The Role of PET in the Diagnosis and Disease Activity Assessment in Large Vessel Vasculitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
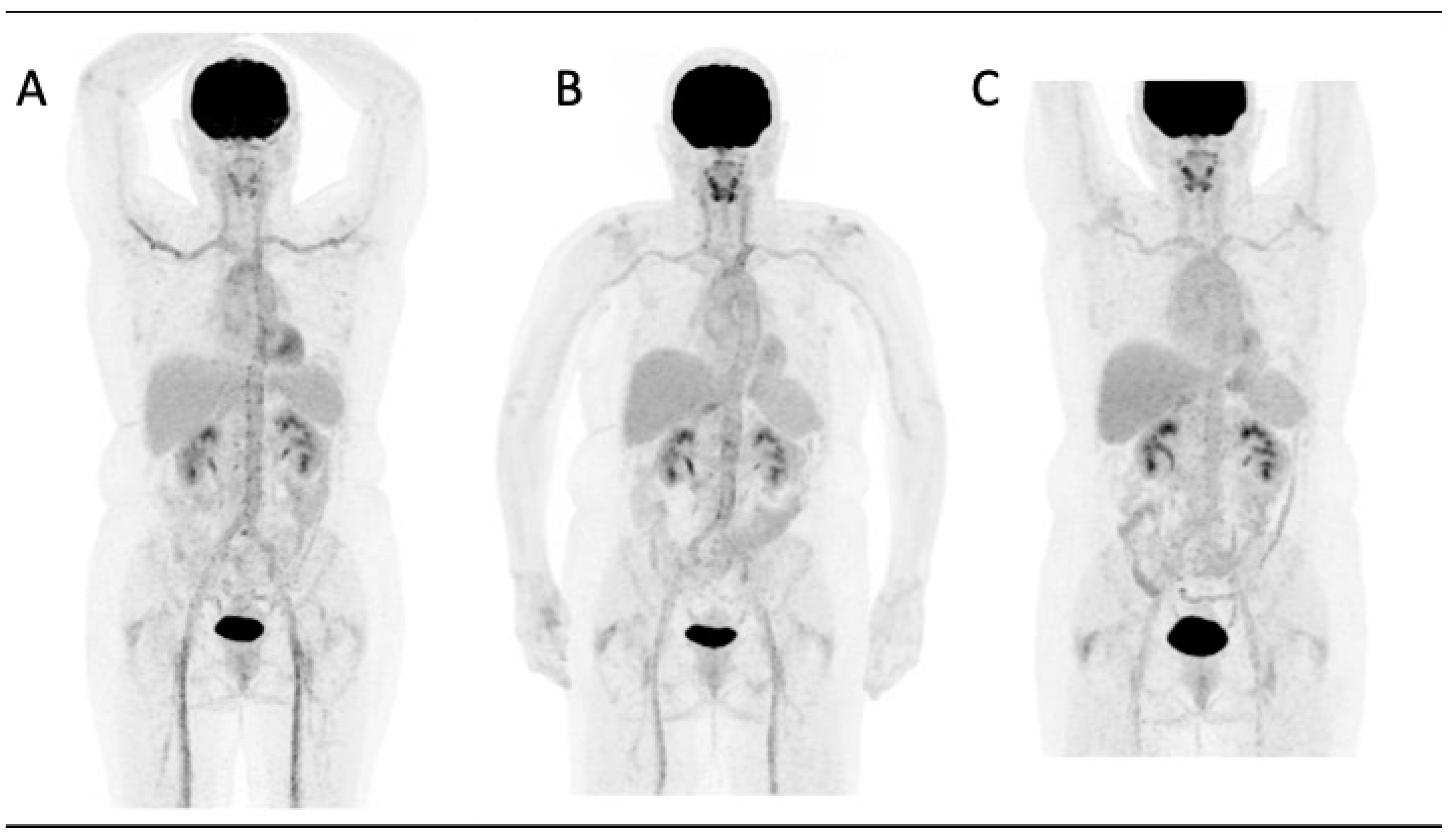
2. FDG-PET in the Diagnosis and Activity Assessment of LVV
2.1. Large Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis
2.2. Takayasu’s Arteritis
3. FDG-PET in the Follow-Up of LVV
3.1. Giant Cell Arteritis
3.2. Takayasu’s Arteritis
3.3. Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu’s Arteritis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 65, 1–11. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23045170/ (accessed on 20 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ponte, C.; Grayson, P.C.; Robson, J.C.; Suppiah, R.; Gribbons, K.B.; Judge, A.; Luqmani, R.A. American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for giant cell arteritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1647–1653. Available online: http://ard.bmj.com/ (accessed on 19 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Suppiah, R.; Robson, J.C.; Gribbons, K.B.; Judge, A.; Craven, A.; Khalid, S.; Hutchings, A.; Danda, D.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1654–1660. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36351705/ (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.-J.; Zhao, K.; Liu, Z.-F.; Wang, G.-L.; Yang, S.-Y.; Zhou, G.-J. A meta-analysis of the value of fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/PET-CT in the evaluation of fever of unknown origin. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, 834–844. Available online: http://www.ejradiology.com/article/S0720048X10005632/fulltext (accessed on 8 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Kubota, K.; Mimori, A. Clinical value of whole-body PET/CT in patients with active rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 423. Available online: https://arthritis-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13075-014-0423-2 (accessed on 8 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-González, S.; Depetris, M.; García-Martínez, A.; Espígol-Frigolé, G.; Tavera-Bahillo, I.; Corbera-Bellata, M.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Alba, M.A.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Grau, J.M.; et al. Positron emission tomography assessment of large vessel inflammation in patients with newly diagnosed, biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: A prospective, case–control study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1388–1392. Available online: https://ard.bmj.com/content/73/7/1388 (accessed on 8 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meller, J.; Strutz, F.; Siefker, U.; Scheel, A.; Sahlmann, C.O.; Lehmann, K.; Conrad, M.; Vosshenrich, R. Early diagnosis and follow-up of aortitis with [18F]FDG PET and MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 30, 730–736. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00259-003-1144-y (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Meignan, M.; Gallamini, A.; Haioun, C. Report on the First International Workshop on interim-PET scan in lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 1257–1260. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10428190903040048 (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayson, P.C.; Alehashemi, S.; Bagheri, A.A.; Civelek, A.C.; Cupps, T.R.; Kaplan, M.J.; Malayeri, A.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Novakovich, E.; Bluemke, D.A.; et al. 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography As an Imaging Biomarker in a Prospective, Longitudinal Cohort of Patients With Large Vessel Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 439–449. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29145713/ (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Hautzel, H.; Sander, O.; Heinzel, A.; Schneider, M.; Müller, H.-W. Assessment of Large-Vessel Involvement in Giant Cell Arteritis with 18F-FDG PET: Introducing an ROC-Analysis–Based Cutoff Ratio. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1107–1113. Available online: https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/49/7/1107 (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Einspieler, I.; Thürmel, K.; Pyka, T.; Eiber, M.; Wolfram, S.; Moog, P.; Reeps, C.; Essler, M. Imaging large vessel vasculitis with fully integrated PET/MRI: A pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 42, 1012–1024. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00259-015-3007-8 (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Martin, O.; Schaarschmidt, B.M.; Kirchner, J.; Suntharalingam, S.; Grueneisen, J.; Demircioglu, A.; Heusch, P.; Quick, H.H.; Forsting, M.; Antoch, G.; et al. PET/MRI Versus PET/CT for Whole-Body Staging: Results from a Single-Center Observational Study on 1,003 Sequential Examinations. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 61, 1131–1136. Available online: https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/61/8/1131 (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, D.; Karabayas, M.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Goel, R.; Goodyear, C.S.; Dhaun, N. Large-vessel vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 7, 93. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41572-021-00327-5 (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmich, B.; Agueda, A.; Monti, S.; Buttgereit, F.; de Boysson, H.; Brouwer, E.; Cassie, R.; Cid, M.C.; Dasgupta, B.; Dejaco, C.; et al. 2018 Update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Rheumatology 2019, 79, 19–30. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31270110/ (accessed on 20 July 2023). [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Ramiro, S.; Duftner, C.; Besson, F.L.; Bley, T.A.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Cimmino, M.A.; Clark, E.; Dasgupta, B.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 636–643. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29358285/ (accessed on 30 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Blockmans, D.; Maes, A.; Stroobants, S.; Nuyts, J.; Bormans, G.; Knockaert, D.; Bobbaers, H.; Mortelmans, L. New arguments for a vasculitic nature of polymyalgia rheumatica using positron emission tomography. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blockmans, D.; Stroobants, S.; Maes, A.; Mortelmans, L. Positron emission tomography in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: Evidence for inflammation of the aortic arch. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108, 246–249. Available online: http://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002934399004246/fulltext (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lariviere, D.; Benali, K.; Coustet, B.; Pasi, N.; Hyafil, F.; Klein, I.; Sacre, K. Positron emission tomography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: A real-life prospective study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4146. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/Fulltext/2016/07260/Positron_emission_tomography_and_computed.20.aspx (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, B.D.; Gormsen, L.C.; Hansen, I.T.; Keller, K.K.; Therkildsen, P.; Hauge, E.-M. Three days of high-dose glucocorticoid treatment attenuates large-vessel 18F-FDG uptake in large-vessel giant cell arteritis but with a limited impact on diagnostic accuracy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 45, 1119–1128. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00259-018-4021-4 (accessed on 9 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Oh, M.-D. FDG PET-CT in the Diagnosis of Takayasu Arteritis Presenting as Fever of Unknown Origin: A Case Report. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 47, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDG-PET Finding in Early-Phase Takayasu Arteritis: Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography [Internet]. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/jcat/Abstract/1999/01000/FDG_PET_Finding_in_Early_Phase_Takayasu_Arteritis.4.aspx (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- Kerr, G.S.; Hallahan, C.W.; Giordano, J.