Rapid Access to Empirical Impact Ionization Cross Sections for Atoms and Ions across the Periodic Table
Abstract
1. Introduction

2. Empirical Approximations for Modeling Impact Ionization Processes
2.1. Empirical Estimates versus Quantum Many-Electron Computations
2.2. Binary-Encounter Approximations
2.3. Use of Semi-Empirical Models
2.4. Resonant Excitation and Capture Contributions to Electron-Impact Ionization
3. Implementation of Partial and Total Electron-Impact Cross Sections
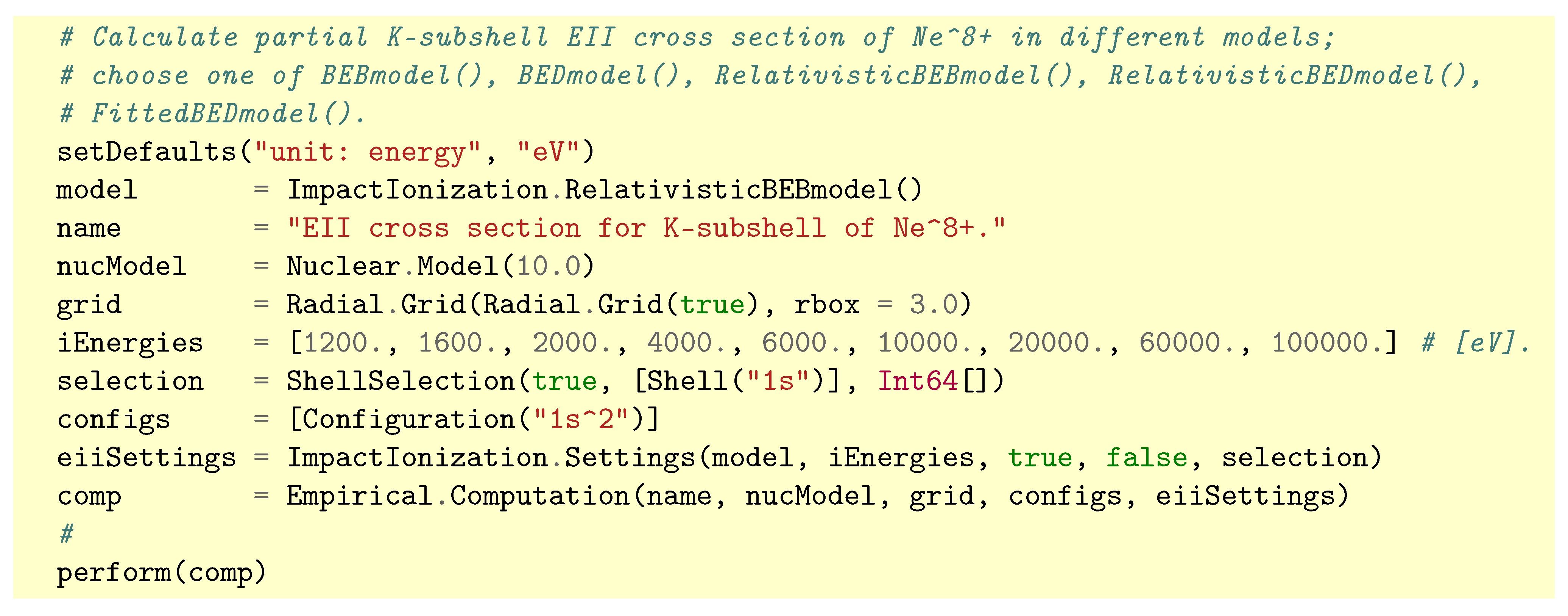
3.1. The Jac Toolbox
3.2. Empirical Estimates of EII Cross Sections within Jac
4. Rapid Access to and Comparison of EII Cross Sections from Different Models
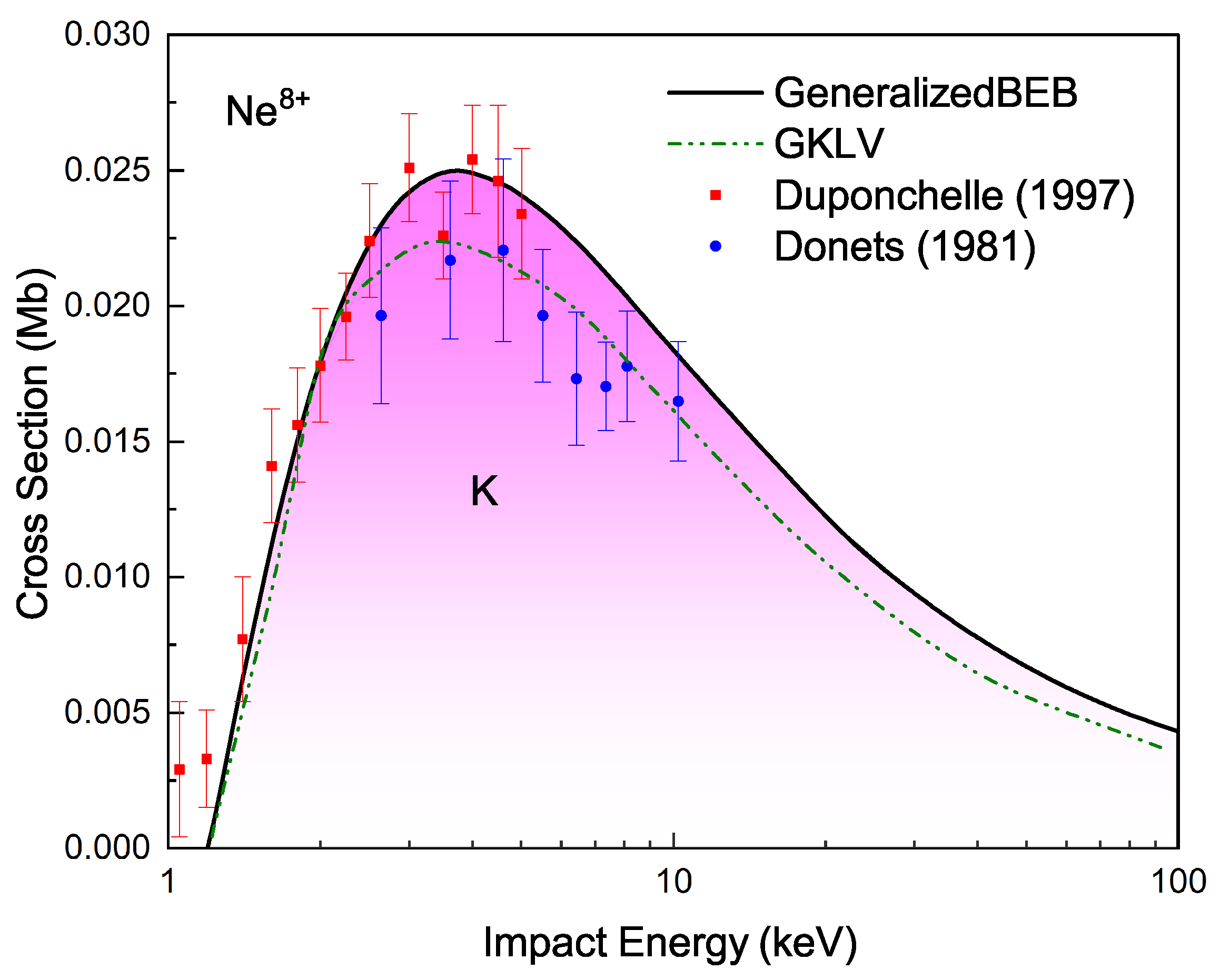
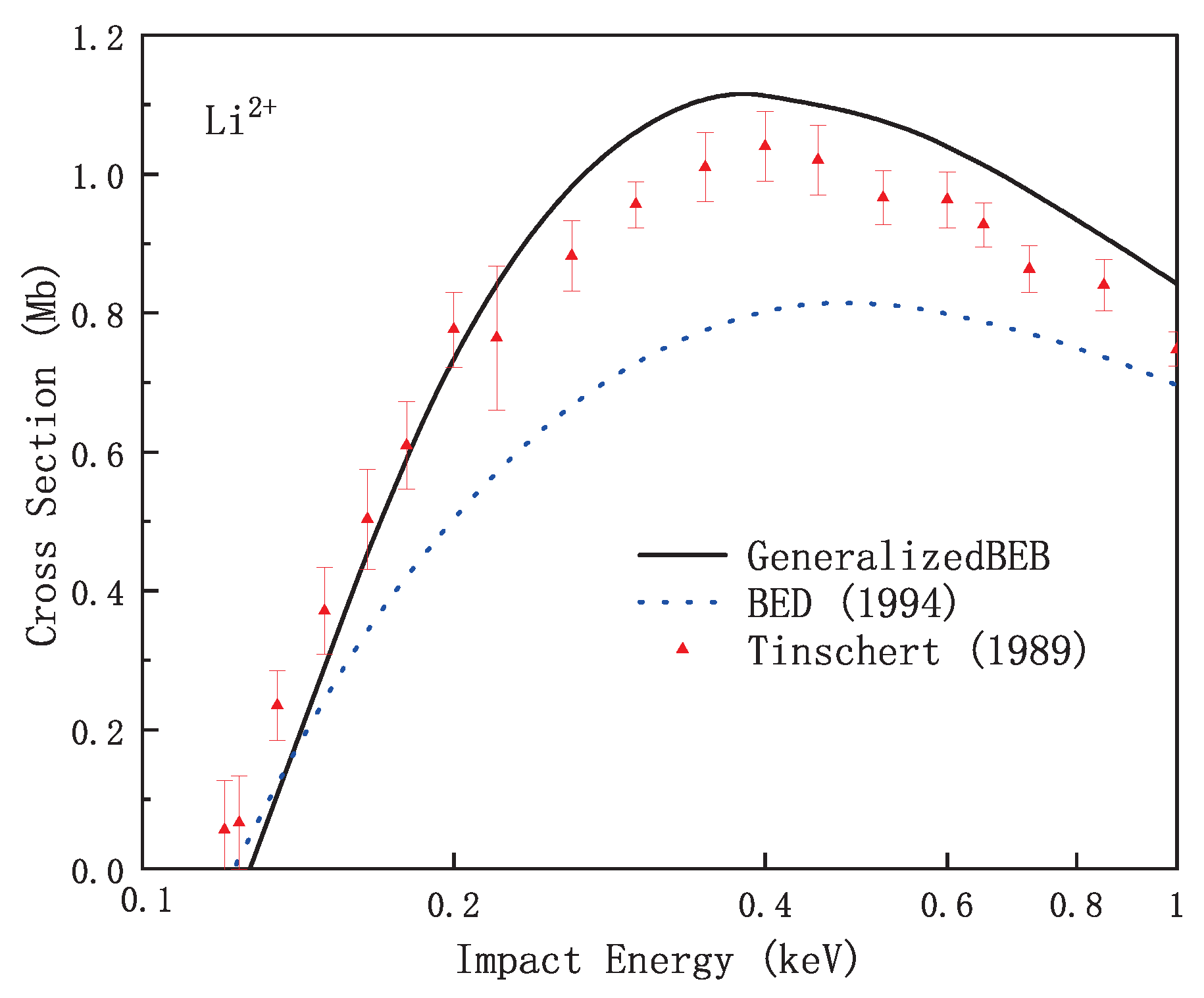
4.1. K-Shell Electron-Impact Ionization of Ions
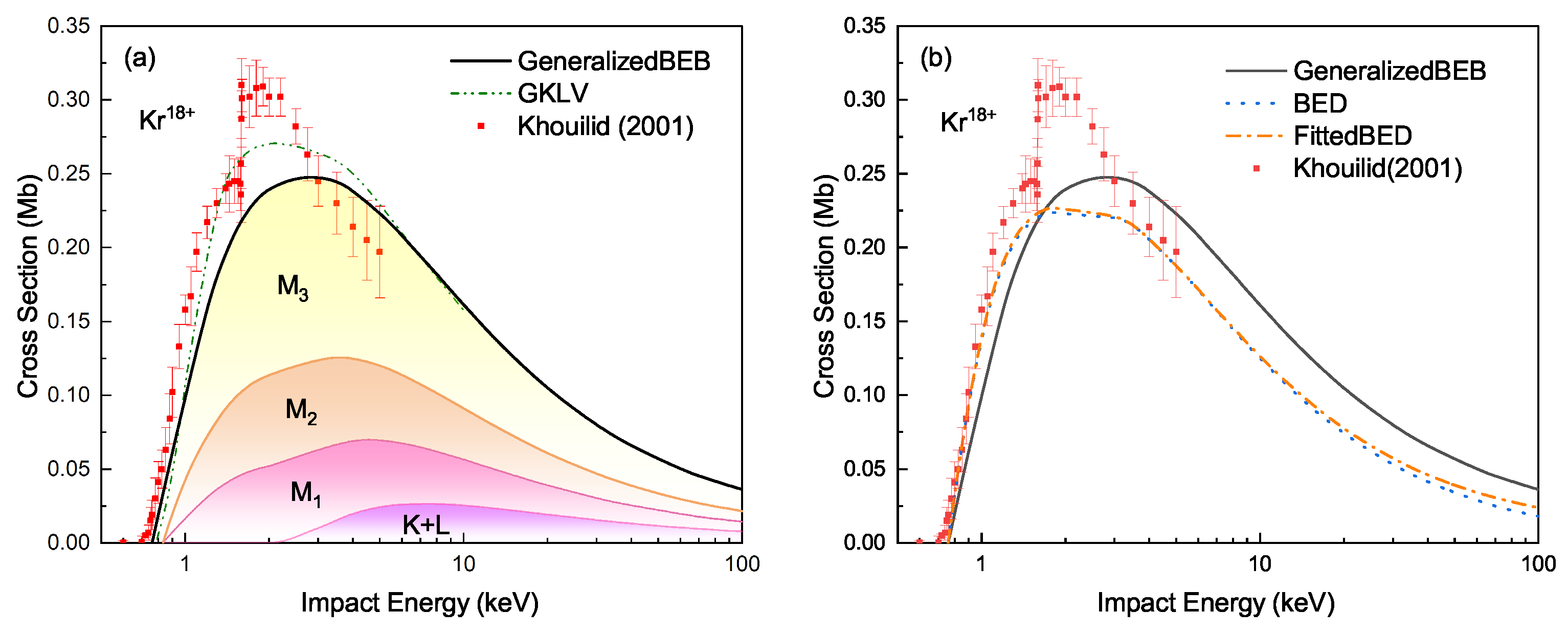
4.2. Partial M-Shell and Total EII Cross Sections for Argon-like Ions
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgess, A.; Chidichimo, M.C. Electron impact ionization of complex ions. Mon. Not. R. Astro. Soc. 1983, 203, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märk, T.D.; Dunn, G.H. (Eds.) Electron Impact Ionization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, P.L.; Stelbovics, A.T. Calculation of electron-impact total-ionization cross sections. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 66, 012707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, P.L.; Stelbovics, A.T. Electron-impact ionization cross sections for elements Z=1 to Z=54. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2004, 86, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Jiao, L.G.; Fritzsche, S. Generalized binary-encounter-Bethe model for electron impact ionization of atoms. J. Phys. B, 2023; accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.K.; Santos, J.P.; Parente, F. Extension of the binary-encounter-dipole model to relativistic incident electrons. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 62, 052710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.A.; Haque, A.K.F.; Billah, M.M.; Basak, A.K.; Karim, K.R.; Saha, B.C. Computation of electron-impact K-shell ionization cross sections of atoms. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 71, 032715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.K.F.; Uddin, M.A.; Shahjahan, M.; Talukder, M.R.; Basak, A.K.; Saha, B.C. Electron impact inner-shell ionization of atoms. Adv. Quantum Chem. 2011, 61, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Bartschat, K.; Burke, P.G. The R-matrix method for electron impact ionisation. J. Phys. B 1987, 20, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Schultz, D.R. Time-dependent close-coupling method for electron-impact ionization of hydrogen. Phys. Rev. A 1996, 53, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S. A fresh computational approach to atomic structures, processes and cascades. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2019, 240, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, I.P. Relativistic Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules: Theory and Computation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lotz, W. Electron-impact ionization cross-sections for atoms up to Z = 108. Z. Phys. 1970, 232, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, P.L.; Stelbovics, A.T. Electron-helium S-wave model benchmark calculations. I. Single ionization and single excitation. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 022715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, S.M. Distorted-wave electron-impact-ionization cross sections for highly ionized neonlike atoms. Phys. Rev. A 1981, 23, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.C.; Pindzola, M.S. Distorted-wave calculations of electron impact ionisation in the Ni isonuclear sequence. J. Phys. B 1988, 21, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badnell, N.R. A Breit-Pauli distorted wave implementation for Autostructure. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2011, 182, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Badnell, N.R.; Del Zanna, G. R-matrix electron-impact excitation data for the C-like iso-electronic sequence. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 634, A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K. Scaling of plane-wave Born cross sections for electron-impact excitation of neutral atoms. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 64, 032713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.J. XLII. Ionization by moving electrified particle. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1912, 23, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.H. The calculation of atomic fields. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1927, 73, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriens, L. Binary-encounter proton-atom collision theory. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1967, 90, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbenstvedt, H. Simple theory for K-Ionization by relativistic electrons. J. Appl. Phys. 1967, 38, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Rudd, M.E. Binary-encounter-dipole model for electron-impact ionization. Phys. Rev. A 1994, 50, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.L.; Gilbody, H.B.; Hughes, J.G.; Kingston, A.E.; Smith, F.J. Recommended data on the electron impact ionization of light atoms and ions. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2008, 41, 095204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.; Parente, F.; Indelicato, P.; Santos, J.P. Modified binary encounter Bethe model for electron-impact ionization. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 1–7, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriens, L.; Smeets, A.H.M. Cross-section and rate formulas for electron-impact ionization, excitation, deexcitation and total depopulation of excited atoms. Phys. Rev. A 1980, 22, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethe, H. Zur Theorie des Durchgangs schneller Korpuskularstrahlen durch Materie. Ann. Phys. 1930, 5, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J. Absolute cross sections for molecular photoabsorption, partial photoionization, and ionic photofragmentation processes. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patoary, M.A.R.; Haque, A.K.F.; Hossain, M.I.; Hosain, M.E.; Uddin, M.A.; Basak, A.K.; Haque, M.M.; Maaza, M.; Saha, B.C. An analytical model for the electron impact K-shell ionization cross sections of atoms. Int. J. Mass Spec. 2017, 415, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.M. Convergent series representation for the generalized oscillator strength of electron-impact ionization and an improved binary-encounter-dipole model. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 64, 042719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.A.; Fazlul Haque, M.A.K.; Basak, A.K.; Saha, B.C. Calculations of electron-impact single-ionization cross sections of helium isoelectronic systems. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 032706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, S.; Martins, M.; Beerwerth, R.; Bari, S.; Holste, K.; Schubert, K.; Viefhaus, J.; Savin, D.W.; Fritzsche, S.; Müller, A. Near L-edge single and multiple photoionization of singly charged iron ions. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerwerth, R.; Buhr, T.; Perry-Sassmannshausen, A.; Stock, S.O.; Bari, S.; Holste, K.; Kilcoyne, A.L.D.; Reinwardt, S.; Ricz, S.; Savin, D.W.; et al. Near L-edge single and multiple photoionization of triply charged iron ions. Astrophys. J. 2019, 887, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Surzhykov, A.; Srivastava, R.; Fritzsche, S. Electron-impact excitation of singly charged metal ions. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 062701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.W.; Tian, Z.Q.; Dong, C.Z.; Surzhykov, A.; Fritzsche, S. Hyperfine-induced effects on Kα1 linear polarization following electron-impact excitation of helium-like Tl79+ ions with nuclear spin I=1/2. New J. Phys. 2023, 25, 093039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S. The Ratip program for relativistic calculations of atomic transition, ionization and recombination properties. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Griffin, D.C.; Bottcher, C. Electron-impact excitation autoionization of Ga II. Phys. Rev. A 1982, 25, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakalka, S.; Kucas, S.; Masys, S.; Kyniene, A.; Momkauskaite, A.; Jonauskas, V. Electron-impact single ionization of the Se3+ ion. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 012708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S.; Palmeri, P.; Schippers, S. Atomic cascade computations. Symmetry 2021, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S. Application of symmetry-adapted atomic amplitudes. Atoms 2022, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S. JAC: User Guide, Compendium & Theoretical Background. Available online: https://github.com/OpenJAC/JAC.jl (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Available online: https://docs.julialang.org (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Bezanson, J.; Chen, J.; Chung, B.; Karpinski, S.; Shah, V.B.; Vitek, J.; Zoubritzky, J. Julia: Dynamism and performance reconciled by design. Proc. ACM Program. Lang. 2018, 2, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, T. Hands-On Design Patterns and Best Practices with Julia; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche, S. Level structure and properties of open f-shell elements. Atoms 2022, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S.; Maiorova, A.V.; Wu, Z.W. Radiative recombination plasma rate coefficients for multiply charged ions. Atoms 2023, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S. Dielectronic recombination strengths and plasma rate coefficients of multiply charged ions. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 656, A163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S.; Surzhykov, A. Approximate atomic Green functions. Molecules 2021, 26, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S. Symbolic evaluation of expressions from Racah’s algebra. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprince, J.; Bautista, M.A.; Fritzsche, S.; Garcia, J.; Kallman, T.R.; Mendoza, C.; Palmeri, P.; Quinet, P. Plasma environment effects on K lines of astrophysical interest. I. Atomic structure, radiative rates, and Auger widths of oxygen ions. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 624, A74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.K.F.; Atiqur, M.; Patoary, R.; Uddin, M.A.; Basak, A.K.; Saha, B.C. Electron Impact Atomic and Ionic Ionization: Analytical, Semiempirical, and Semiclassical Methods. Adv. Quantum Chem. 2016, 73, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donets, E.D.; Ovsyannikov, V.P. Investigation of ionization of positive ions by electron impact. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1981, 80, 916. [Google Scholar]
- Colgan, J.; Fontes, C.J.; Zhang, H.L. Inner-shell electron-impact ionization of neutral atoms. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 062711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecointre, J.; Jureta, J.J.; Defrance, P. Electron-impact ionization of singly-charged neon ions. J. Phys. B 2008, 41, 095204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duponchelle, M.; Khouilid, M.; Oualim, E.M.; Zhang, H.; Defrance, P. Electron-impact ionization of neon ions (q = 4–8). J. Phys. B 1997, 30, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinschert, K.; Müller, A.; Hofmann, G.; Huber, K.; Becker, R.; Gregory, D.C.; Salzborn, E. Experimental cross sections for electron impact ionisation of hydrogen-like Li2+ ions. J. Phys. B 1989, 22, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouilid, M.; Cherkani-Hassani, S.; Rachafi, S.; Teng, H.; Defrance, P. Electron-impact single ionization of krypton ions (q = 12–18). J. Phys. B 2001, 34, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S.; Jiao, L.-G.; Wang, Y.-C.; Sienkiewicz, J.E. Collision Strengths of Astrophysical Interest for Multiply Charged Ions. Atoms 2023, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrance, P. Recommended data for electron impact ionization of noble gas ions. Nucl. Fusion Suppl. 1995, 6, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Blanke, J.H.; Fricke, B.; Finkbener, M. Database Plasmarelevante Atomare Daten; University of Kassel: Kassel, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]


