Piezoresistive and mechanical Behavior of CNT based polyurethane foam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Mechanical Compression Tests
2.4. Piezoresistive Characterizations
2.5. Electronic Microscope
3. Results
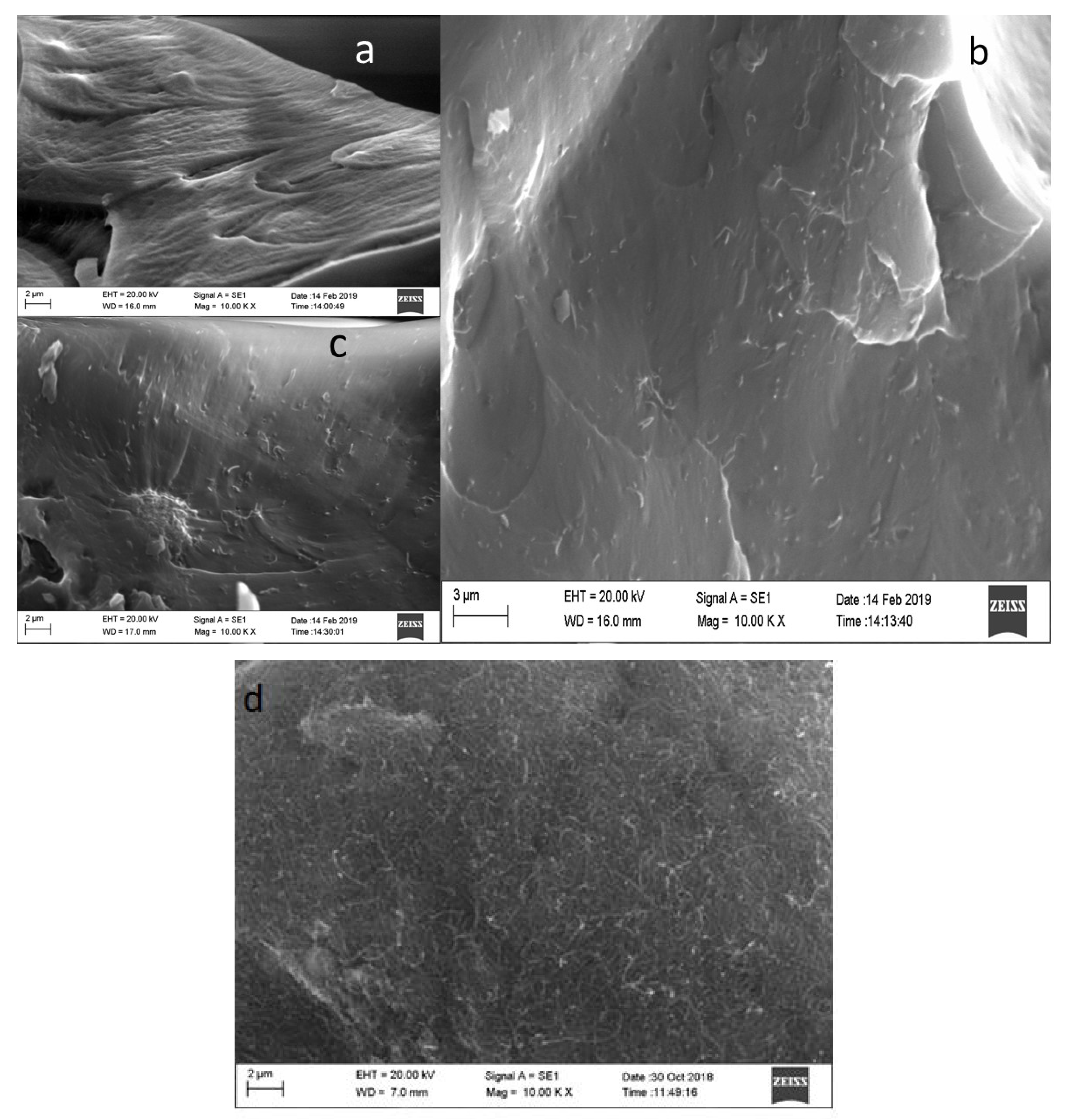
3.1. SEM Images
3.2. Compression Properties of the Composite Materials
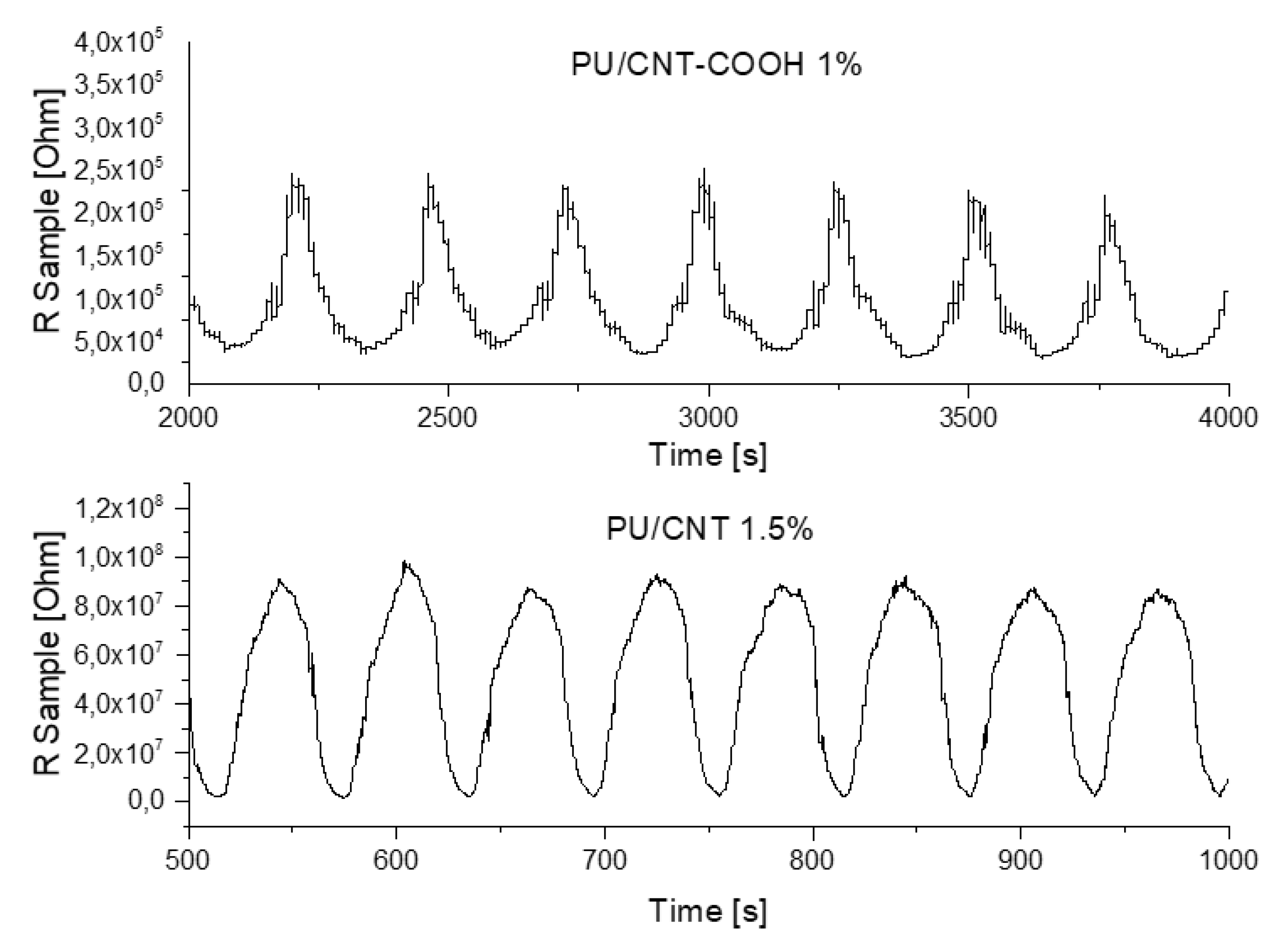
3.3. Piezoresistive Tests
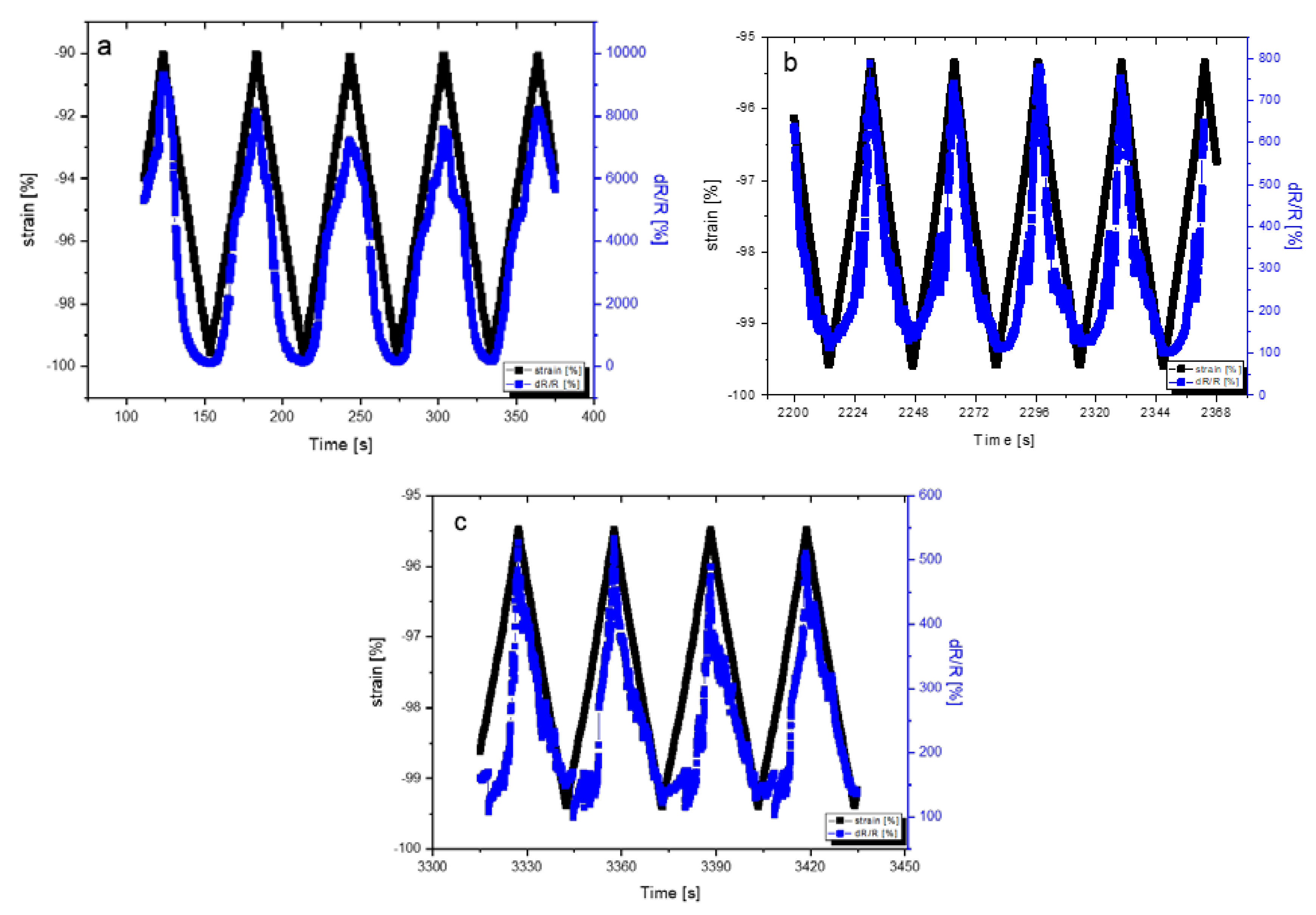
3.4. Cyclic Compressive Loading
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chatterjee, S.; Nafezarefi, F.; Tai, N.H.; Schlagenhauf, L.; Nüesch, F.A.; Chu, B.T.T. Size and synergy effects of nanofiller hybrids including graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes in mechanical properties of epoxy composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 5380–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.T.; Krause, B.; Kretzschmar, B.; Pötschke, P. Influence of a supplemental filler in twin-screw extruded PP/CNT composites using masterbatch dilution. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Isshiki, N.; Saito, H.; Kohno, K.; Toyota, A. Nucleation effect of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes on the crystallization of isotactic poly (1-butene). J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Lin, W.N.; Huang, Y.L.; Tien, H.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Ma, C.C.M.; Li, S.M.; Wang, Y.S. Synergetic effects of graphene platelets and carbon nanotubes on the mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Choi, H.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.Y. Synergistic effect of hybrid graphene nanoplatelet and multi-walled carbon nanotube fillers on the thermal conductivity of polymer composites and theoretical modeling of the synergistic effect. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.R.; Janke, A. Carbon nanotube-filled polycarbonate composites produced by melt mixing and their use in blends with polyethylene. Carbon 2004, 42, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Mu, Y.H.; Tang, Q.; Li, C.Q. Preparation and Performance of PVC/CNT Nanocomposite. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.C.L.; Soares, B.G.; Silva, A.A.; da Silva, J.M.F.; Barra, G.M.O.; Livi, S. Conductive heterogeneous blend composites of PP/PA12 filled with ionic liquids treated-CNT. Polym. Test. 2019, 74, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. The effective conductivity of polymer carbon nanotubes (CNT) nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 131, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Ke, K.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Effect of carbon nanotube morphology on properties in thermoplastic elastomer composites for strain sensors. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesano, F.; Rattalino, I.; Demarchi, D.; Bardelli, F.; Sanginario, A.; Gianturco, A.; Veca, A.; Viazzi, C.; Castelli, P.; Scarano, D.; et al. Structure and properties of metal-free conductive tracks on polyethylene/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites as obtained by laser stimulated percolation. Carbon 2013, 61, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.; Bonab, V.S.; Yuan, D.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Piezoresistive thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites with carbon nanostructures. Carbon 2018, 139, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravanzola, S.; Haznedar, G.; Scarano, D.; Zecchina, A.; Cesano, F. Carbon-based piezoresistive polymer composites: Structure and electrical properties. Carbon 2013, 62, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Orrego, S.; Pan, J.; He, P.; Kang, S.H. Ultrasensitive, flexible, and low-cost nanoporous piezoresistive composites for tactile pressure sensing. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.W.; Thio, T.; Hiura, H.; Lezec, H.J.; Ebbesen, T.W.; Ghaemi, H.F. Electrical conductivity of individual carbon nanotubes. Nature 2003, 382, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosiou, T.C.; Saravanos, D.A. Numerical investigation of mechanisms affecting the piezoresistive properties of CNT-doped polymers using multi-scale models. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Karube, Y.; Yan, C.; Masuda, Z.; Fukunaga, H. Tunneling effect in a polymer/carbon nanotube nanocomposite strain sensor. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2929–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradonna, A.; Badini, C.; Padovano, E.; Veca, A.; De Meo, E.; Pietroluongo, M. Laser Treatments for Improving Electrical Conductivity and Piezoresistive Behavior of Polymer–Carbon Nanofiller Composites. Micromachines 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Huang, W.