Abstract
Recent work on automotive communications based on the Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) standards proposed an approach to handle all the real-time frames in a uniform way regardless of their arrival pattern. According to such an approach, instead of binding all the frames of the same flow to a traffic class, each periodic or event-driven frame is scheduled based on its absolute deadline according to the Earliest Deadline First (EDF) algorithm. The approach does not impose additional frame overhead and does not require complex offline configurations that would be unsuitable for event-driven traffic. However, EDF scheduling cannot support time-driven communications. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a framework that combines the flexibility of online EDF frame scheduling for both periodic and event-driven traffic with the ability to guarantee temporal isolation to time-driven traffic. The paper describes the design of the proposed approach and the performance obtained using the OMNeT++ simulation environment.
1. Introduction and Motivation
Real-time (RT) applications such as those relevant to traffic monitoring and management in smart cities [1,2,3,4,5], safe operation in smart factories [6,7,8,9,10,11], and automated driving [12,13] pose very challenging requirements on the communications, especially in terms of time and safety constraints. Ethernet has always been one of the most investigated technologies for RT communications, in particular for industrial, avionic, and automotive scenarios [14,15,16,17]. Nowadays, Automotive Ethernet is the unanimously recognized solution to reduce the number of heterogeneous communication technologies currently used for in-vehicle communications. Ethernet is an appealing solution to provide RT flows with high bandwidth (e.g., from 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2.5 Gbps, 5 Gbps, up to 10 Gbps) and temporal guarantees on the end-to-end frame delays. To guarantee predictability to RT communications over Ethernet, the main aspects to deal with are (i) how to prevent collisions and (ii) how to limit the effect of the interfering traffic (i.e., best-effort traffic) on RT flows, so that the latter ones can be provided with guaranteed bounded delays. While the first obstacle can be removed by adopting a full-duplex Switched Ethernet with microsegmentation, the second issue still remains. In fact, Switched Ethernet was originally devised to support best-effort (BE) traffic, and, consequently, no mechanisms were provided to distinguish between time-critical and BE flows, to reserve bandwidth to time-critical flows, and to limit the interfering flows that share the channel with the RT ones. For this reason, plain Switched Ethernet, although offering multiple levels of quality of service thanks to the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) tag, was not able to provide bounded latency to RT traffic. In the past, to overcome this problem, traffic shaping techniques were proposed to limit the interference of BE traffic on RT flows. In particular, traffic smoothing techniques based on a token-bucket mechanism controlled by fuzzy rules [18], further improved with genetic algorithms and multiobjective optimization [19], proved to be very effective to reduce the statistical end-to-end delay of RT frames in industrial communications.
A further significant step forward in RT communications over Ethernet networks was the IEEE Audio Video Bridging (AVB) family of standards. AVB introduced (i) a common notion of time, through protocols to manage the network time and support synchronized operations [20], (ii) bandwidth reservation, through the Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) [21], and (iii) differentiated service for RT and BE traffic, through prioritization and Credit-Based Shaping (CBS) [22] applied to the output ports of bridges and end nodes to prevent traffic bursts. The rationale behind the Qav and Qat standards is that the traffic flows that require bounded latency, here called Stream Reservation (SR) flows, are assigned to specific traffic classes called SR classes. Multiple SR classes are possible, but the actual numbers for configuring the classes, which are given in the Qav standard, refer to Class A and Class B only. Such classes are guaranteed bounded delays over seven hops in the network. The SR flows are reserved bandwidth in advance, but to be provided with guaranteed upper bounds on the frame end-to-end delays, they need to adhere to some per-class configuration rules. Such rules, defined in the form of Traffic Specifications (TSpecs), are defined in the IEEE 802.1Qav [22] standard (now part of the IEEE 802.1Q [23] since 2014). For each SR class, the TSpecs cap both the maximum frame size and the maximum number of frames belonging to the class that can be sent in a given time interval, called a class measurement interval.
However, AVB was not still enough for the time-critical and safety-critical flows typically found in industrial and automotive applications (e.g., advanced driver assistance systems, automated driving), which require deterministic communications and very high reliability. To remedy such short-comings, the Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) standards were introduced to provide such properties.
TSN is a family of standards which tackle several aspects. Among them are reliable time synchronization [24], support for scheduled traffic (ST), i.e., a traffic class that requires to be transmitted following a given timing [25], per-stream filtering and policing [26] (both enrolled in the IEEE 802.1Q standard [27] since 2018), frame replication and elimination mechanisms to improve reliability, and many others. As the TSN standards are a flexible toolkit, the network designer can pick the features and mechanisms that match the requirements of the context under consideration and combine them in a modular design, also leveraging the IEEE 802.1Qcc [28] standard for configuration purposes, to fulfill the requirements of diverse application contexts, e.g., industrial, consumer, and automotive.
Another interesting step forward in dealing with RT traffic over TSN networks for in-car communications is a recent online approach that, instead of statically binding each flow to a given traffic class, handles all the frames, both periodic and event-driven (ED), according to the Earliest Deadline First (EDF) scheduling algorithm. The motivation for such a deadline-aware approach, called Deadline-TSN (D-TSN) [29], is that it allows to deal with periodic and event-driven RT frame online and in a uniform way. D-TSN applies an EDF-based approach, which is implemented by leveraging the IEEE 802.1Qci standard on each hop in their path from the source to the destination. D-TSN offers several benefits. First, it is an online scheduling approach, and therefore it does not require offline schedule calculations. Second, as multiple priority levels are available, it is able to support several classes of RT event-driven traffic. Finally, it maintains the standard Ethernet frame format, and therefore it does not introduce any additional frame overhead.
