Efficacy of Corticosteroids and Intravenous Immunoglobulins in a Patient with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Secondary to Sulfadoxine: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
2.1. Medical History
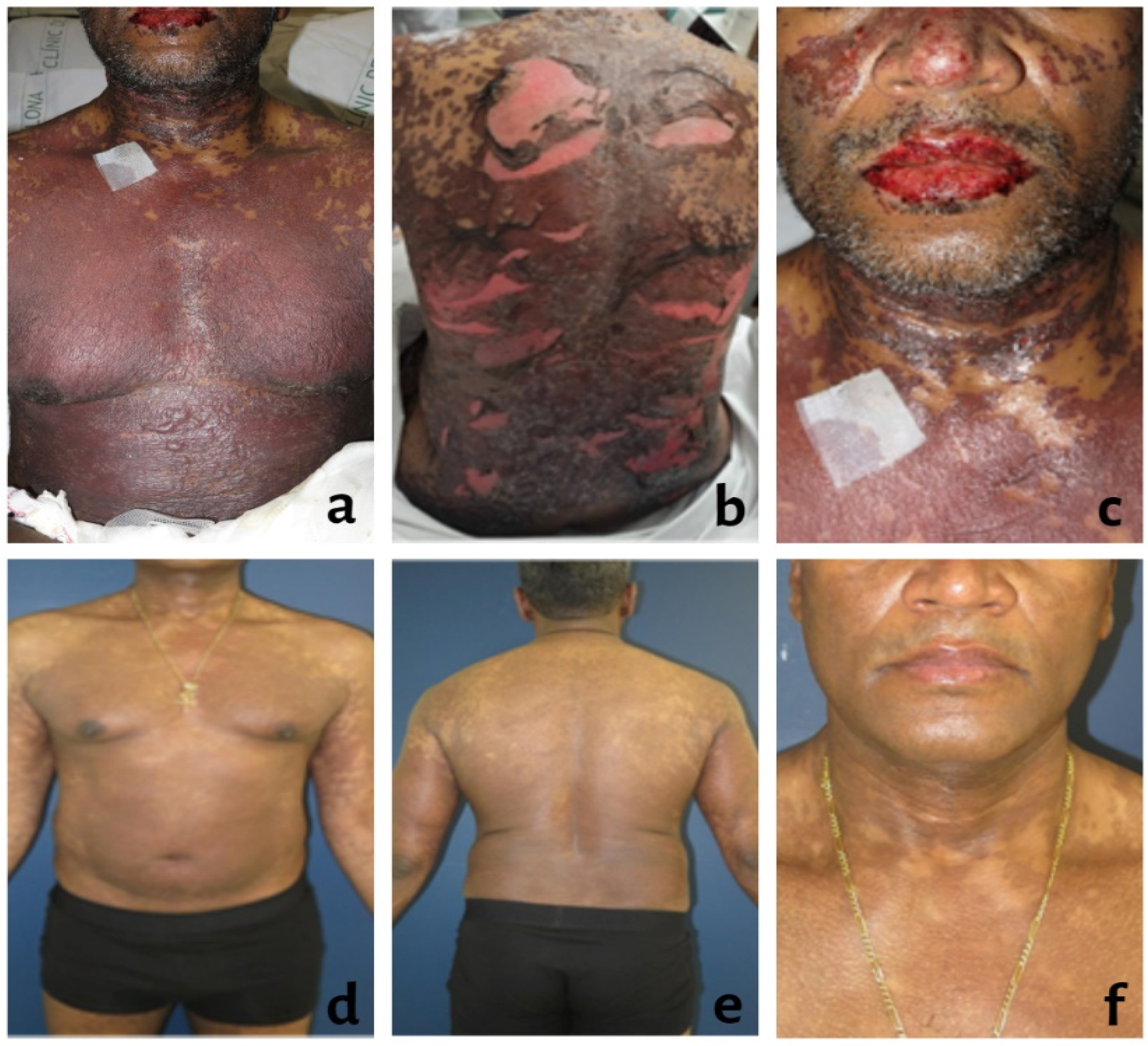
2.1.1. Investigations
2.1.2. Treatment
2.2. Outcome and Follow-Up
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nunes, J.M.; Santareno, S.; Guerreiro, L.; Margalho, A.F. Lyell’s Syndrome and Antimalarials: A Case Report and Clinical Review. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.T.; Chu, C.Y. Treatments for Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 1503709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, A.; Abe, R. Recent advances in managing and understanding Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognia, J.L.; Schaffer, J.V.; Duncan, K.O.; Ko, C.J. Dermatology Essentials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 149–158. ISBN 9780323624534. [Google Scholar]
- Frantz, R.; Huang, S.; Are, A.; Motaparthi, K. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Review of Diagnosis and Management. Medicina 2021, 57, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrandiz-Pulido, C.; Garcia-Patos, V. A review of causes of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, B.; Haddad, C.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Dunant, A.; Liss, Y.; Bork, K.; Haustein, U.F.; Vieluf, D.; Roujeau, J.C.; Le Louet, H. ALDEN, an algorithm for assessment of drug causality in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Comparison with case-control analysis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella-Alonso, A.; Aramburu, J.A.; González-Ruiz, M.Y.; Cachafeiro, L.; Sánchez, M.S.; Lorente, J.A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: A paradigm of criticalillness. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2017, 29, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.; Scherrer, L.A. Efficacy and safety of cyclosporine in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.Y.; Huang, I.H.; Chao, Y.C.; Li, H.; Hsieh, T.S.; Wang, H.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.C.; Kuo, P.H.; et al. Treating toxic epidermal necrolysis with systemic immunomodulating therapies: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, C.A.; Busto, U.; Sellers, E.M.; Sandor, P.; Ruiz, I.; Roberts, E.A.; Janecek, E.; Domecq, C.; Greenblatt, D.J. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 30, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürchler, D.; Mittelholzer, M.L.; Kerr, L. How frequent are notified severe cutaneous adverse reactions to Fansidar? Drug Saf. 1993, 8, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fansidar® (Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine). Prescribing Information; Roche Laboratories: Nutley, NJ, USA, 1996. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2004/18557slr015_fansidar_lbl.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Dibbern, D.A.; Montanaro, A. Allergies to sulfonamide antibiotics and sulfur-containing drugs. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthumchai, N.; Srinoulprasert, Y.; Thantiworasit, P.; Rerknimitr, P.; Tuchinda, P.