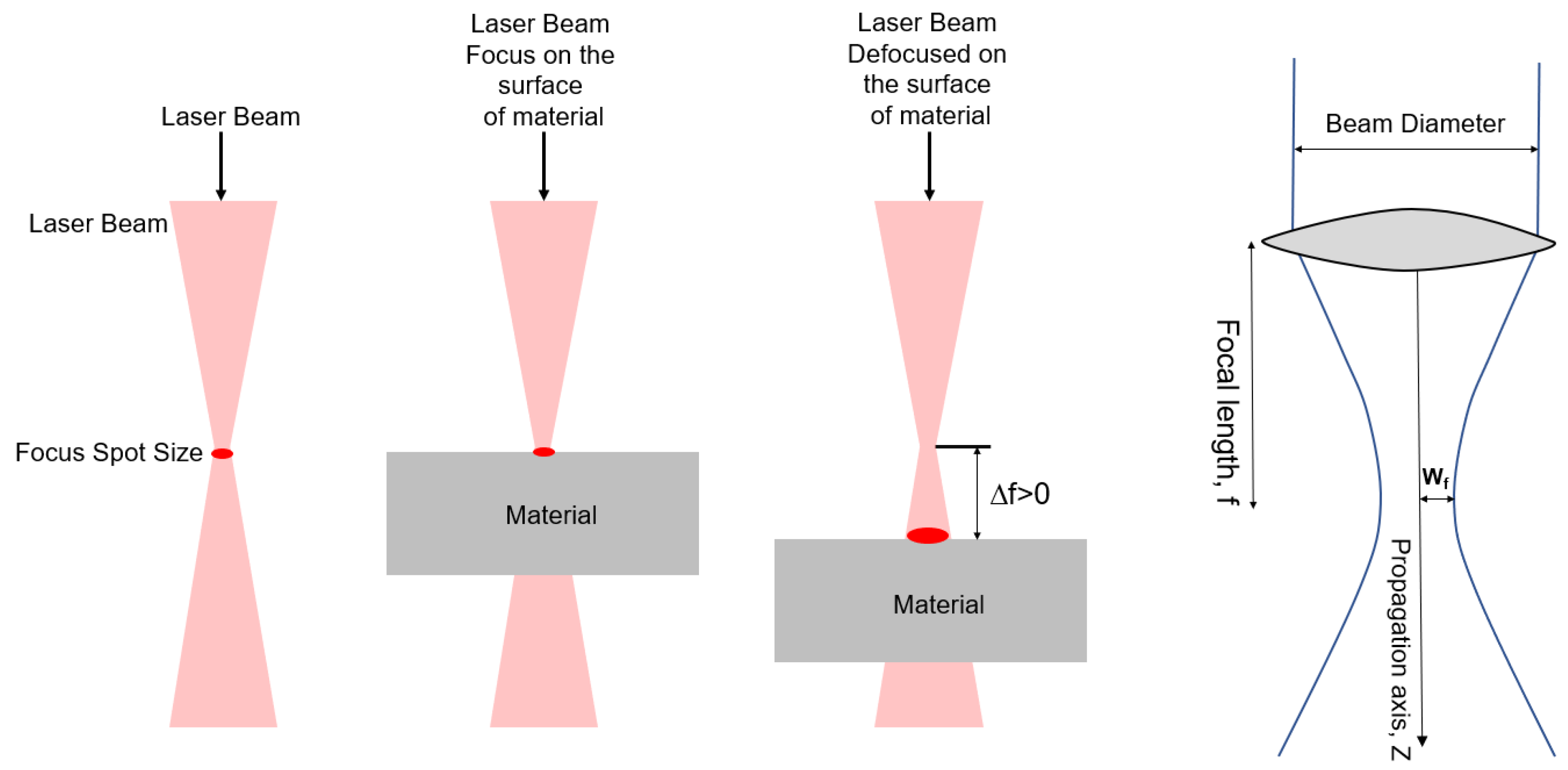
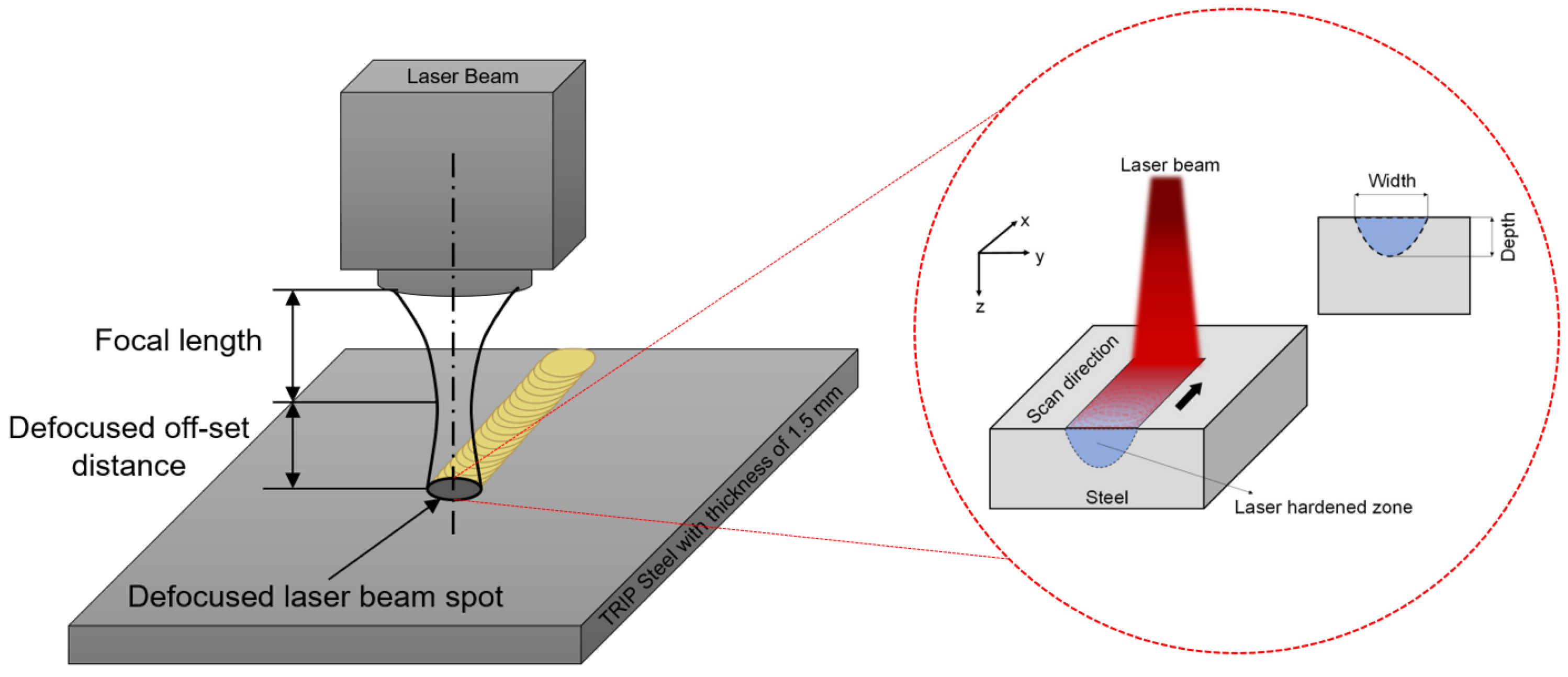
2.1. Samples Preparation and Surface Texturing
2.2. Statistical Response Surface Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization and Experimental Model
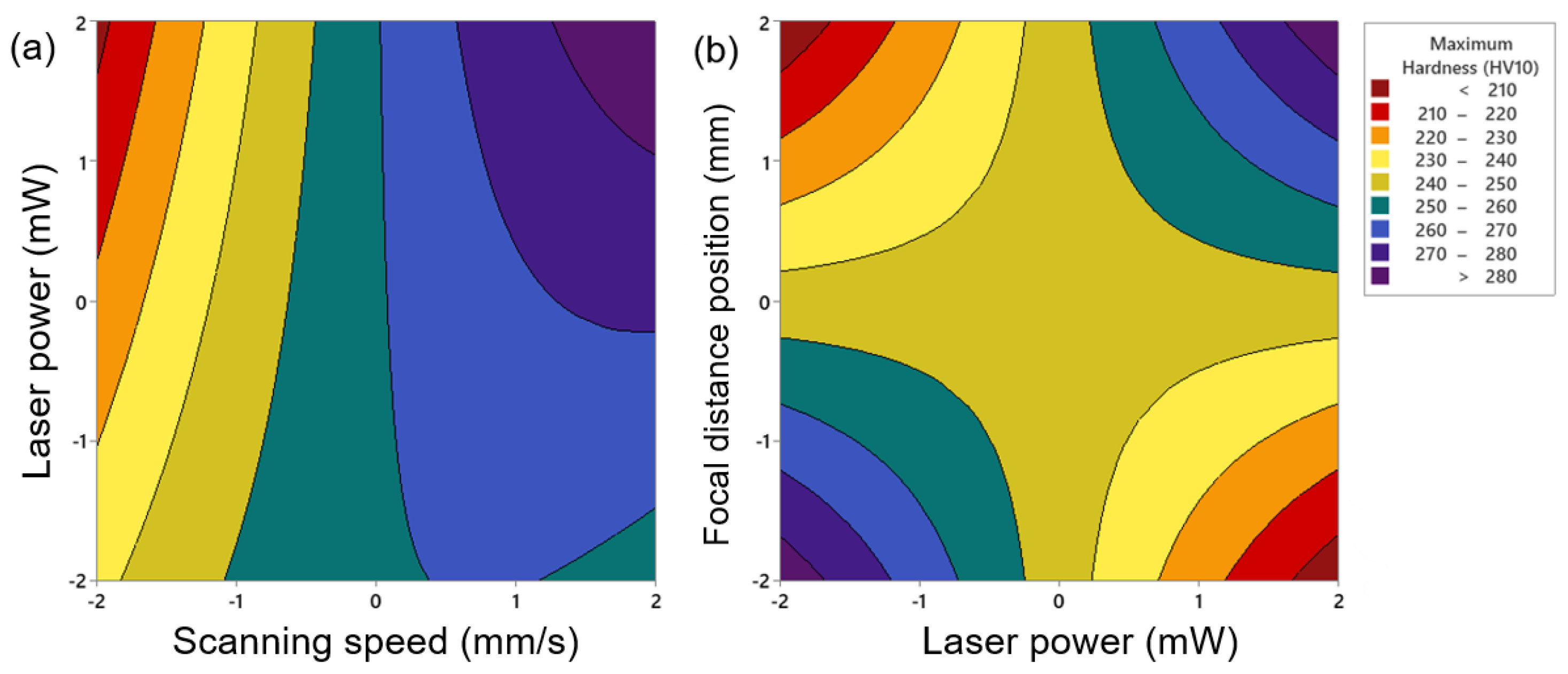
3.2. Superficial Hardness Evolution
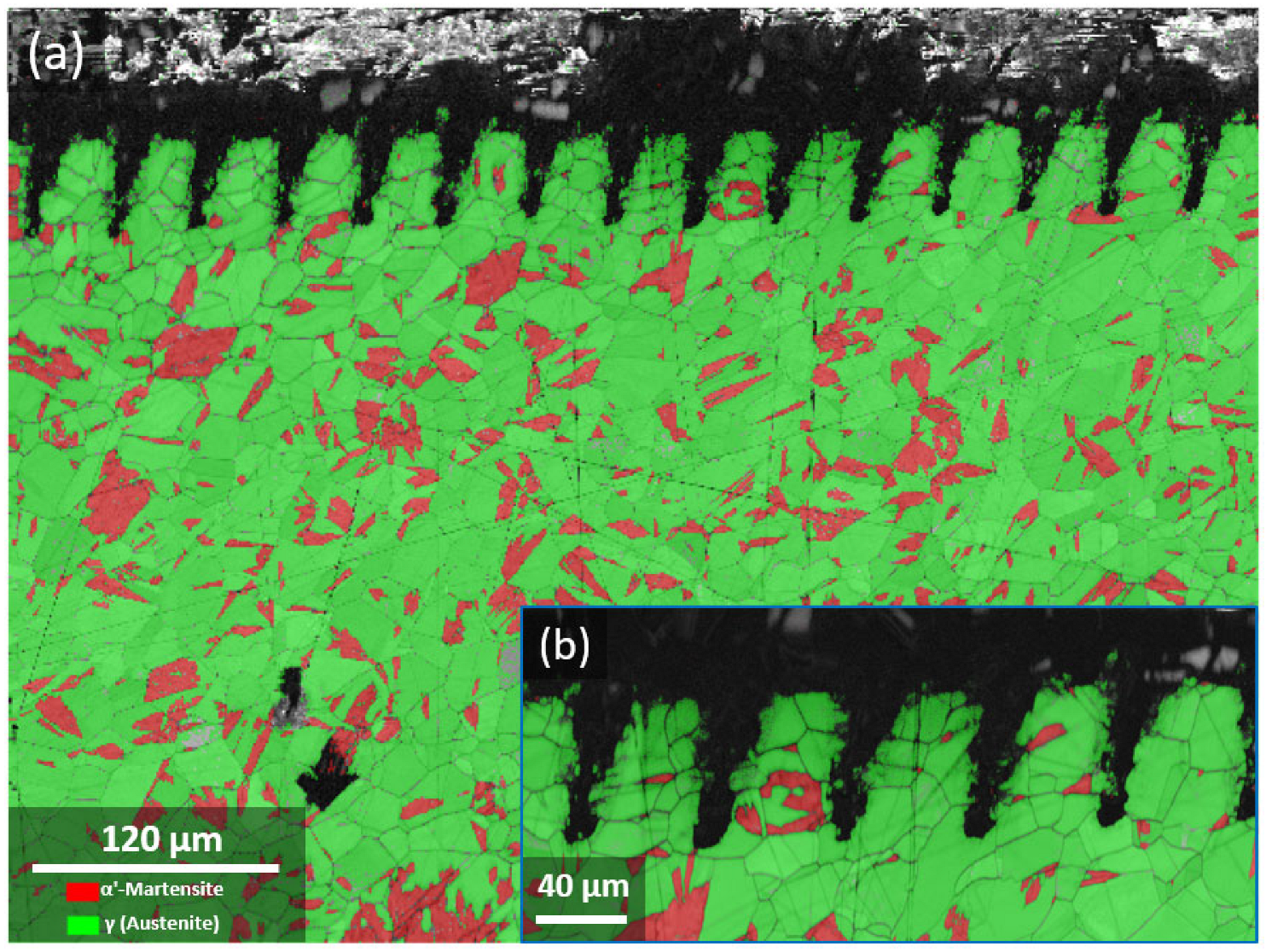
