Molecular Pathophysiology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Clinical Update from a Basic Research Perspective
Abstract
:Highlights
- We explain the mechanisms involved in CTEPH development, including fibrotic thrombus formation, pulmonary vascular remodeling, and abnormal angiogenesis, which lead to elevated pulmonary vascular resistance and right heart failure.
- Improved diagnostic tools, biomarker identification, and therapeutic strategies are still needed to enhance early detection and management of CTEPH, ultimately aiming to reduce diagnostic delay and improve patient outcomes.
- A better understanding of CTEPH progression, including both proximal and distal obstruction of pulmonary arteries associated with the remodeling of pulmonary arteries.
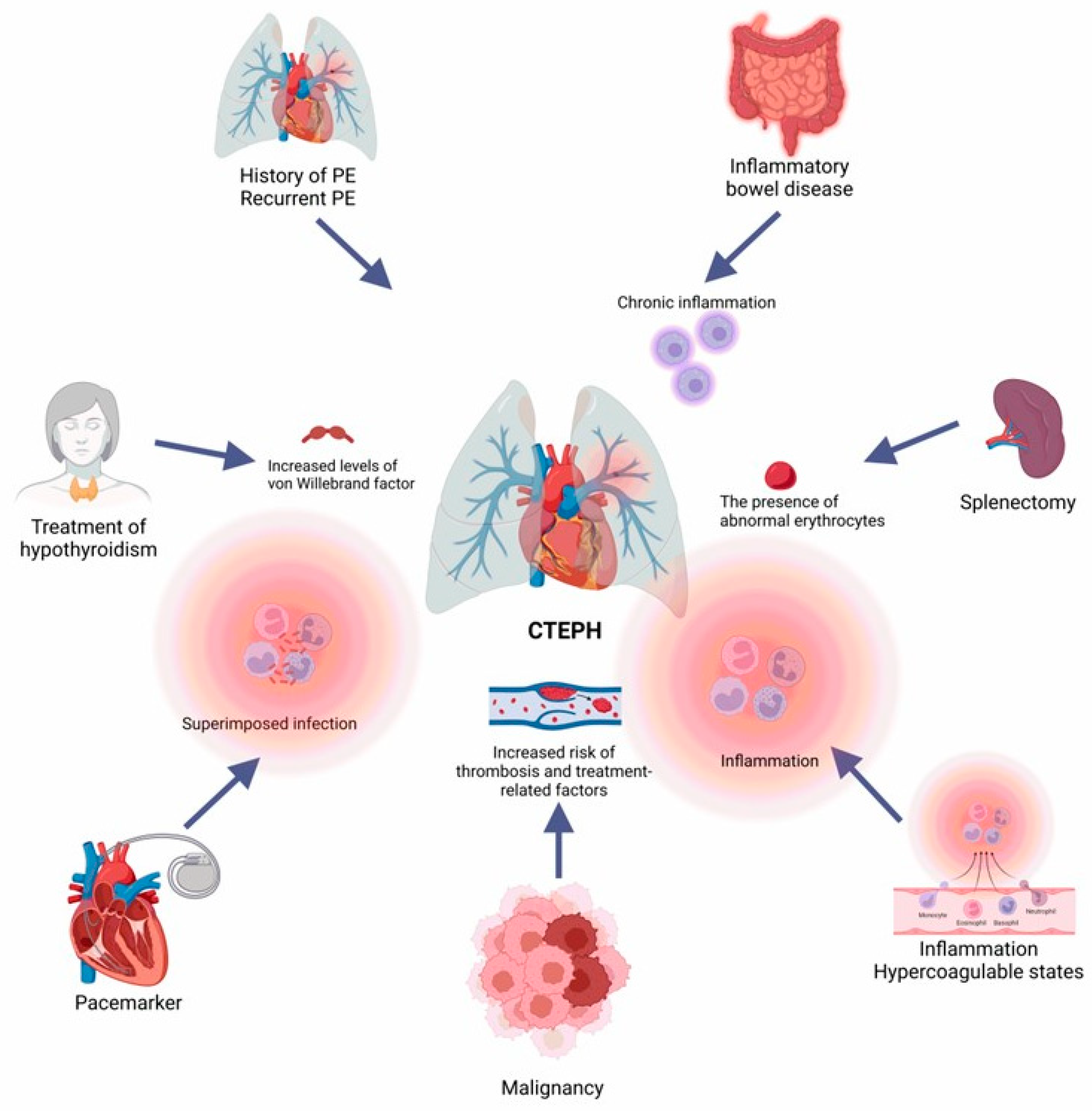
- This narrative review summarizes the risk factors predicting CTEPH, including thrombotic history, hemostatic disorders, and certain medical conditions that help identify CTEPH progression and detection.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Risk Factors and Clinical Presentation
4. CTEPH Diagnosis
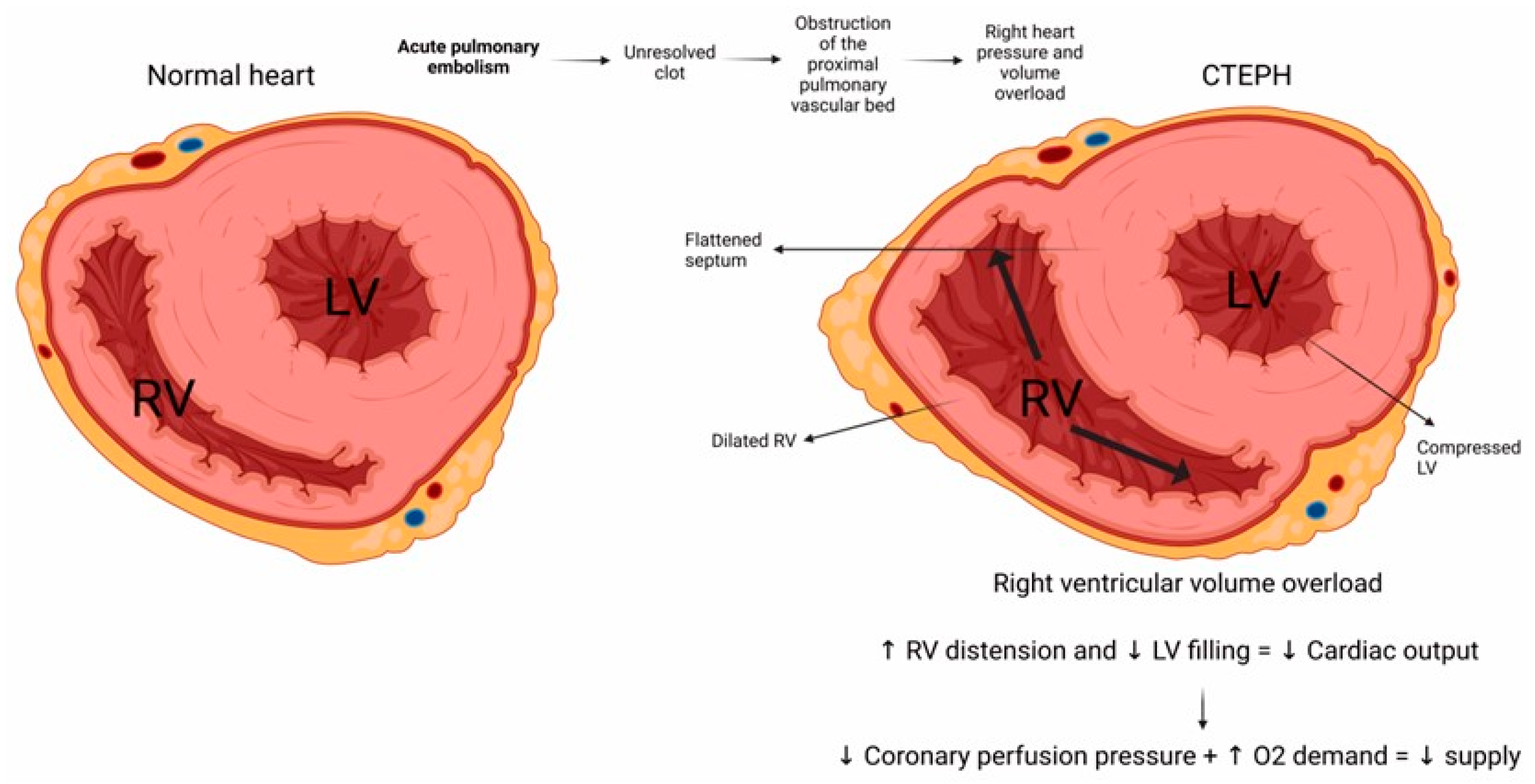
5. CTEPH Pathophysiology
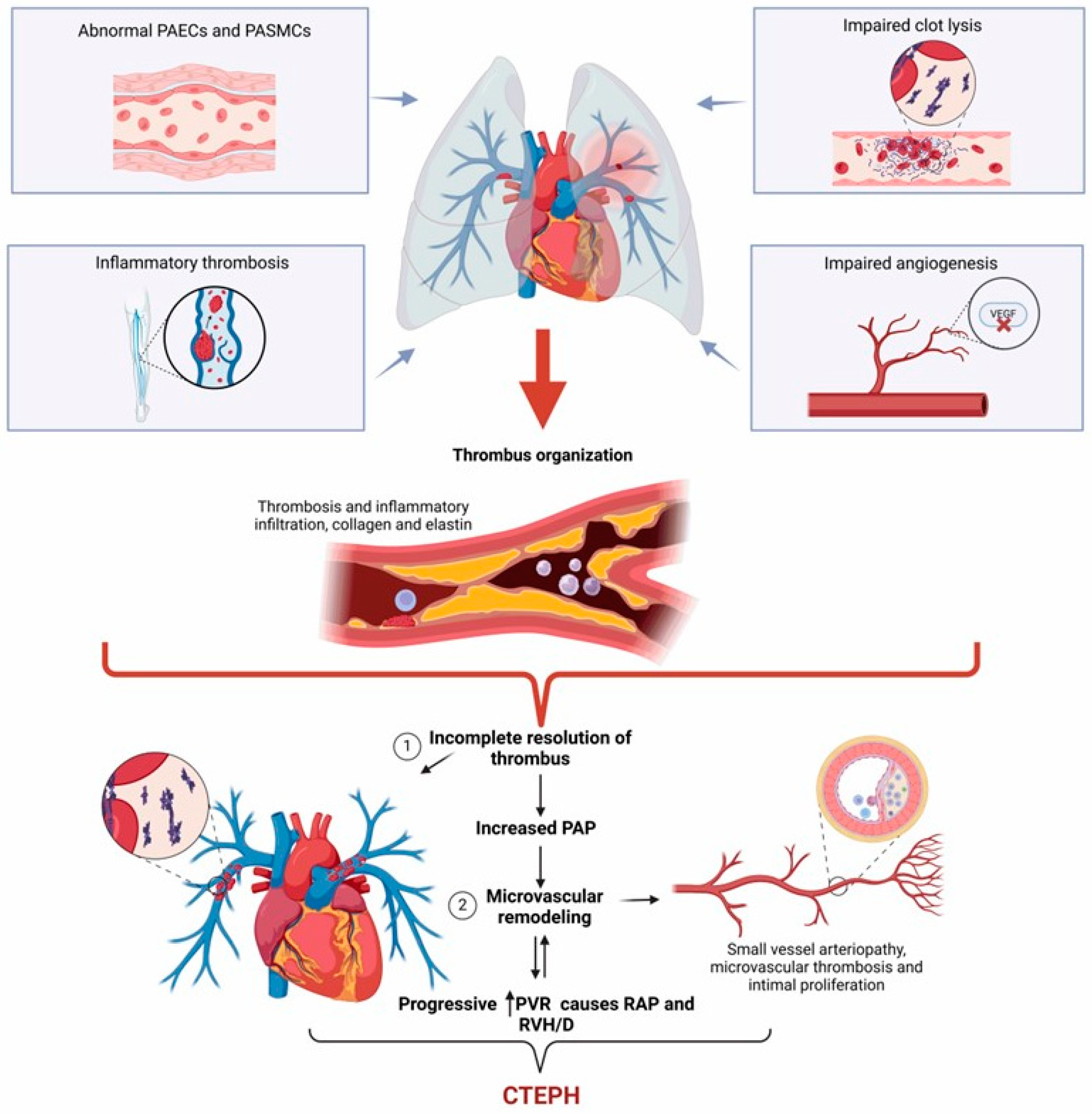
6. Molecular Mechanisms in CTEPH
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jimenez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Hermosillo, L.M.; Cueto-Robledo, G.; Navarro-Vergara, D.I.; Garcia-Cesar, M.; Torres-Rojas, M.B.; Graniel-Palafox, L.E.; Castro-Escalante, K.Y.; Castro-Diaz, A.M. Post-pulmonary embolism syndrome: A reminder for clinicians. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 2024, 32, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Delcroix, M.; Bogaard, H.J. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension from the perspective of patients with pulmonary embolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcroix, M.; Kerr, K.; Fedullo, P. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13 (Suppl. 3), S201–S206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ende-Verhaar, Y.M.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Delcroix, M.; Pruszczyk, P.; Mairuhu, A.T.; Huisman, M.V.; Klok, F.A. Incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism: A contemporary view of the published literature. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullin, C.J.; Klinger, J.R. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Torbicki, A.; Dorfmuller, P.; Kim, N. The pathophysiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfmuller, P.; Gunther, S.; Ghigna, M.R.; Thomas de Montpreville, V.; Boulate, D.; Paul, J.F.; Jais, X.; Decante, B.; Simonneau, G.; Dartevelle, P.; et al. Microvascular disease in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A role for pulmonary veins and systemic vasculature. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hermosillo, L.M.; Cueto-Robledo, G.; Roldan-Valadez, E.; Graniel-Palafox, L.E.; Garcia-Cesar, M.; Torres-Rojas, M.B.; Romero-Martinez, B.; Castro-Escalante, K.Y. Right Heart Catheterization (RHC): A Comprehensive Review of Provocation Tests and Hepatic Hemodynamics in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension (PH). Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egermayer, P.; Peacock, A.J. Is pulmonary embolism a common cause of chronic pulmonary hypertension? Limitations of the embolic hypothesis. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; Lang, I.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Jansa, P.; D’Armini, A.M.; Snijder, R.; Bresser, P.; Torbicki, A.; Mellemkjaer, S.; Lewczuk, J.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Patients With Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Results From an International Prospective Registry. Circulation 2016, 133, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepke-Zaba, J.; Delcroix, M.; Lang, I.; Mayer, E.; Jansa, P.; Ambroz, D.; Treacy, C.; D’Armini, A.M.; Morsolini, M.; Snijder, R.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): Results from an international prospective registry. Circulation 2011, 124, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval Zarate, J.; Jerjes-Sanchez, C.; Ramirez-Rivera, A.; Zamudio, T.P.; Gutierrez-Fajardo, P.; Elizalde Gonzalez, J.; Leon, M.S.; Gamez, M.B.; Abril, F.M.; Michel, R.P.; et al. Mexican registry of pulmonary hypertension: REMEHIP. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2017, 87, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarian, R.; Wartski, M.; Collignon, M.A.; Parent, F.; Herve, P.; Sors, H.; Simonneau, G. Lung perfusion scans and hemodynamics in acute and chronic pulmonary embolism. J. Nucl. Med. 1997, 38, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Yung, G.L.; Marsh, J.J.; Konopka, R.G.; Pedersen, C.A.; Chiles, P.G.; Morris, T.A.; Channick, R.N. Pulmonary vascular remodeling distal to pulmonary artery ligation is accompanied by upregulation of endothelin receptors and nitric oxide synthase. Exp. Lung Res. 2000, 26, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, R.S.; Remillard, C.V.; Agange, N.; Auger, W.R.; Thistlethwaite, P.A.; Yuan, J.X. Molecular biology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 18, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Deng, M.; Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Tao, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhen, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M. The alterations in molecular markers and signaling pathways in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, a study with transcriptome sequencing and bioinformatic analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 961305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, G.; Delahousse, B.; Lacut, K.; Malaviolle, V.; Regina, S.; Blouch, M.T.; Couturaud, F.; Mottier, D.; Oger, E.; Gruel, Y.; et al. Fibrinogen Aalpha-Thr312Ala and factor XIII-A Val34Leu polymorphisms in idiopathic venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2007, 121, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.A.; Marsh, J.J.; Chiles, P.G.; Magana, M.M.; Liang, N.C.; Soler, X.; Desantis, D.J.; Ngo, D.; Woods, V.L., Jr. High prevalence of dysfibrinogenemia among patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Blood 2009, 114, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.M.; Marsh, J.J.; Olman, M.A.; Moser, K.M.; Loskutoff, D.J.; Schleef, R.R. Expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in chronic pulmonary thromboemboli. Circulation 1994, 89, 2715–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermair, J.; Redwan, B.; Alias, S.; Jabkowski, J.; Panzenboeck, A.; Kellermair, L.; Winter, M.P.; Weltermann, A.; Lang, I.M. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 deficiency misguides venous thrombus resolution. Blood 2013, 122, 3376–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alias, S.; Redwan, B.; Panzenboeck, A.; Winter, M.P.; Schubert, U.; Voswinckel, R.; Frey, M.K.; Jakowitsch, J.; Alimohammadi, A.; Hobohm, L.; et al. Defective angiogenesis delays thrombus resolution: A potential pathogenetic mechanism underlying chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochenek, M.L.; Saar, K.; Nazari-Jahantigh, M.; Gogiraju, R.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; Munzel, T.; Mayer, E.; Fink, L.; Schober, A.; Hubner, N.; et al. Endothelial Overexpression of TGF-beta-Induced Protein Impairs Venous Thrombus Resolution: Possible Role in CTEPH. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, J.H.; Dziejman, M.; Liu, M.T.; Leung, J.H.; Lane, T.E.; Luster, A.D. IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 (IP-10; CXCL10)-deficient mice reveal a role for IP-10 in effector T cell generation and trafficking. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynants, M.; Vengethasamy, L.; Ronisz, A.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M.; Quarck, R. NF-kappaB pathway is involved in CRP-induced effects on pulmonary arterial endothelial cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L934–L942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N. New paradigms in inflammatory signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H317–H325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, J.R.; Abman, S.H.; Gladwin, M.T. Nitric oxide deficiency and endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, M.; MacKenzie Ross, R.V.; Kuc, R.E.; Hagan, G.; Sheares, K.K.; Jenkins, D.P.; Goddard, M.; Davenport, A.P.; Pepke-Zaba, J. Endothelin ETA receptors predominate in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Life Sci. 2016, 159, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Z. High Frequency of Pulmonary Hypertension-Causing Gene Mutation in Chinese Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, L.; Nohe, A.; Geissendorfer, T.; Sebald, W.; Henis, Y.I.; Knaus, P. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor complexes on the surface of live cells: A new oligomerization mode for serine/threonine kinase receptors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudarakanchana, N.; Flanagan, J.A.; Chen, H.; Upton, P.D.; Machado, R.; Patel, D.; Trembath, R.C.; Morrell, N.W. Functional analysis of bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor mutations underlying primary pulmonary hypertension. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.X.; Liu, D.; Sun, M.L.; Jiang, X.; Sun, N.; Mao, Y.M.; Jing, Z.C. BMPR2 germline mutation in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Lung 2014, 192, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.C.; Borok, Z. TGF-beta-induced EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L525–L534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.; Robertson, L.; Harrison, R.; Ridout, C.; Vasudevan, P. Somatic mosaicism in ACVRL1 with transmission to several offspring affected with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164, 2121–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Guerrero-Esteo, M.; Botella, L.M.; Banville, D.; Vary, C.P.; Bernabeu, C. Endoglin regulates cytoskeletal organization through binding to ZRP-1, a member of the Lim family of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32858–32868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubrier, F.; Chung, W.K.; Machado, R.; Grunig, E.; Aldred, M.; Geraci, M.; Loyd, J.E.; Elliott, C.G.; Trembath, R.C.; Newman, J.H.; et al. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D13–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.; Huang, J.; Shah, M.; Patel, K.; Gewitz, M.; Sehgal, P.B. Disruption of endothelial-cell caveolin-1alpha/raft scaffolding during development of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2004, 110, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronstein, R.; Seebach, J.; Grossklaus, S.; Minten, C.; Engelhardt, B.; Drab, M.; Liebner, S.; Arsenijevic, Y.; Taha, A.A.; Afanasieva, T.; et al. Caveolin-1 opens endothelial cell junctions by targeting catenins. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, A.M.; Osipenko, O.N.; MacMillan, D.; McFarlane, K.M.; Tate, R.J.; Kempsill, F.E. Two-pore domain K channel, TASK-1, in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Baratella, E.; Caforio, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Wade, B.; Marrocchio, C.; Geri, P.; Pozzan, R.; Andrisano, A.G.; Cova, M.A.; et al. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: An Update. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedullo, P.F.; Auger, W.R.; Kerr, K.M.; Rubin, L.J. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullivan, S.; McCormack, C.; O’Callaghan, M.; Kevane, B.; NiAinle, F.; McCullagh, B.; Gaine, S.P. Characteristics of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in Ireland. Pulm. Circ. 2021, 11, 20458940211048703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra-Filho, M.; Mello, M.F.; Lapa, M.S.; Teixeira, R.H.; Jatene, F.B. Clinical and haemodynamic evaluation of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients scheduled for pulmonary thromboendarterectomy: Is schistosomiasis hypertension an important confounding factor? Clinics 2010, 65, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papamatheakis, D.G.; Poch, D.S.; Fernandes, T.M.; Kerr, K.M.; Kim, N.H.; Fedullo, P.F. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2155–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.M.; Pesavento, R.; Bonderman, D.; Yuan, J.X. Risk factors and basic mechanisms of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A current understanding. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, A.; Mayorga-Carlin, M.; Han, P.; Cassady, S.; John, T.; LaRocco, A.; Etezadi, V.; Jones, K.; Nagarsheth, K.; Toursavadkohi, S.; et al. Risk factors and treatment interventions associated with incomplete thrombus resolution and pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary embolism. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2024, 12, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, E.; Bucciarelli, P.; Passamonti, S.M.; Martinelli, I. Risk factors for venous and arterial thrombosis. Blood Transfus. 