Limnophila aromatica Crude Extracts as Natural Emulsifiers for Formation and Stabilizing of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Samples and Extracts Preparation
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of Extracts
2.3.1. Chemical Composition Characterization
2.3.2. Interfacial Tension Measurements
2.4. Formation of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions
2.5. Emulsions Characterization and Stability Evaluation
2.5.1. Characterization of Emulsions
2.5.2. Evaluation of Emulsions Stability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Limnophila Aromatica Extracts
3.1.1. Extraction Yields and Chemical Compositions of Limnophila Aromatica Extracts
3.1.2. Interfacial Activities of Limnophila Aromatica Extracts
3.2. Emulsifying Properties of Limnophila Aromatica Extracts (LAEs)
3.3. Effect of Extract Concentration on Emulsion Formation and Stabilization
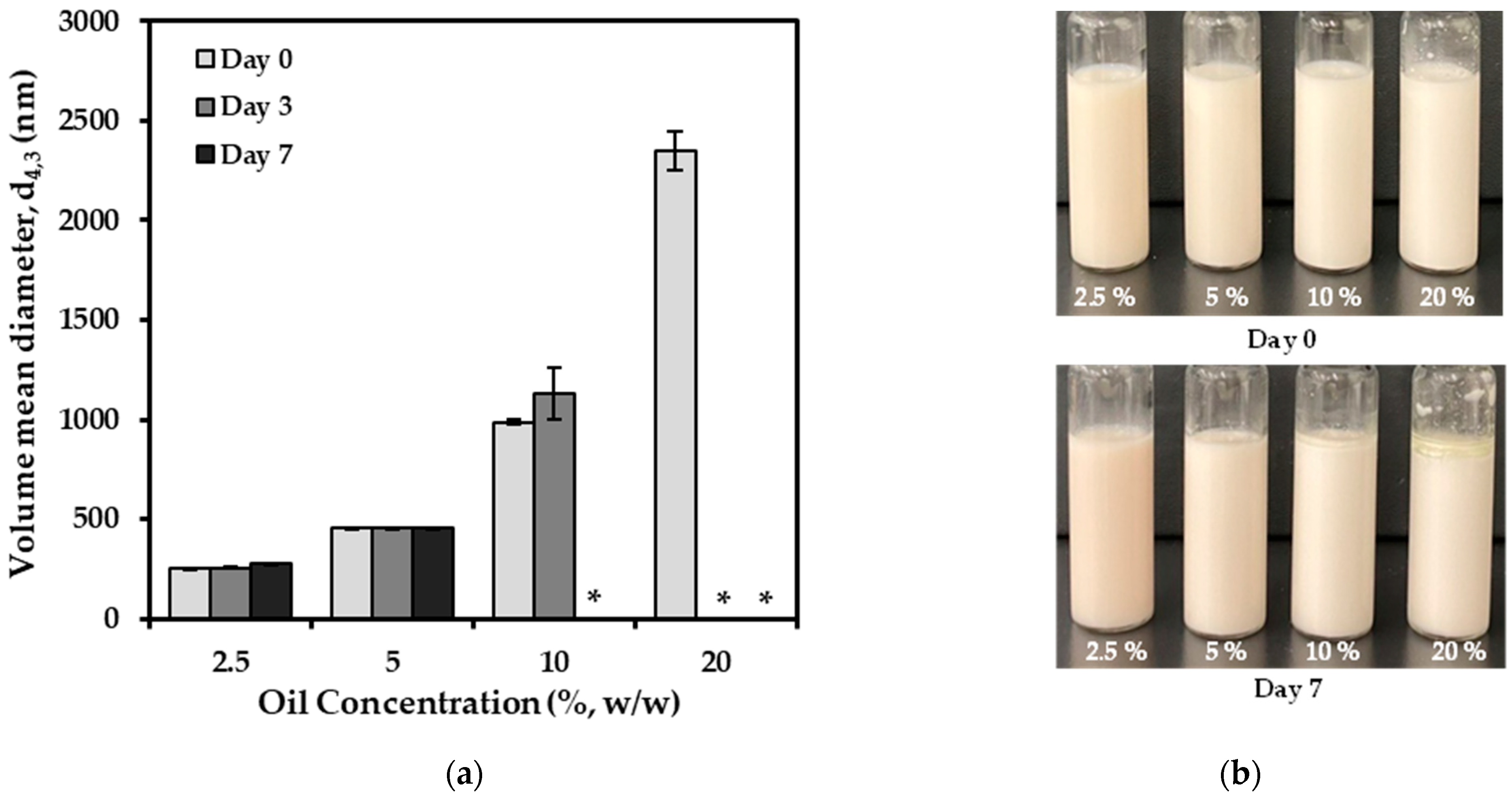
3.4. Effect of Oil Concentrations on Emulsion Formation and Stabilization
3.5. Stability of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickinson, E. Towards more natural emulsifiers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1993, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; McClements, D.J. Progress in natural emulsifiers for utilization in food emulsions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G.; Hieke, S.; Wills, J. Sustainability labels on food products: Consumer motivation, understanding and use. Food Policy 2014, 44, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural emulsifiers—Biosurfactants, phospholipids, biopolymers, and colloidal particles: Molecular and physicochemical basis of functional performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McClements, D.J. Protein-stabilized emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Leser, M.E.; Sher, A.A.; McClements, D.J. Formation and stability of emulsions using a natural small molecule surfactant: Quillaja saponin (Q-Naturale®). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Formulation of food emulsions using natural emulsifiers: Utilization of quillaja saponin and soy lecithin to fabricate liquid coffee whiteners. J. Food Eng. 2017, 209, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregiel, D.; Berlowska, J.; Witonska, I.; Antolak, H.; Proestos, C.; Babic, M.; Babic, L.; Zhang, B. Saponin-Based, Biological-Active Surfactants from Plants. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick, G.R.; Price, K.R.; Tsukamoto, C.; Okubo, K. Saponins. In Toxic Substances in Crop Plants; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 1991; pp. 285–327. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kite, G.C.; Howes, M.J.R.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Metabolomic analysis of saponins in crude extracts of Quillaja saponaria by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for product authentication. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Conrad, J.; Carle, R.; Weiss, J.; Schweiggert, R.M. Phenolic constituents in commercial aqueous quillaja (Quillaja saponaria Molina) Wood extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; Van Staden, J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, J.P.; Heng, L.; de Groot, A.; Gruppen, H. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uluata, S.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Physical Stability, Autoxidation, and Photosensitized Oxidation of ω-3 Oils in Nanoemulsions Prepared with Natural and Synthetic Surfactants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9333–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, B.; Argin, S.; Ozilgen, M.; McClements, D.J. Formation and stabilization of nanoemulsion-based vitamin e delivery systems using natural surfactants: Quillaja saponin and lecithin. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, T.B.