The Mechanism of Joint Reduction of MoO3 and CuO by Combined Mg/C Reducer at High Heating Rates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
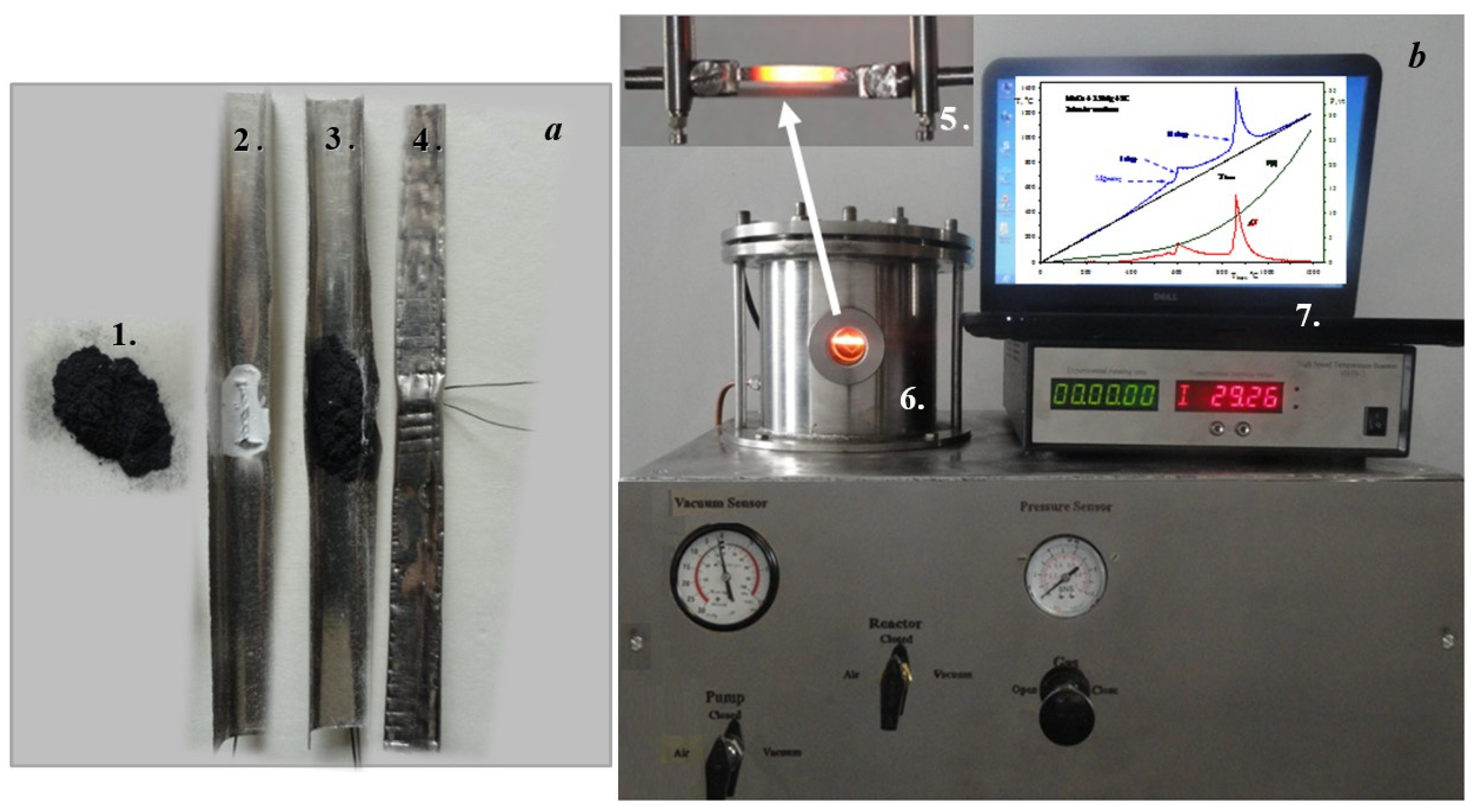
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CuO-MoO3, CuO-C, MoO3-C, MoO3-Mg Binary Systems
3.1.1. CuO-MoO3 System
3.1.2. CuO-C System
3.1.3. MoO3-C System
3.1.4. MoO3-Mg System
3.2. MoO3-Mg-C, MoO3-CuO-Mg and MoO3-CuO-C Ternary Systems
3.2.1. MoO3-Mg-C System
3.2.2. CuO-MoO3-Mg System
3.2.3. CuO-MoO3-C System
3.3. CuO-MoO3-Mg-C Quaternary System
3.4. The Effective Activation Energy of Magnesiothermic Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phasha, M.; Bolokang, A.; Kebede, M. First-principles investigation of W V and W Mo alloys as potential plasma facing materials (PFMs) for nuclear application. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 95, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qiu, W.; Chen, L.; Tang, J. Tungsten–potassium: A promising plasma-facing material. Tungsten 2019, 1, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Q.; Luo, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. Microstructure and bonding strength of diffusion welding of Mo/Cu joints with Ni interlayer. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrvash, H.; Rad, R.Y.; Massoudi, A.; Shokrvash, R. Copper Bimetals and Their Nanocomposites. In Nanorods and Nanocomposites; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agostinetti, P.; Palma, M.D.; Bello, S.D.; Heinemann, B.; Nocentini, R.; Zauner, C.; Langer, H.; Klammer, J. Investigation of the thermo-mechanical properties of electro-deposited copper for ITER. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 417, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souli, I.; Gruber, G.C.; Terziyska, V.L.; Zechner, J.; Mitterer, C. Thermal stability of immiscible sputter-deposited Cu-Mo thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jayasankar, K.; Debata, M.; Mandal, A. Mechanical alloying and properties of immiscible Cu-20 wt.% Mo alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souli, I.; Terziyska, V.L.; Zechner, J.; Mitterer, C. Microstructure and physical properties of sputter-deposited Cu-Mo thin films. Thin Solid Films 2018, 653, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, W.-C.; Bu, C.-Y.; He, K.; Chou, K.-C.; Zhang, G.-H. Sintering behavior of molybdenum-copper and tungsten-copper alloys by using ultrafine molybdenum and tungsten powders as raw materials. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 88, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, F. Formation and homogenisation of Sn Cu interconnects by self-propagated exothermic reactive bonding. Mater. Des. 2019, 174, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.; Braun, S.; Hofmann, C.; Weiser, M.; Wiemer, M.; Otto, T.; Kuhn, H. Reactive Bonding. In 3D and Circuit Integration of MEMS; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, C.; Marin-Ayral, R.; Tédenac, J. Joining of nickel monoaluminide to a superalloy substrate by high pressure self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 337, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinyan, S.; Kirakosyan, H.; Kharatyan, S. Cu–Mo