What is missing in D-TSN is the support for ST. For this reason, this work proposes an approach, called Deadline-ST (D-ST), which builds upon D-TSN and extends it in a way that combines the flexibility offered by online deadline-aware scheduling with the support for ST.
The main contributions of the paper are the following:
- The detailed design of D-ST, which allows for transmitting periodic, RT event-driven, and scheduled traffic within a common framework.
- A simulative assessment of D-ST in a realistic automotive scenario.
The progress beyond the state of the art is that D-ST is able to combine in a single framework three important properties for automotive communications, i.e., (i) the ability to flexibly provide multiple priorities to RT event-driven frames, through online EDF per-frame scheduling, (ii) the ability to guarantee the temporal isolation for time-driven flows, and (iii) the full compliance with the TSN standards. With D-ST, the diverse automotive RT traffic types can obtain the best service from the network without the need for hardware modifications in the Ethernet switches, and this is what the current research on TSN-based automotive communications is mainly striving for. In this context, D-ST is, therefore, a feasible and appropriate solution for automotive communications over TSN networks.
The structure of the paper is the following. Section 2 recaps the relevant literature. Section 3 outlines the TSN standard mechanisms exploited by D-ST. Section 4 describes the D-ST design, and Section 5 presents simulative assessments of D-ST. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper and outlines further research threads.
2. Related Work
While the TSN family of standards keeps growing, thanks to the efforts of the IEEE 802.1 Working Group, recent research has addressed aspects such as the support for RT traffic dynamically added to the network. In fact, in some automotive applications, new flows can be triggered during the system operation by an event, for instance, the connection of trailers to cars or trucks [30]. To deal with this problem, some bandwidth partitioning mechanisms able to accommodate new flows without affecting the temporal guarantees of the already existent ones were proposed [31]. Among the works dealing with RT event-driven traffic in automotive communications, the one in [32] proposed the introduction of a new traffic class, called the ED RT class, and new bandwidth configuration and management mechanisms to provide very low end-to-end delay to RT event-driven flows. ED traffic is also supported by the IEEE 802.1Qcr-2020 [33] standard, which specifies the Asynchronous Traffic Shaping (ATS), i.e., a per-flow token-bucket shaping mechanism that can be used to transmit ED traffic.
With the introduction of the TSN family of standards, many works addressed schedulability analysis and scheduling algorithms for traffic flows on time-sensitive networks [34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The work in [41] proposed a heuristic scheduling approach for time-driven flows while the work in [42] presented a solution to statically schedule time-driven flows according to an EDF-based policy. Such approaches are helpful for offline configuration, but they do not support ED flows. To accommodate novel applications, and hence the introduction of additional flows during the network operation, the works in [30,43] proposed the use of the Software-Defined Networking (SDN) paradigm [44,45,46], which (i) enables a flexible and easy resource allocation [47] thanks to the separation of the centralized control plane from the data plane, and (ii) allows to change the network configuration at run time through lightweight online scheduling [48,49]. To cope with dynamic reconfiguration using the ATS, the work in [50] addresses a configuration technique for the main parameters of the ATS that have an influence on the communication latency. However, the configuration parameters need to be set at design time and their calculation is a complex task [51]. For this reason, the approach in [50] adopts a Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT) solver for the configuration. However, the ATS is not suitable for guaranteeing determinism to time-driven traffic flows. The works in [52,53] propose tools for calculating schedules according to the IEEE 802.1Qbv standard to handle both ST and BE traffic. The goal of both works is to schedule flows using a time-driven approach and calculate the schedule so as to improve the latency of BE flows. However, every time a new RT flow is added, the entire schedule has to be recalculated from scratch. The work in [54] combines the Cyclic Queuing and Forwarding defined in [27] with the support for scheduled traffic. The approach in [54] provides a flexible way to schedule periodic and aperiodic RT traffic, but it cannot be implemented on IEEE 802.1Q legacy devices, as the transmission queues are handled according to policies that are not supported by the standard [27]. The approach presented in [55], called E-TSN, uses the transmission gate mechanism defined in the IEEE 802.1Q standard to create time-slotted transmissions. Some timeslots are reserved for ST transmissions, while other timeslots are shared among ED traffic flows. The approach in [55] allows for the transmission of both ED and ST traffic, but without RT guarantees for ED traffic. Moreover, as timeslots are reserved to the ED traffic, there is a potential bandwidth waste if there are no ED frames in the queue.
The D-TSN approach proposed in [29] is able to support dynamic reconfiguration and to deal with multiple classes of ED flows by realizing online frame scheduling according to the EDF policy [56], but it does not provide support for deterministic communications.
Comparing with the previous works, the approach here proposed for TSN-based networks, i.e., D-ST, is able to both handle dynamic RT flows and to encompass all the different types of RT traffic, i.e., periodic, event-driven, and time-driven, in a common framework, while meeting their diverse time requirements.
Table 1 shows a qualitative comparison among some of the abovementioned related works. In particular, the second and third columns show if and how well the approaches support RT event-driven traffic and scheduled traffic, respectively. The fourth column refers to the compliance with the IEEE 802.1Q standard, while the last column gives the scheduling granularity, i.e., per-class, per-flow, or per-frame. The approaches that provide the best results for each property are those with a higher number of checkmarks.