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Ribeiro, A.; Peres, A.M.; Dias, M.M.; Pinho, S.P.; Barreiro, M.F. Formulation and optimization of nanoemulsions using the natural surfactant saponin from Quillaja bark. Molecules 2020, 25, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralla, T.; Salminen, H.; Tuosto, J.; Weiss, J. Formation and stability of emulsions stabilised by Yucca saponin extract. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralla, T.; Herz, E.; Salminen, H.; Edelmann, M.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.; Weiss, J. Emulsifying Properties of Natural Extracts from Panax ginseng L. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralla, T.; Salminen, H.; Wolfangel, T.; Edelmann, M.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.; Weiss, J. Value addition of red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) by-products: Emulsion formation and stability. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralla, T.; Salminen, H.; Edelmann, M.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.; Weiss, J. Oat bran extract (Avena sativa L.) from food by-product streams as new natural emulsifier. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taarji, N.; da Silva, C.A.R.; Khalid, N.; Gadhi, C.; Hafidi, A.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Isoda, H.; Nakajima, M. Formulation and stabilization of oil-in-water nanoemulsions using a saponins-rich extract from argan oil press-cake. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralla, T.; Salminen, H.; Edelmann, M.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.; Weiss, J. Stability of Emulsions Using a New Natural Emulsifier: Sugar Beet Extract (Beta vulgaris L.). Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhoute, M.; Taarji, N.; Vodo, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Zahar, M.; Isoda, H.; Nakajima, M.; Neves, M.A. Formation and stability of emulsions using crude extracts as natural emulsifiers from Argan shells. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 591, 124536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainassi, F.; Taarji, N.; Benkhalti, F.; Hafidi, A.; Neves, M.A.; Isoda, H.; Nakajima, M. Emulsion Formation and Stabilizing Properties of Olive Oil Cake Crude Extracts. Processes 2021, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taarji, N.; Bouhoute, M.; Chafai, Y.; Hafidi, A.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Tominaga, K.; Isoda, H.; Nakajima, M. Emulsifying Performance of Crude Surface-Active Extracts from Liquorice Root (Glycyrrhiza Glabra). ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philcox, D. A Taxonomic Revision of the Genus Limnophila R.Br. (Scrophulariaceae). Kew Bull. 1970, 24, 101–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, D.; Jash, S.K.; Singh, R.K.; Gangopadhyay, A. Chemical and Pharmacological Aspects of Limnophila Aromatica (Scrophulariaceae): An overview. AJPCT 2014, 2, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.N.; Thang, T.D.; Thai, T.H.; Ogunwande, I.A. Chemical constituents of leaf essential oils of four Scrophulariaceae species grown in Vietnam. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2015, 27, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmachari, G. Limnophila (Scrophulariaceae): Chemical and Pharmaceutical Aspects. Open Nat. Prod. J. 2008, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntipopipat, S.; Muangnoi, C.; Failla, M.L. Anti-inflammatory activities of extracts of thai spices and herbs with lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukongviriyapan, U.; Luangaram, S.; Leekhaosoong, K.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Preeprame, S. Antioxidant and vascular protective activities of Cratoxylum formosum, Syzygium gratum and Limnophila aromatica. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhuiyan, M.N.I.; Akter, F.; Chowdhury, J.U.; Begum, J. Chemical constituents of essential oils from aerial parts of Adenosma capitatum and Limnophila aromatica. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vairappan, C.S.; Nagappan, T. Major volatile hydrocarbons of rice paddy herb, Limnophila aromatica Lam. Merr as possible chemotaxonomic marker. J. Trop. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 11, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Do, Q.D.; Angkawijaya, A.E.; Tran-Nguyen, P.L.; Huynh, L.H.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.H. Effect of extraction solvent on total phenol content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of Limnophila aromatica. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wijaya, C.; Do, Q.D.; Ju, Y.H.; Santoso, S.P.; Putro, J.N.; Laysandra, L.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S. Isolation and characterization of starch from Limnophila aromatica. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhaobao, X.; Chunhong, T.; Gang, C.; Zhisong, S. Studied on corlorimetric determination of oleanolic acid in Chinese quince. Nat. Prod. Res. 2001, 13, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, R.; Saxena, J. Screening of total phenolic and flavonoid content in conventional and non conventional species of curcuma. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting nitrogen into protein-Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K. Effects of sample size, dry ashing temperature and duration on determination of ash content in algae and other biomass. Algal Res. 2019, 40, 101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, H.; Kozłowska, H. Antioxidant activity and total phenolics in selected cereal grains and their different morphological fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2008–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, B.; Anwar, F.; Ashraf, M. Effect of extraction solvent/technique on the antioxidant activity of selected medicinal plant extracts. Molecules 2009, 14, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishikura, Y.; Khokhar, S.; Murray, B.S. Effects of tea polyphenols on emulsification of olive oil in a small intestine model system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aziz, M.M.A.; Ashour, A.S.; Melad, A.S.G. A review on saponins from medicinal plants: Chemistry, isolation, and determination. J. Nanomed. Res. 2019, 7, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, T.H.; Huynh, T.D.; Vo, K.A.; Nguyen, K.A.; Cao, T.S.; Nguyen, K.N.; Nguyen, H.A.H.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Le, N.P.N.; Truong, D.H. Saponin-rich fractions from Codonopsis javanica root extract and their in vitro antioxidant and anti-enzymatic efficacy. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Parks, S.; Roach, P. An optimised aqueous extract of phenolic compounds from bitter melon with high antioxidant capacity. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pace, C.N.; Treviño, S.; Prabhakaran, E.; Scholtz, J.M. Protein structure, stability and solubility in water and other solvents. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pomeranz, Y.; Meloan, C.E. Ash and Minerals. In Food Analysis; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 602–624. [Google Scholar]
- Karefyllakis, D.; Octaviana, H.; van der Goot, A.J.; Nikiforidis, C.V. The emulsifying performance of mildly derived mixtures from sunflower seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodo, S.; Taarji, N.; Bouhoute, M.; de Oliveira Felipe, L.; Neves, M.A.; Kobayashi, I.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Potential of bagasse obtained using hydrothermal liquefaction pre-treatment as a natural emulsifier. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, F.; Zendehboudi, S. A Comprehensive Review on Emulsions and Emulsion Stability in Chemical and Energy Industries. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickinson, E. Structure, stability and rheology of flocculated emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.W.; Gao, P. Emulsions and Microemulsions for Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery. In Handbook of Non-Invasive Drug Delivery Systems; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 59–94. ISBN 9780815520252. [Google Scholar]