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Fauci, A.S.; Rottem, M.; Hoffman, G.S. Takayasu Arteritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 919–929. Available online: http://annals.org/article.aspx?doi=10.7326/0003-4819-120-11-199406010-00004 (accessed on 1 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Soussan, M.; Nicolas, P.; Schramm, C.; Katsahian, S.; Pop, G.; Fain, O.; Mekinian, A. Management of large-vessel vasculitis with FDG-PET: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e622. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25860208/ (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Galli, E.; Muratore, F.; Mancuso, P.; Boiardi, L.; Marvisi, C.; Besutti, G.; Spaggiari, L.; Casali, M.; Versari, A.; Rossi, P.G.; et al. The role of PET/CT in disease activity assessment in patients with large vessel vasculitis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4809–4816. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35258570/ (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Quinn, K.; Alessi, H.D.; Ponte, C.; Rose, E.; A Ahlman, M.; Redmond, C.; Luo, Y.; Bolek, E.C.; A Langford, C.; A Merkel, P.; et al. Use of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to standardize clinical trial recruitment in Takayasu’s arteritis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4047–4055. Available online: https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC9536789 (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Hamrin, B.; Jonsson, N.; Hellsten, S. “Polymyalgia arteritica”. Further clinical and histopathological studies with a report of six autopsy cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1968, 27, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unizony, S.; Arias-Urdaneta, L.; Miloslavsky, E.; Arvikar, S.; Khosroshahi, A.; Keroack, B.; Stone, J.H. Tocilizumab for the treatment of large-vessel vasculitis (giant cell arteritis, Takayasu arteritis) and polymyalgia rheumatica. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Kayani, A.; Prieto-Pena, D.; Tomelleri, A.; Whitlock, M.; Mo, J.; van der Geest, N.; Dasgupta, B. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis: A single centre NHS experience using imaging (ultrasound and PET-CT) as a diagnostic and monitoring tool. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001417. Available online: https://rmdopen.bmj.com/content/6/3/e001417 (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönau, V.; Roth, J.; Tascilar, K.; Corte, G.; Manger, B.; Rech, J.; Schmidt, D.; Cavallaro, A.; Uder, M.; Crescentini, F.; et al. Resolution of vascular inflammation in patients with new-onset giant cell arteritis: Data from the RIGA study. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3851–3861. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/rheumatology (accessed on 11 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Klearman, M.; Collinson, N. Trial of Tocilizumab in Giant-Cell Arteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1493–1495. Available online: http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMc1711031 (accessed on 9 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Peña, D.P.; Martínez-Rodríguez, I.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Calderón-Goercke, M.; Banzo, I.; González-Vela, M.C.; Castañeda, S.; Llorca, J.; González-Gay, M.; Blanco, R. Evidence for uncoupling of clinical and 18-FDG activity of PET/CT scan improvement in tocilizumab-treated patients with large-vessel giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology 2021, 39, S69–S75. [Google Scholar]
