Pulsed Spherical Tokamak—A New Approach to Fusion Reactors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Plasma Current Ramp-Up in a Pulsed ST Reactor
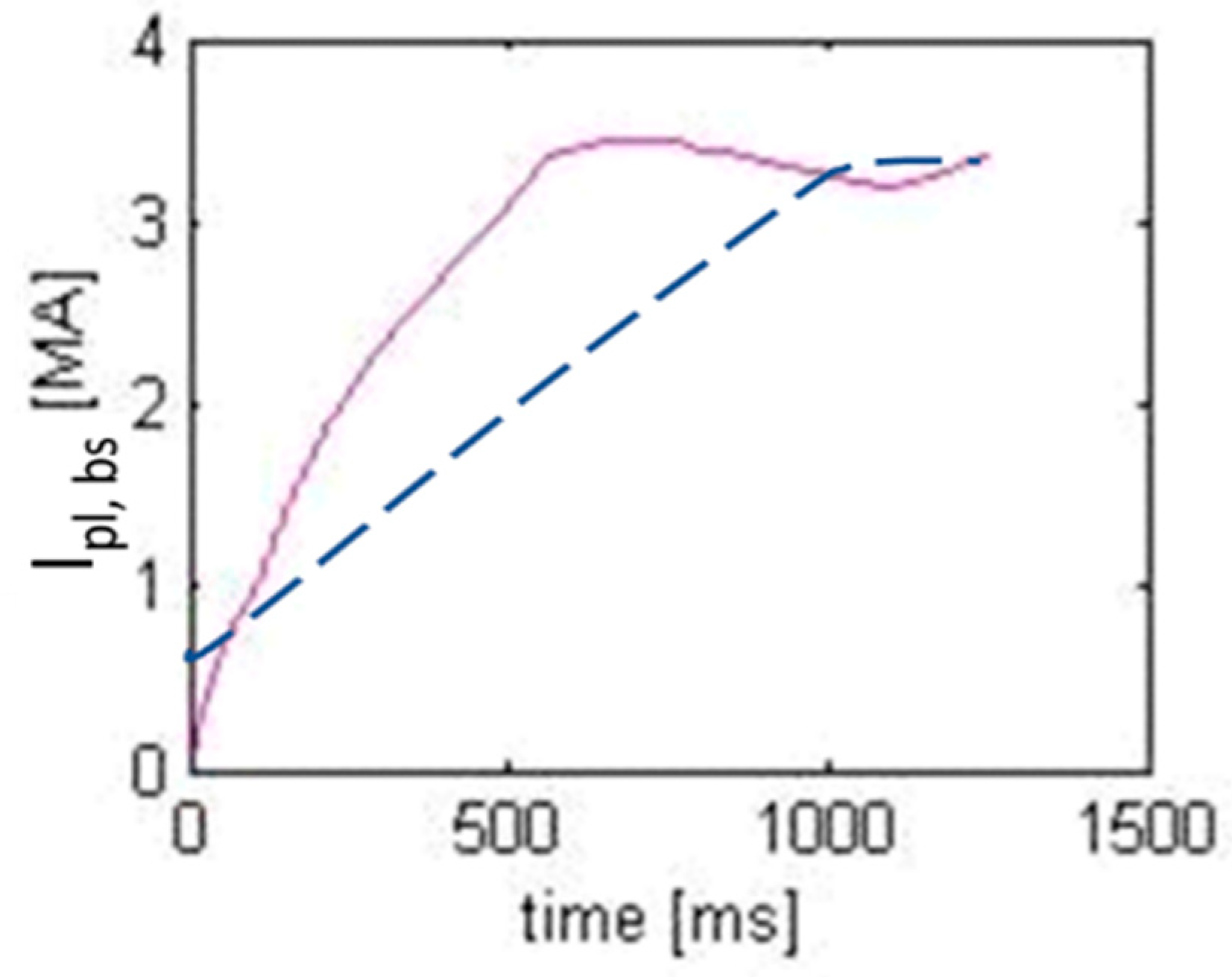
2.1. Previous Studies, Experiments, and Theory
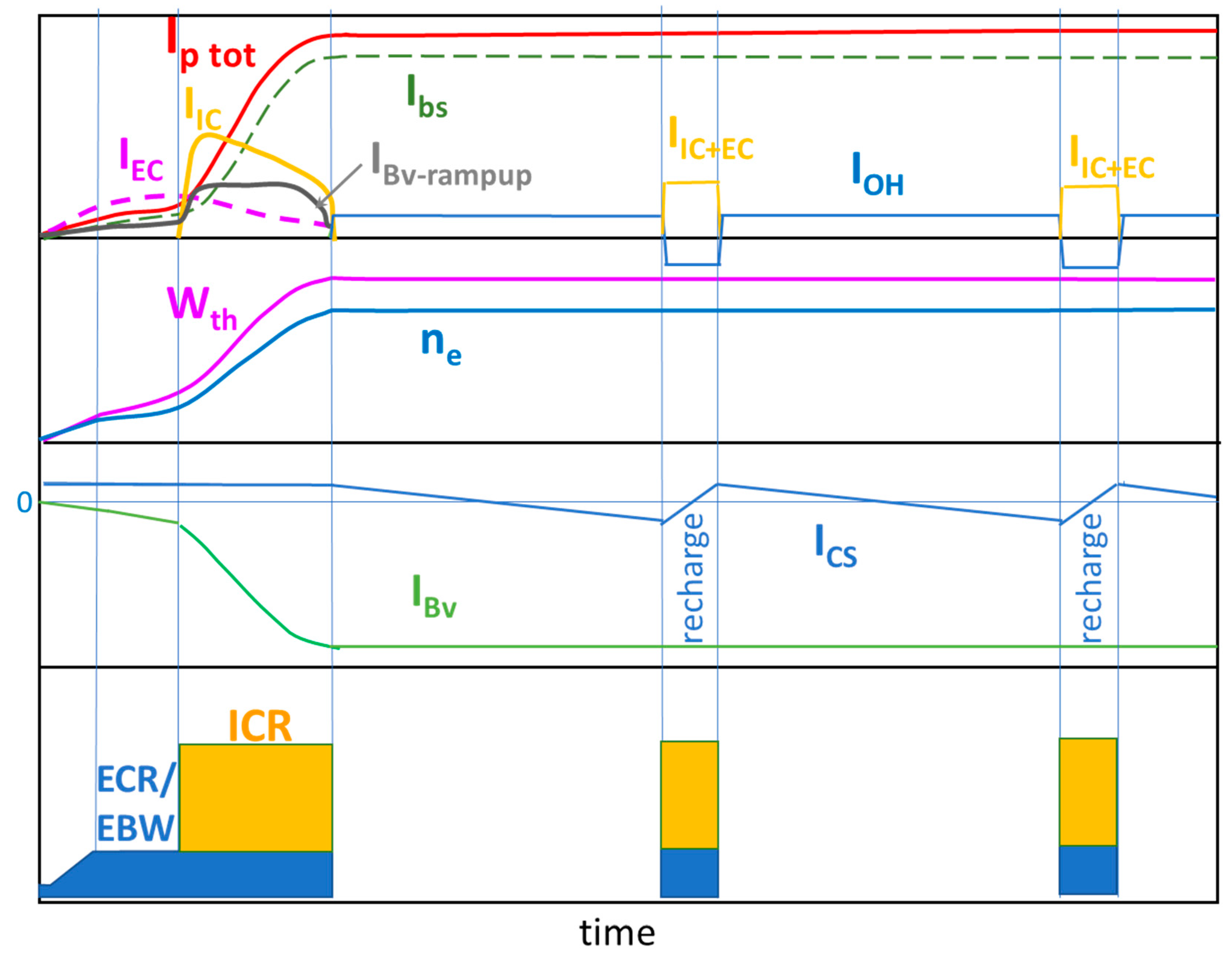