Table 1.
Comparison of state-of-the-art transmission approaches.
The best support for RT event-driven traffic is offered by D-TSN, Hybrid-TSN, and D-ST, thanks to the scheduling policies adopted. Hybrid-TSN and D-ST are also able to offer temporal isolation to ST traffic, with the notable difference that D-ST is fully compliant with IEEE 802.1Q-2018 switches, while Hybrid-TSN requires special handling of the transmission queues. Moreover, D-ST provides a better scheduling granularity, i.e., per-frame.
3. Background
The IEEE 802.1Q-2018 [27] is one of the main reference standards in the TSN family. It defines the functionality of the switches (bridges according to the IEEE terminology) as well as the operation of one or many switches in a Switched Ethernet network. A relevant standard is the IEEE 802.1AS-2011 [20], which specifies protocols to synchronize the local clocks of end nodes and switches. Its 2020 revision, i.e., the IEEE 802.1AS-2020 [24], improves the clock synchronization reliability and introduces replication mechanisms to cope with switch fault or frame loss.
According to [27], in the switches and the end nodes, each Ethernet port has a number of transmission queues, ordered by priority from 0 to 7. The frame to be transmitted is chosen according to the Strict Priority (SP) selection algorithm defined in [27], which picks the frame that is the head of the highest priority queue available for the transmission. Figure 1 shows an example of Ethernet port forwarding architecture. The SP is the green block in Figure 1.
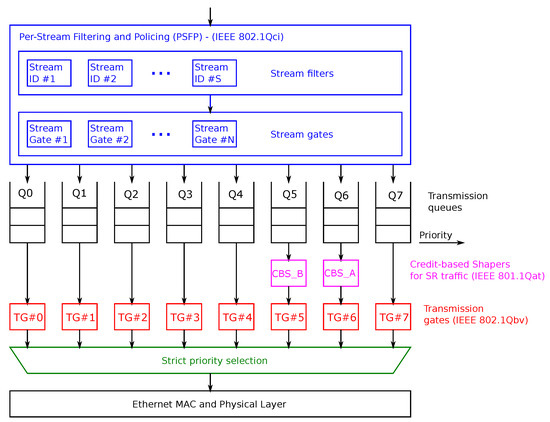
Figure 1.
Ethernet port forwarding architecture according to the IEEE 802.1Q-2018.
3.1. IEEE 802.1Qbv
To introduce the support for ST, the IEEE 802.1Qbv, now included in [27], applies a transmission gate mechanism to the egress queues of a switch port (red blocks in Figure 1), which enables time-driven transmissions, i.e., transmissions that follow a predefined time schedule leveraging the common notion of time realized by the IEEE 802.1AS standard. To this aim, transmission gates are placed at the output of the transmission queues. In particular, there is one transmission gate for each transmission queue and each gate maintains a state (open or closed). When a transmission gate is closed, no frame from the queue is eligible for transmission. Conversely, when the transmission gate is open, the frames can be selected for transmission according to the SP selection. The state of the transmission gates is modified following a transmission gate control list that cyclically repeats, following a transmission gate cycle. Each operation in the transmission gate control list is activated at a precise instant within the transmission gate cycle. Moreover, the IEEE 802.1Qbv standard implements a mechanism that prevents any lower-priority (i.e., non-ST frame) transmission that would exceed the transmission gate closing time. This way, ST flows do not experience jitter due to the ongoing transmission of a lower priority frame.
3.2. Per-Stream Filtering and Policing (PSFP)
The IEEE 802.1Qci—PSFP introduces new functionalities, such as per-stream metering and monitoring, error detection, and error mitigation. To improve reliability, PSFP allows for blocking a stream or a port so as to enforce error containment and to prevent the error propagation. By applying ingress policing and filtering, PSFP improves security by blocking the source of unforeseen or noncompliant traffic. PSFP defines the stream gates, which are placed on top of the transmission queues (blue blocks in Figure 1). Stream gates are traversed by frames, and each frame is mapped to a single stream gate. The PSFP mapping may use one or multiple fields of the Ethernet frame VLAN tag to assign a stream gate to the frame [27]. The stream gates maintain the status of their gates (open or closed) and an Internal Priority Value (IPV). If a gate is closed, the frames traversing it are dropped, otherwise the frames are forwarded to the priority transmission queue assigned by the stream gate IPV. Both the stream gate status and IPV are modified following a stream gate control list, i.e., a list of operations that cyclically repeats. The repetition cycle is called a stream gate cycle. Each operation in the stream gate control list is activated at a precise instant within a stream gate cycle. Using the PSFP, it is possible to change the mapping between the frames and transmission queue (i.e., the priority) over time.
4. Design
This section presents the design of D-ST, the common framework here proposed to uniformly deal with the different types of RT traffic, i.e., periodic, time-driven, and event-driven. In particular, D-ST combines the flexibility of online EDF frame scheduling for both periodic and ED traffic with the ability to guarantee temporal isolation to ST. The solution here presented, D-ST, builds upon the D-TSN approach proposed in [29] and extends it by exploiting the transmission gates provided in [27] to isolate the transmissions of the ST. In particular, in D-ST, the highest priority transmission queue is reserved to ST, and a proper configuration of the gate mechanism prevents low-priority frames from delaying the transmission of ST frames. Although the ST traffic is transmitted with the highest priority, its impact on the frames of the periodic or ED flows that are transmitted following the EDF policy is low, bounded, and easy to calculate.
