Moisture and Glass Transition Temperature Kinetics of Ambient-Cured Carbon/Epoxy Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
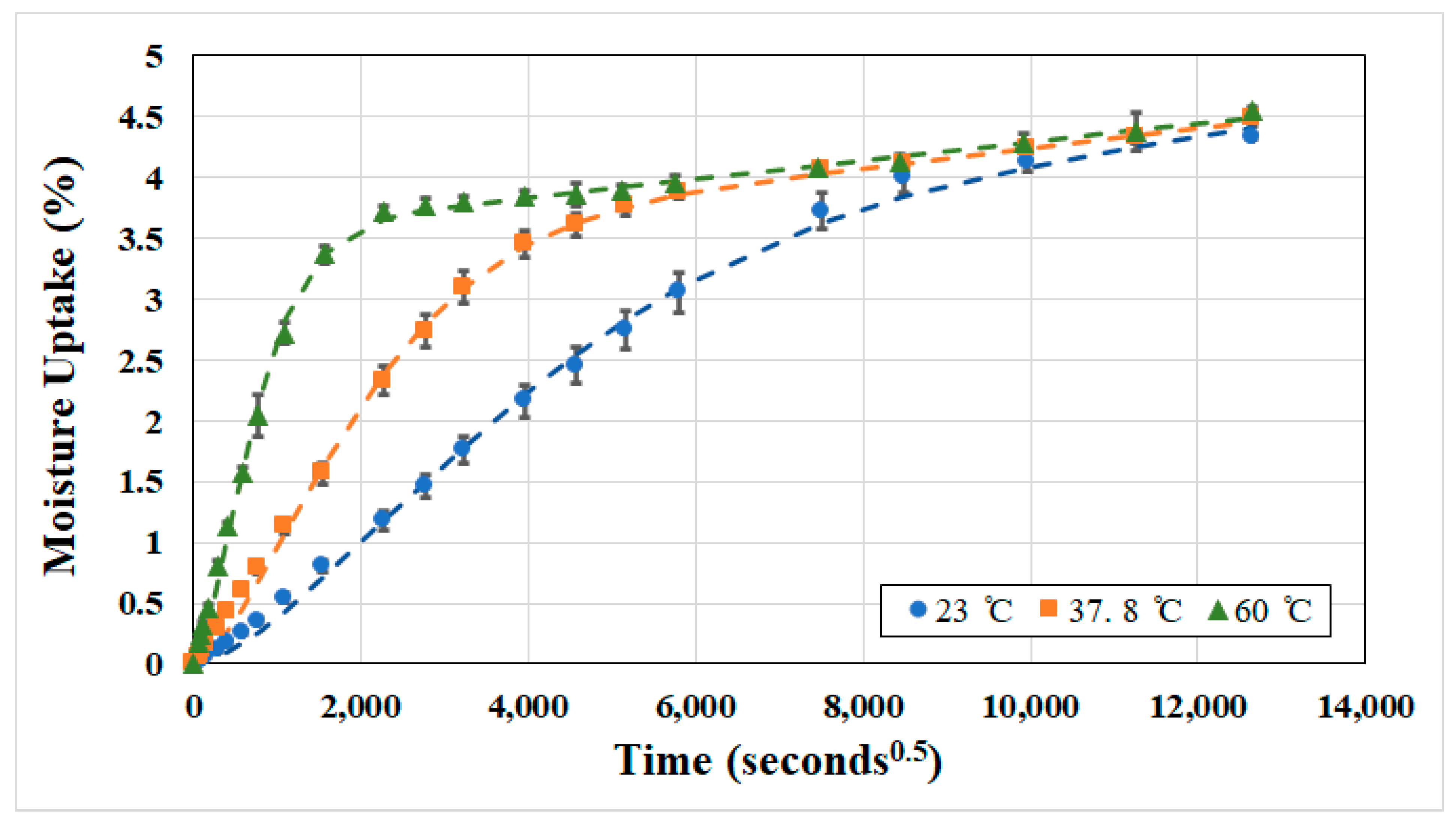
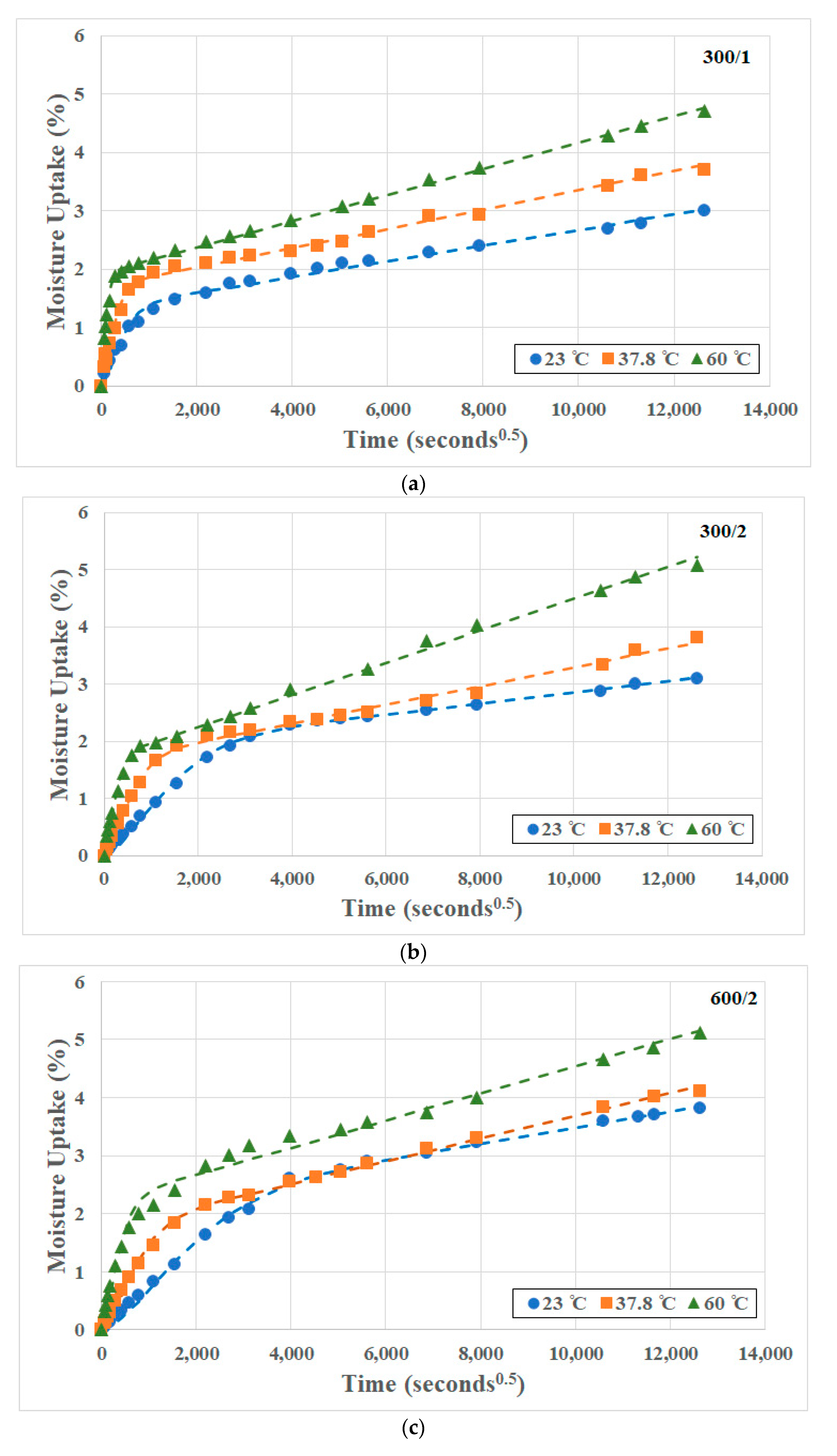
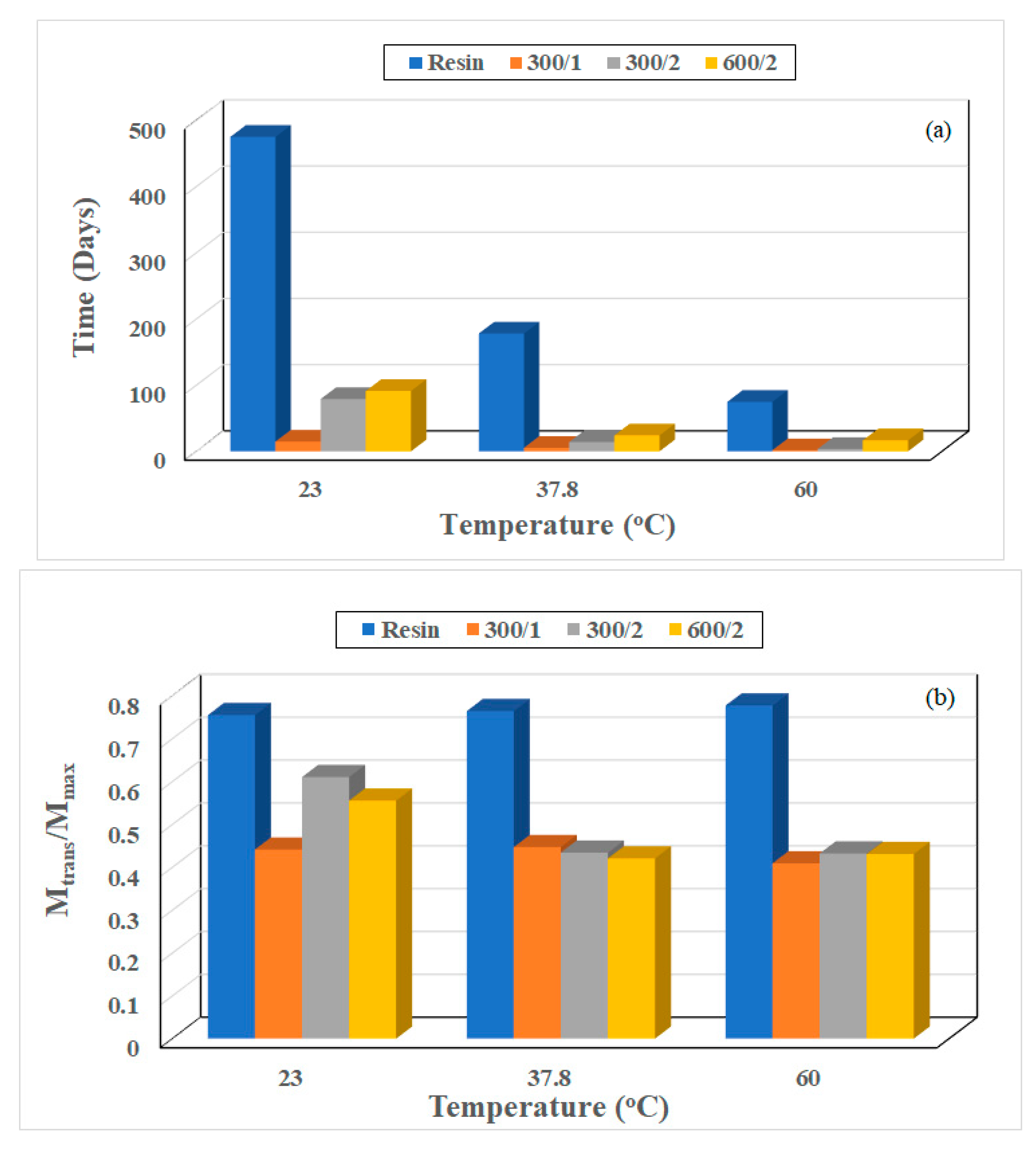
3.1. Moisture Uptake and Kinetics
3.2. Characterization of Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
3.3. Characterization of Flexural Strength
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spelter, A.; Bergmann, S.; Bielak, J.; Hegger, J. Long-term durability of carbon reinforced concrete. An overview and experimental investigation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1651–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Abanilla, M.A. Design factors, reliability, and durability prediction of wet layup carbon/epoxy used in external strengthening. Compos. B 2007, 38, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanilla, M.A.; Karbhari, V.M.; Li, Y. Interlaminar and intralaminar durability characterization of wet layup carbon/epoxy used in external strengthening. Compos. B 2006, 37, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanilla, M.A.; Li, Y.; Karbhari, V.M. Durability characterization of wet layup graphite/epoxy composites used in external strengthening. Compos. B 2005, 37, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, M.J. Thermal expansion and swelling of cured epoxy resin used in graphite/epoxy composite materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1980, 15, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lucas, J.P. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part I: The nature of water in epoxy. Polymer 1999, 40, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, P.; Ramirez, C.; Torres, A.; Abad, M.J.; Cano, J.; Lopez, J.; Lopez-Bueno, I.; Barral, L. Effect of water sorption on the structure and mechanical properties of an epoxy system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.Z.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Swelling of DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin during hygrothermal aging. Polymer 1998, 39, 3253–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’Nève, B.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Water absorption by an epoxy resin and its effect on the mechanical properties and infra-red spectra. Polymer 1993, 34, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.T. Residual stresses in polymer matrix composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.Z.; Delmar, M.