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Yan, X.; Guo, J.; Guo, Z. Electrically conductive strain sensing polyurethane nanocomposites with synergistic carbon nanotubes and graphene bifillers. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12977–12989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abishera, R.; Velmurugan, R.; Gopal, K.V.N. Reversible plasticity shape memory effect in carbon nanotube/epoxy nanocomposites: Shape recovery studies for torsional and bending deformations. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, E189–E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwi, T.A.; Al-Rizzo, H.M.; Rucker, D.G.; Dervishi, E.; Li, Z.; Biris, A.S. Multi-walled carbon nanotube-based RF antennas. Nanotechnology 2010, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-B.; Li, Z.-M.; Shi, L.; Bian, X.-C.; Xiang, Z.-D. Ultralight Conductive Carbon-Nanotube–Polymer Composite. Small 2007, 3, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.-X.; Dai, K.; Xiang, Z.-D.; Li, Z.-M.; Ji, X.; Zhang, W.-Q. Electrical conductivity and major mechanical and thermal properties of carbon nanotube-filled polyurethane foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 3014–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, A.; Gandla, S.; Bohm, S.; McNeill, C.R.; Gupta, D. Highly Exfoliated MWNT-rGO Ink-Wrapped Polyurethane Foam for Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5185–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, T.; Li, D.; Fei, G.; Xia, H. Piezoresistive and compression resistance relaxation behavior of water blown carbon nanotube/polyurethane composite foam. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 72, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifer, N.D.R.; Noked, M.; Nessim, G.D. A straightforward and reliable method for the characterization of carbon nanotube dispersions. Carbon 2010, 49, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icoglu, F.; Ciltas, A.; Simsek, N. Chemosphere A holistic study on potential toxic effects of carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-COOH) on zebra fi sh (Danio rerio) embryos/larvae. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Goodridge, R.D.; Hague, R.J.M. Nanostructural characterization of carbon nanotubes in laser-sintered polyamide 12 by 3D-TEM. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, T.R.; Capasso, M.J.; Cavusoglu, M.E.; Decker, J.; Zeppilli, D.; Zhu, C.; Bakrania, S.; Kadlowec, J.A.; Xue, W. Evaluation of porous polydimethylsiloxane/carbon nanotubes (PDMS/CNTs) nanocomposites as piezoresistive sensor materials. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, G. Experiments on Elastic Polyether Polyurethane Foams Under Multiaxial Loading: Mechanical Response and Strain Fields. J. Appl. Mech. 2011, 78, 031018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Fukunaga, H.; Atobe, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Piezoresistive Strain Sensors Made from Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2011, 11, 10691–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.G. Generalized Formula for the Electric Tunnel Effect between Similar Electrodes Separated by a Thin Insulating Film. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Marom, G.; Kim, J. Composites: Part A Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.G.; Jung, Y.C.; Yoo, H.J.; Cho, J.W. Effect of Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes on Molecular Interaction and Properties of Polyurethane Composites. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, A.; Blaedel, W.J.; Wang, J.; Rochon, A.M.; Gesser, H.D.; Aubert, J.H.; Rand, P.B.; Arnold, C.; Clough, L.R.; Clough, R.L.; et al. Mechanical Damage of Carbon Nanotubes by Ultrasound. Carbon 1996, 34, 814–816. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. Modifications of carbon nanotubes with polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitalsky, Z.; Tasis, D.; Papagelis, K.; Galiotis, C. Progress in Polymer Science Carbon nanotube—Polymer composites: Chemistry, processing, mechanical and electrical properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 357–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlay, İ.; Tudoran, L.B. Percolation Behavior of Electrically Conductive Graphene Nanoplatelets/Polymer Nanocomposites: Theory and Experiment. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2014, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dowden, A.; Deng, H.; Baxendale, M.; Peijs, T. Conductive network formation in the melt of carbon nanotube/thermoplastic polyurethane composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Z. Flexible strain sensors fabricated using carbon-based nanomaterials: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 22, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avil, F.; Cen-Puc, M. Piezoresistivity, Strain, and Damage Self-Sensing of Polymer Composites Filled with Carbon Nanostructures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1701159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Sun, Y. Dispersion and Solubilization of Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2003, 3, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Thomas, I.B.M.; Heights, Y.; York, N. The nature of percolation ‘channels’. Solid State Commun. 1973, 12, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PU sample | Eplateau (MPa) |
|---|---|
| Neat PU | 31 |
| PU/CNT 1.5% | 42 |
| PU/CNT-COOH 1% | 45 |
| PU/CNT-COOH 1.5% | 52 |
| PU foam | Deformation Range (%) | Initial Resistance Value (MOhm) | Final Resistance Value (kOhm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PU CNT-COOH 1% | 95.5–99.8 | >120 1 | 618 |
| PU CNT-COOH 1.5% | 95.5–99.8 | >120 1 | 34 |
| PU foam | Gauge Factor |
|---|---|
| PU CNT 1.5% | 80 |
| PU CNT-COOH 1% | 33 |
| PU CNT-COOH 1.5% | 23 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Meo, E.; Agnelli, S.; Veca, A.; Brunella, V.; Zanetti, M. Piezoresistive and mechanical Behavior of CNT based polyurethane foam. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030131
De Meo E, Agnelli S, Veca A, Brunella V, Zanetti M. Piezoresistive and mechanical Behavior of CNT based polyurethane foam. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Meo, Enea, Simone Agnelli, Antonino Veca, Valentia Brunella, and Marco Zanetti. 2020. "Piezoresistive and mechanical Behavior of CNT based polyurethane foam" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030131
APA StyleDe Meo, E., Agnelli, S., Veca, A., Brunella, V., & Zanetti, M. (2020). Piezoresistive and mechanical Behavior of CNT based polyurethane foam. Journal of Composites Science, 4(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030131





