Abstract
Agricultural residues are generated during the production and processing of agricultural crops. Under modern date palm plantation practices, field operations generate huge quantities of residues, which are discarded with little valorization. The date palm agro-industry produces significant amounts of waste. The accumulation of these residues can cause ecological damage to the oasis ecosystems. There is a lack of comprehensive data on long-term research studies that aim to assess the impact of date palm waste management practices. Composting and/or pyrolysis of date palm residues showed benefits for improving soil physical and chemical properties, particularly in sandy soils. This claim holds particular significance for arid and semi-arid regions, which are characterized by low fertility and are susceptible to soil degradation, accentuated by ongoing climate change. This review summarizes the existing literature concerning the valorization of date palm residues with regards to compost and pyrolysis processes, as well as the impact of their application on soil quality. Further research is required to assess the effects of using date palm residues for better soil amendment management. Research should focus on composting and biochar technologies for date palm residues and their application in arid and semi-arid regions to combat soil erosion and degradation. Increasing the beneficial uses of date palm residues could lead to sustainable and economic growth in dry areas.
1. Introduction
1.1. State of the Art of Crop Residue Management
Crop residue management is a significant concern for stakeholders, particularly in the European Union, where fruit tree cultivation covers 11,301,345 hectares [1]. Woody residues from tree crops are major sources of biomass, with annual pruning yields ranging between 1 and 5 tons of fresh material/ha [1,2]. Mediterranean countries generate substantial quantities of pruning residues annually, with olive orchards contributing 1.31 t/ha of residual dry biomass [3], almond orchards contributing 1.34 t/ha [4], apple orchards contributing up to 4.14 t/ha [5], and vineyards contributing 4.2 t/ha [6]. Despite recommendations from the European Commission advocating for increased use of pruning residues as biomass fuel or composting, these applications remain largely marginal due to technical limitations, legislative issues, and the reuse chain’s low remuneration. As a result, most pruning residues are still outside the bioenergy supply chain [7].
Organic matter addition is an important soil management strategy for increasing the soil’s carbon pool. Most tree prunings generated are either burned in open-air fires or shredded as a soil amendment (e.g., mulch). While the former entails no net environmental benefits, the latter can improve soil conditions, but it can also be a vector for crop diseases. Consequently, some regions prohibit or strongly discourage the use of biomass as fertilizer, while others promote it, often in conjunction with pesticides [8]. According to the EUROPRUNING project [2], farmers often incorporate prunings into the soil not because it is the most effective management strategy, but rather because it is the most straightforward form of waste management. The primary factor determining whether burning or soil amendment is predominant is whether there is a regional or national ban on burning prunings in open-air fires. Furthermore, the integration of prunings into the soil did not have a significant impact on soil organic carbon (SOC) content, but their effects were more pronounced in herbicide-treated, grass-free rows. Grass cover in interrows can provide an alternative carbon source for soil microorganisms, increasing microbial biomass carbon and microbial diversity. Orchards with grass cover showed higher diversity compared to those without [9].
1.2. Challenges for Maintaining Sustainable Agriculture in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas
According to Garcia-Franco et al. (2021) [10], over 47% of the Earth’s land surface is comprised of arid and semi-arid regions, which are characterized by a weak aridity index (AI = precipitation/potential evapo-transpiration). Despite these challenging conditions, drylands are responsible for producing around 44% of the world’s crops [11]. About 70% of these regions are located in Africa and Asia [12]. Arid areas in North Africa are mostly associated with sandy soils (Arenosols, Psamments), which are weakly differentiated, often of aeolian origin, and with an average SOC content of less than 3 g kg−1 in topsoil (≤30 cm) [13]. Cultivated soils are more and more affected by the accumulation of water-soluble salts (NaCl, Na2SO4, etc.), which increase osmotic pressure, diminish water availability, and inhibit plant growth at high concentrations [14]. Calcareous and/or gypsiferous soils, often found in arid and semi-arid regions, have low nutrient levels, which can limit crops’ ability to absorb essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen [15,16]. European Mediterranean soils are more diverse, and their classification may vary from Regosols or Leptosols to Cambisols and Fluvisols [17,18,19].
The cultivation of palm trees is better suited for arid and semi-arid regions worldwide [20]. The palm tree canopy allows for the plantation of underneath crops (e.g., barley, alfalfa, figs, etc.), which are primarily used to feed livestock [21]. Sheep, cattle, or goats produce a large amount of manure each year, traditionally used by farmers to fertilize their crops. But the water scarcity due to the succession of drought years forced oasian farmers to reduce their livestock, leading to low availability of local manure and higher costs if it was available [21]. El Janati et al. (2021) [21] reported that the large areas and high densities of monocropped date palm trees produce a large quantity of dry palms (2.1 t ha−1 at 138 trees ha−1). Recycling these organic waste products is a potential solution to provide organic inputs and address the current manure shortage. El Janati et al. (2023) [22] observed that utilizing date palm compost produced on farms could effectively address the lack of organic inputs and enhance the organic date production chain. In the deserts of the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa, oasian agroecosystems have long been the only viable crop production system. But important changes took place in the Saharan oases in the second half of the 20th century, accompanied by social, economic, agricultural, and environmental transformations [23]. Indeed, the emergence of new technological means such as mechanized hydraulics has allowed rapid agricultural expansion since the 1970s. The Maghreb countries have provided political and economic support for the export variety ‘Deglet Nour’, along with subsidies for the establishment of new areas and the expansion of existing cultivated areas [24]. For instance, in Tunisia, so-called “modern” oases or palm groves, or monocultures of date palms for commercial purposes, represent about 73% of the oasis area [25]. Today, agriculture in arid areas is facing new and complex challenges such as water scarcity, salinization of groundwater and soils, aeolian erosion, ravages caused by diseases, and the exodus of populations that increase the vulnerability of these environments [26,27,28]. The climate change underway in the Maghreb is likely to have a significant impact on oasis environments [12].
Agricultural practices on modern date palm plantations generate large quantities of by-products from seasonal pruning, such as empty fruit bunches, seeds, and stem barks. However, the use of these by-products in North African countries is limited [29], with only a small proportion effectively recovered. These by-products are not widely recognized for their value as bioresources. Currently, there is no efficient and comprehensive system established in the EU for managing pruning waste. Local authorities frequently manage these residues at multiple collection locations, primarily composting them or sending them to landfills [30]. The most common form of biological treatment for reusing wood pruning in agriculture is composting, followed by mechanical fractionation to achieve a uniform green material. This material can then be used as a soil amendment or for other approved purposes, such as landfill cover and revegetation [31]. Currently, waste composting practices in arid and semi-arid regions are rather basic. The process involves collecting and piling the residues in permitted composting plants without any specialized treatments or planned final applications [31]. Additionally, the application of pyrolyzed organic carbon to soils has been assessed worldwide to play a vital role in improving the physical–chemical characteristics of the soil [16]. Date palm biochar can therefore be regarded as a useful and valuable organic amendment. However, the effects of biochar application on soil properties in an arid region are not well understood [29].
Hence, the adoption of sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid regions faces significant obstacles, including, but not limited to, water shortages, soil salinization, and restricted availability of organic resources. Inadequate facilities and a lack of understanding of their impact on soil quality hinder the efficient management of by-products and the implementation of novel methods like composting and pyrolysis, which are crucial. As a result, the goal of this paper is to give an in-depth look at the latest research on finding useful uses for date palm waste, focusing on the composting and pyrolysis methods as well as the possible impacts on soil quality when they are used.
2. Context of Date Palm Cultivation and Residue Production
2.1. Geographic Distribution of the Cultivated Date Palm
Date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.] is a monocotyledon dioecious plant species related to the Arecaceae family, and it has been cultivated for thousands of years [32]. Indeed, Tengberg (2012) [32] reported that the origin of oasis agriculture likely dates to prehistoric times around the Persian Gulf, where the first evidence of date palm cultivation dates back to about the 5th millennium B.C. Date palm spread to North Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, South Asia, southern Africa, America, and Australia, wherever suitable climatic conditions enabled commercial fruit production [33]. Although Mlih et al. (2015) [34] suggest that the date palm originated in North Africa or the Middle East, there is a scarcity of local reports on the origin and ancient history of oasis agrosystems in the MENA region (Middle Eastern and North African region), known as one of the most water-scarce regions globally.
According to El-Janati et al. (2023) [22], approximately 120 million date palm trees exist in the world. The date palm is more suitable for cultivation in arid and semi-arid regions of the globe [20] due to its resilience and adaptability to harsh environmental conditions, including drought, salinity, high temperature, and poor soil conditions. Date palms form the canopy of most of North Africa’s oasis and allow herbaceous crops to grow [35]. It is considered one of the most suitable crops for production in the MENA area, where these prevailing climatic conditions exist [36,37]. These locations are particularly vulnerable to climate change impacts, which may worsen the effects of environmental and soil conditions on date palm production and threaten its long-term sustainability [38,39].
The palm tree is widely marketed as a high-value fruit crop due to its importance in nutritional content and serves as an important food supply in arid regions [34]. Fruit is an excellent source of carbohydrates, proteins, minerals, dietary fibers, and vitamins [40,41,42]. Date fruit is also a source of potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, copper, zinc, and selenium [42,43]. Date palm cultivation in the Mediterranean basin plays an important economic role. Efficient management practices, such as the use of modern irrigation systems, the selection of cultivars best suited to local environmental conditions, and the enhancement of soil water and nutrient retention, help to sustain the cultivation and productivity of date palms [44]. Water scarcity, very high temperatures, salinity, soil deterioration, disease (e.g., bayoud), and pests will be the greatest future obstacles for date palm cultivation [45,46].
2.2. Soil and Climatic Conditions
The date palm shows remarkable adaptability and can thrive in adverse natural conditions. It can thrive in harsh environmental conditions and produce fruit with minimal agricultural inputs and management [47,48,49]. Date palm trees play a critical role in achieving environmental balance. They grow in harsh climatic environments, even in highly saline, sandy soils [50]. Due to their large size, date palms absorb carbon dioxide to a greater extent than other trees. Sharifa et al. (2010) [50] suggested that, since one date palm tree would reduce CO2 by 200 kg annually [51], growing a million trees would absorb 200,000 tons of CO2 as well as the food value. As a result, the date palm becomes a crucial species against global warming, which is primarily due to greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs).
Date palm cultivation primarily occurs in dry land soils with low plant productivity and minimal organic matter inputs [48]. Date palm can bear air temperatures of up to 50 °C for short periods and low air humidity for fruiting if the water is available in the subsoil [52]. However, due to a lack of precipitation, the trees are currently exposed to excessive salts in the soil. In addition to salinity, drought, temperature, and soil-related factors (texture, pH, organic matter, and nutrient content), disease and pest attacks are among the most significant crop production constraints in most arid and semi-arid regions where date palm-producing countries are located [53,54,55]. Because date palm cultivation occurs in arid and semi-arid regions, the soil is often characterized by an alkaline pH and is coarse-textured. Date palms are moderately tolerant to alkaline soils and need adequate aeration and drainage [47]. Alkaline and calcareous soils influence date palm growth, but factors like nutrient availability and fertilizer efficiency, particularly phosphorus, can also influence its development, according to Smith et al. (2013) [56]. Alkaline soils limit the availability of phosphorus, the most pH-sensitive macronutrient, due to their high capacity for Ca2+ retention and precipitation. In arid regions, Evans et al. (2009) [57] reported that producing compost from organic waste products enriched with either animal manure or rock phosphate can increase the availability of P to plants. Date palms require an annual supply of basic cations in proper balance to support their growth [58]. Root uptake of K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ decreases at soil pH levels above 8.0 due to limited nutrient availability and competition from Na+ [59,60]. Therefore, increased K and Mg fertilizer doses are required [44].
With regards to soil texture, date palm trees can be grown in a wide range of soil textural classes, but ideal soil texture conditions are deep sandy and loamy for better root development and drainage [61]. These soils have a low organic matter and nutrient content [62], and because of their sandy texture, their potential to sequester carbon is limited [63], while their potential water-holding capacity is also low. For this reason, large amounts of irrigation water resources are wasted due to poor soil properties [64]. However, when proper drainage and aeration practices are implemented and adequate soil moisture is maintained, sandy soils are ideal for date palm plantations [59,60].
The date palm tree has evolved through natural selection to be a drought- and salt-tolerant plant [59]. Date palms can tolerate soil salt concentrations up to 4.0 dS m−1 [65] and, in many cases, up to 12 dS m−1 [66]. However, an electrical conductivity of 17.9 dS m−1 in soil and 12.0 dS m−1 in water can reduce yields by up to 50%. Fruit production usually stops at 15.6 dS m−1 [67]. Tolerance to salt depends on the genetic potential of the date palm variety, climate, soil drainage, and texture [68]. Cultivating salt-tolerant cultivars is an appropriate strategy to address growing salinity issues. At the seedling level, studies show that local cultivars can grow in soils with an electrical conductivity of 25 dS m−1 [69,70].
2.3. Date Palm Residues
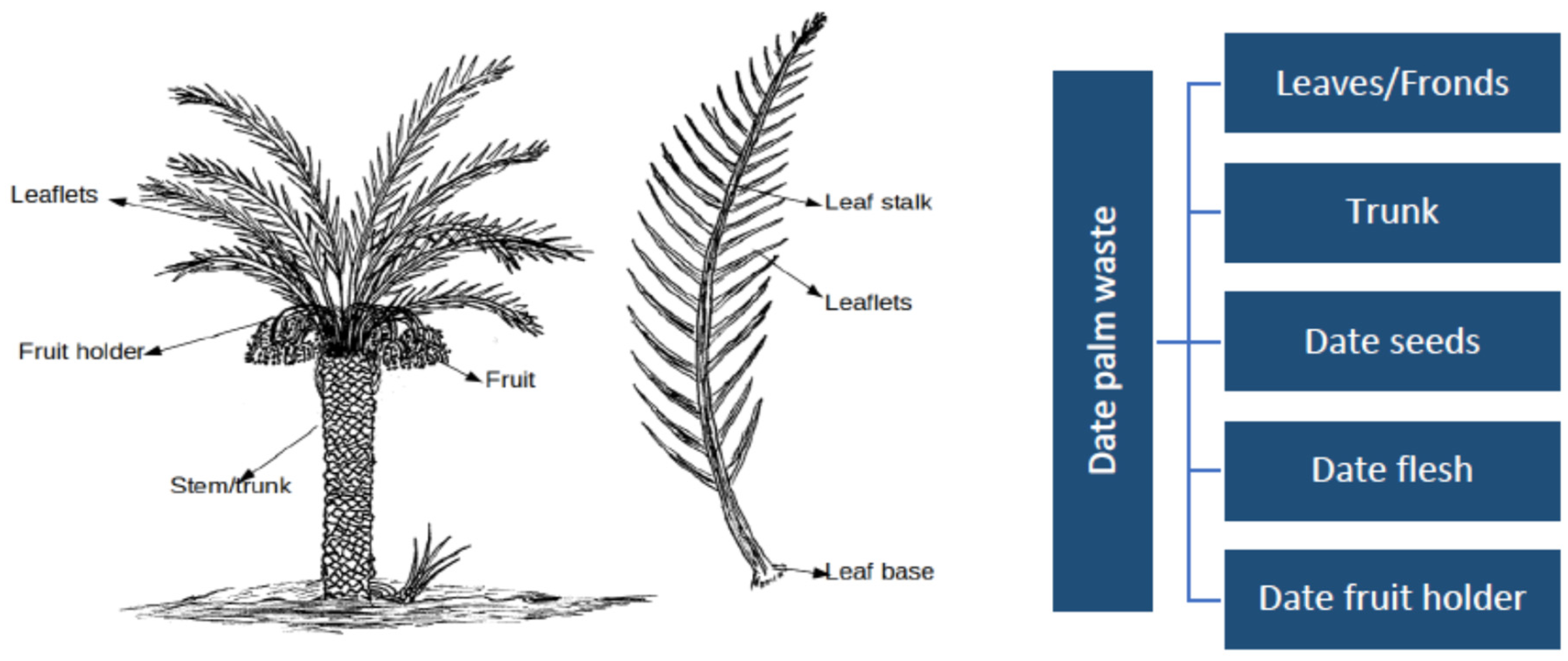
Under modern date palm plantation practices, field operations produce large quantities of empty fruit bunches, seeds, stem barks, cull fruits, leaves, and fronds (Figure 1). These materials are obtained by seasonal pruning of palm trees, which is an important agricultural practice, and discarded with no valorization. Morvan et al. (2022) [29] observed that the North African region effectively recovers only a small proportion of date palm cultivation by-products. Notably, these by-products, such as palm branches, are mostly employed for purposes such as stabilizing sand dunes, constructing fences in an oasis, or providing shade. The recognition and evaluation of their value as bioresources, particularly their potential impact on soil fertility, have received limited attention to date. El-Janati et al. (2023) [22] report that the world produces approximately 1.6 million tons of date palm residues annually. Farmers who primarily attempt to burn or transport the vast quantities of palm waste produced each harvest season face a significant cost. Every year, agricultural land accumulates large amounts of leftovers (fronds and leaves) from harvested date palms [49]. Each date palm tree produces about 20 and 40 kg of dry organic waste annually in Saudi Arabia [71] and Iran [72], respectively, while date pits, by-products of date fruit processing industries, account for almost 10 percent of date fruits [73,74]. In particular, the management of date palm trees generates as much as 16–20 kg of dry leaves per tree per year [74,75]. Similarly, El Janati et al. (2021) [21] observed that oasian agroecosystems generate an estimated 1.5 to 2.4 tons of date palm waste per hectare per year. In fact, date palm leaves represent the primary residues produced on an annual basis by date palm trees [49]. Additionally, the date palm agro-industry generates significant amounts of waste, primarily fallen date fruits, date fruit seeds [pits], and date press cakes. Date fruit contains between 11 and 18% date seeds by weight [76,77].
