Deterioration of Wood Plastics Composites by the White-Rot Fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wood-Plastic Composite Preparation
2.2. Fungus Cultivation
2.3. Composite Preparation for Biodegradation Assay
2.4. Melt Flow Index Test
2.5. Mechanical Testing
2.5.1. Impact Test
2.5.2. Hardness Test
2.6. Weight Loss
2.7. Model Fitting
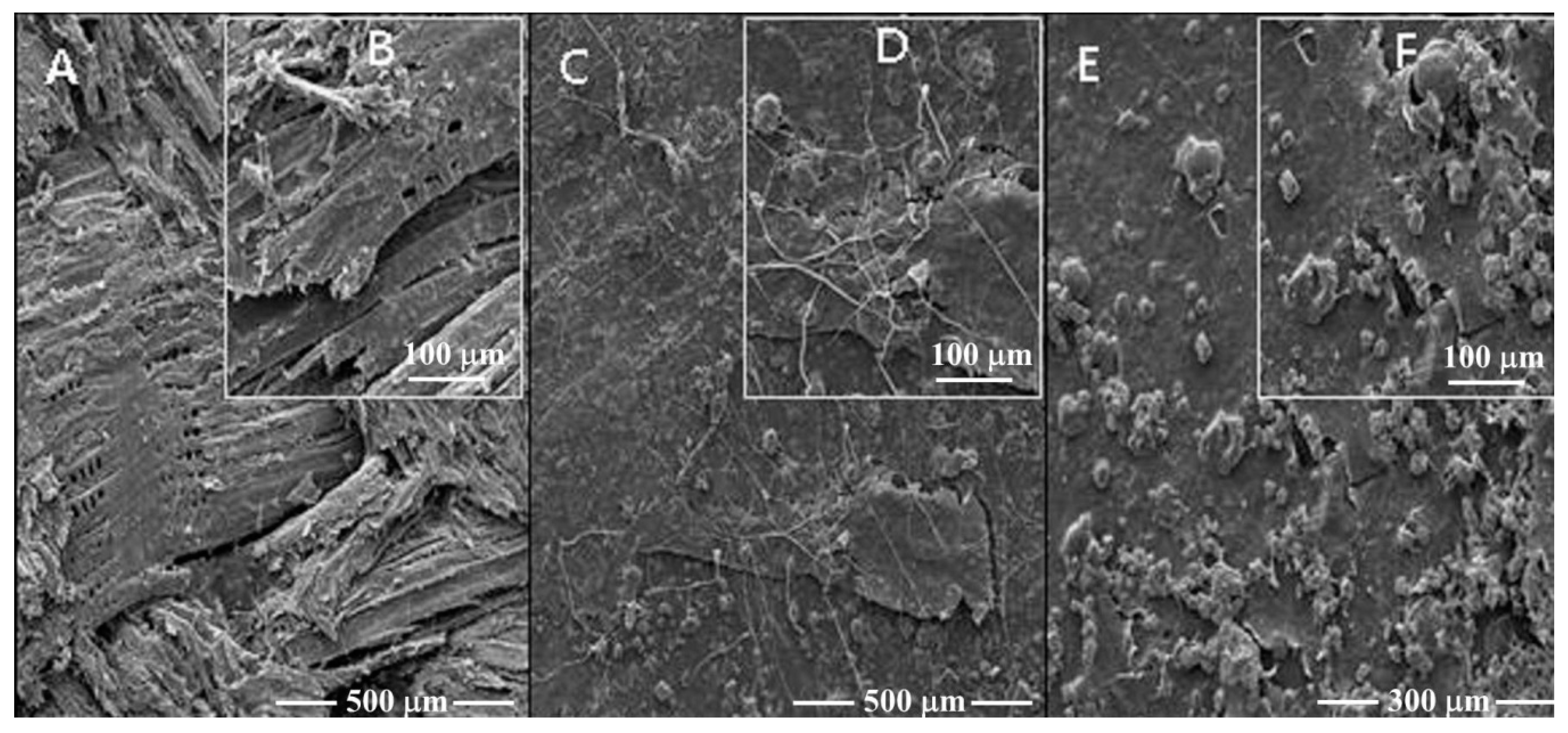
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.9. Fourier Transform Infrared Analysis
2.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Melt Flow Index
3.2. Impact Strength
3.3. Hardness
3.4. Weight Losses
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Analysis
3.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Sain, M. Progress report on natural fiber reinforced composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirasak, S.; Chollakup, R.; Nardin, M. Bio-Based Composites for High-Performance Materials: From Strategy to Industrial Application; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sahari, J.; Sapuan, S.M.; El-Shekeil, Y.A.; Ishak, M.R.; Akhtar, R. Natural Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastic Starch Composites in: Starch-Based Blends, Composites and Nanocomposites; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; pp. 109–142. [Google Scholar]
- Visakh, P.M.; Mathew, A.P.; Thomas, S. Natural Polymers: Their Blends, Composites and Nanocomposites: State of Art, New Challenges and Opportunities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Keskisaari, A.; Kärki, T. Raw material potential of recyclable materials for fiber composites: A review study. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 19, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.R.; Cown, D.J. Processing of Wood for Wood Composites. In Wood Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kuka, E.; Cirule, D.; Kajaks, J.; Janberga, A.; Andersone, I.; Andersons, B. Fungal degradation of wood plastic composites made with thermally modified wood residues. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 721, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.I.; Cooper, P. Recycled plastic/wood composite lumber attacked by fungi. For. Prod. J. 1998, 48, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Schirp, A.; Ibach, R.E.; Pendleton, D.E.; Wolcott, M.P. Biological degradation of wood-plastic composites (WPC) and strategies for improving the resistance of WPC against biological decay. ACS Symp. Ser. 2008, 982, 480–507. [Google Scholar]
