Hemoglobin–Polyaniline Composite and Electrochemical Field Effective Transistors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.1.1. Synthesis of Hb/PANI
2.1.2. Synthesis of Hb/PANI/cholic acid
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Change
3.2. IR
3.3. Luminol Emission
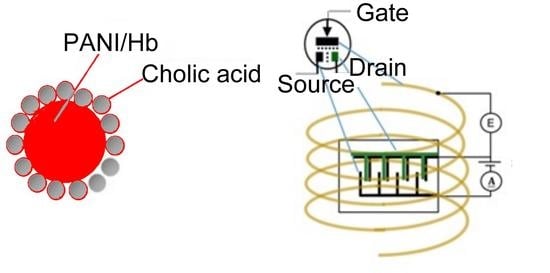
3.4. Transistor
4. Conclusions
5. Techniques
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhéault, J.F.; Gagné, E.; Guertin, M.; Lamoureux, G.; Auger, M.; Lagüe, P. Molecular model of hemoglobin N from Mycobacterium tuberculosis bound to lipid bilayers: A combined spectroscopic and computational study. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 2073–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Tam, M.F.; Simplaceanu, V.; Ho, C. New look at hemoglobin allostery. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1702–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatada, M.; Tran, T.T.; Tsugawa, W.; Sode, K.; Mulchandani, A. Affinity sensor for hemoglobin A1c based on single-walled carbon nanotube field-effect transistor and fructosyl amino acid binding protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, H.; Kerman, K. Revisiting the nitrite reductase activity of hemoglobin with differential pulse voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Sidiq, S.; Pal, S.K. A Simple quantitative method to study protein-lipopolysaccharide interactions by using liquid crystals. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Mulet, X.; Hawley, A.M.; Hinton, T.M.; Mudie, S.T.; Muir, B.W.; Giakoumatos, E.C.; Waddington, L.J.; Kirby, N.M.; Drummond, C.J. Nanostructure and cytotoxicity of self-assembled monoolein-capric acid lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26785–26795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Khan, M.; Park, S.Y. Liquid crystal droplets functionalized with charged surfactant and polyelectrolyte for non-specific protein detection. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 97264–97271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, P.; Mann, E.K.; Jakli, A. Thermotropic liquid crystal films for biosensors and beyond. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2017, 5, 5061–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimal, T.; Agrahari, K.; Sonker, R.K.; Manohar, R. Investigation of thermodynamical, dielectric and electro-optical parameters of nematic liquid crystal doped with polyaniline and silver nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Rong, W.; Shi, C.; Shao, T.; Wang, R. The synthesis and characterization of helical polyaniline in the liquid crystal. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ichikawa, M.; Goto, H. Hemoglobin–Polyaniline Composite and Electrochemical Field Effective Transistors. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5090236
Ichikawa M, Goto H. Hemoglobin–Polyaniline Composite and Electrochemical Field Effective Transistors. Journal of Composites Science. 2021; 5(9):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5090236
Chicago/Turabian StyleIchikawa, Mai, and Hiromasa Goto. 2021. "Hemoglobin–Polyaniline Composite and Electrochemical Field Effective Transistors" Journal of Composites Science 5, no. 9: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5090236
APA StyleIchikawa, M., & Goto, H. (2021). Hemoglobin–Polyaniline Composite and Electrochemical Field Effective Transistors. Journal of Composites Science, 5(9), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5090236