Removing Fluoride from Water by Nanostructured Magnesia-Impregnated Activated Carbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
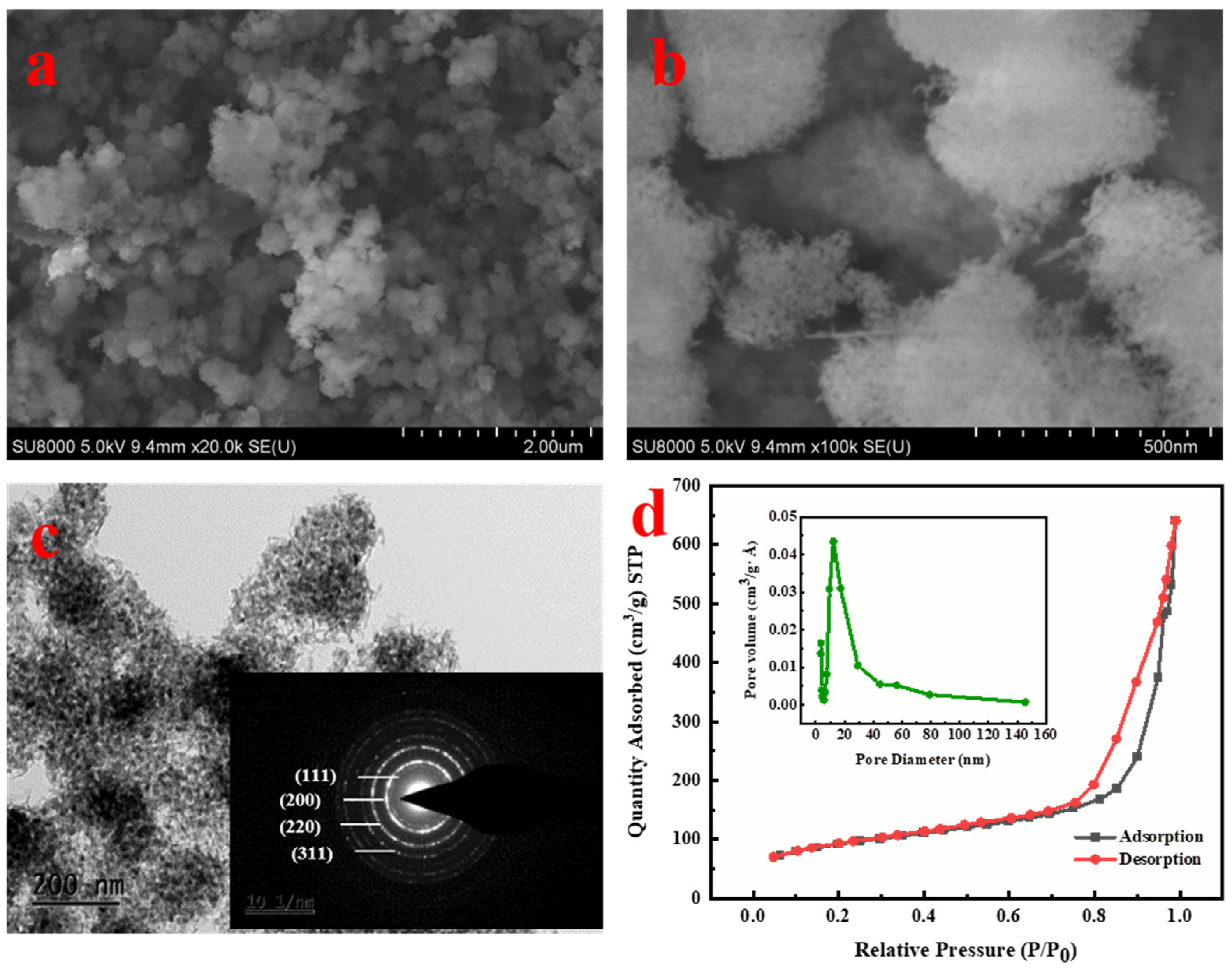
3.1. Sorbent Characterization
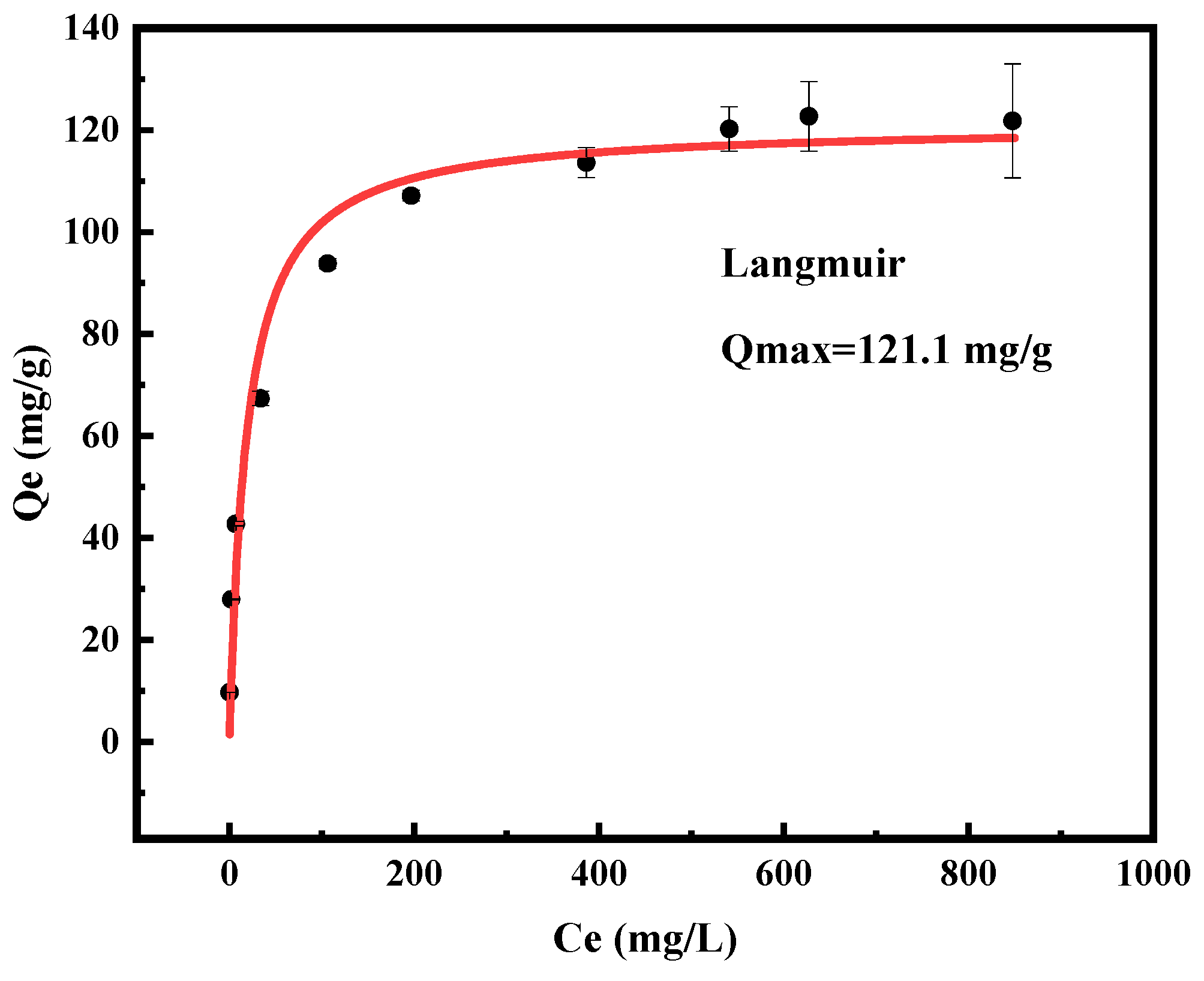
3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
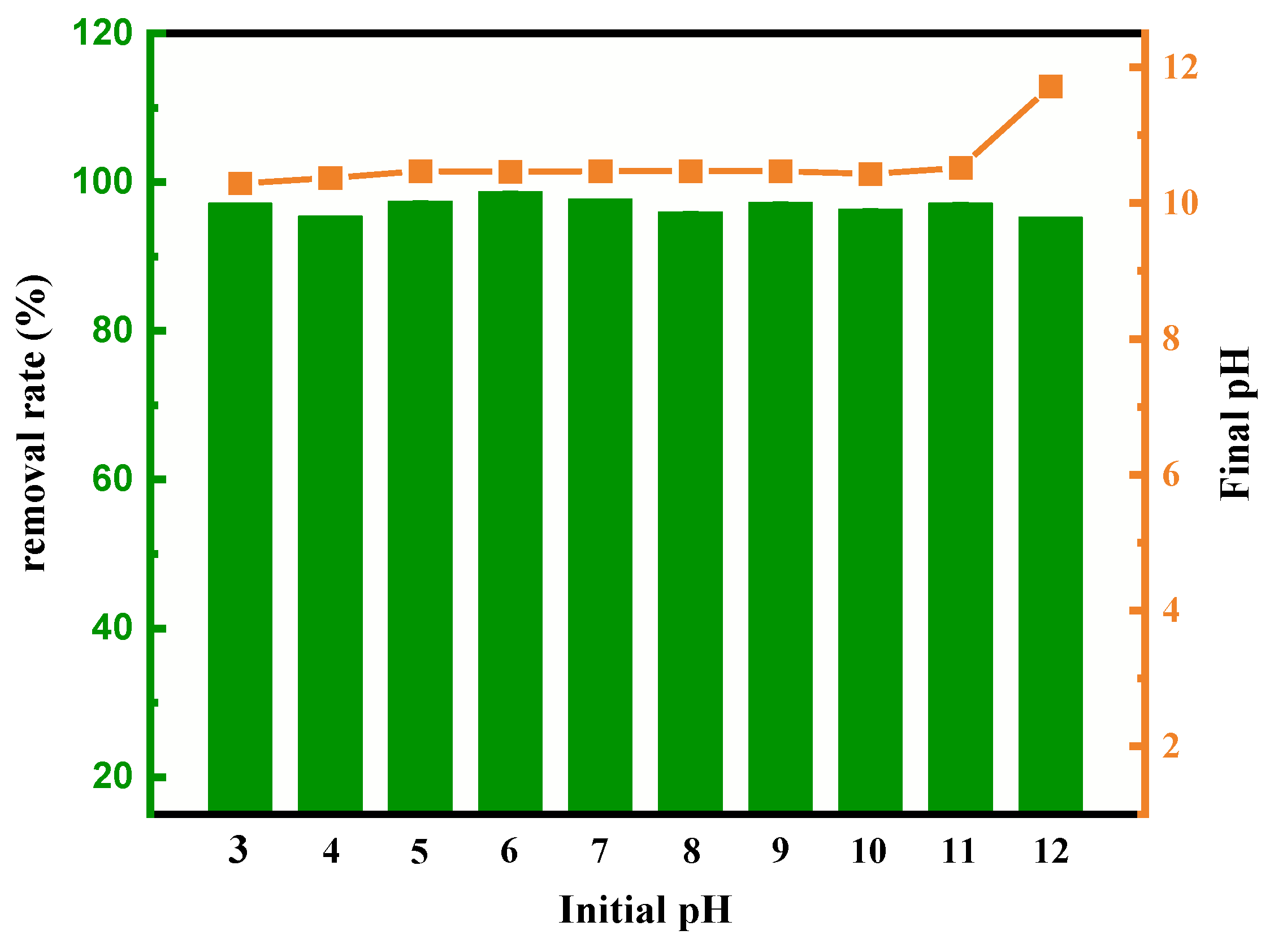
3.4. Influence of Solution pH
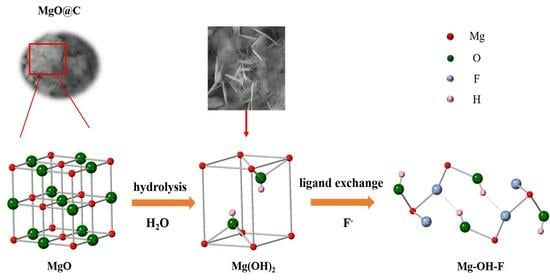
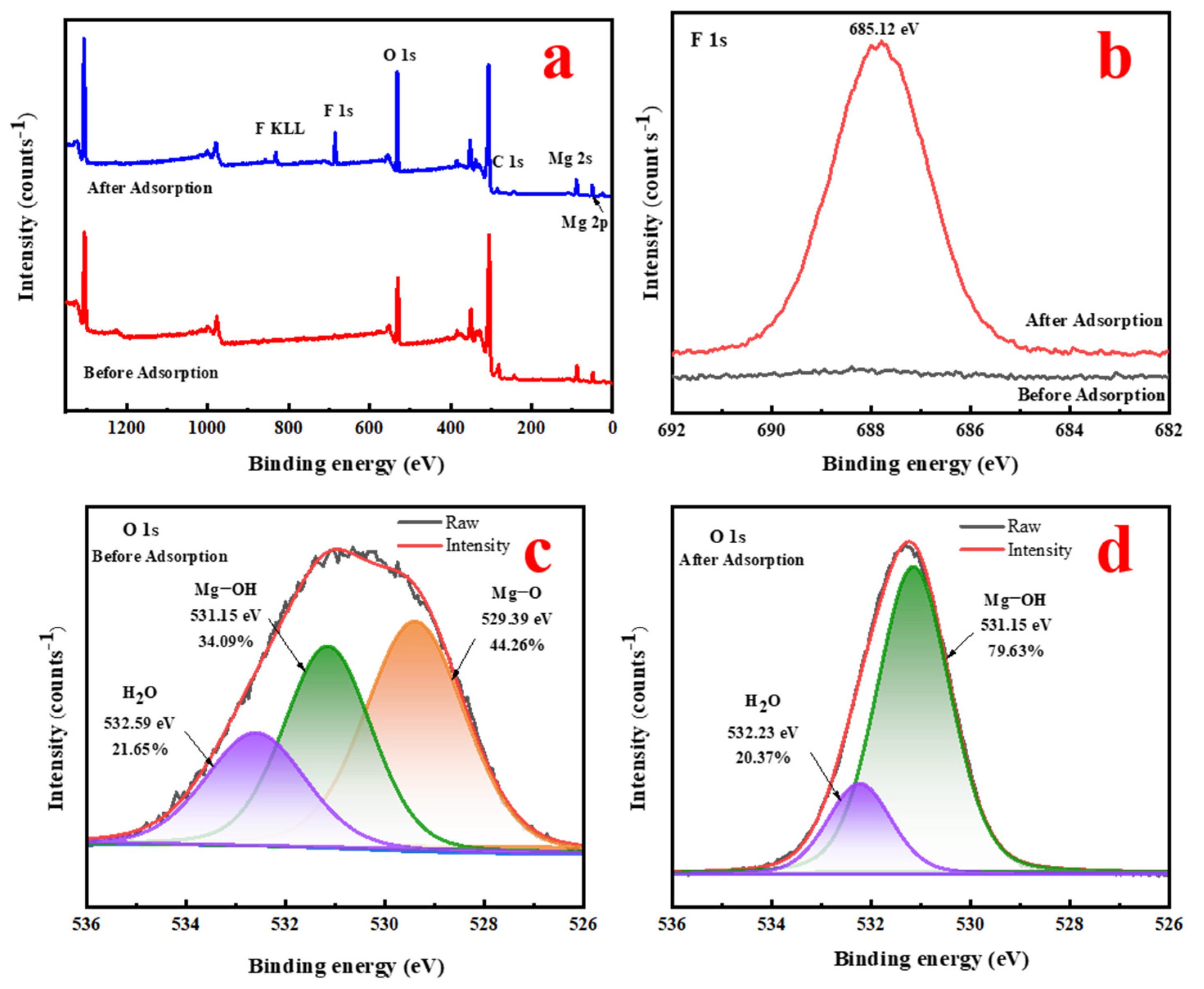
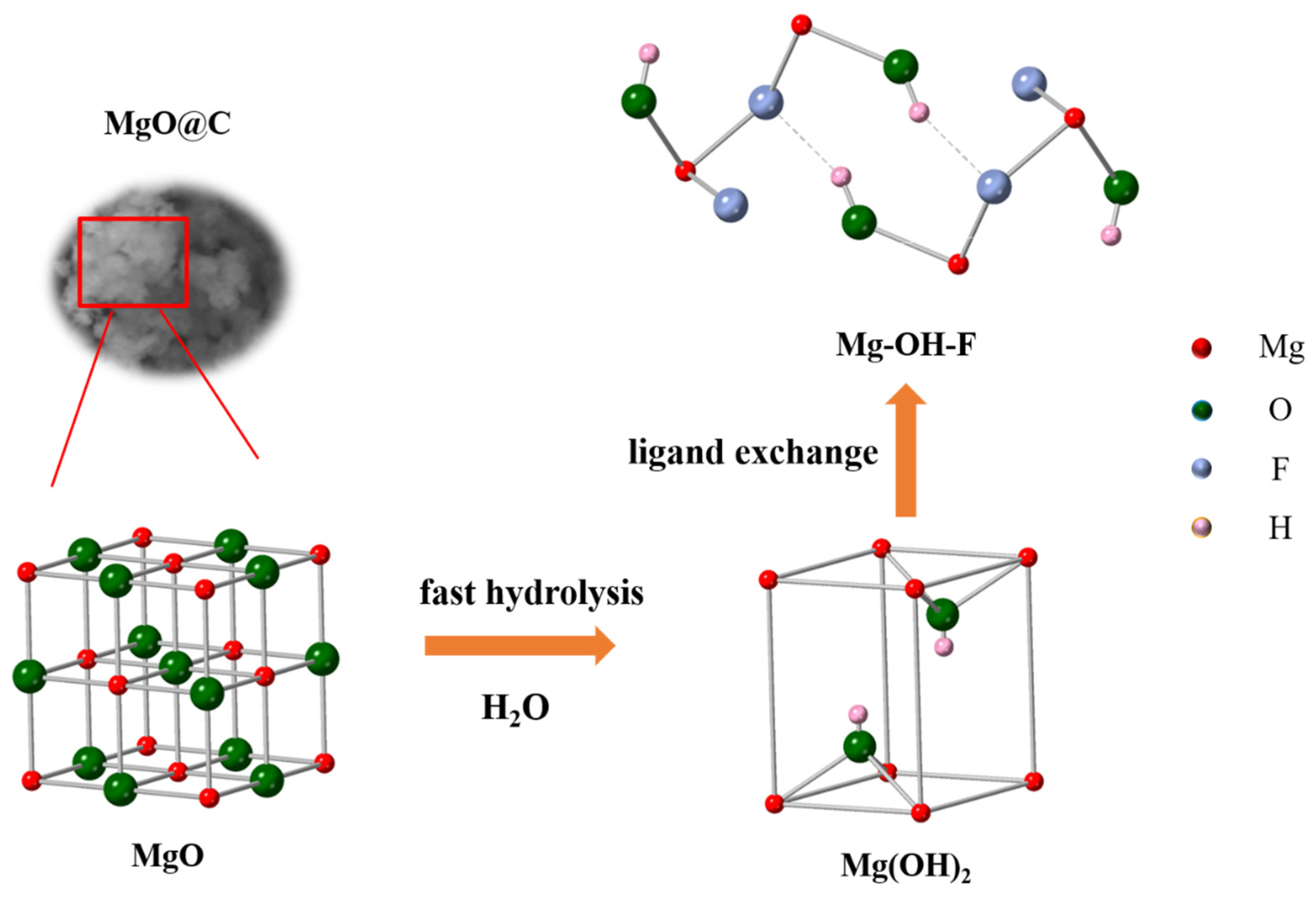
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayoob, S.; Gupta, A.K. Fluoride in drinking water: A review on the status and stress effects. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 433–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Quoc Bao, P.; Gupta, N.; Rezania, S.; Kamyab, H.; Yadav, S.; Vymazal, J.; Kumar, V.; Doan Quang, T.; et al. Fluoride contamination, health problems and remediation methods in Asian groundwater: A comprehensive review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Tripathi, P. Arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater: A review of global scenarios with special reference to India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Howard, K. Groundwater fluoride and arsenic mobilization in a typical deep aquifer system within a semi-arid basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Vengosh, A.; Jeuland, M.; Tekle-Haimanot, R.; Weinthal, E.; Kravchenko, J.; Paul, C.; McCornick, P. Fluoride exposure from groundwater as reflected by urinary fluoride and children’s dental fluorosis in the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.; Anand, S.; Mishra, B.K.; Giles, D.E.; Singh, P. Review of fluoride removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Saha, B. Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2012, 39, 2881–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Apambire, W.B.; Boyle, D.R.; Michel, F.A. Geochemistry, genesis, and health implications of fluoriferous groundwaters in the upper regions of Ghana. Environ. Geol. 1997, 33, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Yenkie, M.K.; Labhsetwar, N.; Rayalu, S. Fluoride in Drinking Water and Defluoridation of Water. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Chen, X.; Gao, P.; Chen, G. Electrochemical removal of fluoride ions from industrial wastewater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rao, Y.; Lan, M.; Liu, X.; Ju, L.; Ju, Y. Optimization of loading flocculation pretreatment of produced water from three gases co-mining using response surface methodology. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 15, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Kumar, E.; Sillanpää, M. Fluoride removal from water by adsorption—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habuda-Stanić, M.; Ravančić, M.E.; Flanagan, A.J.M. A Review on Adsorption of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2014, 7, 6317–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, E.J.; Wang, Y. A Limestone Reactor for Fluoride Removal from Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3247–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.D.; Binning, P.; Stipp, S.L.S. Fluoride Removal by Calcite: Evidence for Fluorite Precipitation and Surface Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9561–9568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, S.; Viswanathan, N. Identification of selective ion-exchange resin for fluoride sorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, C.; Schweizer, M.; Simonnot, M.O.; Sardin, M. Selective removal of fluoride ions by a two-way ion-exchange cyclic process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 3341–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, P.I.; Moulin, P.; Dominguez, L.; Millet, J.C.; Charbit, F. Removal of fluoride from electronic industrial effluentby RO membrane separation. Desalination 2005, 173, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Dickson, J.M. Nanofiltration membrane performance on fluoride removal from water. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, Z.; Bariou, B.; Mameri, N.; Taky, M.; Nicolas, S.; Elmidaoui, A. Fluoride removal from brackish water by electrodialysis. Desalination 2001, 133, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiak, L.J.; Schäfer, A.I. Removal of boron, fluoride and nitrate by electrodialysis in the presence of organic matter. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 334, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhang, K.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Review of fluoride removal from water environment by adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Huang, L.; Yan, J.; Ma, B.; Huang, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, T. Removal of fluoride from industrial wastewater by using different adsorbents: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, Y.S.; Agarwal, M.; Gupta, A.B.; Gupta, S.; Shukla, P. Fluoride occurrences, health problems, detection, and remediation methods for drinking water: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.S.; Bersillon, J.-L.; Gopal, K. Removal of fluoride from drinking water by adsorption onto alum-impregnated activated alumina. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.; Pant, K.K. Equilibrium, kinetics and breakthrough studies for adsorption of fluoride on activated alumina. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 42, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.; Chiou, H.-M. The Adsorption of Fluoride Ion from Aqueous Solution by Activated Alumina. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 133, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagappa, B.; Chandrappa, G.T. Mesoporous nanocrystalline magnesium oxide for environmental remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 106, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Tian, X.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Komarneni, S. Fabrication, performance and mechanism of MgO meso-/macroporous nanostructures for simultaneous removal of As(iii) and F in a groundwater system. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.K.; Park, H.J. Defluoridation from aqueous solution by lanthanum hydroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamble, S.P.; Jagtap, S.; Labhsetwar, N.K.; Thakare, D.; Godfrey, S.; Devotta, S.; Rayalu, S.S. Defluoridation of drinking water using chitin, chitosan and lanthanum-modified chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 129, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichur, A.M.; Jyoti Basu, M. Adsorption of fluoride onto mixed rare earth oxides. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 24, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.; Bhatnagar, A.; Ji, M.; Jung, W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, G.; Song, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yang, J.S.; et al. Defluoridation from aqueous solutions by granular ferric hydroxide (GFH). Water Res. 2009, 43, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, M.; Maiti, A. Defluoridation by highly efficient calcium hydroxide nanorods from synthetic and industrial wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 561, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Yang, S. Remediating fluoride from water using hydrous zirconium oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Tu, H.; Chan, T.; Jing, C. Mechanistic study of simultaneous arsenic and fluoride removal using granular TiO2-La adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Defluoridation of drinking water using adsorption processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, A.; Niinae, M.; Nakata, H.; Fujii, H.; Tasaka, Y. Immobilization of fluoride in artificially contaminated kaolinite by the addition of commercial-grade