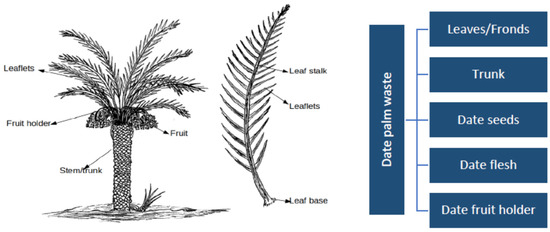
Figure 1.
A date palm tree with its different components (Tahir et al., 2020 [74]).
Farmers commonly leave date palm residues in the field as mulch [33]. However, most farmers discard these materials [78], burn them [22], or bury them in landfills [79] without realizing their potential value. Large-scale production of these wastes [80] not only contributes to a significant loss of raw materials [81], but also poses serious environmental problems. Bashah (1996) [82] noted that leaving raw materials in date palm waste for a long time is likely to be highly flammable. Furthermore, burning them directly in open fields can pose a significant environmental and health risk due to the release of toxic gases [83,84]. Moreover, the accumulation of date palm residues in the field can have harmful effects, such as the proliferation of insects and parasites on date palm trees [85].
3. Sustainable Utilization of Organic Amendments Based on Date Palm Biomass
Date palm trees provide significant amounts of agricultural residue that can be utilized for various purposes, such as feeding livestock and composting [86]. Date fruit contains cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, as well as other solids with high volatile content and low moisture content, making it a valuable biomass resource in regions that grow dates [84]. The low moisture content of date palm waste makes it well suited to thermochemical conversion technologies like combustion, gasification, and pyrolysis [87]. Pyrolysis is a commonly employed thermochemical technology for transforming biomass into liquid and solid forms [88]. Date palm residues (leaves, empty fruit bunches, and petioles) have high ash, high oxygen, low volatiles, and an average heat value when compared to other forms of biomass and energy crops. The outcome of fast pyrolysis in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor at 525 °C was found to be 38.65% biooil (including 10.39% reaction water), 37.23% biochar, and 24.02% non-condensable gas [89]. Furthermore, the exceptional organic composition of date palm residues—including date palm leaves, which contain over 80% organic matter [22]—enables them to be used as a substitute for chemical fertilizers in date palm plantations during compost production. For the sustainable use of date palm biomass, numerous physico-chemical, thermal, and biochemical technologies are available. Thus, the abundance of date palm trees in the MENA and Mediterranean regions can enhance the development of the compost and biochar sectors in the region. Below, the main valorization technologies—pyrolysis and composting—and the effects of final products on soil quality are reviewed.
3.1. Production, Use, and Effects of Date-Palm-Based Biochar on Soil
3.1.1. Principle of Biochar Production
Various organic materials, such as agricultural residues, forest residues, algal biomass, manures, activated sludge, energy crops, and polymers, serve as suitable ingredients for biochar production [90,91]. Carbon-rich materials undergo thermal transformation to produce biochar, a stable solid byproduct. Biochars vary in their physical, chemical, and mechanical properties based on the source material and pyrolysis conditions. Global efforts are increasingly focusing on developing technologies to convert agricultural waste into biochar, driven by escalating energy needs and mounting concerns about greenhouse gas emissions and soil degradation [92,93]. Biochar, bio-oil, and gases like methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide are the byproducts of biomass pyrolysis. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass occurring in the absence of oxygen at temperatures usually ranging from 300 to 700 °C in order to produce liquid biofuel [bio-oil], biochar, and renewable syngas [89].
The biochar production process consists of three distinct stages: pre-pyrolysis, main-pyrolysis, and carbonaceous soil product formation [94,95]. The first stage involves the loss of moisture and some volatiles (<150 °C). Hemicelluloses and cellulose devolatilize and decompose rapidly in the second stage (200–500 °C) [96]. Degradation of lignin and other organic matter with stronger chemical bonds occurs in the final stage (above 500 °C) [97]. The biochar decomposes very slowly in the third step, forming a residue solid that is rich in carbon. When secondary charring occurs, the char becomes less reactive. Pyrolysis will produce mostly biochar at low temperatures (less than 450 °C when the heating rate is very slow) and mostly gases at high temperatures (greater than 800 °C) with rapid heating rates, depending on the thermal environment and the final temperature [98].
Nevertheless, the process of converting several tons of recently harvested plant biomass into biochar for practical use requires a substantial quantity of heat energy, potentially leading to cost limitations. In recent years, researchers have focused significantly on integrating solar energy into biomass pyrolysis. Solar energy offers a sustainable and renewable alternative for pyrolysis, providing it with a comparative advantage over thermal energy use [99,100]. The arid regions’ solar characteristics make them ideal for solar concentration [101]. In a pyrolysis reactor, a solar concentrator with an area of 10 m2, operating at a conversion efficiency of 50%, can harness solar heating energy of up to 92.4 MJ. The amount of energy provided is sufficient to pyrolize over 1 kg of dry biomass to a temperature of 500 °C in around 5 min [102]. A concentrated solar energy system is developed and simulated using SuperPro Designer v8.5 to convert date palm waste into biochar through pyrolysis [103]. Economic analysis demonstrates that this process is more economically viable compared to the traditional process. Environmental impact assessment reveals that concentrated solar energy-based pyrolysis emits only 38% of the CO2 emissions produced by conventional pyrolysis. This indicates that concentrated solar energy pyrolysis is more ecologically sustainable. Caputo and Mašek (2021) [104] developed a system that produces biochar and electricity for soil amendment and energy access. The system is capable of pyrolyzing agricultural waste streams, producing at least 5 kg of biochar per unit per day. The system’s feasibility depends on the actual yield and composition. According to the research by Ndukwu et al. (2020) [100], to improve the efficiency of solar-driven biomass pyrolysis, it is important to think about a number of things, such as the type of feedstock used, the choice of concentrating optics, the thermodynamics of the process, and the yields of the end product. Furthermore, to ensure optimal performance, it is critical to carefully design the installation orientation of solar-thermal systems and the reactor itself. Therefore, while date palm wastes hold great potential for sustainable biomass valorization, addressing technological constraints, such as energy requirements, through innovative solutions like solar-driven pyrolysis is crucial for maximizing their utilization and minimizing environmental impact.
3.1.2. Factors Influencing the Characteristics of Biochar
Biochar appears to be a new potential low-cost and effective material that has a wide range of characteristics, transfusing unique properties. These properties include high water-holding capacity, large specific surface area, enriched surface functional groups, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and a porous structure similar to that of activated carbons [105]. Biochar also has a high degree of chemical and microbial stability due to its molecular structure. The porous structure can protect beneficial soil microorganisms, such as mycorrhizae and bacteria, as well as influence the binding of important nutritive anions and cations. The production factors of biochars correlate with the above properties. Furthermore, the amounts of essential mineral elements in biochar are directly correlated with the concentrations of their components in the original feedstock [106,107,108]. However, the long-term effects of biochar, both the benefits and the disadvantages, are still little studied to date.
Various factors, such as conversion technologies, gas type, catalyst use, heating temperature, and feedstock type, influence the production and properties of biochar [109]. The conversion processes include pyrolysis, gasification, torrefaction, and hydrothermal carbonization. Pyrolysis entails heating biomass in an oxygen-free environment, gasification employs heat under limited oxygen conditions, and torrefaction involves heating (200–300 °C) in an inert atmosphere. Hydrothermal carbonization uses high pressure (2–6 MPa) at lower temperatures [110]. Microwave pyrolysis is a new method that offers rapid, uniform, and selective heating for biochar production [109].
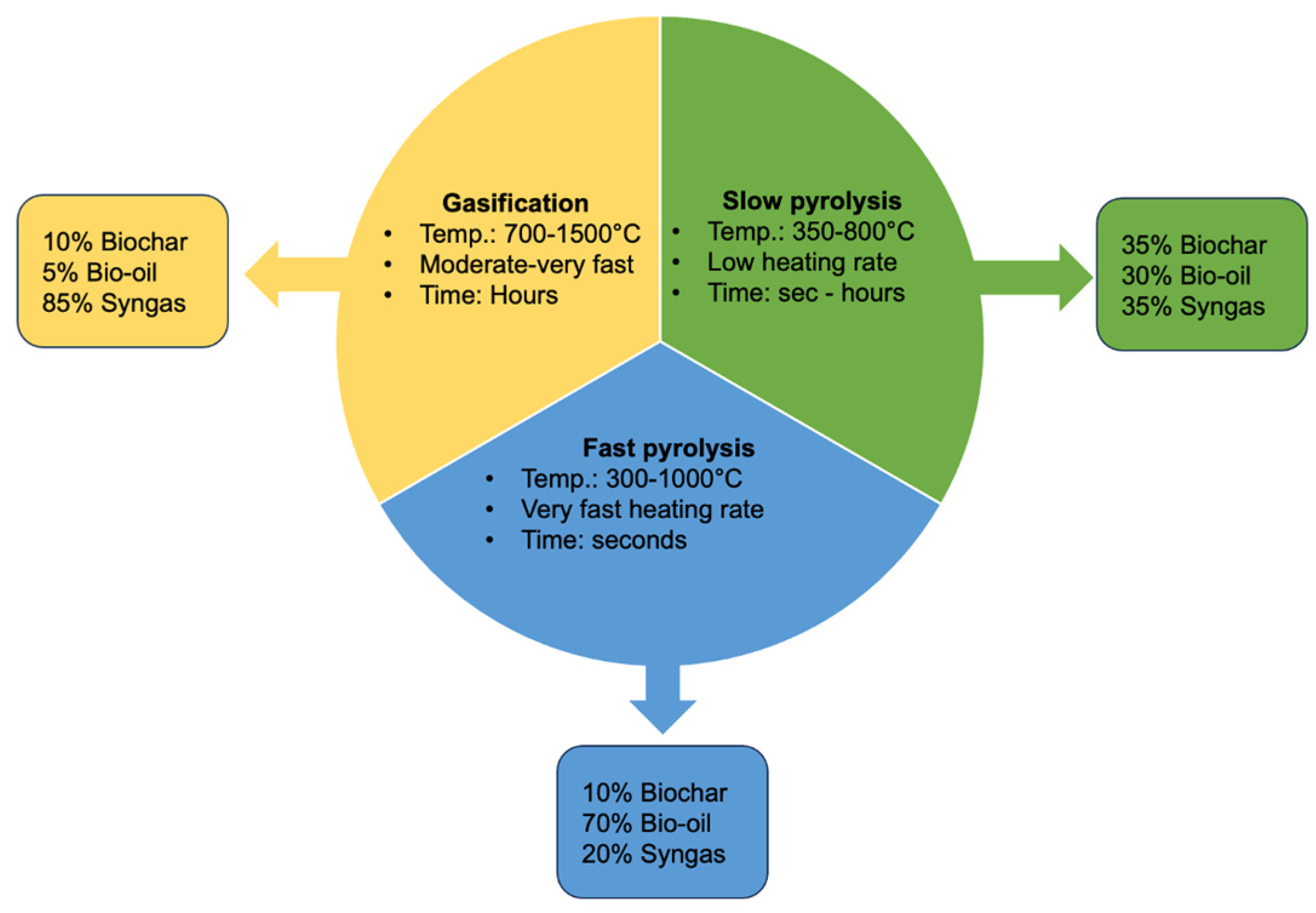
The different thermal conversion technologies and their products are described in Figure 2.
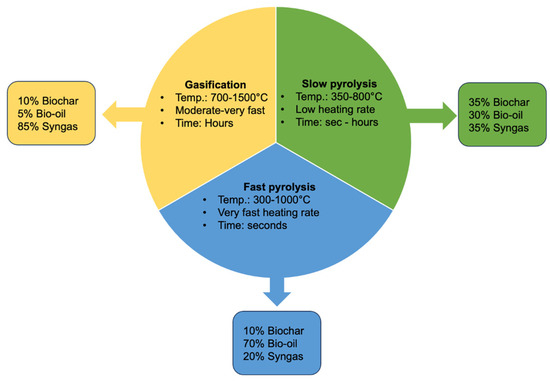
Figure 2.
Biochar production methods and different biochar yields obtained (modified from Tahir et al., 2020 [74]).
Biochar composition varies depending on the source of biomass and the treatment method. Thermal carbonization (TC) biochars are more stable and have a higher carbon sequestration potential than hydrochar made by hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) [111,112,113,114,115,116]. Pyrolysis biochar is more stable and has a higher C sequestration potential [114]. However, after field application of corn silage, HTC char quickly degrades and increases GHG emissions. such as CH4 and CO2 [113,117,118]. Hydrochar application may enhance greenhouse gas emissions due to increased microbial activity [119]. Additionally, slow-pyrolysis char, produced at temperatures below 500 °C, has a consistent impact on GHG emissions and is more long-lasting in soil [118].
Many studies have considered temperature to be a factor influencing biochar properties. According to Pariyar et al. (2020) [120], both the temperatures used in the pyrolysis process and the types of feedstocks had a significant impact on the properties of biochar. The study suggested that biochar produced at high temperatures (specifically 550 °C and 650 °C) exhibits greater efficacy in terms of carbon sequestration. Sun et al. (2014) [121] also demonstrated that pyrolysis temperature and feedstock type have an impact on the production rate, thermal stability, carbon content, and elemental composition of biochar. Biochar envelope density and porosity vary primarily with biomass feedstock [122]. Researchers have observed that temperature enhancement positively impacts the adsorption properties, primarily because it simultaneously increases the specific surface area and pore volume [123,124]. At higher pyrolysis temperatures, the surface area and porosity increase, along with the concentration of nutrients on the surface of the adsorbent, including P, K, Ca, and Mg, which in turn, would allow ion exchange with metals and result in higher adsorption capacities [125].
The literature lacks information on the production and characterization of biochar derived from date palm waste across a broad spectrum of pyrolysis temperatures [79]. The majority of biochar production studies used a muffle furnace contained inside a sealed steel container to regulate the charring temperature within the range of 300 to 800 °C. With an increase in pyrolysis temperature, there was a corresponding drop in moisture, elemental composition, and volatile content. Conversely, the surface basicity, ash, pH value, basic cations, and carbon content increased with higher temperatures. Studies concluded that biochar, with the best carbon sequestration potential, was found at a temperature > 500 °C. Munir et al. (2019) [126] subjected the waste biomass derived from the rachis of date palm trees to pre-treatment using silica or zeolite minerals through the processes of ball milling and sonication. Subsequently, the pre-treated biomass was subjected to pyrolysis at a temperature of 600 °C. Compositing biochars with silica showed the highest potential for carbon sequestration capability (ranging from 64.2% to 95.6%) compared to other biochar types. Changes in the arrangement of structures within the silica–biochar complex help explain why biochars mixed with silica are more resistant to change and better at storing carbon. The authors’ findings suggest that incorporating silica-combined biochars into soil as a soil supplement can effectively prolong the sequestration of soil organic carbon. On the other hand, biochar produced at lower temperatures (<500 °C) does contain more functional groups and has lower pH values, which makes it more suitable for soil with poor fertility and a high pH [74,79]. According to Sizirici et al. (2021) [127], there was a noticeable rise in the pore volume, surface area, pH, and total carbon content of date palm leaf and frond biochar as the pyrolysis temperature increased. Conversely, the biochar’s functional groups, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen content decreased in comparison to the original feedstock.