The following subsections address the D-ST design.
4.1. Overview
Here, similar to in D-TSN, the PSFP is used to change the flows’ priority based on a time schedule. In particular, using a suitable configuration of the PSFP, the property of changing the queue to which the incoming frames are enqueued is exploited in order to implement the EDF policy within the switches. The frames are scheduled online and this allows D-ST to support ED traffic.
Both the switches and the end nodes need to be fully compliant with both the [27] and the [24] standards. At the physical layer, full-duplex Ethernet connections at a fixed data rate () are also required. D-ST transmissions use a given number of transmission queues in each port. Such a value, here referred to as Q, is chosen, taking into account that the highest priority queue is reserved to ST, and therefore it is not used for EDF scheduling. Moreover, if BE traffic is present, to make sure that the RT frames would always be transmitted with a higher priority than the BE frames, the latter would be reserved the lower priority transmission queue and would exploit the spare bandwidth left by the traffic with higher priority. In this case, also the lower priority queue would not be used for EDF scheduling.
The switches are required to be fully compliant with the PSFP, while the end nodes are not required to have this property. In D-ST, a given number of stream gates are used to enable deadline-based frame priority. Such a number, here called N, is configured to be a multiple of Q and its maximum value depends on the adopted hardware. Each flow has a relative deadline .
According to the PSFP standard, a frame can be mapped to a stream gate according to the value of one or multiple Ethernet frame fields. In D-ST the mapping is based on the 12-bit VLAN Identifier (VID) value. In particular, the stream gate control list rules have to be defined so that the IPV of each stream gate is shifted at regular time intervals. This way, as time passes, the incoming frames traversing a given stream gate (i.e., the one corresponding to the frame VID value) are enqueued to higher priority queues. For each VID, the stream gate control list follows a cyclical priority shifting. In D-ST, the period of the cyclical shifting is equal to the number of stream gates used multiplied by the time unit. Moreover, the number of rules is equal to the number of queues used.
The following subsections describe, in detail, the frame transmission mechanisms for the end nodes and for the switches, respectively.
4.1.1. Configuration of the Switches
The stream gates of the switches in D-ST are always open and their stream gate control list is configured once at deployment time. The frame absolute deadline in the switches is encoded in the VID value, which also associates a frame to a stream gate. In D-ST, the number of used VIDs is equal to the number of stream gates N. The first VID starts with and the others VIDs are assigned consecutive values, i.e., . The stream gate control list is configured to be modified at a constant interval, called a time unit (u), within a stream gate cycle. The time unit determines the granularity in encoding of the absolute deadlines. The frames enqueued in the same transmission queue are selected in a first-in first-out (FIFO) order. The number of rules in the stream gate control list is equal to the number of stream gates used for D-ST scheduling. In particular, the stream gate control list is configured so as to change the IPV of each gate over time, according to the following function:
where Q indicates the number of queues in each port used for D-ST transmissions, N is the number of stream gates used for EDF scheduling, is the index of the stream gate (starting from 0 to N − 1), and counts the time units elapsed since a reference time , here assumed to be .
In Function (2), u is the time unit, i.e., a constant interval that determines how often the stream gate control list is modified within a stream gate cycle.
When the stream gate control list is calculated, it is configured in the switches only once during deployment.
4.1.2. Configuration of the End Nodes
At the end nodes, D-ST runs a software component that assigns a VID and a priority to a frame before transmitting it to the Ethernet port. When a frame is generated, the software component calculates the frame absolute deadline , given by the sum of the arrival time of the frame and the relative deadline of the flow . The VID is calculated as
where represents the time required to transmit 1 bit and is the duration of the stream gate cycle, calculated as .
Each sender node is allowed to transmit a frame only when the following conditions are met:
where t is the current time. Moreover, the software component calculates the frame priority to be added in the PCP field of the Ethernet frame. To avoid any additional frame processing delay, the PCP is calculated right before the frame transmission to the Ethernet port, using the following function:
This way, the frame transmission will be scheduled with a priority that is a function of the absolute deadline.
4.2. Combining Scheduled Traffic Support with EDF Scheduling
A limitation of the D-TSN approach in [29] is that EDF scheduling may introduce jitter on the frame transmission, thus making it unsuitable for time-driven flows.
D-ST overcomes this problem by combining D-TSN with the Enhancements for Scheduled Traffic defined in [27]. In particular, in the proposed combination, the highest priority queue is reserved to the ST, which is transmitted according to the gate mechanism provided by [27], while the remaining queues implement EDF scheduling for the other RT traffic classes. As a result, when ST transmissions are scheduled, the transmission gate of the ST queue will be open and the gates of the remaining queues will be closed. The non-ST frames may, therefore, experience a delay due to both the ST frame transmission and the gate temporal isolation mechanism, which prevents starting a non-ST frame transmission that could not complete before the next ST queue gate opening. However, as the ST frames are scheduled and their transmission times are a priori known, the additional delay they introduce on non-ST frames can be easily calculated. Conversely, when no ST traffic transmissions are planned, the ST queue gate will be closed, while the other gates will stay open.
