A Method for Analyzing the Effectiveness of Vibration-Reducing Gloves Based on Vibration Power Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Model
2.2. Calculations of System Responses and Vibraton Transmissibility
2.3. Calculation of Vibration Power Absorption
Ck = C0, C1, C2, C3, C4, Ca, Cg1, Cg2, Cg3, Cg4, Cg5, Cg6, and CHandle
3. Results and Discussion
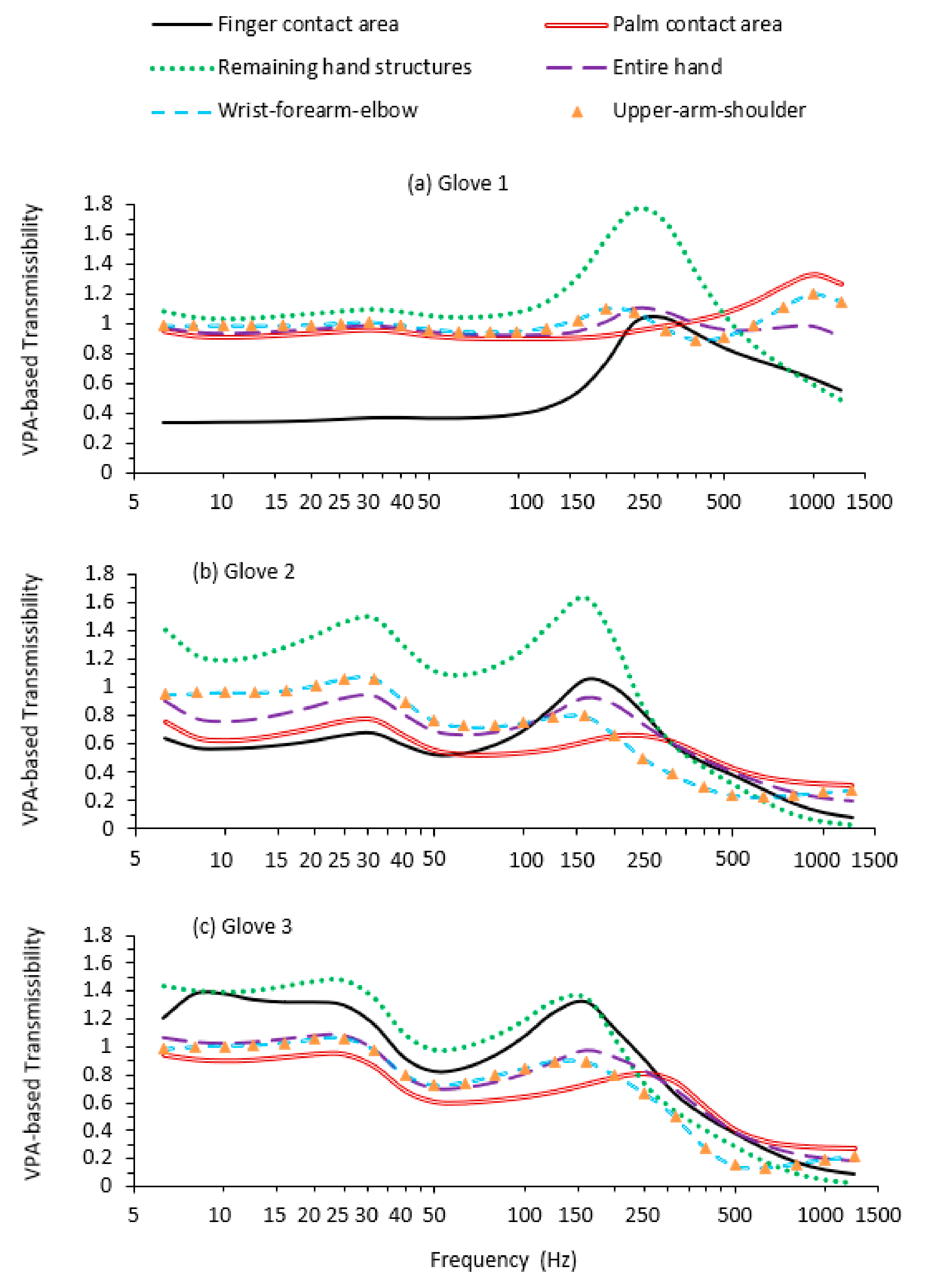
3.1. Distributions of Vibration Power Absorption (VPA)
3.2. The VPA-Based Glove Vibration Transmissibility Spectra
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
Appendix A
= [C1∙(VM0_GH − VM1_GH)2]/[C1∙(VM0_BH − VM1_BH)2]
= [(VM1_GH)2∙(VM0_GH/VM1_GH−1)2]/[(VM1_BH)2∙(VM0_BH/VM1_BH − 1)2]
= [(VM1_GH)2∙(TM0-M1_GH−1)2]/[(VM1_BH)2∙(TM0-M1_BH − 1)2].