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Irreversible interactions between water and DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin during hygrothermal aging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1977, 65, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateauminois, A.; Chabert, B.; Soulier, J.P.; Vincent, L. Dynamic-mechanical analysis of epoxy composites plasticized by water—Artifact and reality. Polym. Compos. 1995, 16, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atadero, R.; Lee, L.; Karbhari, V.M. Consideration of material variability in reliability analysis of FRP strengthened bridge decks. Comp Strs. 2005, 70, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, A.; Broutman, L.J.; Eckstein, B.H. Effect of long-term water exposure on the properties of carbon and graphite fiber reinforced epoxies. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1978, 18, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; de Almeida, S.F.M.; Rezende, M.C. Hygrothermal effects on dynamic mechanical analysis and fracture behavior of polymeric composites. Mater. Res. 2005, 8, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L.; de Cataldis, C. Characterization of the morphological fine structure of commercial thermosetting resins through hygrothermal exposure. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1985, 66, 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Apicella, A.; Tessieri, R.; de Cataldis, C. Sorption modes of water in glassy epoxies. J. Membr. Sci. 1984, 18, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, P.; Karasz, F.E. Epoxy-water interactions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1980, 20, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethrick, R.A.; Hollins, E.A.; McEwan, L.; Pollock, A.; Hayward, D.; Johncock, P. Effect of cure temperature on the structure and water absorption of epoxy/amine thermosets. Polym. Int. 1996, 39, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.-H.; Springer, G.S. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, D.J.; Bascom, W.D.; Motiee, B. Moisture absorption by structural epoxy-matrix carbon-fiber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1985, 24, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirrell, C.D. Diffusion of water vapor in graphite/epoxy composites. In ASTM STP 658, Advanced Composite Materials—Environmental Effects; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1977; pp. 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, S.; Marom, G. Stress dependence of the coefficient of moisture diffusion in composite materials. Polym. Compos. 