Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Circumferentially Welded 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Pipe Joint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Welding
2.2. Welding Simulation
2.2.1. Welding Modeling
2.2.2. Welding Validation
2.3. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization
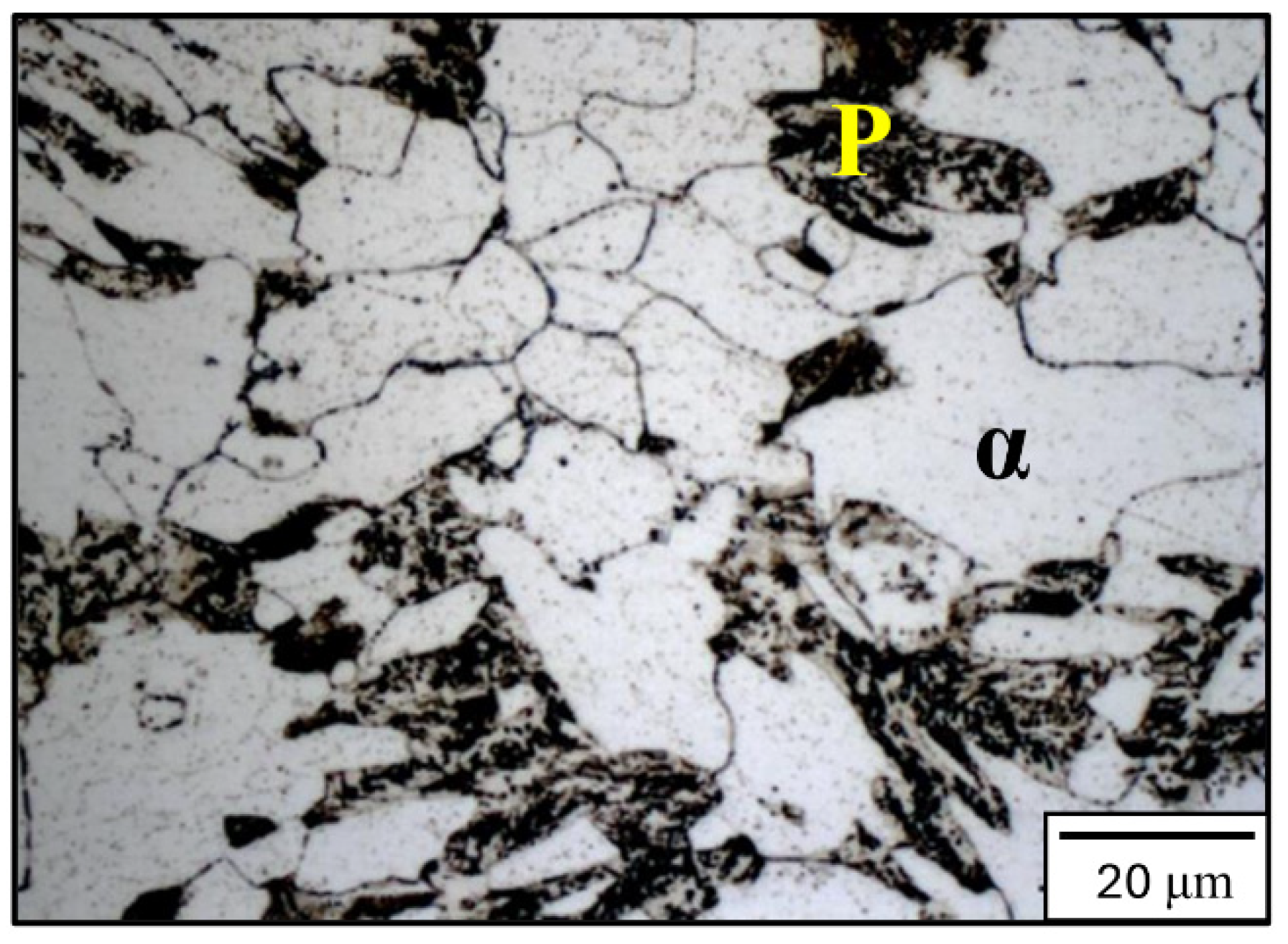
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
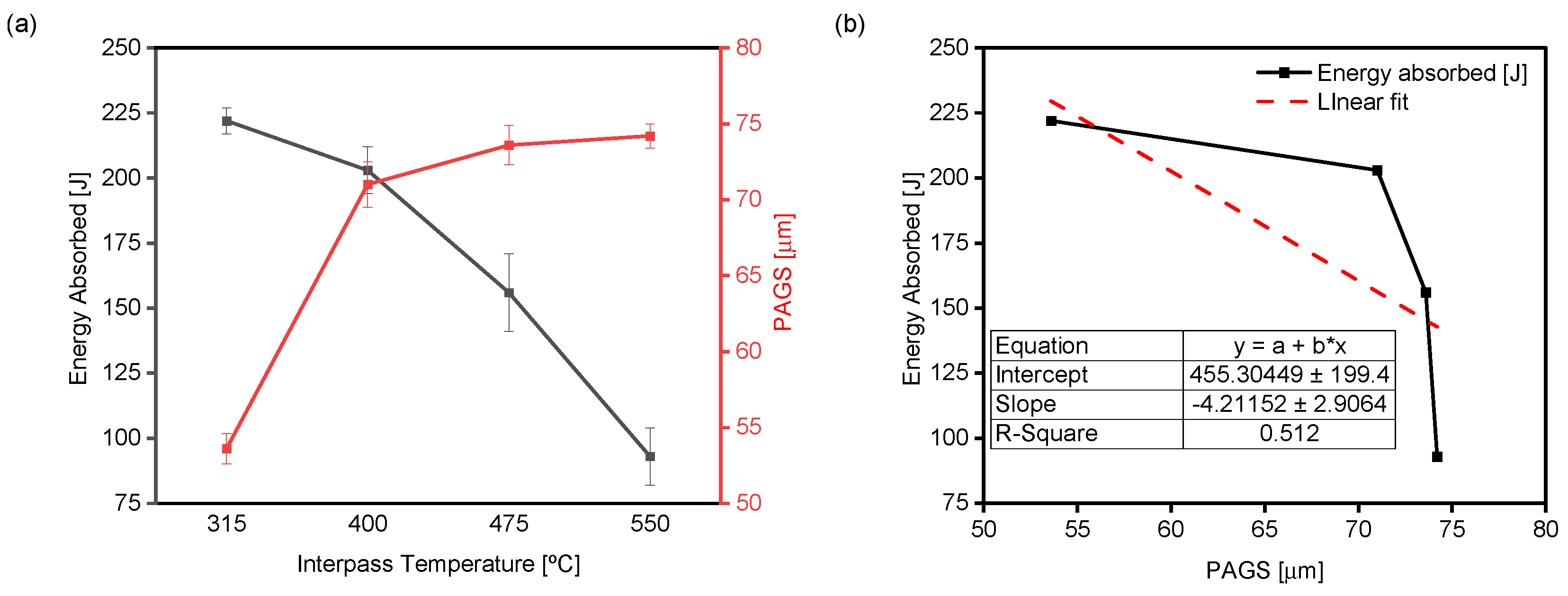
- The increase in IT higher than that indicated by the ASME B31.3 significantly reduces the CVN impact energy of the CGHAZ of the 2.25Cr-1Mo steel.
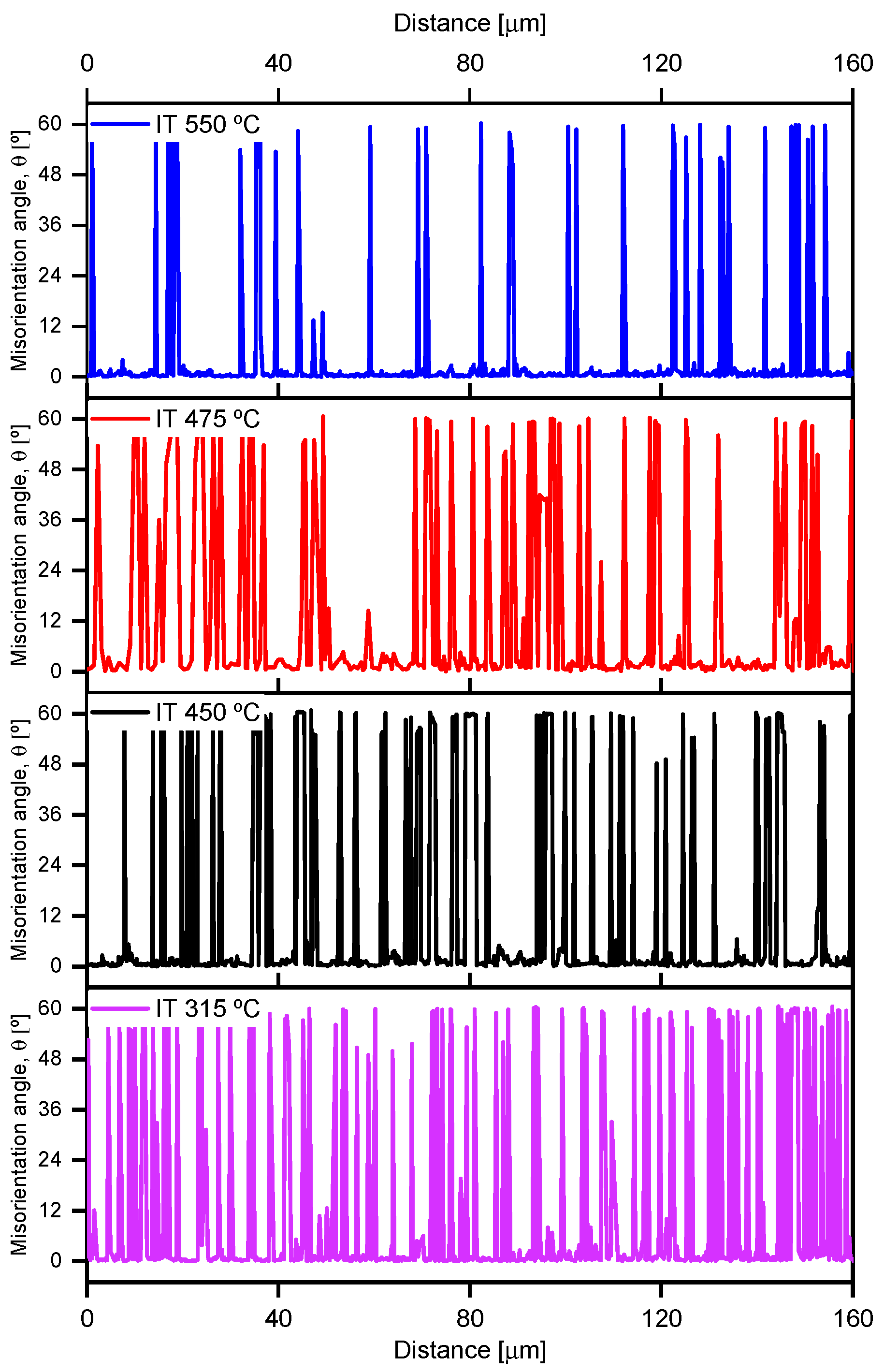
- The primary influence of IT was observed on the effective grain size (EGS), where an increase in IT correlates with coarsening of the grains. There is an inverse relationship between the EGS and the Charpy impact energy.
- The phases/microconstituents present in 2.25Cr-1Mo steel appear to be almost insensitive to variations within the studied IT range, showing little observable change.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbosa, L.H.S.; Modenesi, P.J.; Godefroid, L.B.; Arias, A.R. Fatigue Crack Growth Rates on the Weld Metal of High Heat Input Submerged Arc Welding. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 119, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layus, P.; Kah, P.; Martikainen, J.; Gezha, V.V.; Bishokov, R.V. Multi-Wire SAW of 640 MPa Arctic Shipbuilding Steel Plates. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 75, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, F.; Ding, J.; Williams, S.; Caballero, A.; Pardal, G.; Quintino, L. Tandem Metal Inert Gas Process for High Productivity Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing in Stainless Steel. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalet Rossini, L.F.; Valenzuela Reyes, R.A.; Spinelli, J.E. Double-Wire Tandem GMAW Welding Process of HSLA50 Steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 45, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASME Code for Pressure Piping; B31.3; The American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Dornelas, P.H.G.; Payão Filho, J.d.C.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.P.; Moraes, D.d.O.; Zumpano Júnior, P. Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated HAZ of a Clad API 5L X65 Pipe Joint Welded with a Gas Metal Arc. Weld. World 2022, 66, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, P.H.G.; Payão Filho, J.d.C.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.P.; Moraes, D.d.O.; Zumpano Júnior, P. Studying the Influence of the Interpass Temperature on the Heat-Affected Zone of an API 5L X65 Steel Welded Pipe Joint through Computational and Physical Simulations. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2021, 194, 104548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, J.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, X.C.; Shang, C.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of Interpass Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Pass Weld Metal in a 550-MPa-Grade Offshore Engineering Steel. Weld. World 2017, 61, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Han, Z. Effect of Weld Thermal Cycle on Microstructure and Fracture Toughness of Simulated Heat-Affected Zone for a 800MPa Grade High Strength Low Alloy Steel. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2008, 207, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, K.; Sirin, S.Y.; Kaluc, E. Influence of the Interpass Temperature on t 8/5 and the Mechanical Properties of Submerged Arc Welded Pipe. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2016, 238, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, P.H.G.; Farias, F.W.C.; e Oliveira, V.H.P.M.; de Oliveira Moraes, D.; Júnior, P.Z.; da Cruz Payão Filho, J. Influence of Welding Interpass Temperature on Charpy V-Notch Impact Energy of Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone of AISI 4130 Steel Pipe. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 2197–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.O.P.; Lima, T.N.; Júnior, F.M.d.S.; Callegari, B.; Folle, L.F.; Coelho, R.S. Heat-Affected Zone Microstructural Study via Coupled Numerical/Physical Simulation in Welded Superduplex Stainless Steels. Crystals 2024, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Cho, D.-W.; Kim, J.; Pyo, C. Influence of Thermal Flow and Predicting Phase Transformation on Various Welding Positions. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2024, 60, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, L.-E. FINITE ELEMENT MODELING AND SIMULATION OF WELDING PART 1: INCREASED COMPLEXITY. J. Therm. Stress. 2001, 24, 141–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slováček, M.; Vaněk, M.; Kik, T. Use of Welding Process Numerical Analyses as Technical Support in Industry. Part 2: Methodology and Validation. Biul. Inst. Spaw. 2015, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restecka, M.; Jachym, R. IT Systems Used for Welding Process Simulations and Simulators of Thermal-Strain Cycles. Biul. Inst. Spaw. 2016, 60, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Nyyssönen, T.; Grande, B.; Porter, D. Computational Design of a Novel Medium-Carbon, Low-Alloy Steel Microalloyed with Niobium. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 2978–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Jeon, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, H. Complex Effects of Alloy Composition and Porosity on the Phase Transformations and Mechanical Properties of Powder Metallurgy Steels. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeinifar, S.; Kokabi, A.H.; Hosseini, H.R.M. Effect of Tandem Submerged Arc Welding Process and Parameters of Gleeble Simulator Thermal Cycles on Properties of the Intercritically Reheated Heat Affected Zone. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, L.; Lei, M.K. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Heat-Affected Zone of Repeated Welding AISI 304N Austenitic Stainless Steel by Gleeble Simulator. Metals 2018, 8, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, F.; Yang, R.; Tang, X.; Cui, H. Gleeble Simulation of the HAZ in Inconel 617 Welding. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2015, 225, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Tiwari, Y.N.; Roy, P.K.; Chaudhuri, S.; Bose, S.C.; Ghosh, R.N.; Whittenberger, J.D. Creep Rupture Analysis and Remaining Life Assessment of 2.25Cr–1Mo Steel Tubes from a Thermal Power Plant. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454–455, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldak, J.; Bibby, M.; Moore, J.; House, R.; Patel, B. Computer Modeling of Heat Flow in Welds. Met. Trans. B 1986, 17, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TS 18166; Numerical Welding Simulation—Execution and Documentation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Bate, S.K.; Charles, R.; Warren, A. Finite Element Analysis of a Single Bead-on-Plate Specimen Using SYSWELD. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2009, 86, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, P.H.G.; Payão Filho, J.d.C.; Farias, F.W.C.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.P.; Moraes, D.d.O.; Zumpano Júnior, P. FEM-Thermodynamic Simulation Methodology to Predict the Influence of T8/5 on the Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone of a Cr-Mo Low-Alloy Steel Pipe. J. Manuf. Process 2020, 60, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Welding Society. Welding Processes, Part 1; American Welding Society: Doral, NW, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E112; Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM A370; Standard Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM E92; Standard Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Dornelas, P.H.G.; Payão Filho, J.d.C.