Theoretical Principles and Perspectives of Hyperspectral Imaging Applied to Sediment Core Analysis
Abstract
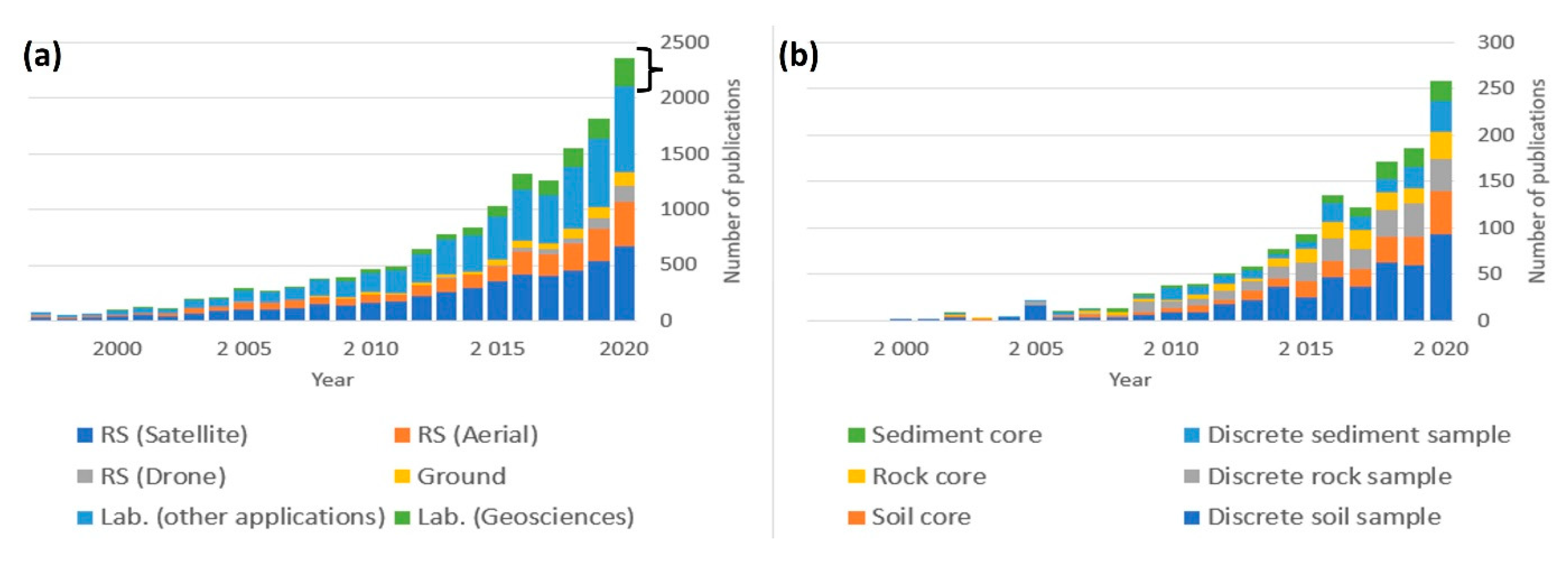
:1. Why Develop a New Sensor for Sediment Color Analysis?
