Diagnosing Lung Abnormalities Related to Heart Failure in Chest Radiogram, Lung Ultrasound and Thoracic Computed Tomography
Abstract
:Highlights
- Various imaging techniques are useful in differentiating lung abnormalities related to HF from pulmonary diseases.
- Lung ultrasound is a novel and emerging imaging tool for the management of HF.
- Recognising lung abnormalities in heart failure is crucial in routine clinical diagnostics.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chest X-ray
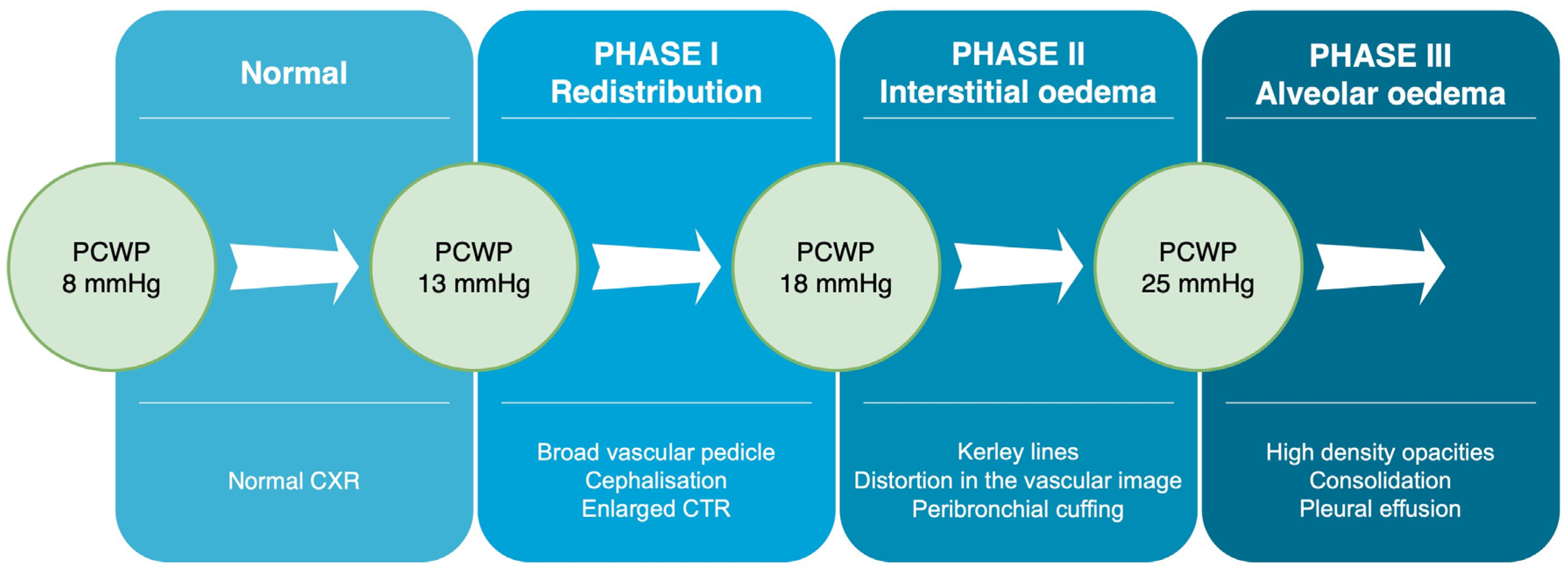
2.1. Pulmonary Features of HF in CXR
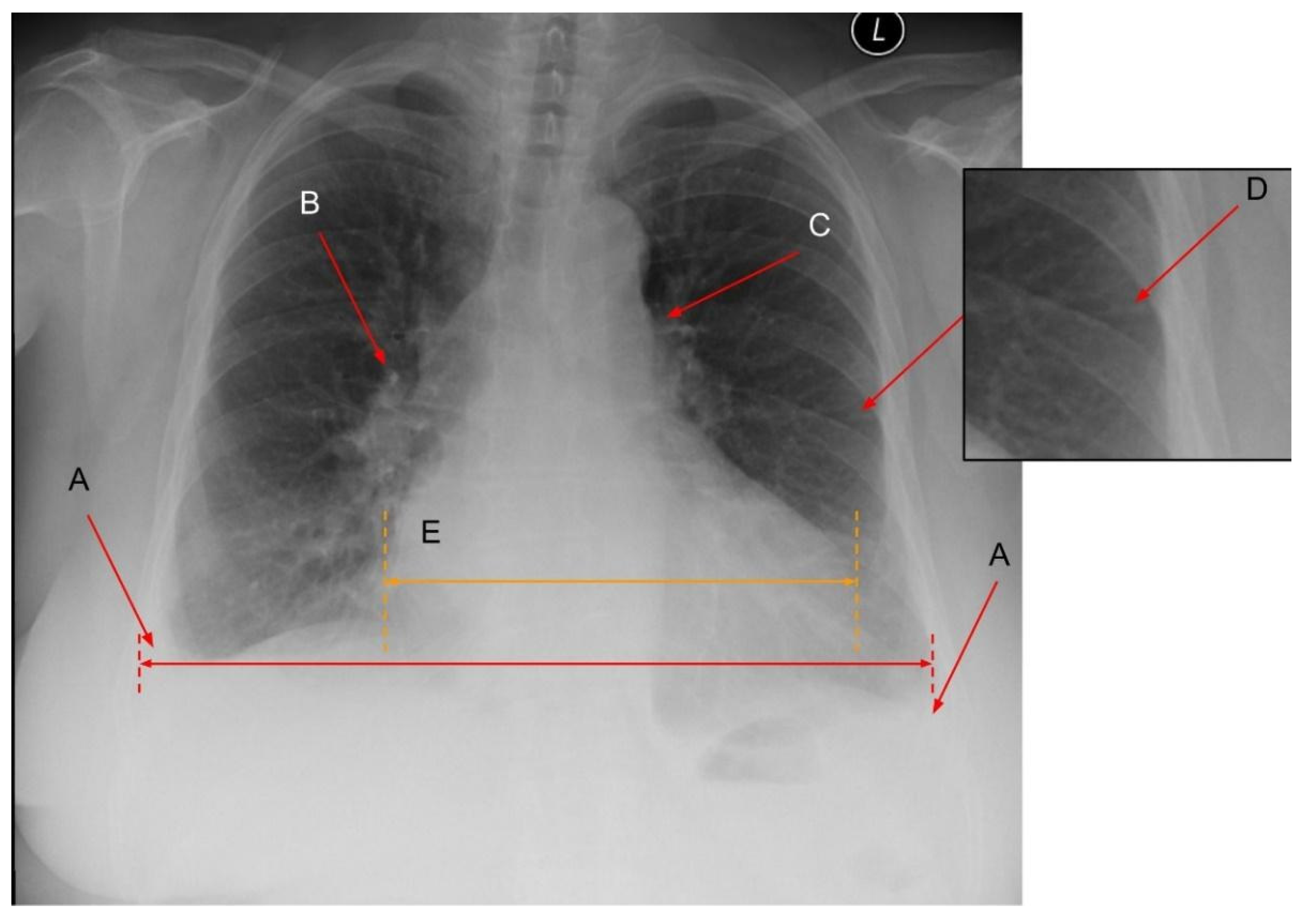
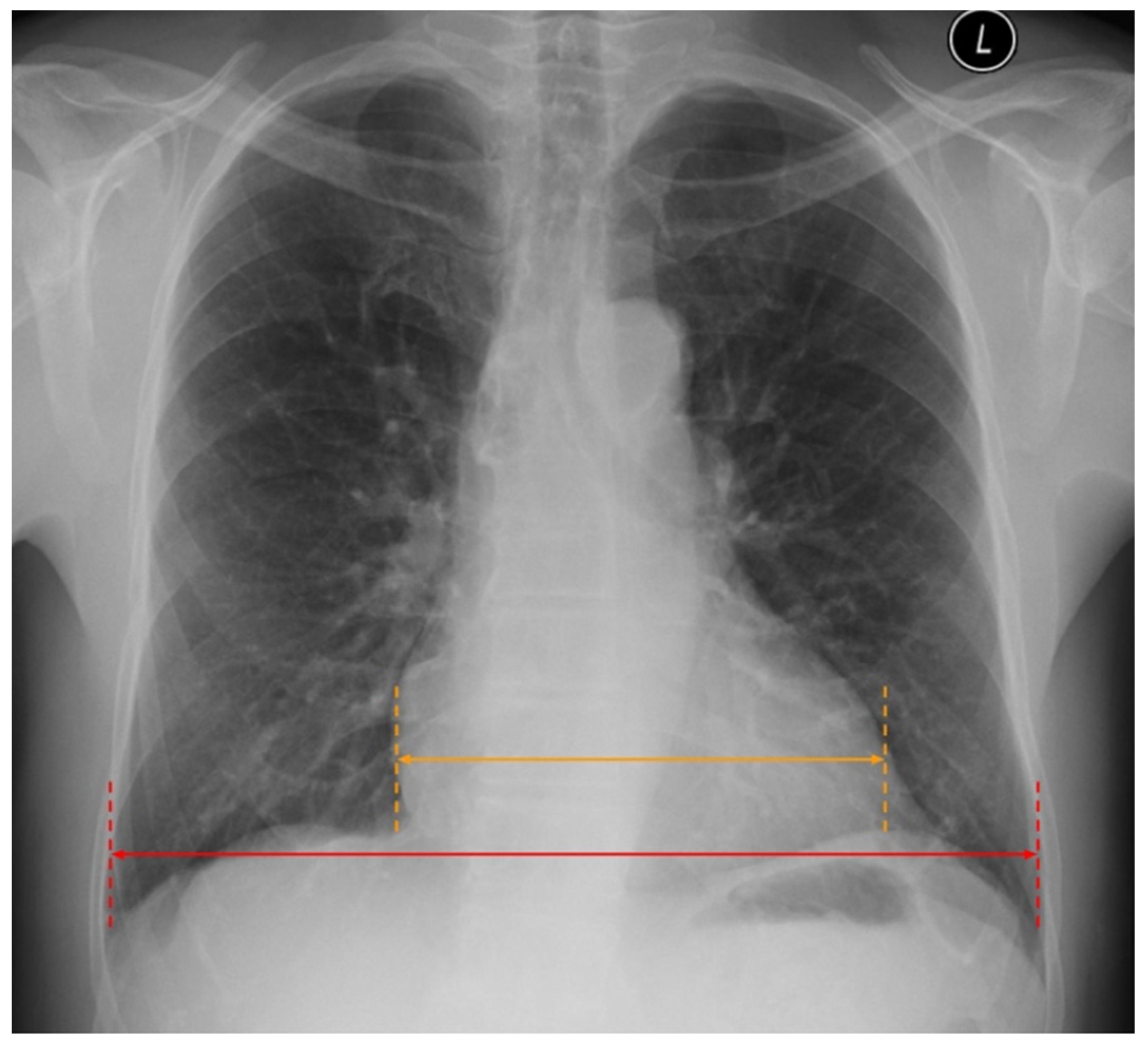
2.1.1. Phase 1—Redistribution in the Lung Vasculature
2.1.2. Phase 2—Interstitial Oedema
2.1.3. Phase 3—Alveolar Oedema
2.1.4. Phase 3—Pleural and/or Pericardial Effusion
2.2. Cardiac Abnormalities Related to HF in CXR
3. Lung Ultrasound (LUS)
3.1. B-Lines
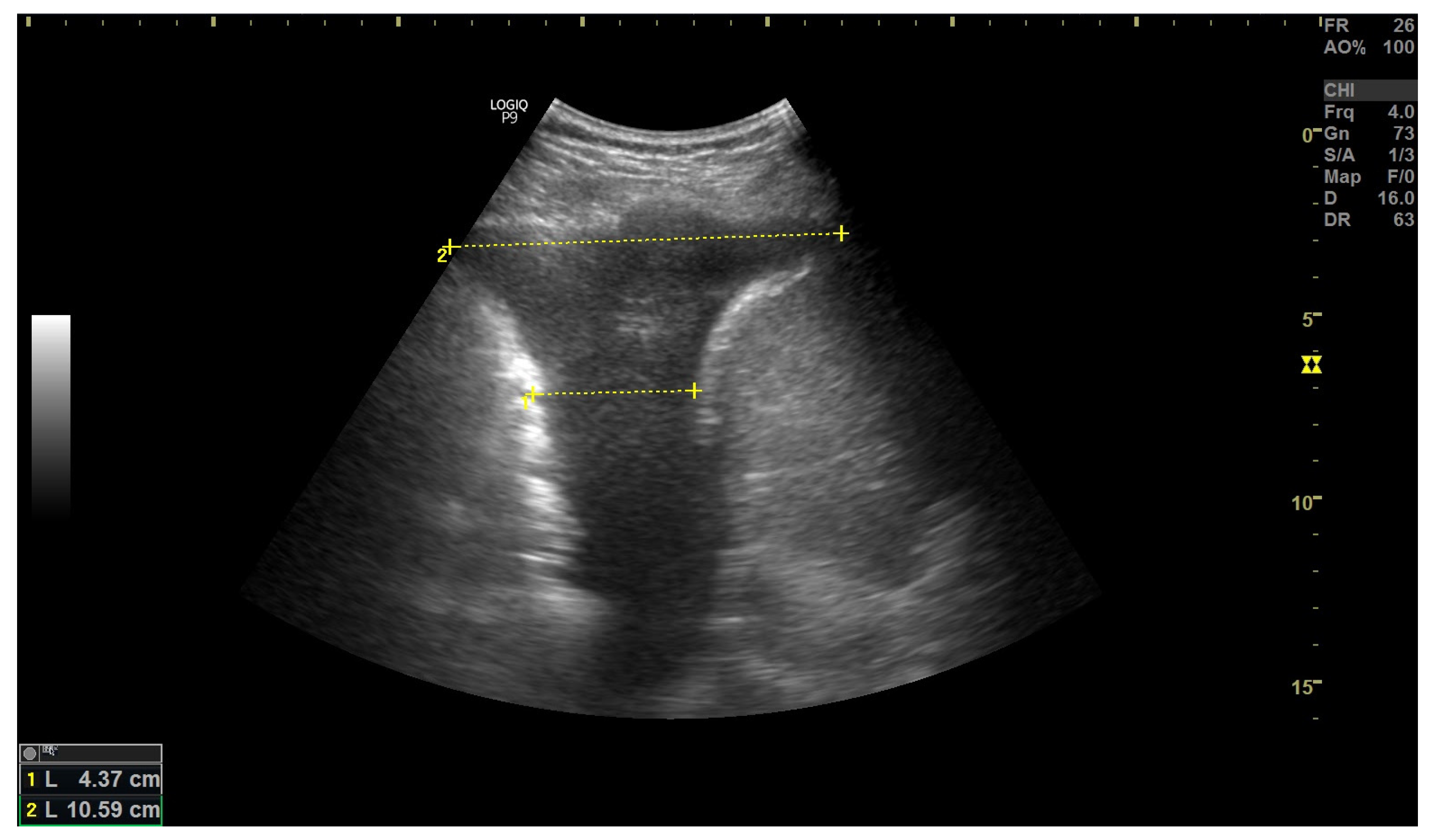
3.2. Inferior Vena Cava Measurement
3.3. Pleural Effusion
4. Chest CT
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHF | Acute heart failure |
| BNP | B-type natriuretic peptide |
| CHF | Chronic heart failure |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTR | Cardiac thoracic ratio |
| CXR | Chest X-ray |
| ECHO | Echocardiography |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| EVLW | Extravascular lung water |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HFmrEF | Heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction |
| HFpEF | Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFrEF | Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| LUS | Lung ultrasound |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| NSTEMI | Non-ST elevated myocardial infarction |
| STEMI | ST elevated myocardial infarction |
References
- Groenewegen, A.; Rutten, F.H.; Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Epidemiology of Heart Failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaeian, B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and Aetiology of Heart Failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.-P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the Special Contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, K.A.A.; Velazquez, E.J. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Time for a Reset. JAMA 2020, 324, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajouli, S.; Ludhwani, D. Heart Failure and Ejection Fraction. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhya, B.; Kitzman, D.W. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: New Approaches to Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar]
- Hindawi Lungs in Heart Failure. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/PM/2012/952741/ (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Speets, A.M.; van der Graaf, Y.; Hoes, A.W.; Kalmijn, S.; Sachs, A.P.; Rutten, M.J.; Gratama, J.W.C.; Montauban van Swijndregt, A.D.; Mali, W.P. Chest Radiography in General Practice: Indications, Diagnostic Yield and Consequences for Patient Management. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2006, 56, 574–578. [Google Scholar]
