Clonal Evolution of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with del(9)(p13p21) into Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Testicular Relapse
Abstract
1. Introduction
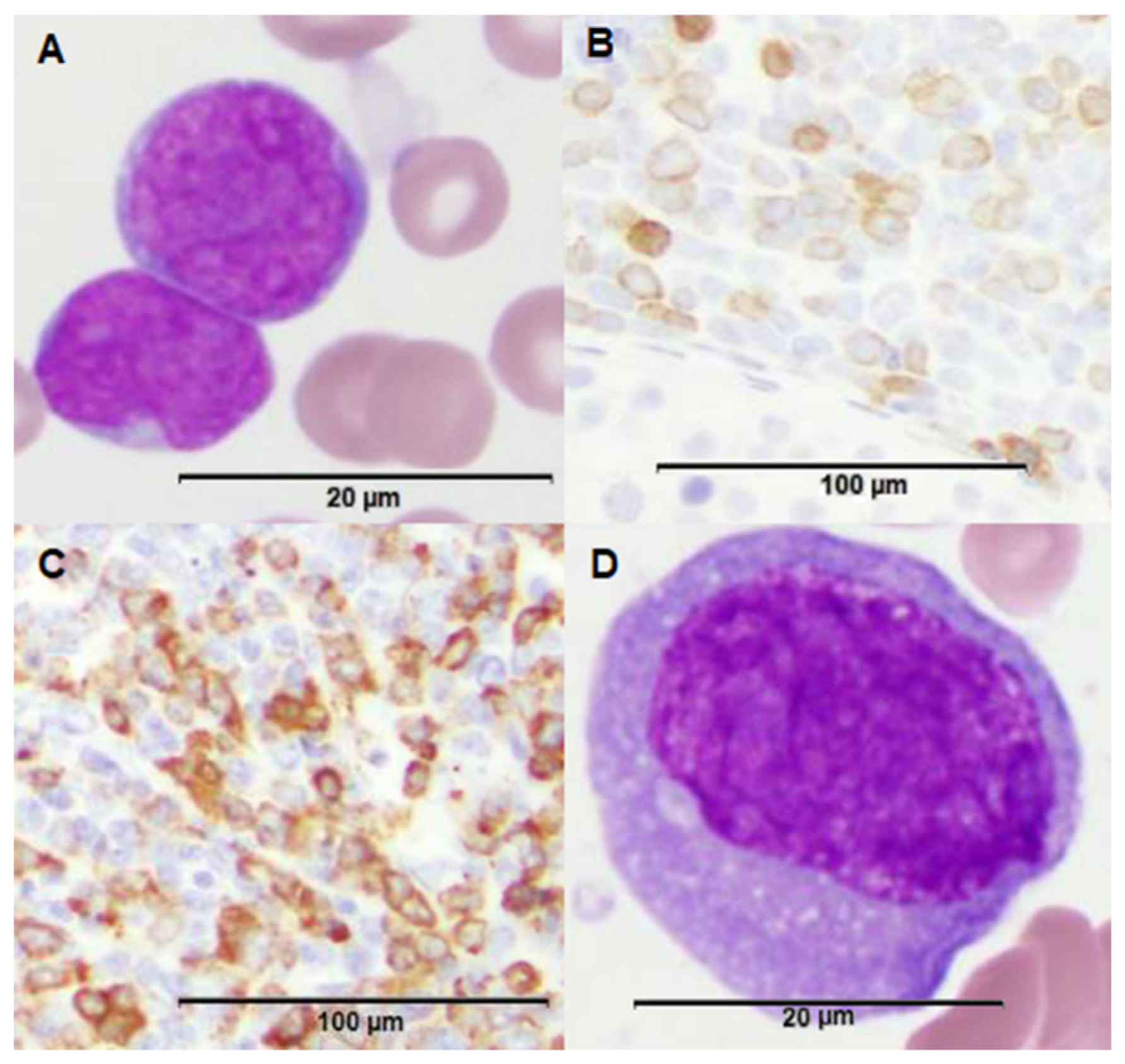
2. Case Presentation Section
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinberg, O.K.; Arber, D.A. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: Historical overview and a new definition. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1844–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bene, M.C.; Porwit, A. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. Sem. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 29, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolach, O.; Stone, R.M. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: Current challenges in diagnosis and therapy. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steensma, D.P. Oddballs: Acute leukemias of mixed phenotype and ambiguous origin. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 25, 1235–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Siddiqi, R.; Naqvi, K. An update on classification, genetics, and clinical approach to mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL). Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorantes-Acosta, E.; Pelayo, R. Lineage switching in acute leukemias: A consequence of stem cell plasticity? Bone Marrow Res. 2012, 2012, 406796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerema, N.A.; Sather, H.N.; Sensel, M.G.; Liu-Mares, W.; Lange, B.J.; Bostrom, B.C.; Nachman, J.B.; Steinherz, P.G.; Hutchinson, R.; Gaynon, P.S.; et al. A ssociation of chromosome arm 9p abnormalities with adverse risk in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report from the Children‘s Cancer Group. Blood 1999, 94, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olopade, O.I.; Jenkins, R.B.; Ransom, D.T.; Malik, K.; Pomykala, H.; Nobori, T.; Cowan, J.M.; Rowley, J.D.; Diaz, M.O. Molecular analysis of deletions of the short arm of chromosome 9 in human gliomas. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco Salas, P.; Fernandez, L.; Vela, M.; Bueno, D.; Gonzalez, B.; Valentin, J.; Lapunzina, P.; Perez-Martinez, A. The role of CDKN2A/B deletions in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 33, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Kuang, P.; Liu, T. Prognostic significance of CDKN2A/B deletions in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: A meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, M.J.; Bray, R.; Gascoyne, R.; Melnick, S.; Parker, J.W.; Picker, L.; Stetler-Stevenson, M. U.S.-Canadian Consensus recommendations on the immunophenotypic analysis of hematologic neoplasia by flow cytometry: Data analysis and interpretation. Cytometry 1997, 30, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, B.L.; Arroz, M.; Barnett, D.; DiGiuseppe, J.; Greig, B.; Kussick, S.J.; Oldaker, T.; Shenkin, M.; Stone, E.; Wallace, P. 2006 Bethesda International Consensus recommendations on the immunophenotypic analysis of hematolymphoid neoplasia by flow cytometry: Optimal reagents and reporting for the flow cytometric diagnosis of hematopoietic neoplasia. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2007, 72 (Suppl. 1), S14–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.E.; Hastings, C. Isolated extramedullary relapse in childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2010, 5, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, D.D.; Eskew, A.; White, T.; McLean, T.W. An unusual case of acute myeloid leukemia: Late isolated testicular relapse followed by isolated central nervous system relapse. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, W.L.; Fontanesi, J.; Hustu, O.; Dahl, G.V.; Kalwinsky, D.K.; Pui, C.H. Testicular relapse in children with acute nonlymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 1990, 66, 2095–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carulli, G.; Marini, A.; Ferreri, M.I.; Azzara, A.; Ottaviano, V.; Lari, T.; Rocco, M.; Giuntini, S.; Petrini, M. B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(4;11)(q21;q23) in a young woman: Evolution into mixed phenotype acute leukemia with additional chromosomal aberrations in the course of therapy. Hematol. Rep. 2012, 4, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.G.; Roman, E.; Nandula, S.V.; Murty, V.V.; Bhagat, G.; Alobeid, B. Congenital MLL-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) switched lineage at relapse to acute myelocytic leukemia (AML) with persistent t(4;11) and t(1;6) translocations and JH gene rearrangement. Leuk. Lymphoma 2005, 46, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridge, S.A.; Cabrera, M.E.; Ford, A.M.; Tapia, S.; Risueno, C.; Labra, S.; Barriga, F.; Greaves, M.F. Rapid intraclonal switch of lineage dominance in congenital leukaemia with a MLL gene rearrangement. Leukemia 1995, 9, 2023–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki, H.; Kanegane, H.; Nomura, K.; Goi, K.; Sugita, K.; Miura, M.; Ishii, E.; Miyawaki, T. Early lineage switch in an infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2009, 90, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Koh, K.N.; Kim, B.E.; Im, H.J.; Jang, S.; Park, C.J.; Chi, H.S.; Seo, J.J. Lineage switch at relapse of childhood acute leukemia: A report of four cases. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasik, C.; Ganguly, S.; Cunningham, M.T.; Hagemeister, S.; Persons, D.L. Infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(11;16)(q23;p13.3) and lineage switch into acute monoblastic leukemia. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2006, 168, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikarashi, Y.; Kakihara, T.; Imai, C.; Tanaka, A.; Watanabe, A.; Uchiyama, M. Double leukemias simultaneously showing lymphoblastic leukemia of the bone marrow and monocytic leukemia of the central nervous system. Am. J. Hematol. 2004, 75, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.J.; Park, C.J.; Jang, S.; Chi, H.S.; Seo, E.J.; Seo, J.J. A case of lineage switch from acute lymphoblastic leukemia to acute myeloid leukemia. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2007, 27, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgornik, H.; Debeljak, M.; Zontar, D.; Cernelc, P.; Prestor, V.V.; Jazbec, J. RUNX1 amplification in lineage conversion of childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2007, 178, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balducci, E.; Nivaggioni, V.; Boudjarane, J.; Bouriche, L.; Rahal, I.; Bernot, D.; Alazard, E.; Duployez, N.; Grardel, N.; Arnoux, I.; et al. Lineage switch from B acute lymphoblastic leukemia to acute monocytic leukemia with persistent t(4;11)(q21;q23) and cytogenetic evolution under CD19-targeted therapy. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1579–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imataki, O.; Ohnishi, H.; Yamaoka, G.; Arai, T.; Kitanaka, A.; Kubota, Y.; Kushida, Y.; Ishida, T.; Tanaka, T. Lineage switch from precursor B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to acute monocytic leukemia at relapse. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 15, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Ogawa, S.; Dugas, M.; Kawamata, N.; Yamamoto, G.; Nannya, Y.; Sanada, M.; Miller, C.W.; Yung, A.; Schnittger, S.; et al. Frequent genomic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome with normal karyotype. Haematologica 2009, 94, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, A.; Tara, H.; Xiang, B.; Bajaj, R.; He, W.; Li, P. Double-minute MYC amplification and deletion of MTAP, CDKN2A, CDKN2B, and ELAVL2 in an acute myeloid leukemia characterized by oligonucleotide-array comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2008, 183, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrusak, O.; de Haas, V.; Stancikova, J.; Vakrmanova, B.; Janotova, I.; Mejstrikova, E.; Capek, V.; Trka, J.; Zaliova, M.; Luks, A.; et al. International cooperative study identifies treatment strategy in childhood ambiguous lineage leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruffi, M.; Sposto, R.; Oberley, M.J.; Kysh, L.; Orgel, E. Therapy for children and adults with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejstrikova, E.; Volejnikova, J.; Fronkova, E.; Zdrahalova, K.; Kalina, T.; Sterba, J.; Jabali, Y.; Mihal, V.; Blazek, B.; Cerna, Z.; et al. Prognosis of children with mixed phenotype acute leukemia treated on the basis of consistent immunophenotypic criteria. Haematologica 2010, 95, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, E.G.; Ali Ansari-Lari, M.; Batista, D.A.; Griffin, C.A.; Fuller, S.; Smith, B.D.; Borowitz, M.J. Acute bilineal leukemia: A rare disease with poor outcome. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, S.J.; Geoerger, B.; Janeway, K.A. Precision medicine in pediatric oncology. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, P.; Simmons, G.L.; Grant, S. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor therapy for hematologic malignancies. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Flow Cytometry Marker | B-ALL Bone Marrow at Diagnosis | Testicular Relapse (2 Years from Diagnosis) | Bone Marrow Relapse (4 Months from Testicular Relapse) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-ALL Component | Myeloid Component | B-ALL Component (0.4% Cells) | Myeloid Component (38% Cells) | ||
| CD2 | − | − | + | − | − |
| CD4 | − | − | + | − | + |
| CD10 | + | − | − | − | − |
| CD11b | − | − | + | − | + |
| CD13 | + | + | + | − | + |
| CD14 | − | − | + | − | − |
| CD15 | − | − | + | − | − |
| CD19 | + | + | − | + | − |
| CD20 | + | − | − | − | − |
| CD22 | + | + | − | + | − |
| CD33 | − | − | + | − | + |
| CD34 | + | + | − | + | − |
| CD36 | − | − | + | − | − |
| CD38 | + | + | + | + | + |
| CD56 | − | − | − | − | + |
| CD58 | + | + | + | + | + |
| CD64 | − | − | + | − | + |
| MPO | − | − | + | − | + |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, L.H.; Park, S.I.; Saxe, D.; Lew, G.; Raikar, S.S. Clonal Evolution of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with del(9)(p13p21) into Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Testicular Relapse. Reports 2019, 2, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2030018
Miller LH, Park SI, Saxe D, Lew G, Raikar SS. Clonal Evolution of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with del(9)(p13p21) into Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Testicular Relapse. Reports. 2019; 2(3):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2030018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Lane H., Sunita I. Park, Debra Saxe, Glen Lew, and Sunil S. Raikar. 2019. "Clonal Evolution of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with del(9)(p13p21) into Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Testicular Relapse" Reports 2, no. 3: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2030018
APA StyleMiller, L. H., Park, S. I., Saxe, D., Lew, G., & Raikar, S. S. (2019). Clonal Evolution of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with del(9)(p13p21) into Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Testicular Relapse. Reports, 2(3), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2030018