1.1. Munsell Lithology Description
1.2. RGB Imaging
1.3. Spectroscopic Analysis
1.4. Hyperspectral Imaging
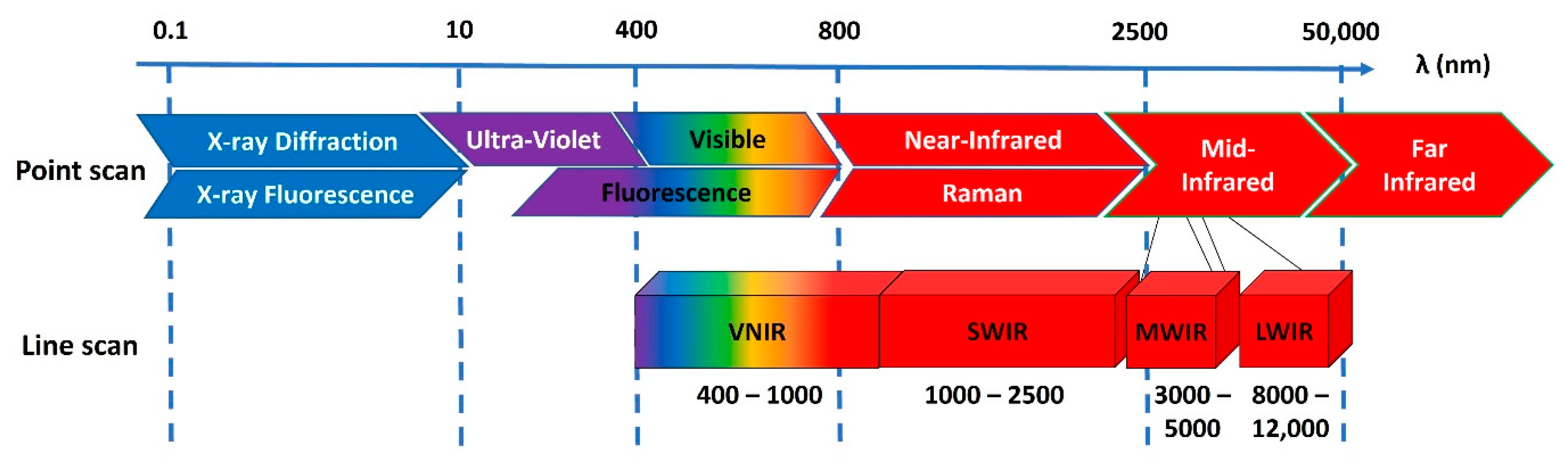
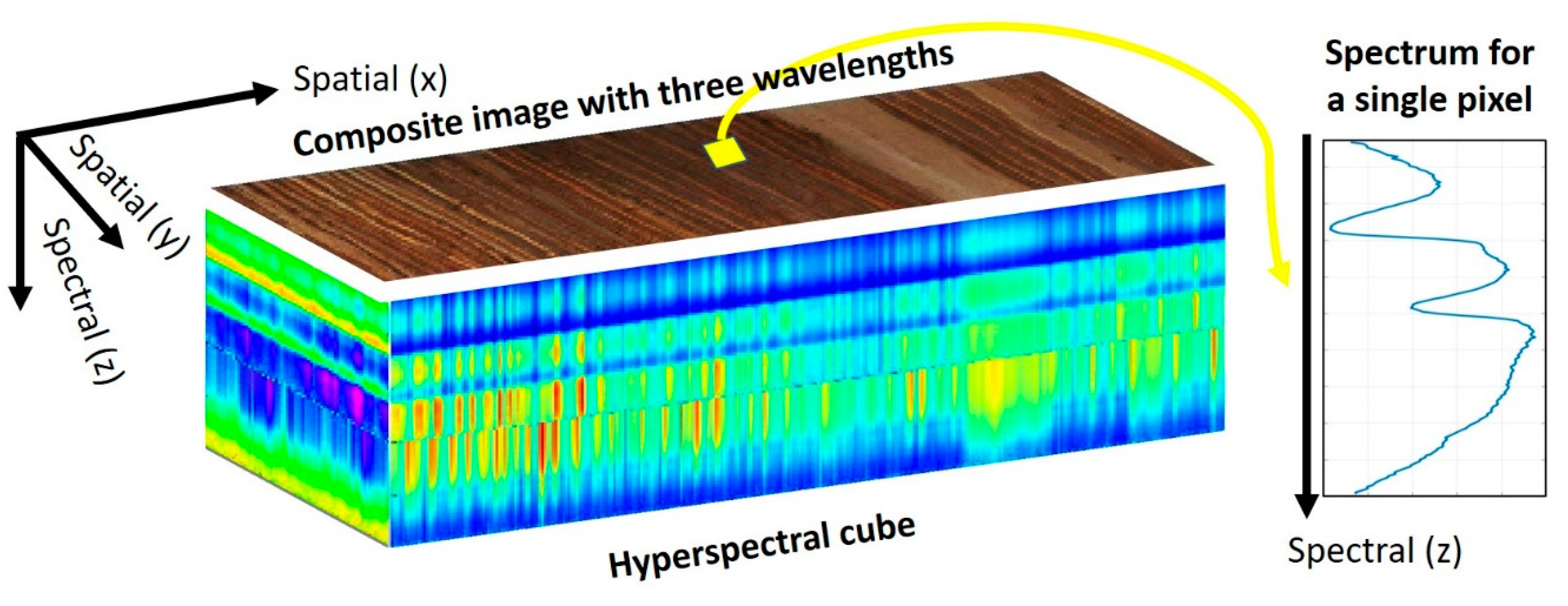
2. What Is Hyperspectral Imaging?
2.1. Hyperspectral Sensors
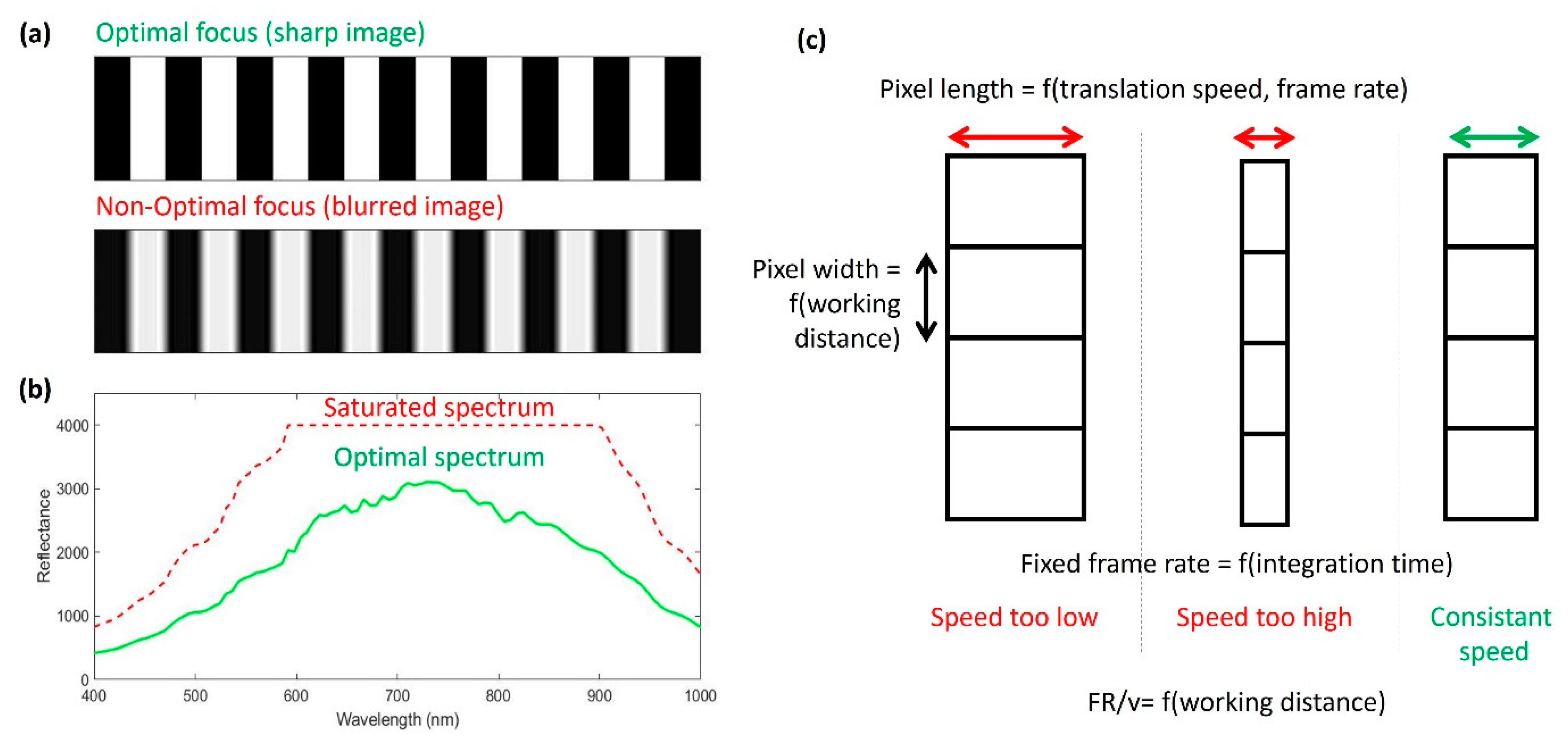
2.2. Acquisitions and Recommendations
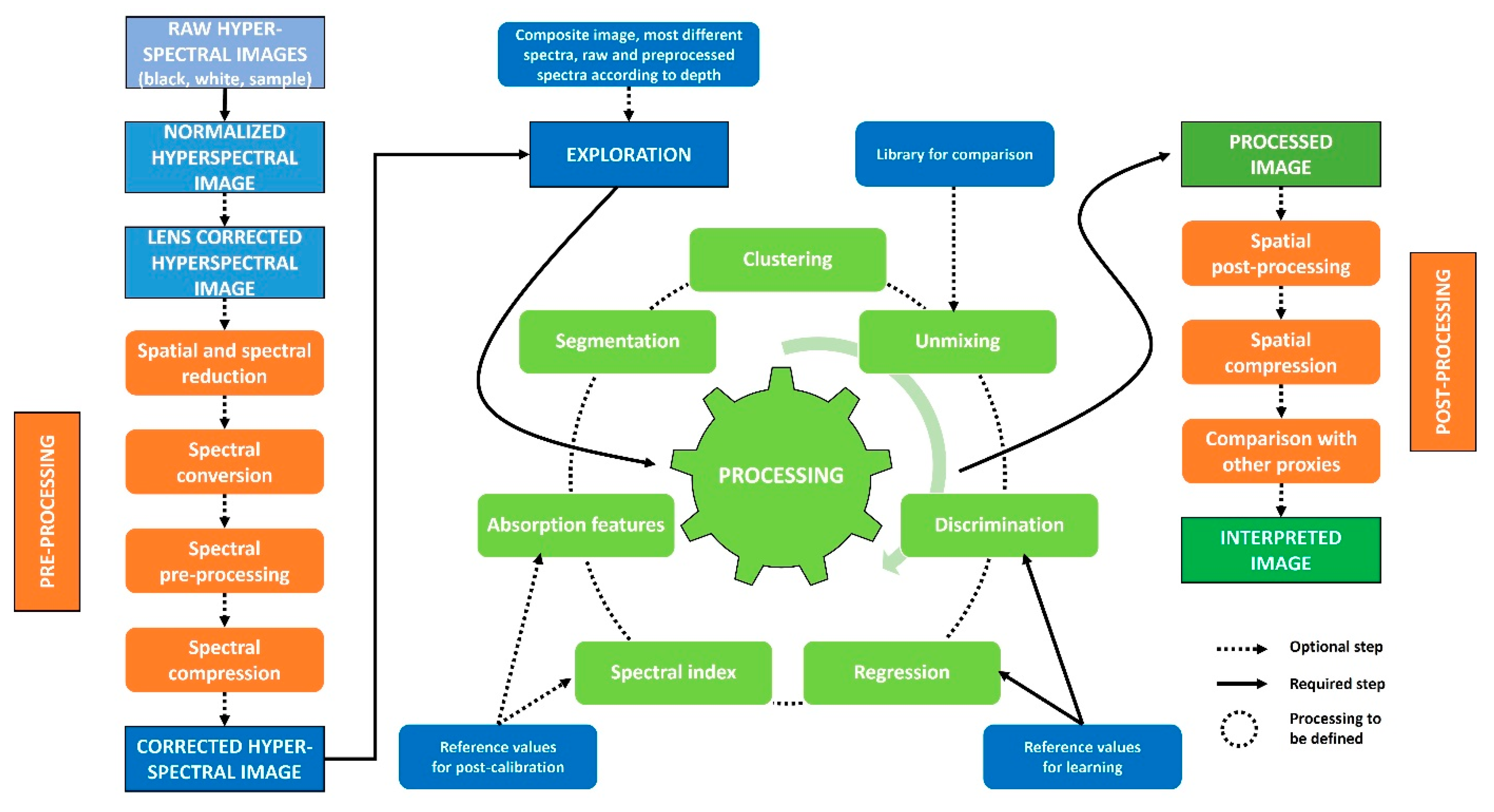
3. How to Process These Data?
3.1. Preprocessing
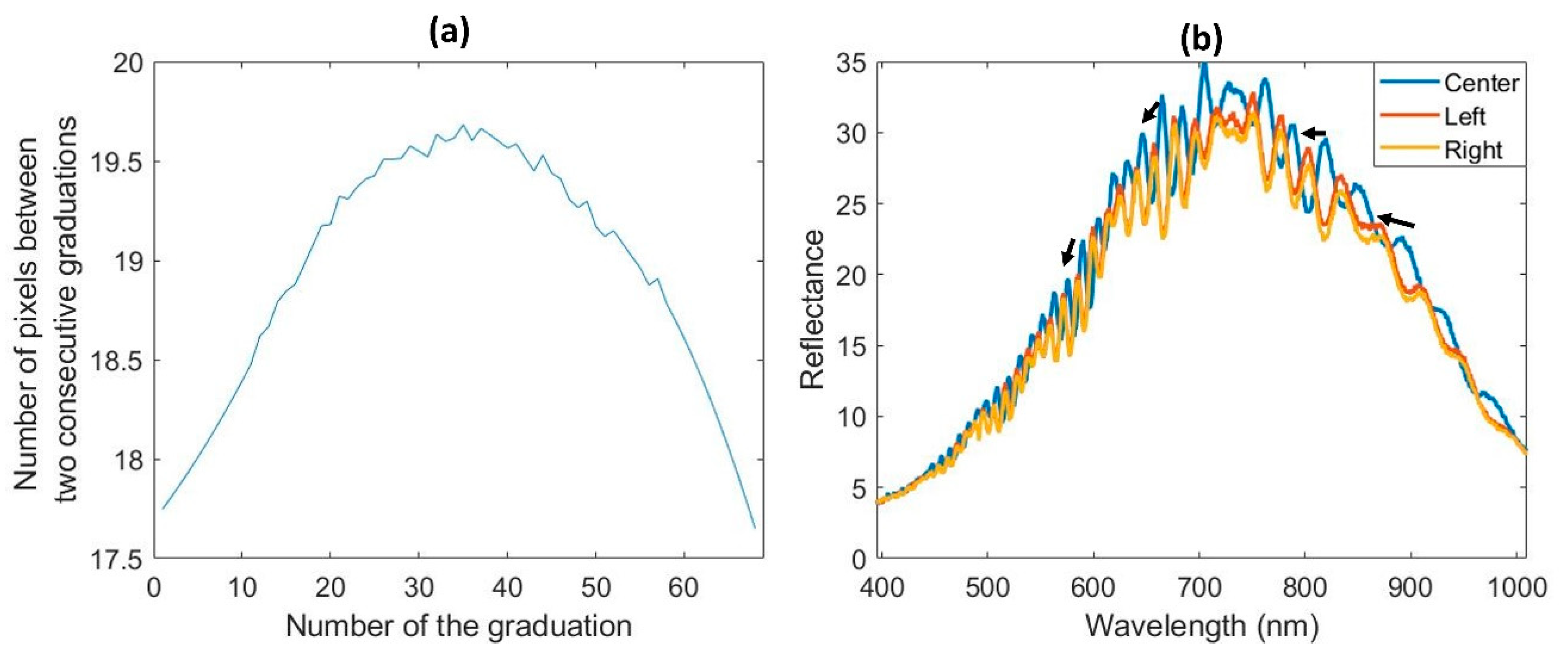
3.1.1. Spatial and Spectral Reduction
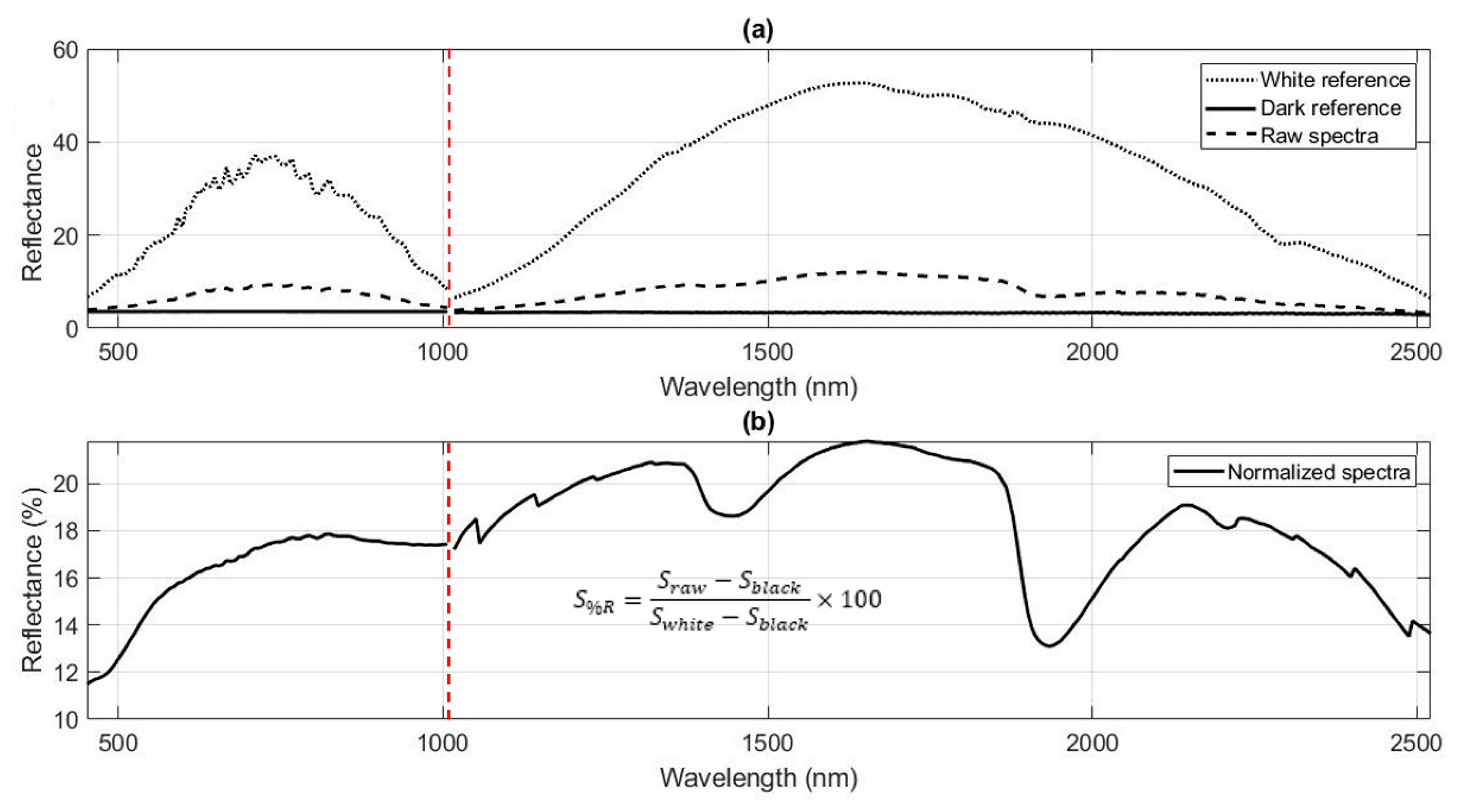
3.1.2. Spectral Conversion
3.1.3. Spectral Preprocessing
3.1.4. Compression
3.2. Exploration
3.2.1. Composite Images
| Sensor–Name | Name | Wavelength | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| VNIR | RGB (Red Green Blue) | 640—545—460 nm | [48] |
| VNIR | CIR (Color InfraRed) | 860—650—555 nm | |
| VNIR | NIR (Near InfraRed) | 900—800—700 nm | |
| SWIR | pRGB (pseudo RGB) | 2162—2199—2349 nm | [85] |
| SWIR | Hydrocarbon | 1722—1760—2311 nm | [86] |
| SWIR | Hydrocarbon | 1722—2311—2349 nm |
3.2.2. Spectral Visualization
3.2.3. Spatial and/or Spectral Distribution
3.3. Processing
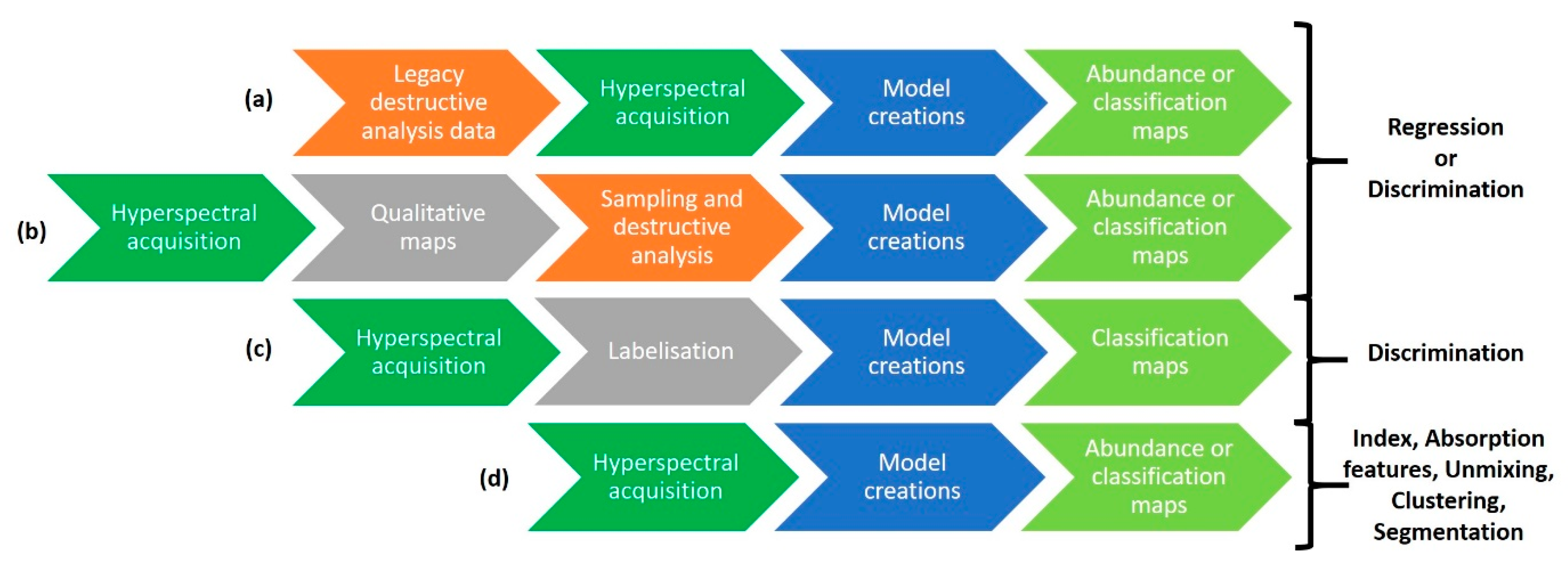
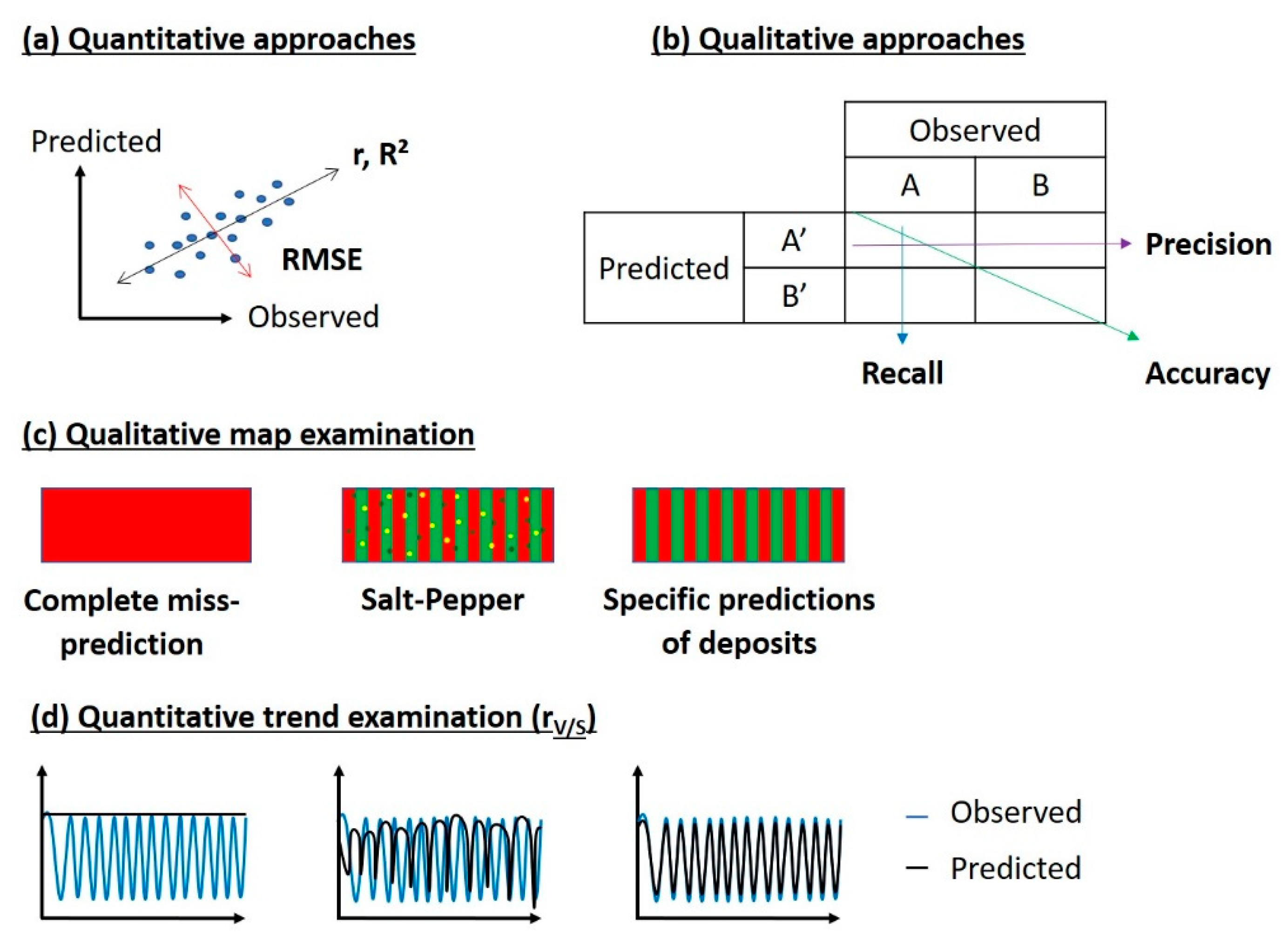
3.3.1. Qualitative Approaches
3.3.2. Quantitative Approaches
3.3.3. Subsampling for Model Calibration (cm vs. µm)
3.3.4. Model Validation and Performance
3.4. Post-Processing
4. What Sedimentary Properties Can Be Derived from It?
4.1. Trophic Status
| Variable Studied | Coefficients | Wavelengths Used (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a + derivatives | d675 | 675 | [136] |
| Chlorophyll a + derivatives | Area650—700 | 650–700 | [27] |
| Chlorophyll a + pheophytin a | RABD590—730 | 590, 690, 730 | [53] |
| Bacteriopheophytin a | RABD845 | 790, 845, 900 | [48] |
| Phycocyanin | aPC | 625 | [129] |
| Carotenoid | RABD510 | 490, 510, 530 | [106] |
| Total pigment content | RABA400—560 | 400–560 | [106] |
| Main sediment components | Q7/4 | 400, 700 | [26] |
4.2. Source to Sink—Fingerprinting
4.3. Organic Matter
4.4. Mineralogy
4.5. Classification and Identification of Sedimentary Deposits
5. How Can We Go Beyond?
5.1. Toward a Multisensor Core Logger
5.2. Data Management
5.3. Integrative Approach Allowing the Selection of Sampling Areas
5.4. Opportunities Still Underexploited
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munsell, A.H. A Color Notation; G.H. Ellis Company: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1905. [Google Scholar]
- Hollister, C.D.; Heezen, B.C. Geologic Effects of Ocean Bottom Currents: Western North Atlantic. In Studies in Physical Oceanography; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: Langhorne, PA, USA, 1972; pp. 37–66. ISBN 9780677151700. [Google Scholar]