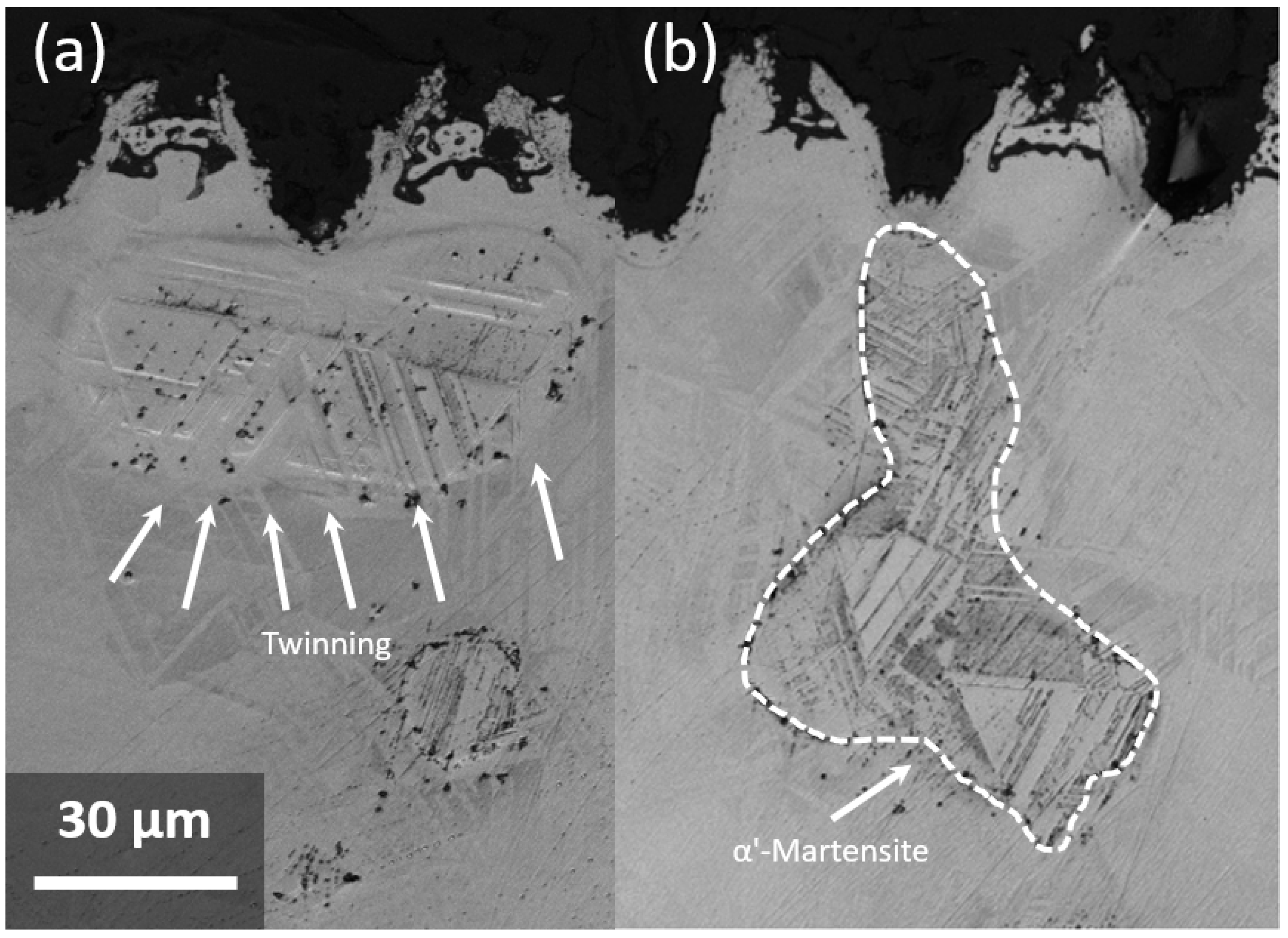
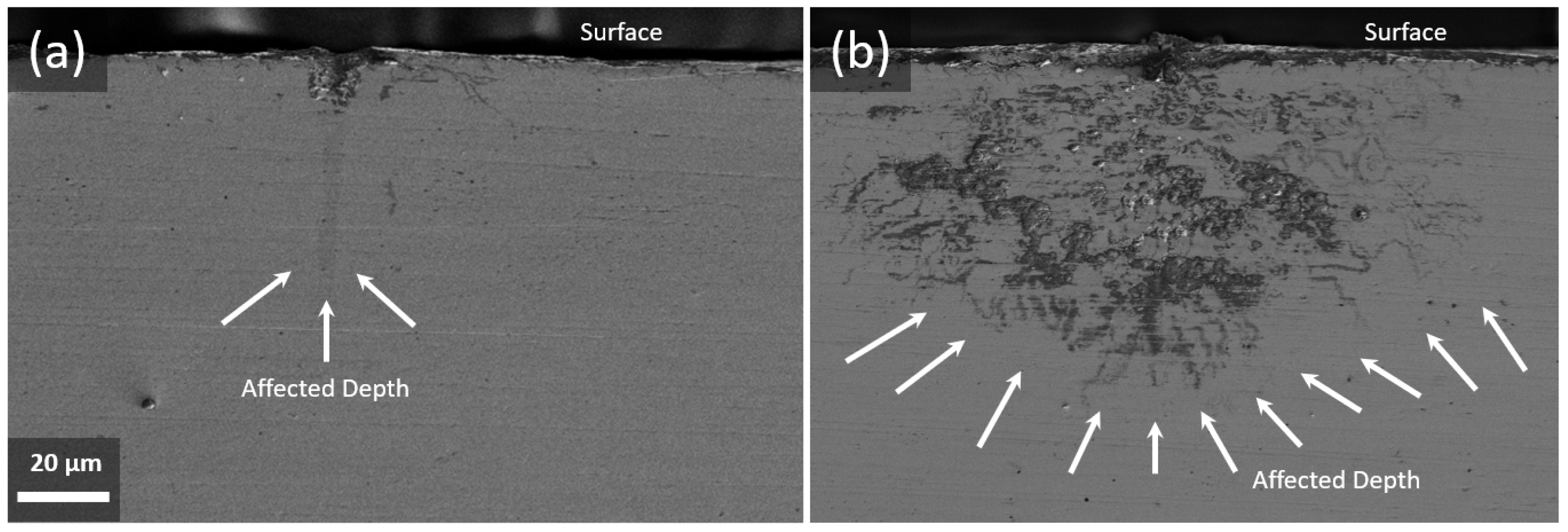
3.3. Hardening Evolution Induced by Laser Texturing
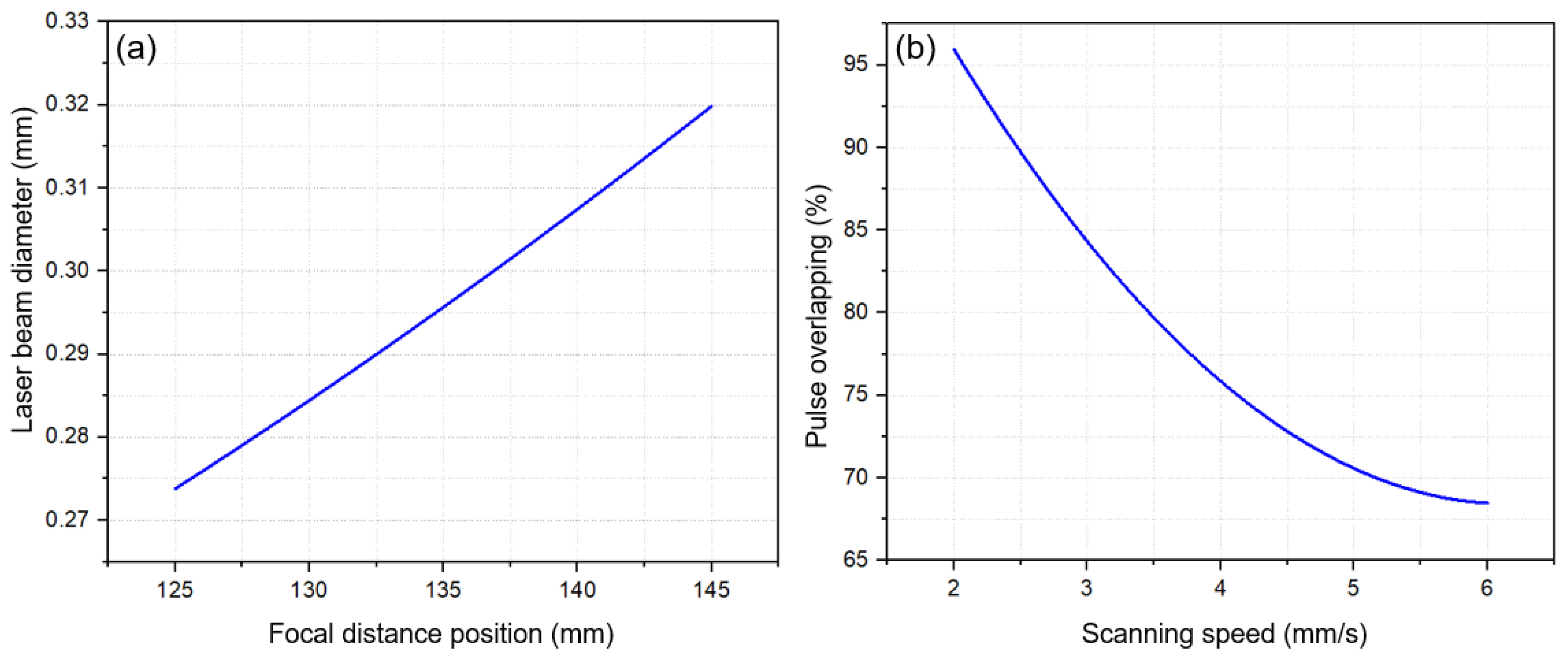
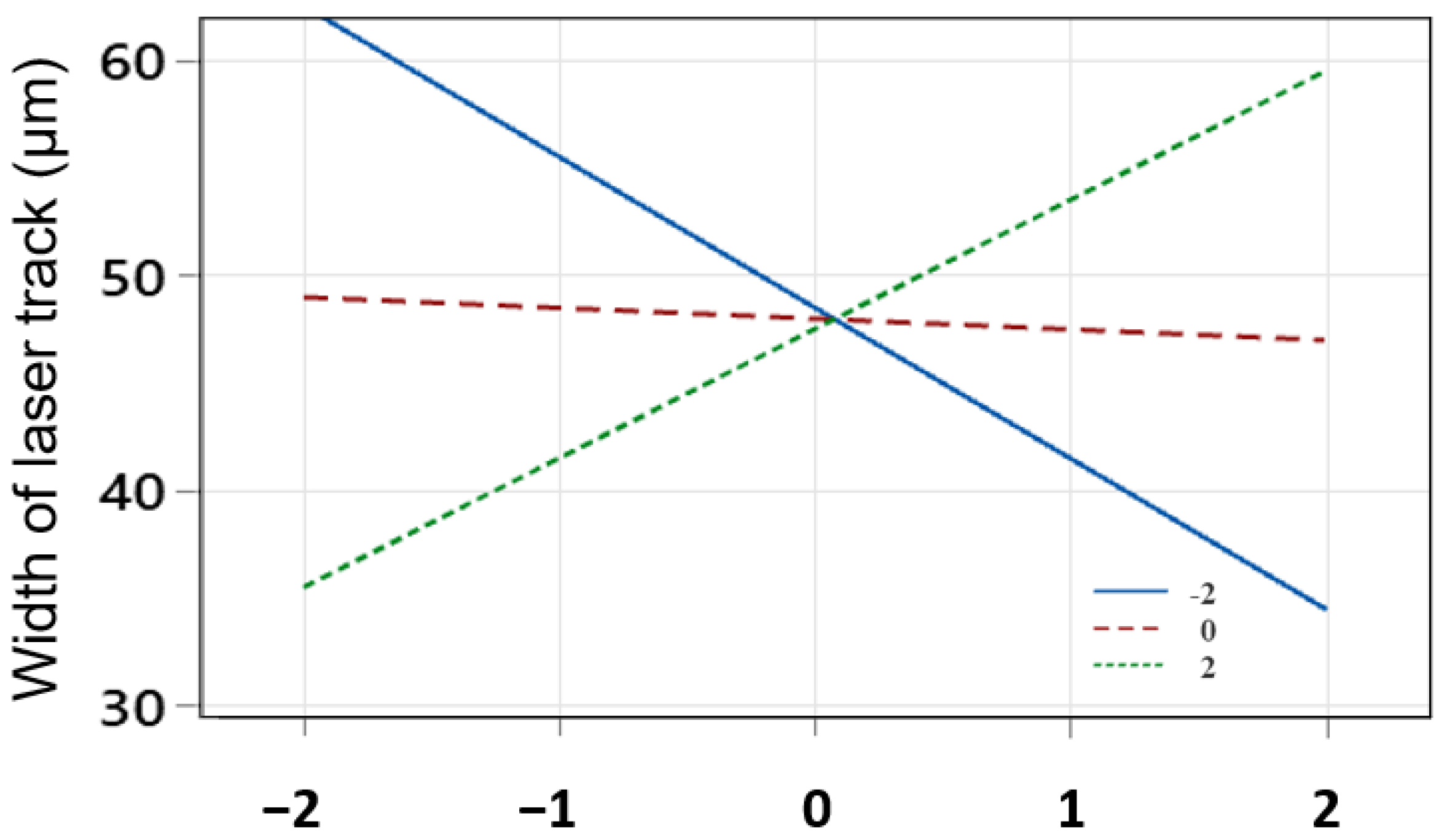
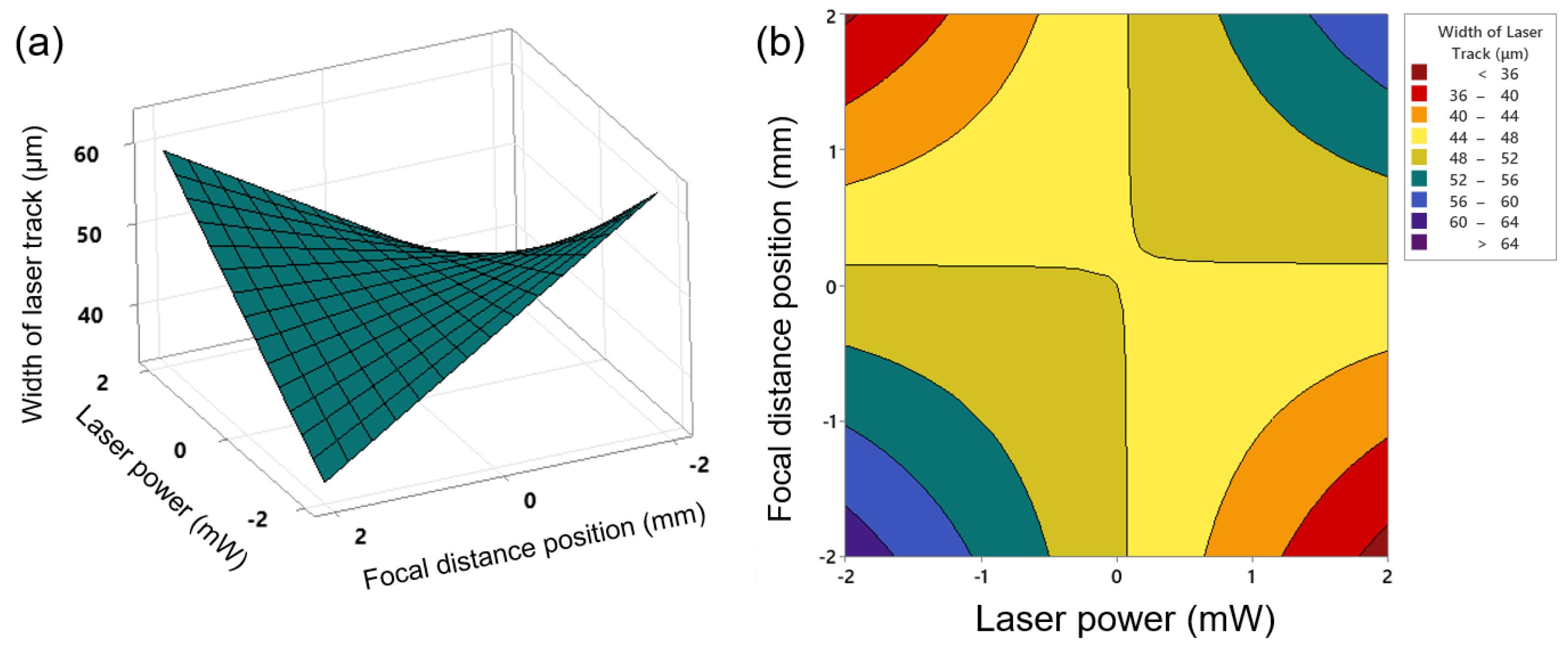
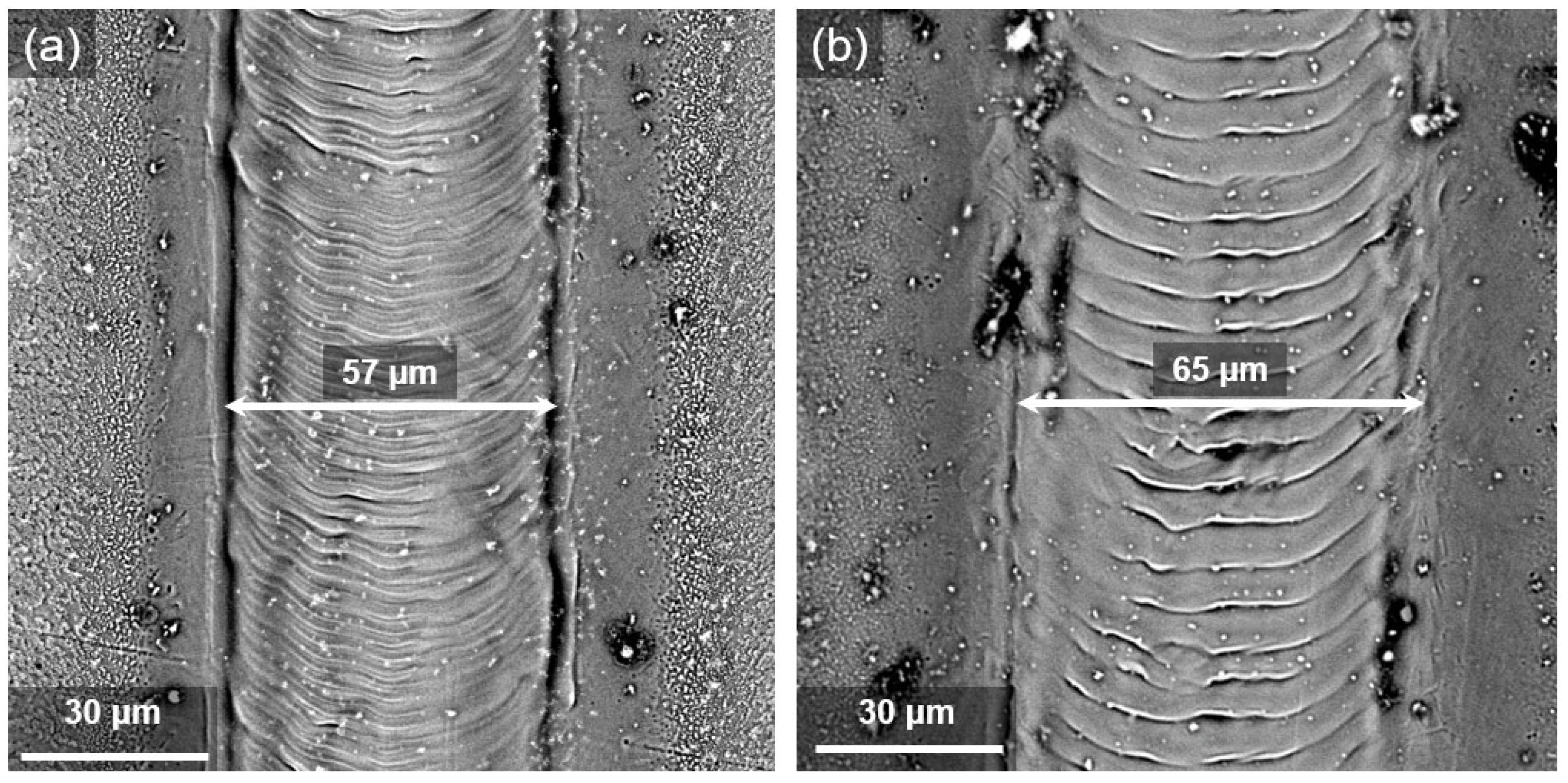
3.4. Width of the Laser Track
4. Conclusions
- By increasing the laser power and decreasing the scanning speed and the focal distance position, due to the increase in the laser energy, the heat input to the surface of the workpiece rises and the phase transformation happens faster. Then, more α′-martensite is present near the surface. As a result, the hardness and depth of the microstructural evolution area increase due to the area near the surface being slightly modified by increasing the among of defects.
- The depth of the microstructural evolution has a direct relationship with laser power, and with increasing it, a larger part of the substrate undergoes the α′-phase transformation because the accumulation of laser energy is concentrated in one point. Thus, the hardened depth reaches about 860 µm.
- As the power of the laser increases, due to the accumulation of heat input, a wider laser track is created. Increasing the focal distance of the laser causes the diameter of the laser spot on the surface to become larger, and in this case, increasing the laser energy causes enough heat to melt the surface. As a result, the width of the laser increases and reaches 65 µm in the maximum state.
- The influence of the laser power parameter on the maximum hardness, depth and width, is more significant than the parameters of focal distance position and scanning speed, due to the application of more concentrated energy on the surface.
