p-Value Histograms: Inference and Diagnostics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Background
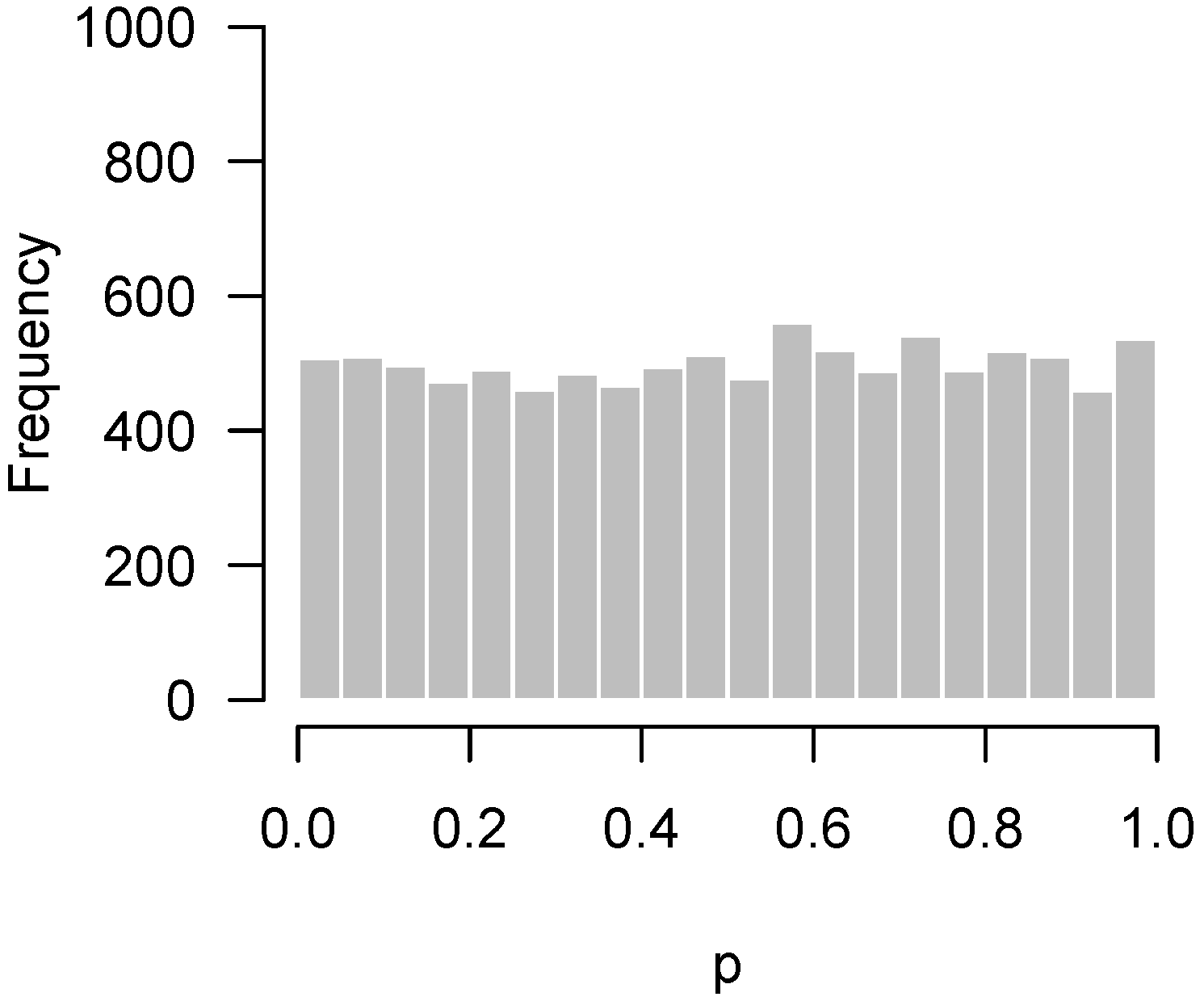
2.2. Higher Criticism
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Causes of Anomalous p-Value Histograms
2.4.1. Low Power
2.4.2. Incorrect Distributional Assumptions
2.4.3. Correlation among Features
2.5. Remedies
3. Discussion
3.1. Alternative Approaches
3.2. Summary
- Higher criticism: Is there a significant excess of low p-values? In other words, is there any evidence of a systematic biological response in the experiment?
- Quality control: Has something gone wrong in this experiment?
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- b <- 0.05
- hist(p, breaks=seq(0, 1, b), col=“gray”, border=“white”)
- # Higher criticism:
- abline(h=qbinom(0.95, length(p), b), col=“red”)
- # Quality control:
- abline(h=qbinom(1 − b*0.05, length(p), b), col=“blue”)
References
- Rogier, E.W.; Frantz, A.L.; Bruno, M.E.C.; Wedlund, L.; Cohen, D.A.; Stromberg, A.J.; Kaetzel, C.S. Secretory antibodies in breast milk promote long-term intestinal homeostasis by regulating the gut microbiota and host gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3074–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Fischl, A.M.; Heron, P.M.; Stromberg, A.J.; Mcclintock, T.S. Activity-Dependent Genes in Mouse Olfactory Sensory Neurons. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukey, J. The Philosophy of Multiple Comparisons. Stat. Sci. 1991, 6, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoho, D.; Jin, J. Higher criticism for detecting sparse heterogeneous mixtures. Ann. Stat. 2004, 32, 962–994. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.; Jin, J. Higher criticism thresholding: Optimal feature selection when useful features are rare and weak. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, P.; Jin, J. Innovated higher criticism for detecting sparse signals in correlated noise. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 1686–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, I.J.; Lin, X. Analytical p-value calculation for the higher criticism test in finite-d problems. Biometrika 2014, 101, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donoho, D.; Jin, J. Higher Criticism for Large-Scale Inference, Especially for Rare and Weak Effects. Stat. Sci. 2015, 30, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, J.C.; Bridges, P.J. NutriPhysioGenomics applications to identify adaptations of cattle to consumption of ergot alkaloids and inorganic versus organic forms of selenium: Altered nutritional, physiological and health states? Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Microarrays, empirical Bayes and the two-groups model. Stat. Sci. 2008, 23, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Large-Scale Inference: Empirical Bayes Methods for Estimation, Testing, and Prediction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Brooks, A.; Klebanov, L.; Yakovlev, A. The effects of normalization on the correlation structure of microarray data. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irizarry, R.; Hobbs, B.; Collin, F.; Beazer-Barclay, Y.; Antonellis, K.; Scherf, U.; Speed, T. Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 2003, 4, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Irizarry, R.A. Modeling of RNA-seq fragment sequence bias reduces systematic errors in transcript abundance estimation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, C.; Hardin, J.; Stoebel, D.M. Selecting between-sample RNA-Seq normalization methods from the perspective of their assumptions. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breheny, P.; Stromberg, A.; Lambert, J. p-Value Histograms: Inference and Diagnostics. High-Throughput 2018, 7, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7030023
Breheny P, Stromberg A, Lambert J. p-Value Histograms: Inference and Diagnostics. High-Throughput. 2018; 7(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreheny, Patrick, Arnold Stromberg, and Joshua Lambert. 2018. "p-Value Histograms: Inference and Diagnostics" High-Throughput 7, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7030023
APA StyleBreheny, P., Stromberg, A., & Lambert, J. (2018). p-Value Histograms: Inference and Diagnostics. High-Throughput, 7(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7030023