- Ericson, D.B.; Ewing, M.; Wollin, G.; Heezen, B.C. Atlantic Deep-Sea Sediment Cores. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 193–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE. Colorimetry—Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, A.D. Principles of Sedimentary Basin Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0-387-90941-7. [Google Scholar]
- Balsam, W.L.; Deaton, B.C.; Damuth, J.E. Evaluating Optical Lightness as a Proxy for Carbonate Content in Marine Sediment Cores. Mar. Geol. 1999, 161, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.; Broecker, W.; Lotti, R.; McManus, J. Abrupt Color Changes in Isotope Stage 5 in North Atlantic Deep Sea Cores: Implications for Rapid Change of Climate-Driven Events. In Start of a Glacial: NATO ASI Series; Kukla, G.J., Went, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 185–205. [Google Scholar]
- Petterson, G.; Odgaard, B.V.; Renberg, I. Image Analysis as a Method to Quantify Sediment Components. J. Paleolimnol. 1999, 22, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renberg, I. Improved Methods for Sampling, Photographing and Varve-counting of Varved Lake Sediments. Boreas 1981, 10, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiljander, M.; Ojala, A.; Saarinen, T.; Snowball, I. Documentation of the Physical Properties of Annually Laminated (Varved) Sediments at a Sub-Annual to Decadal Resolution for Environmental Interpretation. Quat. Int. 2002, 88, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francus, P. Image Analysis, Sediments and Paleoenvironments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; ISBN 978-1-4020-2061-2. [Google Scholar]
- Protz, R.; VandenBygaart, A.J. Towards Systematic Image Analysis in the Study of Soil Micromorphology. Sci. Soils 1998, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damci, E.; Çağatay, M.N. An Automated Algorithm for Dating Annually Laminated Sediments Using X-Ray Radiographic Images, with Applications to Lake Van (Turkey), Lake Nautajarvi (Finland) and Byfjorden (Sweden). Quat. Int. 2016, 401, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.E.; Reichelt, L.; Kuhn, G.; Pfeiffer, M.; Korff, B.; Thurow, J.; Ricken, W. BMPix and PEAK Tools: New Methods for Automated Laminae Recognition and Counting-Application to Glacial Varves from Antarctic Marine Sediment. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiniou, T.; Selmaoui, N.; Laporte-Magoni, C.; Allenbach, M. Calculation of Bedding Angles Inclination from Drill Core Digital Images. In Proceedings of the MVA2007 IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications, Tokyo, Japan, 16–18 May 2007; pp. 