2011, 9, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Lang, I.M. Risk factors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2012, 21, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfarth, H.J.; Gille, J.; Sablotzki, A.; Gerlach, S.; Malcharek, M.; Gosse, A.; Gahr, R.H.; Czeslick, E. Perioperative management of patients with severe pulmonary hypertension in major orthopedic surgery: Experience-based recommendations. GMS Interdiscip. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. DGPW 2015, 4, Doc03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, R.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Incidence and risk factors of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 4751–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Xia, J.; Zhu, N.; Han, X.; Fang, L.; Chai, Y.; Niu, M.; et al. Incidence and risk factors of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in patients with diagnosis of pulmonary embolism for the first time in real world. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwing, J.M.; Vaidya, A.; Auger, W.R. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: An Update. Clin. Chest Med. 2018, 39, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrescu, D.; Sitbon, O.; Weatherald, J.; Howard, L.S. Exertional dyspnoea in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jimenez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1901647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbelen, T.; Godinas, L.; Maleux, G.; Coolen, J.; Claessen, G.; Belge, C.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Diagnosis, operability assessment and patient selection for pulmonary endarterectomy. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 11, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusov, Y.; Singh, I.; Yu, Y.R.; Chun, H.J.; Maron, B.A.; Tapson, V.F.; Lewis, M.I.; Rajagopal, S. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: The Bedside. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Delcroix, M.; Jais, X.; Madani, M.M.; Matsubara, H.; Mayer, E.; Ogo, T.; Tapson, V.F.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Jenkins, D.P. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, S.; Walker, S.; Loudon, B.L.; Gollop, N.D.; Wilson, A.M.; Lowery, C.; Frenneaux, M.P. Assessment of pulmonary artery pressure by echocardiography-A comprehensive review. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2016, 12, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alto, M.; Dimopoulos, K.; Coghlan, J.G.; Kovacs, G.; Rosenkranz, S.; Naeije, R. Right Heart Catheterization for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension: Controversies and Practical Issues. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, B.; Maggio, E.; Schirone, L.; Rocco, E.; Sarto, G.; Spadafora, L.; Bernardi, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Forte, M.; Vecchio, D.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: The diagnostic assessment. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1439402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pennec, R.; Tromeur, C.; Orione, C.; Robin, P.; Le Mao, R.; De Moreuil, C.; Jevnikar, M.; Hoffman, C.; Savale, L.; Couturaud, F.; et al. Lung Ventilation/Perfusion Scintigraphy for the Screening of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH): Which Criteria to Use? Front. Med. 2022, 9, 851935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitman, E.M.; McDermott, S. Pulmonary arteries: Imaging of pulmonary embolism and beyond. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 9, S37–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalan, D.; Delcroix, M.; Held, M. Diagnosis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.T.; Hemnes, A.R. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2016, 6, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Madani, M.M.; Mahmud, E.; Kim, N.H. Evaluation and Management of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest 2023, 164, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, M.; Yaylali, Y.T.; Yildizeli, B.; Tas, S. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Thrombophilia and Incidentally Diagnosed Atrial Septal Defect. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, S.; Howard, L.S.