1985, 6, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, A.R.; Hopfenberg, H.B. Diffusion and relaxation in glassy polymer powders: 2 Separation of diffusion and relaxation parameters. Polymer 1978, 19, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, E.; Long, F.A. Two-stage sorption and desorption of organic vapors in cellulose acetate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H.G.; Kibler, K.G. Langmuir-type model for anomalous moisture diffusion in composite resins. J. Compos. Mater. 1978, 12, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F.; Lee, C.Y.-C. Moisture absorption and hygrothermal aging in a bismaleimide resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 7327–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, J.E.; Sims, G.D.; Maxwell, A.S.; Frenz, S.; Ogin, S.L.; Foreman, C.; Dorey, R.A. On the relationship between moisture uptake and mechanical property changes in a carbon fibre/epoxy composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Long-term hydrothermal aging of carbon-epoxy materials for rehabilitation of civil infrastructure. Compos. A 2022, 153, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiel, G.; Uicich, J.; Fasce, D.; Montemartini, P.E. Diffusion and hydrolysis effects during water aging on an epoxy-anhydride system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 153, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.C.; Alston, S.M.; Korkees, F. An assessment of methods to determine the directional moisture diffusion coefficients of composite materials. Compos. A 2013, 55, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.; Lees, J.M. Water, saltwater and alkaline solution uptake in epoxy thin films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Karbhari, V.M. Segmental relaxation of water-aged ambient cured epoxy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, G.; Karbhari, V.M. DMTA based investigation of hygrothermal aging of an epoxy system used in rehabilitation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Hong, S.K. Effect of sequential thermal aging and water immersion on moisture kinetics and SBS strength of wet layup carbon epoxy composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starink, M.J.; Starink, L.M.P.; Chambers, A.R. Moisture uptake in monolithic and composite materials: Edge correction for rectanguloid samples. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, A.; Hamerton, I.; Herman, H.; Meudhar, A.K.; Shaw, S.J. Studying water uptake effects in resins based on cyanate ester/bismaleimide blends. Polymer 2000, 41, 3945–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateauminois, A.; Vincent, L.; Chabert, B.; Soulier, J.P. Study of the interfacial degradation of a glass-epoxy composite during hygrothermal ageing using water diffusion measurements and dynamic mechanical thermal analysis. Polymer 1994, 35, 4766–4774. [Google Scholar]