Figure 2 shows the forwarding process of an Ethernet switch port with a snapshot of each stream gate status at a generic time t. Note that for each Stream Identifier (SID) the stream gate IPV changes over time.
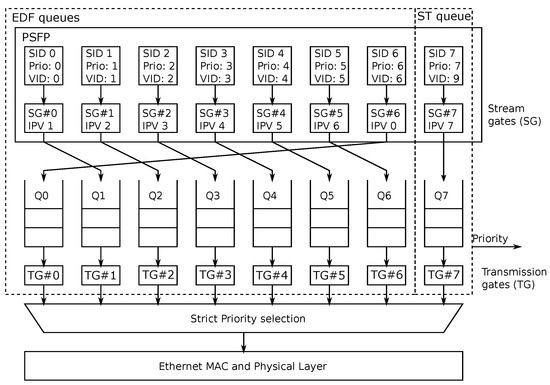
Figure 2.
Ethernet port forwarding architecture according to D-ST.
When a frame arrives to the Ethernet switch port, it is associated with a stream gate according to the frame VID value. For instance, in Figure 2 the VID no. 2 is associated with the stream gate with index 2, i.e., . The stream gate 2 at time t has the IPV equal to 3, therefore the frames traversing the stream gate 2 are enqueued to the transmission queue 3. In this example, N is equal to 7 and the VID 9 is out of the range , so the frames with VID 9 are not scheduled according to the D-ST policy previously described. In fact, VID 9 is associated with the ST traffic at stream gate 7. Such a stream gate never changes its IPV, therefore the ST frames traversing the stream gate 7 are always enqueued to the highest priority queue, i.e., Q7.
5. Performance Assessment
The performances of D-ST were assessed using OMNeT++ [57,58], a simulation environment widely used both in academia [59,60] and in industry. The Network Simulator for Time-Sensitive Networking (NeSTiNg) [61], which extends the Internet Networking (INET) framework, was used to develop the simulation model.
The performance metrics adopted are the frame end-to-end delay (e2eDelay) and the absolute jitter (AbsJitter).
The e2eDelay of the i-th frame of the flow f () is the time interval between the frame generation at the source node (GenTime) and the complete delivery at the destination node (RxTime) measured at the application level, given by Equation (6).
The absolute jitter of the flow f () represents the widest span of e2eDelay values, defined as the difference between the maximum and the minimum e2eDelay measured for the flow f, as shown in Equation (7).
The following subsections present the simulative assessment of D-ST in a realistic automotive scenario.
5.1. Scenario
The considered scenario, similar to the one presented in [32], is shown in Figure 3 and consists of several nodes, i.e., Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), ultrasonic sensors, radars and cameras all connected to four peripheral Electronic Control Units (ECUs) that send raw and aggregated sample data to a centralized controller.
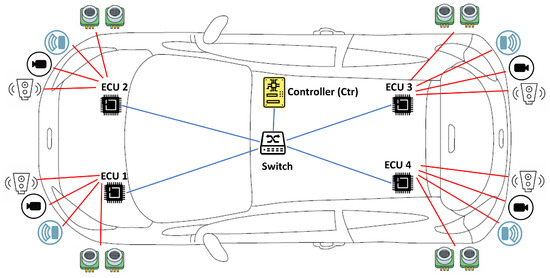
Figure 3.
The simulated scenario.
Table 2 shows the flow parameters of the assessed scenario.

Table 2.
Flow parameters.
As shown in Table 2, each ECU transmits to the controller an ED data flow, here called ADAS sensors, consisting of bursts of frames generated following a random distribution. For example, such data could consist of maps for obstacle detection performed by radars to be included in the Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS). All the peripheral ECUs transmit the same flows. Each flow in Table 2 consists of periodic messages or ED messages with a specific size, e.g., 43 KB for the Video flow. The simulated network operates at 1 Gbps. The deadlines of LiDAR and Ultrasonic flows are set equal to their periods, while the deadlines of the ADAS sensors flows and the video flow are set to 1 ms and 10 ms, respectively.
This section presents the results of two comparative performance assessments. The first comparison is between D-ST and an approach that applies some of the TSN protocols enrolled in [27], i.e., the Credit-Based Shaping, the enhancements for ST (i.e., the transmission gate mechanism for the ST class), and the Strict Priority selection algorithm. Here, such a configuration is called Time-Sensitive Networking with Scheduled Traffic (TSN-ST). The second comparison is between D-ST and D-TSN.
5.2. Comparison between D-ST and TSN-ST
In the D-ST configuration, the two ST flows, i.e., the LiDARs and Ultrasonic flows, are mapped to the highest priority queue, which is reserved to the ST class, while the other flows are handled according to the EDF-based policy. Instead, in the TSN-ST configuration, the LiDARs and Ultrasonic flows are mapped to the ST class (i.e., queue 7), the Video flows are assigned to the SR class A (i.e., queue 6) and undergo the CBS, while the ED ADAS sensor flows are mapped to the highest-priority BE queue, (i.e., queue 5).

Table 3.
Simulation results: maximum end-to-end delay.