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Vannière, B.; Magny, M.; Joannin, S.; Simonneau, A.; Wirth, S.B.; Hamann, Y.; Chapron, E.; Gilli, A.; Desmet, M.; Anselmetti, F.S. Orbital Changes, Variation in Solar Activity and Increased Anthropogenic Activities: Controls on the Holocene Flood Frequency in the Lake Ledro Area, Northern Italy. Clim. Past 2013, 9, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francus, P. An Image-Analysis Technique to Measure Grain-Size Variation in Thin Sections of Soft Clastic Sediments. Sediment. Geol. 1998, 121, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsam, W.L.; Deaton, B.C. Determining the Composition of Late Quaternary Marine Sediments from NUV, VIS, and NIR Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Mar. Geol. 1996, 134, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsam, W.L.; Deaton, B.C.; Damuth, J.E. The Effects of Water Content on Diffuse Reflectance Spectrophotometry Studies of Deep-Sea Sediment Cores. Mar. Geol. 1998, 149, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsam, W.L.; Beeson, J.P. Sea-Floor Sediment Distribution in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep. Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2003, 50, 1421–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.R.; Cramp, A.; Damuth, J.E.; Hiscott, R.N.; Kowsmann, R.O.; Lopez, M.; Nanayama, F.; Normark, W.R. Color-Reflectance Measurements Obtained from Leg 155 Cores. Proc. Ocean. Drill. Program Initial. Rep. 1995, 155, 697–700. [Google Scholar]
- Deaton, B.C.; Balsam, W.L. Visible Spectroscopy—A Rapid Method for Determining Hematite and Goethite Concentration in Geological Materials. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1991, 61, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, A.C.; Rugh, W.; Pisias, N.G.; Veirs, S.; Leg 138 Shipboard Sedimentologists, S.S.P. Color Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Tool for Rapid Characterization of Deep Sea Sediments. Proc. Ocean. Drill. Program Part A Initial. Rep. 1992, 138, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Balsam, W.L.; Damuth, J.E.; Schneider, R.R. Comparison of Shipboard vs. Shore-Based Spectral Data from Amazon Fan Cores: Implications for Interpreting Sediment Composition. Proc. Ocean. Drill. Program Sci. Results 1997, 155, 193–215. [Google Scholar]
