Numerical Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment of Type V Hydrogen Pressure Vessels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mesh Dependency Study
2.2. Validation of the Simulation
2.3. Governing Equation
- is applied internal pressure (MPa);
- r is mean radius of the vessel, r = (Douter + Dinner)/4 (mm);
- E is Young’s modulus of the material (MPa);
- t is wall thickness, t = (Douter − Dinner)/2 (mm).
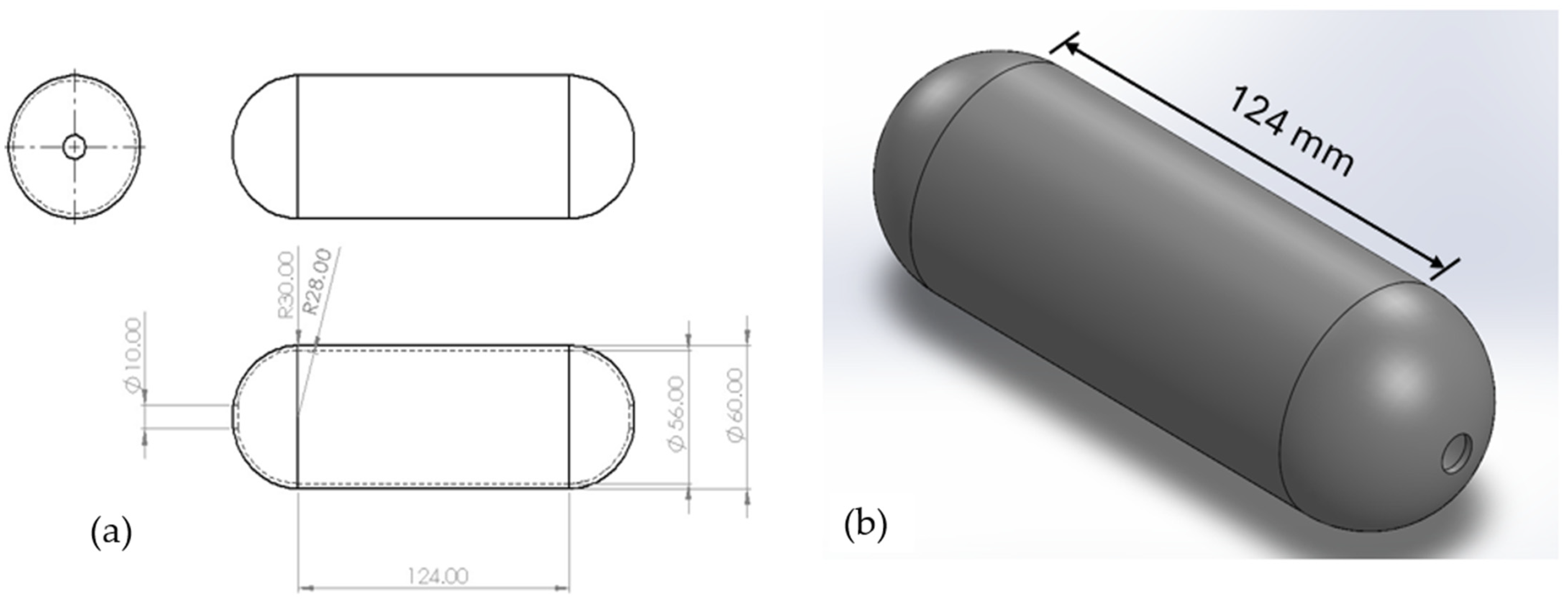
2.4. Input Parameters
- Outer Diameter (Douter): 60 mm
- Inner Diameter (Dinner): 56 mm
- Wall Thickness (t): 2 mm
- Mean Radius (r): 29 mm
- Young’s Modulus (E): 1600 MPa
- Applied Pressures (p): [0, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 3.0] MPa
3. Life Cycle Assessment
- Global Warming Potential (GWP) (kg CO2-eq): Quantifying greenhouse gas emissions.