2.2. Possible Scenario and the Main Requirements
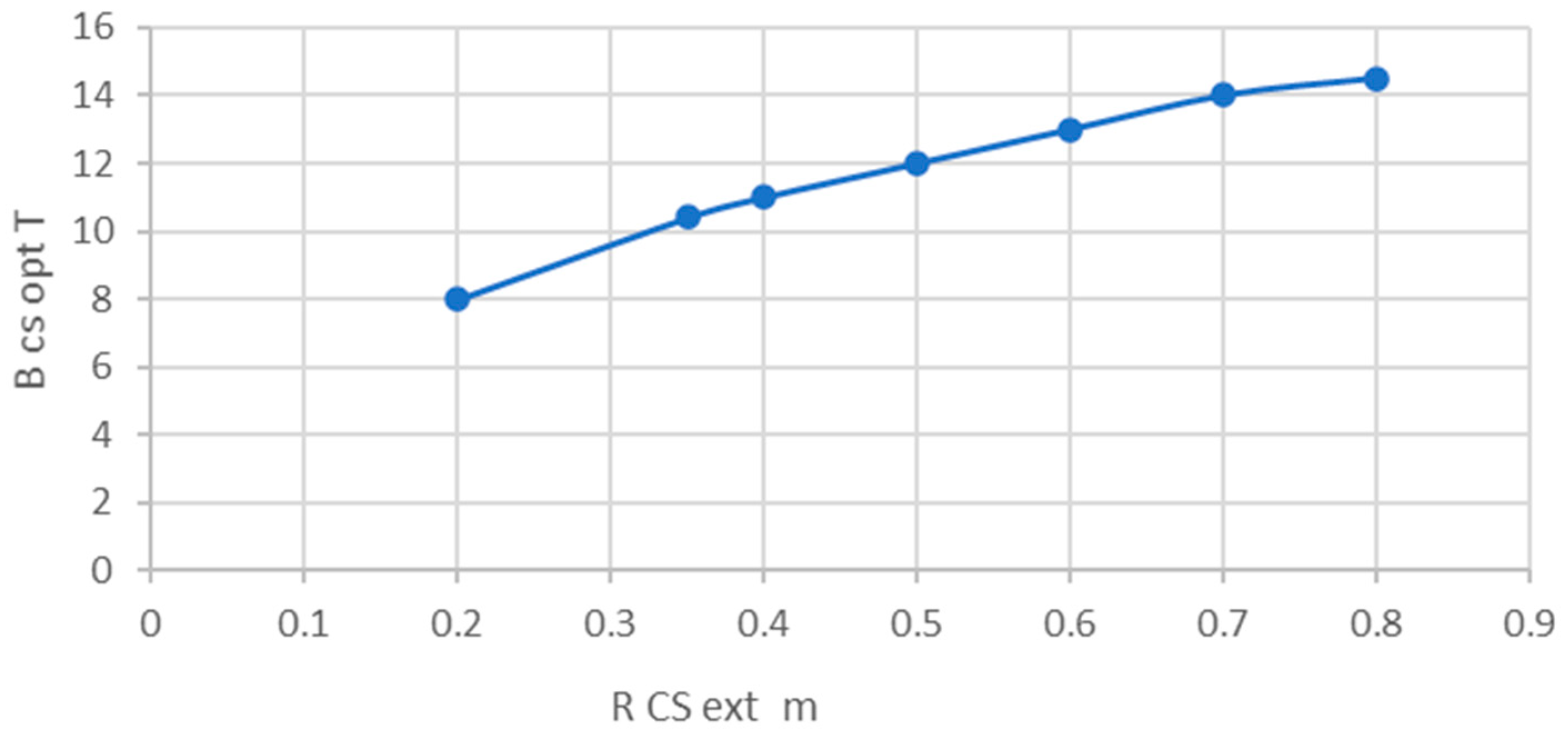
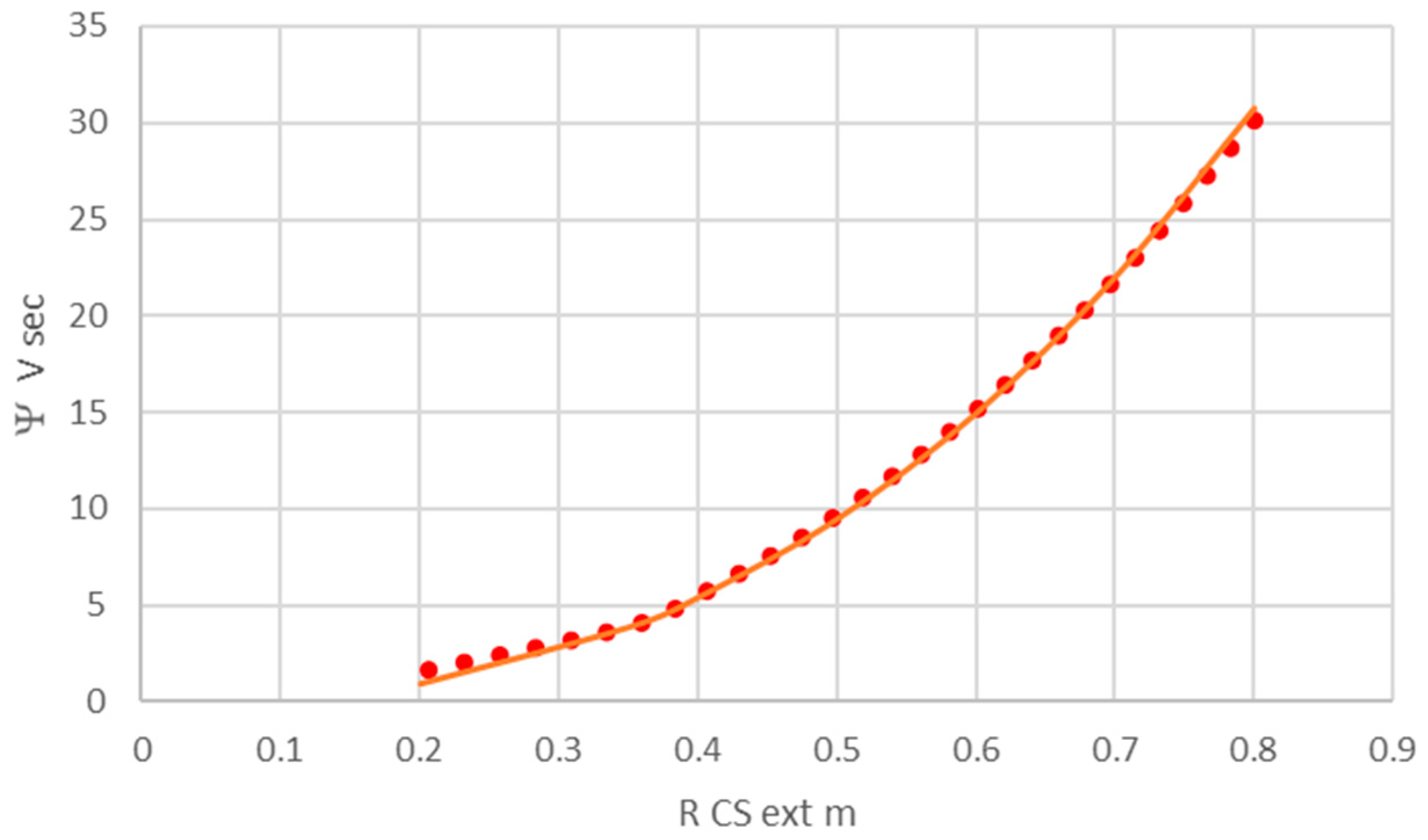
3. Comparison of the Pulsed and Steady-State ST Reactor Options
PVOL = PF/VP MW/m3 secondary inverse cost metric
4. Conclusions
- -
- Reduced need for very expensive non-inductive current drive;
- -
- Lower risk as the steady state operations may have limitations;
- -
- Broader range of possible plasma parameters (not limited by the CD requirements);
- -
- Simpler, faster, and cheaper development path as operations with the CS are well established;
- -
- Possibility to operate at a higher beta;
- -
- Possibility to achieve a higher bootstrap current fraction;
- -
- Stronger increase in the confinement with the toroidal field;
- -
- Better stability, both for -pressure-driven micro instabilities and for the current-driven instabilities.
