Dual In-Situ Water Diffusion Monitoring of GFRPs based on Optical Fibres and CNTs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Epoxy and GFRP Containing CNTs Samples Fabrication
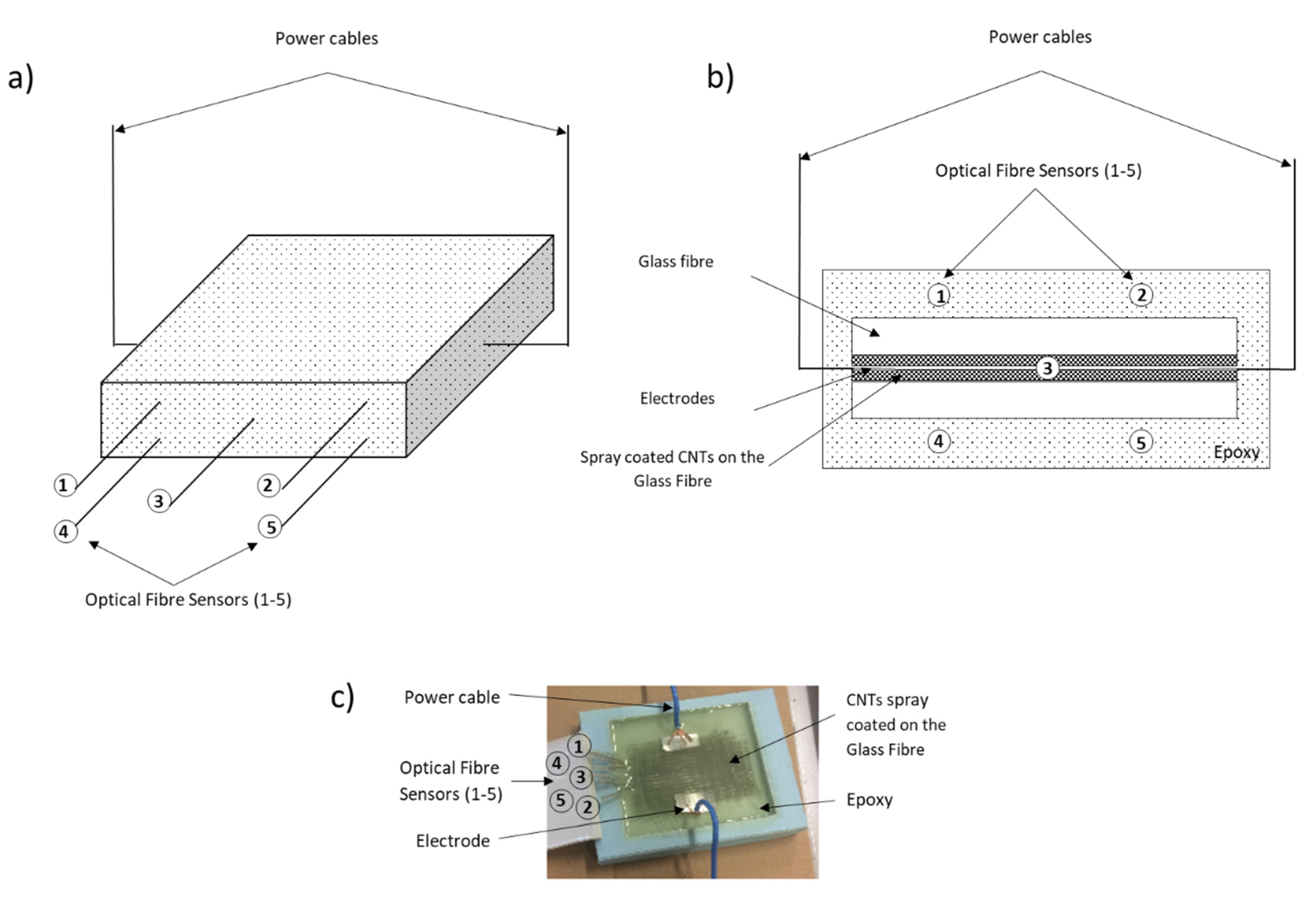
2.2. GFRP Samples Containing Spray Coated CNTs with Embedded OFSs Fabrication
2.3. Optical Fibre Sensors Fabrication and the Interrogation Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the Diffusion Coefficients
3.2. Electrical Conductivity and Water Diffusion Sensing of Epoxy/CNT and GFRP/CNT
3.3. GFRP with Embedded OFSs and CNTs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, D.C.; Wilkerson, J.W.; Zhu, J.; Ayewah, D.O.O. Improvements in mechanical properties of a carbon fiber epoxy composite using nanotube science and technology. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Lupton, D. Design and Manufacture of Bushings for Glass Fibre Production; HVG-Colloquium: Dusseldoff, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Carra, G.; Carvelli, V. Ageing of pultruded glass fibre reinforced polymer composites exposed to combined environmental agents. Compos. Struct. 2014, 108, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass Fiber Differences and Properties, Prince Eng. Build Prince. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.build-on-prince.com/glass-fiber.html (accessed on 18 July 2018).