As shown in Table 3, for the LiDAR and Ultrasonic flows the maximum frame e2eDelays are the same with both approaches, as this traffic is isolated from the other traffic classes. The ADAS sensors flows with D-TSN obtained a maximum frame e2eDelay equal to 0.45 ms, and therefore no deadline miss occurred. Conversely, using TSN-ST, the ED traffic experiences deadline miss, as the maximum e2eDelay is equal to 1.56 ms, while the flow’s relative deadline is 1 ms. This is because with TSN-ST the ED traffic is affected by the interference of both the ST traffic and SR traffic, which are mapped to the two highest-priority classes. Conversely, in both configurations, Video flows do not experience deadline miss. In the TSN-ST configuration, Video flows obtained a slightly lower maximum delay, as such flows have the second highest priority, therefore they do not suffer from the interference of ED traffic. On one hand, this results in lower delays for Video flows, but, on the other hand, this configuration determines deadline miss for the ADAS sensors flows.
The relative deadline D of each frame of the video flow, here called , is calculated according to the following equation:
where is the number of frames a message of the Video flow is split in, and is the frame id within the frame burst. The ST flows, i.e., LiDAR and Ultrasonic, experience a null jitter in both configurations.
To summarize, comparing with TSN-ST, D-ST significantly reduces the end-to-end delay of ED flows (i.e., the ADAS sensors flows) thanks to the frame online EDF scheduling. Moreover, D-ST achieves the same performance for the jitter-sensitive ST flows (LiDAR and Ultrasonic), and better performance for the ED flows, without a significant impact on the periodic RT traffic (i.e., Video).
5.3. Comparison between D-ST and D-TSN
The simulations of D-TSN and D-ST were run with the network configuration parameters set as in Table 4.

Table 4.
Network configuration parameters for D-TSN and D-ST.

Table 5.
Simulation results: maximum end-to-end delay.
As expected, the e2eDelays of LiDAR and Ultrasonic flows in the D-TSN configuration are higher than those obtained using the D-ST configuration, as D-TSN does not support scheduled transmissions. The jitter for LiDAR and Video flows is equal to 40 s and 1 s, respectively; nevertheless, with D-TSN, no deadline miss are experienced. In fact, the maximum e2eDelays of LiDAR and Ultrasonic flows are always lower than their relative deadlines. Moreover, the two approaches obtained the same maximum e2eDelay values for the ED traffic (i.e., the ADAS sensors flows) and similar maximum e2eDelays values for the Video flow.
Summarizing, although D-TSN is able to serve jitter-sensitive flows without deadline miss, it is evident that the EDF schedule cannot avoid jitter, whereas D-ST offers a null jitter to ST flows at the expense of a negligible delay increase for the periodic RT flows.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposed D-ST, a solution that combines the flexibility of online EDF scheduling with the temporal isolation offered by the transmission gate mechanism. D-ST is able to satisfy the requirements of all the RT traffic classes typically found in automotive communications while maintaining the full compliance with the IEEE 802.1Q-2018 standard. This property makes D-ST able to support a broad range of automotive applications over TSN networks, without hardware modifications in the Ethernet switches.
Future work will address how to exploit stochastic [62,63,64] and worst-case [39] analysis for admission control to automatically admit new flows in the network or reject them. Furthermore, extensive experiments with commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) devices will be carried on.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L., L.L.B. and G.P.; methodology, L.L., L.L.B. and G.P.; investigation, L.L., L.L.B. and G.P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L., L.L.B. and G.P.; writing—review and editing, L.L., L.L.B. and G.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of Research through the PRIN 2017 Program, Project SPHERE—Software architecture for Predictable HEterogeneous REal-time systems, project number 20172NNB4T.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AbsJitter | Absolute jitter |
| ADAS | Advanced Driver Assistance System |
| ATS | Asynchronous Traffic Shaping |
| AVB | Audio Video Bridging |
| BE | Best-effort |
| CBS | Credit-Based Shaping |
| COTS | Commercial off-the-shelf |
| D-ST | Deadline-ST |
| D-TSN | Deadline-TSN |
| e2eDelay | End-to-end delay |
| ECU | Electronic Control Unit |
| ED | Event-driven |
| EDF | Earliest Deadline First |
| INET | Internet Networking |
| FIFO | First-in first-out |
| IPV | Internal Priority Value |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| MAC | Medium access control |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| NeSTiNg | Network Simulator for Time-Sensitive Networking |
| OMNeT++ | Objective Modular Network Testbed in C++ |
| PSFP | Per-Stream Filtering and Policing |
| RT | Real-time |
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking |
| SID | Stream Identifier |
| SMT | Satisfiability Modulo Theories |
| SP | Strict Priority |
| SR | Stream Reservation |
| ST | Scheduled Traffic |
| TSN | Time-Sensitive Networking |
| TSN-ST | Time-Sensitive Networking with Scheduled Traffic |
| TSpecs | Traffic Specifications |
| VID | VLAN Identifier |
| VLAN | Virtual LAN |
References