magnesium oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, E. Removal of Fluoride from Water. Public Health Rep. 1937, 52, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettlemoyer, A.C.; Zettlemoyer, E.A.; Walker, W.C. Active Magnesia. II. Adsorption of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K. Layered magnesium oxide for efficient removal of fluoride from groundwater. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, D.; Yu, H.; Guo, J.; He, Y. Amorphous-dominated MgO hollow spheres enhanced fluoride adsorption: Mechanism analysis and machine learning prediction. J. Chem. Phys. 2025, 162, 014702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, K.-S.; Kong, L.-T.; Sun, B.; Shen, W.; Meng, F.-L.; Liu, J.-H. Effective removal of fluoride by porous MgO nanoplates and its adsorption mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 675, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Lin, J.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, F. Enhanced Fluoride Removal from Water by Nanoporous Biochar-Supported Magnesium Oxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 9988–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Suhas. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; de la Puente, G.; Grange, P. Evidence of textural modifications of an activated carbon on liquid-phase oxidation treatments. Microporous Mater. 1997, 12, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.-T.; Jiang, S.; Ho, K.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, C.-H. Mesoporous magnesium oxide and its composites: Preparation, characterization, and removal of 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Jia, Y.; Luo, T.; Kong, L.-T.; Sun, B.; Shen, W.; Meng, F.-L.; Liu, J.-H. Efficient removal of fluoride by hierarchical MgO microspheres: Performance and mechanism study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface-Area and Porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, C.S.; Viswanathan, N.; Meenakshi, S. Defluoridation of water using magnesia/chitosan composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, R.L.; Ovalle-Turrubiartes, J.; Sanchez-Castillo, M.A. Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution on aluminum-impregnated carbon. Carbon 1999, 37, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences-Alvarez, E.; Velazquez-Jimenez, L.H.; Chazaro-Ruiz, L.F.; Diaz-Flores, P.E.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Fluoride removal in water by a hybrid adsorbent lanthanum-carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 455, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, M.S.; Kojima, Y.; Aoyi, O.; Bernardo, E.C.; Matsuda, H. Adsorption equilibrium modeling and solution chemistry dependence of fluoride removal from water by trivalent-cation-exchanged zeolite F-9. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 279, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kumagai, S.; Yoshioka, T. Analysis of F− removal from aqueous solutions using MgO. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 25, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Dhanasinghe, C.; Verpoort, F.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Kao, C.-M. Development of modified MgO/biochar composite for chemical adsorption enhancement to cleanup fluoride-contaminated groundwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.C.; Xu, A.W.; Zhang, L.Z.; Song, R.Q.; Wu, L. Synthesis and characterization of porous magnesium hydroxide and oxide nanoplates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-X.; Xu, D.; Li, X.-Q.; Liu, W.-C.; Jia, Y. Excellent fluoride removal properties of porous hollow MgO microspheres. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5445–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wei, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, C. Highly efficient As(III) removal in water using millimeter-sized porous granular MgO-biochar with high adsorption capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugama, T.; Sabatini, R.; Petrakis, L. Decomposition of chrysotile asbestos by fluorosulfonic acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttke, S.; Coman, S.M.; Scholz, G.; Kirmse, H.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Schroeder, S.L.M.; Kemnitz, E. Novel Sol-Gel Synthesis of Acidic MgF2-x(OH)(x) Materials. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2008, 14, 11488–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, S.; Nilius, N.; Torelli, P.; Renaud, G.; Freund, H.J.; Valeri, S. Competition Between Polar and Nonpolar Growth of MgO Thin Films on Au(111). J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23043–23049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberg, J.T.; Starr, D.E.; Yamamoto, S.; Kaya, S.; Kendelewicz, T.; Mysak, E.R.; Porsgaard, S.; Salmeron, M.B.; Brown, G.E.; Nilsson, A.; et al. Formation of hydroxyl and water layers on MgO films studied with ambient pressure XPS. Surf. Sci. 2011, 605, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Shen, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, J. Removing Fluoride from Water by Nanostructured Magnesia-Impregnated Activated Carbon. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9020022
Yang C, Shen C, Zhang N, Zhang X, Zhao L, Zheng J. Removing Fluoride from Water by Nanostructured Magnesia-Impregnated Activated Carbon. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chen, Chenliang Shen, Nan Zhang, Xusheng Zhang, Liang Zhao, and Jianzhong Zheng. 2025. "Removing Fluoride from Water by Nanostructured Magnesia-Impregnated Activated Carbon" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9020022
APA StyleYang, C., Shen, C., Zhang, N., Zhang, X., Zhao, L., & Zheng, J. (2025). Removing Fluoride from Water by Nanostructured Magnesia-Impregnated Activated Carbon. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9020022