- Leao, A.L.; Ferrao, P.C.; Souza, S.F. State-of-the-art for extrusion and injection moulding FPC: Natural fibre plastics composites in Brazil. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2009, 36, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y.; Wang, L. Wood–Plastic Composite Technology. Curr. For. Rep. 2015, 1, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwa, Z.N.; Yousif, B.F.; Manalo, A.C.; Karunasena, W.A. Review on the degradability of polymeric composites based on natural fibres. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.K. Use of recycled plastics in wood plastic composites—A review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R. Material properties of plastics. In Laser Welding of Plastics; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.H.; Pan, Y.J.; Liu, C.F.; Huang, C.L.; Hsieh, C.T.; Chen, C.K.; Lin, Z.I.; Lou, C.W. Preparation and compatibility evaluation of polypropylene/high density polyethylene polyblends. Materials 2015, 8, 8850–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, M.S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Drzal, L.T.; Schut, E.; Mirsa, M. “Green” composites from recycled cellulose and poly(lactic acid): Physico-mechanical and morphological properties evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 4221–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavooshi, A.; Madhoushi, M.; Shakeri, A.; Khazaeian, A. A comparative study on the effects of material blending method on the physico-mechanical properties of WPCs made from MDF dust. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, S. Handbook of Bioplastics and Biocomposites Engineering Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 588. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, N.; Tahir, P.; Jawaid, M. A review on potentiality of nano filler/natural fiber filled polymer hybrid composites. Polymers 2014, 6, 2247–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.H.; Leu, S.Y.; Yang, T.H.; Lo, S.F. Optimized material composition to improve the physical and mechanical properties of extruded wood-plastic composites (WPCs). Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Dányádi, L.; Janecska, T.; Szabó, Z.; Nagy, G.; Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Wood flour filled PP composites: Compatibilization and adhesion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2838–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittenber, D.B.; Gangarao, H.V.S. Critical review of recent publications on use of natural composites in infrastructure. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visakh, P.M.; Poletto, M. Polypropylene-Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.-E. Polymer biodegradation: Mechanisms and estimation techniques—A review. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage-Meessen, L.; Haon, M.; Uzan, E.; Levasseur, A.; Piumi, F.; Navarro, D.; Taussac, S.; Favel, A.; Lomascolo, A. Phylogeographic relationships in the polypore fungus Pycnoporus inferred from molecular data. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 325, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.V.G.; Turella, T.C.; Santana, R.M.C.; Zattera, A.J. The influence of wood flour particle size and content on the rheological, physical, mechanical and morphological properties of EVA/wood cellular composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, M.J.; Burnard, M.D. Wood-plastic composites—Performance and environmental impacts. In Environmental Impacts of Traditional and Innovative Forest-Based Bioproducts; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Brijwani, K.; Rigdon, A.; Vadlani, P.V. Fungal laccases: Production, function, and applications in food processing. Enzyme Res. 2010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartal, S.N.; Aysal, S.; Terzi, E.; Yilgor, N.; Yoshimura, T.; Tsunoda, K. Wood and Bamboo-PP composites: Fungal and termite resistance, water absorption and FT-IR analyses. Bioresources 2013, 8, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Delgado, M.; Orona-Navar, C.; García-Morales, R.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; Parra, R.; Mahlknecht, J.; Ornelas-Soto, N. Biotransformation kinetics of pharmaceutical and industrial micropollutants in ground waters by a laccase cocktail from Pycnoporus sanguineus CS43 fungi. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2016, 108, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrao, D.R.; Silva Júnior, T.A.F.; Passos, J.R.S.; Sansígolo, C.A.; Minhoni, M.T.A.; Furtado, E.L. Biodegradation of Eucalyptus urograndis by fungi. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2014, 89, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eira, A.F.; Minhoni, M.T.A. Manual Theoretical and Practical Cultivation of Edible Mushrooms, 2nd ed.; Foundation for Research and Agricultural and Forestry, FEPAF: São Paulo, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D1238-04c. Standard Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion Plastometer; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D256-10e1. Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2240-15. Standard Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2017-05. Standard Test Method of Accelerated Laboratory Test of Natural Decay Resistance of Woods (Withdrawn 2014); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schinckel, A.P.; Craig, B.A. Evaluation of alternative nonlinear mixed effects models of swine growth. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2002, 18, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Wedderburn, W.M. Generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1972, 135, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.-Y.; Zeger, S.L. Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika 1986, 1, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, F.A.A.; Calonego, F.W.; Severo, E.T.; Furtado, E.L. Selection of fungi for accelerated decay in stumps of Eucalyptus spp. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 11, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrao, D.R.; Sain, M.; Leao, A.L.; Sameni, J.; Jeng, R.; Jesus, J.P.F.; Monteiro, R.T.R. Fragmentation of lignin from organosol black liquor by White rot fungi. Bioresources 2015, 10, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínková, I.; Kotik, M.; Homolka, L. Biodegradation of phenolic compounds by Basidiomycota and its phenol oxidases: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, M.; Attwood, J.; Hulme, A.; Williams, G.; Shipton, P. Evaluation of weathering in mixed polyethylene and polypropylene products; The Waste & Resources Action Programme: Oxon, UK, 2004; 113p. [Google Scholar]
