Performance Evaluation of an Improved ANFIS Approach Using Different Algorithms to Predict the Bonding Strength of Glulam Adhered by Modified Soy Protein–MUF Resin Adhesive
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Making the Protein Adhesive
2.2.3. Making the Melamine–Urea–Formaldehyde Resin
2.3. Manufacturing Glulam
2.4. Model Development
2.4.1. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
2.4.2. Ant Colony Optimization (ACOR)
2.4.3. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
2.4.4. Differential Evaluation (DE)
2.4.5. Genetic Algorithm
2.5. Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
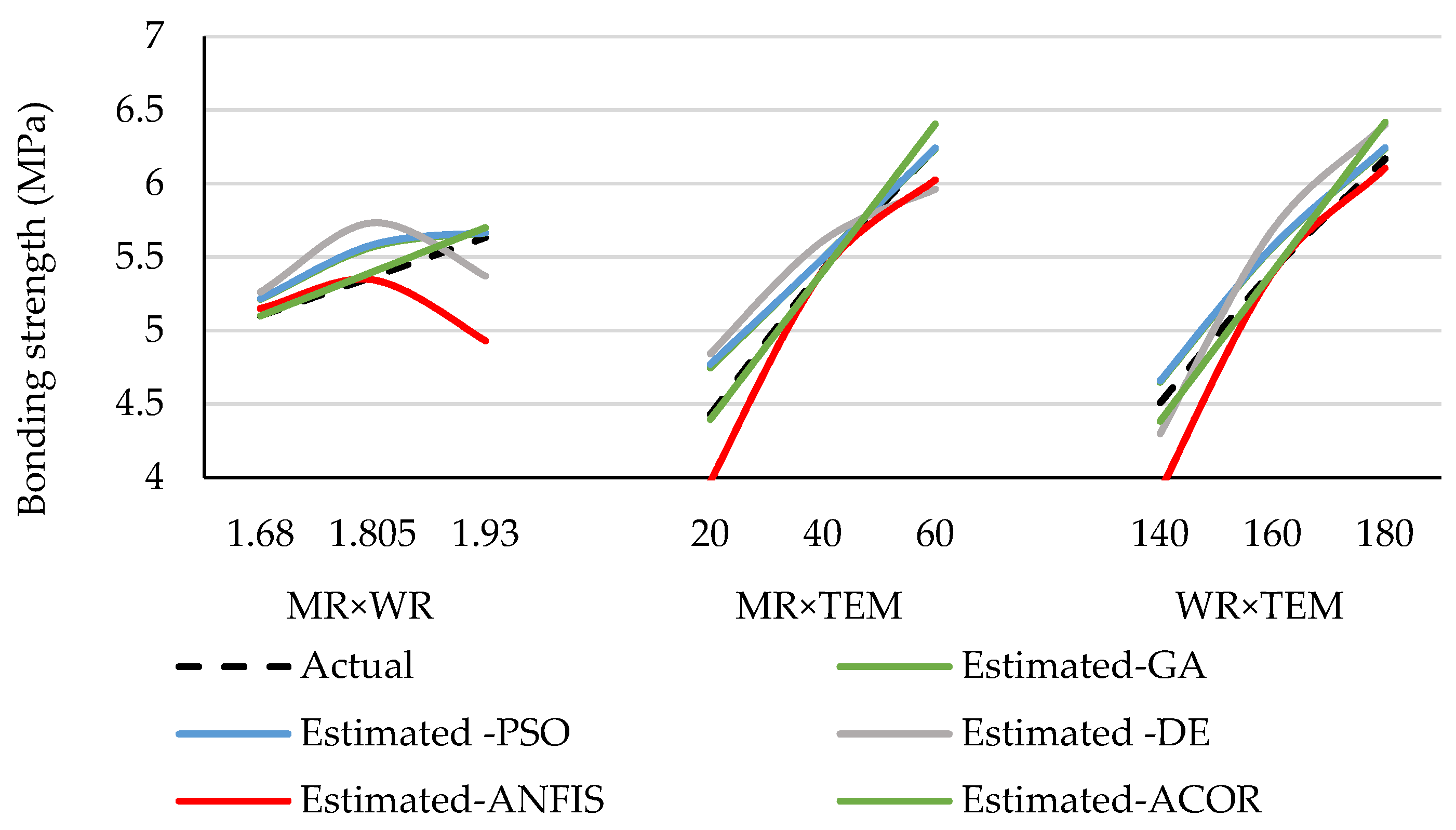
3.1. Accuracy of the Predicted Values Obtained by the Approaches
3.2. Optimized Values of the Preferred Approach
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, H.; Dowd, M.K.; He, Z. Investigation of modified cottonseed protein adhesives for wood composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Choudhary, V.; Mishra, S.; Varma, I.K.; Mattiason, B. Adhesives and plastics based on soy protein products. Ind. Crops Prod. 2002, 16, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchy, N.; Kalapathy, U.; Myers, D. Alkali-modified soy protein with improved adhesive and hydrophobic properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yang, B.; Yuan, C.; Geng, W.; Li, H. Effects of preparation parameters on properties of soy protein-based fiberboard. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 9, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Hosseini, S.B.; Ghahri, S.; Ghofrani, M.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Formaldehyde emission in micron-sized wollastonite-treated plywood bonded with soy flour and urea-formaldehyde resin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Pereira, J.; Paiva, N.; Ferra, J.; Martins, J.M.; Magalhaes, F.D.; Carvalho, L. Natural additive for reducing formaldehyde emissions in urea-formaldehyde resins. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bian, K. Shear strength and water resistance of modified soy protein adhesives. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, X. Adhesive properties of soy proteins modified by urea and guanidine hydrochloride. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, F.; Senyer, N.; Esen, R. Comparison of the multiple regression, ANN, and ANFIS models for prediction of MOE value of OSB panels. Wood Res. 2016, 61, 741–754. [Google Scholar]
- Alhijazi, M.; Safaei, B.; Zeeshan, Q.; Asmael, M.; Harb, M.; Qin, Z. An experimental and metamodeling approach to tensile properties of natural fibers composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4377–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazerian, M.; Naderi, F.; Partovinia, A.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Younesi-Kordkheili, H. Developing adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-based models to predict the bending strength of polyurethane foam-cored sandwich panels. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2022, 236, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N. Advances in Wood Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, Y.J.; Mustapha, K.B.; Shimizu, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Arumugasamy, S.K. Development of surrogate predictive models for the nonlinear elasto-plastic response of medium density fibreboard-based sandwich structures. Int. J. lightweight Mater. 