composite powders obtained by combustion–coreduction process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 54, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasyan, T.; Kirakosyan, H.; Aydinyan, S.; Liu, L.; Kharatyan, S.; Hussainova, I. Mo–Cu pseudoalloys by combustion synthesis and spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 16598–16608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharatyan, S.L. High speed temperature scanner (HSTS) for nonisothermal kinetic studies. In Proceedings of the III International Conference on Nonisothermal Phenomena and Processes: From Thermal Explosion Theory to Structural Makrokinetics, Chernogolovka, Russia, 28–30 November 2016; pp. 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaryan, M.; Nazaretyan, K.; Aydinyan, S.; Kharatyan, S. Joint Reduction of NiO/WO3 Pair and NiWO4 by Mg + C Combined Reducer at High Heating Rates. Metals 2021, 11, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaryan, M.K.; Nazaretyan, K.T.; Aydinyan, S.V.; Kharatyan, S.L. NiO reduction by Mg + C combined reducer at high heating rates. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 146, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobosyan, M.A.; Kirakosyan, K.G.; Kharatyan, S.L.; Martirosyan, K.S. PTFE–Al2O3 reactive interaction at high heating rates. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, K.E. Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys (Revised Reprint), 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 520. [Google Scholar]
- Massih, A.R.; Jernkvist, L.O. Solid state phase transformation kinetics in Zr-base alloys. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinyan, S.V.; Nazaretyan, K.T.; Zargaryan, A.G.; Tumanyan, M.E.; Kharatyan, S.L. Reduction mechanism of WO3 + CuO mixture by combined Mg/C reducer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirakosyan, H.; Minasyan, T.; Niazyan, O.; Aydinyan, S.; Kharatyan, S. DTA/TG study of CuO and MoO3 co-reduction by combined Mg/C reducers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinyan, S.V.; Manukyan, K.V.; Kharatyan, S.L. Combustion synthesis of Mo–Cu nanocomposites by co-reduction of molybdenum and copper oxides. In Proceedings of the XII International Symposium on SHS, South Padre Island, TX, USA, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Minasyan, T.T.; Aydinyan, S.V.; Kharatyan, S.L. Combustion synthesis of Mo-Cu composite powders from oxide precursors with various proportions of metals. Chem. J. Armen. 2016, 69, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt, W.G. The Handbook of Binary Phase Diagrams General Electric Company; Corporate Research and Development, Technology Marketing Operation, The Materials Informations Society, ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1981; Volume 3, p. 522. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann, M.; Ehrenberg, H.; Miehe, G.; Peun, T.; Weitzel, H.; Fuess, H. p–TPhase Diagram of CuMoO4. J. Solid State Chem. 1997, 132, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, H.; Weitzel, H.; Paulus, H.; Wiesmann, M.; Wltschek, G.; Geselle, M.; Fuess, H. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of CuMoO4 at low temperature (γ-phase). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1997, 58, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tali, R.; Tabachenko, V.V.; Kovba, L.M.; Dem’yanets, L.N. The crystal strucure of CuMoO4-III. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 36, 927–928. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanakumar, B.; Ravi, G.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Ganesh, V.; Guduru, R.K. Synthesis of polyoxometalates, copper molybdate (Cu3Mo2O9) nanopowders, for energy storage applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 93, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L.; Bu, Y.; Deng, H.-H.; Chen, R.; Peng, H.; Lin, X.; Chen, W. Colorimetric acid phosphatase sensor based on MoO3 nanozyme. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1105, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manukyan, K.; Aydinyan, S.; Aghajanyan, A.; Grigoryan, Y.; Niazyan, O.; Kharatyan, S. Reaction pathway in the MoO3+Mg+C reactive mixtures. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 31, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Variation of peak temperature with heating rate in differential thermal analysis. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1956, 57, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdasaryan, A.; Niazyan, O.; Khachatryan, H.; Kharatyan, S. DTA/TGA study of molybdenum oxide reduction by Mg/Zn & Mg/C combined reducers at non-isothermal conditions. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015, 51, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Vh, K min−1 | The System under Study | T, K | XRD | T, K | XRD | T, K | XRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | CuO + MoO3 + + 1.1Mg + 2C | 753–793 | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | 793–873 | MoO2, Cu, Mg | 1013–1043 Tmax = 760 | Mo, Cu, MgO, MgO·MoO2 |
| 100 | CuO + MoO3 + + 1.2Mg + 2.15C | 773–823 | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | 923–1003 | MoO2, Cu, Mg | 1143–1163 Tmax = 940 | Mo, Cu, MoO2 (main product), Mo2C, MgO |
| 300 | CuO + MoO3 + + 1.2Mg + 2.15C | 833–873 | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | 933–1013 | MoO2, Cu, Mg | 1213–1263 Tmax = 1523 | Mo, Cu, MgO, MoO2(trace), Mo2C |
| 2600 | CuO + MoO3 + + 1.2Mg + 2.15C | 843–883 | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | 1033–1233 | MoO2, Cu, Mg | 1393–1583 Tmax = 1563 | Mo, Cu, MgO, Mo2C |
| 5200 | CuO + MoO3 + + 1.2Mg + 2.15C | 853–893 | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | 1053–1263 | MoO2, Cu, Mg | 1403–1633 Tmax = 1583 | Mo, Cu, MgO, Mo2C(trace) |
| System [Ref] | Vh/ K min−1 | Reaction, T/K | Ea/ kJ mol−1 | Composition | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO-Mg [22] | 20 | 843–953 | - | Cu, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-Mg [21] | 300 | 953–1073 | 424 | Cu, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-C [22] | 20 | CuO + C 713–803 | Cu2O + C 803–923 | - | Cu2O | Cu | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-C [this work] | 300 | CuO + C 823–973 | Cu2O + C 973–1153 | - | Cu2O | Cu | ||||||||||||||||||||