Date palm residue is a low-cost adsorbent and a sustainable waste management solution due to its abundance in many countries. A 30-day experiment was performed where date palm feedstock and biochar were added to mined soil that was contaminated with heavy metals [128]. The production of biochars was carried out at various charring temperatures (300, 500, and 700 °C) for a duration of 4 h, with a rate of 5 °C per minute. The resulting by-products were then introduced into the soil at different quantities (0, 5, 15, and 30 g kg−1) in order to investigate their immediate impacts on soil respiration, soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC), soil soluble organic carbon, and mobile heavy metal fractions. It was concluded that low-temperature biochar can be utilized as a soil amendment to decrease the movement of heavy metals in mining-contaminated soil as well as reduce the release of CO2-C from the soil. Biochar has anionic organic groups that can bind to heavy metals and remove them through surface complexation, ion exchange reactions, and electrostatic attraction [129,130,131].
Sizirici et al. (2021) [127] used leaf and frond date palm residue as feedstock to derive biochar. The effects of pH, feedstock type, and pyrolysis temperature at 400, 500, and 600 °C on the capacity of date palm waste-derived biochar to remove copper, iron, nickel, and zinc in single and mixed metal solutions were investigated. At different pyrolysis temperatures, biochar obtained from different feedstocks did not show any statistically significant improvements in removing single or mixed metals from aqueous solutions. Biochar derived from date palm waste at low pyrolysis temperatures showed similar metal removal effectiveness as biochar produced at high temperatures. Therefore, a lower pyrolysis temperature provides increased efficiency in heavy metal removal while consuming less energy. The authors concluded that utilizing date palm waste materials to produce biochar is a sustainable solution in terms of cost-effectiveness and impact on global warming potential.
The provided information clearly indicates that date palm residue-produced biochar has the potential to be a cost-effective and efficient material with several beneficial properties, such as improving soil health and sequestering carbon. Temperature conditions, feedstock type, and treatment methods greatly influence the characteristics and effectiveness of biochar in carbon sequestration and heavy metal removal. However, a comprehensive investigation of the long-term impacts of biochar, including both advantages and drawbacks, remains incomplete. Furthermore, while high-temperature biochar has a higher capacity for carbon sequestration, lower-temperature biochar might be more suitable for specific soil conditions and heavy metal removal. This emphasizes the need for tailored strategies in the production and application of biochar.
3.1.3. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil Properties
Badawi (2019) [132] observed that using biochar produced from date palm fronds as a soil amendment enhances soil fertility, conserves moisture, reduces toxic gas emissions, and contributes to global warming mitigation efforts. Farmers use biochar to enhance soil fertility because it is a highly stable organic compound. Date palm biochar can be considered a long-term agriculture adaptation strategy because of its unique mitigation potential and functions to enhance soil health and soil carbon sequestration [84]. Compared to other crop residues, date palm ones are characterized by high caloric values, high volatile content, and a distinct capacity as an organic fertilizer. Alothman et al. (2021) [133] stated that the major constituents of date palm residue are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, apart from other solids with high volatile content and low levels of moistness, which make them an excellent resource for biomass. Therefore, we can regard date palm biomass and the biochar products derived from it as useful and valuable organic amendments [134,135,136]. Biochar incorporation into soils can be considered an agronomic or environmental management method [123], and it offers numerous environmental and financial benefits [137]. Biochar application in soil achieves not only soil remediation from organic and inorganic pollutants [90,128], but it could also improve both physical and chemical properties, improve carbon sequestration to soil, enhance microbial activity and rhizobia nodulation, and consequently increase soil health, crop yield, and soil productivity [138,139,140,141].
Effects on Water Retention and Soil Fertility
The application of biochar derived from date palm residues to soil appears to present a viable approach for enhancing the water retention traits of coarse-textured soils and facilitating the optimization of water resource utilization within irrigated areas [142]. According to Alotaibi and Jeff (2019) [143], biochar can enhance the soil’s water retention capacity, primarily due to its high total porosity. Biochar addition increases the available water in the soil by 4 to 130% [144]. These benefits are more pronounced in soils that are infertile and have a coarse texture [145,146]. Several studies [144,147,148,149,150,151] have reported improvements in soil porosity, decreased soil bulk density, and increased maximum water holding capacity [WHC] in sandy soils. Le Guyader et al. (2024) [142] concluded that the use of organic additions such as compost and biochar made from date palm residues increased soil water retention in proportion to the sand content. The loamy sandy soil treated with biochar increased its available water capacity (AWC) by +80% compared to the untreated soil. In this way, biochar would enhance the resilience of agricultural systems to drought, especially in coarse-textured soils in arid and semi-arid areas where there is a significant and growing need for water to irrigate crops. The total porosity, surface area, and surface properties of biochar determine its effects on hydrological properties. Grass and straw biochars increase WHC to a greater extent than woody biochars [54,152]. Biochars produced at low temperatures (<500 °C) contain more labile carbon and aliphatic compounds [153,154]. Zornoza et al. (2016) [154] indicated that aliphatic compounds confer hydrophobic properties to biochars, which reduces pore filling by water, but the highest treatment temperatures (HTTs) around 500 to 700 °C allow the degradation of aliphatic compounds on the biochar surface. Campos et al. (2020) [155] observed that residence time primarily influenced Aryl-C, Alkyl-C, and hydrophobicity. Therefore, to obtain biochar with high potential for soil WHC improvement, the selection of appropriate feedstock sources and processing are necessary. For example, Khalifa and Yousef (2015) [156] produced biochar from fronds of date palm by carbonization at 400 °C for 30 min in a muffle furnace. The application of biochar in sandy soil (0, 10, 50, and 100 g kg−1 soil) resulted in a notable enhancement in soil water retention by up to 20%. They also noticed an improvement in available water capacity (AWC) of 32, 72, and 109%, respectively. Additionally, a slight increase in CEC was observed, with values rising from 2.5 to 6.7 meq 100 g−1. Furthermore, the use of biochar led to a reduction in the soil’s sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), bringing it below the threshold for sodic conditions (<13).
It has to be noted that the authors suggested that the effects are dose-dependent and that applying large quantities of biochar is necessary to achieve significant improvements in sandy soil characteristics. Indeed, Karbout et al. (2019) [157] investigated the use of various quantities of biochar (untreated soil, 5 t ha−1, 10 t ha−1, 15 t ha−1, and 20 t ha−1) on sandy soil located in southern Tunisia. Biochar is produced by subjecting date palm tree residues to pyrolysis in oxygen-limited conditions at a temperature of around 500 °C. The findings suggest a positive correlation between higher rates of biochar application and increased soil nutrient status. As the rate of biochar increases, so does the amount of water in the soil, which reaches a maximum of 20 t ha−1. This is because the typically employed application rate of 10 g kg−1, as observed in earlier studies [138,144], does not provide significant benefits.
On the other hand, Wang et al. (2019) [158] stated that biochar production inevitably produces polyaromatic hydrocarbons [PAHs]. The results showed that biochar amendments in soils may threaten food safety and human health, but biochar-borne PAHs in soils and food crops represent negligible cancer risks. To reduce cancer risks, avoid applying biochars with high PAH content at higher rates (e.g., ≥20 t/ha). The feedstock type and pyrolysis temperature significantly influence the composition of PAHs in biochar, as concluded by Alharbi et al. (2023) [159]. These characteristics must be considered while producing and using biochar. Additional research is advised to determine the relationships between the temperature at which pyrolysis occurs and the specific kinds of raw materials used, as well as the formation of PAHs. It is recommended to monitor the levels of PAHs before applying biochar to the soil.
Several studies have explored the effects of biochar application on soil nutrient availability. Zhang et al. (2017) [160] applied twelve biochars from various sources, such as walnut shells, corn cobs, corn straws, and rice straws, at different pyrolyzed temperatures in a pot experiment. They showed that biochars generally decreased the available N, increased the available P and K, and also increased the ryegrass biomass. According to Mihoub et al. (2022) [161], biochar modified with citric acid and inorganic phosphorus in calcareous sandy soil has the potential to function as a slow-release fertilizer. This methodology presents numerous benefits, including its cost-effectiveness and its environmentally sustainable characteristics, rendering it a feasible alternative to conventional mineral fertilization techniques. Glaser and Lehr (2019) [162] conducted a meta-analysis and found availability of P increased on average by a factor of 5.1 and 2.4 in acidic and neutral soils, respectively, but it had no effect in alkaline soils or at biochar application rates below 10 t ha−1 or with biochars produced at HTT < 600 °C.
The application of biochar influences soil nitrogen dynamics and greenhouse gas emissions, affecting ammonia and nitrate levels [128,163,164,165]. However, its effects on soil ammonium content are inconsistent [166,167], and its impact on net nitrification rates varies [168,169]. Βiochar application may have no effect on gross or net nitrification rates in agricultural soils [169,170], which can be explained by the fact that agricultural ecosystems are already characterized by high nitrification rates [171]. Studies also report reduced N2O emissions from biochar-amended soils [166,172]. While biochar has been shown to decrease CH4 emissions [173], its ability to reduce greenhouse gases is variable due to factors such as biochar type and soil conditions [173]. Biochar’s nitrate sorption capacity depends on factors like pyrolysis temperature and surface area, with some biochars showing higher sorption rates [174,175]. However, the capacity of biochar for nutrient retention and leaching prevention varies depending on the specific type of biochar and soil conditions [176]. Meta-analyses suggest that biochar may not always affect crop yields, especially in low-nutrient or nutrient-rich soils [177]. Techniques like biochar enrichment of fertilizers or co-composting with organic materials show promise for improving nutrient efficiency [178,179,180,181,182].
Effects on Soil pH
Biochar, with its alkaline properties, has been shown to increase soil pH, reducing the hazards caused by soil acidification and naturally acidic soils [183,184,185]. A meta-analysis of 371 studies [141] found that the addition of biochar to soils resulted in a tendency for soil pH to rise, reducing its acidity. The biochar surface contains functional groups (e.g., -COO-, and O-,) that react with metals and H+ from the soil solution, partially alleviating soil acidity. Furthermore, biochar has a remarkable ability to adsorb and immobilize Al3+ ions [186]. Its alkalinity may react with the toxic Al ions, resulting in AlOH3, potentially neutralizing their detrimental impact. The enhancement in pH was dependent on the pyrolysis temperature, with the acidified soil improvement effects of biochar produced at elevated temperatures being more pronounced than those of biochar prepared at reduced temperatures [187,188]. Conversely, it is anticipated that biochar will have a little effect on the pH of neutral to alkaline soil [145,189,190,191] except for feedstock (soil pH = 8.07) and BC300 (carbonization at 300 °C, soil pH = 8.14) treatments that showed a minor but significant decrease in soil pH compared to the control (soil pH = 8.25) [143]. Alotaibi and Jeff (2019) [143] postulated that chemical oxidation and microbial decomposition of BC within the soil are responsible for the reduction in soil pH observed in alkaline soils after the application of BC. Additionally, an increase in soil electrical conductivity was recorded. The presence of soluble salts in biochar is the cause, as biochar produced in arid regions contains a high salt content due to soil salinity, irrigation water, and biomass type [192]. Further monitoring is necessary for frequent application to arid soils [193].
Effects on Carbon Sequestration
Studies have found that integrating date palm biochar into the soil contributes to soil carbon sequestration [124,141], mitigating climate change impacts [120,194]. When considering the incorporation of biochar into the soil, it has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, sequester carbon, and improve soil quality [195,196,197,198]. However, it should be noted that soil amendments rich in organic decomposable materials may increase the efflux of carbon dioxide from the soil. The EuroChar project results [112] confirmed that biochar produced through a commercial gasification method maintains sufficient stability in the soil environment, making it potentially useful for carbon sequestration. According to Al-Wabel et al. (2019) [128], date palm biochars exhibited much lower cumulative soil respiration than date palm feedstock, even with low-temperature biochar, indicating that the biochar has C sequestration potential. Moreover, date palm feedstock and biochar (300 °C) with an increasing addition rate lowered soil pH, whereas SOC, CO2-C efflux, and soil MBC were increased compared to the control.
The Impacts on Contaminant Remediation
Many studies have shown that biochars effectively immobilize various inorganic and organic pollutants [194,199,200,201,202], thereby reducing plant uptake and food chain transfer [203]. Biochars can also facilitate heavy metal precipitation in soil, stabilizing copper, cadmium, and organic matter in acidic soil conditions [204]. Date palm biomass and biochar effectively reduce soil contamination from heavy metals [128,205]. Changeable factors such as pyrolysis temperature, biochar dosage, and metal type affect the reduction of metal availability. Date seed biochar has a strong ability to adsorb Pb [II], Ni [II], and Cu [II] from aqueous media, even when these metals are present together [206]. The order of adsorption capacities and selectivity is Pb2+ > Cu2+ > Ni2+. Low-temperature date palm biochar significantly reduced the mobile content of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in mining-contaminated soil, as well as minimized soil CO2-C efflux [128]. Biochars can also be used as alternative sorbents to remove different types of organic and inorganic contaminants from aqueous solutions [105]. The pH and porosity of biochar derived from date seeds increased with the pyrolysis temperature, making it an appropriate medium for the removal of heavy metals in wastewater treatment systems [207]. As stated by Mahdi et al. (2018) [208], the adsorption capacity demonstrated an upward trend in relation to both the pyrolysis temperature and heating duration. Producing biochar at a temperature of 550 °C and heating it for 3 h resulted in the most effective adsorption. It is worth mentioning that activated carbon derived from date seeds is one of the most widely used adsorbents due to its adsorption capability and low-cost raw material [209]. Sizirici et al. (2021) [127] reported that the efficacy of date palm leaf or frond biochar in removing metals from water and wastewater remains consistent regardless of the pyrolysis temperature. Hence, adopting a strategy that reduces energy consumption for biochar production at lower temperatures while maintaining the same level of effective removal efficiency would present a mutually beneficial solution in terms of sustainability and economic considerations.
Effects on Soil Microbiology
Biochar has been found to improve soil parameters such as pH, C:N ratio, dissolved organic carbon, total carbon, and K concentrations, which can affect the dynamics of microbial communities. However, there are varied effects of biochar on soil microbial communities [210]. In short-term field trials, biochar can stimulate microbial activity in acidic soil [211], but after 14 months, the pH returns to initial conditions and no increase in microbial activity is detected. Additionally, in short- and mid-term field trials [3–5 years], biochar addition has a minimal impact on microbial parameters such as biomass, respiration, abundance, diversity, and composition [212,213,214,215,216,217]. However, biochar application can cause a significant shift in microbial communities in two core sites, which could help understand how biochar contributes to soil fertility [114]. Additionally, Zhu et al. (2017) [218] found that biochar addition alters soil properties, alters microbial activity, and may negatively impact soil microorganisms due to the toxicity of reactive organic substances and heavy metals. Liao et al. (2016) [219] concluded that cotton straw biochar increased soil microbial biomass, carbon substrate utilization, and enzyme activity related to C and N transformation. Al-Wabel et al. (2019) [128] showed that date palm feedstock and biochar, with an increasing addition rate, significantly increased soil microbial biomass carbon compared to the control. Ming et al. (2016) [220] conducted a study where they separately added various biochars derived from straw residues and wood chips to paddy soil. The authors showed that biochar amendments modified the soil’s microbial properties and, more specifically, increased the overall abundance of bacteria as well as the concentration of phospholipid fatty acids. Khadem et al. (2017) [221] examined how the addition of corn stalk biochar to two calcareous soils influences the activity of several cellular enzymes involved in C and N cycling and microbial metabolism. In arid soils, biochar may improve enzyme activities and, consequently, soil quality, carbon sequestration, and biogeochemical cycles. Zhu et al. (2017) [218] also examined the changes in soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, urease, and alkaline phosphatase activities with biochar addition. In most cases, biochar increased microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen in the shallower soil layer, and alkaline phosphatase activity. Moreover, there were fluctuations in enzyme activities during the growth periods and depths.