2021, 4, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, F.; Mousavi, S.R.; Peyma, A.B.; Moodi, Y. Prediction of compressive strength of fiber-reinforced polymers-confined cylindrical concrete using artificial intelligence methods. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2022, 41, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Kaya, E. Training ANFIS by using and adaptive and hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm (aABC) for the identification of nonlinear static systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 3531–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, A.A.; Alwanas, A.A.H.; Salih, S.Q.; Ali, Z.H.; Tran, M.T.; Yaseen, Z.M. Shear strength of SFRCB without stirrups simulation: Implementation of hybrid artificial intelligence model. Eng. Comput. 2020, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, M.A.; Nataraja, M.C.; Ravi Kumar, C.N. Design of high performance concrete mixes through particle swarm optimization. J. Intell. Syst. 2010, 19, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, M.; Grünewald, S.; Coenders, J. Ant colony optimization for ultra high performance concrete structures. In Designing and Building with UHPFRC; Toutlemonde, F., Resplendino, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, G.; Fiore, A.; Marano, G.C. Optimum design of prestressed concrete beams using constrained differential evolution algorithm. Struct. Multidiscipl. Optim. 2014, 49, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello Coello, C.A.; Christiansen, A.D.; Hernández, F.S. A simple genetic algorithm for the design of reinforced concrete beams. Eng. Comput. 1997, 13, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, K.; Shen, S.L.; Sun, W.J.; Yin, Z.Y.; Zhou, A. Prediction model of shield performance during tunneling via incorporating improved particle swarm optimization into ANFIS. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39659–39671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Behroyan, I.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Shirazian, S. High-performance hybrid modeling chemical reactors using differential evolution based fuzzy inference system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Rad, H.N.; Hasanipanah, M.; Armaghani, D.J.; Qasem, S.N. Design and implementation of a new tuned hybrid intelligent model to predict the uniaxial compressive strength of the rock using SFS-ANFIS. Eng. Comput. 2021, 37, 2717–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penghui, L.; Ewees, A.A.; Beyaztas, B.H.; Qi, C.; Salih, N.Q.; Al-Ansari, N.; Bhagat, S.K.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Singh, V.P. Metaheuristic optimization algorithms hybridized with artificial intelligence model for soil temperature prediction: Novel model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 51884–51904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.T.; Van Pham, M.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Nguyen, L.X.; Pham, H.M. Whale optimization algorithm and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system: A hybrid method for feature selection and land pattern classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 5078–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bui, X.N.; Trung, N.T.; Nguyen, H.; Bui, H.B. Prediction of rock size distribution in mine bench blasting using a novel ant colony optimization-based boosted regression tree technique. Nat. Resour. Res. 2020, 29, 867–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, A.; Zenner, E.K.; Panahi, M.; Shahabi, H. Hybrid artificial intelligence models based on a neuro-fuzzy system and metaheuristic optimization algorithms for spatial prediction of wildfire probability. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 266–267, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, K.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.; Yuan, D.J.; Xu, Y.S. Optimization of EPB shield performance with adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and genetic algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sari, P.a.; Suhatril, M.; Osman, N.; Muazu, M.A.; Katebi, J.; Abavisani, A.; Ghaffari, N.; Chahnasir, E.S.; Wakil, K.; Khorami, M.; et al. Developing a hybrid adoptive neuro-fuzzy inference system in predicting safety of factors of slopes subjected to surface eco-protection techniques. Eng. Comput. 2020, 36, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Melini, W.H.; Mohtar, H.W.; Ameen, A.M.S.; Ebtehaj, I.; Razali, S.F.M.; Bonakdari, H.; Salih, S.Q.; Al-Ansari, N.; Shahid, S. Implementation of univariate paradigm for streamflow simulation using hybrid data-driven model: Case study in tropical region. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74471–74481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnamkhasti, M.J. A hybrid of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and genetic algorithm. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 25, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnamkhasti, M.J. ANFISGA-adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system genetic algorithm. Glob. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2011, 11, 15036870. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, L.N.; Ji, X. Prediction of concrete compressive strength: Research on hybrid models genetic based algorithms and ANFIS. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 67, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, J.; Xia, S.; Ou, C.; Fu, C.; Yi, M.; Li, W.; Jing, M.; Lv, W.; Xiao, H. Improve performance of soy protein adhesives with a low molar ratio melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1549, 032083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M. Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1985, 15, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, K.; Dorigo, M. Ant colony optimization for continuous domains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 185, 1155–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. A new optimizer using particles swarm theory. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Hussein, S.H.; Ghazali, K.H.; Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Optimized adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system using metaheuristic algorithms: Application of shield tunnelling ground surface settlement prediction. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6666699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, M.A. Modeling global solar radiation using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalao, J.P.S.; Pousinho, H.M.I.; Mendes, V.M.F. Hybrid wavelet-PSO-ANFIS approach for short-term electricity prices forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihabudheen, K.V.; Pillai, G.N. Recent advances in neuro-fuzzy system: A survey. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 152, 136–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Azad, A.; Kashi, H.; Saeedian, A.; Hashemi, S.A.A.; Ghorbani, S. Modeling groundwater quality parameters using hybrid neuro-fuzzy methods. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.; Manoochehri, M.; Kashi, H.; Farzin, S.; Karami, H.; Nourani, V.; Shiri, J. Comparative evaluation of intelligent algorithms to improve adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system performance in precipitation modelling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaghani, D.J.; Asteris, P.G.A. Comparative study of ANN and ANFIS models for the prediction of cement-based mortar materials compressive strength. Neural Comput. Applic. 2021, 33, 4501–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercy, L.J.; Prakash, S. Experimental investigation and neuro fuzzy modeling of inplane shear strength for self-healing GFRP. Transac. Ind. Inst. Met. 2016, 69, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, X.S. Low density particleboard from wheat straw and corn pith. Ind. Crops Prod. 2002, 15, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigalupe, A.; He, Z.; Escobar, M.M. Effects of rheology and viscosity of bio-based adhesives on bonding performance. In Bio-Based Wood Adhesives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q. Rheology Properties. In Colloid and Interface Chemistry for Water Quality Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigalupe, A.; Molinari, F.; Eisenberg, P.; Escobar, M.M. Adhesive properties of urea-formaldehyde resins blended with soy protein concentrate. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2020, 3, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Yan, Y. Preparation and rheological studies on the solvent based acrylic pressure sensitive adhesives with different crosslinking density. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigalupe, A.; Poliszuk, A.K.; Eisenberg, P.; Escobar, M.M. Rheological behavior and bonding performance of an alkaline soy protein suspension. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, C.; Pizzi, A.; Garcia, R. The effect of humidity on crosslinked and entanglement networking of formaldehyde-based wood adhesives. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 1998, 56, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachtanapun, P.; Heiden, P. Thermoplastic polymers as modifiers for urea-formaldehyde (UF) wood adhesives. II Procedures for the preparation and characterization of thermoplastic-modified UF wood composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Chu, F.; Wang, C.; Jin, C.; Wang, S.; Pang, J. Combinations of soy protein and polyacrylate emulsions as wood adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 82, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.K. Urea/formaldehyde resins. In Reactive Polymers Fundamentals and Applications; William Andrew Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Properties of a new renewable sesame protein adhesive modified by urea in the absence and presence of zinc oxide. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 46388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norstrom, E.; Demircan, D.; Fogelström, L.; Khabbaz, F.; Malmström, E. Green binders for wood adhesives. Appl. Adhes. Bond. Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 13–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vnucec, D.; Kutnar, A.; Gorsek, A. Soy-based adhesives for wood-bonding—A review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 910–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.S. Thermal and mechanical properties of soy proteins. In Bio-Based Polymers and Composites; Wool, R., Sun, X.S., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 292–326. [Google Scholar]