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.P.; Moraes, D.d.O.; Zumpano Júnior, P. Effect of the Interpass Temperature on Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Gas Metal Arc Welded API 5L X70 Pipe Joint. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrefaey, A.; Javadi, Y.; Francis, J.A.; Callaghan, M.D.; Leonard, A.J. Evolution of Microstructure and Toughness in 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Welds. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2018, 165, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönmaier, H.; Krein, R.; Schmitz-Niederau, M.; Schnitzer, R. Influence of the Heat Input on the Dendritic Solidification Structure and the Mechanical Properties of 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V Submerged-Arc Weld Metal. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 7138–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, P.H.G.; Payão Filho, J.d.C.; Farias, F.W.C.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.P.; Moraes, D.d.O.; Zumpano Júnior, P. Influence of the Interpass Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Weld Metal (AWS A5.18 ER70S-6) of a Narrow Gap Welded API 5L X70 Pipe Joint. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 199, 104690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipetzky, P.; Kreher, W. Grain Boundary Toughness Effects on Crack Propagation in Brittle Polycrystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 205, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, D.; Knott, J.F.; Davis, C.L. Charpy-Impact-Toughness Prediction Using an “Effective” Grain Size for Thermomechanically Controlled Rolled Microalloyed Steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, S. Effect of Microstructural Types on Toughness and Microstructural Optimization of Ultra-Heavy Steel Plate: EBSD Analysis and Microscopic Fracture Mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.S. Effects of Grain Size on Fracture Toughness in Transition Temperature Region of Mn–Mo–Ni Low-Alloy Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 359, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Bernstein, I.M. The Process of Crack Initiation and Effective Grain Size for Cleavage Fracture in Pearlitic Eutectoid Steel. Met. Trans. A 1979, 10, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, N.J.; Yoo, J.Y. Effective Grain Size and Charpy Impact Properties of High-Toughness X70 Pipeline Steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORSOK M630; Material Data Sheets and Element Data Sheets for Piping. Norwegian Technology Centre: Oslo, Norway, 2020.