- Bellan, M.; Puta, E.; Croce, A.; Sacchetti, G.M.; Orsini, F.; Zecca, E.; Soddu, D.; Gavelli, F.; Avanzi, G.C.; Castello, L.; et al. Role of positron emission tomography in the assessment of disease burden and risk of relapse in patients affected by giant cell arteritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 39, 1277–1281. Available online: https://iris.uniupo.it/handle/11579/108627 (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammel, A.M.; Hsiao, E.; Schembri, G.; Bailey, E.; Nguyen, K.; Brewer, J.; Schrieber, L.; Janssen, B.; Youssef, P.; Fraser, C.L.; et al. Cranial and large vessel activity on positron emission tomography scan at diagnosis and 6 months in giant cell arteritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 582–588. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1756-185X.13805 (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunder, G.G.; Bloch, D.A.; Michel, B.A.; Stevens, M.B.; Arend, W.P.; Calabrese, L.H.; Edworthy, S.M.; Fauci, A.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Lie, J.T.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 1122–1128. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2202311/ (accessed on 20 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Quinn, K.A.; Gribbons, K.B.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Civelek, A.C.; Novakovich, E.; Merkel, P.A.; Ahlman, M.A.; Grayson, P.C. Effect of Treatment on Imaging, Clinical, and Serologic Assessments of Disease Activity in Large-vessel Vasculitis. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 47, 99–107. Available online: https://www.jrheum.org/content/47/1/99 (accessed on 20 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- van der Geest, K.S.M.; Treglia, G.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Brouwer, E.; Sandovici, M.; Jamar, F.; Gheysens, O.; Slart, R.H.J.A. Diagnostic value of [18F]FDG-PET/CT for treatment monitoring in large vessel vasculitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 48, 3886–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, A.L.F.; Castro, M.F.; Arraes, A.E.D.; Savioli, B.; Sato, E.I.; de Souza, A.W.S. A retrospective cohort study to assess PET-CT findings and clinical outcomes in Takayasu arteritis: Does 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in arteries predict relapses? Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 1123–1131. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00296-020-04551-2 (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Besutti, G.; Muratore, F.; Mancuso, P.; Ferrari, M.; Galli, E.; Spaggiari, L.; Monelli, F.; Casali, M.; Versari, A.; Boiardi, L.; et al. Vessel inflammation and morphological changes in patients with large vessel vasculitis: A retrospective study. RMD Open 2022, 8, e001977. Available online: https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC8734042 (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Quinn, K.A.; Ahlman, M.A.; Malayeri, A.A.; Marko, J.; Civelek, A.C.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Grayson, P.C. Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Angiography and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Large-Vessel Vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marvisi, C.; Galli, E.; Ricordi, C.; Durmo, R.; Roncali, M.; Muratore, F.; Salvarani, C.; Versari, A. The Role of PET in the Diagnosis and Disease Activity Assessment in Large Vessel Vasculitis. Hemato 2023, 4, 321-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4040026
Marvisi C, Galli E, Ricordi C, Durmo R, Roncali M, Muratore F, Salvarani C, Versari A. The Role of PET in the Diagnosis and Disease Activity Assessment in Large Vessel Vasculitis. Hemato. 2023; 4(4):321-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarvisi, Chiara, Elena Galli, Caterina Ricordi, Rexhep Durmo, Massimo Roncali, Francesco Muratore, Carlo Salvarani, and Annibale Versari. 2023. "The Role of PET in the Diagnosis and Disease Activity Assessment in Large Vessel Vasculitis" Hemato 4, no. 4: 321-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4040026
APA StyleMarvisi, C., Galli, E., Ricordi, C., Durmo, R., Roncali, M., Muratore, F., Salvarani, C., & Versari, A. (2023). The Role of PET in the Diagnosis and Disease Activity Assessment in Large Vessel Vasculitis. Hemato, 4(4), 321-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4040026