- Migneault, S.; Koubaa, A.; Riedl, B.; Nadji, H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, S.Y. Potential of pulp and paper sludge as a formaldehyde scavenger agent in MDF resins. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Preparation of reinforced soy protein adhesive using silane coupling agent as an enhancer. Bioresources 2014, 9, 5448–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, Z.A.; Park, B.D. Influence of acrylamide copolymerization of urea–formaldehyde resin adhesives to their chemical structure and performance. J. App. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Huang, H.; Wu, G.; Sun, H.; Chang, Z. The effect of hydrolyzed soy protein isolate on the structure and biodegradability of urea– formaldehyde adhesives. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Bai, Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. A high performance soy protein-based bio-adhesive enhanced with a melamine/epichlorohydrin prepolymer and its application on plywood. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67669–67676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Fan, B.; Gao, Z.; Shi, J. Liquefaction of soybean protein and its effects on the properties of soybean protein adhesive. Pigment. Resin Technol. 2017, 46, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| No | x1 (MR) | x2 (WR) | x3 (TEM) | No | x1 (MR) | x2 (WR) | x3 (TEM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.93:1 (1) | 20 (−1) | 140 (−1) | 18 | 1.805 (0) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) |
| 2 | 1.68:1 (−1) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) | 19 | 1.805 (0) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) |
| 3 | 1.805:1 (0) | 40 (0) | 140 (−1) | 20 | 1.805 (0) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) |
| 4 | 1.93:1 (1) | 60 (1) | 140 (−1) | 21 | 1.68 (−1) | 60 (1) | 180 (1) |
| 5 | 1.93:1 (1) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) | 22 | 1.805 (0) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) |
| 6 | 1.68:1 (−1) | 20 (−1) | 140 (−1) | 23 | 1.68 (−1) | 20 (−1) | 180 (1) |
| 7 | 1.805:1 (0) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) | 24 | 1.93 (1) | 60 (1) | 140 (−1) |
| 8 | 1.68:1 (−1) | 20 (−1) | 180 (1) | 25 | 1.93 (1) | 60 (1) | 180 (1) |
| 9 | 1.93:1 (1) | 20 (−1) | 180 (1) | 26 | 1.68 (−1) | 60 (1) | 140 (−1) |
| 10 | 1.805:1 (0) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) | 27 | 1.805 (0) | 20 (−1) | 160 (0) |
| 11 | 1.68:1 (−1) | 20 (−1) | 140 (−1) | 28 | 1.805 (0) | 20 (−1) | 160 (0) |
| 12 | 1.93:1 (1) | 20 (−1) | 180 (1) | 29 | 1.93 (1) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) |
| 13 | 1.68:1 (−1) | 60 (1) | 140 (−1) | 30 | 1.805 (0) | 40 (0) | 180 (1) |
| 14 | 1.805:1 (0) | 60 (1) | 160 (0) | 31 | 1.93 (1) | 60 (1) | 180 (1) |
| 15 | 1.805:1 (0) | 60 (1) | 160 (0) | 32 | 1.93 (1) | 20 (−1) | 140 (−1) |
| 16 | 1.805:1 (0) | 40 (0) | 140 (−1) | 33 | 1.805 (0) | 40 (0) | 180 (1) |
| 17 | 1.68:1 (−1) | 60 (1) | 180 (1) | 34 | 1.68 (−1) | 40 (0) | 160 (0) |