- McKague, E.L., Jr.; Reynolds, J.D.; Halkias, J.E. Swelling and glass transition relations for epoxy material in humid environments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1978, 22, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel, I.; Valentin, D. Hydrothermal effects on the physico-chemical properties of pure and glass fiber reinforced polyester and vinylester resins. Polym. Compos. 1993, 14, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.M.; Marshall, G.P.; Pinzelli, R.F. The diffusion of liquids into resins and composites. Polym. Compos. 1982, 3, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F. Effect of temperature on moisture absorption in a bismaleimide resin and its carbon fiber composite. Polymer 2002, 43, 3987–3997. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, S.I. Chemical and Engineering Thermodynamics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Apicella, A.; Migliaresi, C.; Nicolais, L.; Iaccarino, L.; Roccotelli, S. The water ageing of unsaturated polyester-based composites: Influence of resin chemical structure. Composites 1983, 14, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijovic, J.; Lin, K.-F. T he effect of hygrothermal fatigue on physical/mechanical properties and morphology of neat epoxy resin and graphite/epoxy composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 2527–2549. [Google Scholar]
- Mouzakis, D.E.; Kager-Kocsis, J. Effects of gasoline absorption on the tensile impact response of HDPE/SelarTM laminar microlayer composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 68, 561–569. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J.; Park, G.S. Diffusion in Polymers; Academic Press: London, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Priestley, R.D.; McKenna, G.B. Physical aging of an epoxy subsequent to relative humidity jumps through the glass concentration. J. Polym. Sci. B. Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2107–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Portan, D.V.; Kontaxis, L.C. Interrelation between fiber-matrix interphasial phenomena and flexural stress relaxation behavior of a glass fiber-polymer composite. Polymers 2021, 13, 978. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, R.; Salmén, L.; Lavebratt, H.; Stenberg, B. Comparison of dynamic mechanical measurements and Tg determinations with two different instruments. Polym. Test. 1994, 13, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, M.; Taylor, M.S. Ideal copolymers and the second-order transitions of the synthetic rubbers. I. Non-crystalline copolymers. J. Appl. Chem. 1952, 2, 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, F.N.; Bueche, F. Viscosity and glass temperature relations for polymer-diluent systems. J. Polym. Sci. 1961, 50, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Pascault, J.P.; Williams, J.J. Glass transition temperature versus conversion relationships for thermosetting polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1990, 28, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, W.W. The effect of diffusion of water into epoxy resins and their carbon-fibre reinforced composites. Composites 1981, 12, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.M.; Greenfield, D.C.L. The Use of dynamic mechanical methods to study the effect of absorbed Water on temperature-dependent properties of an epoxy resin-carbon fibre composite. Br. Polym. J. 1986, 18, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Vanlandingham, M.R.; Eduljee, R.F.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Moisture diffusion in epoxy systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Dynamic mechanical analysis of the effect of water on E-glass-vinylester composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tual, N.; Carrer, N.; Davies, P.; Bonnemains, T.; Lolive, E. Characterization of seawater aging effects on mechanical properties of carbon/epoxy composites for tidal turbine blades. Compos. A 2015, 78, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloglu, G.E.; Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C. Moisture absorption of composites with interfacial storage. Compos. A 2020, 134, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Composite | Fabric Areal Weight (gsm) | Number of Layers | Thickness (mm) | Fiber Mass Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300/1 | 300 | 1 | 0.72 | 35 |
| 300/2 | 300 | 2 | 1.34 | 39 |
| 600/2 | 600 | 2 | 1.80 | 44 |
| Temperature of Immersion (°C) | Dr (×10−7 mm2/s) | kr (×10−4 mm2/s) | Mtrans (%) | Mmax (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 1.04 | 0.280 | 3.274 | 4.338 |
| 37.8 | 3.77 | 0.236 | 3.435 | 4.496 |
| 60 | 25.4 | 0.216 | 3.532 | 4.546 |
| Material | Temperature of Immersion (°C) | Deff (×10−7 mm2/s) | keff (×10−4 mm2/s) | D (=Deff × L2) (×10−7 mm2/s) | k (=keff × L1) (×10−4 mm2/s) | Mtrans (%) | Mmax (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300/1 | 23 | 1.089 | 0.293 | 1.648 | 1.015 | 1.326 | 3.008 |
| 37.8 | 3.947 | 0.247 | 4.174 | 0.969 | 1.702 | 3.809 | |
| 60 | 26.59 | 0.226 | 28.41 | 1.172 | 1.922 | 4.702 | |
| 300/2 | 23 | 1.130 | 0.304 | 0.585 | 0.507 | 1.893 | 3.102 |
| 37.8 | 4.096 | 0.256 | 3.502 | 0.992 | 1.655 | 3.804 | |
