Integration of Laser Scanner, Ground-Penetrating Radar, 3D Models and Mixed Reality for Artistic, Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Dissemination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To create a three-dimensional digital model with a high level of structural detail that can be implemented in a BIM or CAD environment to design any future restoration of the structure.
- To enable the integrated management of the digital model of the survey area, which allows for a dynamic exploration of the study area and allows for access to and analysis of the information based on geospatial attributes, maintaining a high level of detail.
2. Materials and Methods
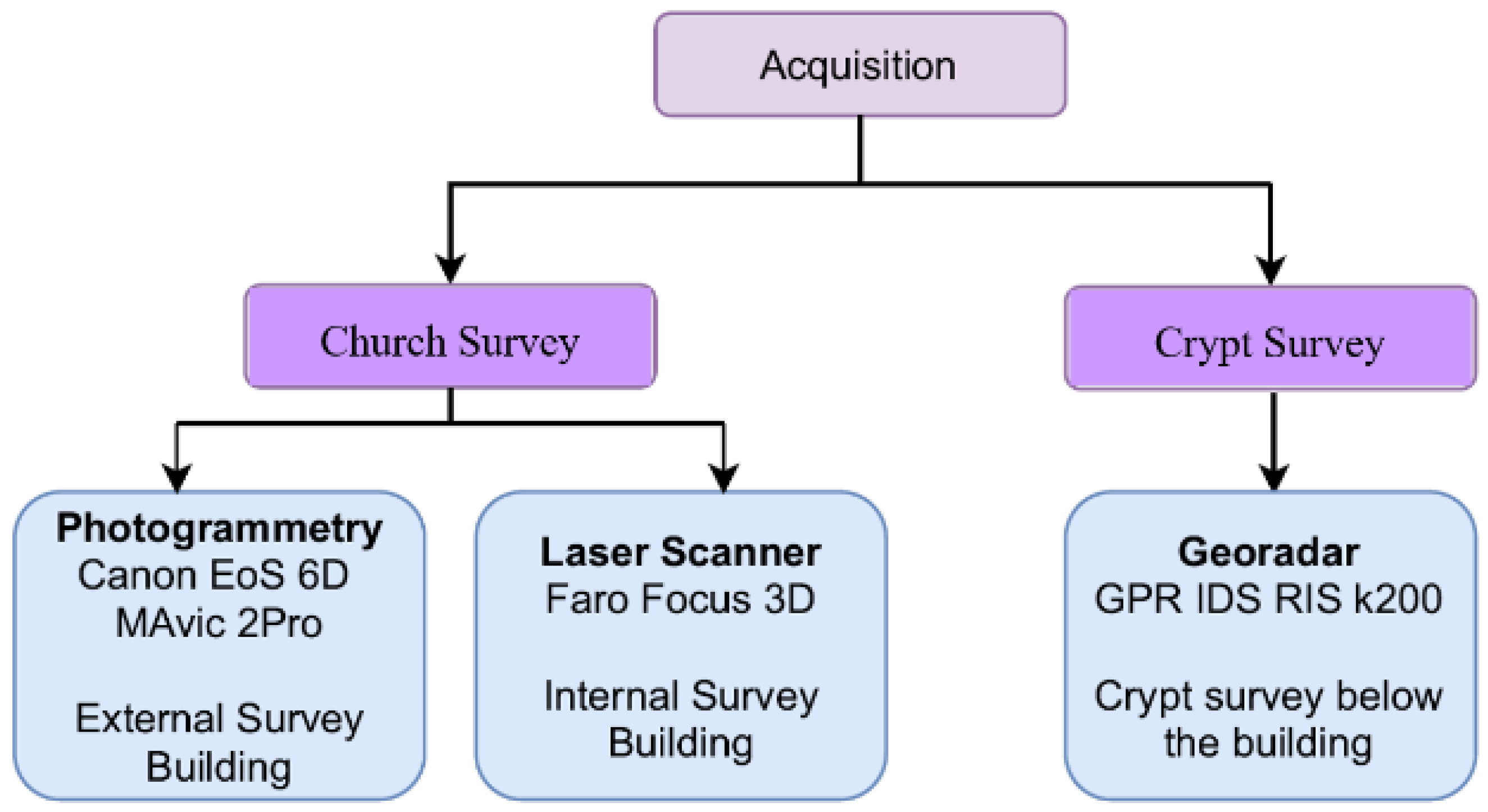
2.1. Data Acquisition
- (1)
- Uploading data within the MatLab environment;
- (2)
- Signal plot;
- (3)
- Signal normalization;
- (4)
- Background noise reduction;
- (5)
- Filtering;
- (6)
- Downstream graphical representation of the process.