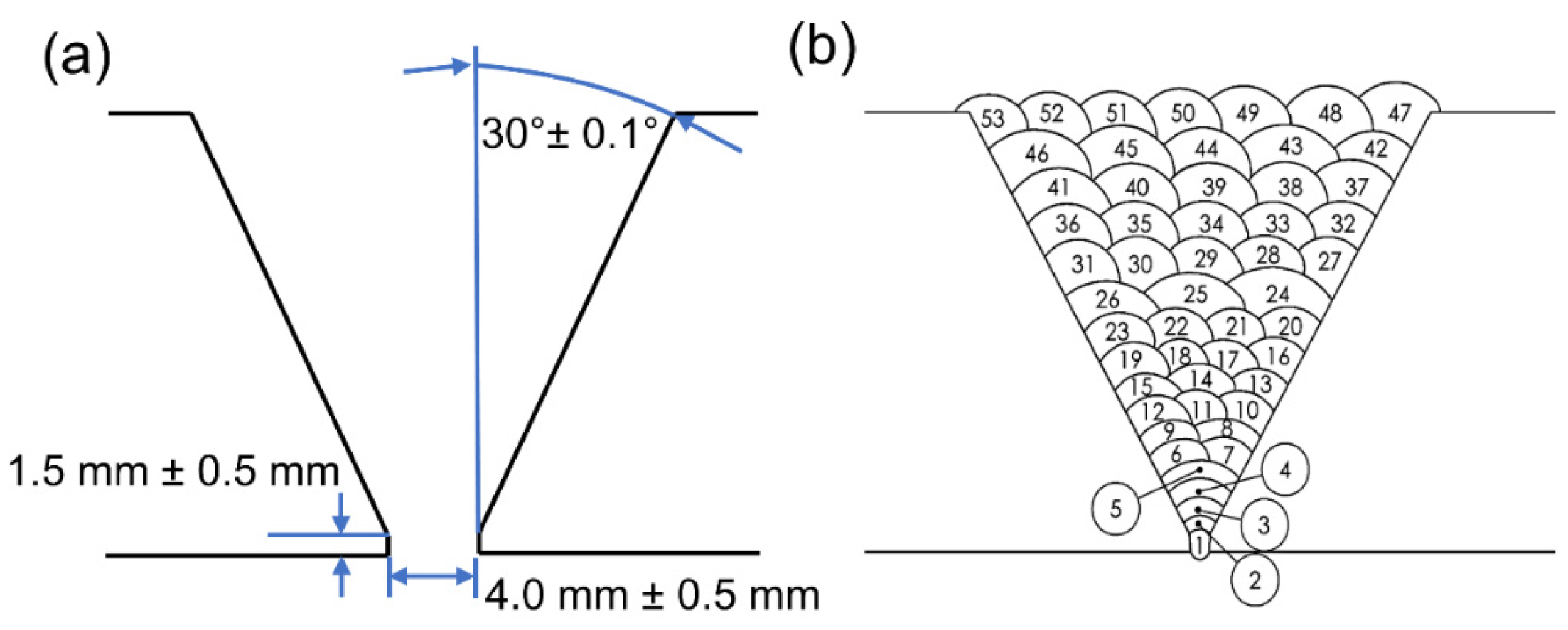


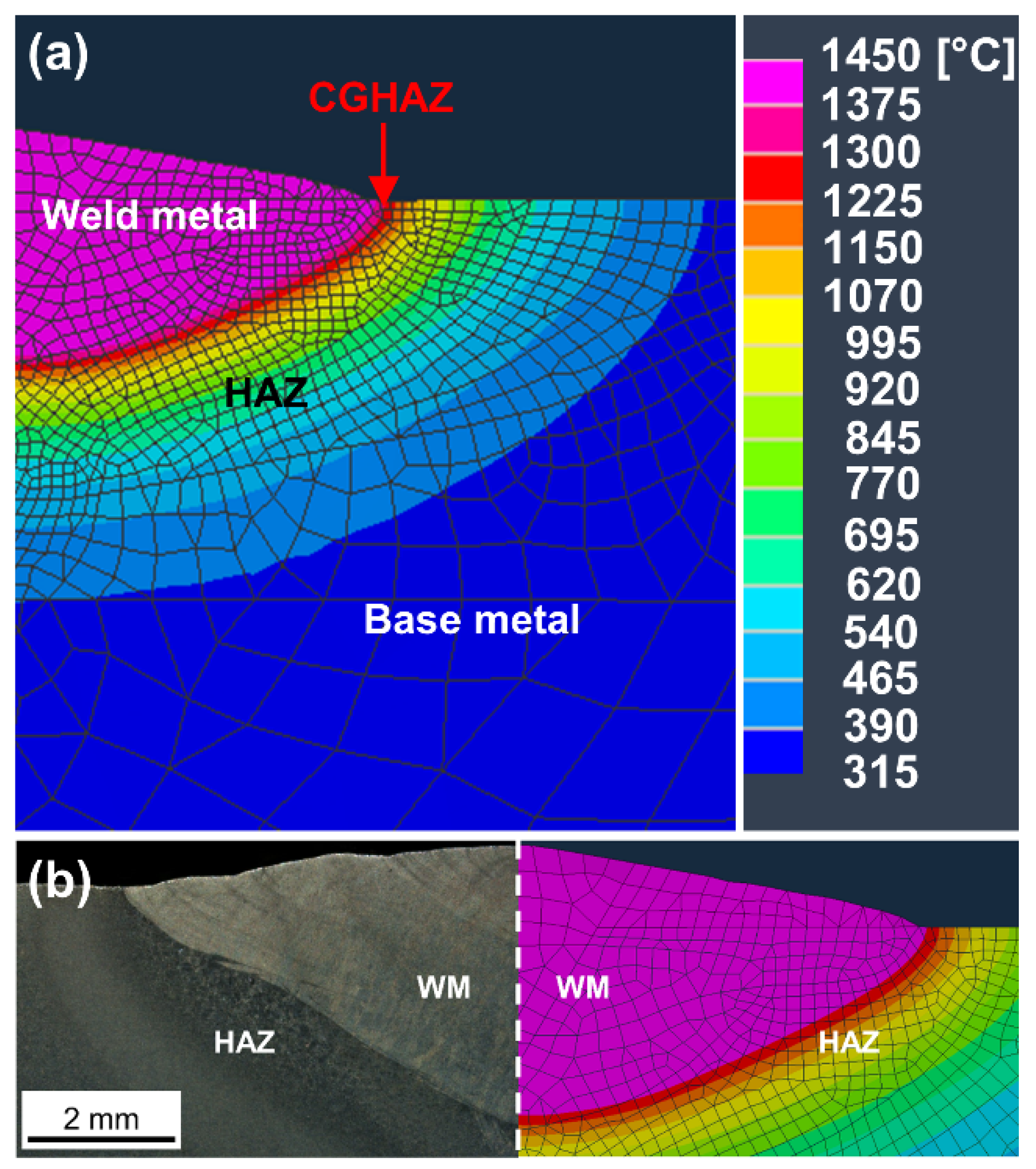

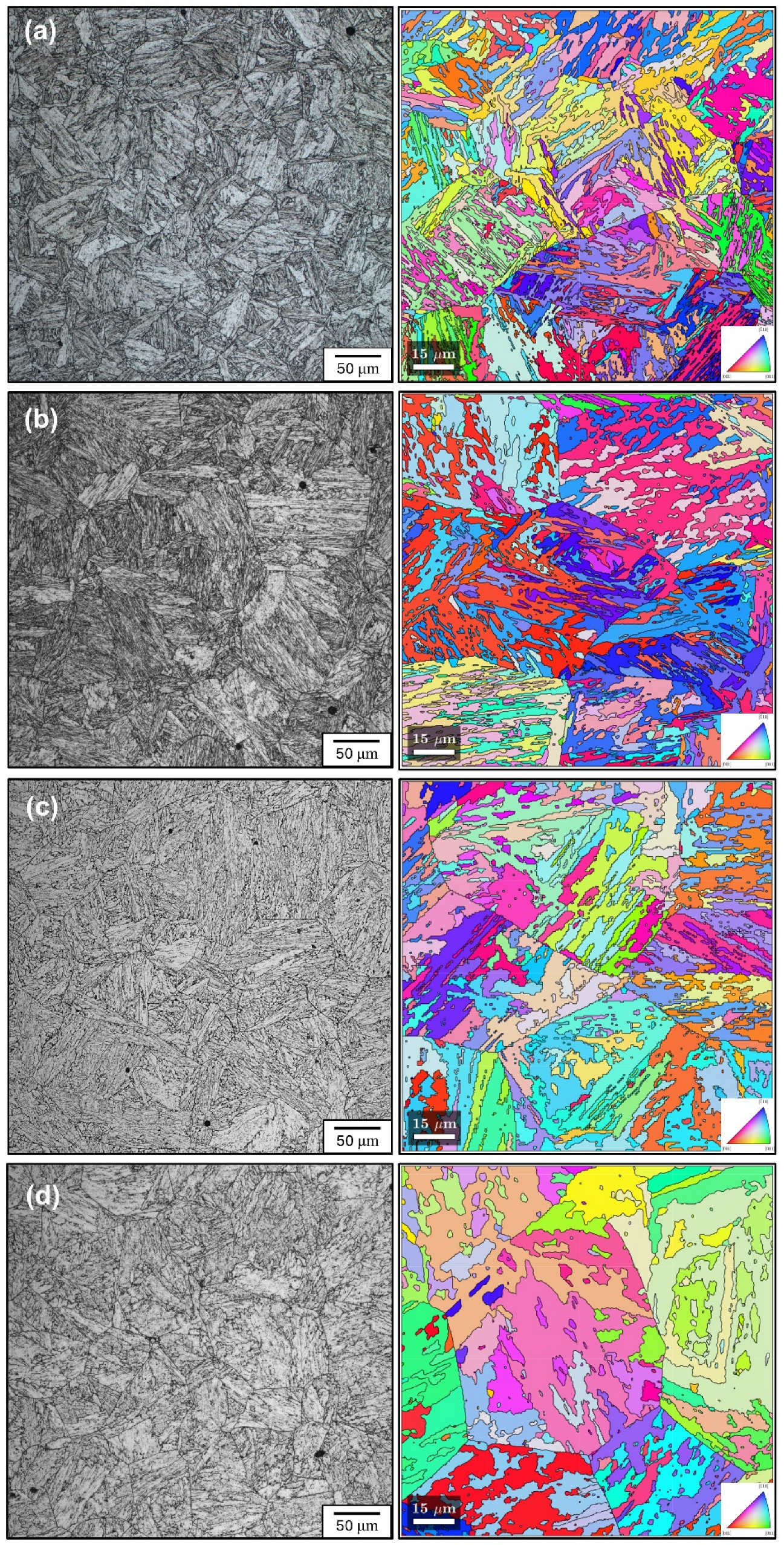
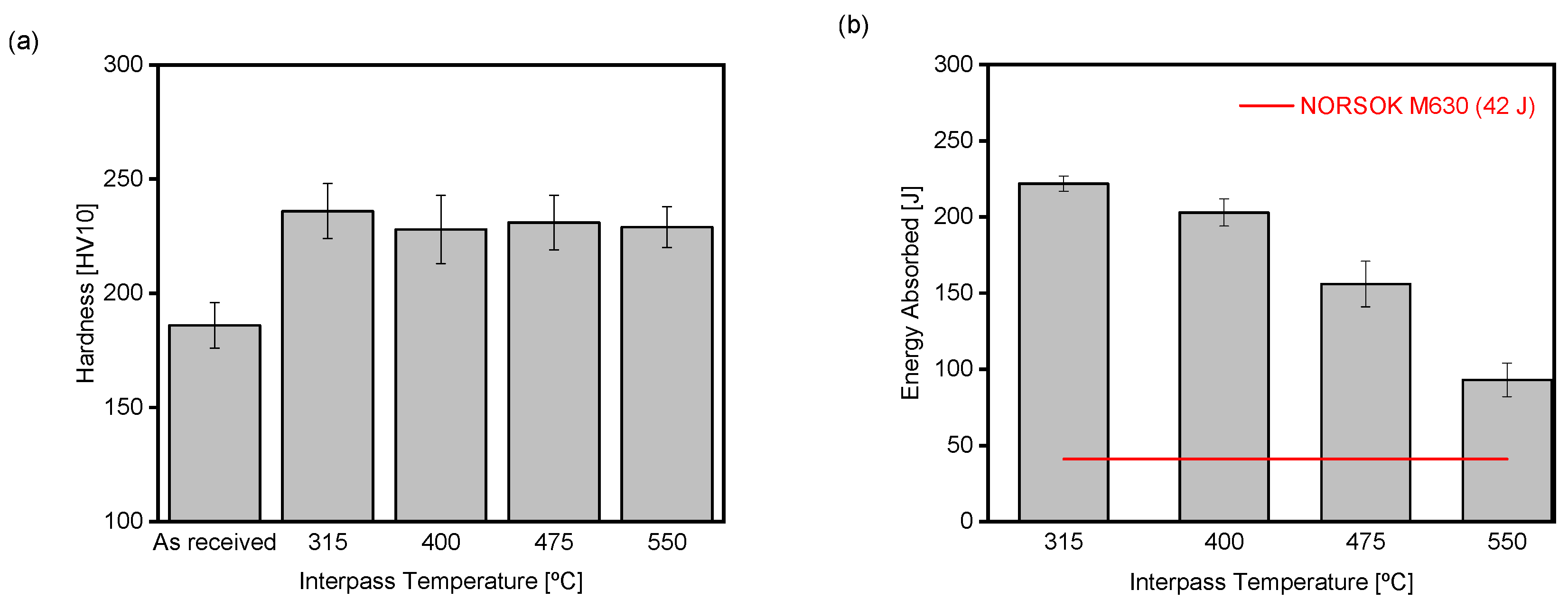

| Chemical Element | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Nb+Ti+V | Al | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt [%] | 0.14 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 2.09 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.08 | Bal. |
| Parameter | GTAW Pass | SAW Pass | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root (1) | Hot (2–4) | Fill (5–46) | Cap (47–53) | |
| Welding position | 5G | 1GR | ||
| Filler metal | AWS A5.28 (ER90S-B3) | AWS A5.23 (F9P2-EB3R-B3R) | ||
| Shielding gas | 99.99%Ar | – | ||
| Flux | – | AWS S 62 4 FB SNi1Mo | ||