- -
- Lower requirements on the volt-second capability of the CS due to the ability to reach full plasma current without using the CS.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sykes, A.; Turner, M.F.; Patel, S. Beta Limits in Tokamaks due to High-n Ballooning Modes. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics, Aachen, Germany, 5–9 September 1983; Volume 2, pp. 363–366. Available online: http://libero.ipp.mpg.de/libero/PDF/EPS_11_Vol2_1983.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Sykes, A.; Gryaznevich, M.P.; Kingham, D.; Costley, A.E.; Hugill, J.; Smith, G.; Buxton, P.; Gibson, K.; Wilson, H.R.; Ball, S.; et al. The Spherical Tokamak Path to Fusion Power—Revisited. In Proceedings of the 25th Symposium on Fusion Engineering (SOFE), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 June 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassby, D.L. A Small Aspect-Ratio Torus for Demonstrating Thermonuclear Ignition. In Proceedings of the A Technical Committee Meeting and Workshop on Fusion Reactor Design, Madison, WI, USA, 10–21 October 1977; 1978 IAEA TC-147/9. IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1978. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/09/415/9415687.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Peng, Y.-K.; Strickler, D. Features of spherical torus plasmas. Nucl. Fusion 1986, 26, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambaugh, R.D.; Chan, V.S.; Miller, R.L.; Schaffer, M.J. The Spherical Tokamak Path to Fusion Power. Fusion Technol. 1998, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-M.K.; Hicks, J.B. Engineering Feasibility of Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak Reactors, Fusion Technology. In Proceedings of the 19th Symposium on Fusion Technology, London, UK, 2–6 June 1991; Keen, B.E., Huguet, M., Hemsworth, R., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publisher B.V.: London, UK, 1991; Volume 2, p. 1287. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1022679 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Kikuchi, M. Steady state tokamak reactor based on the bootstrap current. Nucl. Fusion 1990, 30, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmabadi, F. The ARIES Team Spherical torus concept as power plants—The ARIES-ST study. Fusion Eng. Des. 2003, 65, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hender, T.; Bond, A.; Edwards, J.; Karditsas, P.; McClements, K.; Mustoe, J.; Sherwood, D.; Voss, G.; Wilson, H. Spherical tokamak power plant design issues. Fusion Eng. Des. 2000, 48, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, J.; Brown, T.; El-Guebaly, L.; Boyer, M.; Canik, J.; Colling, B.; Raman, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Buxton, P.; et al. Fusion nuclear science facilities and pilot plants based on the spherical tokamak. Nucl. Fusion 2016, 56, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, C.; Kinsey, J.; Holcomb, C.; Deboo, J.; Doyle, E.; Ferron, J.; Garofalo, A.; Hyatt, A.; Jackson, G.; Luce, T.; et al. High-beta, steady-state hybrid scenario on DIII-D. Nucl. Fusion 2015, 56, 016016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oost, G.; Jaspers, R. Thermonuclear Burn Criteria. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2012, 61, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, D.C. Pulsed fusion reactors. Contemp. Phys. 1977, 18, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeschitz, G. An economical viable tokamak fusion reactor based on the ITER experience. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377, 20170433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Inoue, N.; Wang, J.F.; Yamamoto, T.; Yoshida, Z.; Okano, K.; Hatayama, A.; Amano, T. Advanced design of a pulsed tokamak fusion reactor. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research, Seville, Spain, 26 September–1 October 1994; Proceedings Series; IAEA-CN--60/F-P8. International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1995; pp. 803–808, ISBN 92-0-103695-7. Available online: http://www-naweb.iaea.org/napc/physics/FEC/STIPUB948_VOL2.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022), ISSN 0074-1884.
- Segal, D.J.; Cerfon, A.J.; Freidberg, J.P. Steady state versus pulsed tokamak reactors. Nucl. Fusion 2021, 61, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuyanov, V.A.; Gryaznevich, M.P. Modular fusion power plant. Fusion Eng. Des. 2017, 122, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valovič, M.; Akers, R.; Cunningham, G.; Garzotti, L.; Lloyd, B.; Muir, D.; Patel, A.; Taylor, D.; Turnyanskiy, M.; Walsh, M.; et al. Scaling of H-mode energy confinement with Ip and BT in the MAST spherical tokamak. Nucl. Fusion 2009, 49, 075016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, S.; Bell, M.; Bell, R.; Fredrickson, E.; Leblanc, B.; Lee, K.; Lynch, S.; Sabbagh, S. Energy confinement scaling in the low aspect ratio National Spherical Torus Experiment (NSTX). Nucl. Fusion 2006, 46, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, S.M.; Bell, R.E.; Gates, D.; LeBlanc, B.P.; Levinton, F.M.; Menard, J.E.; Mueller, D.; Rewoldt, G.; Sabbagh, S.A.; Wang, W.; et al. Scaling of Electron and Ion Transport in the High-Power Spherical Torus NSTX. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 175002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, P.F.; Connor, J.W.; Costley, A.E.; Gryaznevich, M.P.; McNamara, S. On the energy confinement time in spherical tokamaks: Implications for the design of pilot plants and fusion reactors. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2018, 61, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitarai, O.; Takase, Y. Plasma Current Rampup by the Outer Vertical Field Coils in a Spherical Tokamak Reactor. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2003, 43, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryaznevich, M.; Akers, R.J.; Counsell, G.F.; Cunningham, G.; Dnestrovskij, A.; Field, A.R.; Hender, T.C.; Kirk, A.; Lloyd, B.; Meyer, H.; et al. Next-step-targeted experiments on the Mega-Amp Spherical Tokamak. Phys. Plasmas 2003, 10, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dnestrovskij AYu Tsaun, S.; Gryaznevich, M.; Sykes, A. Bv Ramp up Effect in Spherical Tokamaks. In Proceedings of the 30th European Physical Society Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics, St Petersburg, Russia, 7–11 July 2003; European Conference Abstracts. European Physical Society: Mulhouse, France, 2003; Volume 27A, p. 3.105. Available online: http://ocs.ciemat.es/EPS2003/PDF/P3_105.PDF (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Takase, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Gao, X.; Gryaznevich, M.; Ide, S.; Itoh, S.; Kamada, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Mitarai, O.; Miura, Y.; et al. Plasma Current Start-up. Ramp-up. and Achievement of Advanced Tokamak Plasmas without the Use of Ohmic Heating Solenoid in JT-60U. J. Plasma Fusion Res. 2002, 78, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takase, Y.; Knowlton, S.; Porkolab, M. Plasma Current Ramp-up and Ohmic-Heating Transformer Recharging Experiments using Lower-HybridWaves on a Tokamak. Phys. Fluids 1987, 30, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryaznevich, M.; Shevchenko, V.; Sykes, A. Plasma formation in START and MAST spherical tokamaks. Nucl. Fusion 2006, 46, S573–S583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, S.; Ide, S.; Itoh, S.; Mitarai, O.; Naito, O.; Ozeki, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Takase, Y.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Formation of Advanced Tokamak Plasmas without the Use of an Ohmic-Heating Solenoid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, M.C.R.; Ludwig, G.O. Scaling of bootstrap current on equilibrium and plasma profile parameters in tokamak plasmas. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2008, 50, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, R.; Ludwig, G.O.; Del Bosco, E.; de Andrade, M.C.R.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Mcnamara, B.; Edmonds, E.; Gryaznevich, M.; et al. Physics and Engineering Basis of Multi-Functional Compact Tokamak Reactor Concept. In Proceedings of the 22nd IAEA Conference, Geneva, Switzerland, 13–18 October 2008; FT/P3-20 (IAEA, 2009). Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/43652638 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Gryaznevich, M.P.; Nicolai, A.; Buxton, P. Fast particles in a steady-state compact FNS and compact ST reactor. Nucl. Fusion 2014, 54, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITER Physics Expert Group on Confinement and Transport; ITER Physics Expert Group on Confinement Modelling and Database; ITER Physics Basis Editors. Chapter 2: Plasma confinement and transport. Nucl. Fusion 1999, 39, 2175–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, R.; (Tokamak Energ Ltd, Abingdon, OXON, UK). Private Communication. 2021.
- Gryaznevich, M.P.; Hender, T.C.; Howell, D.F.; Challis, C.D.; Koslowski, H.R.; Gerasimov, S.; Joffrin, E.; Liu, Y.Q.; Saarelma, S.; Contributors, J.-E. Experimental studies of stability and beta limit in JET. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2008, 50, 124030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidberg, J.P.; Mangiarotti, F.J.; Minervini, J. Designing a tokamak fusion reactor—How does plasma physics fit in? Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 070901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gryaznevich, M.; Chuyanov, V.A.; Takase, Y. Pulsed Spherical Tokamak—A New Approach to Fusion Reactors. Plasma 2022, 5, 247-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020019
Gryaznevich M, Chuyanov VA, Takase Y. Pulsed Spherical Tokamak—A New Approach to Fusion Reactors. Plasma. 2022; 5(2):247-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleGryaznevich, Mikhail, Valery A. Chuyanov, and Yuichi Takase. 2022. "Pulsed Spherical Tokamak—A New Approach to Fusion Reactors" Plasma 5, no. 2: 247-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020019
APA StyleGryaznevich, M., Chuyanov, V. A., & Takase, Y. (2022). Pulsed Spherical Tokamak—A New Approach to Fusion Reactors. Plasma, 5(2), 247-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5020019