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Hoeper, M.M. Systemic Consequences of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right-Sided Heart Failure. Circulation 2020, 141, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, N.; Watanabe, R.; Tomoe, T.; Toyoda, S.; Yasu, T.; Nakamoto, T. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneau, G.; Dorfmuller, P.; Guignabert, C.; Mercier, O.; Humbert, M. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: The magic of pathophysiology. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 11, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Francis, C.M.; Bauer, N.N.; Gassman, N.R.; Stevens, T. A cancer amidst us: The plexiform lesion in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L1142–L1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Dong, X.; Gong, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Examining the Development of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension at the Single-Cell Level. Hypertension 2022, 79, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, S.; Rizwani, W.; Joshi, B.; Kunigal, S.; Chellappan, S.P. TNF-alpha response of vascular endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells involve differential utilization of ASK1 kinase and p73. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.M.; Carpenter, L.C.; Koutakis, P.; Swanson, S.A.; Zhu, Z.; Hanna, M.; DeSpiegelaere, H.K.; Pipinos, I.I.; Casale, G.P. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 produced by vascular smooth muscle cells predicts fibrosis in the gastrocnemius of patients with peripheral artery disease. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A distinct disease entity. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayer, N.; Ltaief, Z.; Liaudet, L.; Lechartier, B.; Aubert, J.D.; Yerly, P. Pressure Overload and Right Ventricular Failure: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenvoort, C.A. Pathology of pulmonary thromboembolism. Chest 1995, 107, 10S–17S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; Torbicki, A.; Gopalan, D.; Sitbon, O.; Klok, F.A.; Lang, I.; Jenkins, D.; Kim, N.H.; Humbert, M.; Jais, X.; et al. ERS statement on chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, S.; Pretorius, G.V. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 35, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, K.M.; Bloor, C.M. Pulmonary vascular lesions occurring in patients with chronic major vessel thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Chest 1993, 103, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, C.; Pistritto, A.M.; Gerges, M.; Friewald, R.; Hartig, V.; Hofbauer, T.M.; Reil, B.; Engel, L.; Dannenberg, V.; Kastl, S.P.; et al. Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.A.; Marsh, J.J.; Chiles, P.G.; Auger, W.R.; Fedullo, P.F.; Woods, V.L., Jr. Fibrin derived from patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension is resistant to lysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, M.N.; Kasap, B.; Yuvaci, H.U.; Turhan, N. Association between platelet indices and first trimester miscarriage. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossent, E.J.; Meijboom, L.J.; Bogaard, H.J.; Klok, F.A. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension anno 2021. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2021, 36, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; de Perrot, M.; Jais, X.; Jenkins, D.P.; Lang, I.M.; Matsubara, H.; Meijboom, L.J.; Quarck, R.; Simonneau, G.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Realising the potential of multimodal management. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichota, A.; Szewczyk, E.M.; Gwozdzinski, K. Factors Affecting the Formation and Treatment of Thrombosis by Natural and Synthetic Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Boyer-Neumann, C.; Parent, F.; Eschwege, V.; Jaillet, H.; Meyer, D.; Simonneau, G. Thrombotic risk factors in pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonderman, D.; Wilkens, H.; Wakounig, S.; Schafers, H.J.; Jansa, P.; Lindner, J.; Simkova, I.; Martischnig, A.M.; Dudczak, J.; Sadushi, R.; et al. Risk factors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Szydlo, R.; Gibbs, S.; Laffan, M. Hereditary and acquired thrombotic risk factors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2010, 21, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltham, M.; Burnand, K.G.; Collins, M.; McGuinness, C.L.; Singh, I.; Smith, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances venous thrombus recanalisation and organisation. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 89, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modarai, B.; Burnand, K.G.; Sawyer, B.; Smith, A. Endothelial progenitor cells are recruited into resolving venous thrombi. Circulation 2005, 111, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, T.W.; Myers, D.D.; Henke, P.K. Mechanisms of venous thrombosis and resolution. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.M.; Madani, M. Update on chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2014, 130, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, J.H.; Hirth, A.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Distler, O. Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 47, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.E.; Grover, S.P.; Humphries, J.; Saha, P.; Patel, A.P.; Patel, A.S.; Lyons, O.T.; Waltham, M.; Modarai, B.; Smith, A. Antiangiogenic therapy inhibits venous thrombus resolution. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarck, R.; Wynants, M.; Verbeken, E.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M. Contribution of inflammation and impaired angiogenesis to the pathobiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattula, S.; Byrnes, J.R.; Wolberg, A.S. Fibrinogen and Fibrin in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, e13–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntharalingam, J.; Goldsmith, K.; van Marion, V.; Long, L.; Treacy, C.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Toshner, M.R.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Eikenboom, J.C.; Morrell, N.W. Fibrinogen Aalpha Thr312Ala polymorphism is associated with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remkova, A.; Simkova, I.; Valkovicova, T. Platelet abnormalities in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 9700–9707. [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita, N.; Shirakawa, R.; Fukumoto, Y.; Sugimura, K.; Miyata, S.; Miura, Y.; Nochioka, K.; Miura, M.; Tatebe, S.; Aoki, T.; et al. Platelets are highly activated in patients of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarck, R.; Wynants, M.; Ronisz, A.; Sepulveda, M.R.; Wuytack, F.; Van Raemdonck, D.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M. Characterization of proximal pulmonary arterial cells from chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.; Kirshner, H.F.; Nazo, N.; Ali, S.; Ganapathi, A.; Cumming, I.; Zhuang, Y.; Choi, I.; Warman, A.; Jassal, C.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Distinct Immune and Smooth Muscle Cell Populations that Contribute to Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Guignabert, C.; Bonnet, S.; Dorfmuller, P.; Klinger, J.R.; Nicolls, M.R.; Olschewski, A.J.; Pullamsetti, S.S.; Schermuly, R.T.; Stenmark, K.R.; et al. Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: State of the art and research perspectives. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricard, N.; Bailly, S.; Guignabert, C.; Simons, M. The quiescent endothelium: Signalling pathways regulating organ-specific endothelial normalcy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas, A.; Guignabert, C.; Barbera, J.A.; Bartsch, P.; Bhattacharya, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Dewachter, L.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Dorfmuller, P.; et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelium: The orchestra conductor in respiratory diseases: Highlights from basic research to therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ro, A.; Kageyama, N.; Tanifuji, T.; Sakuma, M. Autopsy-proven untreated previous pulmonary thromboembolism: Frequency and distribution in the pulmonary artery and correlation with patients’ clinical characteristics. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietra, G.G.; Capron, F.; Stewart, S.; Leone, O.; Humbert, M.; Robbins, I.M.; Reid, L.M.; Tuder, R.M. Pathologic assessment of vasculopathies in pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 25S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, N.; Hoeper, M.M.; Humbert, M.; Torbicki, A.; Vachiery, J.L.; Barbera, J.A.; Beghetti, M.; Corris, P.; Gaine, S.; Gibbs, J.S.