| 60 | 27.60 | 0.234 | 19.18 | 1.667 | 1.686 | 5.083 | |
| 600/2 | 23 | 1.158 | 0.311 | 0.593 | 0.647 | 2.116 | 3.812 |
| 37.8 | 4.197 | 0.262 | 3.796 | 1.133 | 1.729 | 4.115 | |
| 60 | 28.28 | 0.240 | 14.01 | 1.163 | 2.202 | 5.115 |
| Material | Heat of Absorption (kJ/mol K) | |
|---|---|---|
| At Mtrans | At Mmax | |
| Resin | 1.65 | 1.0 |
| 300/1 | 8.04 | 9.81 |
| 300/2 | 2.39 | 10.95 |
| 600/2 | 1.34 | 6.62 |
| Composite | Temperature of Immersion (°C) | Permeability (×10−9 mm2/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At Mtrans | At Mmax | ||
| 300/1 | 23 | 2.19 | 4.96 |
| 37.8 | 7.09 | 15.89 | |
| 60 | 54.60 | 133.59 | |
| 300/2 | 23 | 1.11 | 1.81 |
| 37.8 | 5.79 | 13.35 | |
| 60 | 32.34 | 97.49 | |
| 600/2 | 23 | 1.25 | 2.26 |
| 37.8 | 6.56 | 15.62 | |
| 60 | 30.85 | 71.66 | |
| Temperature of Immersion (°C) | Composite | % Drop in Tg at 60 Months | Drop in Tg per % Moisture Uptake |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 300/1 | −19.6 | 6.82 |
| 300/2 | −22.1 | 6.95 | |
| 600/2 | −25.0 | 6.37 | |
| 37.8 | 300/1 | −17.0 | 4.68 |
| 300/2 | −18.5 | 4.74 | |
| 600/2 | −19.4 | 4.56 | |
| 60 | 300/1 | −20.5 | 4.55 |
| 300/2 | −24.3 | 4.65 | |
| 600/2 | −25.1 | 4.38 |
| Composite | Temperature of Immersion (°C) | Time Period under Consideration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Months | 4 Months | 60 Months | ||
| 300/1 | 23 | 7.27 | 6.69 | 19.87 |
| 37.8 | 8.84 | 9.54 | 25.22 | |
| 60 | 13.60 | 13.78 | 30.15 | |
| 300/2 | 23 | 5.02 | 11.57 | 22.98 |
| 37.8 | 12.72 | 16.07 | 28.57 | |
| 60 | 16.85 | 17.75 | 32.25 | |
| 600/2 | 23 | 11.55 | 28.19 | 44.98 |
| 37.8 | 15.99 | 32.98 | 48.95 | |
| 60 | 21.39 | 35.93 | 49.54 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassanpour, B.; Karbhari, V.M. Moisture and Glass Transition Temperature Kinetics of Ambient-Cured Carbon/Epoxy Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7110447
Hassanpour B, Karbhari VM. Moisture and Glass Transition Temperature Kinetics of Ambient-Cured Carbon/Epoxy Composites. Journal of Composites Science. 2023; 7(11):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7110447
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassanpour, Behnaz, and Vistasp M. Karbhari. 2023. "Moisture and Glass Transition Temperature Kinetics of Ambient-Cured Carbon/Epoxy Composites" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 11: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7110447
APA StyleHassanpour, B., & Karbhari, V. M. (2023). Moisture and Glass Transition Temperature Kinetics of Ambient-Cured Carbon/Epoxy Composites. Journal of Composites Science, 7(11), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7110447