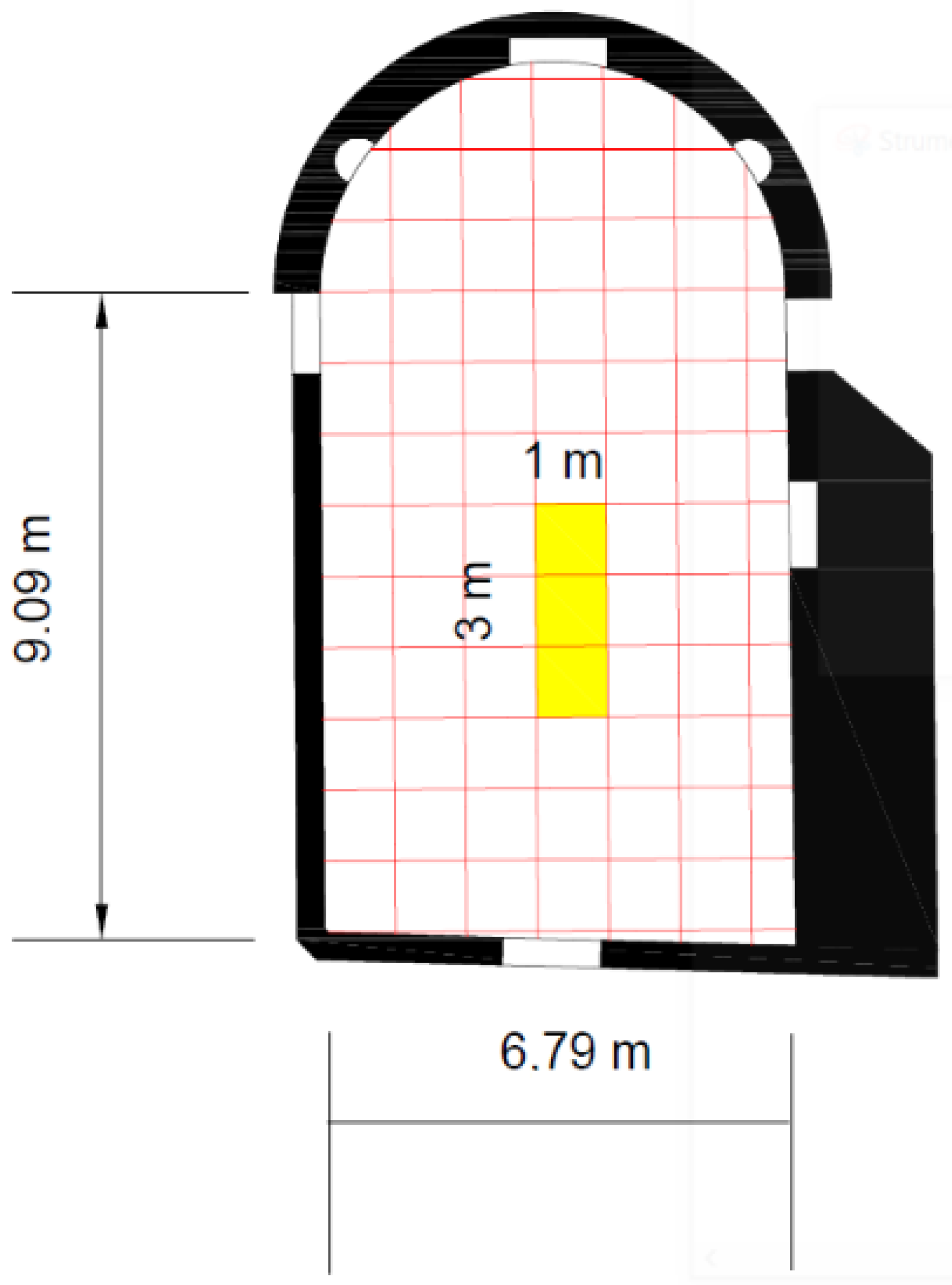
- Single radargram processing along x and representative curve extraction of the identified object;
- Single radargram processing along y and representative curve extraction of the identified object;
- Insertion of curves in 3D space;
- Creation of an interpolation surface of the different curves;
- Creation of an STL file.
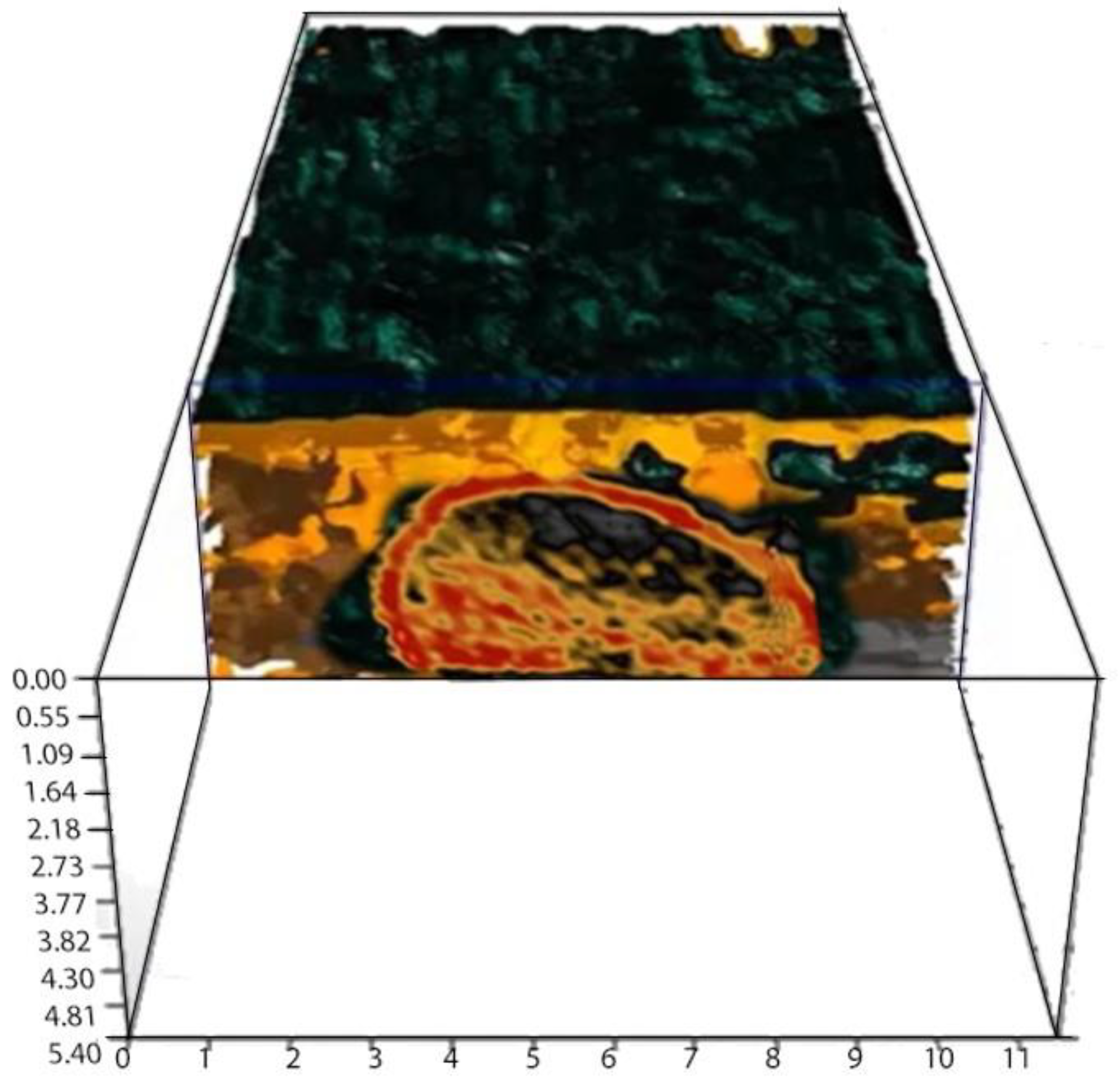
- Extraction of the most important complex signal attributes;
- Two-dimensional elaboration in the different directions of the areas of interest;
- Choice of threshold value;
- Three-dimensional rendering of the alleged target.
2.2. 3D Merge
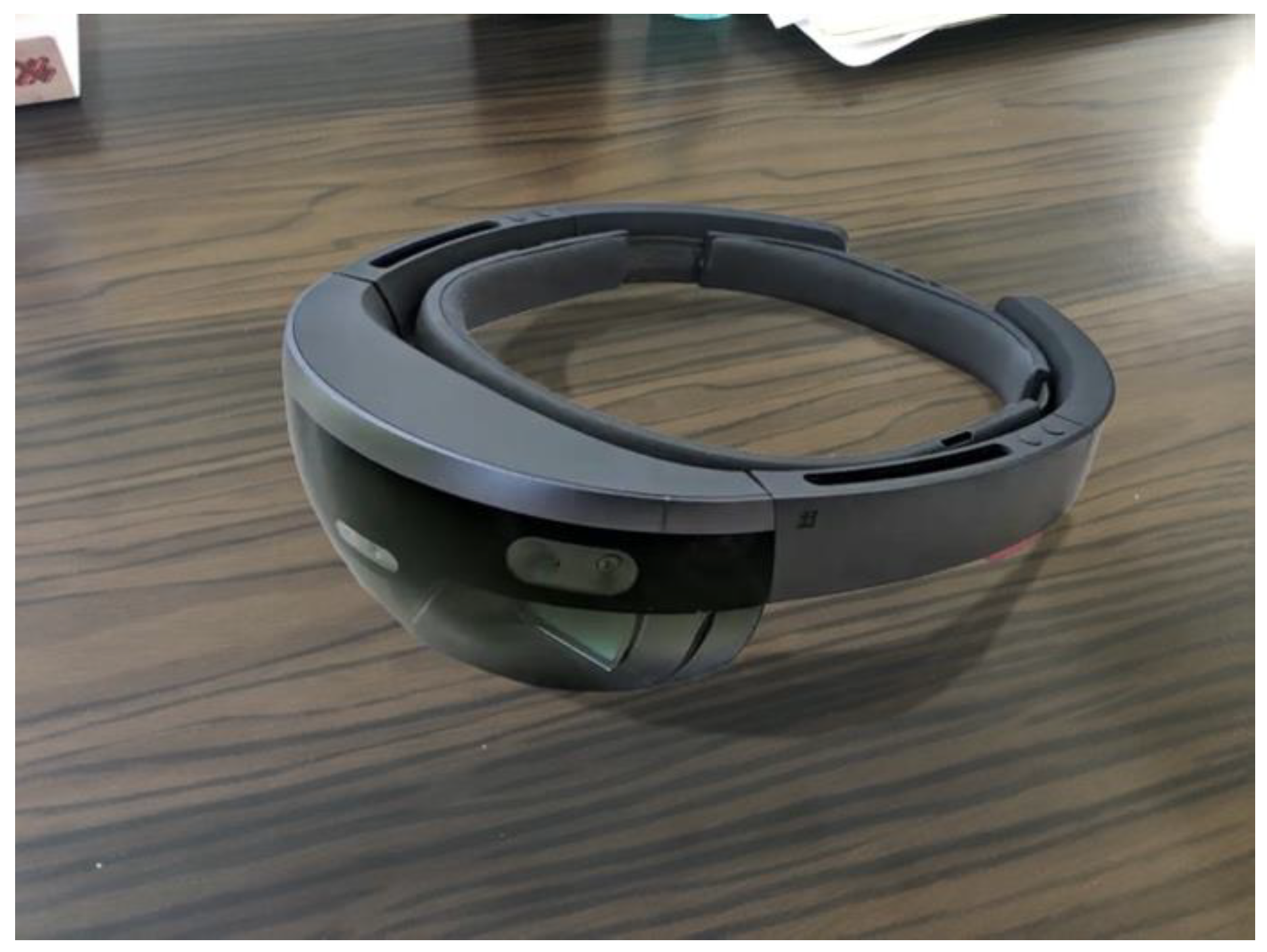
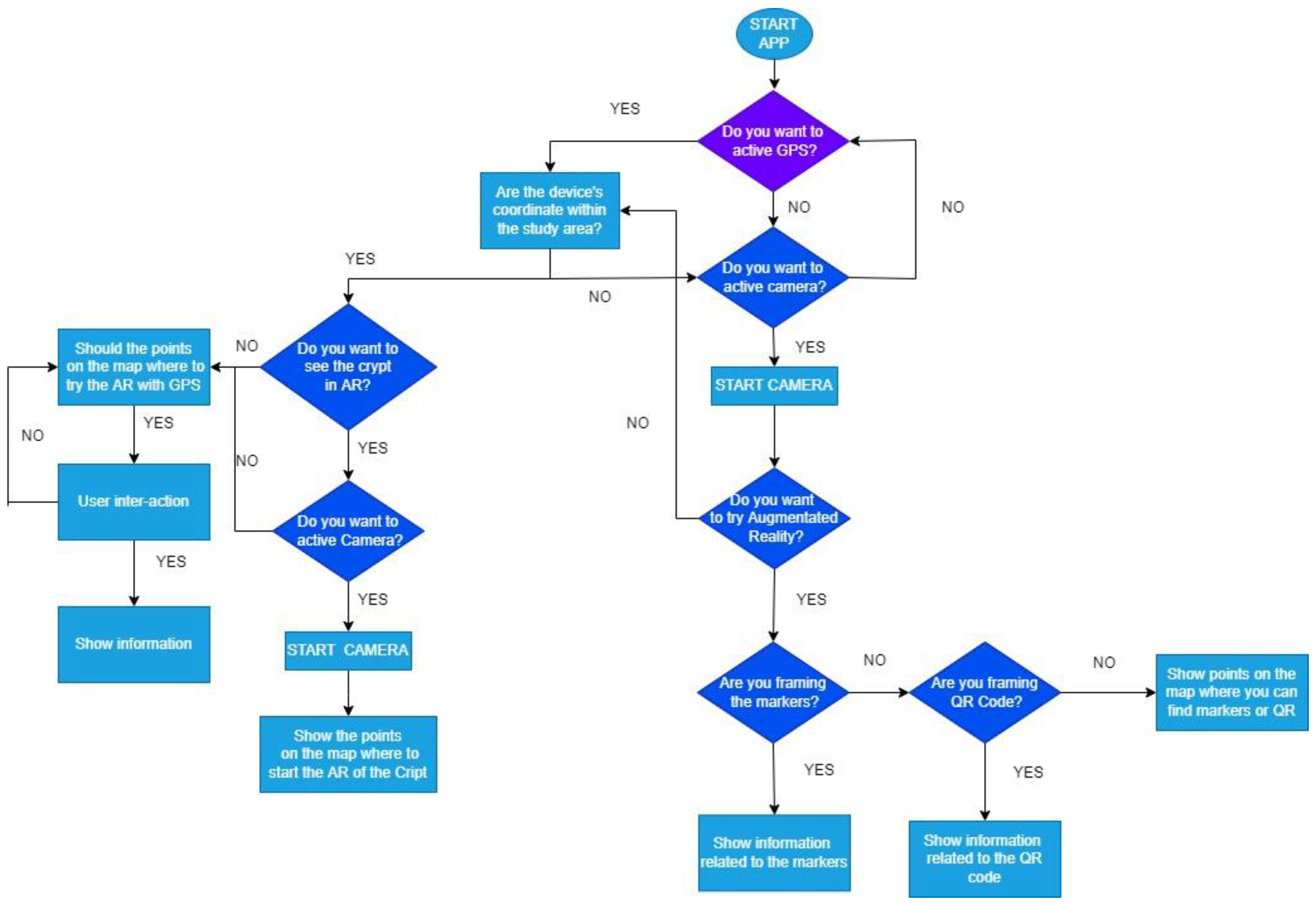
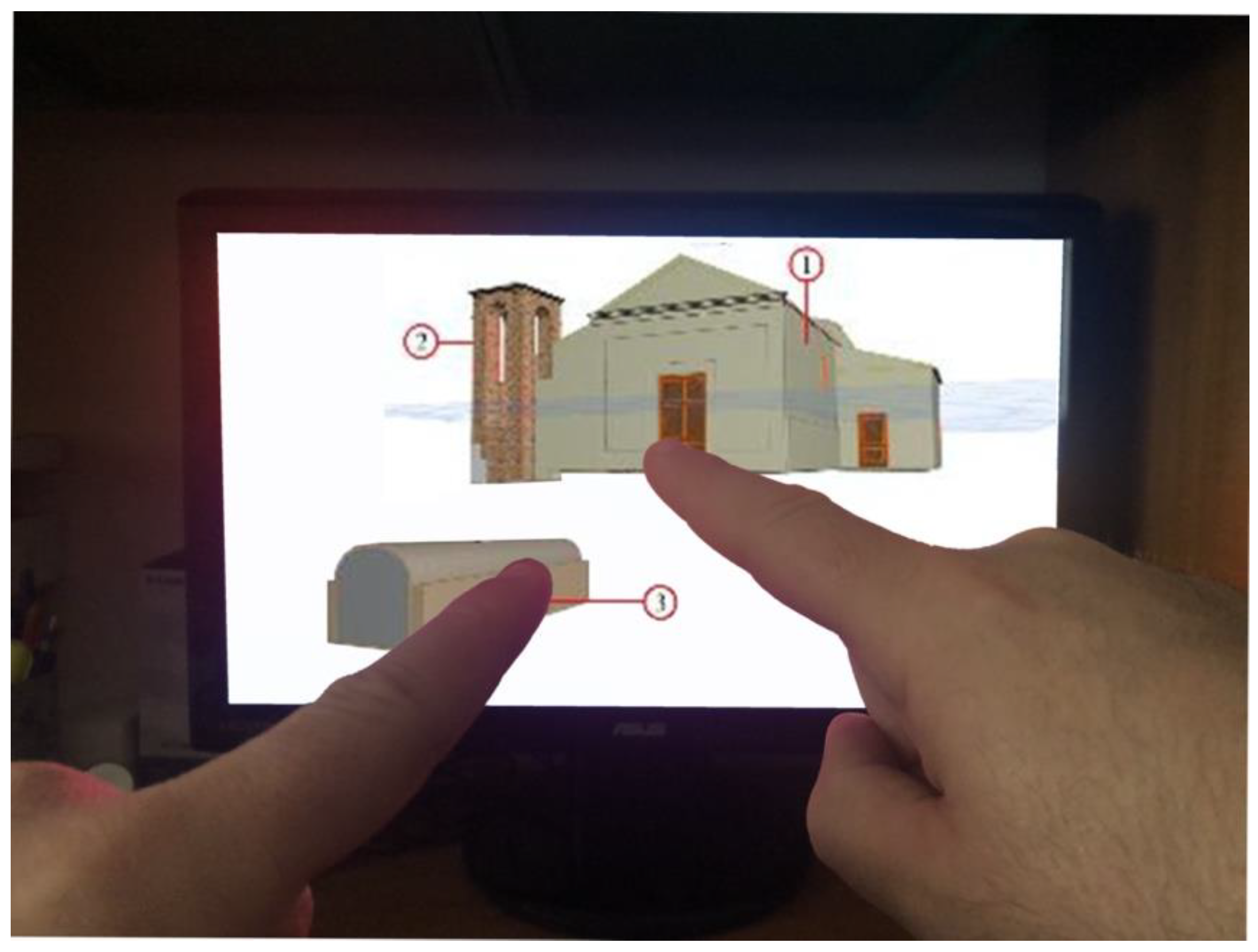
3. The Developed App
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akca, D.; Gruen, A. Generalized Least Squares Multiple 3D Surface Matching; ISPRS WS Laser Scanning [cd rom]; Part 3/W52; IAPRS: Espoo, Finland, 2007; Volume 36, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadabadian, A.H.; Robson, S.; Boehm, J.; Shortis, M.; Wenzel, K.; Fritsch, D. A comparison of dense matching algorithms for scaled surface reconstruction using stereo camera rigs. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 78, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltsavias, E.; Gruen, A.; Zhang, L.; Waser, L.T. High-quality image matching and automated generation of 3D tree models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzetti, L.; Remondino, F.; Scaioni, M. Orientation and 3D modelling from markerless terrestrial images: Combining accuracy with automation. Photogramm. Rec. 2010, 25, 356–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.; Furini, A.; Russo, V.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Russo, P. Accuracy of cultural heritage 3D models by RPAS and terrestrial photogrammetry, The International Archives of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 5, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Büyüksalih, G.; Li, Z. Practical experiences with automatic aerial triangulation using different software packages. Photogramm. Rec. 2005, 18, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Balletti, C.; Beltrame, C.; Guerra, F.; Vernier, P. Digital Survey Techniques for the Documentation of Wooden Shipwrecks. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuca, B.; Brumana, R.; Scaioni, M.; Oreni, D. Spatial data management of temporal map series for cultural and environmental heritage. Int. J. Spat. Data Infrastruct. Res. 2011, 6, 97–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Scovanner, P.; Shah, M. A 3-Dimensional SIFT descriptor and its application to action recognition. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Multimedia, Augsburg, Germany, 25–29 September 2007; pp. 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltner, A.; Schneider, D. Analysis of Different Methods for 3D Reconstruction of Natural Surfaces from Parallel—Axes UAV Images. Photogramm. Rec. 2015, 30, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonstad, M.A.; Dietrich, J.F.; Courville, B.C.; Jensen, J.L.; Carbonneau, P.E. Topographic structure from motion: A new development in Photogrammetric measurement. Eart. Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinzato, E.; Bressan, C.; Marinetti, S.; Bison, P.G.; Bonacina, C. Monitoring of the Scrovegni Chapel by IR thermography: Giotto at infrared. Elsevier Sci. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2002, 43, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haala, N.; Hastedt, H.; Wolf, K.; Ressl, C.; Baltrusch, S. Digital photogrammetric camera evaluation, generation of digital elevation models. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2010, 2, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heipke, C. Automation of interior, relative, and absolute orientation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1997, 52, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, M.; Kassera, M. Implementation of a low-cost photogrammetric methodology for 3D modelling of ceramic fragments. In Proceedings of the XXI International CIPA Symposium, Athens, Greece, 1–6 October 2004. ISSN 16821750. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, K. Photogrammetry–Geometry from Images and Laser Scans; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo, J.A.B.; Torres da Motta, J.M.S. Registro e alinhamento de imagens de profundidade obtidas com digitalizador para o modelamento de objetos com análise experimental do algoritmo ICP. ABCM Symp. Ser. Mechatron. 2014, 6, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Khalloufi, H.; Azough, A.; Ennahnahi, N.; Kaghat, F.Z. Low-cost terrestrial photogrammetry for 3d modeling of historic sites: A case study of the marinids’ royal necropolis city of fez, Morocco. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2020, 20, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzopoulos, J.N.; Stefanakis, D.; Georgopoulos, A.; Tapinaki, S.; Pantelis, V.; Liritzis, I. Use of various surveying technologies to 3d digital mapping and modelling of cultural heritage structures for maintenance and restoration purposes: The tholos in delphi, Greece. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2017, 17, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollefeys, M.; Van Gool, L.; Vergauwen, M.; Cornelis, K.; Verbiest, F.; Tops, J. Image-based 3D acquisition of archaeological heritage and applications. In Proceedings of the 2001 Conference on Virtual Reality, Archeology, and Cultural Heritage, Glyfada, Greece, 28–30 November 2001; pp. 255–262, ISBN 1581134479. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzoli, A.; Mussio, L. Quickly solutions particularly in close range photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 34, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Remondino, F.; Menna, F. Image-based surface measurement for close-range heritage documentation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaudo, F.; Bornaz, L.; Ardissone, P. 3D high accuracy survey and modelling for Cultural Heritage Documentation and Restoration. In Proceedings of the Vast 2007–Future Technologies to Empower Heritage Professionals, Brighton, UK, 26–29 November 2007; Archaeolingua: Budapest, Hungary, 2007; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rusinkiewicz, S.; Levoy, M. Efficient