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Mayer, E.; Simonneau, G.; Rubin, L.J. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2006, 113, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, C.; Gerges, M.; Friewald, R.; Fesler, P.; Dorfmuller, P.; Sharma, S.; Karlocai, K.; Skoro-Sajer, N.; Jakowitsch, J.; Moser, B.; et al. Microvascular Disease in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Hemodynamic Phenotyping and Histomorphometric Assessment. Circulation 2020, 141, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulate, D.; Perros, F.; Dorfmuller, P.; Arthur-Ataam, J.; Guihaire, J.; Lamrani, L.; Decante, B.; Humbert, M.; Eddahibi, S.; Dartevelle, P.; et al. Pulmonary microvascular lesions regress in reperfused chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, T.; Dang, B.; Wang, X. Overexpressed microRNA (miR)-382-3p promoted vascular remodeling via suppressing autophagy-related protein 7 (ATG7) in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Curr. Mol. Med. 2023; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Ding, H.; Lv, X.; Lian, N.; Zhao, J.; Deng, C. The role of inflammation in a rat model of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension induced by carrageenan. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, K.M.; Olle, S.; Fuge, J.; Welte, T.; Hoeper, M.M.; Lerch, C.; Maegel, L.; Haller, H.; Jonigk, D.; Schiffer, L. CXCL13 in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Gao, J.; An, X.; Liu, Y.; Su, P. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2631–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Leng, D.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, W.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, Y. Microarray Analysis and Detection of MicroRNAs Associated with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8529796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kigel, B.; Rabinowicz, N.; Varshavsky, A.; Kessler, O.; Neufeld, G. Plexin-A4 promotes tumor progression and tumor angiogenesis by enhancement of VEGF and bFGF signaling. Blood 2011, 118, 4285–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platoshyn, O.; Remillard, C.V.; Fantozzi, I.; Sison, T.; Yuan, J.X. Identification of functional voltage-gated Na+ channels in cultured human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Pflug. Arch. 2005, 451, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mediator | Mechanism Involved | Possible Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrinogen and fibrinolytic abnormalities | |||
| Fibrinogen | Mutation in Aα-Thr312Ala of the fibrinogen protein sequence. Mutation in β-chain P235L/γ R375W of the fibrinogen protein sequence. Mutation in β-chain P235L/γ Y114H and P235L of the fibrinogen protein sequence. Mutation in α-chain L69H and R554H of the fibrinogen protein sequence. | These mutations lead to a modified fibrin structure in clots, promoting thrombus non-resolution. Patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) share several fibrin abnormalities, where fibrin resists physiological thrombolysis, impairing thrombus resolution. | [18,19] |
| Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) | Increase in circulating levels | PAI-1 contributes to impaired clot dissolution, a key feature of the chronic nature of thromboembolism in CTEPH. | [20] |
| Platelet function | |||
| Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) | Deficiency | PECAM-1 is a glycopeptide receptor expressed in platelets, endothelial cells, and many other cell types. PECAM-1 is involved in leukocyte trafficking and inflammatory responses involved in thrombus resolution. | [21] |
| Impaired angiogenesis | |||
| Fetal liver kinase-1 (Flk-1) | Deletion | Flk-1 deletion inhibits thrombus angiogenesis and delays thrombus resolution in mouse models of deep vein thrombosis. | [22] |
| Endothelial function | |||
| Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) | Receptor deletion | Experimental disruption of the endothelial angiogenic signaling via VEGF receptor (VEGFR) deletion or VEGFR phosphorylation inhibition impairs venous thrombus resolution. | [23] |
| Inflammatory response | |||
| Interferon gamma-induced protein-10 (IP-10) | Increased expression | IP-10 increased expression promotes T cell adhesion to endothelial cells and inhibits bone marrow colony formation and angiogenesis. | [24] |
| Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) | Upregulation | NF-κB upregulation induces endothelial cell dysfunction in CTEPH and prompts increased expression of interleukin (IL-) 8, IL-1 beta, c-c motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). | [25,26] |
| Small-vessel disease | |||
| Nitric oxide-soluble guanylate cyclase-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (NO–sGC–cGMP) pathway | Dysfunction | Vascular endothelium-derived NO inhibits platelet aggregation and smooth muscle cell growth. NO activates sGC to synthesize cGMP, a second messenger with many actions including smooth muscle relaxation. Plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine, a NO synthase inhibitor, are increased in patients with CTEPH. | [27] |
| Endothelin-1 (ET-1) | Elevation | ET-1 promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation within chronic clots in CTEPH and small-vessel disease. | [28] |
| Bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor (BMPR2) | Heterozygous germline mutation | BMPR2 promotes pulmonary artery endothelial cell (PAEC) survival, thus protecting the pulmonary arteries from damage. Mutations of BMPR2 result in downregulation Smad signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), with resultant loss of the antiproliferative effect. | [29,30,31,32] |
| Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) | Increased expression | TGF-beta 1 promotes extracellular matrix protein production and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). | [33] |
| Activin A Receptor Type 1 (ACVRL1) | Somatic mosaicism | ACVRL1 is one of the TGF-beta 1 type I receptors interacting with BMPR2. | [34] |
| Endoglin (ENG) | Increased expression | ENG promotes response to ligands such as TGF-beta 1, Activin A, and BMPR2. Since ENG expression during embryogenesis is linked to cardiovascular system development, it may play a role in vascular remodeling in CTEPH. | [35] |
| Suppressor of Mothers against Decapentaplegic 9 (SMAD9) | Missense mutations | The SMAD9 signal pathway is associated with vascular remodeling. | [36] |
| Caveolin-1 (CAV1) | Missense mutation | CAV1 is a membrane protein of caveolae abundant in the vascular endothelium and other cells of the lung. CAV1 loss increases constitutive endothelial permeability and reduces vascular endothelial-cadherin (VE-cadherin) and β-catenin levels. Furthermore, loss of the endothelial barrier function is a significant phenomenon of inflammation. | [37,38] |
| Potassium channel subfamily K member 3 (KCNK3) | Increased expression | KCNK3 channels are major contributors to the resting potential in human PASMCs. KCNK3 are pH-sensitive channels responsible for driving modulatory effects in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez-Hermosillo, L.M.; Cueto-Robledo, G.; Navarro-Vergara, D.I.; Torres-Rojas, M.B.; García-Cesar, M.; Pérez-Méndez, O.; Escobedo, G. Molecular Pathophysiology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Clinical Update from a Basic Research Perspective. Adv. Respir. Med. 2024, 92, 485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92060044
Gonzalez-Hermosillo LM, Cueto-Robledo G, Navarro-Vergara DI, Torres-Rojas MB, García-Cesar M, Pérez-Méndez O, Escobedo G. Molecular Pathophysiology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Clinical Update from a Basic Research Perspective. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2024; 92(6):485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92060044
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez-Hermosillo, Leslie Marisol, Guillermo Cueto-Robledo, Dulce Iliana Navarro-Vergara, Maria Berenice Torres-Rojas, Marisol García-Cesar, Oscar Pérez-Méndez, and Galileo Escobedo. 2024. "Molecular Pathophysiology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Clinical Update from a Basic Research Perspective" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 92, no. 6: 485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92060044
APA StyleGonzalez-Hermosillo, L. M., Cueto-Robledo, G., Navarro-Vergara, D. I., Torres-Rojas, M. B., García-Cesar, M., Pérez-Méndez, O., & Escobedo, G. (2024). Molecular Pathophysiology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Clinical Update from a Basic Research Perspective. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 92(6), 485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92060044