- Considering the percentage coverage of the parameters obtained by the regression equation and the correspondence of the regression equation and analysis of variance with the remaining graphs, experimental modelling with the response surface method is a suitable model for investigating the effects of steel surface hardening with cost and time-saving.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Rezayat, M.; Roa, J.J.; Mateo, A. Phase Transformation and Residual Stresses after Laser Surface Modification of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel. Proc. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2848, 020005. [Google Scholar]
- Sobih, M. Laser-Based Machining—An Advanced Manufacturing Technique for Precision Cutting. In Advanced Machining and Finishing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 417–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Verma, R.; Kango, S.; Sharma, V.S. Recent Progresses and Applications in Laser-Based Surface Texturing Systems. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevič, V.; Čermák, A.; Mikalauskas, S.; Kožmín, P.; Indrišiūnas, S.; Račiukaitis, G. Processing of Ultra-Hard Materials with Picosecond Pulses: From Research Work to Industrial Applications. J. Laser Appl. 2018, 30, 32202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzin, S.P.; Kazanskiy, N.L.; Stiglbrunner, C. Analysis of the Advantages of Laser Processing of Aerospace Materials Using Diffractive Optics. Metals 2021, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xie, H.; Ge, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Wang, B.; Jin, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y. Laser Cutting Technologies and Corresponding Pollution Control Strategy. Processes 2022, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.S.; Sun, C.; Liu, X.; Qu, H.J.; French, A.J.; Freyer, P.D.; Garner, F.A.; Shao, L.; Wharry, J.P. Effect of Laser Welding on Deformation Mechanisms in Irradiated Austenitic Stainless Steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 528, 151878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, V.M.; de Figueiredo Mansur, R.A.; de Carvalho, S.M.; de Siqueira, R.H.M.; de Lima, M.S.F. Effect of Laser Welding on Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviour of Dual Phase 600 Steel Sheets. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, S.; Do, T.; Tran, P. FDM-Based 3D Printing of Polymer and Associated Composite: A Review on Mechanical Properties, Defects and Treatments. Polymers 2020, 12, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Meiabadi, S.; Casalino, G.; Ghaleeh, M.; Baby, B.; Ganapathi, H.; Jose, J.; Abdulla, M.S.; Tallon, P.; et al. Mathematical Modelling of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing of Poly Vinyl Alcohol Parts through Statistical Design of Experiments Approach. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Aboutorabi Sani, A.; Talafi Noghani, M.; Saghafi Yazdi, M.; Taheri, M.; Moghanian, A.; Mohammadi, M.A.; Moradi, M.; Mateo, A.; Besharatloo, H. Effect of Lateral Laser-Cladding Process on the Corrosion Performance of Inconel 625. Metals 2023, 13, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Moradi, M.; Mateo, A. Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Surface Processing of AISI 301LN Steel: Effect on Surface Topography and Mechanical Properties. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 3025–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daido, H.; Nishiuchi, M.; Pirozhkov, A.S. Review of Laser-Driven Ion Sources and Their Applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 056401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalem, K.; Barka, N.; Sattarpanah Karganroudi, S.; Sadeghian, A.; Mouradi, M. Effects of Laser Process Parameters on the Hardness Profile of AISI 4340 Cylindrical Samples: Statistical and Experimental Analyses. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 122, 2849–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.D.; Balasubramanian, K.R.; Buvanashekaran, G. Laser Surface Hardening: A Review. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerniti, A.G.; El Ouafi, A.; Barka, N. Single Track Laser Surface Hardening Model for AISI 4340 Steel Using the Finite Element Method. Model. Numer. Simul. Mater. Sci. 2016, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, E.; Fortunato, A.; Ascari, A.; Sorgente, D.; Scintilla, L.D.; Palumbo, G. A Thermal Model for Laser Hardening Simulation. Volume 1: Processing. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Charlotte, NC, USA, 8–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaddah, M.; Khan, A.; Groom, K.; Mumtaz, K. Use of 450-808 Nm Diode Lasers for Efficient Energy Absorption during Powder Bed Fusion of Ti6Al4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 2461–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Moradi, M.; Casalino, G.; Roa Rovira, J.J.; Mateo, A. Overview of Surface Modification Strategies for Improving the Properties of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metals 2023, 13, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutua, J.; Nakata, S.; Onda, T.; Chen, Z.-C. Optimization of Selective Laser Melting Parameters and Influence of Post Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Maraging Steel. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, D.; Tag, R.; Habib, B.A. Statistical Sequential Experimentation: Preliminary Mixed Factorial Design, I-Optimal Mixture Design Then Finally Novel Design Space Expansion for Optimization of Tazarotene Cubosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Yazdi, M.S.; Moradi, M.; Bodaghi, M. Statistical Analysis of Experimental Factors for Synthesis of Copper Oxide and Tin Oxide for Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 127, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigler, S.M. Mathematical Statistics in the Early States. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacking, I. Telepathy: Origins of Randomization in Experimental Design. Isis 1988, 79, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffke, N.; Heiligers, B. 30 Approximate Designs for Polynomial Regression: Invariance, Admissibility, and Optimality. In Handbook of Statistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 1149–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Chai, L.; Deng, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Microstructure and Properties of Pure Titanium Coating on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Laser Cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 416, 127137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xia, J.; Chai, L.; Murty, K.L.; Guo, N.; Daymond, M.R. Correlation of Microstructural, Textural Characteristics and Hardness of Ti–6Al–4V Sheet β-Cooled at Different Rates. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 8346–8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Sang, P.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.-C. Phase Interaction Induced Texture in a Plasma Sprayed-Remelted NiCrBSi Coating during Solidification: An Electron Backscatter Diffraction Study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hanson, T.E.; Ho, Y. Flexible Bivariate Correlated Count Data Regression. Stat. Med. 2020, 39, 3476–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, T.; Numano, K. The Role of the CO2 Laser and Fractional CO2 Laser in Dermatology. Laser Ther. 2014, 23, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.C.; Guo, C. Femtosecond Laser-produced Optical Absorbers for Solar-thermal Energy Harvesting. EcoMat 2021, 4, e12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Chen, C.