| MoO3-Mg [33] | 20 | 923–973 | 123 | Mo, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| MoO3-Mg [this work] | 300 | 943–1058 | 110 | Mo, MoO2, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| MoO3-C [22,33] | 20 | MoO3 + C 773–873 | MoO2 + C 1103–1173 | - | MoO2 | Mo | ||||||||||||||||||||
| MoO3-C [this work] | 300 | MoO3 + C 833–953 | MoO2 + C 1123–1373 | - | MoO2 | Mo and/or Mo2C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-Mg-C [22] | 20 | CuO + C 703–813 | Cu2O + Mg 923–1063 | - | Cu2O, Mg | Cu, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-Mg-C [21] | 300 | CuO + C 923–1023 | Cu2O + Mg 1023–1053 | 320 | Cu2O, Mg | Cu, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| MoO3-Mg-C [33] | 20 | MoO3 + C 833–903 | MoO2 + Mg 973–1073 | 197 | MoO2, Mg | Mo, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| MoO3-Mg-C [this work] | 300 | MoO3 + C 953–1073 | MoO2 + Mg 1123–1163 | 102 | MoO2, Mg | Mo, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-MoO3-Mg [22] | 20 | CuO + MoO3 823–903 | CuMoO4 + Mg 903–1073 | - | CuMoO4, Mg, MgMoO4 | Cu6Mo5O18, Mo, MoO2·MgO, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-MoO3-Mg [this work] | 300 | CuO + MoO3 940–1073 | Cu3Mo2O9 + Mg 1143–1273 | Cu6Mo5O18 + Cu2O + Mg 1273–1373 | - | Cu3Mo2O9, Mg | Cu, Cu2O, Cu6Mo5O18 MgMoO4, Mg | Cu, Mo, MoO2·MgO, MgO | ||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-MoO3-C [22] | 20 | CuO + C 703–803 | Cu2O + MoO3 + C 803–923 | - | Cu2O, MoO3 | Cu, MoO2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-MoO3-C [this work] | 300 | CuO + MoO3 + C 823–913 | Cu6Mo5O18 + MoO2 + C 923–1023 | MoO2 + C 1023–1393 | MoO2 + Mo2C 1393–1573 | - | Cu6Mo5O18 Cu, MoO2 | Cu, MoO2 | Mo2C, MoO2, Cu | Mo, Cu | ||||||||||||||||
| CuO-MoO3-Mg-C [22] | 20 | CuO + C 753–793 | Cu2O + MoO3 + C 793–873 | MoO2 + Mg 993–800 | - | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | Cu, MoO2, Mg | Mo, Cu, MgO, MgO·MoO2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| CuO-MoO3-Mg-C [this work] | 300 | CuO + C 833- 943 | Cu2O + MoO3 + C 943–1023 | MoO2 + Mg 1213–1263 | 155 | Cu2O, MoO3, Mg | Cu, MoO2, Mg | Mo, Cu, MgO, Mo2C, MoO2 (trace) | ||||||||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirakosyan, H.; Nazaretyan, K.; Aydinyan, S.; Kharatyan, S. The Mechanism of Joint Reduction of MoO3 and CuO by Combined Mg/C Reducer at High Heating Rates. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120318
Kirakosyan H, Nazaretyan K, Aydinyan S, Kharatyan S. The Mechanism of Joint Reduction of MoO3 and CuO by Combined Mg/C Reducer at High Heating Rates. Journal of Composites Science. 2021; 5(12):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120318
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirakosyan, Hasmik, Khachik Nazaretyan, Sofiya Aydinyan, and Suren Kharatyan. 2021. "The Mechanism of Joint Reduction of MoO3 and CuO by Combined Mg/C Reducer at High Heating Rates" Journal of Composites Science 5, no. 12: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120318
APA StyleKirakosyan, H., Nazaretyan, K., Aydinyan, S., & Kharatyan, S. (2021). The Mechanism of Joint Reduction of MoO3 and CuO by Combined Mg/C Reducer at High Heating Rates. Journal of Composites Science, 5(12), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120318