- Butnaru, E.; Darie-Niţă, R.N.; Zaharescu, T.; Balaeş, T.; Tănase, C.; Hitruc, G.; Doroftei, F.; Cornelia, V. Gamma irradiation assisted fungal degradation of the polypropylene/biomass composites. Rad. Phys. Chem. 2016, 125, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiyi, J.S.; McDonald, A.G. Degradation of polypropylene in naturally and artificially weathered plastic matrix composites. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2014, 16, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibers: Can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyba, O.; Douglas, C.J.; Mansfield, S.D. Syringyl-rich lignin renders poplars more resistant to degradation by wood decay fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2560–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kord, B. Effect of wood flour content on the hardness and water uptake of thermoplastic polymer composites. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 12, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, I.; Kord, B. Long-term water absorption behavior of polypropylene/wood flour/organoclay hybrid nanocomposite. Iran Polym. J. 2009, 18, 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibers. J. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinihashemi, K.; Modirzare, M.; Safdari, V.; Kord, B. Decay resistance, hardness, water absorption and thickness swelling of a bagasse fiber/plastic composite. Bioresources 2011, 6, 3289–3299. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhrul, T.; Islam, M.A. Degradation behavior of natural fiber reinforced polymer matrix composites. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhey, S.; Laks, P.; Richter, D. Laboratory decay resistance of woodfiber/thermoplastic composites. For. Prod. J. 2001, 51, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mankowski, M.; Morrel, J.J. Patterns of fungal attack in wood plastic composites following exposure in a soil block test. Wood Fiber Sci. 2000, 32, 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Catto, A.L.; Montagna, L.S.; Almeida, S.H.; Silveira, R.M.B.; Santana, R.M.C. Wood plastic composites weathering: Effects of compatibilization on biodegradation in soil and fungal decay. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2016, 109, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, J.; Freitag, C.M.; Silva, A.; Morrell, J.J. Wood/plastic ratio: effect on performance of borate biocides against a brown rot fungus. Holzforschung 2004, 58, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiyi, J.S.; McDonald, A.G. Physical morphology and quantitative characterization of chemical changes of weathered PVC/Pine composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtela, V.; Hamalainen, K.; Karki, T. The effect of preservatives on the properties of wood after modification. Balt. For. 2014, 20, 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.L.; Cooper, P.A.; Sain, M. Evaluate of proposed test methods to determine decay resistance of natural fiber plastic composites. For. Prod. J. 2005, 55, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zabihzadeh, S.M.; HosseiniHashemi, S.K.; MehreganNikoo, H.; Sepidehdam, S.M.J. Influence of fungal decay on physico-mechanical properties of a commercial extruded bagasse/PP composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 29, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H’ng, P.S.; Lee, A.N.; Hang, C.M.; Lee, S.H.; Khalina, A.; Paridah, M.T. Biological durability of injection moulded wood plastic composite boards. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Ramírez, M.G.; Ochoa-Ruiz, H.G.; Fuentes-Talavera, F.J.; García-Enriquez, S.; Cerpa-Gallegos, M.A.; Silva-Guzmán, J.A. Evaluation of accelerated decay of wood plastic composites by Xylophagus fungi. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2009, 63, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, J.J.; Stark, N.M.; Pendleton, D.E.; McDonald, A.G. Durability of wood-plastic composites. Wood Des. Focus 2006, 16, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek, H.; Oldak, D.; Malanowski, P.; Chaberska, H. Effect of short wavelength UV-irradiation on ageing of polypropylene/cellulose composition. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2005, 88, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hamdan, S.; Hasan, M.; Ahmed, A.S.; Rahman, M.R. Effect of coupling reactions on the mechanical and biological properties of tropical wood polymer composites (WPC). Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2012, 72, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yu, J.; Tesso, T.; Dowell, F.; Wang, D. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lignocellulosic biomass using infrared techniques: A mini-review. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butylina, S.; Hyvarinen, M.; Karki, T. Accelerated weathering of wood–polypropylene composites containing minerals. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pickering, K.L.; Farrell, R.L. Determination of interfacial shear strength of white rot fungi treated hemp fibre reinforced polypropylene. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabbe, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; Thompson, L.; Walz, S.L.; Schultz, W.W. Biodegradation of a colloidal ester-based polyurethane by soil fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr. 1994, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, J.P. Infrared study of polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1960, 3, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Segura, C.; Bustamante-García, V.; Cápiro, O.G.; Jiménez, R. Torrefaction of wood and bark from Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus nitens: Focus on volatile evolution vs feasible temperatures. Energy 2015, 93, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.L.; Xing, X.S.; Li, R.K.Y.; Tjonga, S.C.; Mai, Y.W. An investigation on the processing of sisal fibre reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Kaymakci, A.; Güleç, T. Potential use of decayed wood in production of wood plastic composite. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Yan, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.C. Overcome the recalcitrance of eucalyptus bark to enzymatic hydrolysis by concerted ionic liquid pretreatment. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.X.; Blin, J. A review on pyrolysis of biomass constituents: Mechanisms and composition of the products obtained from the conversion of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Paterson, N.; Blamey, J.; Millan, M. Cellulose, xylan and lignin interactions during pyrolysis oflignocellulosic biomass. Fuel 2017, 191, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, E.; Várhegyi, G.; Faix, O. Thermal decomposition of polypropylene in thepresence of wood-derived materials. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2000, 56, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







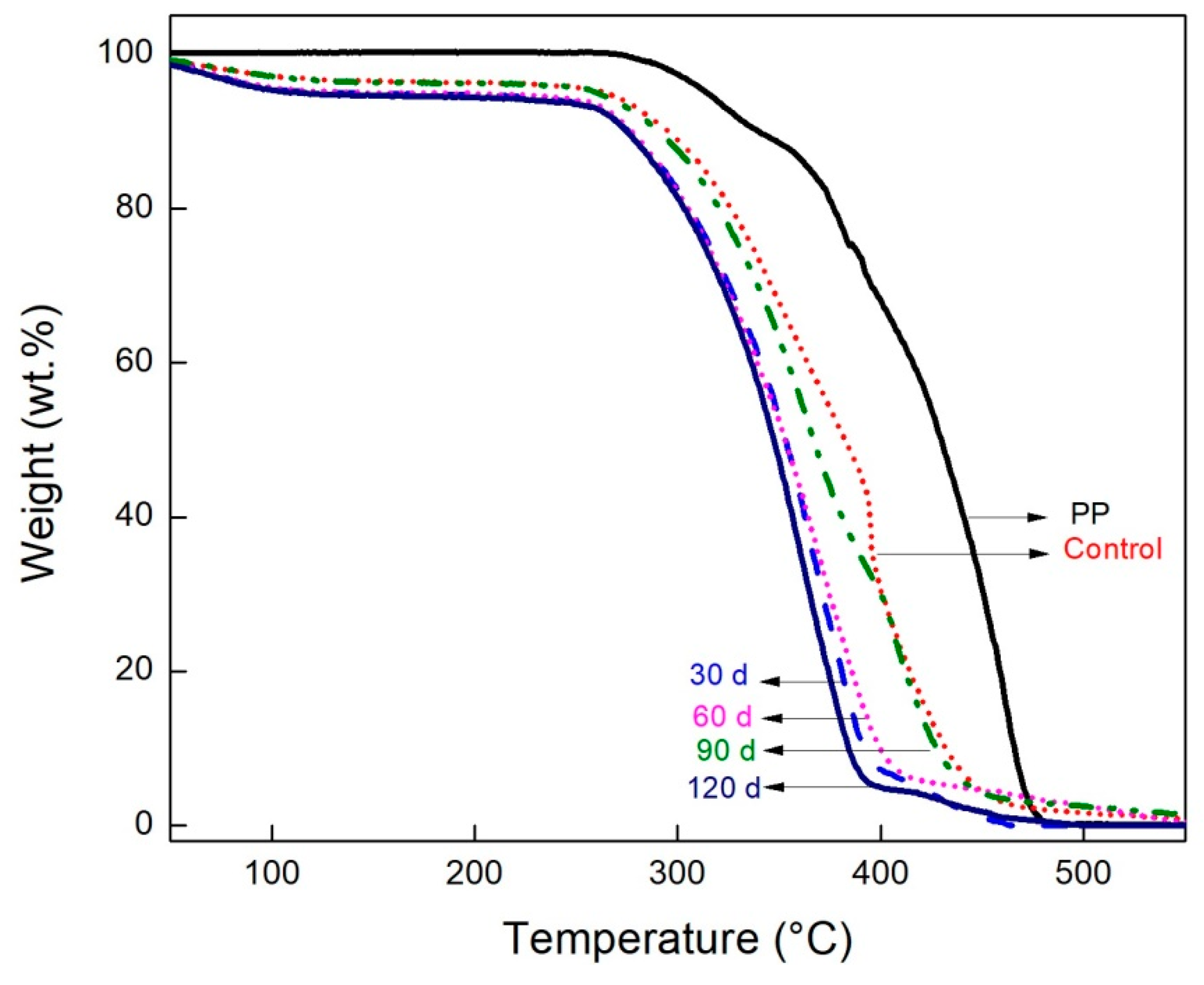
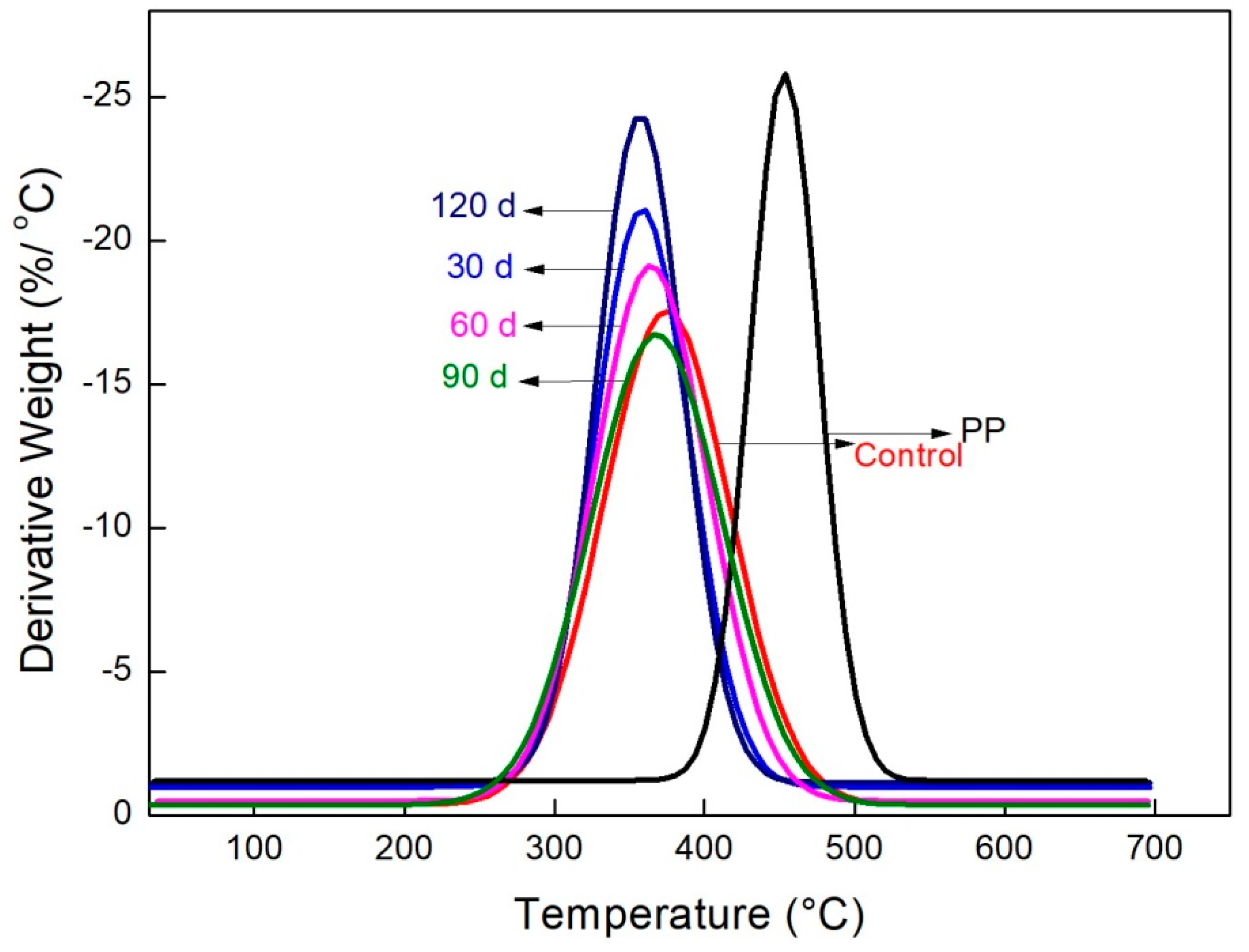
| Samples | Ti (°C) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| PP | 285 | 453 |
| Control | 233 | 374 |
| 30 d | 247 | 358 |
| 60 d | 245 | 364 |
| 90 d | 234 | 368 |
| 120 d | 250 | 357 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cesarino, I.; Dias, O.A.T.; Negrão, D.R.; Rocha, L.L.N.; Leão, A.L. Deterioration of Wood Plastics Composites by the White-Rot Fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3010024
Cesarino I, Dias OAT, Negrão DR, Rocha LLN, Leão AL. Deterioration of Wood Plastics Composites by the White-Rot Fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus. Journal of Composites Science. 2019; 3(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCesarino, Ivana, Otávio Augusto Titton Dias, Djanira Rodrigues Negrão, Ligia Linardi Niero Rocha, and Alcides Lopes Leão. 2019. "Deterioration of Wood Plastics Composites by the White-Rot Fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus" Journal of Composites Science 3, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3010024
APA StyleCesarino, I., Dias, O. A. T., Negrão, D. R., Rocha, L. L. N., & Leão, A. L. (2019). Deterioration of Wood Plastics Composites by the White-Rot Fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus. Journal of Composites Science, 3(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3010024







