Hadronic Light-by-Light Corrections to the Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. aμ in QFT
2.1. Basics
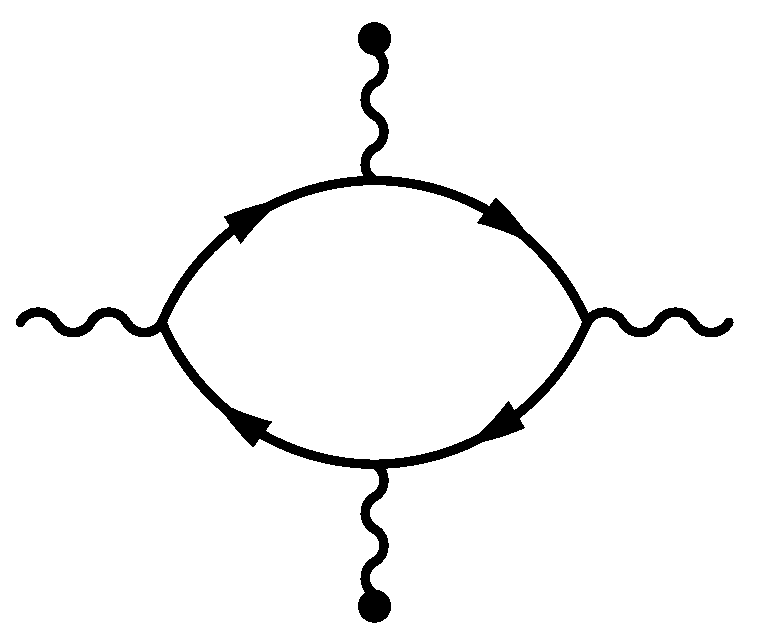
2.2. Specializing to HLbL Scattering Amplitudes
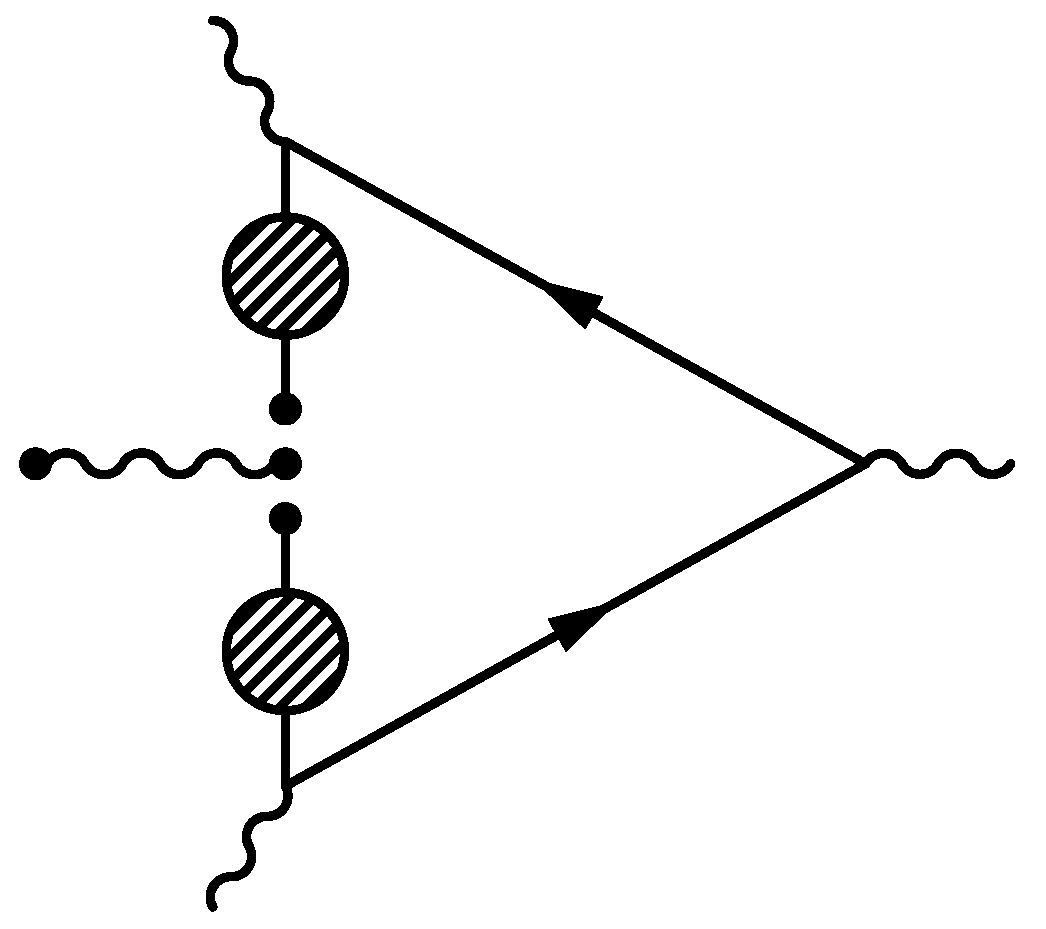
2.3. Dispersive Computation of the HLbL Amplitude
2.3.1. Unitarity of the S-Matrix
2.3.2. Sugawara–Kanazawa Theorem and Schwarz Reflection Identity
- has finite limits in the positive real infinity direction above and below the right-hand cut.
- The limit of in the negative real infinity direction above and below the left-hand cut exists.
- If is divergent in a certain infinite direction, such a divergence is weaker than a polynomial with finite power N such that .
2.3.3. Tensor Decomposition of
2.4. Master Formula for the HLbL Contribution to
- The integral over in spherical coordinates is considered in the first place. It is possible to take any four momenta as a reference for the angular integral; it does not matter because the integrals will go over all the possible values anyway. We take as a reference.
- The integrand is only dependent on one angle (in ), and it is therefore convenient to assign as one of the three Euclidean angles over which the angular integrals of the four-momentum is performed. It is relevant which of these three angles we are referring to, because it will determine what the Jacobian will look like. In the master formula, there is a term , a sine squared, which means does not represent either the polar or azimuthal angle of the three-dimensional sphere embedded in the four-dimensional space. Thus, the angular integral on yields:where and represent the three-dimensional polar and azimuthal angles of the four-dimensional space.
- Once the angular integrals on have been performed, there is no dependence on or another angle left on the integrand. This means that we can perform the four-dimensional solid angle integral on , which yields .
3. Operator Product Expansion of
3.1. OPE of in an Electromagnetic Background Field: A First Look
- second rank antisymmetric tensor;
- odd charge conjugation parity (remember, in this regard, the famous Furry’s theorem).