- Speets, A.M. Chest Radiography and Abdominal Ultrasound in General Practice. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- King, M.; Kingery, J.; Casey, B. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Heart Failure. Am. Fam. Physician 2012, 85, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.; Pellicori, P.; Dobbs, K.; Bulemfu, J.; Sokoreli, I.; Urbinati, A.; Brown, O.; Sze, S.; Rigby, A.S.; Kazmi, S.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Chest X-ray in Patients Hospitalised for Heart Failure. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, P.; Javaloyes, P.; Masip, J.; Gil, V.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Martín-Sánchez, F.J.; Jacob, J.; Garrido, J.M.; Herrera-Mateo, S.; López Díez, M.P.; et al. Prognostic value of chest radiographs in patients with acute heart failure: The Radiology in Acute Heart Failure (RAD-ICA) study. Emergencias 2019, 31, 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kostura, M.; Smalley, C.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. Right Heart Failure: A Narrative Review for Emergency Clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 58, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigo, M.; Huber, L.C.; Winnik, S.; Mikulicic, F.; Guidetti, F.; Frank, M.; Flammer, A.J.; Ruschitzka, F. Right Ventricular Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Card Fail Rev 2019, 5, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroft, L.J.M.; van der Velden, L.; Girón, I.H.; Roelofs, J.J.H.; de Roos, A.; Geleijns, J. Added Value of Ultra-Low-Dose Computed Tomography, Dose Equivalent to Chest X-ray Radiography, for Diagnosing Chest Pathology. J. Thorac. Imaging 2019, 34, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mant, J.; Doust, J.; Roalfe, A.; Barton, P.; Cowie, M.R.; Glasziou, P.; Mant, D.; McManus, R.J.; Holder, R.; Deeks, J.; et al. Systematic Review and Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Diagnosis of Heart Failure, with Modelling of Implications of Different Diagnostic Strategies in Primary Care. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13, 1–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kee, K.; Naughton, M.T. Heart Failure and the Lung. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maw, A.M.; Hassanin, A.; Ho, P.M.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Moss, A.; Juarez-Colunga, E.; Soni, N.J.; Miglioranza, M.H.; Platz, E.; DeSanto, K.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasonography and Chest Radiography in Adults With Symptoms Suggestive of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2019, 2, e190703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.; Jairam, M.P.; Chow, R.; Chiu, N.; Shen, M.; Alhassan, A.; Lo, C.-H.; Chen, A.; Kennel, P.J.; Poterucha, T.J.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasonography Versus Chest Radiography in Adults With Symptoms of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 174, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, L. Effectiveness of Chest Radiography, Lung Ultrasound and Thoracic Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioncel, O.; Ambrosy, A.P.; Bubenek, S.; Filipescu, D.; Vinereanu, D.; Petris, A.; Christodorescu, R.; Macarie, C.; Gheorghiade, M.; Collins, S.P. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and in-Hospital Management of Pulmonary Edema. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 17, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvey, M.; Allen, G. Managing Acute Pulmonary Oedema. Aust. Prescr. 2017, 40, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, B. Vascular Pedicle. Available online: https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-10064 (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Milne, E.N.; Pistolesi, M.; Miniati, M.; Giuntini, C. The Vascular Pedicle of the Heart and the Vena Azygos. Part I: The Normal Subject. Radiology 1984, 152, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shi, R.; Mahler, S.; Gaspard, J.; Gorchynski, J.; D’Etienne, J.; Arnold, T. Vascular Pedicle Width on Chest Radiograph as a Measure of Volume Overload: Meta-Analysis. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 12, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barile, M. Pulmonary Edema: A Pictorial Review of Imaging Manifestations and Current Understanding of Mechanisms of Disease. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2020, 7, 100274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Lenke, N.; Rudez, J.; Staub, D.; Laule-Kilian, K.; Klima, T.; Perruchoud, A.P.; Mueller, C. Use of Chest Radiography in the Emergency Diagnosis of Acute Congestive Heart Failure. Heart 2006, 92, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kissane, J.; Neutze, J.A.; Singh, H. (Eds.) Radiology Fundamentals: Introduction to Imaging & Technology, 6th ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9783030221720. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, B. Septal Lines in Lung. Available online: https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-1552 (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Koga, T.; Fujimoto, K. Images in Clinical Medicine. Kerley’s A, B, and C Lines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, H. Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gluecker, T.; Capasso, P.; Schnyder, P.; Gudinchet, F.; Schaller, M.-D.; Revelly, J.-P.; Chiolero, R.; Vock, P.; Wicky, S. Clinical and Radiologic Features of Pulmonary Edema. RadioGraphics 1999, 19, 1507–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.P.; Lindsell, C.J.; Storrow, A.B.; Abraham, W.T.; ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee, Investigators and Study Group. Prevalence of Negative Chest Radiography Results in the Emergency Department Patient with Decompensated Heart Failure. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2006, 47, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczyński, P.; Górska, K.; Konopka, D.; Al-Haj, D.; Filipiak, K.J.; Krenke, R. Significance of Congestive Heart Failure as a Cause of Pleural Effusion: Pilot Data from a Large Multidisciplinary Teaching Hospital. Cardiol. J. 2020, 27, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Rull, J.L.; Bielsa, S.; Conde-Martel, A.; Aramburu-Bodas, O.; Llàcer, P.; Quesada, M.A.; Suárez-Pedreira, I.; Manzano, L.; Barquero, M.M.-P.; Porcel, J.M.; et al. Pleural Effusions in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Prevalence and Prognostic Implications. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 52, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.M. Pleural Effusions from Congestive Heart Failure. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H. Pericardial and Pleural Effusions in Decompensated Chronic Heart Failure. Am. Heart J. 2000, 139, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-B.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, D.-E.; Cui, H.-Y.; Qin, M.; Huang, C.-X. Prognosis Investigation in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Pericardial Effusion. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, G.M.; Keller, P.; Schmid, F.; Wolfrum, M.; Osranek, M.; Falk, C.; Noll, G.; Enseleit, F.; Reinthaler, M.; Meier, P.; et al. Haemodynamically Irrelevant Pericardial Effusion Is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Filippo, O.; Gatti, P.; Rettegno, S.; Iannaccone, M.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Lazaros, G.; Brucato, A.; Tousoulis, D.; Adler, Y.; Imazio, M. Is Pericardial Effusion a Negative Prognostic Marker? Meta-Analysis of Outcomes of Pericardial Effusion. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 20, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrugno, L.; Bignami, E.; Orso, D.; Vargas, M.; Guadagnin, G.M.; Saglietti, F.; Servillo, G.; Volpicelli, G.; Navalesi, P.; Bove, T. Utility of Pleural Effusion Drainage in the ICU: An Updated Systematic Review and META-Analysis. J. Crit. Care 2019, 52, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, C.W.; Omland, T.; Clopton, P. Diagnostic Value of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and Chest Radiographic Findings in Patients with Acute Dyspnea. ACC Curr. J. Rev. 2004, 13, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Mota, T.; Morais, H.; Matias, F.; Costa, C.; Oliveira, A.G.; Ceia, F.; EPICA Investigators. The Value of the Electrocardiogram and Chest X-ray for Confirming or Refuting a Suspected Diagnosis of Heart Failure in the Community. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 807–812, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, J.L.; Ferrier, K. Is Cardiomegaly on Chest Radiograph Representative of True Cardiomegaly: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study Comparing Cardiac Size on Chest Radiograph to That on Echocardiography. N. Z. Med. J. 2017, 130, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Naing, P.; Forrester, D.; Kangaharan, N.; Muthumala, A.; Mon Myint, S.; Playford, D. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Growing Global Epidemic. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 48, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A. BLUE-Protocol and FALLS-Protocol: Two Applications of Lung Ultrasound in the Critically Ill. Chest 2015, 147, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Mathis, G.; Blaivas, M.; Volpicelli, G.; Seibel, A.; Wastl, D.; Atkinson, N.S.S.; Cui, X.-W.; Fan, M.; Yi, D. Lung B-Line Artefacts and Their Use. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muniz, R.T.; Mesquita, E.T.; Junior, C.V.S.; de Andrade Martins, W. Pulmonary Ultrasound in Patients with Heart Failure—Systematic Review. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2018, 110, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, L. Prognosis in Heart Failure: Look at the Lungs. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International Evidence-Based Recommendations for Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picano, E.; Scali, M.C.; Ciampi, Q.; Lichtenstein, D. Lung Ultrasound for the Cardiologist. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiro, S.; Porot, G.; Rossignol, P.; Ambrosio, G.; Carluccio, E.; Tritto, I.; Huttin, O.; Lemoine, S.; Sadoul, N.; Donal, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of Pulmonary Congestion Assessed by Lung Ultrasound Imaging during Heart Failure Hospitalisation: A Two-Centre Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corradi, F.; Brusasco, C.; Vezzani, A.; Santori, G.; Manca, T.; Ball, L.; Nicolini, F.; Gherli, T.; Brusasco, V. Computer-Aided Quantitative Ultrasonography for Detection of Pulmonary Edema in Mechanically Ventilated Cardiac Surgery Patients. Chest 2016, 150, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, M.; Alehagen, U.; Johansson, P. Imaging Congestion with a Pocket Ultrasound Device: Prognostic Implications in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2015, 21, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Bruni, A.; Morettini, G.; Vitali, L.; Brunelli, F.; Tinarelli, F.; Simonte, R.; Rossi, E.; Bellucci, M.; De Girolamo, G.; et al. Lung Ultrasound to Evaluate Aeration Changes in Response to Recruitment Maneuver and Prone Positioning in Intubated Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia: Preliminary Study. Ultrasound J. 2023, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzini, C.; Di Dio Perna, M.; Pesce, G.; Garbin, U.; Fratta Pasini, A.M.; Ticinesi, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Meschi, T.; Casadei, A.; Soresi, M.; et al. Lung Ultrasound in Internal Medicine Efficiently Drives the Management of Patients with Heart Failure and Speeds up the Discharge Time. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartini, S.; Frizzi, J.; Borselli, M.; Sarcoli, E.; Granai, C.; Gialli, V.; Cevenini, G.; Guazzi, G.; Bruni, F.; Gonnelli, S.; et al. Which Method Is Best for an Early Accurate Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure? Comparison between Lung Ultrasound, Chest X-ray and NT pro-BNP Performance: A Prospective Study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhi, G.; Zhang, L.; Huang, D.; Shen, D.; Zhang, M. The Application of Lung Ultrasound in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure in Heart Failure with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction. Echocardiography 2017, 34, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, K.H.; Merz, A.A.; Lewis, E.F.; Claggett, B.L.; Crousillat, D.R.; Lau, E.S.; Silverman, M.B.; Peck, J.; Rivero, J.; Cheng, S.; et al. Pulmonary Congestion by Lung Ultrasound in Ambulatory Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction and Hypertension. J. Card. Fail. 2018, 24, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, M.; Conangla, L.; Lupón, J.; de Antonio, M.; Moliner, P.; Santiago-Vacas, E.; Codina, P.; Zamora, E.; Cediel, G.; González, B.; et al. Prognostic Value of Lung Ultrasound in Chronic Stable Ambulatory Heart Failure Patients. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2021, 74, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanoğlu, A.; Çelebi Yamanoğlu, N.G.; Parlak, İ.; Pınar, P.; Tosun, A.; Erkuran, B.; Akgür, A.; Satılmış Siliv, N. The Role of Inferior Vena Cava Diameter in the Differential Diagnosis of Dyspneic Patients; Best Sonographic Measurement Method? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blehar, D.J.; Dickman, E.; Gaspari, R. Identification of Congestive Heart Failure via Respiratory Variation of Inferior Vena Cava Diameter. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, K.; Madeen, K.; Nakayama, T.; Tsudo, H.; Kuroda, T.; Abe, T. Rapid Evaluation by Lung-Cardiac-Inferior Vena Cava (LCI) Integrated Ultrasound for Differentiating Heart Failure from Pulmonary Disease as the Cause of Acute Dyspnea in the Emergency Setting. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2012, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Mathis, G.; Cui, X.-W.; Ignee, A.; Hocke, M.; Hirche, T.O. Ultrasound of the Pleurae and Lungs. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.; Rizk, R.; Essam, H.; Abouelnour, A. Validation of Equations for Pleural Effusion Volume Estimation by Ultrasonography. J. Ultrasound 2017, 20, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, C.B.; Clive, A.; Hallifax, R.; Pietersen, P.I.; Asciak, R.; Davidsen, J.R.; Bhatnagar, R.; Bedawi, E.O.; Jacobsen, N.; Coleman, C.; et al. European Respiratory Society Statement on Thoracic Ultrasound. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Vetrugno, L.; Longhini, F. Lung Ultrasound Monitoring: Impact on Economics and Outcomes. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimberg, A.; Shigueoka, D.C.; Atallah, A.N.; Ajzen, S.; Iared, W. Diagnostic Accuracy of Sonography for Pleural Effusion: Systematic Review. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2010, 128, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gargani, L. Lung Ultrasound: A New Tool for the Cardiologist. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2011, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewin, S.; Goldberg, L.; Dec, G.W. The Spectrum of Pulmonary Abnormalities on Computed Chest Tomographic Imaging in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scillia, P.; Delcroix, M.; Lejeune, P.; Mélot, C.; Struyven, J.; Naeije, R.; Gevenois, P.A. Hydrostatic Pulmonary Edema: Evaluation with Thin-Section CT in Dogs. Radiology 1999, 211, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.M.C.; Marchiori, E.; Rodrigues, R.; Gasparetto, E.; Souza, A.S., Jr.; Escuissato, D.; Nobre, L.F.; Zanetti, G.; de Araujo Neto, C.; Irion, K. Hydrostatic Pulmonary Edema: High-Resolution Computed Tomography Aspects. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2006, 32, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngom, A.; Dumont, P.; Diot, P.; Lemarié, E. Benign Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy in Congestive Heart Failure. Chest 2001, 119, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scillia, P.; Bankier, A.A.; Gevenois, P.A. Computed Tomography Assessment of Lung Structure and Function in Pulmonary Edema. Crit. Rev. Comput. Tomogr. 