= (VM0_GH)2/(VM0_BH)2 = (TOn-M0)2
= (TM0-M1_GH∙VM1_GH)2/(TM0-M1_BH∙VM1_BH)2
= (VM1_GH)2/(VM1_BH)2 = RWrist-forearm-elbow.
References
- Brown, A.P. The effects of anti-vibration gloves on vibration induced disorders: A case study. J. Hand Ther. 1990, 3, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetzer, T.; Haydon, P.; Reynolds, D.D. Effective intervention with ergonomics, antivibration gloves, and medical surveillance to minimize hand-arm vibration hazards in the workplace. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 45, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HSE 2019. Hand-arm vibration, the control of vibration at work regulations 2005. In Guidance on Regulations; TSO: Norwich, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.G.; McDowell, T.W.; Welcome, D.E.; Wu, J.Z.; Rakheja, S. Analysis of anti-vibration gloves mechanism and evaluation methods. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 321, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10819. Mechanical Vibration and Shock—Hand-Arm Vibration—Measurement and Evaluation of the Vibration Transmissibility of Gloves at the Palm of the Hand; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, D.R.; Peterson, T.; Asaki, S.; Kudernatsch, A.J.; Brammer, M.G.; Cherniack. Incorporating a finger adapter into ISO 10819 assessments to measure the vibration transmissibility of gloves at the fingers. In Proceedings of the 5th American Conference on Human Vibration, Guelph, ON, Canada, 10–13 June 2014; pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.S.; Welcome, D.E.; Warren, C.; McDowell, T.W.; Dong, R.G. Development of a finger adapter method for testing and evaluating vibration-reducing gloves and materials. Measurement 2019, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.J.; Macfarlane, C.R.; Norman, C.D. The transmission of vibration to the hand and the influence of Gloves. In Vibration Effects on the Hand and Arm in Industry; Brammer, A.J., Taylor, W., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Paddan, G.S.; Griffin, M.J. Measurement of glove and hand dynamics using knuckle vibration. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Hand-Arm Vibration 2001, Section 15, Nancy, France, 1 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.H.; Wang, M.J.J.; Lin, S.C. Evaluating the effects of wearing gloves and wrist support on hand-arm response while operating an in-line pneumatic screwdriver. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 1999, 24, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; McDowell, T.W.; Welcome, D.E.; Smutz, W.P.; Schopper, A.W.; Warren, C.; Wu, J.Z.; Rakheja, S. On-the-Hand Measurement Methods for Assessing Effectiveness of Anti-Vibration Gloves. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2003, 32, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcome, D.E.; Dong, R.G.; Xu, X.S.; Warren, C.; McDowell, T.W. The effects of vibration-reducing gloves on finger vibration. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2014, 44, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamouda, K.; Rakheja, S.; Dewangan, K.N.; Marcotte, P. Fingers’ vibration transmission and grip strength preservation performance of vibration reducing gloves. Appl. Ergon. 2018, 66, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.S.; Welcome, D.E.; Warren, C.; McDowell, T.W.; Lin, H.; Xiao, B.; Chen, Q.; Dong, R.G. The vibration responses of a handheld workpiece and the hand arm system. In Proceedings of the 7th American Conference on Human Vibration 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–15 June 2018; pp. 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; Xu, X.S.; McDowell, T.W. An improved vibration model of glove-hand-arm system. In Proceedings of the 8th American Conference on Human Vibration, (Postponed to 2021). [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, T.W.; Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; Warren, C.; Xu, X.S. Vibration-reducing gloves: Transmissibility at the palm of the hand in three orthogonal directions. Ergonomics 2013, 56, 1823–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ISO 5349-1. Mechanical Vibration—Measurement and Evaluation of Human Exposure to Hand-Transmitted Vibration—Part 1: General Requirements; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cundiff, J.S. Energy dissipation in human hand-arm exposed to random vibration. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 59, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidström, I.M. Vibration injury in rock drillers, chiselers, and grinders. Some views on the relationship between the quantity of energy absorbed and the risk of occurrence of vibration injury. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hand-Arm Vibration, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1 January 1977; pp. 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.G.; Schopper, A.W.; McDowell, T.W.; Welcome, D.E.; Wu, J.Z.; Smutz, W.P.; Warren, C.; Rakheja, S. Vibration Energy Absorption (VEA) in Human Fingers-Hand-Arm System. Med. Eng. Phys. 2004, 26, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W.; Wu, J.Z.; Schopper, A.W. Frequency weighting derived from power absorption of fingers-hand-arm system under zh-axis. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2311–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.H.; Dong, R.G.; Rakheja, S.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W.; Wu, J.Z. A method for analyzing absorbed power distribution in the hand and arm substructures when operating vibrating tools. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 311, 1286–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W.; Xu, X.S.; Krajnak, K.; Wu, J.Z. A proposed theory on biodynamic frequency weighting for hand-transmitted vibration exposure. Ind. Health 2012, 50, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