- Debret, M.; Desmet, M.; Balsam, W.; Copard, Y.; Francus, P.; Laj, C. Spectrophotometer Analysis of Holocene Sediments from an Anoxic Fjord: Saanich Inlet, British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Geol. 2006, 229, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debret, M.; Sebag, D.; Desmet, M.; Balsam, W.; Copard, Y.; Mourier, B.; Susperrigui, A.-S.; Arnaud, F.; Bentaleb, I.; Chapron, E.; et al. Spectrocolorimetric Interpretation of Sedimentary Dynamics: The New “Q7/4 Diagram”. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michelutti, N.; Wolfe, A.P.; Vinebrooke, R.D.; Rivard, B.; Briner, J.P. Recent Primary Production Increases in Arctic Lakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Characterization of Pigments of Prokaryotes and Their Use in Taxonomy and Classification. In Methods in Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 38, pp. 261–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Balsam, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Rapid and Quantitative Measurement of Hematite and Goethite in the Chinese Loess-Paleosol Sequence by Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpoorter, C.; Carrère, V.; Combe, J.-P. Visible, near-Infrared Spectrometry for Simultaneous Assessment of Geophysical Sediment Properties (Water and Grain Size) Using the Spectral Derivative-Modified Gaussian Model. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 2098–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T. Using Data Mining to Model and Interpret Soil Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutis, E.A. Spectral Reflectance Properties of Hydrocarbons: Remote-Sensing Implications. Science 1989, 245, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croudace, I.W.; Rothwell, R.G. Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores: Applications of a Non-Destructive Tool for the Environmental Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9789401798495. [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell, R.G.; Croudace, I.W. Twenty Years of XRF Core Scanning Marine Sediments: What Do Geochemical Proxies Tell Us? In Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.H.F.; Van Der Gaast, S.J.; Koster, B.; Vaars, A.J. CORTEX, a Shipboard XRF-Scanner for Element Analyses in Split Sediment Cores. Mar. Geol. 1998, 151, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, B.; Sandmann, D.; Gilbricht, S. SEM-Based Automated Mineralogy and Its Application in Geo-and Material Sciences. Minerals 2020, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, W.D. X-Ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals. Clays Clay Miner. 1990, 38, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.M.; Utkin, A.B. Application of Laser-Induced Fluorescence in Functional Studies of Photosynthetic Biofilms. Processes 2018, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldstadt, J.; St Germain, R.; Grundl, T.; Schweitzer, R. An In Situ Laser-Induced Fluorescence System for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Sediments; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DA, USA, 2002.