2004, 45, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayem, H.A.; Gohari, A.; Endo, Y.; Shwarzberg, H.; Afari, A.; Waite, S.A. Chest Computed Tomography Features Predictive of Elevated B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Independent of Renal Function: Diagnostic Implications for Evaluation of Congestive Heart Failure. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2013, 37, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, D.M.; Bankier, A.A.; MacMahon, H.; McLoud, T.C.; Müller, N.L.; Remy, J. Fleischner Society: Glossary of Terms for Thoracic Imaging. Radiology 2008, 246, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, A.; Schiebler, M.L.; Lynch, D.A.; Hatabu, H. Interstitial Lung Abnormalities: State of the Art. Radiology 2021, 301, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambataro, G.; Ferrara, C.A.; Torrisi, S.E.; Spadaro, C.; Vignigni, G.; Vancheri, A.; del Papa, N.; Orlandi, M.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L.; et al. “Usual” Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features: A Prospective Study on a Cohort of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staub, N.C.; Nagano, H.; Pearce, M.L. Pulmonary Edema in Dogs, Especially the Sequence of Fluid Accumulation in Lungs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1967, 22, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Miyagi, Y.; Tachi, K.; Sakabe, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Hishida, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Sasaki, F.; Koga, S. Measurement of Lung Density in Congestive Heart Failure by Computed Tomography. Jpn. Heart J. 1984, 25, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erly, W.K.; Borders, R.J.; Outwater, E.K.; Zaetta, J.M.; Borders, G.T. Location, Size, and Distribution of Mediastinal Lymph Node Enlargement in Chronic Congestive Heart Failure. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2003, 27, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabbert, V.; Canevet, G.; Baixas, C.; Galinier, M.; Deken, V.; Duhamel, A.; Otal, P.; Joffre, F.; Remy, J.; Remy-Jardin, M. Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy in Congestive Heart Failure: A Sequential CT Evaluation with Clinical and Echocardiographic Correlations. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 881–889. [Google Scholar]
- Sintou, A.; Mansfield, C.; Iacob, A.; Chowdhury, R.A.; Narodden, S.; Rothery, S.M.; Podovei, R.; Sanchez-Alonso, J.L.; Ferraro, E.; Swiatlowska, P.; et al. Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy, Class-Switched Auto-Antibodies and Myocardial Immune-Complexes During Heart Failure in Rodents and Humans. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





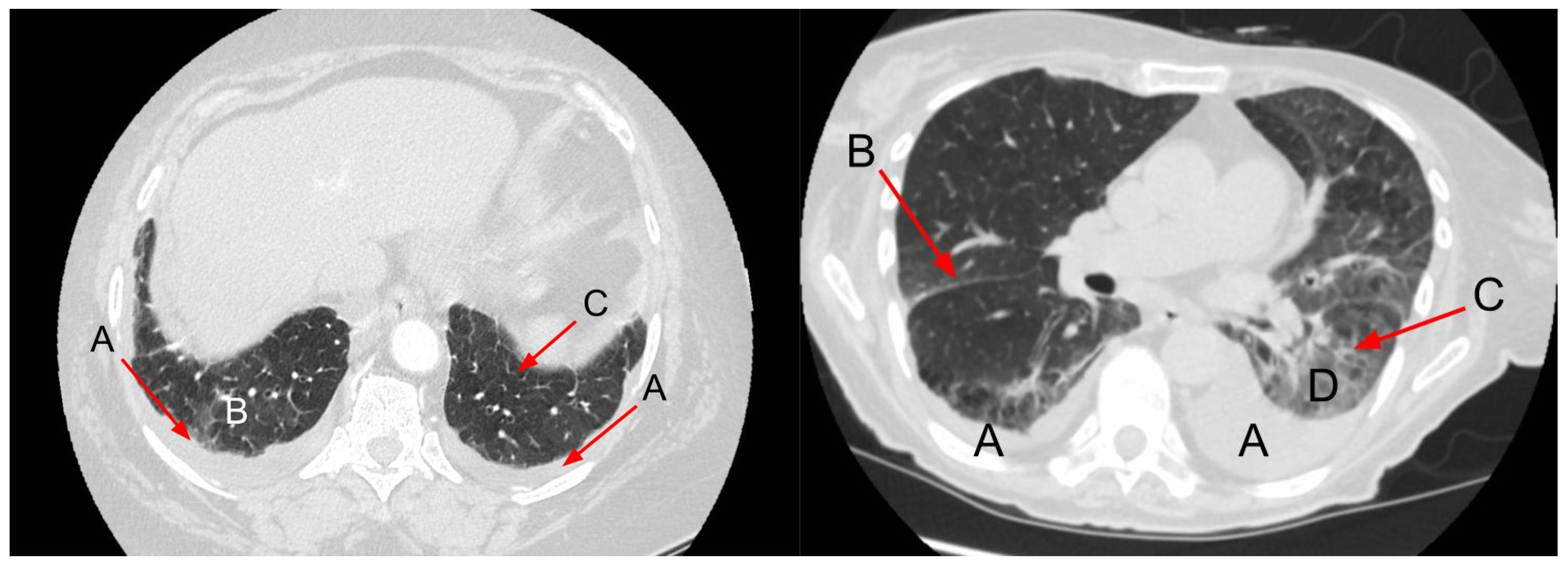



| HF-Related | ILD-Related |
|---|---|
| Interlobar septal thickening (smooth) | Interlobar septal thickening (smooth or beaded) |
| Mediastinal lymphadenopathy | Mediastinal lymphadenopathy |
| Diffuse heterogeneous increase in lung density | Mosaic attenuation |
| Ground-glass opacities | Ground-glass opacities |
| Consolidation | Consolidation |