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Rerkpattanapipat, T.; Chanprapaph, K.; Disphanurat, W.; Chakkavittumrong, P.; et al. The measurement of drug-induced interferon γ-releasing cells and lymphocyte proliferation in severe cutaneous adverse reactions. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Doval, I.; LeCleach, L.; Bocquet, H.; Otero, X.L.; Roujeau, J.C. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch. Dermatol. 2000, 136, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Azhary, R.A.; Wang, M.Z.; Wentworth, A.B.; Hickson, L.J. Treatment of Severe Drug Reactions by Hemodialysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, Y.M.; Hirahara, K.; Mizukawa, Y.; Kano, Y.; Shiohara, T. Efficacy of plasmapheresis for the treatment of severe toxic epidermal necrolysis: Is cytokine expression analysis useful in predicting its therapeutic efficacy? J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.K.; Patel, P.B.; Thakkar, S. Comparison of effectiveness of interventions in reducing mortality in patients of toxic epidermal necrolysis: A network meta-analysis. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2021, 87, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, A.; Olabi, B.; Langley, A.; Beecker, J.; Mutter, E.; Shelley, A.; Worley, B.; Ramsay, T.; Saavedra, A.; Parker, R.; et al. Systemic interventions for treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 3, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Navarro, I.; Briz-Redón, Á.; Botella-Estrada, R. Systemic therapies for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A SCORTEN-based systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesi, R.; Del Tacca, M. Hematologic toxicity of immunosuppressive treatment. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escolà-Rodríguez, A.; Marcos-Fendian, Á.; Bastida, C.; Gil Lianes, J.; Castro, P.; Mascaró, J.M.; Soy Muner, D. Efficacy of Corticosteroids and Intravenous Immunoglobulins in a Patient with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Secondary to Sulfadoxine: A Case Report and Literature Review. Reports 2023, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030035
Escolà-Rodríguez A, Marcos-Fendian Á, Bastida C, Gil Lianes J, Castro P, Mascaró JM, Soy Muner D. Efficacy of Corticosteroids and Intravenous Immunoglobulins in a Patient with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Secondary to Sulfadoxine: A Case Report and Literature Review. Reports. 2023; 6(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscolà-Rodríguez, Alba, Ángel Marcos-Fendian, Carla Bastida, Javier Gil Lianes, Pedro Castro, José Manuel Mascaró, and Dolors Soy Muner. 2023. "Efficacy of Corticosteroids and Intravenous Immunoglobulins in a Patient with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Secondary to Sulfadoxine: A Case Report and Literature Review" Reports 6, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030035
APA StyleEscolà-Rodríguez, A., Marcos-Fendian, Á., Bastida, C., Gil Lianes, J., Castro, P., Mascaró, J. M., & Soy Muner, D. (2023). Efficacy of Corticosteroids and Intravenous Immunoglobulins in a Patient with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Secondary to Sulfadoxine: A Case Report and Literature Review. Reports, 6(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030035