- Acidification Potential (AP) (kg SO2-eq): Assessing impacts from SO2 and NOₓ emissions.
- Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential (POCP) (kg C2H4-eq): Evaluating VOC and NOₓ contributions to ground-level ozone formation.
- Particulate Matter Formation (PMF) (kg PM10): Quantifying PM emissions from transportation and energy use.
4. Results
5. End-of-Life Scenarios
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarhan, C.; Çil, M.A. A Study on Hydrogen, the Clean Energy of the Future: Hydrogen Storage Methods. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Sun, H.; Zhang, W.; Mei, C. Review on Key Technologies of Hydrogen Generation, Storage and Transportation Based on Multi-Energy Complementary Renewable Energy. Diangong Jishu Xuebao/Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2021, 36, 446–462. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhamed, A.J.; Adam, N.M.; Ab-Kadir, M.Z.A.; Hairuddin, A.A. Review of Solar Parabolic-Trough Collector Geometrical and Thermal Analyses, Performance, and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Gao, L.; Xu, Z.; Teo, S.; Zhang, C.; Kamata, Y.; Hayase, S.; Ma, T. High Electrical Conductivity 2D MXene Serves as Additive of Perovskite for Efficient Solar Cells. Small 2018, 14, e1802738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. The Effect of Carbon Emission Trend on Urban Thermal Environment from the Perspective of Transportation Energy Consumption. Int. J. Heat. Technol. 2022, 40, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, J.; Shao, Z.; Lei, K.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Optimal Dispatch of Hydrogen/Electric Vehicle Charging Station Based on Charging Decision Prediction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 48, 26964–26978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, M.G.; Hazrat, M.A.; Sattar, M.A.; Jahirul, M.I.; Shearer, M.J. The Future of Hydrogen: Challenges on Production, Storage and Applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 272, 116326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Lu, L.; Huang, Z. Flammability Limits of Hydrogen-Enriched Natural Gas. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 6937–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kim, S.J. Recent Progress in Hydrogen Flammability Prediction for the Safe Energy Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, O.; Rehme, J.; Cerin, P.; Huisingh, D. Hydrogen Production in the Swedish Power Sector: Considering Operational Volatilities and Long-Term Uncertainties. Energy Policy 2021, 148, 111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peräkylä, O.; Riva, M.; Heikkinen, L.; Quéléver, L.; Roldin, P.; Ehn, M. Experimental Investigation into the Volatilities of Highly Oxygenated Organic Molecules (HOMs). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, G.P. Development of a QFD Trade-off Methodology for Automotive Hydrogen Tanks. Int. J. Product. Qual. Manag. 2012, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Pan, H.; Liu, Z.; Andersson, M. Numerical Modeling for Rapid Charging of Hydrogen Gas Vessel in Fuel Cell Vehicle. Processes 2023, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.; Bera, T.; Semwal, K.; Badhe, R.M.; Sharma, A.; Kapur, G.S.; Ramakumar, S.S.V.; Neogi, S. Effects of Dome Shape on Burst and Weight Performance of a Type-3 Composite Pressure Vessel for Storage of Compressed Hydrogen. Compos. Struct. 