3.2. OPE of in an Electromagnetic Background Field: Theoretical Framework
4. Computation of Un-Renormalized Wilson Coefficients
5. OPE of in an Electromagnetic Background Field: Renormalization
5.1. Mixing of the Operator
5.2. Mixing of the Operator
5.3. Mixing of the Operator
5.4. Mixing of the Operator
5.5. Mixing of the Operator
5.6. Mixing of the Operator
5.7. Mixing of the Operator
6. Computation of the Quark Loop by the Method of Bijnens
7. Computation of the Quark Loop Amplitude in Our Work
7.1. First Stages of the Quark Loop Computation
7.1.1. Tensor Loop Integral Decomposition
7.1.2. Computation of Scalar Integrals with Shifted Dimensions
7.2. Final Stages of the Quark Loop Computation and Analysis
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Mellin–Barnes Integrals, Multivariate Residues, and Hypergeometric Functions
Appendix A.1. General Properties of Mellin–Barnes Integrals
Appendix A.2. Multivariate Generalization of Jordan’s Lemma for Mellin–Barnes Integrals
- Group the singular planes of the gamma functions in the numerator of (A1) in P divisors that satisfy the compatibility condition with respect to the faces of .
- Study all possible P combinations of gamma functions in the numerator of (A1) such that each gamma function belongs to a different divisor .
- Determine which of these combinations have isolated intersection points, that is, poles.
- Discard all poles that do not belong to .
- Compute the residues of the integrand of (A1) for all relevant poles.
Appendix B. Triangle Scalar Loop Integrals in Arbitrary Dimensions
References
- Fan, X.; Myers, T.G.; Sukra, B.A.D.; Gabrielse, G. Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 071801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Nio, M. Revised and improved value of the QED tenth-order electron anomalous magnetic moment. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 036001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.H.; Yu, C.; Zhong, W.; Estey, B.; Müller, H. Measurement of the fine-structure constant as a test of the Standard Model. Science 2018, 360, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, L.; Yao, Z.; Cladé, P.; Guellati-Khélifa, S. Determination of the fine-structure constant with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion. Nature 2020, 588, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Nio, M. Tenth-Order QED Contribution to the Electron g-2 and an Improved Value of the Fine Structure Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 111807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, S. Calculating the five-loop QED contribution to the electron anomalous magnetic moment: Graphs without lepton loops. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 096004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.W.; Bousquet, B.; Brown, H.N.; Bunce, G.; Carey, R.M.; Cushman, P.; Danby, G.T.; Debevec, P.T.; Deile, M.; Deng, H.; et al. Final report of the E821 muon anomalous magnetic moment measurement at BNL. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 072003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi, B.; Albahri, T.; Al-Kilani, S.; Allspach, D.; Alonzi, L.P.; Anastasi, A.; Anisenkov, A.; Azfar, F.; Badgley, K.; Baeßler, S.; et al. Measurement of the Positive Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment to 0.46 ppm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 141801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguillard, D.P.; Albahri, T.; Allspach, D.; Anisenkov, A.; Badgley, K.; Baeßler, S.; Bailey, I.; Bailey, L.; Baranov, V.A.; Barlas-Yucel, E.; et al. Measurement of the Positive Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment to 0.20 ppm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 161802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, T.; Asmussen, N.; Benayoun, M.; Bijnens, J.; Blum, T.; Bruno, M.; Caprini, I.; Carloni Calame, C.; Cè, M.; Colangelo, G.; et al. The anomalous magnetic moment of the muon in the Standard Model. Phys. Rep. 2020, 887, 1–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, J.P.; Poireau, V.; Tisserand, V.; Garra Tico, J.; Grauges, E.; Palano, A.; Eigen, G.; Stugu, B.; Brown, D.N.; Kerth, L.T.; et al. Precise measurement of the e+e-→π+π-(γ) cross section with the initial-state radiation method at BABAR. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 032013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, A.; Babusci, D.; Berlowski, M.; Bloise, C.; Bossi, F.; Branchini, P.; Budano, A.; Balkeståhl, L.C.; Cao, B.; Ceradini, F.; et al. Combination of KLOE σ(e+e-→π+π-γ(γ)) measurements and determination of aμπ+π- in the energy range 0.10 < s < 0.95 GeV2. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablikim, M.; Achasov, M.N.; Ai, X.C.; Albayrak, O.; Albrecht, M.; Ambrose, D.J.; Amoroso, A.; An, F.; An, Q.; Bai, J.Z. Measurement of the e+e-→π+π- cross section between 600 and 900 MeV using initial state radiation. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 753, 629–638, Erratum in Phys. Lett. B 2021, 812, 135982.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achasov, M.N.; Baykov, A.A.; Barnyakov, A.Y.; Beloborodov, K.I.; Berdyugin, A.V.; Berkaev, D.E.; Bogdanchikov, A.G.; Botov, A.A.; Dimova, T.V.; Druzhinin, V.P.; et al. Measurement of the e+e-→π+π- process cross section with the SND detector at the VEPP-2000 collider in the energy region 0.525 < s < 0.883 GeV. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, F.V.; Akhmetshin, R.R.; Amirkhanov, A.N.; Anisenkov, A.V.; Aulchenko, V.M.; Bashtovoy, N.S.; Berkaev, D.E.; Bondar, A.E.; Bragin, A.V.; Eidelman, S.I.; et al. Measurement of the e+e-→π+π- cross section from threshold to 1.2 GeV with the CMD-3 detector. arXiv, 2023; arXiv:2302.08834. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.L.; Fedotovich, G.V.; Akhmetshin, R.R.; Amirkhanov, A.N.; Anisenkov, A.V.; Aulchenko, V.M.; Bashtovoy, N.S.; Bondar, A.E.; Bragin, A.V.; Eidelman, S.I.; et al. Charged particle identification with the liquid xenon calorimeter of the CMD-3 detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2021, 1015, 165761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakumova, E.V.; Achasov, M.N.; Blinov, V.E.; Cai, X.; Dong, H.Y.; Fu, C.D.; Harris, F.A.; Kaminsky, V.V.; Krasnov, A.A.; Liu, Q.; et al. The beam energy measurement system for the Beijing electron–positron collider. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 2011, 659, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, F.; Antonelli, A.; Antonelli, M.; Archilli, F.; Bacci, C.; Beltrame, P.; Bencivenni, G.; Bertolucci, S.; Bini, C.; Bloise, C.; et al. Measurement of σ(e+e-→π+π-γ(γ)) and the dipion contribution to the muon anomaly with the KLOE detector. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 670, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, B.; Karyotakis, Y.; Lees, J.P.; Poireau, V.; Prencipe, E.; Prudent, X.; Tisserand, V.; Garra Tico, J.; Grauges, E.; Martinelli, M.; et al. Precise Measurement of the e+e-→π+π-(γ) Cross Section with the Initial State Radiation Method at BABAR. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 231801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemany, R.; Davier, M.; Höcker, A. Improved determination of the hadronic contribution to the muon (g-2) and to α(MZ2) Using new data from hadronic τ decays. Eur. Phys. J. C-Part. Fields 1998, 2, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni Calame, C.; Passera, M.; Trentadue, L.; Venanzoni, G. A new approach to evaluate the leading hadronic corrections to the muon g-2. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 746, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbiendi, G.; Calame, C.M.C.; Marconi, U.; Matteuzzi, C.; Montagna, G.; Nicrosini, O.; Passera, M.; Piccinini, F.; Tenchini, R.; Trentadue, L.; et al. Measuring the leading hadronic contribution to the muon g-2 via μe scattering. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Carloni Calame, C.M.; Chiesa, M.; Di Vita, S.; Engel, T.; Fael, M.; Laporta, S.; Mastrolia, P.; Montagna, G.; Nicrosini, O.; et al. Theory for muon-electron scattering @ 10 ppm. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsanyi, S.; Fodor, Z.; Guenther, J.N.; Hoelbling, C.; Katz, S.D.; Lellouch, L.; Lippert, T.; Miura, K.; Parato, L.; Szabo, K.K.; et al. Leading hadronic contribution to the muon magnetic moment from lattice QCD. Nature 2021, 593, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazavov, A.; Davies, C.; DeTar, C.; El-Khadra, A.X.; Gámiz, E.; Gottlieb, S.; Jay, W.I.; Jeong, H.; Kronfeld, A.S.; Lahert, S.; et al. Light-quark connected intermediate-window contributions to the muon g-2 hadronic vacuum polarization from lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, T.; Boyle, P.A.; Bruno, M.; Giusti, D.; Gülpers, V.; Hill, R.C.; Izubuchi, T.; Jang, Y.C.; Jin, L.; Jung, C.; et al. Update of Euclidean windows of the hadronic vacuum polarization. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 054507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cè, M.; Gérardin, A.; von Hippel, G.; Hudspith, R.J.; Kuberski, S.; Meyer, H.B.; Miura, K.; Mohler, D.; Ottnad, K.; Paul, S.; et al. Window observable for the hadronic vacuum polarization contribution to the muon g-2 from lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, C.; Bacchio, S.; Dimopoulos, P.; Finkenrath, J.; Frezzotti, R.; Gagliardi, G.; Garofalo, M.; Hadjiyiannakou, K.; Kostrzewa, B.; Jansen, K.; et al. Lattice calculation of the short and intermediate time-distance hadronic vacuum polarization contributions to the muon magnetic moment using twisted-mass fermions. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 074506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altherr, A.; Bushnaq, L.; Campos, I.; Catillo, M.; Cotellucci, A.; Dale, M.; Fritzsch, P.; Gruber, R.; Komijani, J.; Lücke, J.; et al. Strange and charm contributions to the HVP from C* boundary conditions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.04385. [Google Scholar]
- Colangelo, G.; Davier, M.; El-Khadra, A.X.; Hoferichter, M.; Lehner, C.; Lellouch, L.; Mibe, T.; Roberts, B.L.; Teubner, T.; Wittig, H.; et al. Prospects for precise predictions of aμ in the Standard Model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.15810. [Google Scholar]
- Colangelo, G.; El-Khadra, A.X.; Hoferichter, M.; Keshavarzi, A.; Lehner, C.; Stoffer, P.; Teubner, T. Data-driven evaluations of Euclidean windows to scrutinize hadronic vacuum polarization. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 833, 137313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffer, P.; Colangelo, G.; Hoferichter, M. Puzzles in the hadronic contributions to the muon anomalous magnetic moment. J. Instrum. 2023, 18, C10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetshin, R.R.; Aulchenko, V.M.; Banzarov, V.S.; Barkov, L.M.; Bashtovoy, N.S.; Bondar, A.E.; Bondarev, D.V.; Bragin, A.V.; Dhawan, S.K.; Eidelman, S.I.; et al. High-statistics measurement of the pion form factor in the ρ-meson energy range with the CMD-2 detector. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 648, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Hoferichter, M.; Procura, M.; Stoffer, P. Dispersion relation for hadronic light-by-light scattering: Theoretical foundations. J. High Energy Phys. 2015, 2015, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Hoferichter, M.; Procura, M.; Stoffer, P. Dispersion relation for hadronic light-by-light scattering: Two-pion contributions. J. High Energy Phys. 2017, 2017, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoferichter, M.; Hoid, B.L.; Kubis, B.; Leupold, S.; Schneider, S.P. Pion-Pole Contribution to Hadronic Light-By-Light Scattering in the Anomalous Magnetic Moment of the Muon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, G.; Hoferichter, M.; Procura, M.; Stoffer, P. Rescattering Effects in the Hadronic-Light-by-Light Contribution to the Anomalous Magnetic Moment of the Muon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 232001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilkin, I.; Hoferichter, M.; Stoffer, P. A dispersive estimate of scalar contributions to hadronic light-by-light scattering. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 820, 136502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanke, M.; Hoferichter, M.; Kubis, B. On the transition form factors of the axial-vector resonance f1(1285) and its decay into e+e−. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappiello, L.; Catà, O.; D’Ambrosio, G.; Greynat, D.; Iyer, A. Axial-vector and pseudoscalar mesons in the hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon (g-2). Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 016009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutgeb, J.; Rebhan, A. Axial vector transition form factors in holographic QCD and their contribution to the anomalous magnetic moment of the muon. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 114015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutgeb, J.; Rebhan, A. Hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon g-2 from holographic QCD with massive pions. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 094017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutgeb, J.; Mager, J.; Rebhan, A. Hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon g-2 from holographic QCD with solved U(1)A problem. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 054021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, C.; Bacchio, S.; Burri, S.; Finkenrath, J.; Gasbarro, A.; Hadjiyiannakou, K.; Jansen, K.; Kanwar, G.; Kostrzewa, B.; Ottnad, K.; et al. η→γ*γ* transition form factor and the hadronic light-by-light η-pole contribution to the muon g-2 from lattice QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 054509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, C.; Bacchio, S.; Bergner, G.; Burri, S.; Finkenrath, J.; Gasbarro, A.; Hadjiyiannakou, K.; Jansen, K.; Kanwar, G.; Kostrzewa, B.; et al. Pion transition form factor from twisted-mass lattice QCD and the hadronic light-by-light π0-pole contribution to the muon g-2. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 094514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, T.; Christ, N.; Hayakawa, M.; Izubuchi, T.; Jin, L.; Jung, C.; Lehner, C.; Tu, C. Hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon anomaly from lattice QCD with infinite volume QED at physical pion mass. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04423. [Google Scholar]
- Gérardin, A.; Verplanke, W.E.A.; Wang, G.; Fodor, Z.; Guenther, J.N.; Lellouch, L.; Szabo, K.K.; Varnhorst, L. Lattice calculation of the π0, η and η′ transition form factors and the hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon g-2. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.04570. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, E.H.; Hudspith, R.J.; Gérardin, A.; Green, J.R.; Meyer, H.B.; Ottnad, K. Hadronic light-by-light contribution to (g-2)μ from lattice QCD: A complete calculation. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.H.; Hudspith, R.J.; Gérardin, A.; Green, J.R.; Meyer, H.B. The charm-quark contribution to light-by-light scattering in the muon (g-2) from lattice QCD. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmussen, N.; Chao, E.H.; Gérardin, A.; Green, J.R.; Hudspith, R.J.; Meyer, H.B.; Nyffeler, A. Hadronic light-by-light scattering contribution to the muon g-2 from lattice QCD: Semi-analytical calculation of the QED kernel. J. High Energy Phys. 2023, 2023, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Sanda, A.I. Hadronic Light-by-Light Scattering Effect on Muon g-2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; de Rafael, E.; Zheng, H. Low-energy behaviour of two-point functions of quark currents. Z. Phys. C Part. Fields 1994, 62, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Hoferichter, M.; Procura, M.; Stoffer, P. Dispersive approach to hadronic light-by-light scattering. J. High Energy Phys. 2014, 2014, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; Gámiz, E.; Lipartia, E.; Prades, J. QCD Short-distance constraints and hadronic approximations. J. High Energy Phys. 2003, 2003, 055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, M.; Nyffeler, A. Resonance estimates of O(p6) low-energy constants and QCD short-distance constraints. Eur. Phys. J. C-Part. Fields 2001, 21, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Hagelstein, F.; Hoferichter, M.; Laub, L.; Stoffer, P. Short-distance constraints on hadronic light-by-light scattering in the anomalous magnetic moment of the muon. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 051501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Hagelstein, F.; Hoferichter, M.; Laub, L.; Stoffer, P. Longitudinal short-distance constraints for the hadronic light-by-light contribution to (g-2)μ with large-Nc Regge models. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Hagelstein, F.; Hoferichter, M.; Laub, L.; Stoffer, P. Short-distance constraints for the longitudinal component of the hadronic light-by-light amplitude: An update. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; Hermansson-Truedsson, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, A. Short-distance constraints for the HLbL contribution to the muon anomalous magnetic moment. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 798, 134994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; Hermansson-Truedsson, N.; Laub, L.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, A. Short-distance HLbL contributions to the muon anomalous magnetic moment beyond perturbation theory. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; Hermansson-Truedsson, N.; Laub, L.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, A. The two-loop perturbative correction to the (g-2)μ HLbL at short distances. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtabovenko, V.; Mertig, R.; Orellana, F. FeynCalc 9.3: New features and improvements. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020, 256, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtabovenko, V.; Mertig, R.; Orellana, F. New developments in FeynCalc 9.0. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2016, 207, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertig, R.; Böhm, M.; Denner, A. Feyn Calc - Computer-algebraic calculation of Feynman amplitudes. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1991, 64, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayan, B.; Banik, S.; Friot, S.; Ghosh, S. Multiple Series Representations of N-fold Mellin-Barnes Integrals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 151601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barut, A.O. The Theory of the Scattering Matrix; The MacMillan Company: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Arkani-Hamed, N.; Huang, T.C.; Huang, Y.T. Scattering amplitudes for all masses and spins. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, S.J.; Sullivan, J.D. W-Boson Contribution to the Anomalous Magnetic Moment of the Muon. Phys. Rev. 1967, 156, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldins, J.; Brodsky, S.J.; Dufner, A.J.; Kinoshita, T. Photon-Photon Scattering Contribution to the Sixth-Order Magnetic Moments of the Muon and Electron. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 1, 2378–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, M.; Nyffeler, A. Hadronic light-by-light corrections to the muon g-2: The pion-pole contribution. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 073034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegerlehner, F. The Anomalous Magnetic Moment of the Muon; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.E. Bremsstrahlung of Very Low-Energy Quanta in Elementary Particle Collisions. Phys. Rev. 1958, 110, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascalutsa, V.; Pauk, V.; Vanderhaeghen, M. Light-by-light scattering sum rules constraining meson transition form factors. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauk, V.; Vanderhaeghen, M. Anomalous magnetic moment of the muon in a dispersive approach. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilkin, I.; Vanderhaeghen, M. Light-by-light scattering sum rules in light of new data. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 014019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelstein, F.; Pascalutsa, V. Dissecting the Hadronic Contributions to (g-2)μ by Schwinger’s Sum Rule. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 072002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskin, M.; Schroeder, D. An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, M.; Kanazawa, A. Subtractions in Dispersion Relations. Phys. Rev. 1961, 123, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelstam, S. Determination of the Pion-Nucleon Scattering Amplitude from Dispersion Relations and Unitarity. General Theory. Phys. Rev. 1958, 112, 1344–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, R.; Neuman, M. Non-Linear Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields. Phys. Rev. 1950, 80, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, W.A.; Tung, W.K. Invariant Amplitudes for Photon Processes. Phys. Rev. 1968, 173, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, G.; Fischer, C.S.; Heupel, W.; Williams, R. The muon g-2: Dyson-Schwinger status on hadronic light-by-light scattering. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.7876v2. [Google Scholar]
- Tarrach, R. Invariant amplitudes for virtual compton scattering off polarized nucleons free from kinematical singularities, zeros and constraints. Il Nuovo C. A (1965–1970) 1975, 28, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, H. Bateman Manuscript Project. In Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorken, J.D. Regge Behavior of Forward Elastic Scattering Amplitudes. J. Math. Phys. 1964, 5, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Lepage, G.; Brodsky, S.J. Exclusive processes in quantum chromodynamics: Evolution equations for hadronic wavefunctions and the form factors of mesons. Phys. Lett. B 1979, 87, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, G.P.; Brodsky, S.J. Exclusive processes in perturbative quantum chromodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 1980, 22, 2157–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko, V.A.; Radyushkin, A.V. Comparison of the QCD Sum Rule Approach and Perturbative QCD Analysis for γ*γ*→π0 Process. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1983, 38, 476–483. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, V.A.; Shifman, M.A.; Vainshtein, A.I.; Voloshin, M.B.; Zakharov, V.I. Use and misuse of QCD sum rules, factorization and related topics. Nucl. Phys. B 1984, 237, 525–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsky, A.S. The π0γγ Form-factor at Various Virtualities of the Photons in the Sum Rule Method and in Perturbative QCD. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1987, 46, 938–942. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Manohar, A.V. The decays Z→γπ, Z→Wπ, and the pion form factor. Phys. Lett. B 1990, 244, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoferichter, M.; Hoid, B.L.; Kubis, B.; Leupold, S.; Schneider, S.P. Dispersion relation for hadronic light-by-light scattering: Pion pole. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, B.L.; Smilga, A.V. Nucleon magnetic moments and magnetic properties of the vacuum in QCD. Nucl. Phys. B 1984, 232, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, A.; Marciano, W.J.; Vainshtein, A. Refinements in electroweak contributions to the muon anomalous magnetic moment. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 073006, Erratum in Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 119901.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, V.A.; Shifman, M.A.; Vainshtein, A.I.; Zakharov, V.I. Calculations in external fields in quantum chromodynamics. Technical review. Fortschritte Phys. 1984, 32, 585–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifman, M.A.; Vainshtein, A.I.; Zakharov, V.I. QCD and resonance physics. theoretical foundations. Nucl. Phys. B 1979, 147, 385–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifman, M.A.; Vainshtein, A.I.; Zakharov, V.I. QCD and resonance physics. Applications. Nucl. Phys. B 1979, 147, 448–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, V. Proper time in classical and quantum mechanics. Phys. Z. Sowjetunion 1937, 12, 404–425. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shifman, M.A. Wilson loop in vacuum fields. Nucl. Phys. B 1980, 173, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, W.; Weiser, J. Quantization of gauge-fields in the fock-schwinger gauge. Z. Phys. C Part. Fields 1986, 31, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strichartz, R. A Guide to Distribution Theory and Fourier Transform; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shuryak, E.; Vainshtein, A. Theory of power corrections to deep inelastic scattering in quantum chromodynamics: (II). Q-4 effects; polarized target. Nucl. Phys. B 1982, 201, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Blum, T.; Colangelo, G.; Collins, S.; Morte, M.D.; Dimopoulos, P.; Dürr, S.; Feng, X.; Fukaya, H.; Golterman, M.; et al. FLAG Review 2021. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluberg-Stern, H.; Zuber, J.B. Ward identities and some clues to the renormalization of gauge-invariant operators. Phys. Rev. D 1975, 12, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluberg-Stern, H.; Zuber, J.B. Renormalization of non-Abelian gauge theories in a background-field gauge. I. Green’s functions. Phys. Rev. D 1975, 12, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluberg-Stern, H.; Zuber, J.B. Renormalization of non-Abelian gauge theories in a background-field gauge. II. Gauge-invariant operators. Phys. Rev. D 1975, 12, 3159–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydychev, A.I. A simple formula for reducing Feynman diagrams to scalar integrals. Phys. Lett. B 1991, 263, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydychev, A.I. Some exact results for N-point massive Feynman integrals. J. Math. Phys. 1991, 32, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarino, G.; Veltman, M. One-loop corrections for e+e- annihilation into μ+μ- in the Weinberg model. Nucl. Phys. B 1979, 160, 151–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.K.; Kunszt, Z.; Melnikov, K.; Zanderighi, G. One-loop calculations in quantum field theory: From Feynman diagrams to unitarity cuts. Phys. Rep. 2012, 518, 141–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.J.; Rietkerk, R. MultivariateResidues: A Mathematica package for computing multivariate residues. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2018, 222, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friot, S.; Greynat, D. On convergent series representations of Mellin-Barnes integrals. J. Math. Phys. 2012, 53, 023508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J. Über die Convergenz der hypergeometrischen Reihen zweier und dreier Veränderlichen. Math. Ann. 1889, 34, 544–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.H.; Tran, D.T. One-loop three-point Feynman integrals with Appell F1 hypergeometric functions. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2019, 2019, 063B01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, H.M.; Karlsson, P.W. Multiple Gaussian Hypergeometric Series; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, L.J. Generalized Hypergeometric Functions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, K.; Vainshtein, A. Hadronic light-by-light scattering contribution to the muon anomalous magnetic moment reexamined. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; Hermansson-Truedsson, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, A. Constraints on the hadronic light-by-light in the Melnikov-Vainshtein regime. J. High Energy Phys. 2023, 2023, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnens, J.; Hermansson-Truedsson, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, A. Short-distance constraints on the hadronic light-by-light. EPJ Web Conf. 2022, 274, 06010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Friot, S. Multiple Mellin-Barnes integrals with straight contours. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, O.N.; Tsikh, A.K. Studying the multiple Mellin-Barnes integrals by means of multidimensional residues. Sib. Math. J. 1998, 39, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikael Passare, A.T.; Zhdanov, O. Aspects of Mathematics: Contributions to Complex Analysis and Analytic Geometry; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1994; Volume E26, pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, P.; Harris, J. Principles of Algebraic Geometry; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Passare, M.; Tsikh, A.K.; Cheshel, A.A. Multiple Mellin-Barnes integrals as periods of Calabi-Yau manifolds with several moduli. Theor. Math. Phys. 1996, 109, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.W. The Asymptotic Expansion of Integral Functions Defined by Generalised Hypergeometric Series. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1907, s2-5, 59–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikh, A.K. Translations of Mathematical Monographs: Multidimensional Residues and Their Applications; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1992; Volume 103. [Google Scholar]
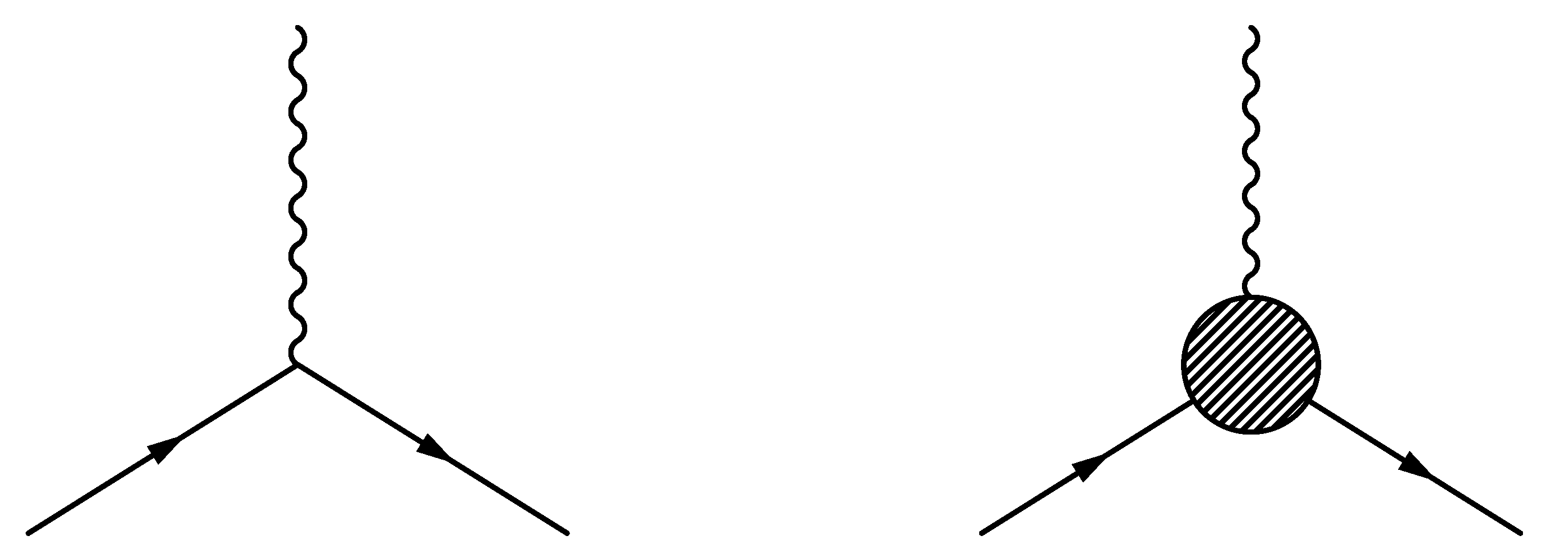

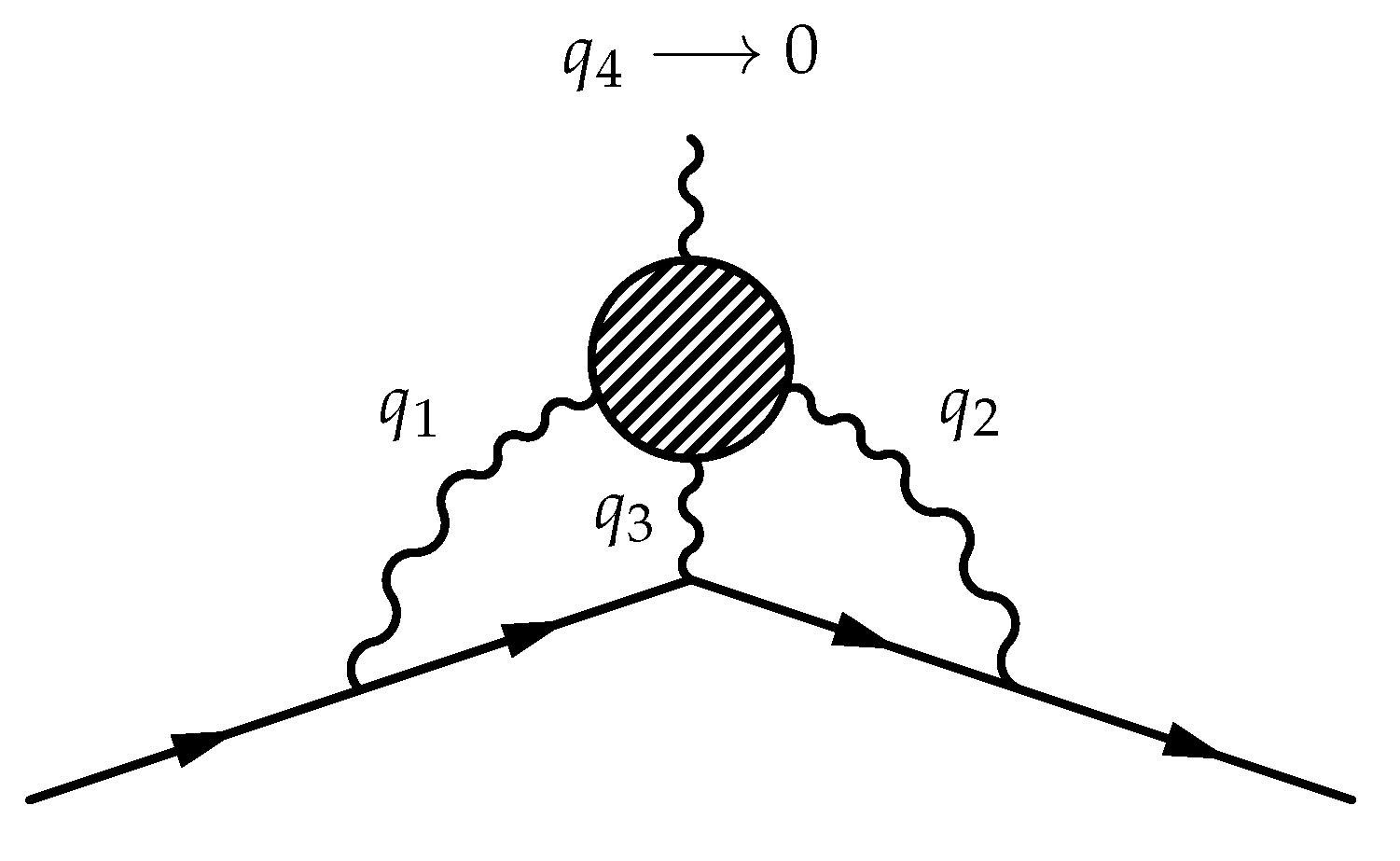
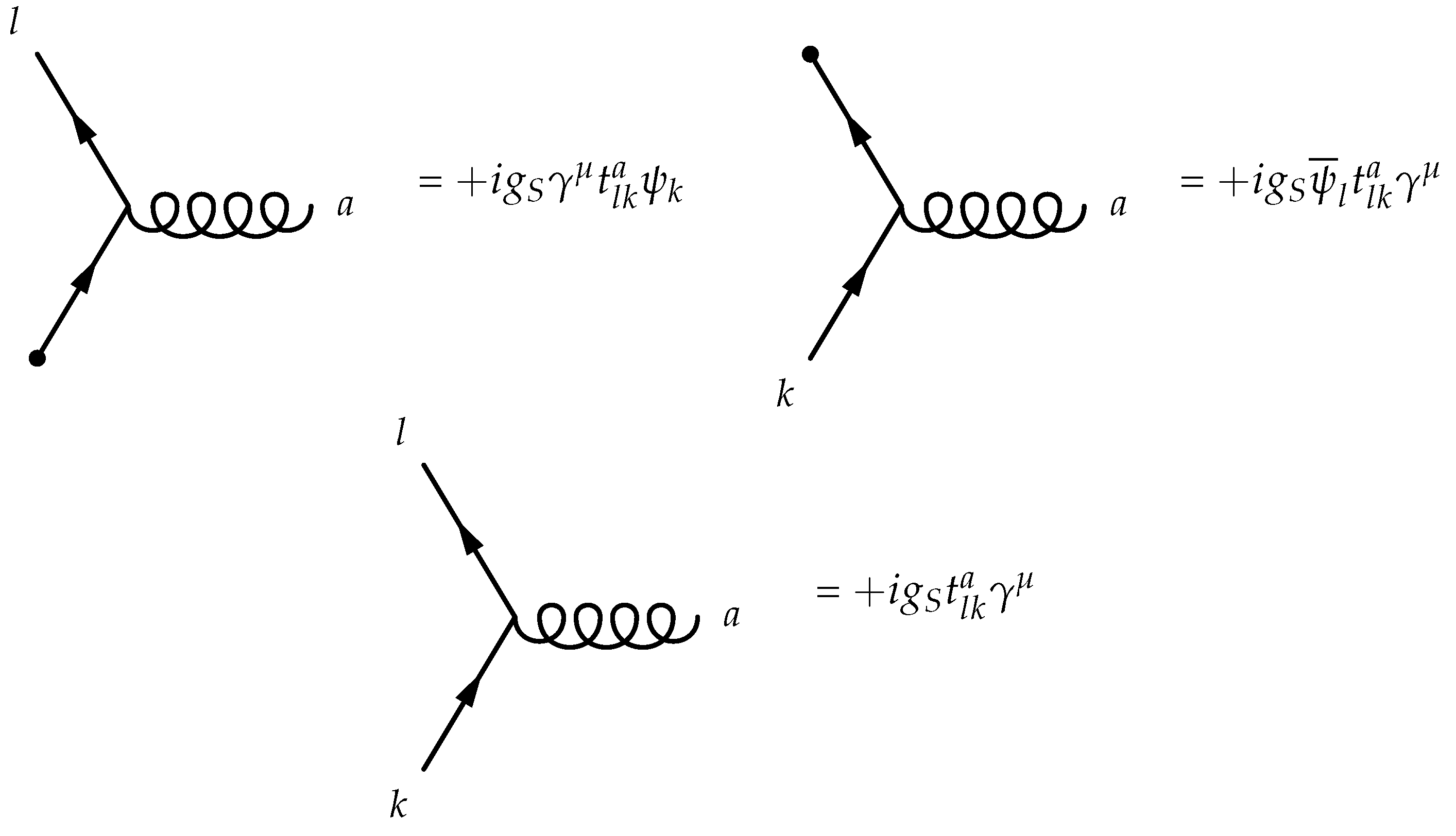
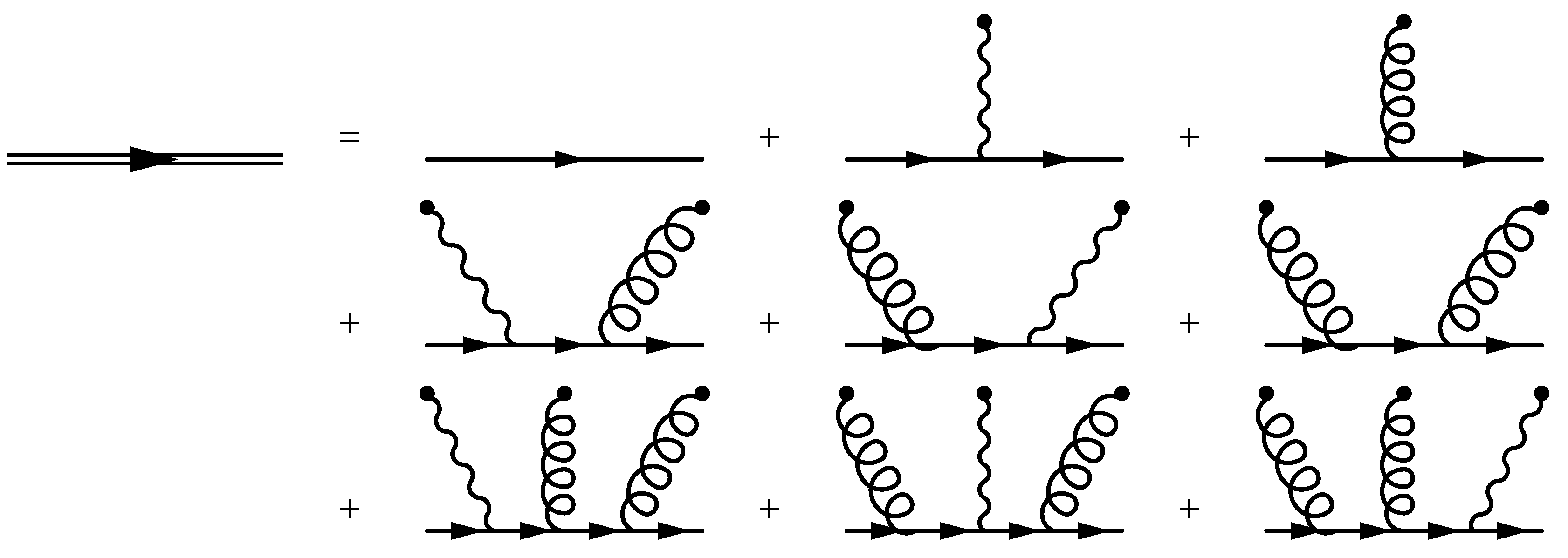
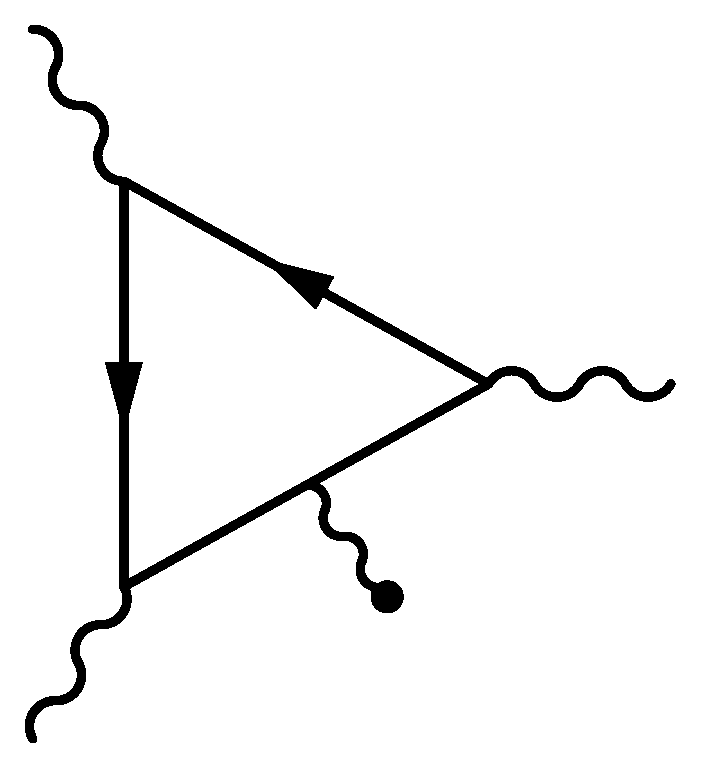
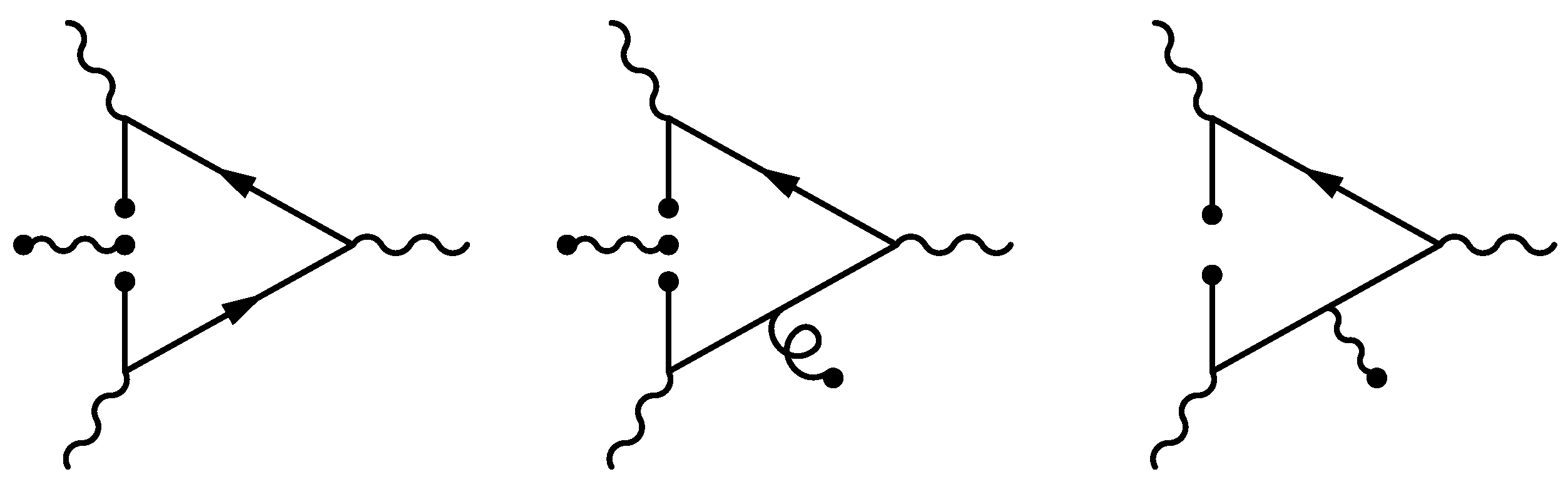
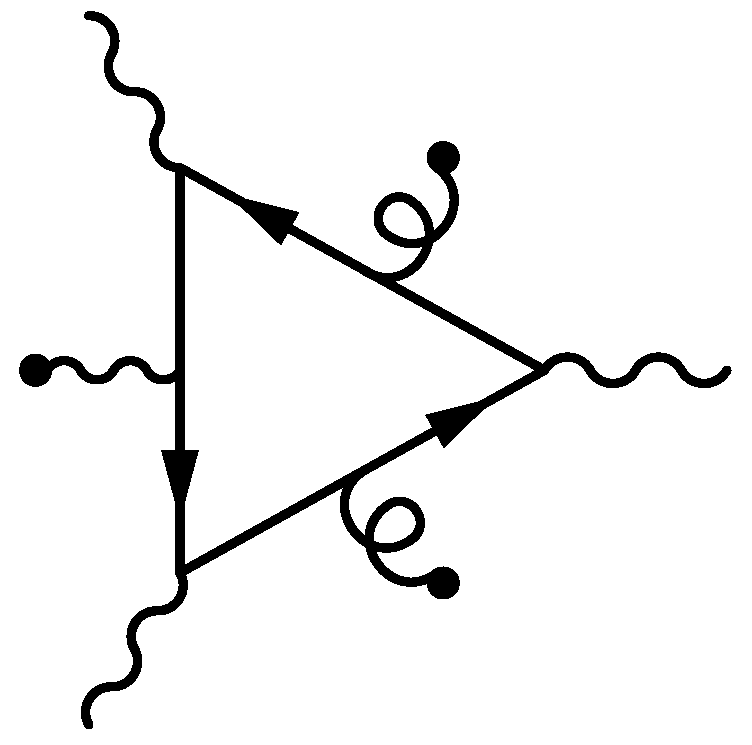
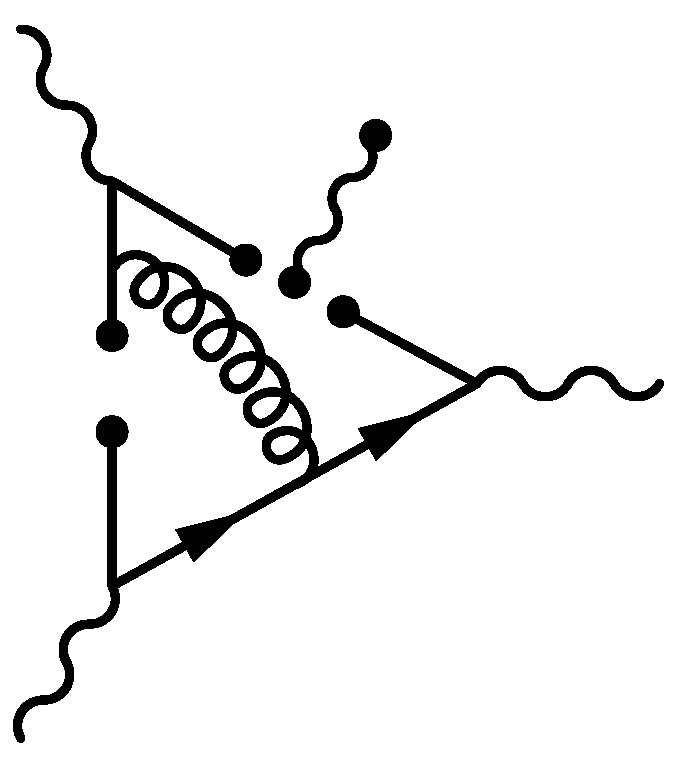


| Dirac Matrices’ Basis Element | Available Structures |
|---|---|
| 1 | , |
| , , , , , | |
| , | |
| , , , , , | |
| , , , , , |
| OPE Element | Magnetic Susceptibility | Mass Order | Contribution to from | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 GeV | 2 GeV | |||
| 1 | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
| GeV | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melo, D.; Reyes, E.; Fazio, R. Hadronic Light-by-Light Corrections to the Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment. Particles 2024, 7, 327-381. https://doi.org/10.3390/particles7020020
Melo D, Reyes E, Fazio R. Hadronic Light-by-Light Corrections to the Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment. Particles. 2024; 7(2):327-381. https://doi.org/10.3390/particles7020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelo, Daniel, Edilson Reyes, and Raffaele Fazio. 2024. "Hadronic Light-by-Light Corrections to the Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment" Particles 7, no. 2: 327-381. https://doi.org/10.3390/particles7020020
APA StyleMelo, D., Reyes, E., & Fazio, R. (2024). Hadronic Light-by-Light Corrections to the Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment. Particles, 7(2), 327-381. https://doi.org/10.3390/particles7020020







