Nitrogen Budget and Statistical Entropy Analysis of the Tiber River Catchment, a Highly Anthropized Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
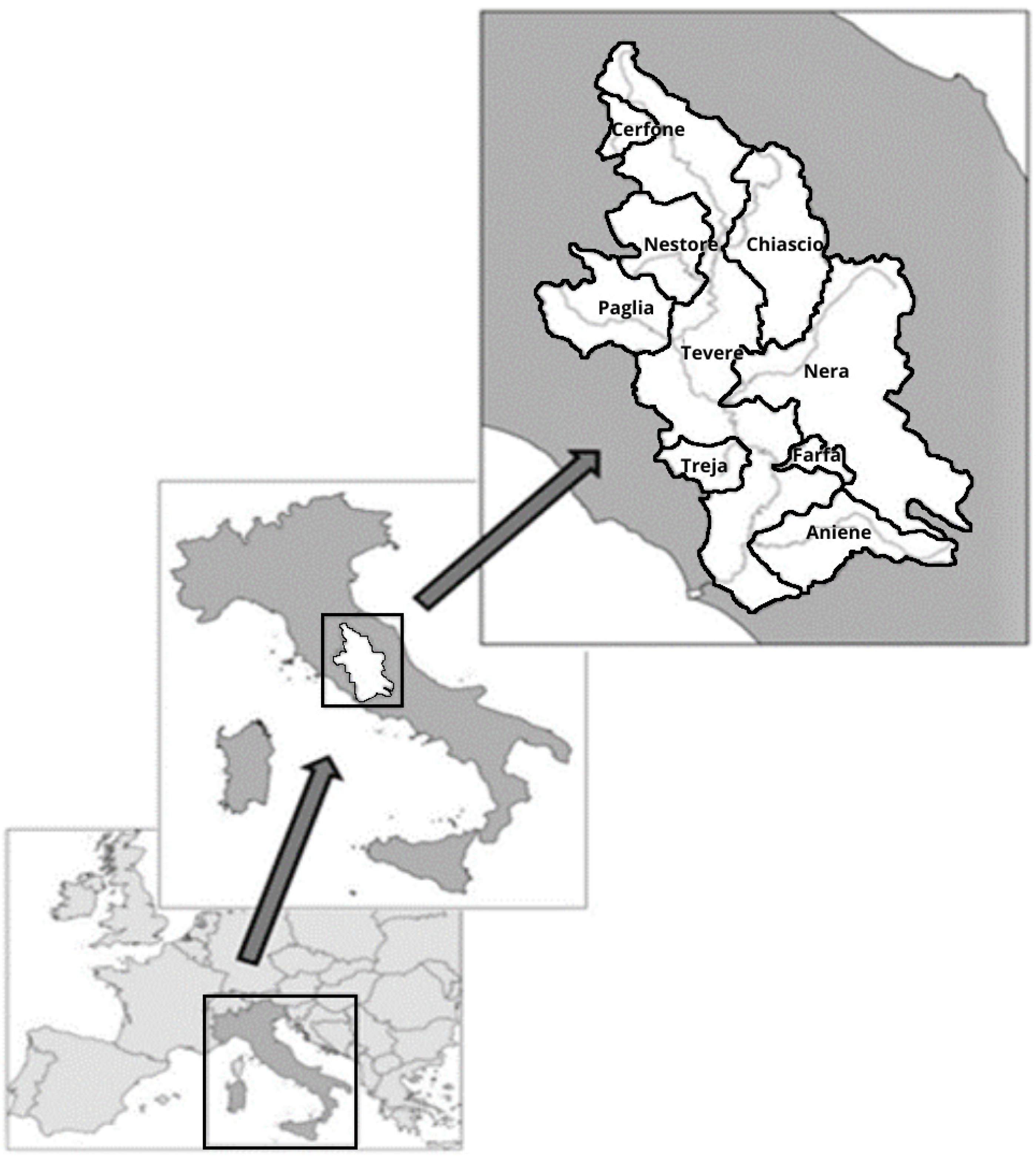
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Entropy Analysis
2.5. Simulations of N Performance Variation in the TRC System
3. Results
3.1. Nitrogen Budget
3.2. Random Forest Analysis
3.3. Soil Type Distribution at the Catchment and Sub-Catchment Levels
3.4. The Relative Statistical Entropy Analysis: Actual Management Scenario
3.5. The Relative Statistical Entropy Analysis: Different Management Scenarios
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkan, A.; Serdar, S.; Fidan, D.; Akbaş, U.; Zengin, B.; Kılıç, M.B. Physico-Chemical Characteristics and Nutrient Levels of the Eastern Black Sea Rivers Ali. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 13, 847–859. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.N.; Solanki, R.; Nirmal Kumar, J.I. An assessment of seasonal variation and water quality index of Sabarmati River and Kharicut canal at Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 1970, 10, 2771–2782. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesharaju, K.; Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.; Prakash, K. Physico-Chemical and Bacteriological Investigation on the River Cauvery of Kollegal Stretch in Karnataka. Kathmandu Univ. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 1970, 6, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ananthan, G.; Sampathkumar, P.; Palpandi, C.; Kannan, L. Distribution of heavy metals in Vellar estuary, Southeast coast of India. J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Monit. 2006, 16, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.Y.; Artigas, F.; Hobble, C.; Lee, Y.S. Assessment of anthropogenic influences on surface water quality in urban estuary, northern New Jersey: Multivariate approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2777–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valença, A.P.M.C.; Santos, P.J.P. Macrobenthic community for assessment of estuarine health in tropical areas (Northeast, Brazil): Review of macrofauna classification in ecological groups and application of AZTI Marine Biotic Index. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, Ç.; Alp, A.; Demirkiran, A.R.; Üçkardeş, F. Assessment of surface water quality of the Ceyhan River basin, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 167, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikakou, M. Modelling nitrogen in the Yeilirmak River catchment in Northern Turkey: Impacts of future climate and environmental change and implications for nutrient management. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2404–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Cape, J.N.; Reis, S.; Sheppard, L.J.; Jenkins, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first Century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, G.; Thieu, V.; Garnier, J.; Silvestre, M. Modelling the N cascade in regional watersheds: The case study of the Seine, Somme, and Scheldt rivers. Agric Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Hornbeck, J.W.; Mitchell, M.J.; Adams, M.B.; Castro, M.S.; Driscoll, C.T.; Kahl, J.S.; Kochenderfer, J.N.; Likens, G.E.; Lynch, J.A.; et al. Input-output budgets of inorganic nitrogen for 24 forest watersheds in the Northeastern United States: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 151, 373–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passy, P.; Gypens, N.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Thieu, V.; Rousseau, V.; Callens, J.; Parent, J.-Y.; Lancelot, C. A model reconstruction of riverine nutrient fluxes and eutrophication in the Belgian Coastal Zone since 1984. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kroeze, C.