Synthesis
Biochar application can improve agricultural production and sustain the oasis environment in poor countries. Karbout et al. (2019) [157] show that biochar dramatically alters sandy soil physical and chemical qualities and increases crop production. Biochar could assist developing countries in accepting climate-smart agricultural practices, thereby mitigating climate change and reducing vulnerability. While these benefits offer promise, low-cost and carbon-neutral technologies (i.e., transposable to farmers in the regions concerned) need to be identified to produce high-quality date palm biochar on a large scale. To ensure broad application and maximum benefits, processing date palm residues must occur on a continuous basis to prevent overexploitation and potential negative environmental risks. Given that date palm trees represent the main crop in the Oasian agroecosystems, field trials need to evaluate the optimal frequency and rate of biochar addition, including amending them. Karbout et al. (2019) [157] highlighted the key question of whether farmers in southern Tunisia will accept biochar as a novel supplement, combined with manure or compost, to address the waste problem in the oasis system. In addition, the effects of biochar on soil properties are very different depending on the type of biochar. The primary reason for this is the method of producing biochar and its interaction with the soil [120]. These interactions include redox reactions, adsorption-desorption processes, as well as precipitation and dissolution phenomena. The impact is additionally influenced by the composition of the feedstock, specifically the mineral fraction, the conditions of the pyrolysis process, the particle size of the biochar, the rate at which biochar is applied, and the specific type of soil being treated [145,222,223,224,225,226]. According to Alotaibi and Jeff (2019) [143], the benefits of biochar derived from date palm residues [frond midrib and frond base residue] in sandy desert soil depend on the pyrolysis temperature and biochar aging process. Biochar increased soil water retention by 46%, especially with biochar aging in soil, when averaged across the incubation period (14, 30, 45, and 60 days). Unlike the BCs with high pyrolysis temperatures, the BCs with low pyrolysis temperatures (300 °C and 400 °C) significantly improved water retention. This may be due to the presence of oxygen-containing groups on the surfaces, making the low-temperature biochar less hydrophobic [154,227]. Additionally, high-temperature biochar pyrolysis (500 °C and 600 °C) improved soil physical properties, specifically in terms of bulk density and total porosity.
It is worth mentioning that while date palm biochar has demonstrated benefits in productive agricultural systems (including both irrigated and dry systems), its application in areas with severe water scarcity is severely limited [228] due to moisture and salinity restrictions [229]. A recent bibliometric study highlighted the limited number of studies on biochar application under arid conditions [230]. At present, little research has explored the effects of biochar in arid and semi-arid regions, particularly on the biological functioning of the soil [228,231]. In addition, little is known about biochar transport, even within the soil profile. Studies have already measured significant losses of biochar particles during and after spreading to the soil caused by wind erosion and water-preferential erosion of black carbon in various contexts [232,233]. While biochars with high total pore volumes are more likely to increase soil water retention capacity (i.e., grass-derived biochars), their lower envelope density may lead to more rapid erosion [122]. Hence, field trials should make it possible to verify the hypotheses put forward in the specific context of dry areas and to check the significance of the potential effects expected on crop productivity.
Using date palm leftovers to make biochar has the potential to improve soil fertility, water retention, and overall agricultural productivity. Nevertheless, the efficiency of biochar is dependent upon factors such as pyrolysis temperature, application rate, and soil type. Additional research is required to thoroughly study the effects of biochar, especially in dry environments, and improve its use for sustainable soil management and crop production, despite its potential advantages for agricultural systems in both irrigated and arid regions.
3.2. Production, Use, and Effects of Date-Palm-Based Compost on Soil
3.2.1. Principle of Compost Production
Composting is the most popular method for biologically decomposing organic waste. It is a process that progressively decomposes raw organic matter, such as tree residues from pruning, cereal straws, animal manures, or the organic fraction of solid urban waste, into stabilized humus [234]. The ease of implementation and adaptability to a variety of farming systems make composting an attractive agricultural practice and a cost-effective and sustainable method of managing organic waste products [235]. During composting, the organic wastes are stabilized by their conversion into humic substances while inactivating pathogen flora, allowing compost to be used for soil amendment [236,237].
3.2.2. Factors Influencing the Characteristics of Compost
The composting process and final product quality are especially related to their stability and maturity [238,239,240,241]. Composting effectively stabilizes organic residues by converting them into humic substances, rendering some of the pathogenic flora inactive. Consequently, compost can be used as a soil amendment [237]. Furthermore, throughout the composting period, the main process parameters (temperature, pH, humidity, and C:N) are monitored to determine the compost’s maturity. Various physico-chemical parameters and biological parameters are used to assess this process. These are important criteria for its safe use in agriculture, because immature compost may produce phytotoxic compounds that damage seed germination as well as plant growth [241]. The effectiveness of the composting process depends on the composition of the raw materials, composting conditions, moisture levels, turning frequency, and temperature control. Physicochemical parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), water content, and carbon/nitrogen ratio (C:N), as well as biological parameters such as microbial diversity, respiration rates, germination index, tests for pathogens, and insecticide evaluation, play an essential role in determining the success of composting practices [242,243,244,245]. The C:N ratio is one of the main parameters influencing the composting process, judging the degree of organic matter evolution (i.e., its ability to quickly break down in the soil) and the type of compost [246]. When the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio is less than 20, the early decomposition process releases the mineral N [247]. The C:N ratio is considered the initial optimum ratio at 25–30 [248]. The optimal C:N ratio for basic materials, according to Misra et al. (2003) [249], is between 25:1 and 30:1, although ratios between 20:1 and 40:1 are also acceptable. On the other hand, Safwat et al. (2007) [250] suggested that for date palm compost to support microbial growth, the optimal C:N ratio at the end of the decomposition process is between 10 and 12. Hao et al. (2004) [251] stated that nutrient losses during composting are a key environmental issue as they reduce the fertilizer value of the final compost. Many studies, though, have shown that this parameter cannot be used in a strict way because it shows that products with a high C:N ratio decompose quickly while products with a low C:N ratio decompose slowly [252,253]. Thus, high-C:N materials can significantly enrich SOC as long as the fiber/cell content ratio is sufficiently high [254].
Composts have been used to promote plant growth, but concerns have been raised about their application due to their high sodium content [255]. Particularly, arid regions of North Africa, like Tunisia and Algeria, produce composts that contain substances that reduce biological activity and complicate the decomposition process. Due to rising soil salinity issues and rapid water evaporation, farmers in these regions may hesitate to incorporate compost into their crops [256,257]. Composts with high levels of soluble salts may be suitable for use when crops are not present or cannot be planted immediately after application [258]. To prevent salt toxicity in plants, compost with high electrical conductivity (EC > 5 dS m−1) should be incorporated into soils or other growing media [255]. Composts with high EC values and low NaCl content will not cause harm if the soils they are applied to do not exceed an overall EC of 4 dS m−1 after application. Applying composts with high EC can remediate saline-sodic soils by enhancing the cation exchange capacity, which in turn facilitates the leaching of Na+ from the soil. Many researchers have investigated the feasibility of incorporating additional substances, such as zeolites, into compost to decrease EC [259,260,261]. Turan (2008) [260] and Chan et al. (2016) [261] illustrated that the incorporation of zeolite resulted in a decrease in the EC of compost made from a variety of raw materials. Zeolite has a high CEC because of its crystalline structure, which facilitates cation absorption [262]. Zeolite has a high CEC because of its crystalline structure, which facilitates cation absorption [262].
While date palm compost can serve as an effective soil amendment, concerns about its high sodium content and soluble salts highlight challenges in ensuring its suitability for agricultural use. Strategies to mitigate these concerns include incorporating additional substances like zeolites and leaching with high-quality water. Indeed, due to its high CEC, zeolite can reduce salinity and heavy metal availability during composting; however, its beneficial effect is limited at low pH [261]. Leaching compost with high-quality water can reduce salts to produce leachate if elevated EC levels are a concern [263]. Furthermore, studies suggest that irrigating enriched soils with compost and high-quality water can mitigate vegetative salt stress that may occur during the planting process [264]. During the initial leaching events, the compost retained a large portion of calcium and magnesium while removing the majority of Na+ ions. Nevertheless, there is a possibility of nutrient loss, including that of N, P, and K [263]. To tackle this issue, composting facilities have the option to reintroduce leachate into compost or new feedstocks [265], dilute it for use as fertilizer or weed control, or dispose of it in a constructed wetland [266]. These techniques might not be suitable for large composting facilities characterized by elevated nutrient concentrations and oxygen requirements [267]. Electrocoagulation/flotation, filtration, biofilters, anaerobic bioreactors, membrane bioreactors, and advanced oxidation processes are some ways to treat leachate. As stated by Roy et al. (2018) [268], biological treatments, such as membrane bioreactors and filtration, are most efficient and economical. Overall, addressing the above constraints is crucial to maximizing the benefits of date palm compost while minimizing potential negative impacts on soil health and crop productivity.
3.2.3. Composting of Date Palm Residues—Added Value of Compost
The date palm waste recycling process is not a new technology, but it is considered the most important biological process within the environmental system that aims to maintain environmental balance [250]. Because of the vast volumes of palm waste produced throughout each crop season, farmers always attempt to burn or transport it outside the oasis. This presents a significant challenge for the farmers. Safwat et al. (2007) [250] concluded that farmers could utilize date palm branches to produce high-quality compost instead of burning them. Composting could provide an economical and environmentally significant method to reduce date palm waste [269]. El Janati et al. (2023) [22] emphasized that composting date palms is a viable option for enhancing circularity in oasis agroecosystems. Enhancing the organic matter content and fertilizer value facilitates the sustained production of valuable products from date palms. Only a few studies have considered the valorization of date palm residues in arid areas with composting [241,270]. Commercial-scale composting of date palm waste can use either the traditional windrow method or a more advanced method, such as vermicomposting. El Janati et al. (2023) [22] stated that before establishing windrows, they pre-process crushed date palm residues by immersing them in a water basin. This was performed to encourage the growth of microorganisms on the date palm particles and enhance the potential of crushed date palms to be broken down by composting. Windrows are rotated to manipulate temperature and humidity, facilitating the growth of microbes on the feedstock aggregates and ensuring the uniformity of the final products. In its initial stage, the windrow that forms a natural slope is compact at the top [86], and El Janati et al. (2023) [22] estimate that it can reach a maximum height of 1.4 m. The windrows’ final shape depends on the configuration of the available land.
Date palm waste contains approximately >80% organic content, making it ideal for composting, but suffers from a significant lack of nitrogen compared to other wastes. Additionally, there is a high lignin content in date palm residues (≈30 wt.%), especially the rachis [49,270]. This makes the composting of date palm tree residues difficult and time-consuming [80]. Recently, Giagnoni et al. (2019) [271] defined co-composting as a designed technique that allows the aerobic degradation of organic waste mixtures, primarily aiming at obtaining a product with specific characteristics. In contrast to conventional composting practices, a notable difference is the use of the waste ad-mixture, which is used not only to initiate and maintain the biodegradation process but also to facilitate the combination of various waste components to produce customized products with specific characteristics. Furthermore, by using tailored co-composting protocols, this approach enables the reclamation and valorization of natural resources like degraded or polluted soils and sediments.
It is well recognized that in the case of composting low-nutrient feedstock, additions are used to improve the overall nutritional content of the compost [272]. Combining date palm residues with other organic materials, especially animal manures, accelerates the composting process and produces higher-quality compost [22,269,273]. Indeed, manure is a source of nutrients and microflora that increases microbial activity during composting [22]. Benabderrahim et al. (2018) [269] produced compost from date palm wastes using cow manure. The following steps guide compost’s mechanical production: (1) Collection of palm tree wastes. (2) Grinding residues. (3) Soaking the ground material in water (7–10 days). (4) Drying and mixing with cow manure in a 3:1 volume ratio. (5) Preparation of windrows and fortnightly mixing of a specific quantity of water that has been aged for a duration of 6 months before its utilization is conducted with the aim of eliminating any potential pathogens. The authors concluded that field-grown Medicago sativa plants benefited greatly from the application of date palm compost at a rate of 30 t ha−1. The characteristics of palm compost and cattle manure obtained are shown in Table 1 [269].

Table 1.
Characteristics of palm compost and cow manure (Benabderrahim et al., 2018 [269]).
Additionally, palm leaflets can co-compose with goat manure when it is available [241]. Goat waste is rarely used, and palm waste composting is blended at 32% in previously barely reported efforts. Waste-soaking prior to windrow management increased the biodegradability of crushed date palm. This increased microbial activity and decreased composting. The remaining wastewater from the soaking step was used for windrow humidification during the mesophilic and thermophilic phases. The wastewater from the soaking stage was utilized to humidify the windrows during the mesophilic and thermophilic stages. The resulting compost had a neutral pH level and a relatively high EC. A low C:N ratio and a high germination index (GI) value (88%) further demonstrated its stability. Based on its organic matter content of less than 55% and total nitrogen content of less than 3%, the compost that was developed was defined as vegetal compost.
El Janati et al. (2022) [22] found that composting date palm leaves can improve the circularity of oasis agroecosystems. Co-composting date palm residues with sheep manure over two growing seasons enhanced the silage corn productivity and nutrient uptake (N, P) in an arid agroecosystem [22]. Conversely, the application of date palm leaf compost alone led to mineral nitrogen starvation in the soil. Adding manure improves the quality of the final composts by enhancing the sanitation of the initial feedstock and increasing the initial nitrogen content. The initial stages of composting in mixtures containing manure led to a 40% reduction in organic matter content across all windrows, indicating organic matter mineralization and organic matter loss. The addition of date palm residues, sheep manure, and rock phosphate resulted in a final total phosphorus concentration of 0.52% (d.w.) in the compost.
Compost derived from water-soaked mixed date palm waste and goat manure can serve as a beneficial organic amendment for soils, as found by Abid et al. (2020) [241]. The compost demonstrated a rapid temperature increase and a long maturation phase, reducing organic matter content by 36% and changing the C:N ratio from 60 to 20. The compost did not exhibit phytotoxicity effects on indicator plants, thus qualifying it as green waste compost [NF U44-051]. This efficient, environmentally friendly, and economically viable solution for date palm waste treatment is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Dhehibi et al. (2020) [86] conducted feasibility and technical research to create a recycling date palm by product unit in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries for producing compost from date palm waste. The following stages outline the compost production procedure: 1. Collection of date palm waste considering the fact that each date palm tree produces about 20 kg of dry basis. 2. Grinding [crushing], the homogenization of the crushed product 3. Adding treated biosolid sludge to the crushed product is necessary to initiate and promote the composting process. 4. Windrow formation process.
3.2.4. Monitoring the Composting Process
The monitoring process for composting date palm residue relies on three important factors: humidity, aeration, and temperature [86]. The composting site selection within the oasis farm is critical, as it can help reduce the risk of drying out in the sun. To compensate for evaporation and enhance oxygenation, it is recommended to regularly water, turn and aerate compost (ideally every 15 days). The periodic aeration of the compost, as microorganisms require air and thus oxygen to function correctly, is a key principle regulating composting. By incorporating fibrous parts (cut branches measuring around 5 cm in length), you can improve ventilation. Moreover, the authors stated that a low nitrogen content in the date palm compost mixture prevents its degradation. If the nitrogen content is excessive, the compost can overheat and kill microorganisms.