2022, 293, 115732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapre, S.; Pareek, K.; Vyas, M. Investigation of Structural Stability of Type IV Compressed Hydrogen Storage Tank during Refueling of Fuel Cell Vehicle. Energy Storage 2020, 2, e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohrmann, K.; Hajek, M. Bilinear Approach to Tensile Properties of Flax Composites in Finite Element Analyses. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enqi, W.; Shiheng, Z.; Weipu, X.; Yin, M.; Yue, C. Fatigue Analysis of High-Pressure Hydrogen Storage Vessel Based on Optimum Autofrettage Pressure. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2023, 42, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lv, H.; Zhang, L.; He, P.; Zhang, C. Experiment, Simulation, Optimization Design, and Damage Detection of Composite Shell of Hydrogen Storage Vessel-A Review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2023, 42, 507–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Chu, J.K.; Hou, S.J.; Xu, P.; Zheng, J.Y. Numerical Simulation and Optimal Design for Composite High-Pressure Hydrogen Storage Vessel: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, M.; Kumar, P.; Singh, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, A. Dynamic Response of an Irregular Heterogeneous Anisotropic Poroelastic Composite Structure Due to Normal Moving Load. Acta Mech. 2020, 231, 2303–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Hasbi, S.; Ahmad, E.Z.; Sagar, S.; Daoush, W.M.; Inam, F. Comparative Analysis of Mechanical Response in Epoxy Nanocomposites Reinforced with MXene and Other Carbon-Based Nano-Fillers: An Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Adv. Res. Micro Nano Eng. 2024, 26, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, S.M.; Tajul Arifin, A.M.; Taib, I.; Rahim, M.Z.; Nor Salim, N.A. Simulating the Optimization of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer as a Wrapping Structure on Piping System Using SolidWorks. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2021, 21, 2038–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siregar, I.; Saedon, J.B.; Adenan, M.S.; Nor, N.M.; Pazai, N.M.I.M. Contact Phenomena in Micromachining: Modelling and Simulation. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering, Medan City, Indonesia, 16 October 2018; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 505. [Google Scholar]
- Cassola, S.; Duhovic, M.; Schmidt, T.; May, D. Machine Learning for Polymer Composites Process Simulation—A Review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 246, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Rejab, M.R.M.; Azeem, M.; Hassan, S.A.; Yang, B.; Kumar, A.P. Opportunities and Challenges on Composite Pressure Vessels (CPVs) from Advanced Filament Winding Machinery: A Short Communication. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 57, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikroni, M.; Koutsoukis, G.; Vlachos, D.; Kostopoulos, V.; Vavouliotis, A.; Trakakis, G.; Athinaios, D.; Nikolakea, C.; Zacharakis, D. Design, Analysis, and Testing of a Type V Composite Pressure Vessel for Hydrogen Storage. Polymers 2024, 16, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, G.; Yan, Y.; Ni, Z. Cryogenic Mechanical and Hydrogen-Barrier Properties of Carbon Fiber Composites for Type V Cryo-Compressed Hydrogen Storage Vessels. Compos. Commun. 