| Reticular/reticulonodular pattern Tree-in-bud sign Subpleural curvilinear line Honeycombing Traction bronchiectasis, bronchiolectasis |
| CXR | LUS | CT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main findings | Redistribution | - Cephalisation - Broaden vascular pedicle | - No distinctive changes | - Enlarged vascular diameter - Cephalisation (within lobes) |
| Interstitial pulmonary oedema | - Distorted hilar image - Peribronchovascular cuffing - Kerley lines | - The presence of >2 B-lines in one intercostal space - Homogeneous, bilateral, gravity-dependent distribution | - Interlobular septal thickening - Peribronchovascular thickening - Mediastinal lymphadenopathy | |
| Alveolar pulmonary oedema | - Angel wing/bat wing/butterfly pattern | - Increasing number of B-lines - Interstitial alveolar syndrome (sonographic “white lung”) | - Increased density - Ground-glass opacity - Consolidation | |
| Pleural effusion | - Detectable > 200 mL (PA) and > 100 mL (lateral) - Poor accuracy in determining the fluid character | - High sensitivity—detection > 50 mL (the most sensitive imaging) - Additional information about the fluid character | - High sensitivity - Limited accuracy in determining fluid character | |
| Advantages | - Moderate accessibility - Inexpensive | - High accessibility (quick bedside examination) - Inexpensive - Higher sensitivity than CXR - Following the actual clinical response to therapy - No radiation dose - Easily repeatable | - Differential diagnosis - High sensitivity - The highest resolution | |
| Disadvantages | - Limited sensitivity - Gravity-dependent - High interobserver variability - Minor radiation exposure (PA 0.1 mSv;) | - Limited surface/visualisation - Patient-dependent (low- quality study in the obese) - Training required | - Scarce availability - Expensive - High radiation risk (LD-CT 1–2 mSv; standard CT 7–8 mSv) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siwik, D.; Apanasiewicz, W.; Żukowska, M.; Jaczewski, G.; Dąbrowska, M. Diagnosing Lung Abnormalities Related to Heart Failure in Chest Radiogram, Lung Ultrasound and Thoracic Computed Tomography. Adv. Respir. Med. 2023, 91, 103-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020010
Siwik D, Apanasiewicz W, Żukowska M, Jaczewski G, Dąbrowska M. Diagnosing Lung Abnormalities Related to Heart Failure in Chest Radiogram, Lung Ultrasound and Thoracic Computed Tomography. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2023; 91(2):103-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiwik, Dominika, Wojciech Apanasiewicz, Małgorzata Żukowska, Grzegorz Jaczewski, and Marta Dąbrowska. 2023. "Diagnosing Lung Abnormalities Related to Heart Failure in Chest Radiogram, Lung Ultrasound and Thoracic Computed Tomography" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 91, no. 2: 103-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020010
APA StyleSiwik, D., Apanasiewicz, W., Żukowska, M., Jaczewski, G., & Dąbrowska, M. (2023). Diagnosing Lung Abnormalities Related to Heart Failure in Chest Radiogram, Lung Ultrasound and Thoracic Computed Tomography. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 91(2), 103-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020010