Other organic materials could also be used to prepare date palm compost. For example, Habchi et al. (2020) [80] used different amounts of alfalfa [Medicago sativa L.] plant as a nitrogen source (20%, 30%, 40%, and 50%) to facilitate the degradation of date palm wastes and accelerate the composting process. Changes in the physicochemical properties of the obtained composts were mainly due to variations in the contents of date palm waste and Medicago sativa L. used. Dhehibi et al. (2020) [86] added treated biosolid sludge to the crushed material of date palm to initiate and promote the composting process. This treated biosolid sludge came from the treatment plants in neighboring areas and was transported to the site. Vico et al. (2018) [270] explored the use of co-composting palm waste with urban and agri-food sector sludge as a treatment alternative for organic waste streams. The process allowed for sanitization conditions (temperature values increased during the initial week, exceeding 40 °C, and remained consistent for over two weeks), and increased the economic value of the composts due to their high nutrient content and favorable physical characteristics. However, the salt content in composts with the highest proportions of sewage sludge may limit their agronomic application.
In horticulture, many researchers have demonstrated the importance of the potential advantages derived from the economically viable use of composted date palm materials as a soilless substrate. Raja et al. (2021) [274] provided strong evidence that the appropriate composting of finely ground date palm materials over a period of 30 weeks resulted in the most favorable physicochemical properties compared to peat moss used as a control, uncomposted date palm residues, and date palm residues composted for 15 weeks. Aydi et al. (2023) [78] concluded that date palm waste-based substrates, particularly trunk compost, could offer a more cost-effective alternative to the commonly used coconut fiber substrates in soilless cultures in Tunisia. The study’s findings indicated that using date palm and coconut fiber substrates resulted in enhanced vegetative growth. When compared to traditional soil-based cultivation methods, using substrates derived from date palm waste resulted in notable improvements in both the vegetative growth and fruit yield of melon.
Overall, composting date palm waste provides a sustainable solution for managing agricultural by-products, promoting environmental balance and circularity in oasis agroecosystems, and addressing waste disposal challenges. It is important to highlight that date palm composting involves the presence of a high lignin concentration in date palm leftovers, which complicates and prolongs the composting process. Additionally, there is a notable deficiency of nitrogen in comparison to other types of waste.
3.2.5. Effects of Compost Application on Soil Properties
Sustainable soil management aims to enhance soil organic matter by preserving, protecting, and augmenting its content through optimal agronomic practices. This can be achieved through various management strategies, such as providing organic fertilizers, manure, compost, or soil improvers [234]. Compost products can be used as a conditioner and enhancer for soil structure, increasing soil organic matter, reducing plant pathogens, and stimulating plant growth [275,276,277]. Recycling plant residue biomass in combination with compost has enhanced soil organic matter (SOM) in Mediterranean tree crops like olive, peach, kiwifruit, and apricot [278,279,280]. Compost amendments can reduce the need for inorganic fertilizers by the organic grower [281]. Organic fertilizing and compost supply farming operations are generally effective in establishing a rapid and progressive increase in soil organic matter content and boosting soil fertility [279,282,283]. However, Kavvadias et al. (2018) [284] found that adding compost from shredded pruning residues or olive mill by-products had no significant effect on soil organic matter, total and inorganic nitrogen, or soil microbial properties. Ferrara et al. (2015) [285] and Jokela et al. (2009) [286] found slight changes in soil organic matter and chemical parameters after soil amendment, suggesting it may take years for some quality indicators to fully respond. Transitioning between conventional and organic farming practices can lead to decreased nitrogen availability and yields due to a shift in biological activity and N sources that are not immediately available for plant use [277]. The impact of organic amendments on soil nitrogen dynamics can be described by assimilation efficiency, C:N ratio, and microbial biomass C:N ratio [287,288]. Compost additions have a strong nutrient-supplying capacity [289], and external carbon sources such as compost, farmyard manure, and slurry result in the highest increases in SOC concentrations compared to similar mineral N fertilization rates [289], as well as improved soil physical conditions and increased soil microbial activity [290,291].
With regards to the impact of date palm compost on soil properties in arid and semi-arid regions, El Janati et al. (2021) [21] reported that agricultural soils in oasis regions have poor structure and low organic matter content (i.e., <1.5%). As a result, recycling date palm waste through composting in a circular agriculture model is hugely important to promoting oasis sustainability. In Tunisian oasis ecosystems [292], the application of organic fertilizers such as date palm waste compost is strongly recommended to improve the main soil physicochemical properties [organic matter and water retention capacity], which can positively affect plant yield and promote agroecosystem health [132,269,292,293]. Benabderrahim et al. (2018) [269] found that applying palm waste compost at 30 t ha−1 improved the main soil properties (organic matter and water retention capacity) while decreasing their electric conductivity. They concluded that the palm tree compost could effectively serve as an organic fertilizer for surrounding crops, replacing chemical fertilization with satisfactory results at appropriate doses. Adding organic matter to salinity-affected soils enhances the leaching of sodium chloride, reduces the exchangeable sodium rate and EC, and boosts water infiltration, the soil’s water retention capacity, and its overall stability [294]. Composting and/or pyrolysis of date palm residues proved to be a viable alternative to improving the water retention properties of sandy and loamy soils. Le Guyader et al. (2023) [142] tested different types of organic amendments at a dose of 60 t ha−1, considering 0–20 cm of depth: compost alone, biochar alone, and a mixture of compost and biochar (50:50 in weight). Their findings indicate that coarse-textured soil treated with organic amendments had a higher AWC. Incorporating biochar, either alone or in conjunction with compost, into a specific soil resulted in greater water retention than applying compost alone. Coarse-textured soils exhibited a more notable enhancement in their water retention characteristics. In addition, Ghouili et al. (2022) [292] stated that date palm waste compost significantly increased plant growth and barley grain yield. They suggested that this could be due to the stimulation of genes involved in the assimilation and transport of nitrogen and phosphorus in barley plants’ leaves and roots.
In terms of the microbiological context, the tested sandy soil exhibited a higher organic carbon content, and all treatments (chicken manure compost and composted date palm tree wastes) showed an increase in the number of microorganisms compared to the control [132]. Ghouili et al. (2023) [295] demonstrated that the application of date palm waste compost significantly improved soil microbial diversity and richness during the tillering, booting, and maturing stages of barley growth. In particular, palm compost fertilization significantly raised the fungal richness and diversity indices relative to the control, while the bacterial richness and diversity indices decreased significantly. They suggested that applying date palm waste decomposition products may have stimulated soil fungi growth due to changes in soil pH, nutrient content, and SOC levels. Therefore, to maximize its effectiveness in sustainable soil management practices, we must address challenges such as poor soil structure and low organic matter content in arid and semi-arid regions, despite the benefits of date palm waste compost in promoting soil health and productivity.
4. Concluding Remarks
Date palm is considered one of the most appropriate crops for cultivation in the Mediterranean and the MENA region, where harsh environmental conditions prevail. However, every year, agricultural lands accumulate large amounts of residues (dry leaves, stems, and seeds) from harvested date palms. Farmers in date-producing countries that primarily aim to burn or dispose of large amounts of palm residue each year suffer substantial expenses and contribute to environmental degradation. Moreover, the date palm agro-industry generates significant amounts of waste. On the other hand, there is a lack of comprehensive data on long-term research studies that aim to assess the impact of long-term date palm residue management practices on soil quality and productivity. This claim holds particular significance for arid and semi-arid regions, which exhibit greater susceptibility to both climate change and soil degradation.
Date palm residues can be composted and/or pyrolyzed as a viable alternative to enhance the water retention properties of coarse-textured soils, although there is limited information available on the composting and biochar processing of these residues. With regards to the pyrolysis of tree residues, biochar appears to be a new potential low-cost and effective material that has a wide range of characteristics, transfusing unique properties. Biochar characteristics vary depending on the raw biomass materials and biochar production conditions. Date palm biochar can be considered a long-term agriculture adaptation strategy due to its unique mitigation potential and functions to enhance soil health and soil carbon sequestration. Biochar has been reported to be an effective immobilizing agent for a wide range of inorganic and organic pollutants, thereby reducing plant uptake and food chain transfer. Biochar application in soil results in not only soil remediation from organic and inorganic pollutants but also improvements in both soil physical and chemical properties, including carbon sequestration. Specifically, the unique properties of biochar, such as its porous structure, influence microbial biomass and composition, providing an ideal environment for microbes to develop and colonize. The production conditions of the biochar, the application rate, and the specific soil type can all impact the extent of these effects. Researchers have conducted limited research to explore the mechanisms through which biochar application influences the soil properties of arid and semi-arid soils, as well as to investigate the long-term impact of biochar. Research on using various components of the date palm for biochar production may be contracted, along with determining the most efficient dosage for soil application. Future studies should also investigate biochars with different characteristics to alleviate soil contamination from heavy metals.
Composting can provide an economical and environmentally relevant method to reduce date palm residues. Date palm residues contain approximately 80% organic matter, making them ideal for composting, but they suffer from a significant lack of nitrogen compared to other wastes. However, co-composting date palm residues with other organic materials, particularly animal manures, speeds up the composting process and produces higher-quality compost. Most regions that cultivate date palm typically have agricultural soils with poor structure and low organic matter content. In a circular agriculture model, recycling date palm waste through composting is of great interest to promote sustainability. Only a few studies, however, have considered the valorization of date palm residues in arid and semi-arid regions with composting. Research limitations in co-composting may relate to manure typology and abundance. Recent research showed that the application of date palm compost improved the main soil’s physicochemical properties. Compost can also promote beneficial microorganisms, resulting in increased plant availability of essential nutrients, the production of substances involved in plant growth, and the suppression of some pathogens, thereby enhancing crop yield and disease resistance. Farmers in arid regions, on the other hand, are hesitant to incorporate compost into their crops due to concerns about phytotoxicity from soluble salts. In areas with limited irrigation water and rapid water evaporation, compost with high EC values should be used to prevent salt toxicity in plants, as long as the soils do not exceed an overall EC of 4 dS m−1. Future research could emphasize the time efficiency of composting processes and the use of other agricultural wastes in combination with date palm waste. To combat soil erosion and degradation, researchers should focus on utilizing the compost produced from composting date palm wastes and residues in arid areas.
Additional research is required to determine the long-term effects of date palm biochar and compost on the environment in general and on the microbial community exhibiting specific soil functions in the plant rhizosphere in particular. Increasing the beneficial uses of palm waste will increase people’s interest in planting this crop, which can lead to sustainable industrial and economic growth in various areas. Therefore, we must explore the potential of date palms in various applications to motivate industries to produce value-added products from date palm waste for future use.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, V.K., E.L.G. and M.E.M.; writing—review and editing, all authors; project administration, X.M.; funding acquisition, X.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted in ISFERALDA project, funded by PRIMA, a program funded by the EC under the H2020 framework and the ANR (ANR-21-PRIM-0004).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Aliaño-González, M.J.; Gabaston, J.; Ortiz-Somovilla, V.; Cantos-Villar, E. Wood Waste from Fruit Trees: Biomolecules and Their Applications in Agri-Food Industry. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUROPRUNING Project: Development and Implementation of a New, and Non-Existent, Logistics Chain for Biomass from Pruning. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/312078/reporting (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Velázquez-Martí, B.; Fernández-González, E.; López-Cortés, I.; Salazar-Hernández, D.M. Quantification of the residual biomass obtained from pruning of trees in Mediterranean olive groves. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3208–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Martí, B.; Fernández-González, E.; López-Cortés, I.; Salazar-Hernández, D.M. Quantification of the residual biomass obtained from pruning of trees in Mediterranean almond groves. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagnotti, N.; Pari, L.; Picchi, G.; Spinelli, R. Technology alternatives for tapping the pruning residue resource. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Martí, B.; Fernández-González, E.; López-Cortés, I.; Salazar-Hernández, D.M. Quantification of the residual biomass obtained from pruning of vineyards in Mediterranean area. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3453–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyjakon, A.; García-Galindo, D. Implementing Agricultural Pruning to Energy in Europe: Technical, Economic and Implementation Potentials. Energies 2019, 12, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K. Τhe potential of mulch to transmit three tree pathogens. J. Arboric. 2005, 31, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, B.; Xue, J.; Li, Y. Grass cover increases soil microbial abundance and diversity and extracellular enzyme activities in orchards: A synthesis across China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Franco, N.; Wiesmeier, M.; Colocho Hurtarte, L.C.; Fella, F.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Almagro, M.; García Martínez, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Pruning residues incorporation and reduced tillage improve soil organic matter stabilization and structure of salt-affected soils in Citrus tree orchard under semi-arid climate conditions. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 19–30 April 2021. EGU21-7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.; Johnson, I.; Dudley, N. Drylands. In Global Land Outlook, 1st ed.; United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD): Luxemburg, 2017; pp. 247–269. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Shukla, P.R., Skea, J., Calvo Buendia, E., Masson-Delmotte, V., Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Zhai, P., Slade, R., Connors, S., van Diemen, R., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Yost, J.L.; Hartemink, A. Soil organic carbon in sandy soils: A review. Adv. Agron. 2019, 158, 217–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmal, M.; Maqbool, Z.; Khan, K.S.; Hussain, Q.; Ijaz, S.S.; Iqbal, M.; Aziz, I.; Hussain, A.; Abbas, M.S.; Rafa, H.U. Integrated use of biochar and compost to improve soil microbial activity, nutrient availability, and plant growth in arid soil. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Hussain, Q.; Khan, K.S.; Akmal, M.; Ijaz, S.S.; Hayat, R.; Khalid, A.; Azeem, M.; Rashid, M. Response of soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activity to biochar amendment in the organic carbon deficient arid soil: A 2-year field study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Destouni, G.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kalantari, Z. Soil degradation in the European Mediterranean region: Processes, status and consequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, S.; Dondeyne, S.; Deckers, S. World reference base for soil resources [WRB]. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, 2nd ed.; Goss, M.J., Oliver, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdruli, P.; Kapur, S.; Çelik, I. Soils of the Mediterranean Region, Their Characteristics, Management and Sustainable Use. In Sustainable Land Management: Learning from the Past for the Future; Kapur, S., Eswaran, H., Blum, W.E.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, G.; Wiehle, M.; Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Buerkert, A. Effects of soil characteristics and date palm morphological diversity on nutritional composition of Pakistani dates. Exper. Agric. 2016, 53, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Janati, M.; Akkal-Corfini, N.; Bouaziz, A.; Oukarroum, A.; Robin, P.; Sabri, A.; Chikhaoui, M.; Thomas, Z. Benefits of circular agriculture for cropping systems and soil fertility in oases. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Janati, M.; Robin, P.; Akkal-Corfini, N.; Bouaziz, A.; Sabri, A.; Chikhaoui, M.; Zahra, T.; Oukarroum, A. Composting date palm residues promotes circular agriculture in oases. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 13, 14859–14872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, A.; Hammani, A.; Kuper, M. Les oasis en Afrique du Nord: Dynamiques territoriales et durabilité des systèmes de production agricole. Cah. Agric. 2018, 27, 14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargette, M.; Loireau, M. Diversification des Socio- et Agrosystèmes dans les Oasis du Maghreb: Place de l’Agriculture Familiale et du Palmier Dattier-Portail Agricultures Familiales. Agropolis International. 2014. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/27617017/Diversification_des_socio_et_agrosyst%C3%A8mes_dans_les_oasis_du_Maghreb_place_de_lagriculture_familiale_du_palmier_dattier (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Hamada, N. Ministry of the Environment and Sustainable Development, Republic of Tunisia. In The Future of Drylands; Lee, C., Schaaf, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abla, B.; Bouayad, A.; Diaou, M.; Kaassis, N.; Tidjani Maliki, M. Agrobiodiversité et Durabilité des Systèmes de Production Oasiens dans la Palmeraie d’Aoufouss Errachidia—Maroc; ICRA: Montepellier, France; INRA: Rabat, Morocco, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ait, A. Systemes de production et strategies des agriculteurs dans les oasis de la region dlErrachidia au Maroc. New Medit 2003, 2, 737–743. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, M.H. Dynamiques Agraires et Perspectives d’Actions de Développement Rural des Bassins Versants des Oasis de Tafilalet, Province d’Errachidia, Maroc—Sécheresse). Mémoire d’Ingénieur des Techniques Agricoles de Clermont Ferrand. 2005, p. 116. Available online: http://www.secheresse.info/spip.php?article28154 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Morvan, X.; Boumaraf, B.; Kavvadias, V.; Moussa, M.; Lamine, H.; Sbih, M.; Bendjeddou, F.; Zaakir, A.; Gommeaux, M.; Karbout, N.; et al. ISFERALDA project: Using organic amendments based on date palm residues to enhance soil fertility in oases agroecosystems. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. EGU22-9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagnoni, L.; Martellini, T.; Scodellini, R.; Cincinelli, A.; Renella, G. Co-composting: An Opportunity to Produce Compost with Designated Tailor-Made Properties. In Organic Waste Composting through Nexus Thinking; Hettiarachchi, H., Caucci, S., Schwärzel, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGRISED—Project LIFE17 ENV/IT/000269 “Use of Dredged Sediments for Creating Innovative Growing Media and Technosols for Plant Nursery and Soil Rehabilitation”. Overview of National and EU Legislation Action A.1. Available online: http://www.lifeagrised.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/AGRISED-Deliverable-Action-A.1-Overview-of-national-and-EU-legislation.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Tengberg, M. Beginnings and early history of date palm garden cultivation in the Middle East. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 86, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.V. Enhancement of date palm as a source of multiple products: Examples from other industrialized palms. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2012, 24, 408–414. [Google Scholar]
- Mlih, R.; Bol, R.; Amelung, W.; Brahim, N. Soil organic matter amendments in date palm groves of the Middle Eastern and North African region: A mini-review. J. Arid Land. 2016, 8, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battesti, V.; Gros-Balthazard, M.; Ogéron, C.; Ivorra, S.; Terral, J.F.; Newton, C. Date Palm Agrobiodiversity [Phoenix dactylifera L.] in Siwa Oasis, Egypt: Combining Ethnography, Morphometry, and Genetics. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreveld, W.H. Date Palm Products; FAO Agricultural Services Bulletin, No. 101; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1993; Available online: https://www.fao.org/docrep/t0681e/t0681e00.htm#con (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- El Bouhssini, M.; De Socorro, J.R.F. Date Palm Pests and Diseases: Integrated Management Guide; International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas [ICARDA]: Lebanon, Beirut, 2018; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8914 (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Shabani, F.; Kumar, L.; Taylor, S. Climate Change Impacts on the Future Distribution of Date Palms: A Modeling Exercise Using CLIMEX. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, F.; Kumar, L. Sensitivity analysis of CLIMEX parameters in modeling potential distribution of Phoenix dactylifera L. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assirey, E.A.R. Nutritional composition of fruit of 10 date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.] cultivars grown in Saudi Arabia. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, W.; Ammar, E. Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Wastes: Valorization: A Circular Economy Approach. In Mediterranean Fruits Bio-Wastes: Chemistry, Functionality and Technological Applications; Ramadan, M.F., Farag, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 404–430. [Google Scholar]
- Nehdi, I.; Omri, S.; Khalil, M.I.; Al-Resayes, S.I. Characteristics and chemical composition of date palm [Phoenix canariensis] seeds and seed oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 32, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnaoui, A.; El Houmaizi, M.A.; Asehraou, A.; Sindic, M.; Deroanne, C.; Hakkou, A. Chemical composition and microbial quality of dates grown in Figuig Oasis of Morocco. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, K.D.; Alharbi, H.A.; Yaish, M.W.; Ahmed, I.; Alharbi, S.A.; Alotaibi, F.; Kuzyakov, Y. Date palm cultivation: A review of soil and environmental conditions and future challenges. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2429–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Dinar, H.; Munir, M.; Mohammed, M. Drought-Tolerance Screening of Date Palm Cultivars under Water Stress Conditions in Arid Regions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjraoui, K.; Haida, W.; Kerboub, Y. Gen. Palm diseases and pests [case of bayoud disease:vascular fusarium] fusarium oxysporum f. sp. albedinis in the wilaya of Adrar. Biodv. J. Date 2017, 1, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.T.; Krueger, R.R. The date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.]: Overview of biology, uses, and cultivation. HortScience 2007, 42, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Juhany, L.I. Degradation of date palm trees and date production in Arab countries: Causes and potential rehabilitation. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 3998–4010. [Google Scholar]
- Jonoobi, M.; Shafie, M.; Shirmohammadli, Y.; Ashori, A.; Zarea-Hosseinabadi, H.; Mekonnen, T. A review on date palm tree: Properties, characterization and its potential applications. J. Renew. Mater. 2019, 7, 1055–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.O.; Sanduk, M.; Taleb, H.M. Τhe date palm and its role in reducing soil salinity and global warming. Acta Hortic. 2010, 882, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A. Climate Change and Global Warming—Scientific Basis with Proposed Solutions; Sustainable Development Report; Iraq Energy Institute: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, R.H.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G. Saline Agriculture for Irrigated Lands in Pakistan: A Handbook; Monagraph No. 50; ACIAR [Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research]: Canberra, Australia, 1998; 142p.