- Gibson, A.G. The Cost Effective Use of Fibre Reinforced Composites Offshore; HSE Books: Newcastle, UK, 2003; p. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Bristol, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Milsom, B.; Olivero, M.; Milanese, D.; Giannis, S.; Martin, R.H.; Terenzi, A.; Kenny, J.; Ferraris, M.; Perrone, G.; Salvo, M. Glass optical fibre sensors for detection of through thickness moisture diffusion in glass reinforced composites under hostile environments. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2015, 114, S76–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bach, H.; Neuroth, N. The Properties of Optical Glass, 2nd ed.; Springer: Mainz, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Růžek, R.; Kadlec, M.; Tserpes, K.; Karachalios, E. Strain monitoring in stiffened composite panels using embedded fibre optical and strain gauge sensors. In Proceedings of the 7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring (EWSHM 2014–2nd European Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society), Nantes, France, 8–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) Sensor Principle, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.fbgs.com/technology/fbg-principle/ (accessed on 17 July 2018).
- Stetter, J.R.; Penrose, W.R.; Yao, S. Sensors, Chemical Sensors, Electrochemical Sensors, and ECS. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhuang, R.-C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.-W.; Mäder, E. Glass Fibers with Carbon Nanotube Networks as Multifunctional Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.F.; Xiao, S.H.; Feng, C.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Li, X. Resistive humidity sensitivity of arrayed multi-wall carbon nanotube nests grown on arrayed nanoporous silicon pillars. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.-P.; Lim, L.-T.; Min, N.K.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.J.; Park, C.W. Novel resistive-type humidity sensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube/polyimide composite films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, J.; Deva, D. Carbon Nanotube-polymer composites for sensor applications. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 2321. [Google Scholar]
- Terrones, M. Science and Technology of the Twenty-First Century: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2003, 33, 419–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Huo, S.; Briscoe, J.; Tu, W.; Picot, O.T.; Rezai, A.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. Filtration effects of graphene nanoplatelets in resin infusion processes: Problems and possible solutions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 139, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Porwal, H.; Tu, W.; Evans, J.; Newton, M.; Busfield, J.J.C.; Peijs, T.; Bilotti, E. Universal Control on Pyroresistive Behavior of Flexible Self-Regulating Heating Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kuwata, M.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. Improved fracture toughness and integrated damage sensing capability by spray coated CNTs on carbon fibre prepreg. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 70, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. Dissolvable thermoplastic interleaves for carbon nanotube localization in carbon/epoxy laminates with integrated damage sensing capabilities. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 17, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, B.C.; Olivero, M.; Sangermano, M.; Salvo, M. Towards smart polymer composites: Detection of moisture diffusion through epoxy by evanescent wave optical fibre sensors. Polym. Test. 2018, 71, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. Optimization of Three-Roll Mill Parameters for In-Situ Exfoliation of Graphene. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Crespo, M.; Porwal, H.; Picot, O.; Santagiuliana, G.; Huang, Z.; Barbieri, E.; Pugno, N.M.; Peijs, T.; et al. In Situ Exfoliation of Graphene in Epoxy Resins: A Facile Strategy to Efficient and Large Scale Graphene Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, A.; Kar, K.K. Effect of Coating Time and Temperature on Electroless Deposition of Cobalt-Phosphorous for the Growth of Carbon Nanotubes on the Surface of E-Glass Fibers/Fabric. Full Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2011, 19, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakowski, K.; Narozny, M.; Szociński, M.; Darowicki, K. Influence of water salinity on corrosion risk-the case of the southern Baltic Sea coast. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4871–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starink, M.J.; Starink, L.M.P.; Chambers, A.R. Moisture uptake in monolithic and composite materials: Edge correction for rectanguloid samples. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagani, A.; Fan, Y.; Muliana, A.H.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Micromechanical modeling of anisotropic water diffusion in glass fiber epoxy reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 52, 2321–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Alimohammadi, F.; Shamei, A.; Rahimi, M.K. In situ synthesis of nano silver on cotton using Tollens’ reagent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, M.; Sangermano, M.; Marro Bellot, C.; Olivero, M. Optical Sensor, Process for Making Such Sensor and Evaluation System Comprising at Least One of Such Sensors. Pat. Appl. 2018WO–IT00059 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marro Bellot, C.; Sangermano, M.; Olivero, M.; Salvo, M. Optical Fiber Sensors for the Detection of Hydrochloric Acid and Sea Water in Epoxy and Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prolongo, S.; Gude, M.; Ureña, A. Water uptake of epoxy composites reinforced with carbon nanofillers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavasin, M.; Salvo, M.; Sangermano, M. Study on Accelerated Exposure Testing and Thermal Insulation for a Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer in Simulated Oil & Gas Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Marro Bellot, C.; Salvo, M.; Sangermano, M. Design, Processing and Characterisation of New Optical Fibre Sensors for Harsh Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, January 2019. [Google Scholar]






| Sensor Type | Depth (mm) | Experimental Time (h) | Theoretical Time (h) | Corrected Theoretical Time (h) | |
| Optical Glass Fibre Sensors | 1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 16 ± 4 | ||
| 2 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 16 | 13 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | |
| 3 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 43 | 39 ± 5 | 40 ± 5 | |
| 4 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 18 | 16 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | |
| 5 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 19 | 16 ± 1 | 16 ± 1 | |
| CNTs | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 48 | 38 ± 5 | 40 ± 5 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marro Bellot, C.; de Leo, G.; Zhang, H.; Kernin, A.; Scarponi, C.; Sangermano, M.; Olivero, M.; Bilotti, E.; Salvo, M. Dual In-Situ Water Diffusion Monitoring of GFRPs based on Optical Fibres and CNTs. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030097
Marro Bellot C, de Leo G, Zhang H, Kernin A, Scarponi C, Sangermano M, Olivero M, Bilotti E, Salvo M. Dual In-Situ Water Diffusion Monitoring of GFRPs based on Optical Fibres and CNTs. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(3):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030097
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarro Bellot, Cristian, Giulia de Leo, Han Zhang, Arnaud Kernin, Claudio Scarponi, Marco Sangermano, Massimo Olivero, Emiliano Bilotti, and Milena Salvo. 2020. "Dual In-Situ Water Diffusion Monitoring of GFRPs based on Optical Fibres and CNTs" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 3: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030097
APA StyleMarro Bellot, C., de Leo, G., Zhang, H., Kernin, A., Scarponi, C., Sangermano, M., Olivero, M., Bilotti, E., & Salvo, M. (2020). Dual In-Situ Water Diffusion Monitoring of GFRPs based on Optical Fibres and CNTs. Journal of Composites Science, 4(3), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4030097








