Genetic and Epigenetic Study of Monozygotic Twins Affected by Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
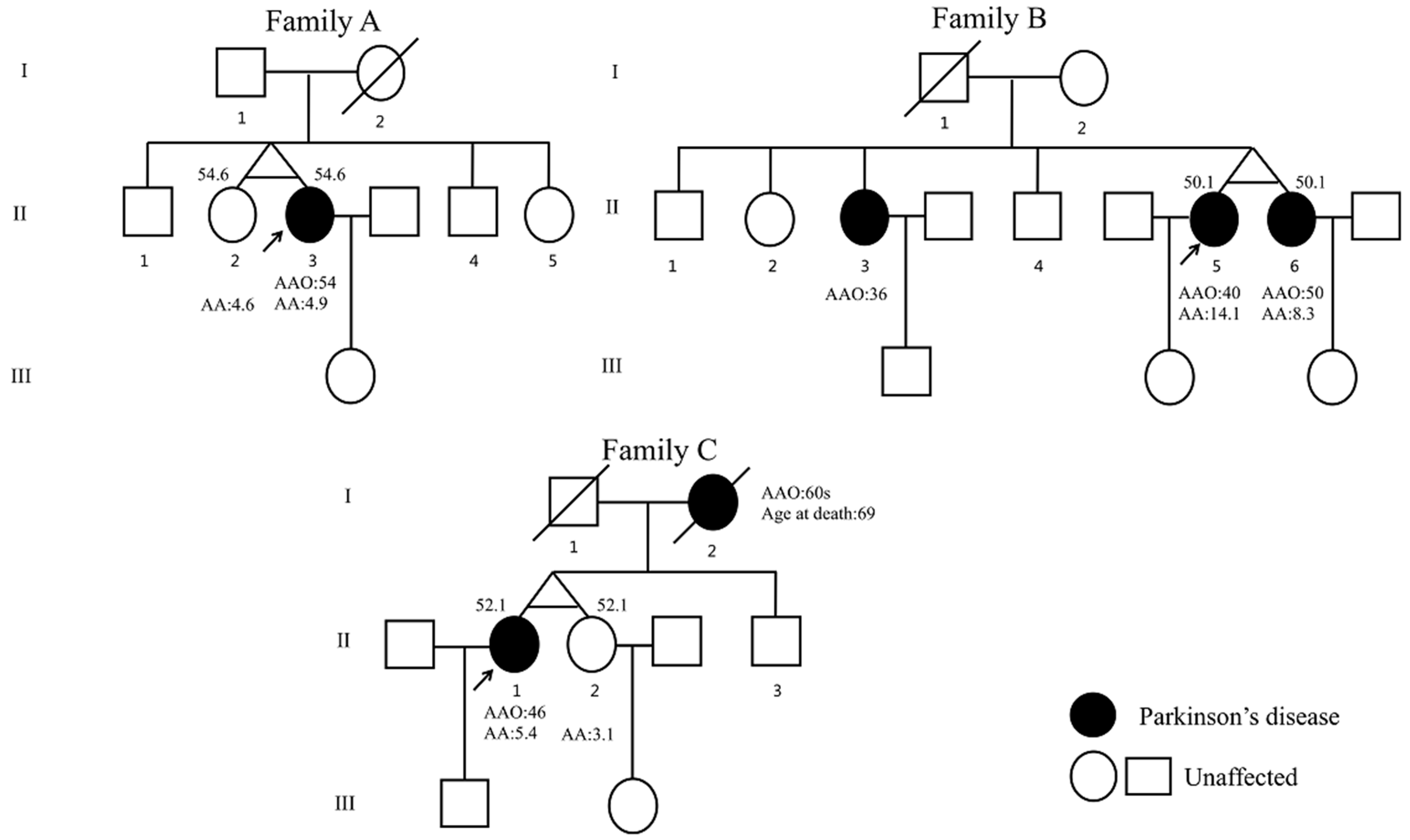
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill-Burns, E.M.; Ross, O.; Wissemann, W.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.; Zareparsi, S.; Siuda, J.; Lynch, T.; Wszolek, Z.; Silburn, P.; Mellick, G.; et al. Identification of Genetic Modifiers of Age-at-Onset for Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3849–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Gonzalez-Latapi, P.; Marras, C.; Visanji, N.; Yang, W.; Sato, C.; Lang, A.; Rogaeva, E.; Zhang, M. Epigenetic Clock Acceleration Is Linked to Age at Onset of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xi, Z.; Ghani, M.; Jia, P.; Pal, M.; Werynska, K.; Moreno, D.; Sato, C.; Liang, Y.; Robertson, J.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Study of Als-Discordant Identical Twins with Double Mutations in Sod1 and Arhgef28. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1268–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.; Yunusova, Y.; van Blitterswijk, M.; Dib, S.; Ghani, M.; Moreno, D.; Sato, C.; Liang, Y.; Singleton, A.; Robertson, J.; et al. Identical Twins with the C9orf72 Repeat Expansion Are Discordant for Als. Neurology 2014, 83, 1476–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.; et al. Mds Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ge, J.; Wu, P.; Zuo, C.; Ding, Z.; Wang, J. Onset-Related Subtypes of Parkinson’s Disease Differ in the Patterns of Striatal Dopaminergic Dysfunction: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qu, J.; Zhou, M. Identification of Driver Genes and Somatic Mutations in Cell-Free DNA of Patients with Pulmonary Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.; Kia, D.; Noyce, A.; Xue, A.; et al. Identification of Novel Risk Loci, Causal Insights, and Heritable Risk for Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Ono, S.; Imamura, A.; Okazaki, Y.; Kinoshita, A.; Mishima, H.; Nakane, H.; Ozawa, H.; Yoshiura, K.; Kurotaki, N. Deep sequencing reveals variations in somatic cell mosaic mutations between monozygotic twins with discordant psychiatric disease. Hum. Genome Var. 2017, 4, 17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, M.; Bundo, M.; Ueda, J.; Yoshikawa, A.; Nishimura, F.; Sasaki, T.; Kakiuchi, C.; Kasai, K.; Kato, T.; Iwamoto, K. Identification of somatic mutations in monozygotic twins discordant for psychiatric disorders. NPJ Schizophr. 2018, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltz Steinberg, K.; Nicholas, T.; Koboldt, D.; Yu, B.; Mardis, E.; Pamphlett, R. Whole genome analyses reveal no pathogenetic single nucleotide or structural differences between monozygotic twins discordant for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Rudakou, U.; Krohn, L.; Mufti, K.; Ruskey, J.; Asayesh, F.; Estiar, M.; Spiegelman, D.; Surface, M.; Fahn, S.; et al. Analysis of Heterozygous PRKN Variants and Copy-Number Variations in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2021, 36, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.F.; Dong, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, N.; Yan, X.; Xia, K.; Tang, B. Exon dosage analysis of parkin gene in Chinese sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 604, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Azim, F.; Saju, H.; Zargaran, A.; Shirzad, M.; Kamal, M.; Fatema, K.; Rehman, S.; Azad, M.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S. Pesticides and Parkinson’s disease: Current and future perspective. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 115, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascherio, A.; Chen, H.; Weisskopf, M.; O’Reilly, E.; McCullough, M.; Calle, E.; Schwarzschild, M.; Thun, M. Pesticide exposure and risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Hsiao, I.T.; Huang, S.H.; Lui, C.C.; Yen, T.C.; Chang, W.N.; Huang, C.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, Y.Y.; Lin, K.J. ¹⁸F-FP-(+)-DTBZ positron emission tomography detection of monoaminergic deficient network in patients with carbon monoxide related parkinsonism. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 845–852, e59–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, R.; Cereda, E.; Akpalu, A.; Sarfo, F.; Cham, M.; Laryea, R.; Obese, V.; Oppon, K.; Del Sorbo, F.; Bonvegna, S.; et al. Natural history of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease and the long-duration response to levodopa. Brain 2020, 143, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Chou, M.; Lin, C.; Kao, C. Increased risk of Parkinson disease in patients with carbon monoxide intoxication: A population-based cohort study. Medicine 2015, 94, e869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Plaat, D.A.; de Jong, K.; de Vries, M.; van Diemen, C.; Nedeljković, I.; Amin, N.; Kromhout, H.; Vermeulen, R.; Postma, D.; van Duijn, C.; et al. Occupational Exposure to Pesticides Is Associated with Differential DNA Methylation. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunicki, M.; Stell, L.; Dinakarpandian, D.; de Planell-Saguer, M.; Lucas, R.; Hammond, S.; Balmes, J.; Zhou, X.; Paglino, T.; Sabatti, C.; et al. Exposure to No(2), Co, and Pm(2.5) Is Linked to Regional DNA Methylation Differences in Asthma. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.; Postuma, R.; Adler, C.; Bloem, B.; Chan, P.; Dubois, B.; Gasser, T.; Goetz, C.; Halliday, G.; Joseph, L.; et al. MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2015, 30, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balck, A.; Borsche, M.; Kasten, M.; Lohmann, K.; Seibler, P.; Brüggemann, N.; Klein, C. Discordance in monozygotic Parkinson’s disease twins—Continuum or dichotomy? Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, T.; Rogaeva, E. DNA Methylation Clocks and Their Predictive Capacity for Aging Phenotypes and Healthspan. Neurosci. Insights 2020, 15, 2633105520942221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; McKeever, P.; Xi, Z.; Moreno, D.; Sato, C.; Bergsma, T.; McGoldrick, P.; Keith, J.; Robertson, J.; Zinman, L.; et al. DNA methylation age acceleration is associated with ALS age of onset and survival. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tartaglia, M.; Moreno, D.; Christine, S.; McKeever, P.; Weichert, A.; Keith, J.; Robertson, J.; Zinman, L.; Rogaeva, E. DNA methylation age-acceleration is associated with disease duration and age at onset in C9orf72 patients. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picillo, M.; Lizarraga, K.; Friesen, E.; Chau, H.; Zhang, M.; Sato, C.; Rooke, G.; Munhoz, R.; Rogaeva, E.; Fraser, P.; et al. Parkinsonism due to A53E alpha-synuclein gene mutation: Clinical, genetic, epigenetic, and biochemical features. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2018, 33, 1950–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S.; Ritz, B. Increased epigenetic age and granulocyte counts in the blood of Parkinson’s disease patients. Aging 2015, 7, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Features | Family A | Family B | Family C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II-2 | II-3 | II-3 | II-5 | II-6 | II-1 | II-2 | |