- Costa, D.G.; Collotta, M.; Pau, G.; Duran-Faundez, C. A fuzzy-based approach for sensing, coding and transmission configuration of visual sensors in smart city applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, F.; Birgani, O.; Koppelaar, H.; Radenović, S. Using fuzzy logic to improve the project time and cost estimation based on Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 3, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannizzotto, G.; La Rosa, F.; Lo Bello, L. A wireless sensor network for distributed autonomous traffic monitoring. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Human System Interaction, Rzeszow, Poland, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, S. Semantic interoperability between IEC 61850 and oneM2M for IoT-enabled smart grids. Sensors 2021, 21, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajjaj, S.; El Houssaini, S.; Hain, M.; El Houssaini, M.A. Performance Assessment and Modeling of Routing Protocol in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Using Statistical Design of Experiments Methodology: A Comprehensive Study. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Leonardi, L.; Lo Bello, L. A Novel MAC Protocol for Low Datarate Cooperative Mobile Robot Teams. Electronics 2020, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, S.; Rahman, M.; Fawad. A Comprehensive Survey of Digital Twins and Federated Learning for Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Internet of Vehicles (IoV) and Internet of Drones (IoD). Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, E.; Lo Bello, L. Cross-channel interference in IEEE 802.15.4 networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS 2008), Dresden, Germany, 21–23 May 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Fedullo, T.; Tramarin, F.; Vitturi, S. The impact of rate adaptation algorithms on wi-fi-based factory automation systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Lo Bello, L. A priority-aware multichannel adaptive framework for the IEEE 802.15.4e-LLDN. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6360–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Alderisi, G.; Lo Bello, L. Introducing multi-level communication in the IEEE 802.15.4e protocol: The MultiChannel-LLDN. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Emerging Technology and Factory Automation (ETFA 2014), Barcelona, Spain, 16–19 September 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Daoud, R.M.; Amer, H.H.; Elsayed, H.M.; Sallez, Y. Fault-Tolerant Ethernet-Based Vehicle On-Board Networks. In Proceedings of the IECON 2006—32nd Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics, Paris, France, 6–10 November 2006; pp. 4662–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurst, F.; Dasari, D.; Hamann, A.; Ziegenbein, D.; Sanudo, I.; Capodieci, N.; Bertogna, M.; Burgio, P. System performance modelling of heterogeneous hw platforms: An automated driving case study. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Kallithea, Greece, 28 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- ARINC 664 P7; Aircraft Data Network, PART 7 Avionics Full-Duplex Switched Ethernet Network. Aeronautical Radio. Inc.: Annapolis, MD, USA, 2009.
- AS6802; Time-Triggered Ethernet Standard AS6802. SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.sae.org/standards/content/as6802 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Ferrari, P.; Sisinni, E.; Bellagente, P.; Rinaldi, S.; Pasetti, M.; de Sá, A.O.; Machado, R.C.; Carmo, L.F.d.C.; Casimiro, A. Model-based stealth attack to networked control system based on real-time Ethernet. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 7672–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashjaei, M.; Mubeen, S.; Lundbäck, J.; Gålnander, M.; Lundbäck, K.L.; Nolte, T. Modeling and Timing Analysis of Vehicle Functions Distributed over Switched Ethernet. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017-43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 8419–8424. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenzano, A.; Caponetto, R.; Lo Bello, L.; Mirabella, O. Fuzzy traffic smoothing: An approach for real-time communication over Ethernet networks. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS 2002), Vasteras, Sweden, 28–30 August 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Bello, L.; Kaczynski, G.A.; Mirabella, O. Improving the real-time behavior of Ethernet networks using traffic smoothing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2005, 1, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 802.1AS-2011; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications in Bridged Local Area Networks. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011.
- 802.1Qat-2010; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks Amendment 14: Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP). IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010.
- 802.1Qav-2009; IEEE Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks Amendment 12: Forwarding and Queuing Enhancements for Time-Sensitive Streams. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; p. C1-72.
- 802.1Q-2014; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks, Bridges and Bridged Networks. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014.
- 802.1AS-2020 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.1AS-2011); IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–421. [CrossRef]
- 802.1Qbv-2016; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Bridges and Bridged Networks-Amendment 25: Enhancements for Scheduled Traffic. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [CrossRef]
- 802.1Qci-2017; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Bridges and Bridged Networks–Amendment 28: Per-Stream Filtering and Policing. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–65. [CrossRef]
- 802.1Q-2018; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Bridges and Bridged Networks. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018.
- 802.1Qcc-2018; IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan Area Networks—Bridges and Bridged Networks-Amendment 31: Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) Enhancements and Performance Improvements. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018.