| No | Ex. | ANFIS | ACOR | PSO | DE | GA | No | Ex. | ANFIS | ACOR | PSO | DL | GA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.71 | 2.11 | 3.74 | 4.94 | 3.76 | 4.93 | 18 | 5.02 | 5.45 | 5.40 | 5.49 | 5.77 | 5.49 |
| 2 | 5.13 | 5.15 | 5.10 | 5.13 | 5.37 | 5.16 | 19 | 5.7 | 5.45 | 5.40 | 5.49 | 5.77 | 5.49 |
| 3 | 4.94 | 4.54 | 4.38 | 4.94 | 4.42 | 4.92 | 20 | 5.6 | 5.45 | 5.40 | 5.49 | 5.77 | 5.49 |
| 4 | 5.03 | 5.03 | 5.65 | 5.19 | 4.84 | 5.19 | 21 | 7.82 | 7.75 | 7.18 | 7.75 | 7.08 | 7.75 |
| 5 | 5.7 | 5.75 | 5.70 | 5.80 | 5.43 | 5.80 | 22 | 5.08 | 5.45 | 5.40 | 5.49 | 5.77 | 5.49 |
| 6 | 2.49 | 2.72 | 3.02 | 2.95 | 3.13 | 2.95 | 23 | 4.98 | 4.98 | 5.07 | 4.98 | 5.39 | 4.95 |
| 7 | 5.5 | 5.45 | 5.40 | 5.49 | 5.77 | 5.49 | 24 | 5.36 | 5.03 | 5.65 | 5.19 | 4.84 | 5.18 |
| 8 | 4.24 | 4.98 | 5.08 | 4.99 | 5.39 | 4.95 | 25 | 6.67 | 6.10 | 7.66 | 6.80 | 6.65 | 6.79 |
| 9 | 5.54 | 5.66 | 5.75 | 5.59 | 6.16 | 5.60 | 26 | 5.14 | 5.14 | 5.12 | 5.26 | 5.33 | 5.24 |
| 10 | 5.8 | 5.45 | 5.40 | 5.49 | 5.77 | 5.49 | 27 | 4.15 | 4.39 | 4.38 | 5.38 | 5.76 | 5.29 |
| 11 | 2.95 | 2.72 | 3.02 | 2.95 | 3.13 | 2.95 | 28 | 4.63 | 4.39 | 4.38 | 5.38 | 5.76 | 5.29 |
| 12 | 5.66 | 5.66 | 5.75 | 5.59 | 6.16 | 5.60 | 29 | 5.8 | 5.75 | 5.70 | 5.79 | 5.43 | 5.79 |
| 13 | 5.38 | 5.14 | 5.12 | 5.26 | 5.33 | 5.24 | 30 | 6.03 | 6.03 | 6.42 | 6.07 | 6.71 | 6.07 |
| 14 | 6.10 | 6.10 | 6.42 | 6.20 | 5.89 | 6.20 | 31 | 6.92 | 6.10 | 7.66 | 6.80 | 6.65 | 6.79 |
| 15 | 6.3 | 6.10 | 6.42 | 6.20 | 5.89 | 6.20 | 32 | 4.94 | 2.11 | 3.74 | 4.93 | 3.76 | 4.93 |
| 16 | 4.15 | 4.54 | 4.38 | 4.94 | 4.42 | 4.93 | 33 | 6.13 | 6.03 | 6.42 | 6.07 | 6.71 | 6.07 |
| 17 | 7.69 | 7.75 | 7.18 | 7.75 | 7.08 | 7.75 | 34 | 5.18 | 5.15 | 5.10 | 5.13 | 5.37 | 5.16 |
| Source | ANFIS | ANFIS-ACOR | ANFIS-DE | ANFIS-PSO | ANFIS-GA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Test dataset | 0.4715 | 0.8870 | 0.4635 | 0.7798 | 0.8108 |
| Training dataset | 0.9655 | 0.8664 | 0.7664 | 0.9810 | 0.9809 | |
| RMSE | 0.7192 | 0.4711 | 0.6157 | 0.3535 | 0.3366 | |
| MAE | 0.3575 | 0.3636 | 0.4905 | 0.2135 | 0.2082 | |
| SSE | 17.5885 | 7.5470 | 12.8904 | 4.2479 | 3.8523 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazerian, M.; Naderi, F.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Performance Evaluation of an Improved ANFIS Approach Using Different Algorithms to Predict the Bonding Strength of Glulam Adhered by Modified Soy Protein–MUF Resin Adhesive. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7030093
Nazerian M, Naderi F, Papadopoulos AN. Performance Evaluation of an Improved ANFIS Approach Using Different Algorithms to Predict the Bonding Strength of Glulam Adhered by Modified Soy Protein–MUF Resin Adhesive. Journal of Composites Science. 2023; 7(3):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7030093
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazerian, Morteza, Fatemeh Naderi, and Antonios N. Papadopoulos. 2023. "Performance Evaluation of an Improved ANFIS Approach Using Different Algorithms to Predict the Bonding Strength of Glulam Adhered by Modified Soy Protein–MUF Resin Adhesive" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 3: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7030093
APA StyleNazerian, M., Naderi, F., & Papadopoulos, A. N. (2023). Performance Evaluation of an Improved ANFIS Approach Using Different Algorithms to Predict the Bonding Strength of Glulam Adhered by Modified Soy Protein–MUF Resin Adhesive. Journal of Composites Science, 7(3), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7030093