2023, 43, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zhou, W.; Ni, Z. Review on Linerless Type V Cryo-Compressed Hydrogen Storage Vessels: Resin Toughening and Hydrogen-Barrier Properties Control. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 114009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, T.; Cheng, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, K. A Review of the Research Progress and Application of Key Components in the Hydrogen Fuel Cell System. Processes 2024, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H. Study on the Application of Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Passenge Cars and Prospects. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem (ICREE 2023), Eskişehir, Turkey, 22–24 September 2023; Volume 424. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R. Hydrogen Fuel Cell vs. Electric Cars: What You Need to Know but Couldn’t Ask. 2020. Available online: https://www.euronews.com/green/2020/02/13/hydrogen-fuel-cell-vs-electric-cars-what-you-need-to-know-but-couldn-t-ask (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Al Rashid, A.; Khan, S.A.; Koç, M. Life Cycle Assessment on Fabrication and Characterization Techniques for Additively Manufactured Polymers and Polymer Composites. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2024, 12, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, N.; Alshehri, A.S.; You, F. Large Language Models for Life Cycle Assessments: Opportunities, Challenges, and Risks. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 466, 142824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goridkov, N.; Wang, Y.; Goucher-Lambert, K. What’s in This LCA Report? A Case Study on Harnessing Large Language Models to Support Designers in Understanding Life Cycle Reports. Procedia CIRP 2024, 122, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornago, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Low, J.S.C. How Can Transformers and Large Language Models like ChatGPT Help LCA Practitioners? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 196, 107062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Ilyas, R.A.; Awang, N.; Hasbi, S.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Advances in Sustainable Nanocomposites. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Che Nasir, N.A.; Hasbi, S. Tensile and Corrosion Resistance Studies of MXenes/Nanocomposites: A Review. In Advanced Structured Materials; Springer Science and Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 167, pp. 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi, A.; Zeinedini, A. Impact Response of E-Glass/Epoxy Composite Bi-Directional Corrugated Core Sandwich Panels. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, S.; Han, G.H.; Kim, S.; Rhee, K.Y. Effect of Dehydroxylation/Amorphization Degree of Bentonite on the Microstructure, Thermal Stability, and Mechanical Strength of Basalt Epoxy Composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamineni, J.N.; Burela, R.G. Modelling Fabrication and Burst Testing of Type IV 3D Printed Plastic Liner Composites Overwrapped Pressure Vessel. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2024, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aravind, D.; Krishnasamy, S.; Rajini, N.; Siengchin, S.; Kumar, T.S.M.; Chandrasekar, M.; Yorseng, K. Thermal and Tensile Properties of 3D Printed ABS-Glass Fibre, ABS-Glass Fibre-Carbon Fibre Hybrid Composites Made by Novel Hybrid Manufacturing Technique. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2024, 37, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webo, W.; Masu, L.M.; Nziu, P.K. Finite Element Analysis and Experimental Approaches of Mono and Hybrid Nanocellulosic Composites under Tensile Test. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 020001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Ryu, Y.; Saidpour, M. Stress Analysis of Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels. Mod. Mech. Eng. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, U.A.; Hall, D.E. Simplified Lamé’s Equations to Determine Contact Pressure and Hoop Stress in Thin-Walled Press-Fits. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 138, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Ramkumar, J.; Milani, A.S. A Simplified Damage Prediction Framework for Milling of Unidirectional Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Plastics. Adv. Manuf. Polym. Compos. Sci. 2015, 1, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, M.; Yahya, A.; Arif, A.F.; Jaber, H.; Alkheder, M. Burst Pressure Performance Comparison of Type V Hydrogen Tanks. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 81, 906917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO14040; Life Cycle Assessment: Best Practices of ISO14040 Series. Sub-Committee on Standards and Conformance: Singapore, 2004; pp. 7690–7695.
- Chen, Y.; Liebau, U.; Guruprasad, S.M.; Trofimenko, I.; Minke, C. Advancing Life Cycle Assessment of Sustainable Green Hydrogen Production Using Domain-Specific Fine-Tuning by Large Language Models Augmentation. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 2494–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Petropoulos, F.; Kang, Y. Large Language Models: Their Success and Impact. Forecasting 2023, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwal, S.S.; Zhang, Q.; Devi, N.; Thakur, V.K. Carbon-Based Polymer Nanocomposite for High-Performance Energy Storage Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| S. No | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Young’s Modulus | 1.6 GPa |
| 2 | Poisson’s ratio | 0.41045 |
| 3 | Density | 1030 kg/m3 |
| 4 | Bulk Modulus | 2.978 GPa |
| 5 | Tensile Strength | 45 MPa |
| 6 | Flexural Modulus | 2.1 GPa |
| 7 | Impact Resistance | 15 kJ/m2 |
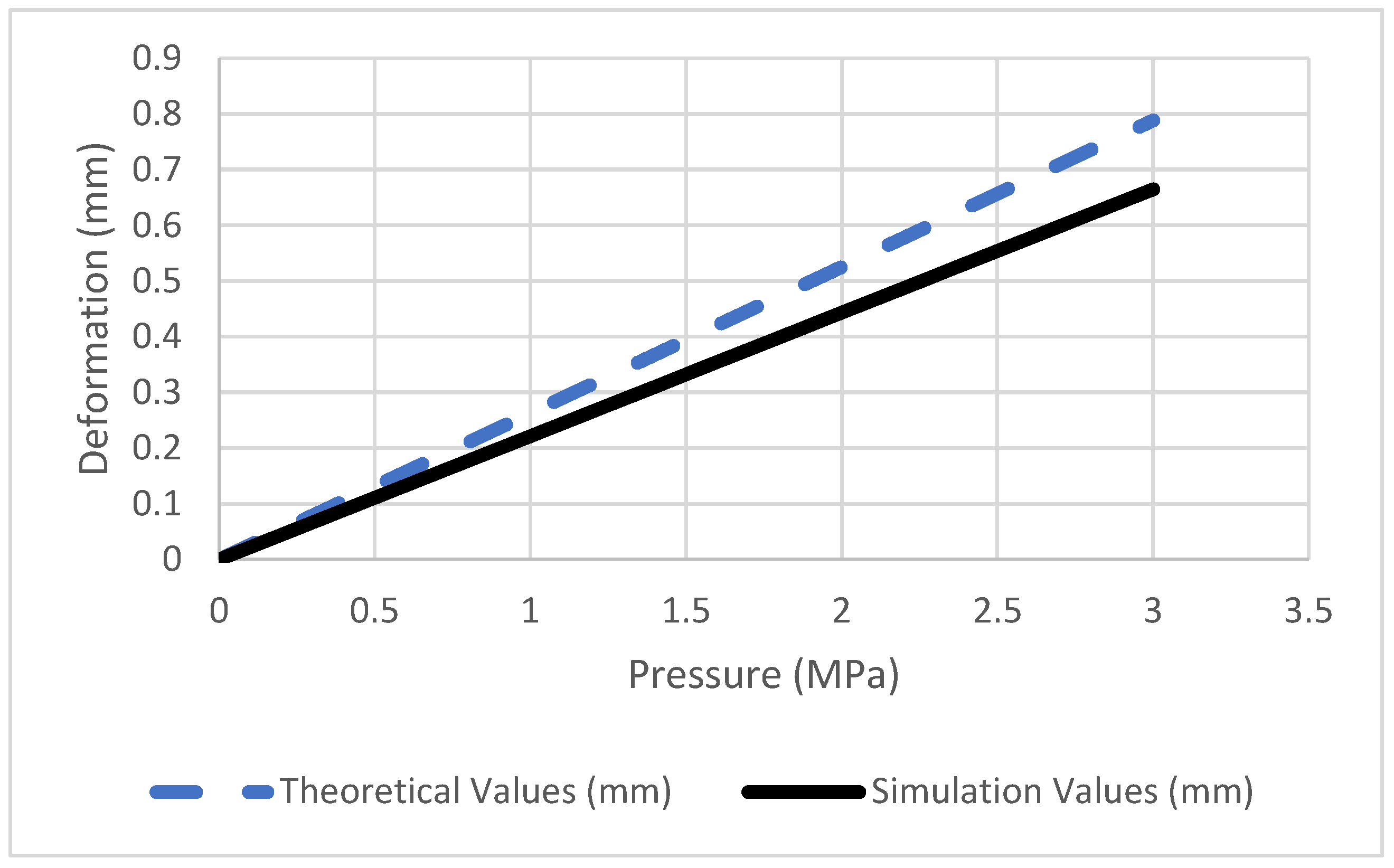
| Pressure (MPa) | Theoretical Deformation (mm) | Simulation Deformation (mm) | Percentage Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0.2628125 | 0.22165 | 15.66 |
| 1.2 | 0.315375 | 0.26598 | 15.66 |
| 1.4 | 0.36794 | 0.31031 | 15.66 |
| 1.6 | 0.4205 | 0.35464 | 15.66 |
| 1.8 | 0.4730625 | 0.39897 | 15.66 |
| 2 | 0.525625 | 0.4433 | 15.66 |
| 2.2 | 0.5781875 | 0.48763 | 15.66 |
| 2.4 | 0.63075 | 0.53196 | 15.66 |