- Losso, J.N.; Khachatryan, A.; Ogawa, M.; Godber, J.S.; Shih, F. Random centroid optimization of phosphatidylglycerol stabilized lutein-enriched oil-in-water emulsions at acidic pH. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Lipid oxidation in corn oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by casein, whey protein isolate, and soy protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1696–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can Karaca, A.; Nickerson, M.T.; Low, N.H. Lentil and chickpea protein-stabilized emulsions: Optimization of emulsion formulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 13203–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, S.; Drusch, S. Saponins—Self-assembly and behavior at aqueous interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 243, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, S.; Keppler, J.K.; Drusch, S. Mixtures of Quillaja saponin and beta-lactoglobulin at the oil/water-interface: Adsorption, interfacial rheology and emulsion properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 518, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, J.C.; Kleinschmidt, F.; El Harrak, A.; Griffiths, A.D. Kinetic aspects of emulsion stabilization by surfactants: A microfluidic analysis. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6088–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ethanol Concentration | Extraction Yield | Protein Content | Saponin Content | Phenol Content | Ash Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% (v/v) | 5.95 ± 0.55 d | 5.38 ± 0.27 a | 7.75 ± 0.20 d | 3.70 ± 0.04 e | 24.50 ± 1.88 b |
| 25% (v/v) | 8.67 ± 0.37 b | 4.97 ± 0.33 ab | 8.17 ± 0.10 d | 5.37 ± 0.08 d | 21.96 ± 1.96 bc |
| 50% (v/v) | 9.53 ± 0.15 a | 4.56 ± 0.06 bc | 17.17 ± 0.37 c | 9.20 ± 0.13 c | 19.69 ± 0.73 c |
| 75% (v/v) | 7.72 ± 0.09 c | 4.36 ± 0.06 c | 20.14 ± 0.40 b | 11.68 ± 0.12 b | 14.74 ± 0.55 d |
| 99.5% (v/v) | 1.22 ± 0.08 e | 3.81 ± 0.29 d | 23.87 ± 0.54 a | 12.79 ± 0.07 a | 30.86 ± 2.20 a |
| Extract Concentration | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 15 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1% (w/w) | 836 ± 19 | 834 ± 5 | 832 ± 16 |
| 0.25% (w/w) | 627 ± 8 | 640 ± 12 | 638 ± 5 |
| 0.5% (w/w) | 481 ± 6 | 486 ± 6 | 483 ± 3 |
| 1% (w/w) | 424 ± 5 | 509 ± 5 | * |
| 1.5% (w/w) | 659 ± 83 | * | * |
| 2% (w/w) | 718 ± 72 | * | * |
| Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 15 | Day 21 | Day 30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 °C | 435 ± 1 | 446 ± 5 | 460 ± 4 | 481 ± 2 | 482 ± 18 |
| 25 °C | 442 ± 5 | 466 ± 1 | 484 ± 7 | 482 ± 3 | 496 ± 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soeung, R.; Felipe, L.d.O.; Bouhoute, M.; Taarji, N.; Nakajima, M.; Neves, M.A. Limnophila aromatica Crude Extracts as Natural Emulsifiers for Formation and Stabilizing of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020026
Soeung R, Felipe LdO, Bouhoute M, Taarji N, Nakajima M, Neves MA. Limnophila aromatica Crude Extracts as Natural Emulsifiers for Formation and Stabilizing of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoeung, Rasmey, Lorena de Oliveira Felipe, Meryem Bouhoute, Noamane Taarji, Mitsutoshi Nakajima, and Marcos A. Neves. 2022. "Limnophila aromatica Crude Extracts as Natural Emulsifiers for Formation and Stabilizing of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020026
APA StyleSoeung, R., Felipe, L. d. O., Bouhoute, M., Taarji, N., Nakajima, M., & Neves, M. A. (2022). Limnophila aromatica Crude Extracts as Natural Emulsifiers for Formation and Stabilizing of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020026