- Lee, C.K.; Ko, E.J.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, Y.J. Partial Least Square Regression Method for the Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Soil Environment Using Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N. Spectroscopy of Rocks and Minerals, and Principles of Spectroscopy. In Remote Sensing for the Earth Sciences: Manual of Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Rencz, A.N., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1–50. ISBN 0471294055. [Google Scholar]
- Viviano-Beck, C.E.; Seelos, F.P.; Murchie, S.L.; Kahn, E.G.; Seelos, K.D.; Taylor, H.W.; Taylor, K.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Wisemann, S.M.; Mustard, J.F.; et al. Revised CRISM Spectral Parameters and Summary Products Based on the Currently Detected Mineral Diversity on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. E Planets 2014, 119, 1403–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madejová, J.; Gates, W.P.; Petit, S. IR Spectra of Clay Minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 8, pp. 107–149. ISBN 9780081003558. [Google Scholar]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near Infrared, Mid Infrared or Combined Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Simultaneous Assessment of Various Soil Properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, S.M.; Minasny, B.; Holden, N.M.; McBratney, A.B. Synergistic Use of Vis-NIR, MIR, and XRF Spectroscopy for the Determination of Soil Geochemistry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouinat, L.; Sabatier, P.; Poulenard, J.; Etienne, D.; Crouzet, C.; Develle, A. One Thousand Seven Hundred Years of Interaction between Glacial Activity and Flood Frequency in Proglacial Lake Muzelle (Western French Alps). Quat. Res. 2017, 87, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldt, B.R.; Kaufman, D.S.; Mckay, N.P.; Briner, J.P. Holocene Summer Temperature Reconstruction from Sedimentary Chlorophyll Content, with Treatment of Age Uncertainties, Kurupa Lake, Arctic Alaska. Holocene 2015, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, C.; Grosjean, M.; Fischer, D.; Wunderle, S.; Tylmann, W.; Rein, B. Hyperspectral Imaging Spectroscopy: A Promising Method for the Biogeochemical Analysis of Lake Sediments. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacq, K. Traitement d’images Multispectrales et Spatialisation Des Données Pour La Caractérisation de La Matière Organique Des Phases Solides Naturelles; Université Grenoble Alpes: Grenoble, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Exem, A. Reconstructions de Changements Environnementaux Dans Les Archives Lacustres Par Imagerie Hyperspectrale; Université de Rouen Normandie: Rouen, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Juan, A. Hyperspectral Image Analysis. When Space Meets Chemistry. J. Chemom. 2018, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, S.; Rey, F.; Gobet, E.; Gilli, A.; Tinner, W.; Grosjean, M. Early Human Impact in a 15,000-Year High-Resolution Hyperspectral Imaging Record of Paleoproduction and Anoxia from a Varved Lake in Switzerland. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 239, 106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Rimer, D.; Butz, C.; Grosjean, M. A High-Resolution Pigment and Productivity Record from the Varved Ponte Tresa Basin (Lake Lugano, Switzerland) since 1919: Insight from an Approach That Combines Hyperspectral Imaging and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Paleolimnol. 2018, 60, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Zander, P.; Szidat, S.; Lloren, R.; Grosjean, M. The Influences of Historic Lake Trophy and Mixing Regime Changes on Long-Term Phosphorus Fraction Retention in Sediments of Deep Eutrophic Lakes: A Case Study from Lake Burgäschi, Switzerland. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 2715–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, C.; Grosjean, M.; Goslar, T.; Tylmann, W. Hyperspectral Imaging of Sedimentary Bacterial Pigments: A 1700-Year History of Meromixis from Varved Lake Jaczno, Northeast Poland. J. Paleolimnol. 2017, 58, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrel, P.; Jacq, K.; Van Exem, A.; Escarguel, G.; Dietre, B.; Debret, M.; Mcgowan, S.; Ducept, J.; Gauthier, E.; Oberhänsli, H. Evidence for Centennial-Scale Mid-Holocene Episodes of Hypolimnetic Anoxia in a High-Altitude Lake System from Central Tian Shan (Kyrgyzstan). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 252, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Exem, A.; Debret, M.; Copard, Y.; Verpoorter, C.; De Wet, G.; Lecoq, N.; Sorrel, P.; Werner, A.; Roof, S.; Laignel, B.; et al. New Source-to-Sink Approach in an Arctic Catchment Based on Hyperspectral Core-Logging (Lake Linné, Svalbard). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 203, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, S.; de Souza Filho, C.R.; Nanni, M.R.; Batezelli, A. Multi-Scale Mapping of Oil-Sands in Anhembi (Brazil) Using Imaging Spectroscopy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speta, M.; Rivard, B.; Feng, J. Shortwave Infrared (1.0–2.5 Μm) Hyperspectral Imaging of the Athabasca West Grand Rapids Formation Oil Sands. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2018, 102, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacq, K.; Perrette, Y.; Fanget, B.; Sabatier, P.; Coquin, D.; Martinez-Lamas, R.; Debret, M.; Arnaud, F. High-Resolution Prediction of Organic Matter Concentration with Hyperspectral Imaging on a Sediment Core. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tusa, L.; Kern, M.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Blannin, R.; Gloaguen, R.; Gutzmer, J. Evaluating the Performance of Hyperspectral Short-Wave Infrared Sensors for the Pre-Sorting of Complex Ores Using Machine Learning Methods. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivard, B.; Harris, N.B.; Feng, J.; Dong, T. Inferring Total Organic Carbon and Major Element Geochemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Shale Core from Hyperspectral Imagery. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2018, 102, 2101–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, S.; Seidel, P.; Ghamisi, P.; Zimmermann, R.; Tusa, L.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Contreras, I.C.; Gloaguen, R. Multi-Sensor Spectral Imaging of Geological Samples: A Data Fusion Approach Using Spatio-Spectral Feature Extraction. Sensors 2019, 19, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Seidel, P.; Lorenz, S. Multiple Optical Sensor Fusion for Mineral Mapping of Core Samples. Sensors 2020, 20, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacq, K.; Martinez-Lamas, R.; Van Exem, A.; Debret, M. Hyperspectral Core-Logger Image Acquisition; Protocols.io: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rost, E.; Hecker, C.; Schodlok, M.C.; van der Meer, F.D. Rock Sample Surface Preparation Influences Thermal Infrared Spectra. Minerals 2018, 8, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, J.; Baumback, M.M.; Bowles, J.H.; Grossmann, J.M.; Antoniades, J.A. Comparison of Low-Cost Hyperspectral Sensors. In Proceedings of the Imaging Spectrometry IV, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–24 July 1998; Volume 3438, pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Amigo, J.M.; Babamoradi, H.; Elcoroaristizabal, S. Hyperspectral Image Analysis. Tutorial 2015, 896, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacq, K. JacqKevin/Hyperspectral_Imaging_Sediment_Core. 2021. Available online: https://githubhot.com/@JacqKevin (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Vidal, M.; Amigo, J.M. Pre-Processing of Hyperspectral Images. Essential Steps before Image Analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 117, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.T.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.F.; Xu, Q.J.; Wu, D.; Li, W.W.; Yao, J.L. Subsetting Hyperspectral Core Imaging Data Using a Graphic-Identification-Based IDL Program. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 106, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, A. Bestimmung Der Absorption Des Rothen Lichts in Farbigen Flüssigkeiten. Ann. Phys. 1852, 162, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinnan, Å. Pre-Processing in Vibrational Spectroscopy—When, Why and How. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7124–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, P.; Malegori, C.; Simonetti, R.; Casale, M. The Impact of Signal Pre-Processing on the Final Interpretation of Analytical Outcomes—A Tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard Normal Variate Transformation and De-Trending of Near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; MacDougall, D.; Martens, H. Linearization and Scatter-Correction for Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectra of Meat. Appl. Spectrosc. 1985, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.A.; Berman, M.; Switzer, P.; Craig, M.D. A Transformation for Ordering Multispectral Data in Terms of Image Quality with Implications for Noise Removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, K. On Lines and Planes of Closest Fit to Systems of Points in Space. Philos. Mag. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, R.; Dandy, G.; Maier, H. Review of Input Variable Selection Methods for Artificial Neural Networks. Artif. Neural Networks Methodol. Adv. Biomed. Appl. 2011, 10, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiaobo, Z.; Jiewen, Z.; Povey, M.J.W.; Holmes, M.; Hanpin, M. Variables Selection Methods in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 667, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIE. ISO/CIE 11664-4:2019—Colorimétrie—Partie 4: Espace Chromatique L*a*b* CIE 1976; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- CIE. IEC 61966-2-1:1999: Multimedia Systems and Equipment—Colour Measurement and Management—Part 2-1: Colour Management—Default RGB Colour Space—SRGB; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bora, D.J.; Gupta, A.K.; Khan, F.A. Comparing the Performance of L*A*B* and HSV Color Spaces with Respect to Color Image Segmentation. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2015, 5, 192–203. [Google Scholar]
- Speta, M.; Gingras, M.K.; Rivard, B. Shortwave Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging: A Novel Method For Enhancing the Visibility of Sedimentary And Biogenic Features In Oil-Saturated Core. J. Sediment. Res. 2016, 86, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafutto, R.D.P.M.; de Souza Filho, C.R.; Rivard, B. Characterization of Mineral Substrates Impregnated with Crude Oils Using Proximal Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, R.W.; Stone, L.A. Computer Aided Design of Experiments. Technometrics 1969, 11, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupnik, D.; Khan, S. Close-Range, Ground-Based Hyperspectral Imaging for Mining Applications at Various Scales: Review and Case Studies. Earth-Science Rev. 2019, 198, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.F.; Williams, D. Optical Properties of Water in the Near Infrared. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L.; Soille, P. Watersheds in Digital Spaces: An Efficient Algorithm Based on Immersion Simulations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavlasová, A.; Procházka, A.; Mudrová, M. Wavelet Based Image Segmentation. Comput. Sci. 2006, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhaus, H. Sur La Division Des Corps Materiels En Parties. Bull. Polish Acad. Sci. 1956, 4, 801–804. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical Grouping to Optimize an Objective Function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianca, B.L.; Gheorghe, P.S. Unsupervised Clustering for Hyperspectral Images. Symmetry 2020, 12, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cariou, C.; Chehdi, K. Unsupervised Nearest Neighbors Clustering with Application to Hyperspectral Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Signoroni, A.; Savardi, M.; Baronio, A.; Benini, S. Deep Learning Meets Hyperspectral Image Analysis: A Multidisciplinary Review. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.A. The Use of Multiple Measurements in Taxonomic Problems. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification And Regression Trees; Routledge: London, UK, 1984; ISBN 9781315139470. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, P. The Condensed Nearest Neighbor Rule. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1968, 14, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Rayens, W. Partial Least Squares for Discrimination. J. Chemom. 2003, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hamida, A.; Benoit, A.; Lambert, P.; Ben Amar, C. 3-D Deep Learning Approach for Remote Sensing Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4420–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivakhnenko, A.; Lapa, V.G. Cybernetic Predicting Devices; CCM Information Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Khaledian, Y.; Miller, B.A. Selecting Appropriate Machine Learning Methods for Digital Soil Mapping. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 81, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, B.; Sirocko, F. In-Situ Reflectance Spectroscopy—Analysing Techniques for High-Resolution Pigment Logging in Sediment Cores. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2002, 91, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Roy, R.; Launeau, P.; Cathelineau, M.; Quirt, D. Alteration Mapping on Drill Cores Using a HySpex SWIR-320m Hyperspectral Camera: Application to the Exploration of an Unconformity-Related Uranium Deposit (Saskatchewan, Canada). J. Geochemical Explor. 2017, 172, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, F.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S.; Santini, F.; Casa, R. Reducing the Influence of Soil Moisture on the Estimation of Clay from Hyperspectral Data: A Case Study Using Simulated PRISMA Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15561–15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A.; Bakker, W.H.; van der Werff, H.M.A.; Zegers, T.E.; Oosthoek, J.H.P.; Omer, Z.A.; Marsh, S.H.; van der Meer, F.D. Mapping the Wavelength Position of Deepest Absorption Features to Explore Mineral Diversity in Hyperspectral Images. Planet. Space Sci. 2014, 101, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, S.; De Souza Filho, C.R. Iterative Curve Fitting: A Robust Technique to Estimate the Wavelength Position and Depth of Absorption Features from Spectral Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5964–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral Unmixing Overview: Geometrical, Statistical, and Sparse Regression-Based Approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keshava, N. A Survey of Spectral Unmixing Algorithms. Lincoln Lab. J. 2003, 14, 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kokaly, R.F.; Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Livo, K.E.; Hoefen, T.M.; Pearson, N.C.; Wise, R.A.; Benzel, W.M.; Lowers, H.A.; Driscoll, R.L.; et al. USGS Spectral Library Version 7; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, Virginia, 2017.