| 2.6 | 0.6833125 | 0.57629 | 15.66 |
| 2.8 | 0.735875 | 0.62062 | 15.66 |
| 3 | 0.7884375 | 0.66495 | 15.66 |
| Properties | Kevlar/Epoxy | Basalt/Epoxy | E-Glass Fiber/Epoxy | Carbon T-700/Epoxy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density ρ (kg/m3) | 1380 | 1830 | 1800 | 1570 |
| Orthotropic Elasticity | ||||
| Young Modulus X, E1 (GPa) | 5.5 | 38.9 | 30.9 | 132 |
| Young Modulus Y, E2 (GPa) | 5.5 | 7.47 | 7.33 | 10.3 |
| Young Modulus Z, E3 (GPa) | 5.5 | 7.47 | 7.33 | 10.3 |
| Poisson’s Ratio XY, ν12 | 0.34 | 0.281 | 0.281 | 0.25 |
| Poisson’s Ratio XZ, ν13 | 0.34 | 0.281 | 0.281 | 0.25 |
| Poisson’s Ratio YZ, ν23 | 0.4 | 0.455 | 0.448 | 0.38 |
| Shear Modulus XY, G12 (GPa) | 2.2 | 2.71 | 2.69 | 6.5 |
| Shear Modulus XZ, G13 (GPa) | 2.2 | 2.71 | 2.69 | 6.5 |
| Shear Modulus YZ, G23 (GPa) | 1.8 | 2.54 | 2.53 | 3.91 |
| Orthotropic Stress Limits | ||||
| Tensile Stress X, (MPa) | 1400 | 1220 | 860 | 2100 |
| Tensile Stress Y, (MPa) | 30 | 62.1 | 62.3 | 24 |
| Tensile Stress Z, (MPa) | 30 | 62.1 | 62.5 | 65 |
| Compression Stress X, (MPa) | 335 | 780 | 580 | 1050 |
| Compression Stress Y, (MPa) | 158 | 93.1 | 93.4 | 132 |
| Compression Stress Z, (MPa) | 158 | 93.1 | 93.4 | 132 |
| Shear Stress, τ (MPa) | 49 | 85.7 | 85.8 | 75 |
| Material | Kevlar/Epoxy | Basalt Epoxy | E-Glass Fiber Epoxy | Carbon T-700/Epoxy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burst Pressure PBurst | 93.33 MPa | 81.33 MPa | 57.33 MPa | 140 MPa |
| Allowable Working Pressure | 41.48 MPa | 36.15 MPa | 25.48 MPa | 62.22 MPa |
| Material | Fibre Weight (g) | Epoxy Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon T-700/Epoxy | 111.23 | 56.7 |
| Kevlar/Epoxy | 97.76 | 56.7 |
| E-Glass Fiber/Epoxy | 127.52 | 56.7 |
| Basalt/Epoxy | 129.64 | 56.7 |
| Component | Material | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | Carbon T-700/Epoxy, Kevlar Epoxy, E-Glass Fiber Epoxy, Basalt/Epoxy | 111.23 |
| Polymer matrix | Epoxy | 56.7 |
| Boss | Aluminium Alloy | 192 |
| Coating (1 mm) | Polyethylene | 33 |
| Seal (O-ring) | NBR | 1.7 |
| Gasket (Flat Ring) | NBR | 0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saharudin, M.S.; Hasbi, S.; Sahu, S.K.; Ma, Q.; Younas, M. Numerical Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment of Type V Hydrogen Pressure Vessels. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020075
Saharudin MS, Hasbi S, Sahu SK, Ma Q, Younas M. Numerical Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment of Type V Hydrogen Pressure Vessels. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(2):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020075
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaharudin, Mohd Shahneel, Syafawati Hasbi, Santosh Kumar Sahu, Quanjin Ma, and Muhammad Younas. 2025. "Numerical Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment of Type V Hydrogen Pressure Vessels" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 2: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020075
APA StyleSaharudin, M. S., Hasbi, S., Sahu, S. K., Ma, Q., & Younas, M. (2025). Numerical Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment of Type V Hydrogen Pressure Vessels. Journal of Composites Science, 9(2), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9020075