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Yin, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z. Effect of a Constant Laser Energy Density on the Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Xia, C.; Yu, Y. Macroscopic and Microstructural Features of Metal Thin-Wall Fabricated by Laser Material Deposition: A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Tian, Y. A Review on Macroscopic and Microstructural Features of Metallic Coating Created by Pulsed Laser Material Deposition. Micromachines 2022, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolgár, M.K.; Nagy, E.; Daróczi, L.; Benke, M.; Mertinger, V.; Beke, D.L. Acoustic Emission During Austenite → ε Martensitic Phase Transformation in TWIP/TRIP Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 3495–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Luo, K.Y.; Yang, D.K.; Cheng, X.N.; Hu, J.L.; Dai, F.Z.; Qi, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.S.; Wang, Q.W.; et al. Effects of Laser Peening on Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) of ANSI 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2012, 60, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, G.; Duenow, U.; Seitz, H. Effect of Laser Pulse Overlap and Scanning Line Overlap on Femtosecond Laser-Structured Ti6Al4V Surfaces. Materials 2020, 13, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cr | Ni | Mn | Si | N | Mo | C | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17.6 | 6.50 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.02 | Bal. |
| Wavelength (nm) | Gain Medium | Pulse Energy@ kHz (µJ) | Output Power @kHz (mW) | Pulse Width (FWHM) (ns) | Beam Diameter at the Waist (1/e2) (mm) | Beam Divergence, Full Angle (1/e2) (mRad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 349 | Nd:YLF | 120 µJ | 120 | 5 | 0.145 ± 0.02 | 3.0 ± 0.5 |
| Variable | Symbol | Units | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning speed | S | mm/s | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Laser power | P | mW | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| Focal distance position | FDP | mm | 125 | 130 | 135 | 140 | 145 |
| Input Parameters | Output Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Laser Power (mW) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Focal Distance Position (mm) | Maximum Hardness (HV10) | Depth of the Microstructural Evolution (μm) | Width of Laser Track (μm) | Laser Beam Diameter (mm) | Pulse Overlapping (%) |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 263 | 720 | 52 | 0.296 | 74.3 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 260 | 690 | 49 | 0.273 | 74.3 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 269 | 830 | 59 | 0.285 | 71.2 |
| 4 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 248 | 590 | 41 | 0.307 | 84.6 |
| 5 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 256 | 790 | 43 | 0.317 | 71.2 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 259 | 690 | 46 | 0.295 | 74.3 |
| 7 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 223 | 520 | 34 | 0.296 | 95.1 |
| 8 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 264 | 710 | 50 | 0.297 | 74.3 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 261 | 680 | 51 | 0.296 | 73.2 |
| 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 273 | 860 | 59 | 0.301 | 68.1 |
| 11 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 231 | 640 | 33 | 0.285 | 84.6 |
| 12 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 257 | 730 | 47 | 0.299 | 74.3 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 261 | 680 | 46 | 0.322 | 75.4 |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 268 | 740 | 55 | 0.284 | 71.2 |
| 15 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 234 | 580 | 34 | 0.309 | 84.6 |
| 16 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 276 | 760 | 61 | 0.311 | 71.2 |
| 17 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 252 | 570 | 43 | 0.283 | 84.6 |
| Source of Variation | Degree of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F-Value | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 6 | 3151.45 | 525.24 | 78.37 | - | 0.000 |
| Linear | 3 | 2475.69 | 825.23 | 123.13 | - | 0.000 |
| Scanning speed (mm/s) | 1 | 2475.06 | 2475.06 | 369.29 | 19.22 | 0.000 |
| Laser power (mW) | 1 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.050 |
| Focal distance position (mm) | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.925 |
| Square | 1 | 230.51 | 230.51 | 34.39 | - | 0.000 |
| Scanning Speed (mm/s) × Scanning Speed (mm/s) | 1 | 230.51 | 230.51 | 34.39 | -5.86 | 0.000 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 2 | 445.25 | 222.62 | 33.22 | - | 0.000 |
| Scanning Speed (mm/s) × Laser Power (mW) | 1 | 120.13 | 120.13 | 17.92 | 4.23 | 0.002 |
| Laser Power (mW) × Focal Distance Position (mm) | 1 | 325.12 | 325.12 | 48.51 | 6.96 | 0.000 |
| Error | 10 | 67.02 | 6.70 | - | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 8 | 59.02 | 7.38 | 1.84 | - | 0.399 |
| Pure Error | 2 | 8.00 | 4.00 | |||
| Total | 16 | 3218.47 | ||||
| R-Sq = 97.92% | R-Sq(adj) = 96.67% | |||||
| Source of Variation | Degree of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F-Value | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3 | 131,025 | 43,675 | 99.12 | - | 0.000 |
| Linear | 2 | 126,025 | 63,013 | 143.01 | - | 0.000 |
| Scanning Speed (mm/s) | 1 | 126,025 | 126,025 | 286.02 | 16.91 | 0.000 |
| Laser Power (mW) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | −0.00 | 1.000 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 1 | 5000 | 5000 | 11.35 | - | 0.005 |
| Scanning Speed (mm/s) × Laser Power (mW) | 1 | 5000 | 5000 | 11.35 | −3.35 | 0.005 |
| Error | 13 | 5728 | 441 | - | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 11 | 4861 | 442 | 1.02 | - | 0.594 |
| Pure Error | 2 | 867 | 433 | |||
| Total | 16 | 136,753 | ||||
| R-Sq = 95.81% | R-Sq(adj) = 94.84% | |||||
| Source of Variation | Degree of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F-Value | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 4 | 989.50 | 247.375 | 31.41 | - | 0.000 |
| Linear | 3 | 905.00 | 301.667 | 38.31 | - | 0.000 |
| Scanning Speed (mm/s) | 1 | 900.00 | 900.000 | 114.29 | 10.69 | 0.000 |
| Laser Power (mW) | 1 | 4.00 | 4.000 | 0.51 | −0.71 | 0.0490 |
| Focal Distance Position (mm) | 1 | 1.00 | 1.000 | 0.13 | −0.36 | 0.728 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 1 | 84.50 | 84.500 | 10.73 | - | 0.007 |
| Laser Power (mW) ×·Focal Distance Position (mm) | 1 | 84.50 | 84.500 | 10.73 | 3.28 | 0.007 |
| Error | 12 | 94.50 | 7.875 | |||
| Lack-of-Fit | 10 | 73.83 | 7.383 | 0.71 | 0.709 | |
| Pure Error | 2 | 20.67 | 10.333 | |||
| Total | 16 | 1084.00 | ||||
| R-Sq = 91.28% | R-Sq(adj) = 88.8% | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezayat, M.; Mateo, A.; Roa, J.J. Exploring the Effects of Laser Surface Modification on AISI 301LN Steel: A Micro-Mechanical Study. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7060191
Rezayat M, Mateo A, Roa JJ. Exploring the Effects of Laser Surface Modification on AISI 301LN Steel: A Micro-Mechanical Study. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2023; 7(6):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7060191
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezayat, Mohammad, Antonio Mateo, and Joan Josep Roa. 2023. "Exploring the Effects of Laser Surface Modification on AISI 301LN Steel: A Micro-Mechanical Study" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 7, no. 6: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7060191
APA StyleRezayat, M., Mateo, A., & Roa, J. J. (2023). Exploring the Effects of Laser Surface Modification on AISI 301LN Steel: A Micro-Mechanical Study. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 7(6), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7060191