- Mohamed, O.Z.; Yassine, B.; El Hassan, A.; Abdellatif, H.; Rachid, B. Evaluation of compost quality and bioprotection potential against Fusarium wilt of date palm. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroeger, J.E.; Pourhashem, G.; Medlock, K.B.; Masiello, C.A. Water cost savings from soil biochar amendment: A spatial analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Zine, M.; El Hilali, R.; Haggoud, A.; Achbani, E.H.; Bouamri, R. Effects and relationships of compost dose and organic additives on compost tea properties, efficacy against fusarium oxysporum and potential effect on endomycorrhization and growth of Zea mays L. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 4431–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Ashmore, M.R.; Black, H.I.J.; Burgess, P.J.; Evans, C.D.; Quine, T.A.; Thomson, A.M.; Hicks, K.; Orr, H.G. REVIEW: The role of ecosystems and their management in regulating climate, and soil, water and air quality. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 812–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Condon, J.; Evans, J.; Condon, J. New fertilizer options for managing phosphorus for organic and low-input farming systems. Crop Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mardi, M.O.; Al Julanda Al Said, F.; Bakheit Sakit, C.; Al Kharusi, L.M.; Al Rahbi, I.N.; Al Mahrazi, K. Effect of Pollination Method, Fertilizer and Mulch Treatments on the Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Date Palm [Phoenix dactylifera] Fruit I: Physical Characteristics. Acta Hortic. 2006, 736, 317–328. Available online: http://www.actahort.org/books/736/736_30.htm (accessed on 14 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; de Wet, P.F. Climatic requirements of date palm. In Date Palm Cultivation; Zaid, A., Ed.; Plant Production and Protection Paper No. 156; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zaid, A.; De Wet, P.F. Origin, geographical distribution and nutritional values of date palm. In Date Palm Cultivation; Zaid, A., Ed.; Plant Production and Protection Paper No. 156; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liebenberg, P.J.; Zaid, A. Date palm irrigation. In Date Palm Cultivation; Zaid, A., Ed.; Plant Production and Protection Paper No. 156; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dregne, H.E. Land degradation in the drylands. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2002, 16, 99–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kösters, R.; Preger, A.C.; Du Preez, C.C.; Amelung, W. Re-aggregation dynamics of degraded cropland soils with prolonged secondary pasture management in the South African Highveld. Geoderma 2013, 192, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchart, E.; Albrecht, A.; Bernoux, M.; Βrauman, A.; Chotte, J.L.; Feller, C.; Ganry, F.; Hien, E.; Manlay, R.; Masse, D.; et al. Organic matter and biofunctioning in tropical sandy soils and implications for its management. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on the Management of Tropical Sandy Soils for Sustainable Agriculture: A Holistic Approach for Sustainable Development of Problem Soils in the Tropics, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 28 November 2005. 33p. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoliya, P.J.; Pandey, A.N. Soil salinity and water status affect growth of Phoenix dactylifera seedlings. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. 2003, 31, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcar, N.E.; Crawford, D.F.; Leppert, P.M.; Jovanovic, T.; Floyd, R.; Farrow, R. Trees for Saltland: A Guide to Selecting Native Species for Australia; CSIRO, Forestry and Forest Products: Canberra, Australia, 1995; 72p, Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/102.100.100/234346?index=1 (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Maas, E.V.; Poss, J.A. Salt sensitivity of wheat at various growth stages. Irrig. Sci. 1989, 10, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kharusi, L.; Assaha, D.V.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Yaish, M.W. Screening of date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.] cultivars for salinity tolerance. Forests 2017, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muaini, A.; Green, S.; Dakheel, A.; Abdullah, A.H.; Abou Dahr, W.A.; Dixon, S.; Kemp, P.; Clothier, B. Irrigation management with saline groundwater of a date palm cultivar in the hyper-arid United Arab Emirates. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkoaik, F.N.; Khalil, A.I.; Alqumajan, T. Performance evaluation of a static composting system using date palm residues. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 7, 972–983. [Google Scholar]
- Mallaki, M.; Fatehi, R. Design of a biomass power plant for burning date palm waste to cogenerate electricity and distilled water. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehma, A.; Longo, H.F. Valorisation des Sous-Produits du Palmier Dattier en vue de Leur Utilisation en Alimentation du Betail. Rev. Energ. Ren. Prod. Valoris.-Biomasse 2001, 59–64. Available online: https://www.doc-developpement-durable.org/file/Culture/Arbres-Fruitiers/FICHES_ARBRES/Palmier-dattier/UtilisationEnAlimentationBetailDesSous-ProduitsPalmierDattier.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Tahir, A.H.F.; Al-Obaidy, A.H.M.J.; Mohammed, F.H. Biochar from date palm waste, production, characteristics and use in the treatment of pollutants: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 737, 012171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydeniz-Güneşer, B. Valorization of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) Wastes and By-Products. In Mediterranean Fruits Bio-Wastes, Chemistry, Functionality and Technological Applications; Ramadan, M.F., Farag, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besbes, S.; Blecker, C.; Deroanne, C.; Drira, N.E.; Attia, H. Date seeds: Chemical composition and characteristic profiles of the lipid fraction. Food Chem. 2004, 84, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shankiti, A.; Gill, S. Biochar from date palm and Conocarpus waste for improvement of soil quality and biomass production. Biosalinity News 2014, 15, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Aydi, S.; Sassi Aydi, S.; Rahmani, R.; Bouaziz, F.; Souchard, J.P.; Merah, O.; Abdelly, C. Date-Palm Compost as Soilless Substrate Improves Plant Growth, Photosynthesis, Yield and Phytochemical Quality of Greenhouse Melon [Cucumis melo L.]. Agronomy 2023, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.R.A.; Abduljabbar, A.; Vithanage, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.; Elfaki, J.; Abdulazeem, S.S.; Sani, M.I. Biochar production from date palm waste: Charring temperature induced changes in composition and surface chemistry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 115, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, A.; Kalloum, S.; Bradai, L. Follow the degradation of organic matter during composting of date palm [phoenix dactylifera L] waste by physicochemical properties, UV-visible and FT-IR analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. 2020, 102, 2895–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Ali, H. Bahkali. Valorization of date palm [Phoenix dactylifera] fruit processing by-products and wastes using bioprocess technology—Review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashah, M. Date Variety in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; King Abdulaziz University Guidance Booklet Palms and Dates, King Abdulaziz University Press: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1996; pp. 1225–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Torigoe, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Numata, O.; Yazaki, S.; Matsunaga, M.; Boku, N.; Hiura, M.; Ino, H. Influence of emission from rice straw burning on bronchial asthma in children. Pediatr. Int. 2000, 42, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burezq, H.; Davidson, M.K. Biochar from date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.] residues—A critical review. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, H.A.F.; Abdel-Banat, B.M.A.; Al-Hajhoj, M.R. Arthropod pests of date palm and their management. CAB Rev. 2017, 12, 049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhehibi, B.; Nejatian, A.; El Dine Hilali, M.; Belgacem, A.O.; Niane, A.A.; Ibrahim, A.O. Developing Sustainable Production Systems for Date Palm in the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries; Feasibility and Technical Study for Establishing Recycling Date Palm by Product Unit [Date Palm Waste] to Produce Organic Fertilizers [Compost] in the GCC Countries; ICARDA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2020; 11p. [Google Scholar]
- Bharath, G.; Hai, A.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Jayaraman, R.; Taher, H.; Bastidas-Oyanedel, J.R.; Ashraf, M.T.; Schmidt, J.E. Systematic production and characterization of pyrolysis-oil from date tree wastes for bio-fuel applications. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 135, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lee, M.K.; Chang, Y.M. Fast pyrolysis of rice husk: Product yields and compositions. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Mously, H.; Midani, M.; Atef, E. Date Palm Byproducts for Green Fuels and Bioenergy Production. In Date Palm Byproducts: A Springboard for Circular Bio Economy; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 271–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.R.; Patel, A.K.; Jaisi, D.P.; Adhikari, S.; Lu, H.; Khanal, S.K. Environmental application of biochar: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simitzis, J.; Ioannou, Z. Activated carbonaceous materials based on thermosetting binder precursors. In Activated Carbon: Classifications, Properties and Applications; Kwiatkowski, J.F., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.K.; Strezov, V.; Yin Chan, K.; Nelson, P.F. Agronomic properties of wastewater sludge biochar and bioavailability of metals in production of cherry tomato [Lycopersicon esculentum]. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.K.; Strezov, V.; Chan, K.Y.; Ziolkowski, A.; Nelson, P.F. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production and nutrient properties of wastewater sludge biochar. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, X.J.; Lee, L.Y.; Gan, S.; Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.; Ng, H.K. Biochar potential evaluation of palm oil wastes through slow pyrolysis: Thermochemical characterization and pyrolytic kinetic studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 236, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbas, A.; Caglar, A.; Akdeniz, F.; Gullu, D. Conversion of Olive Husk to Liquid Fuel by Pyrolysis and Catalytic Liquefaction. Energy Sources 2000, 22, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Dong, X.; Ime, I.M.; Gao, B.; Ma, L.Q. Pyrolytic temperatures impact lead sorption mechanisms by bagasse biochars. Chemosphere 2014, 105, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Aguiar, E.; Gascó, G.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Méndez, A. The effect of biochar and compost from urban organic waste on plant biomass and properties of an artificially copper polluted soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 124, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A. Biofuels 2015: Upgrading liquids from fast pyrolysis of biomass. Arch. Chem. Res. 2020, 4, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Mondal, A.K.; Chintala, V.; Tauseef, S.M.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, J.K. Thermochemical pyrolysis of biomass using solar energy for efficient biofuel production: A review. Biofuels 2021, 12, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndukwu, M.C.; Horsfall, I.T.; Ubouh, E.A.; Orji, F.N.; Ekop, I.E.; Ezejiofor, N.R. Review of solar- biomass pyrolysis systems: Focus on the configuration of Thermal-solar systems and reactor orientation. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 33, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.D.; Kubo, I.; Ohadi, M.; Alili, A.A. Measurement of solar energy radiation in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugaard, D.E.; Brown, R.C. Enthalpy for pyrolysis for several types of biomass. Energy Fuel 2003, 17, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.; Yusuf, A.; Ajumobi, O.; Dzidzienyo, P. Pyrolysis of date palm waste to biochar using concentrated solar thermal energy: Economic and sustainability implications. Waste Manag. 2019, 93, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, C.; Mašek, O. SPEAR [Solar Pyrolysis Energy Access Reactor]: Theoretical Design and Evaluation of a Small-Scale Low-Cost Pyrolysis Unit for Implementation in Rural Communities. Energies 2021, 14, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Gu, Y. Application of biochar for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Jatav, H.; Kumar Singh, S.; Singh Jatav, S.; Rajput, V.D.; Parihar, M.; Kumar Mahawer, S.; Kumar Singhal, R. Importance of Biochar in Agriculture and Its Consequence. In Applications of Biochar for Environmental Safety; Abdelhafez, A.A., Abbas, M.H.H., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hina, K.; Bishop, P.; Arbestain, M.C.; Calvelo-Pereira, R.; MacIá-Agulló, J.A.; Hindmarsh, J.; Hanly, J.A.; Hedley, M.J. Producing biochars with enhanced surface activity through alkaline pretreatment of feedstocks. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.-X.; Zhang, A.-F.; Zou, J.-W.; Li, L.-Q.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zheng, J.-W. Biochar from agro-byproducts used as amendment to croplands: An option for low carbon agriculture. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2010, 26, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, R.; Zuhaidi, N.F.Q.; Yusof, Y.; Jamel, J.; Kanakaraju, D.; Ngaini, Z. Chemically treated microwave-derived biochar: An overview. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 107, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambo, H.S.; Dutta, A. A comparative review of biochar and hydrochar in terms of production, physico-chemical properties and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igalavithana, A.D.; Mandal, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Vithanage, M.; Parikh, S.J.; Fungai, N.D.M.; Rizwan, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Al-Wabel, M.; Bolan, N.; et al. Advances and future directions of biochar characterization methods and applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2275–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUROCHAR-Biochar for Carbon Sequestration and Large-Scale Removal of Greenhouse Gases [GHG] from the Atmosphere: FP7-ENVIRONMENT—Specific Programme “Cooperation”: Environment [including Climate Change], ENV.2010.3.1.8-1—Development of Technologies for Long-Term Carbon Sequestration. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/265179/reporting (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Schimmelpfennig, S.; Müller, C.; Grünhage, L.; Koch, C.; Kammann, C. Biochar, hydrochar and uncarbonized feedstock application to permanent grassland—Effects on greenhouse gas emissions and plant growth. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, M.; Woods, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Biochar—EuroChar Project. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 22–27 April 2012. 547, Geophysical Research Abstracts Volume 14, EGU2012-547-1. [Google Scholar]
- Berge, N.D.; Kammann, C.; Ro, K.; Libra, J. Environmental applications of hydrothermal carbonization technology: Biochar production, carbon sequestration, and waste conversion. In Sustainable Carbon Materials from Hydrothermal Processes; Titirici, M.-M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 295–340. [Google Scholar]
- Naisse, C.; Girardin, C.; Lefevre, R.; Pozzi, A.; Maas, R.; Stark, A.; Rumpel, C. Effect of physical weathering on the carbon sequestration potential of biochars and hydrochars in soil. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammann, C.; Ratering, S.; Eckhard, C.; Müller, C. Biochar and hydrochar effects on greenhouse gas [carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane] fluxes from soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malghani, S.; Gleixner, G.; Trumbore, S.E. Chars produced by slow pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization vary in carbon sequestration potential and greenhouse gases emissions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 62, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Limon, M.S.H.; Romić, M.; Islam, M.A. Hydrochar-based soil amendments for agriculture: A review of recent progress. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariyar, P.; Kumari, K.; Jain, M.K.; Jadhao, P.S. Evaluation of change in biochar properties derived from different feedstock and pyrolysis temperature for environmental and agricultural application. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Lian, F.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhu, L.Y.; Song, Z.G. Biochars derived from various crop straws: Characterization and Cd [II] removal potential. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 10, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, C.E.; Chuang, V.J.; Masiello, C.A.; Gonnermann, H.; Gao, X.; Dugan, B.; Driver, L.E.; Panzacchi, P.; Zygourakis, K.; Davies, C.A. New approaches to measuring biochar density and porosity. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 66, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation, 2nd ed.; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015; 976p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, H.T.; Lu, W.J.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Ren, L. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and heavy metal adsorptive performance of biochar derived from municipal sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Faraj, A.S.; Abduljabbar, A.; Sik Ok, Y.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Date palm waste-derived biochar composites with silica and zeolite: Synthesis, characterization and implication for carbon stability and recalcitrant potential. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2019, 41, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizirici, B.; Fseha, Y.H.; Yildiz, I.; Delclos, T.; Khaleel, A. The effect of pyrolysis temperature and feedstock on date palm waste derived biochar to remove single and multi-metals in aqueous solutions. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2021, 31, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Farraj, A.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Abduljabbar, A.; Al-Faraj, A.I.; Sallam, A.S. Date palm waste biochars alter a soil respiration, microbial biomass carbon, and heavy metal mobility in contaminated mined soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.; Xu, J. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: Mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Hu, H.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Xing, Z.; Ali, U.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu contaminated soil by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate: Speciation transformation, risk evaluation and mechanism inquiry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, R.; Ji, S.; Xie, L.; Zhang, H. Effects of biochar derived from sewage sludge and sewage sludge/cotton stalks on the immobilization and phytoavailability of Pb, Cu, and Zn in sandy loam soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.A. Production of Biochar from Date Palm Fronds and its Effects on Soil Properties. Mater. Res. Proc. 2019, 11, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, O.Y.; Kian, L.K.; Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Khiari, R. Cellulose nanocrystal extracted from date palm fibre: Morphological, structural and thermal properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 159, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Yu, Q.J.; El Hanandeh, A. Removal of lead[II] from aqueous solution using date seed-derived biochar: Batch and column studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Utilization of date biomass waste and date seed as bio-fuels source. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensidhom, G.; Ben Hassen-Trabelsi, A.; Alper, K.; Sghairoun, M.; Zaafouri, K.; Trabelsi, I. Pyrolysis of Date palm waste in a fixed-bed reactor: Characterization of pyrolytic products. Bioresour. Technol 2018, 247, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraseni, T.; Chen, G.; Guangren, Q. Towards a faster and broader application of biochar: Appropriate marketing mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 67, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, W.; Kookana, R.; Katayama, A. Characteristics of biochar and its application in remediation of contaminated soil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, A.H.; Najar, G.R.; Ganie, M.A.; Sofi, J.A.; Ali, T. Biochar for sustainable soil health: A review of prospects and concerns. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, L.A.; Harpole, W.S. Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: A meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guyader, E.; Morvan, X.; Miconnet, V.; Marin, B.; Moussa, M.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Delgado-Iniesta, M.J.; Girods, P.; Fontana, S.; Sbih, M.; et al. Influence of Date Palm-Based Biochar and Compost on Water Retention Properties of Soils with Different Sand Contents. Forests 2024, 15, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, K.D.; Jeff, J. Addition of biochar to a sandy desert soil: Effect on crop growth, water retention and selected properties. Agronomy 2019, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H. Biochar and Soil Physical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Lee, S.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Farooq, M.; Song, H.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar application to low fertility soils: A review of current status, and future prospects. Geoderma 2019, 337, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondi, M.O.; Xia, X.; Nahayo, A.; Liu, X.; Korai, P.K.; Pan, G. Quantification of biochar effects on soil hydrological properties using meta-analysis of literature data. Geoderma 2016, 274, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Peters, A.; Trinks, S.; Schonsky, H.; Facklam, M.; Wessoolek, G. Impact of biochar and hydrochar addition on water retention and water repellency of sandy soil. Geoderma 2013, 202, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulyett, J.; Sakrabani, R.; Kibbilewhite, M.; Hann, M. Impact of biochar addition on water retention, nitrification and carbon dioxide evolution from sandy loam soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gła, T.; Palmowska, J.; Zaleski, T.; Gondek, K. Effect of biochar application on soil hydrological properties and physical quality of sandy soil. Geoderma 2016, 281, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiamonte, G.; Crescimanno, G.; Parrino, F.; De Pasquale, C. Effect of biochar on the physical and structural properties of a desert sandy soil. Catena 2019, 175, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Zhuravel, A.; Silva, F.C.; Amaro, A.; Ben-Hur, M.; Keizer, J.J. The influence of biochar particle size and concentration on bulk density and maximum water holding capacity of sandy vs sandy loam soil in a column experiment. Geoderma 2019, 347, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, L.D.; Zehetner, F.; Rampazzo, N.; Wimmer, B.; Soja, G. Long-term effects of biochar on soil physical properties. Geoderma 2016, 282, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Watts, D.W.; Amonette, J.E.; Ippolito, J.A.; Lima, I.M.; Gaskin, J.; Das, K.C.; Steiner, C.; Ahmedna, M.; et al. Biochars Impact on Soil-Moisture Storage in an Ultisol and Two Aridisols. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Moreno-Barriga, F.; Acosta, J.A.; Muñoz, M.A.; Faz, A. Stability, nutrient availability and hydrophobicity of biochars derived from manure, crop residues, and municipal solid waste for their use as soil amendments. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Miller, A.Z.; Knicker, H.; Costa-Pereira, M.F.; Merino, A.; De la Rosa, J.M. Chemical, physical and morphological properties of biochars produced from agricultural residues: Implications for their use as soil amendment. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, N.; Yousef, L.F. A short report on changes of quality indicators for a sandy textured soil after treatment with biochar produced from fronds of date palm. Energy Procedia 2015, 74, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karbout, N.; Bol, R.; Brahim, N.; Moussa, M.; Bousnina, H. Applying biochar from date palm waste residues to improve the organic matter, nutrient status and water retention in sandy oasis soils. J. Res. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 07, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Odinga, E.S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, B.; Waigi, M.G.; Gao, Y. Polyaromatic hydrocarbons in biochars and human health risks of food crops grown in biochar-amended soils: A synthesis study. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, H.A.; Alotaibi, K.D.; El-Saeid, M.H.; Giesy, J.P. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons [PAHs] and Metals in Diverse Biochar Products: Effect of Feedstock Type and Pyrolysis Temperature. Toxics 2023, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Z.; He, Q.; Zhang, F. Effect of biochar on the presence of nutrients and ryegrass growth in the soil from an abandoned indigenous coking site: The potential role of biochar in the revegetation of contaminated site. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihoub, A.; Amin, A.E.E.A.Z.; Motaghian, H.R.; Saeed, M.F.; Naeem, A. Citric Acid [CA]–Modified Biochar Improved Available Phosphorus Concentration and Its Half-Life in a P-Fertilized Calcareous Sandy. Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Lehr, V.I. Biochar effects on phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, C.; Das, K.C.; Melear, N.; Lakly, D. Reducing nitrogen loss during poultry litter composting using biochar. J. Environ. Qual 2010, 39, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramírez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans [Phaseolus vulgaris L.] increases with bio-char additions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Ahmedna, M.; Rehrah, D.; Watts, D.W. Switchgrass biochar affects two Aridisols. J. Environ. Qual 2012, 41, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.J.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Hipps, N.A. Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: A review. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailegnaw, N.S.; Mercl, F.; Pračke, K.; Száková, J.; Tlustoš, P. High temperature-produced biochar can be efficient in nitrate loss prevention and carbon sequestration. Geoderma 2019, 338, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, T.H.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Gundale, M.J.; Holben, W.E. Wildfire-produced charcoal directly influences nitrogen cycling in ponderosa pine forests. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, S.; Riondino, M.; Baronti, S.; Esposito, F.R.; Marzaioli, R.; Rutigliano, F.A. Impact of biochar application to a mediterranean wheat crop on soil microbial activity and greenhouse gas fluxes. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cai, Z.C.; Chang, S.X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.B. Wheat straw and its biochar have contrasting effects on inorganic N retention and N2O production in a cultivated black chernozem. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.J.; Condron, L.M.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. A Review of Biochar and Soil Nitrogen Dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalirwa, D.; Sudo, S.; Wacal, C.; Zaw Oo, A.; Sasagawa, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Masunaga, T.; Nishihara, E. Impact of fresh and aged palm shell biochar on N2O emissions, soil properties, nutrient content and yield of Komatsuna [Brassica rapa var. perviridis] under sandy soil conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammann, C.; Ippolito, J.; Hagemann, N.; Borchard, N.; Luz Cayuela, M.; Estavillo, J.M.; Fuertes-Mendizabal, T.; Jeffery, S.; Kern, J.; Novak, J.; et al. Biochar as a tool to reduce the agricultural greenhouse-gas burden—Knowns, unknowns and future research needs. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2017, 25, 114–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, M.; Pan, B. Limited role of biochars in nitrogen fixation through nitrate adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, S.; van der Veen, B.; Farkas, E.; Kocatürk-Schumacher, N.P.; Dieguez-Alonso, A.; Budai, A.; Rasse, D. A re-analysis of NH4+ sorption on biochar: Have expectations been too high? Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Shen, Q.; Lehmann, J.; Singh, B.; Sabir, M. Biochar effects on crop yields with and without fertilizer: A meta-analysis of field studies using separate controls. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 36, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, A.; Song, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of biochar-based controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen-use efficiency of oilseed rape [Brassica napus L.]. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndoung, O.C.N.; Figueiredo, C.C.de; Ramos, M.L.G. A scoping review on biochar-based fertilizers: Enrichment techniques and agro-environmental application. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.-P.; Pandit, B.H.; Cornelissen, G.; Kammann, C.I. Biochar-Based Fertilization with Liquid Nutrient Enrichment: 21 Field Trials Covering 13 Crop Species in Nepal. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2324–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavo Adolfo, G.-F.; Wolf-Anno, B.; Martin, R.; Christina, S. Co-composting of biochar and nitrogen-poor organic residues: Nitrogen losses and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Waste Manag. 2022, 143, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prost, K.; Borchard, N.; Siemens, J.; Kautz, T.; Séquaris, J.-M.; Möller, A.; Amelung, W. Biochar Affected by Composting with Farmyard Manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, D.N.; Mulcahy, D.L.; Dietz, D. Biochar soil amendment increases tomato seedling resistance to drought in sandy soils. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 88, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, R. Effects of amendment of different biochars on soil carbon mineralization and sequestration. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Muhammad, N.; Wu, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Potential role of biochars in decreasing soil acidification- A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Chen, B. Dual role of biochars as adsorbents for aluminum: The effects of oxygen-containing organic components and the scattering of silicate particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8759–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.N.H.; Hasan, M.; Uddain, J.; Subramaniam, S. Impact of application of Trichoderma and biochar on growth, productivity and nutritional quality of tomato under reduced N-P-K fertilization. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Kang, X.; Yan, X.; Yin, N.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zhuge, Y. Biochar mitigation of soil acidification and carbon sequestration is influenced by materials and temperature. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhang, X.C. Effect of Biochar on pH of Alkaline Soils in the Loess Plateau: Results from Incubation Experiments. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 14, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, B. Biochar to improve soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Farooq, M.; Nawaz, A.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Ammara, U.; Ok, Y.S.; Siddique, K.H.M. Biochar for crop production: Potential benefits and risks. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 17, 685–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; LEE, X.; Wang, B. Characterization of biochars produced from seven biomasses grown in three different climate zones. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Yang, F.; Xing, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, Z.; Holtzman, R.; Kan, I.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Use of biochar to manage soil salts and water: Effects and mechanisms. Catena 2022, 211, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartey, O.D.; Zhao, B. Biochar preparation, characterization, and adsorptive capacity and its effect on bioavailability of contaminants: An overview. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 715398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soils and sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for environmental management: An introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management Science and Technology; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Earthscans: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sohi, S.P.; Krull, E.; Lopez-Capel, E.; Bol, R. A review of biochar and its use and function in soil. Adv. Agron. 2010, 105, 47–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, F.P.; Baronti, S.; Lugato, E.; Genesio, L.; Castaldi, S.; Fornasier, F.; Miglietta, F. Biochar as a strategy to sequester carbon and increase yield in durum wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahrouky, M.; EL-Naggar, A.H.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Dynamics of CO2 emission and biochemical properties of a sandy calcareous soil amended with Conocarpus waste and biochar. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Usman, A.R.A.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Aly, A.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Elmaghraby, S.; Al-Omran, A. Conocarpus biochar as a soil amendment for reducing heavy metal availability and uptake by maize plants. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ibrahim, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Abbas, T.; Ok, Y.S. Mechanisms of biochar mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2230–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Bian, R.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Joseph, S.; Crowley, D.; Pan, G.; Li, L. Effects of biochar on availability and plant uptake of heavy metals—A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H.; Huang, Q. Biochar produced from the straw of common crops simultaneously stabilizes soil organic matter and heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Hussain, Q.; Usman, A.R.A.; Ahmad, M.; Abduljabbar, A.; Sallam, A.S.; Ok, Y.S. Impact of biochar properties on soil conditions and agricultural sustainability: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2124–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; El Hanandeh, A.; Yu, Q. Competitive adsorption of heavy metal ions [Pb2+, Cu2+, and Ni2+] onto date seed biochar: Batch and fixed bed experiments. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; El Hanandeh, A.; Qimimg, J.Y. Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Seed characterization for biochar preparation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Engineering, Project, and Production Management, Gold Coast, Australia, 2–4 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Yu, Q.J.; El Hanandeh, A. Investigation of the kinetics and mechanisms of nickel and copper ions adsorption from aqueous solutions by date seed derived biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, B.S.; El–Hendawy, A.A. Porosity development in activated carbons obtained from date pits under chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2002, 52, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués, I.; Mazzurco Miritana, V.; Passatore, L.; Zacchini, M.; Peruzzi, E.; Carloni, S.; Pietrini, F.; Marabottini, R.; Chiti, T.; Massaccesi, L.; et al. Biochar soil amendment as carbon farming practice in a Mediterranean environment. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 33, e00634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutigliano, F.A.; Romano, M.; Marzaioli, R.; Baglivo, I.; Baronti, S.; Miglietta, F.; Castaldi, S. Effect of biochar addition on soil microbial community in a wheat crop. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 60, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; Sleutel, S.; Case, S.D.C.; Alberti, G.; McNamara, N.P.; Zavalloni, C.; Vervisch, B.; delle Vedove, G.; De Neve, S. C mineralization and microbial activity in four biochar field experiments several years after incorporation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, P.; Rosell-Melé, A.; Colomer-Ventura, F.; Denef, K.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Riba, M.; Alcañiz, J.M. Belowground biota responses to maize biochar addition to the soil of a Mediterranean vineyard. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, S.; Vaccari, F.P.; Miglietta, F.; Calzolari, C.; Lugato, E.; Orlandini, S.; Pini, R.; Zulian, C.; Genesio, L. Impact of biochar application on plant water relations in Vitis vinifera [L.]. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 53, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Viger, M.; Arnold, E.C.; Harris, Z.M.; Ventura, M.; Miglietta, F.; Girardin, C.; Edwards, R.J.; Rumpel, C.; Fornasier, F.; et al. Biochar alters the soil microbiome and soil function: Results of next-generation amplicon sequencing across Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. Bioenergy 2017, 9, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, E.A.N.; Mattana, S.; Alcañiz, J.M.; Pérez-Herrero, E.; Domene, X. Gasifier biochar effects on nutrient availability, organic matter mineralization, and soil fauna activity in a multi-year Mediterranean trial. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 215, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, M.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Barrón, V.; del Campillo, M.C.; Gallardo, A.; Fuentes, M.; Villar, R. Wheat growth and yield responses to biochar addition under Mediterranean climate conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.X.; Xiao, Q.; Cheng, H.Y.; Shi, B.J.; Shen, Y.-F.; Li, S.Q. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial activity after biochar addition in a dryland maize field in North-Western China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.; Ma, L.; Min, W.; Ye, J.; Hou, Z. Effects of biochar on soil microbial community composition and activity in drip-irrigated desert soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 72, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wu, M. Soil N transformation and microbial community structure as affected by adding biochar to a paddy soil of subtropical China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, A.; Raiesi, F. Influence of biochar on potential enzyme activities in two calcareous soils of contrasting texture. Geoderma 2017, 308, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Sadasivam, B.Y.; Reddy, K.R.; Wang, C.; Spokas, K. Review of the effects of biochar amendment on soil properties and carbon sequestration. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2015, 20, 04015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, S.; Jensen, E.S.; Jensen, L.S. Microbial mineralization and assimilation of black carbon: Dependency on degree of thermal alteration. Org. Geochem. 2008, 39, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Subbotina, I.; Chen, H.; Bogomolova, I.; Xu, X. Black carbon decomposition and incorporation into soil microbial biomass estimated by 14 C labeling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C.; Teixeira, W.G.; Lehmann, J.; Nehls, T.; Luis, J.; Macêdo, V.D.; Blum, W.E.H.; Zech, W. Long term effects of manure, charcoal and mineral fertilization on crop production and fertility on a highly weathered Central Amazonian upland soil. Plant Soil 2007, 291, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, W.; Harsh, J.B.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Fortuna, A.M.; Dallmeyer, I.; Garcia-Pérez, M. The role of biochar porosity and surface functionality in augmenting hydrologic properties of a sandy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatta, A.; Fike, J.; Battaglia, M.; Galbraith, J.; Baig, M. Effects of biochar on soil fertility and crop productivity in arid regions: A review. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, G.; Wu, G.; Kibue, G.W.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, K.; Joseph, S. Biochar helps enhance maize productivity and reduce greenhouse gas emissions under balanced fertilization in a rainfed low fertility inceptisol. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, A.; Ibrahimi, K.; Trabelsi, F. Biochar application to soil under arid conditions: A bibliometric study of research status and trends. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Ali, S.; Ilyas, M.; Riaz, M.; Akhtar, K.; Ali, K.; Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Khan, I.; Shah, S. Enhancing phosphorus availability, soil organic carbon, maize productivity and farm profitability through biochar and organic–inorganic fertilizers in an irrigated maize agroecosystem under semi-arid climate. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 37, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Li, J.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mohanty, S. Generation, Resuspension, and Transport of Particulate Matter From Biochar-Amended Soils: A Potential Health Risk. GeoHealth 2020, 4, e2020GH000311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, C.; Chaplot, V.; Planchon, O.; Bernadou, J.; Valentin, C.; Mariotti, A. Preferential erosion of black carbon on steep slopes with slash and burn agriculture. Catena 2006, 65, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libutti, A.; Cammerino, A.R.B.; Monteleone, M. Management of Residues from Fruit Tree Pruning: A Trade-Off between Soil Quality and Energy Use. Agronomy 2021, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, R.T. The Practical Handbook of Compost Engineering; CRC Press, Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; 752p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Influence of bulking agents on physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage composting of green waste. Waste Manag. 2015, 48, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doña-Grimaldi, V.M.; Palma, A.; Ruiz-Montoya, M.; Morales, E.; Díaz, M.J. Energetic valorization of MSW compost valorization by selecting the maturity conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachicha, S.; Cegarra, J.; Sellami, F.; Hachicha, R.; Drira, N.; Medhioub, K.; Ammar, E. Elimination of polyphenols toxicity from olive mill wastewater sludge by its co-composting with sesame bark. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 161, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaeen, M.; Nafez, A.H.; Bina, B.; Nabavi, B.F.; Hassanzadeh, A. Respiration and enzymatic activities as indicators of stabilization of sewage sludge composting. Waste Manag. 2015, 39, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Conte, A.; Belgiorno, V.; Siciliano, A.; Guida, M. The evolution of compost stability and maturity during the full-scale treatment of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, W.; Mahmoud, I.B.; Masmoudi, S.; Triki, M.A.; Mounier, S.; Ammar, E. Physico-chemical and spectroscopic quality assessment of compost from date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.] waste valorization. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; JarbouiJarboui, R.; El Feki, H.; Gea, T.; Medhioub, K.; Ammar, E. Characterization of olive mill wastes composts and their humic acids: Stability assessment within different particle size fractions. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Belgiorno, V.; Guida, M. Compost from organic solid waste: Quality assessment and European regulations for its sustainable use. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 94, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Li, M.; Xi, B.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, X.; Qi, H.; Zhu, C. Characterisation of dissolved organic matter extracted from the bio-oxidative phase of co-composting of biogas residues and livestock manure using spectroscopic techniques. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 10, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindintwali, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Yu, X. Lignocellulosic crop residue composting by cellulolytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria: A novel tool for environmental sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.C.; Forney, L.J.; Huang, A.J.; Drew, S.; Czuprenski, M.; Lindeberg, J.D.; Reddy, C.A. Effects of Turning Frequency, Leaves to Grass Mix Ratio and Windrow vs. Pile Configuration on the Composting of Yard Trimmings. Compost. Sci. Util. 1996, 4, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkenhead, J.A.; McDowell, W.H. Soil C:N ratio as a predictor of annual riverine DOC flux at local and global scales. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, M.; Wong, J.W.C.; Wong, M.H. Review on evaluation of compost maturity and stability of solid waste. Shanghai Environ. Sci. 1999, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, R.V.; Roy, R.N.; Hiraoka, H. On Farm Composting Methods; Land and Water Discussion Paper 2; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003; 37p. [Google Scholar]
- Safwat, M.S. A Organic Farming of Date Palm and Recycling of Their Wastes. Afr. Crop Sci. Conf. Proc. 2007, 8, 2109–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Chang, C.; Larney, F.J. Carbon, nitrogen balances and greenhouse gas emission during cattle feedlot manure composting. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linères, M.; Djakovitch, J.L. Caractérisation de la stabilité biologique des apports organiques par l’analyse biochimique. In Matières Organiques et Agricultures; Decroux, J., Ignazi, J.C., Eds.; GEMAS-COMIFER: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mary, B.; Fresneau, C.; Morel, J.L.; Mariotti, A. C and N cycling during decomposition of root mucilage, roots and glucose in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganry, F.; Thuriès, L. Intérêt des fumiers pour restaurer la fertilité des sols en zone semi-aride d’Afrique. In Restauration de la Productivité des sols Tropicaux et Mediterraneens: Contribution à L’agroécologie; Roose, E., Ed.; IRD: Marseille, France, 2017; pp. 179–195. [Google Scholar]
- Gondek, M.; Weindorf, D.C.; Thiel, C.; Kleinheinz, G. Soluble Salts in Compost and Their Effects on Soil and Plants: A Review. Compos. Sci. Util. 2020, 28, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Crohn, D.M. Compost induced soil salinity: A new prediction method and its effect on plant growth. Compos. Sci. Util. 2012, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodabadi, M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Sinobas, L.R.; Pazira, E.; Neshat, A. Reclamation of calcareous saline sodic soil with different amendments [I]: Redistribution of soluble cations within the soil profile. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Composting Council [USCC]. Field Guide to Compost Use. 2001. 94p. Available online: https://www.mncompostingcouncil.org/uploads/1/5/6/0/15602762/fgcu.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Soudejani, H.T.; Kazemian, H.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A. Application of zeolites in organic waste composting: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.G. The effects of natural zeolite on salinity level of poultry litter compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.T.; Selvam, A.; Wong, J.W. Reducing nitrogen loss and salinity during ‘struvite’ food waste composting by zeolite amendment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Reddy, D.D. Zeolites and their potential uses in agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2011, 113, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksheem, A.M.; Bennett, J.M.; Antille, D.L.; Raine, S.R. Towards a method for optimized extraction of soluble nutrients from fresh and composted chicken manures. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.D. Crop and irrigation management strategies for saline-sodic soils and waters aimed at environmentally sustainable agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 323, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Peng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, W.; Cai, H.; Liu, G.; Wu, Z. Microbial inoculum with leachate recirculated cultivation for the enhancement of OFMSW composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymazal, J.; Svehla, J.; Kropfelova, L.; Chrastny, V. Trace metals in Phragmites australis and Phalaris arundinacea growing in constructed and natural wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshoodeh, R.; Alavi, N.; Majlesi, M.; Paydary, P. Compost leachate treatment by a pilot-scale subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 105, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Azaïs, A.; Benkaraache, S.; Drogui, P.; Tyagi, R.D. Composting leachate: Characterization, treatment and future perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 323–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabderrahim, M.A.; Elfalleh, W.; Belayadi, H.; Haddad, M. Effect of date palm waste compost on forage alfalfa growth, yield, seed yield and minerals uptake. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vico, A.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Bustamante, M.A.; Agulló, E.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Sáez, J.A.; Paredes, C.; Pérez-Espinosa, A.; Moral, R. Valorization of date palm [Phoenix dactylifera L.] pruning biomass by cocomposting with urban and agri-food sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 226, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giagnoni, L.; Maienza, A.; Baronti, S.; Primo, F.; Genesio, L.; Taiti, C.; Martellini, T.; Scodellini, R.; Cincinelli, A.; Costa, C.; et al. Long-term soil biological fertility, volatile organic compounds and chemical properties in a vineyard soil after biochar amendment. Geoderma 2019, 344, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthod, J.; Rumpel, C.; Dignac, M.F. Composting with additives to improve organic amendments. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.A. Co-Composting Date Palm Tree Wastes and Its Effects on Soil Fertility. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 925, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.M.; Khalaf, N.H.; Alkubaisy, S.A. Utilization of Date Palm Waste Compost as Substitute for Peat Moss. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 904, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoitink, H.A.J.; Fahy, P.C. Basis for the control of soilborne plant pathogens with composts. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1986, 24, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manios, T. The composting potential of different organic solid wastes: Experience from the island of Crete. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorpas, A. Compost Evaluation and Utilization. In Composting: Processing, Materials and Approaches; Pereira, J.C., Bolin, L.J., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 31–68. [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro, G.; Celano, G.; Dichio, B.; Xiloyannis, C. Effects of soil-protecting agricultural practices on soil organic carbon and productivity in fruit tree orchards. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, G.; Dichio, B.; Briccoli Bati, C.; Xiloyannis, C. Soil management affects carbon dynamics and yield in a Mediterranean peach orchard. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 161, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubouris, G.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Kavvadias, V.; Digalaki, N.; Psarras, G. Sustainable agricultural practices for improving soil carbon and nitrogen content in relation to water availability—An adapted approach to Mediterranean olive groves. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 2687–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulos, G.; Kasapi, K.A.; Koubouris, G.; Psarras, G.; Arampatzis, G.; Hatzigiannakis, E.; Kavvadias, V.; Xiloyannis, C.; Montanaro, G.; Malliaraki, S.; et al. Adaptation of Mediterranean Olive Groves to Climate Change through Sustainable Cultivation Practices. Climate 2020, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.E.; Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M.; Poss, J.A.; Läuchli, A.E.; Suarez, D.L. pH dependent salinity-boron interactions impact yield, biomass, evapotranspiration and boron uptake in broccoli [Brassica oleracea L.]. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, G.; Dumontet, S.; Xiloyannis, C.; Nuzzo, V.; Dichio, B.; Arcieri, M. Green manure plant biomass evaluation and total mineral nitrogen in the soil of a peach orchard system. Acta Hortic. 1998, 465, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadias, V.; Papadopoulou, M.; Vavoulidou, E.; Theocharopoulos, S.; Repas, S.; Koubouris, G.; Psarras, G.; Kokkinos, G. Effect of addition of organic materials and irrigation practices on soil quality in olive groves. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Mazzeo, A.; Matarrese, A.M.S.; Pacifico, A.; Fracchiolla, I.M.; Al Chamill, Z.; Lasorella, I.C.; Montemurro, P.; Mondelli, D. Soil management systems: Effects on soil properties and weed flora. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2015, 36, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, W.E.; Grabber, J.H.; Karlen, D.L.; Balser, T.C.; Palmquist, D.E. Cover crop and liquid manure effects on soil quality indicators in a corn silage system. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustin, M. Le Compost: Gestion de la Matiere Organique; Dubusc, F., Ed.; Editions François Dubusc: Paris, France, 1987; 954p. [Google Scholar]
- Parnaudeau, V.; Nicolardot, B.; Pagès, J. Relevance of Organic Matter Fractions as Predictors of Wastewater Sludge Mineralization in Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CATCH-C Project, Compatibility of Agricultural Management Practices and Types of Farming in the EU to Enhance Climate Change Mitigation and Soil Health. 7th Framework Programme for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration. Available online: https://www.catch-c.eu/ (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Wander, M.M.; Traina, S.J.; Stinner, B.R.; Peters, S.E. Organic and conventional management effects on biologically active soil organic matter pools. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunapala, N.; Scow, K.M. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass and activity in conventional and organic farming systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouili, E.; Hidri, Y.; Cheikh M’Hamed, H.; Somenahally, A.; Xue, Q.; El Akram Znaïdi, I.; Jebara, M.; Nefissi Ouertani, R.; Muhovski, Y.; Riahi, J.; et al. Date palm waste compost promotes plant growth and nutrient transporter genes expression in barley [Hordeum vulgare L.]. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 149, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Mlih, R.; Bouajila, A.; Karbout, N.; Bol, R. Soil OC and N stocks in the saline soil of Tunisian gataaya oasis eight years after application of manure and compost. Land 2022, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shakweer, M.H.; El-Sayad, A.E.A.; Ejes, M.S.A. Soil and plant analysis as a guide for interpretation of the improvement efficiency of organic conditioners added to different soils in Egypt. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 2067–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouili, E.; Abid, G.; Hogue, R.; Jeanne, T.; D’Astous-Pagé, J.; Sassi, K.; Hidri, Y.; M’Hamed, H.C.; Somenahally, A.; Xue, Q.; et al. Date Palm Waste Compost Application Increases Soil Microbial Community Diversity in a Cropping Barley [Hordeum vulgare L.] Field. Biology 2023, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).