- Lau, I.C.; LeGras, M.; Laukamp, C.; Mason, P.; Warren, P. CSIRO Shortwave Infrared Spectral Library—Evaluation and Status Report 2017 Report EP175249; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meerdink, S.K.; Hook, S.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Abbott, E.A. The ECOSTRESS Spectral Library Version 1.0. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 230, 111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, M.-D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Collaborative Sparse Regression for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhtar, N.; Shafait, F.; Mian, A. SUnGP: A Greedy Sparse Approximation Algorithm for Hyperspectral Unmixing. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bui, T.; Orberger, B.; Blancher, S.B.; Mohammad-Djafari, A.; Pilliere, H.; Salaun, A.; Bourrat, X.; Maubec, N.; Lefevre, T.; Rodriguez, C.; et al. Building a Hyperspectral Library and Its Incorporation into Sparse Unmixing for Mineral Identification. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4261–4264. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Ruhe, A.; Wold, H.; Dunn, W.J., III. The Collinearity Problem in Linear Regression. The Partial Least Squares (PLS) Approach to Generalized Inverses. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 1984, 5, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J.H. Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Ann. Stat. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. Statistical Learning Theory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 9780471030034. [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model for Information Storage and Organization in The Brain. Psychol. Rev. 1958, 65, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacq, K.; Rapuc, W.; Benoit, A.; Coquin, D.; Fanget, B.; Perrette, Y.; Sabatier, P.; Wilhelm, B.; Debret, M.; Arnaud, F. Sedimentary Structure Discrimination with Hyperspectral Imaging in Sediment Cores. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, P. Some Considerations about NIR Spectroscopy: Closing Speech at NIR-2009. NIR News 2010, 21, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderveld, K. Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization. In Graphics Gems IV; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 474–485. ISBN 9780123361561. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, J. Introduction to Mathematical Morphology. Comput. Vision Graph. Image Process. 1986, 35, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, P.D.; Wienhues, G.; Grosjean, M. Scanning Hyperspectral Imaging for In Situ Biogeochemical Analysis of Lake Sediment Cores: Review of Recent Developments. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacobi, Y.Z.; Köhler, J.; Leunert, F.; Gitelson, A. Phycocyanin-Specific Absorption Coefficient: Eliminating the Effect of Chlorophylls Absorption. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leavitt, P.R.; Hodgson, D.A. Sedimentary Pigments. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2006; pp. 295–325. ISBN 0306476681. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, G.C. Fluorescence of Photosynthetic Pigments in Vitro and in Vivo George. In Chlorophyll a Fluorescence. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2004; pp. 43–63. ISBN 978-1-4020-3217-2. [Google Scholar]
- Scheer, H. An Overview of Chlorophylls and Bacteriochlorophylls: Biochemistry, Biophysics, Functions and Applications. In Chlorophylls and Bacteriochlorophylls: Biochemistry, Biophysics, Functions and Applications; Grimm, B., Porra, R.J., Rüdiger, W., Scheer, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-1-4020-4515-8. [Google Scholar]
- Persichetti, G.; Viaggiu, E.; Testa, G.; Congestri, R.; Bernini, R. Spectral Discrimination of Planktonic Cyanobacteria and Microalgae Based on Deep UV Fluorescence. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Gong, N.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Sun, C.; Fang, W.; Men, Z. Effect of PH on Fluorescence and Absorption of Aggregates of Chlorophyll a and Carotenoids. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 173, 107975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotas, V.; Plante-Cuny, M.R. Identification et Quantification Des Pigments Chlorophylliens et Carotenoides Des Sediments Marins: Un Protocole d’analyse Par HPLC. Oceanol. Acta 1996, 19, 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.; Vinebrooke, R.D.; Sanchez-azofeifa, A.; Rivard, B.; Wolfe, A.P. Inferring Sedimentary Chlorophyll Concentrations with Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Novel Approach to Reconstructing Historical Changes in the Trophic Status of Mountain Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boardman, J.W. Geometric Mixture Analysis of Imaging Spectrometry Data. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; Volume 4, pp. 2369–2371. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Rogge, D.; Rivard, B. Comparison of Lithological Mapping Results from Airborne Hyperspectral VNIR-SWIR, LWIR and Combined Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Milesi, C.; Nemani, R.R.; Raja, S.K.; Ganguly, S.; Wang, E. Sparse Unmixing via Variable Splitting and Augmented Lagrangian for Vegetation and Urban Area Classification Using Landsat Data. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences—ISPRS Archives, Kona, HI, USA, 21–23 July 2015; Volume 40, pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Schodlok, M.C.; Whitbourn, L.; Huntington, J.; Mason, P.; Green, A.; Berman, M.; Coward, D.; Connor, P.; Wright, W.; Jolivet, M.; et al. HyLogger-3, a Visible to Shortwave and Thermal Infrared Reflectance Spectrometer System for Drill Core Logging: Functional Description. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 63, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusa, L.; Andreani, L.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Contreras, C.; Ivascanu, P.; Gloaguen, R.; Gutzmer, J. Mineral Mapping and Vein Detection in Hyperspectral Drill-Core Scans: Application to Porphyry-Type Mineralization. Minerals 2019, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koerting, F.; Rogass, C.; Kaempf, H.; Lubitz, C.; Harms, U.; Schudack, M.; Kokaly, R.; Mielke, C.; Boesche, N.; Altenberger, U. Drill Core Mineral Analysis by Means of the Hyperspectral Imaging Spectrometer Hyspex, XRD and ASD in Proximity of the Mýtina Maar, Czech Republic. In Proceedings of the ISPRS—International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Kish Island, Iran, 23–25 November 2015; Volume XL-1-W5, pp. 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sellier, V.; Navratil, O.; Laceby, J.P.; Legout, C.; Allenbach, M.; Lefèvre, I.; Evrard, O. Combining Colour Parameters and Geochemical Tracers to Improve Sediment Source Discrimination in a Mining Catchment (New Caledonia, South Pacific Islands). Soil 2021, 7, 743–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legout, C.; Poulenard, J.; Nemery, J.; Navratil, O.; Grangeon, T.; Evrard, O.; Esteves, M. Quantifying Suspended Sediment Sources during Runoff Events in Headwater Catchments Using Spectrocolorimetry. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1478–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosinsky, A.; Foerster, S.; Segl, K.; Kaufmann, H. Spectral Fingerprinting: Sediment Source Discrimination and Contribution Modelling of Artificial Mixtures Based on VNIR-SWIR Spectral Properties. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulenard, J.; Legout, C.; Némery, J.; Bramorski, J.; Navratil, O.; Douchin, A.; Fanget, B.; Perrette, Y.; Evrard, O.; Esteves, M. Tracing Sediment Sources during Floods Using Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform Spectrometry (DRIFTS): A Case Study in a Highly Erosive Mountainous Catchment (Southern French Alps). J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, O.; Poulenard, J.; Némery, J.; Ayrault, S.; Gratiot, N.; Duvert, C.; Prat, C.; Lefèvre, I.; Bonté, P.; Esteves, M. Tracing Sediment Sources in a Tropical Highland Catchment of Central Mexico by Using Conventional and Alternative Fingerprinting Methods. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulenard, J.; Perrette, Y.; Fanget, B.; Quetin, P.; Trevisan, D.; Dorioz, J.M. Infrared Spectroscopy Tracing of Sediment Sources in a Small Rural Watershed (French Alps). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2808–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on Ignition as a Method for Estimating Organic and Carbonate Content in Sediments: Reproducibility and Comparability of Results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawchai, S.; Kylander, M.E.; Chabangborn, A.; Löwemark, L.; Wohlfarth, B. Testing Commonly Used X-Ray Fluorescence Core Scanning-Based Proxies for Organic-Rich Lake Sediments and Peat. Boreas 2016, 45, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Mouazen, A.M.; Wetterlind, J. Visible and near Infrared Spectroscopy in Soil Science. Adv. Agron. 2010, 107, 163–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, A.; Nocita, M.; Tóth, G.; Montanarella, L.; van Wesemael, B. Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon at the European Scale by Visible and Near InfraRed Reflectance Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimpouris, E.; Tsakiridis, N.L.; Theocharis, J.B. Using Autoencoders to Compress Soil VNIR–SWIR Spectra for More Robust Prediction of Soil Properties. Geoderma 2021, 393, 114967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohland, M.; Ludwig, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ludwig, B. Determination of Soil Properties with Visible to Near- and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy: Effects of Spectral Variable Selection. Geoderma 2014, 223, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, N.M.; Grunwald, S.; McDowell, M.L.; Bruland, G.L.; Myers, D.B.; Harris, W.G. Modelling Soil Carbon Fractions with Visible Near-Infrared (VNIR) and Mid-Infrared (MIR) Spectroscopy. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baes, A.U.; Bloom, P.R. Diffuse Reflectance and Transmission Fourier Transform Infrared (DRIFT) Spectroscopy of Humic and Fulvic Acids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J.; Goh, K.M. Infrared Spectra of Humic Acids and Related Substances. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1971, 35, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzykowski, M.; Chodak, M. Near Infrared Spectroscopy-A Tool for Chemical Properties and Organic Matter Assessment of Afforested Mine Soils. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fallah, R.; Rouillon, R.; Vouvé, F. Spectral Characterization of the Fluorescent Components Present in Humic Substances, Fulvic Acid and Humic Acid Mixed with Pure Benzo(a)Pyrene Solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 199, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okparanma, R.N.; Mouazen, A.M. Determination of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon (TPH) and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) in Soils: A Review of Spectroscopic and Nonspectroscopic Techniques. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2013, 48, 458–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivard, B.; Lyder, D.; Feng, J.; Gallie, A.; Cloutis, E.; Dougan, P.; Gonzalez, S.; Cox, D.; Lipsett, M.G. Bitumen Content Estimation of Athabasca Oil Sand from Broad Band Infrared Reflectance Spectra. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 88, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, R.K.; Nawar, S.; Alamar, M.C.; Coulon, F.; Mouazen, A.M. Almost 25 Years of Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Analytical Method Development for Petroleum Hydrocarbons Analysis in Soil and Sediment: State-of-the-Art, Progress and Trends. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1497–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockia Jency, D.; Umadevi, M.; Sathe, G.V. SERS Detection of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Using β-Cyclodextrin Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles on Agriculture Land Soil. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, D.; Woignier, T.; Lesueur-Jannoyer, M.; Achard, R.; Rangon, L.; Barthès, B.G. Determination of Soil Content in Chlordecone (Organochlorine Pesticide) Using near Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy (NIRS). Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 3120–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Chen, Y.; Meng, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, X. Rapid Prediction of Atrazine Sorption in Soil Using Visible Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Bartholomeus, H.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Geissen, V. Predicting Soil Microplastic Concentration Using Vis-NIR Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsi, M.; Esposito, S.; Moroni, M. Hyperspectral Characterization of Marine Plastic Litters. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Convolutional Neural Network for Soil Microplastic Contamination Screening Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacq, K.; Giguet-Covex, C.; Sabatier, P.; Perrette, Y.; Fanget, B.; Coquin, D.; Debret, M.; Arnaud, F. High-Resolution Grain Size Distribution of Sediment Core with Hyperspectral Imaging. Sediment. Geol. 2019, 393–394, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguet-Covex, C.; Arnaud, F.; Poulenard, J.; Enters, D.; Reyss, J.-L.; Millet, L.; Lazzaroto, J.; Vidal, O. Sedimentological and Geochemical Records of Past Trophic State and Hypolimnetic Anoxia in Large, Hard-Water Lake Bourget, French Alps. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 43, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapkanski, S.; Jacq, K.; Brocard, G.; Vittori, C.; Debret, M.; De Giorgi, A.U.; D’’Ottavio, D.; Giuffré, M.E.; Goiran, J.-P. Calibration of Short-Wave InfraRed (SWIR) Hyperspectral Imaging Using Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform Spectroscopy (DRIFTS) to Obtain Continuous Logging of Mineral Abundances along Sediment Cores. Sediment. Geol. 2022, 428, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, N.; Parbhakar-Fox, A.; Moltzen, J.; Feig, S.; Goemann, K.; Huntington, J. Applications of Hyperspectral Mineralogy for Geoenvironmental Characterisation. Miner. Eng. 2017, 107, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, K.M.; Roberts, S.J.; Perren, B.; Butz, C.; Sime, L.; Davies, S.; Van Nieuwenhuyze, W.; Grosjean, M.; Hodgson, D.A. Holocene Dynamics of the Southern Hemisphere Westerly Winds and Possible Links to CO2 Outgassing. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, N.; Kidron, G.J.; Ben-Dor, E. Surface Properties of Stabilizing Coastal Dunes: Combining Spectral and Field Analyses. Sedimentology 2007, 54, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Khan, S.; Godet, A. Integrated Ground-Based Hyperspectral Imaging and Geochemical Study of the Eagle Ford Group in West Texas. Sediment. Geol. 2018, 363, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Schneider, S.; Monteiro, S.T. Consistency of Measurements of Wavelength Position from Hyperspectral Imagery: Use of the Ferric Iron Crystal Field Absorption at ∼900 Nm as an Indicator of Mineralogy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2843–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, C.; van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A.; Bakker, W.H.; Fagbohun, B.J.; Riley, D.; van der Werff, H.M.A.; van der Meer, F.D. Mapping the Wavelength Position of Mineral Features in Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 79, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalm, M.; Buxton, M.W.N.; van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A. Discriminating Ore and Waste in a Porphyry Copper Deposit Using Short-Wavelength Infrared (SWIR) Hyperspectral Imagery. Miner. Eng. 2017, 105, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, N.; van der Meer, F.; van der Werff, H. Determination of Carbonate Rock Chemistry Using Laboratory-Based Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4149–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, S.; Murphy, R.J.; Melkumyan, A. Evaluating the Performance of a New Classifier—The GP-OAD: A Comparison with Existing Methods for Classifying Rock Type and Mineralogy from Hyperspectral Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 98, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malmir, M.; Tahmasbian, I.; Xu, Z.; Farrar, M.B.; Bai, S.H. Prediction of Soil Macro- and Micro-Elements in Sieved and Ground Air-Dried Soils Using Laboratory-Based Hyperspectral Imaging Technique. Geoderma 2019, 340, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, P.D.; Żarczyński, M.; Tylmann, W.; Rainford, S.; Grosjean, M. Seasonal Climate Signals Preserved in Biochemical Varves: Insights from Novel High-Resolution Sediment Scanning Techniques. Clim. Past 2021, 17, 2055–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, I.F.; Oliva, M.; Giralt, S.; Martín-Herrero, J. Detection of Tephra Layers in Antarctic Sediment Cores with Hyperspectral Imaging. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapuc, W.; Jacq, K.; Develle, A.-L.; Sabatier, P.; Fanget, B.; Perrette, Y.; Coquin, D.; Debret, M.; Wilhelm, B.; Arnaud, F. XRF and Hyperspectral Analyses as an Automatic Way to Detect Flood Events in Sediment Cores. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 409, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Gloaguen, R.; Jakob, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Gloaguen, R. The Need for Accurate Geometric and Radiometric Corrections of Drone-Borne Hyperspectral Data for Mineral Exploration: MEPHySTo—A Toolbox for Pre-Processing Drone-Borne Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaillet, S.; Ployon, E.; Villemin, T. Images et Modèles 3D En Milieux Naturels. Collect. EDYTEM 2011, 12, 216. [Google Scholar]
- Piqueras Solsona, S.; Maeder, M.; Tauler, R.; de Juan, A. A New Matching Image Preprocessing for Image Data Fusion. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 164, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yuen, J.; Torralba, A. SIFT Flow: Dense Correspondence across Scenes and Its Applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 978–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Juan, A.; Gowen, A.; Duponchel, L.; Ruckebusch, C. Image Fusion. In Data Fusion Methodology and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 311–344. ISBN 9780444639844. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for Scientific Data Management and Stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAIR Play in Geoscience Data. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 961. [CrossRef]
- Emile-Geay, J.; Mckay, N.P. Paleoclimate Data Standards. PAGES Mag. 2016, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mckay, N.P.; Emile-Geay, J. Technical Note: The Linked Paleo Data Framework—A Common Tongue for Paleoclimatology. Clim. Past 2016, 12, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, M.N.; Tolwinski-Ward, S.E.; Thompson, D.M.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Applications of Proxy System Modeling in High Resolution Paleoclimatology. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 76, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khider, D.; Emile-Geay, J.; McKay, N.P.; Gil, Y.; Garijo, D.; Ratnakar, V.; Alonso-Garcia, M.; Bertrand, S.; Bothe, O.; Brewer, P.; et al. PaCTS 1.0: A Crowdsourced Reporting Standard for Paleoclimate Data. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 2019, 34, 1570–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrill, C.; Thrasher, B.; Lockshin, S.N.; Gille, E.P.; McNeill, S.; Shepherd, E.; Gross, W.S.; Bauer, B.A. The Paleoenvironmental Standard Terms (PaST) Thesaurus: Standardizing Heterogeneous Variables in Paleoscience. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaiah, B.A.; Jones, S.D.; Bellman, C.; Malthus, T.J. Critical Metadata for Spectroscopy Field Campaigns. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3662–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plomp, E. Going Digital: Persistent Identifiers for Research Samples, Resources and Instruments. Data Sci. J. 2020, 19, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.; Darroch, L.; Krahl, R.; Habermann, T.; Devaraju, A.; Schwardmann, U.; D’onofrio, C.; Häggström, I. Persistent Identification of Instrument. Data Sci. J. 2020, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M. How to Write a Reproducible Lab Protocol. Nature 2021, 597, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacq, K.; Rapuc, W.; Benoit, A.; Coquin, D.; Fanget, B.; Perrette, Y.; Sabatier, P.; Wilhelm, B.; Debret, M.; Pignol, C.; et al. Sedimentary structure discrimination with hyperspectral imaging in sediment cores [Data set]. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. H2020 Programme. Guidelines on FAIR Data Management in Horizon 2020; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, Ú.C.; Samawi, R.; Anjanappa, S.; Klykov, R.; Adeboye, O.O.; Agic, H.; Ahm, A.C.; Boag, T.H.; Bowyer, F.; Brocks, J.J.; et al. The Sedimentary Geochemistry and Paleoenvironments Project. Geobiology 2021, 19, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogé, F.; Gomez, C.; Jolivet, C.; Joffre, R. Which Strategy Is Best to Predict Soil Properties of a Local Site from a National Vis–NIR Database? Geoderma 2014, 213, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T.; Ben-Dor, E.; Brown, D.J.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Shepherd, K.D.; Shi, Z.; Stenberg, B.; Stevens, A.; Adamchuk, V.; et al. A Global Spectral Library to Characterize the World’s Soil. Earth-Science Rev. 2016, 155, 198–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knadel, M.; Deng, F.; Alinejadian, A.; Wollesen de Jonge, L.; Moldrup, P.; Greve, M.H. The Effects of Moisture Conditions—From Wet to Hyper Dry—On Visible Near-Infrared Spectra of Danish Reference Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchini, A.; Grosjean, M. Quantification of Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll b and Pheopigments a in Lake Sediments through Deconvolution of Bulk UV–VIS Absorption Spectra. J. Paleolimnol. 2020, 64, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusa, L.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Contreras, C.; Shahi, K.R.; Fuchs, M.; Gloaguen, R.; Gutzmer, J. Drill-Core Mineral Abundance Estimation Using Hyperspectral and High-Resolution Mineralogical Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras Acosta, I.C.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Tusa, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Gloaguen, R. A Machine Learning Framework for Drill-Core Mineral Mapping Using Hyperspectral and High-Resolution Mineralogical Data Fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4829–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Munsell Color Chart | RGB Image | Spectroscopy | Hyperspectral Imaging | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach based on | Visual | Sensor | Sensor | Sensor |
| Analysis conditions | User and lighting dependent | Controlled | Controlled | Controlled |
| Optimal resolution | Centimeters | Micrometers | Millimeters | Micrometers |
| Sampling | Punctual | Continuous | Punctual | Continuous |
| Information (number) | Qualitative (1) | Qualitative (1–3) | Semiquantitative (>50) | Semiquantitative (>50) |
| Time | +(++) | + | ++(+) | + |
| Easy to use | +++ | +++ | +++ | +(+) |
| Easy to process | +++ | +(+) | +(+) | +(+) |
| Cost | 0 | 100 | 1000–10,000 | 20,000–800,000 |
| Reference | [1,2] | [8,11] | [6,24,26,34] | [48,49,50] |
| Variable Studied | Coefficients | Wavelengths Used (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxides | d555 | 555 | [22] |
| Goethite | d535 | 535 | |
| Hematite | d575 | 575 | |
| Lithogenic material (chlorite, illite, biotite) | R570/R630 | 570; 630 | [106] |
| Lithogenic material (basaltic lithics) | R850/R900 | 850; 900 | [173] |
| Clay content | BD2170—2270 | 2170; 2270 | [108] |
| Clay content | SWIRFI | 2133; 2209; 2225 | [174] |
| Chlorite | IndexChlorites | 2187; 2275 | [107] |
| Kaolins | IndexKaolins | 2153; 2192 | |
| Micas | IndexMicas | 2139; 2200; 2294 | |
| Calcite | BD2340 | 2340 | [175] |
| Category | Example of Metadata | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Instrument | Sensor name, manufacturer, range and spectral resolution, focal length, slit width, detector, number of spatial and spectral pixels, data units |
| 2 | Reference Standard | Types of standard and their signatures (white, dark…) |
| 3 | Calibration | Calibration equation with black and white and for precalibration to correct radiometric and geometric distortions |
| 4 | Hyperspectral signal properties | Translation bench speed, frame rate, exposure time, pixel size and resolution, depth of field |
| 5 | Illumination information | Type of illuminant and its signature |
| 6 | General project information | Funding methods, partners and expected objectives for the samples |
| 7 | Location information | GPS position, site name, depth and length of sample |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacq, K.; Debret, M.; Fanget, B.; Coquin, D.; Sabatier, P.; Pignol, C.; Arnaud, F.; Perrette, Y. Theoretical Principles and Perspectives of Hyperspectral Imaging Applied to Sediment Core Analysis. Quaternary 2022, 5, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat5020028
Jacq K, Debret M, Fanget B, Coquin D, Sabatier P, Pignol C, Arnaud F, Perrette Y. Theoretical Principles and Perspectives of Hyperspectral Imaging Applied to Sediment Core Analysis. Quaternary. 2022; 5(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat5020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacq, Kévin, Maxime Debret, Bernard Fanget, Didier Coquin, Pierre Sabatier, Cécile Pignol, Fabien Arnaud, and Yves Perrette. 2022. "Theoretical Principles and Perspectives of Hyperspectral Imaging Applied to Sediment Core Analysis" Quaternary 5, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat5020028