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Gerbens-Leenes, W. Past and future trends in grey water footprints of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs to major world rivers. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater-Marine continuum: Dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries Coasts 2009, 32, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puckett, L.J. Identifying the Major Sources of Nutrient Water Pollution: A national watershed-based analysis connects nonpoint and point sources of nitrogen and phosphorus with regional land use and other factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 408A–414A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 2002, 31, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertel, O.; Skjøth, C.A.; Reis, S.; Bleeker, A.; Harrison, R.M.; Cape, J.N.; Fowler, D.; Skiba, U.; Simpson, D.; Jickells, T.; et al. Governing processes for reactive nitrogen compounds in the European atmosphere. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4921–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somma, F. River Basin Network on Water Framework Directive and Agriculture: Practical Experiences and Knowledge Exchange in Support of the WFD Implementation (2010–2012); European Commission-Joint Research Centre-Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Reference JRC78538 Luxembourg; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Balestrini, R.; Arese, C.; Delconte, C.A.; Lotti, A.; Salerno, F. Nitrogen removal in subsurface water by narrow buffer strips in the intensive farming landscape of the Po River watershed, Italy. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlke, J.K.; Verstraeten, I.M.; Kraemer, T.F. Effects of surface-water irrigation on sources, fluxes, and residence times of water, nitrate, and uranium in an alluvial aquifer. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, K. The dependence of chemical weathering rates on fluid residence time. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 294, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlke, J.K.; O’Connell, M.E.; Prestegaard, K.L. Groundwater stratification and delivery of nitrate to an incised stream under varying flow conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 36, 664–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, P.J.; Helton, A.M.; Poole, G.; Hall, R.O.; Hamilton, S.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Tank, J.L.; Ashkenas, L.R.; Cooper, L.; Dahm, C.N.; et al. Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 2008, 452, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; Dekok, T.M.; Levallois, P.; Brender, J.; Gulis, G.; Nolan, B.T.; VanDerslice, J. Workgroup report: Drinking-water nitrate and health-Recent findings and research needs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, E.A. The contribution of manure and fertilizer nitrogen to atmospheric nitrous oxide since 1860. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, L.; Mayer, B. Nitrogen budget for the Oldman River Basin, southern Alberta, Canada. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2006, 75, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollheim, W.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Green, P.; Harrison, J.; Linder, E.; Peterson, B.J.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Global N removal by freshwater aquatic systems using a spatially distributed, within-basin approach. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neal, C.; Jarvie, H.P.; Neal, M.; Hill, L.; Wickham, H. Nitrate concentrations in river waters of the upper Thames and its tributaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 365, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.; Jarvie, H.P.; Love, A.; Neal, M.; Wickham, H.; Harman, S. Water quality along a river continuum subject to point and diffuse sources. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbe, L.; Delgado, P.; Salgado, E.; Flügel, W.A. Nitrate pollution of surface water induced by agricultural non-point pollution in the Pocochay watershed, Chile. Desalination 2008, 226, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, L.; García-Gómez, H.; Gimeno, B.S.; Rovira, J.V. Agriculture-induced increase in nitrate concentrations in stream waters of a large Mediterranean catchment over 25 years (1981–2005). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6034–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flohre, A.; Fischer, C.; Aavik, T.; Bengtsson, J.; Berendse, F.; Bommarco, R.; Ceryngier, P.; Clement, L.W.; Dennis, C.; Eggers, S.; et al. Agricultural intensification and biodiversity partitioning in European landscapes comparing plants, carabids, and birds. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carstensen, J.; Andersen, J.H.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Conley, D.J. Deoxygenation of the Baltic Sea during the last century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5628–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mockler, E.M.; Deakin, J.; Archbold, M.; Gill, L.; Daly, D.; Bruen, M. Sources of nitrogen and phosphorus emissions to Irish rivers and coastal waters: Estimates from a nutrient load apportionment framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Marín, L.A.; Wheater, H.S.; Lindenschmidt, K.E. Assessment of nutrient loadings of a large multipurpose prairie reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, J.S.; Brown, C.M. Detecting groundwater contamination of a river in Georgia, the USA using baseflow sampling. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y. Estimation of shallow groundwater discharge and nutrient load into a river. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 38, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.B.; Bohlke, J.K.; Boyer, E.; David, M.B.; Harvey, J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Tobias, C.R.; Tonitto, C.; Wollheim, W. Dynamic modeling of nitrogen losses in river networks unravels the coupled effects of hydrological and biogeochemical processes. Biogeochemistry 2009, 93, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.; Bu, F.; Xu, X.; Cao, J.; Shu, W. Seasonal variations of dissolved inorganic nutrients transported to the Linjiang Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breemen, N.V.; Boyer, E.W.; Goodale, C.L.; Jaworski, N.A.; Paustian, K.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Lajtha, K.; Mayer, B.; Van Dam, D.; Howarth, R.W.; et al. Where did all the nitrogen go? Fate of nitrogen inputs to large watersheds in the north-eastern USA. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, L.J.; Tesoriero, A.J.; Dubrovsky, N.M. Nitrogen contamination of surficial aquifers-A growing legacy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Common implementation strategy for the water framework directive (2000/60/EC). In Guidance document no. 7—Monitoring under the Water Framework Directive; Office for Official Publications of the Europe: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Teodosiu, C.; Barjoveanu, G.; Teleman, D. Sustainable water resources management 1. River basin management and the EC water framework directive. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2003, 2, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Report from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council on the implementation of the European Statistical Programme 2013–2017; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium; Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Montoya, M.D.M.; Arce, M.I.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Suárez, M.L.; Prat, N.; Gómez, R. Establishing physico-chemical reference conditions in Mediterranean streams according to the European Water Framework Directive. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Report from the commission to the European parliament and the council on the implementation of the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). In River Basin Management Plans; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium; Luxembourg, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, J.N.; Hiram Levy, I.I.; Kasibhatla, P.S. Year 2020: Consequences of population growth and development on deposition of oxidized nitrogen. Ambio 1994, 23, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzoni, M.; Gustavino, B.; Ferrari, C.; Gatti, L.G.; Fano, E.A. An integrated approach to the assessment of the environmental quality of the Tiber River in the urban area of Rome: A mutagenesis assay (micronucleus test) and an analysis of macrobenthic community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 162, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto di ricerca sulle acque Roma. Indagini Sull’inquinamento del Fiume Tevere; Istituto di ricerca sulle acque Roma: Roma, Italy, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Casini, M.; Giussani, E. Il Tevere a Roma. Autorità di Bacino del Fiume Tevere—Citera; Edizioni Ambiente: Milano, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Oenema, O.; Kros, H.; De Vries, W. Approaches, and uncertainties in nutrient budgets: Implications for nutrient management and environmental policies. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERSAF Lombardia. ERSAF Lombardia (2016) Allegato A—“Programma d’Azione regionale per la protezione delle acque dall’inquinamento provocato dai nitrati provenienti da fonti agricole nelle zone vulnerabili ai sensi della Direttiva nitrati 91/676/CEE”. Available online: https://www.ersaf.lombardia.it/it/file/2103/08bbc92c/Allegato+A+Programma+d%27Azione+Nitrati+2016-2019.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Regione Emilia Romagna, Deliberazione dell’Assemblea Legislativa della Regione Emilia-Romagna del 16 gennaio 2007, n. 96-Attuazione del decreto del Ministro delle Politiche agricole e forestali 7 aprile 2006. Programma d’azione per le zone vulnerabili ai nitrati da fonte agricola. Bollettino Ufficiale Regione Emilia-Romagna. 2007. Available online: https://bur.regione.emilia-romagna.it/archivio/bollettino_download?anno=2007&num_boll=16. (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- McKee, L.J.; Eyre, B.D. Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets for the sub-tropical Richmond River catchment, Australia. Biogeochemistry 2000, 50, 207–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, E.; Landi, G.; Sassano, A.; De Franchi, A.S. Harvest management effects on lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) forage production and quality in a hilly environment in southern Italy. In Optimal Forage Systems for Animal Production and the Environment, Proceedings of the 12th Symposium of the European Grassland Federation, Pleven, Bulgaria, 26–28 May 2003; Bulgarian Association for Grassland and Forage Production (BAGFP): Bulgaria, Balkans, 2003; pp. 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Herridge, D.F.; Peoples, M.B.; Boddey, R.M. Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvagiotti, F.; Cassman, K.; Specht, J.; Walters, D.; Weiss, A.; Dobermann, A. Nitrogen uptake, fixation, and response to fertilizer N in soybeans: A review. F Crop Res. 2008, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, T.E.; Weller, D.E. Human contributions to terrestrial nitrogen flux. Bioscience 1996, 46, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Weerden, T.J.; Jarvis, S.C. Ammonia emission factors for N fertilizers applied to two contrasting grassland soils. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 95, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussink, D.W.; Oenema, O. Ammonia volatilization from dairy farming systems in temperate areas: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 1998, 51, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asman, W.A.H. Factors influencing local dry deposition of gases with special reference to ammonia. Atmos Env. 1998, 32, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smil, V. Nitrogen in crop production: An account of global flows. Glob. Biogeochem Cycles 1999, 13, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagos, P.; Van Liedekerke, M.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L. European Soil Data Centre: Response to European policy support and public data requirements. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthof, G.; Oudendag, D.; Witzke, H.; Asman, W.; Klimont, Z.; Oenema, O. Integrated Assessment of Nitrogen Losses from Agriculture in EU-27 using MITERRA-EUROPE. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging Predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. ST4_Method_Random_Forest. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L.; Cutler, A. Manual--Setting Up, Using, And Understanding Random Forests V4.0, Technical report, University of California, Berkeley. 2003. Available online: https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/Using_random_forests_v4.0.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Vitale, M.; Proietti, C.; Cionni, I.; Fischer, R.; De Marco, A. Random forests analysis: A useful tool for defining the relative importance of environmental conditions on crown defoliation. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechberger, H.; Brunner, P.H. A new, entropy-based method to support waste and resource management decisions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobańtka, A.P.; Zessner, M.; Rechberger, H. The extension of statistical entropy analysis to chemical compounds. Entropy 2012, 14, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobańtka, A.P.; Thaler, S.; Zessner, M.; Rechberger, H. Extended statistical entropy analysis for the evaluation of nitrogen budgets in Austria. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bürgmann, H.; Widmer, F.; Sigler, W.V.; Zeyer, J. mRNA extraction and reverse transcription-PCR protocol for detection of nifH gene expression by Azotobacter vinelandii in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marco, A.; Screpanti, A.; Attorre, F.; Proietti, C.; Vitale, M. Assessing ozone and nitrogen impact on net primary productivity with a Generalised Non-Linear Model. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, update 2015. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Oenema, O.; Brentrup, F.; Lammel, J.; Bascou, P.; Billen, G.; Dobermann, A.; Erisman, J.W.; Garnett, T.; Hammel, M.; Haniotis, T.; et al. Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)—An Indicator for the Utilization of Nitrogen in Agriculture and Food Systems; EU Nitrogen Expert Panel; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Gozzi, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Buccianti, A.; Vaselli, O.; Nisi, B. Statistical methods for the geochemical characterisation of surface waters: The case study of the Tiber River basin (Central Italy). Comput. Geosci. 2019, 131, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sub-Catchment | Area (ha) | Population (×106) | Utilised Agricultural Area (UAA) (ha) | Total N Input (t N/yr) | Total N Input/UAA t N/(ha yr) | Total N Output (t N/yr) | Total N Output/UAA t N/(ha yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiber | 560,502 | 2.874 | 267,821 | 35,351 | 0.132 | 28,455 | 0.106 |
| Nera | 411,429 | 0.389 | 133,315 | 13,321 | 0.100 | 9520 | 0.071 |
| Chiascio | 163,052 | 0.215 | 76,475 | 10,395 | 0.136 | 7279 | 0.095 |
| Paglia | 129,746 | 0.079 | 50,356 | 5249 | 0.104 | 6179 | 0.123 |
| Aniene | 114,560 | 0.358 | 30,904 | 2459 | 0.080 | 1157 | 0.037 |
| Nestore | 87,137 | 0.086 | 36,087 | 4972 | 0.138 | 3716 | 0.103 |
| Treja | 40,223 | 0.059 | 18,980 | 2094 | 0.110 | 2196 | 0.116 |
| Cerfone | 29,794 | 0.013 | 11,161 | 1011 | 0.091 | 865 | 0.077 |