| Current type/polarity | DC/- | DC/+ | ||
| Voltage [V] | 11–13.5 | 11.8–16.2 | 26.4–32.2 | 26.7–32.6 |
| Welding current, I [A] | 111–136 | 159–262 | 435–531 | 456–558 |
| Welding speed, WS [cm/min] | 5.6–6.8 | 8.1–12.1 | 28.7–35.0 | 28.9–36.5 |
| Stick-out [mm] | – | 10–20 | ||
| Heat input, HI [kJ/mm] | 1.3–1.6 | 1.4–2.1 | 2.4–2.9 | 2.5–3.0 |
| Interpass temperature, IT [°C] | 315 | |||
| Preheating temperature, T0 [°C] | 230 | |||
| Heat Source | ff | a | b | cf | cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.17 | 2.75 | 0.80 | 7.70 | 2.30 |
| 2 | 1.20 | 7.50 | 0.60 | 7.50 | 2.50 |
| IT [°C] | t8/5 [s] | Cooling Rate [°C/s] |
|---|---|---|
| 315 | 15 | 20.0 |
| 400 | 30 | 10.0 |
| 475 | 80 | 3.8 |
| 550 | 210 | 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dornelas, P.H.G.; Payão Filho, J.d.C.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.P.; Farias, F.W.C. Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Circumferentially Welded 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Pipe Joint. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060248
Dornelas PHG, Payão Filho JdC, Moraes e Oliveira VHP, Farias FWC. Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Circumferentially Welded 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Pipe Joint. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2024; 8(6):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060248
Chicago/Turabian StyleDornelas, Paulo Henrique Grossi, João da Cruz Payão Filho, Victor Hugo Pereira Moraes e Oliveira, and Francisco Werley Cipriano Farias. 2024. "Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Circumferentially Welded 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Pipe Joint" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 8, no. 6: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060248
APA StyleDornelas, P. H. G., Payão Filho, J. d. C., Moraes e Oliveira, V. H. P., & Farias, F. W. C. (2024). Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Circumferentially Welded 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Pipe Joint. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 8(6), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060248