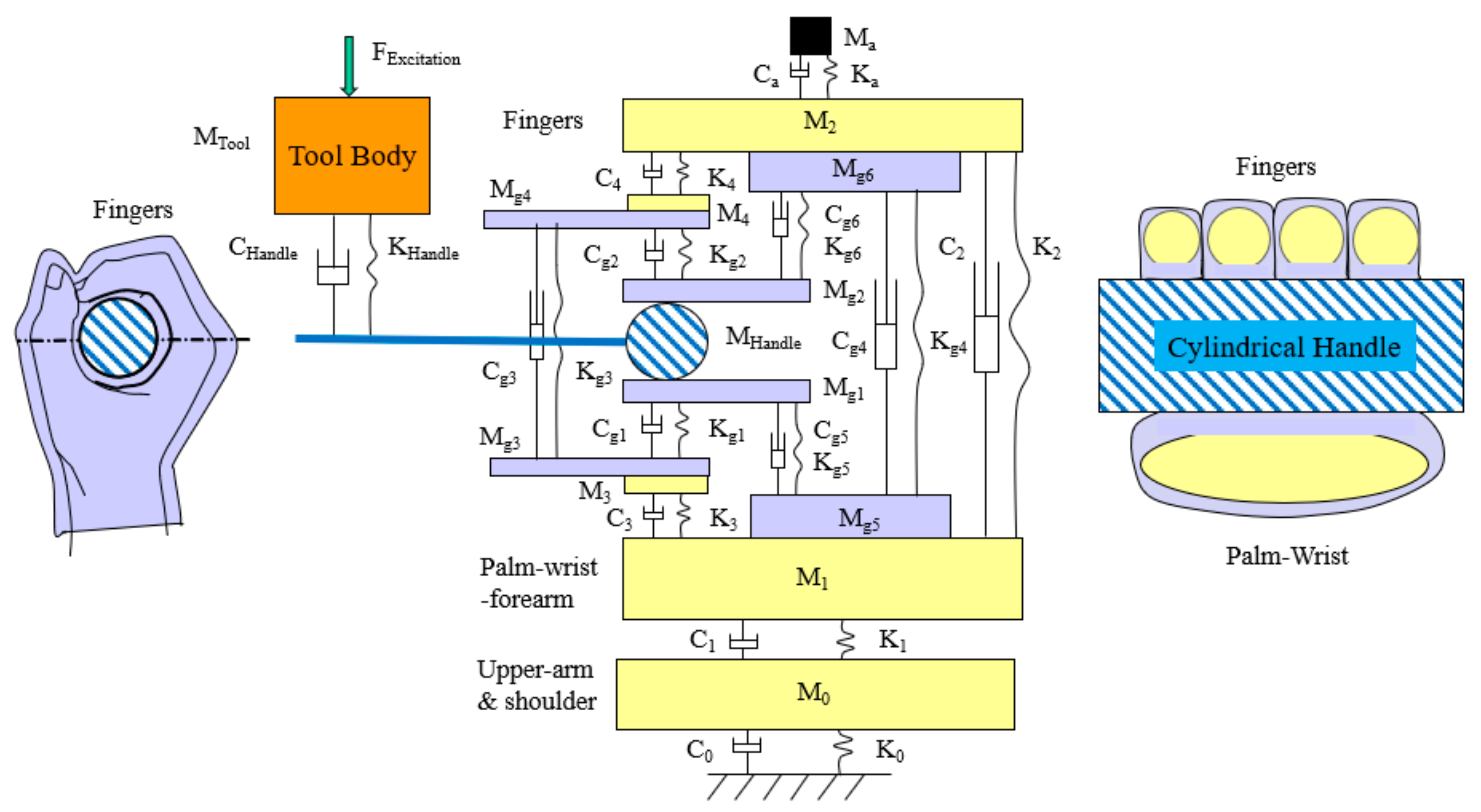


| Tool and Hand–Arm System | Glove-Specific Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID and Unit | Value | ID and Unit | Glove 1 | Glove 2 | Glove 3 |
| M0 (kg) | 5.25 | Mg1 (kg) | 0.0013 | 0.0089 | 0.0071 |
| M1 (kg) | 1.3568 | Mg2 (kg) | 0.0011 | 0.011 | 0.0102 |
| M2 (kg) | 0.0626 | Mg3 (kg) | 0.001 | 0.0035 | 0.001 |
| M3 (kg) | 0.0352 | Mg4 (kg) | 0.0033 | 0.0019 | 0.001 |
| M4 (kg) | 0.0232 | Mg5 (kg) | 0.0335 | 0.1246 | 0.0397 |
| K0 (N/m) | 11,013 | Mg6 (kg) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| K1 (N/m) | 4,054 | Kg1 (N/m) | 2,603,723 | 121,484 | 125,310 |
| K2 (N/m) | 5734 | Kg2 (N/m) | 913,279 | 202,023 | 194,219 |
| C0 (N·s/m) | 13.93 | Kg3 (N/m) | 5000 | 1836 | 3023 |
| C1 (N·s/m) | 86.58 | Kg4 (N/m) | 336 | 0.001 | 736 |
| C2 (N·s/m) | 34.29 | Kg5 (N/m) | 0.001 | 6003 | 0.001 |
| Ma (kg) | 0.0025 | Kg6 (N/m) | 58,016 | 2276 | 0.001 |
| MHandle (kg) | 2.0 | Cg1 (N·s/m) | 284.13 | 48.62 | 15.11 |
| KHandle (N/m) | 1500 | Cg2 (N·s/m) | 271.02 | 40.31 | 34.03 |
| CHandle (N·s/m) | 20.0 | Cg3 (N·s/m) | 0.001 | 11.24 | 3.94 |
| MTool (kg) | 1.0 | Cg4 (N·s/m) | 3.16 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Cg5 (N·s/m) | 7.30 | 56.21 | 49.21 | ||
| Cg6 (N·s/m) | 16.85 | 8.16 | 9.63 | ||
| Parameter Values for Bare Hand (BH) | Parameter Values for Gloved Hand (GH) | ||||
| K3 (N/m) | 40,346 | K3 (N/m) | 40,346 | 40,346 | 42,254 |
| K4 (N/m) | 124,918 | K4 (N/m) | 124,918 | 147,087 | 124,918 |
| C3 (N·s/m) | 96.0 | C3 (N·s/m) | 84.94 | 35.46 | 57.96 |
| C4 (N·s/m) | 92.5 | C4 (N·s/m) | 53.19 | 52.70 | 65.04 |
| Ka (N/m) | 4874 | Ka (N/m) | 5497 | 6365 | 5658 |
| Ca (N·s/m) | 1.64 | Ca (N·s/m) | 2.57 | 4.19 | 3.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, R.G.; Xu, X.S.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W. A Method for Analyzing the Effectiveness of Vibration-Reducing Gloves Based on Vibration Power Absorption. Vibration 2021, 4, 16-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration4010002
Dong RG, Xu XS, Welcome DE, McDowell TW. A Method for Analyzing the Effectiveness of Vibration-Reducing Gloves Based on Vibration Power Absorption. Vibration. 2021; 4(1):16-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration4010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Ren G., Xueyan S. Xu, Daniel E. Welcome, and Thomas W. McDowell. 2021. "A Method for Analyzing the Effectiveness of Vibration-Reducing Gloves Based on Vibration Power Absorption" Vibration 4, no. 1: 16-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration4010002
APA StyleDong, R. G., Xu, X. S., Welcome, D. E., & McDowell, T. W. (2021). A Method for Analyzing the Effectiveness of Vibration-Reducing Gloves Based on Vibration Power Absorption. Vibration, 4(1), 16-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration4010002