| Sex | Female | Female | Female | Female | Female | Female | Female |
| PD AAO, years | - | 54 | 36 | 40 | 50 | 46 | - |
| ASC, years | 55 | 55 | 54 | 51 | 51 | 52 | 52 |
| AOA, years | 55 | 55 | 54 | 51 | 51 | 52 | 52 |
| Types of diet | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Occupation | Doctor | Retired cashier of a pesticide and chemical fertilizer company | NA | Worker | Worker in a shoe factory | Civil servant | Civil servant |
| Chemical toxins exposure | No | pesticide and chemical fertilizer | NA | No | No | carbon monoxide poisoning at age 45 | No |
| Head trauma | No | No | NA | No | No | Yes | No |
| Surgery with general anesthesia | No | No | NA | No | No | Ovariectomy | No |
| Cigarette smoking | No | No | NA | No | No | No | No |
| Alcoholic consumption | No | No | NA | light | light | No | No |
| Physical activity in leisure time | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Exposure to pathogens or infectious agents | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Other medical history | No | No | NA | lumbar disc herniation | lumbar disc herniation | No | No |
| Cardinal symptoms of PD | - | Bradykinesia, rigidity | Tremor, Bradykinesia, rigidity | Tremor, Bradykinesia, rigidity | Tremor, Bradykinesia, rigidity | Tremor, Bradykinesia, rigidity | - |
| Family history of PD | No | No | AR | AR | AR | AD | AD |
| Years of education | NA | 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 12 | - |
| LEDD, mg | - | NA | 451 | 150 | 250 | 800 | - |
| H&Y stage | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | - |
| MMSE score | - | NA | NA | 24 | 28 | NA | - |
| UPDRS-III score | - | 30 (Med-off) | 29 (Med-on) | NA | 33 (Med-off) | 35 (Med-on) | - |
| Methods of genetic analysis | MLPA + WGS | MLPA + WGS | MLPA | MLPA + WGS | MLPA + WGS | MLPA + WGS | WGS |
| Results of genetic analysis | exon 1–3 del (het) in PRKN | exon 1–3 del (het) in PRKN | Exon 2–4 del (het), c.2T > C, p.Met1Thr (het) (NM_004562.3) in PRKN | Exon 2–4 del (het), c.2T > C, p.Met1Thr (het) (NM_004562.3) in PRKN | Exon 2–4 del (het), c.2T > C, p.Met1Thr (het) (NM_004562.3) in PRKN | - | - |
| 11C-CFT PET/CT results | NA | Decreased DAT uptake ratios in bilateral caudate and putamen, especially in the left side | NA | NA | NA | Decreased DAT uptake ratios in bilateral caudate and putamen, especially in the left side | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.-M.; Yang, W.-L.; Rogaeva, E.; Lang, A.E.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Genetic and Epigenetic Study of Monozygotic Twins Affected by Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2023, 7, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7020011
Sun Y-M, Yang W-L, Rogaeva E, Lang AE, Wang J, Zhang M. Genetic and Epigenetic Study of Monozygotic Twins Affected by Parkinson’s Disease. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. 2023; 7(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yi-Min, Wan-Li Yang, Ekaterina Rogaeva, Anthony E. Lang, Jian Wang, and Ming Zhang. 2023. "Genetic and Epigenetic Study of Monozygotic Twins Affected by Parkinson’s Disease" Clinical and Translational Neuroscience 7, no. 2: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7020011
APA StyleSun, Y.-M., Yang, W.-L., Rogaeva, E., Lang, A. E., Wang, J., & Zhang, M. (2023). Genetic and Epigenetic Study of Monozygotic Twins Affected by Parkinson’s Disease. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, 7(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7020011