| Farfa | 18,011 | 0.017 | 8562 | 1109 | 0.130 | 432 | 0.050 |
| TRC | 1,554,454 | 4.090 | 633,662 | 75,961 | 0.120 | 59,798 | 0.094 |
| INPUT | t N/year | % of the total |
| Animal farming | 14,649.73 | 19.25% |
| Synthetic fertilization | 23,400.36 | 30.75% |
| Biological fixation | 34,496.55 | 45.33% |
| Atmospheric deposition | 3552.67 | 4.67% |
| Σinput | 76,099.31 | 100% |
| OUTPUT | t N/year | % of the total |
| Food, horticulture and industrial crops uptake | 50,874.46 | 79.43% |
| Nitrogen leaching | 2645.05 | 4.13% |
| Ammonia volatilization | 5203.13 | 8.12% |
| Denitrification in soil | 3805.01 | 5.94% |
| Runoff | 1522.00 | 2.38% |
| Σoutput | 64,046.66 | 100% |
| Σinput − Σoutput | 12,052.65 |
| Importance Rank | Tiber River Catchment | Sub-Catchments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiber | Aniene | Paglia | Nera | Chiascio | ||
| 1 | Total N loss by denitrification (Livestock + Agriculture) | Total N loss by denitrification (Livestock + Agriculture) | N load by atmospheric deposition | Animal husbandry load density | N load by atmospheric deposition | Total N load by biological fixation |
| 2 | N load by atmospheric deposition | Total N load by biological fixation | Total N load by biological fixation | Total N load due to livestock industry | Total N load due to livestock industry | |
| 3 | Utilised Agricultural Area | N load by atmospheric deposition | Total N loss by denitrification (Livestock + Agriculture) | Total N load by biological fixation | Utilised Agricultural Area | |
| 4 | Total N load due to livestock industry | Utilised Agricultural Area | N load by residents | Total N loss by denitrification (Livestock + Agriculture) | ||
| 5 | Total N loss (sum of fractions effectively lost) | Total N load due to livestock industry | ||||
| 6 | Nitrogen losses from non-nitrogen fixing plants | Total N loss (sum of fractions effectively lost) | ||||
| 7 | Total N load by biological fixation | |||||
| Hin | Hout | Hmax | ΔH | RSEin | RSEout | NUE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aniene | 0.843 | 7.861 | 10.914 | 833% | 0.077 | 0.720 | 24% |
| Cerfone | 1.688 | 2.323 | 9.814 | 46% | 0.171 | 0.251 | 88% |
| Chiascio | 1.721 | 5.158 | 13.085 | 200% | 0.132 | 0.394 | 84% |
| Farfa | 0.587 | 9.436 | 9.503 | 1508% | 0.062 | 0.993 | 23% |
| Nera | 1.967 | 3.455 | 13.416 | 76% | 0.147 | 0.257 | 60% |
| Nestore | 2.210 | 3.830 | 11.896 | 73% | 0.186 | 0.322 | 96% |
| Paglia | 1.607 | 1.698 | 12.616 | 6% | 0.127 | 0.135 | 119% |
| Tiber | 1.917 | 2.692 | 14.842 | 40% | 0.129 | 0.181 | 92% |
| Treja | 1.132 | 2.361 | 11.282 | 109% | 0.100 | 0.209 | 65% |
| Tiber River Catchment | 1.906 | 2.885 | 15.967 | 51% | 0.119 | 0.181 | 84% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Marco, A.; Fornasier, M.F.; Screpanti, A.; Lombardi, D.; Vitale, M. Nitrogen Budget and Statistical Entropy Analysis of the Tiber River Catchment, a Highly Anthropized Environment. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems6010017
De Marco A, Fornasier MF, Screpanti A, Lombardi D, Vitale M. Nitrogen Budget and Statistical Entropy Analysis of the Tiber River Catchment, a Highly Anthropized Environment. Soil Systems. 2022; 6(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems6010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Marco, Alessandra, Maria Francesca Fornasier, Augusto Screpanti, Danilo Lombardi, and Marcello Vitale. 2022. "Nitrogen Budget and Statistical Entropy Analysis of the Tiber River Catchment, a Highly Anthropized Environment" Soil Systems 6, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems6010017
APA StyleDe Marco, A., Fornasier, M. F., Screpanti, A., Lombardi, D., & Vitale, M. (2022). Nitrogen Budget and Statistical Entropy Analysis of the Tiber River Catchment, a Highly Anthropized Environment. Soil Systems, 6(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems6010017