| Model | Features and Limitations |
|---|---|
| Generalized binary-encounter Bethe (BEB): | suitable for non-relativistic and relativistic impact energies and most not-too-heavy elements. This model is parameter-free and easy to use [5] and expands the EII cross sections of Kim and coworkers [6,19]. It is often applied to light and medium elements with , as well as to the EII of (sub-)valence shells. The relativistic version of this model is suggested for impact energies keV; ImpactIonization.BEBmodel, ImpactIonization.RelativisticBEBmodel. |
| Binary-encounter-dipole (BED): | a modified BEB model following the studies of Huo [31] and Uddin and coworkers [32]. Again, this model is suitable for both non-relativistic and relativistic impact energies, but is based especially on fit parameters; ImpactIonization.BEDmodel, RelativisticBEDmodel. |
| Parameter-dependent (fitted) BED: | another modified BEB model due to Haque and coworkers [8,30]. This model can be applied to a good range of impact energies by making use of different fit coefficients for the K-, L- and M-subshells. It incorporates certain ionic and relativistic corrections and has been applied successfully up to ultra-high energies 2 GeV for atomic targets with nuclear charge ; ImpactIonization.FittedBEDmodel. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fritzsche, S.; Jiao, L.; Visentin, G. Rapid Access to Empirical Impact Ionization Cross Sections for Atoms and Ions across the Periodic Table. Plasma 2024, 7, 106-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma7010008
Fritzsche S, Jiao L, Visentin G. Rapid Access to Empirical Impact Ionization Cross Sections for Atoms and Ions across the Periodic Table. Plasma. 2024; 7(1):106-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleFritzsche, Stephan, Liguang Jiao, and Giorgio Visentin. 2024. "Rapid Access to Empirical Impact Ionization Cross Sections for Atoms and Ions across the Periodic Table" Plasma 7, no. 1: 106-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma7010008
APA StyleFritzsche, S., Jiao, L., & Visentin, G. (2024). Rapid Access to Empirical Impact Ionization Cross Sections for Atoms and Ions across the Periodic Table. Plasma, 7(1), 106-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma7010008