- Patti, G.; Lo Bello, L.; Leonardi, L. Deadline-Aware Online Scheduling of TSN Flows for Automotive Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberle, M.; Heimgaertner, F.; Loehr, H.; Nayak, N.; Grewe, D.; Schildt, S.; Menth, M. Softwarization of Automotive E/E Architectures: A Software-Defined Networking Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference (VNC), New York, NY, USA, 16–18 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, L.; Lo Bello, L.; Patti, G. Bandwidth partitioning for Time-Sensitive Networking flows in automotive communications. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 3258–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Bello, L.; Patti, G.; Vasta, G. Assessments of Real-Time Communications over TSN Automotive Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 802.1Qcr-2020; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Bridges and Bridged Networks-Amendment 34:Asynchronous Traffic Shaping. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–151. [CrossRef]
- Thiele, D.; Ernst, R. Formal worst-case performance analysis of time-sensitive Ethernet with frame preemption. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 21st International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujosa, D.; Ashjaei, M.; Papadopoulos, A.; Proenza, J.; Nolte, T. LETRA: Mapping Legacy Ethernet-Based Traffic into TSN Traffic Classes. In Proceedings of the 2021 26th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Vasteras, Sweden, 7 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Patti, G.; Alderisi, G.; Lo Bello, L. SchedWiFi: An innovative approach to support scheduled traffic in ad-hoc industrial IEEE 802.11 networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA 2015), Luxembourg, 8–11 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Wan, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Gu, M. Online Scheduling for Dynamic VM Migration in Multicast Time-Sensitive Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 3778–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedullo, T.; Morato, A.; Tramarin, F.; Rovati, L.; Vitturi, S. A Comprehensive Review on Time Sensitive Networks with a Special Focus on Its Applicability to Industrial Smart and Distributed Measurement Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Bello, L.; Ashjaei, M.; Patti, G.; Behnam, M. Schedulability analysis of Time-Sensitive Networks with scheduled traffic and preemption support. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 144, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, A.A.; Hamad, G.B.; Mohamed, O.A. Routing and Scheduling of Time-Triggered Traffic in Time-Sensitive Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 4525–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.A.; Ayaz, S.; Leinmüller, T.; Chandra, M. Dynamic Scheduling and Routing for TSN based In-vehicle Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlk, M.; Brejchová, K.; Hanzálek, Z.; Tang, S. Large-scale periodic scheduling in time-sensitive networks. Comput. Oper. Res. 2022, 137, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, T.; Meyer, P.; Korf, F.; Schmidt, T.C. Software-defined networks supporting time-sensitive in-vehicular communication. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 89th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Spring), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28 April–1 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Shah, N.; Amin, R.; Alshamrani, S.S.; Alotaibi, A.; Raza, S.M. Software-defined networking: Categories, analysis, and future directions. Sensors 2022, 22, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, S.; Risso, F. Transforming a traditional home gateway into a hardware-accelerated SDN switch. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 10, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, S.H.; Zeebaree, S.; Saeed, R.H.; Ameen, S.Y.; Shukur, H.M.; Omar, N.; Sadeeq, M.A.; Ageed, Z.S.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Yasin, H.M. Comparison of software defined networking with traditional networking. Asian J. Res. Comput. Sci. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, L.; Lo Bello, L.; Aglianò, S. Priority-based bandwidth management in virtualized software-defined networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wan, H.; Zhao, X. Flow Scheduling for Conflict-Free Network Updates in Time-Sensitive Software-Defined Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, N.G.; Dürr, F.; Rothermel, K. Incremental Flow Scheduling and Routing in Time-Sensitive Software-Defined Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, J.; Samii, S. Synthesis of Queue and Priority Assignment for Asynchronous Traffic Shaping in Switched Ethernet. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS), Paris, France, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, K.M.; Abbas, M.; Radenović, S. A logarithmic time complexity algorithm for pattern searching using product—Sum property. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 62, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.C.T.; Schneider, B.; Nigam, V. TSNSCHED: Automated Schedule Generation for Time Sensitive Networking. In Proceedings of the 2019 Formal Methods in Computer Aided Design (FMCAD), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–25 October 2019; pp. 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtan, B.; Ashjaei, M.; Daneshtalab, M.; Sjödin, M.; Mubeen, S. Synthesising Schedules to Improve QoS of Best-Effort Traffic in TSN Networks. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems, Association for Computing Machinery. Nantes, France, 7–9 April 2021; RTNS’2021. pp. 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Hu, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, M.; Li, Z. A Hybrid Traffic Scheduling Strategy for Time-Sensitive Networking. Electronics 2022, 11, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; He, X.; Wu, J.; Cao, H.; Dong, L.; Dang, F.; Liu, Y. E-TSN: Enabling Event-triggered Critical Traffic in Time-Sensitive Networking for Industrial Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 42nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Bologna, Italy, 10–13 July 2022; pp. 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, D.; Biondi, A.; Buttazzo, G. Handling Transients of Dynamic Real-Time Workload Under EDF Scheduling. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2019, 68, 820–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMNeT++ Discrete Event Simulator. Available online: http://www.omnetpp.org (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Varga, A. A practical introduction to the OMNeT++ simulation framework. In Recent Advances in Network Simulation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–51. [Google Scholar]
- Houtan, B.; Bergström, A.; Ashjaei, M.; Daneshtalab, M.; Sjödin, M.; Mubeen, S. An Automated Configuration Framework for TSN Networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT’21), Valencia, Spain, 10–12 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia, F.; Collotta, M.; Leonardi, L.; Lo Bello, L.; Patti, G. Novel Extensions to Enhance Scalability and Reliability of the IEEE 802.15.4-DSME Protocol. Electronics 2020, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, J.; Hellmanns, D.; Carabelli, B.; Nayak, N.; Dürr, F.; Kehrer, S.; Rothermel, K. NeSTiNg: Simulating IEEE Time-sensitive Networking (TSN) in OMNeT++. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Networked Systems (NetSys), Munich, Germany, 18–21 March 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczynski, G.A.; Lo Bello, L.; Nolte, T. Deriving exact stochastic response times of periodic tasks in hybrid priority-driven soft real-time systems. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (EFTA 2007), Patras, Greece, 25–28 September 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Fontanelli, D.; Greco, L.; Palopoli, L. Optimal resource allocation for stochastic systems performance optimisation of control tasks undergoing stochastic execution times. Int. J. Control. 2022, 95, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.; Lopez, J.; Garcia, M.; Campos, A.; Kim, K.; Lo Bello, L. Pessimism in the stochastic analysis of real-time systems: Concept and applications. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS 2004), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–8 December 2004; pp. 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).