Variants of the ICP Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on 3D Digital Imaging and Modeling, Quebec City, QU, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Barrile, V.; Fotia, A.; Candela, G.; Bernardo, E. Geomatics techniques for cultural heritage dissemination in augmented reality: Bronzi di riace case study. Heritage 2019, 2, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrile, V.; Bernardo, E.; Bilotta, G. An experimental HBIM processing: Innovative tool for 3D model reconstruction of morpho-typological phases for the cultural heritage. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrile, V.; Fotia, A.; Bernardo, E.; Candela, G. Geomatics techniques for submerged heritage: A mobile app for tourism. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2020, 16, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrile, V.; Fotia, A.; Ponterio, R.; Mollica Nardo, V.; Giuffrida, D.; Mastelloni, M.A. A combined study of art works preserved in the archaeological museums: 3D survey, spectroscopic approach and augmented reality. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrile, V.; Bernardo, E.; Bilotta, G.; Fotia, A. Bronzi di Riace Geomatics Techniques in Augmented Reality for Cultural Heritage Dissemination. In Geomatics and Geospatial Technologies; ASITA 2021, Communications in Computer and Information Science; Borgogno-Mondino, E., Zamperlin, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1507, pp. 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrile, V.; Fotia, A. A proposal of a 3D segmentation tool for HBIM management. Appl. Geomat. 2022, 14, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarros, D.; Stamatopoulos, M.I.; Anagnostopoulos, C.N. Information technology and archaeological excavations: A brief overview. Sci. Cult. 2022, 8, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, E.; Lampropoulos, K.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Moropoulou, A. Deep Learning approach for the identification of structural layers in historic monuments from ground penetrating radar images. Sci. Cult. 2022, 8, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liritzis, I.; Laskaris, N.; Vafiadou, A.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Volonakis, P.; Papageorgopoulou, C.; Bratitsi, M. Archaeometry: An overview. Sci. Cult. 2020, 6, 49–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
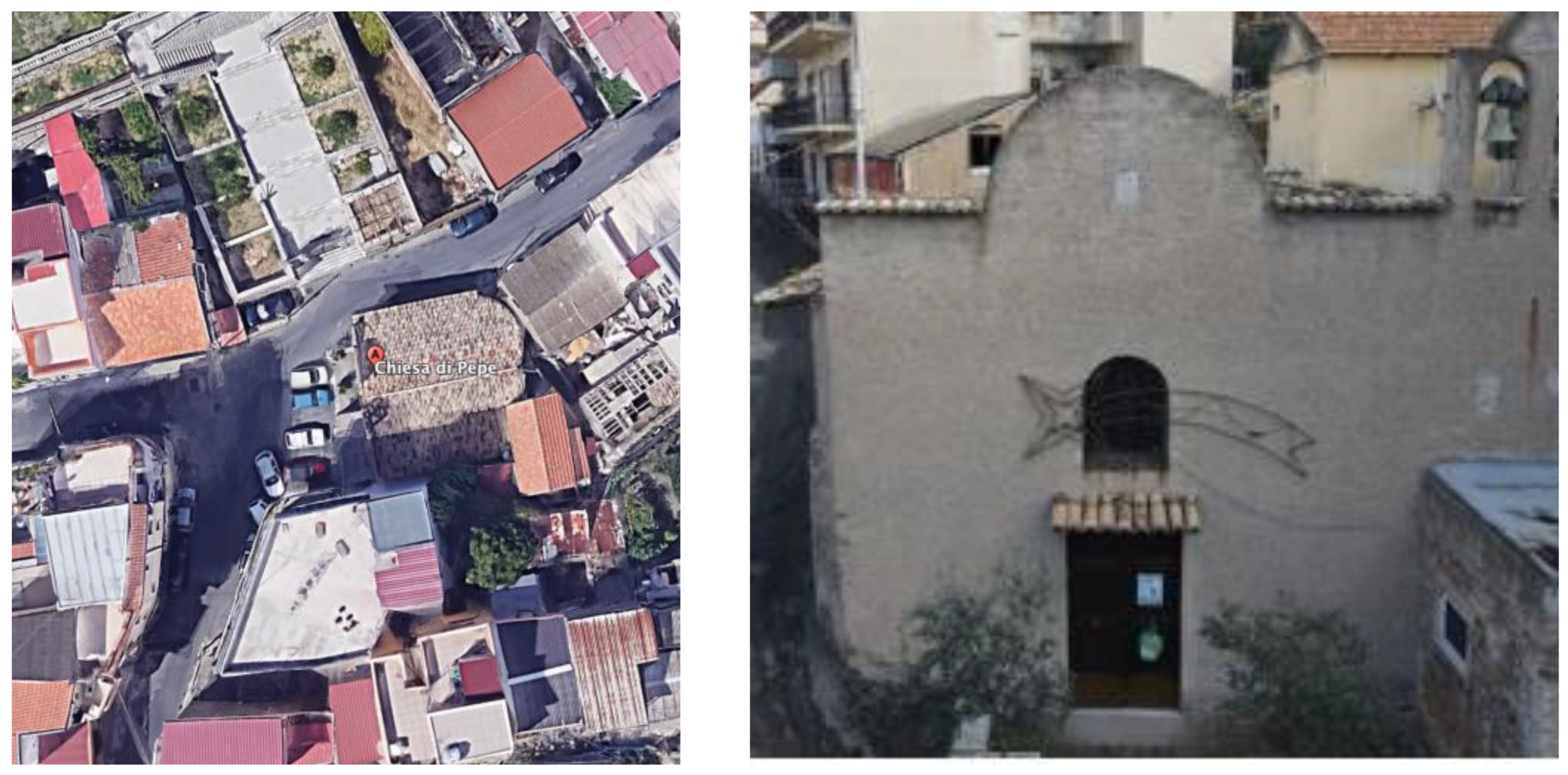
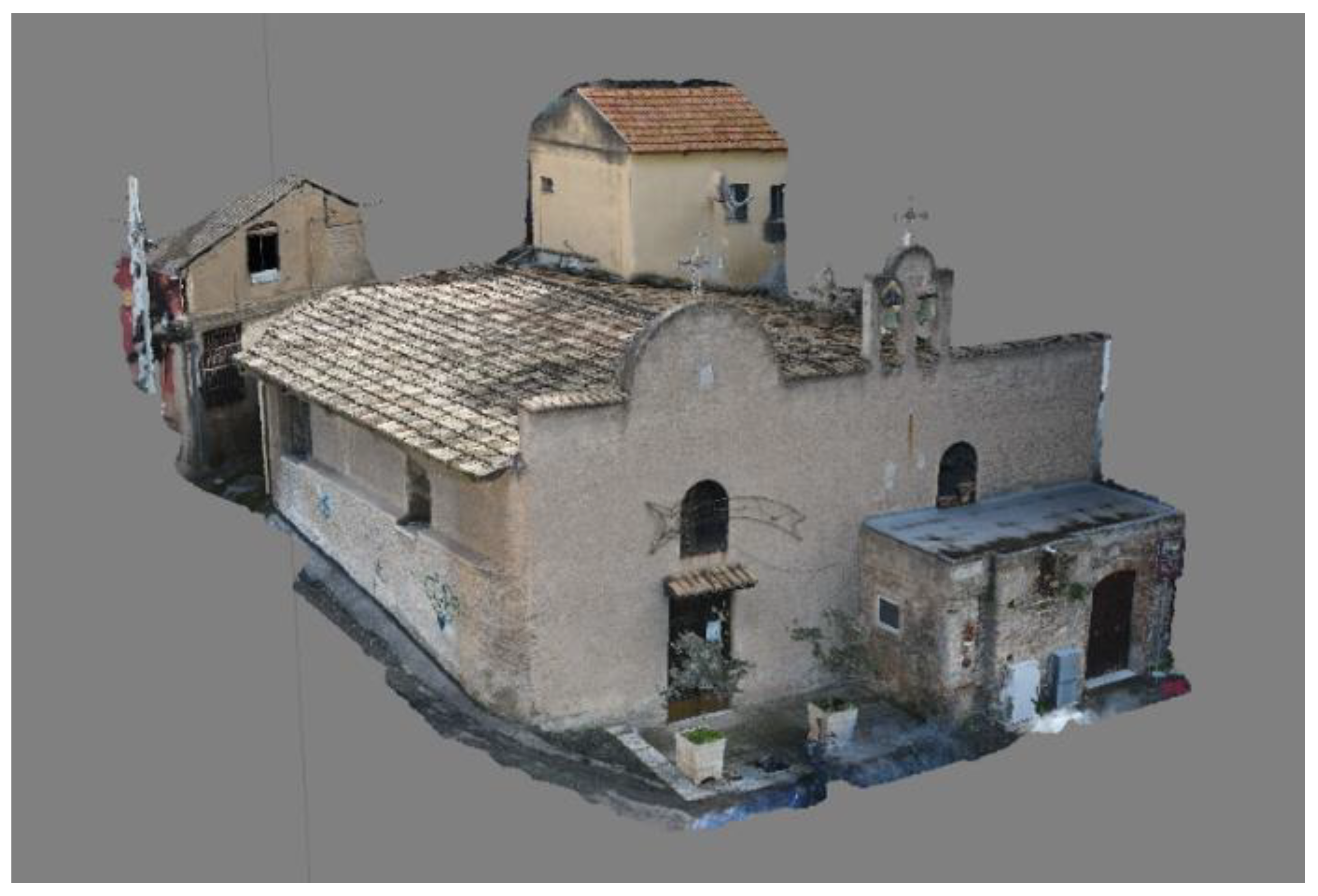
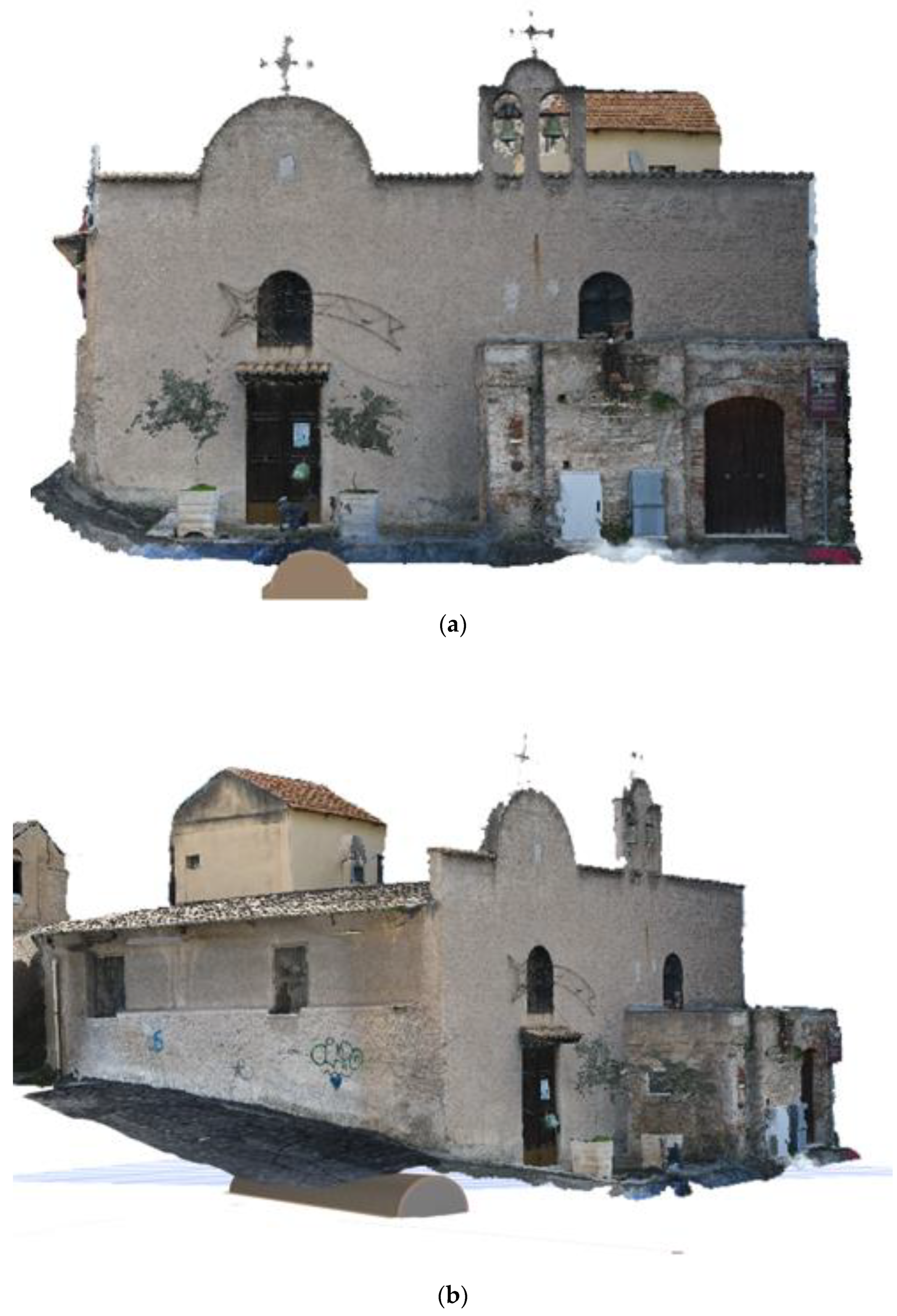
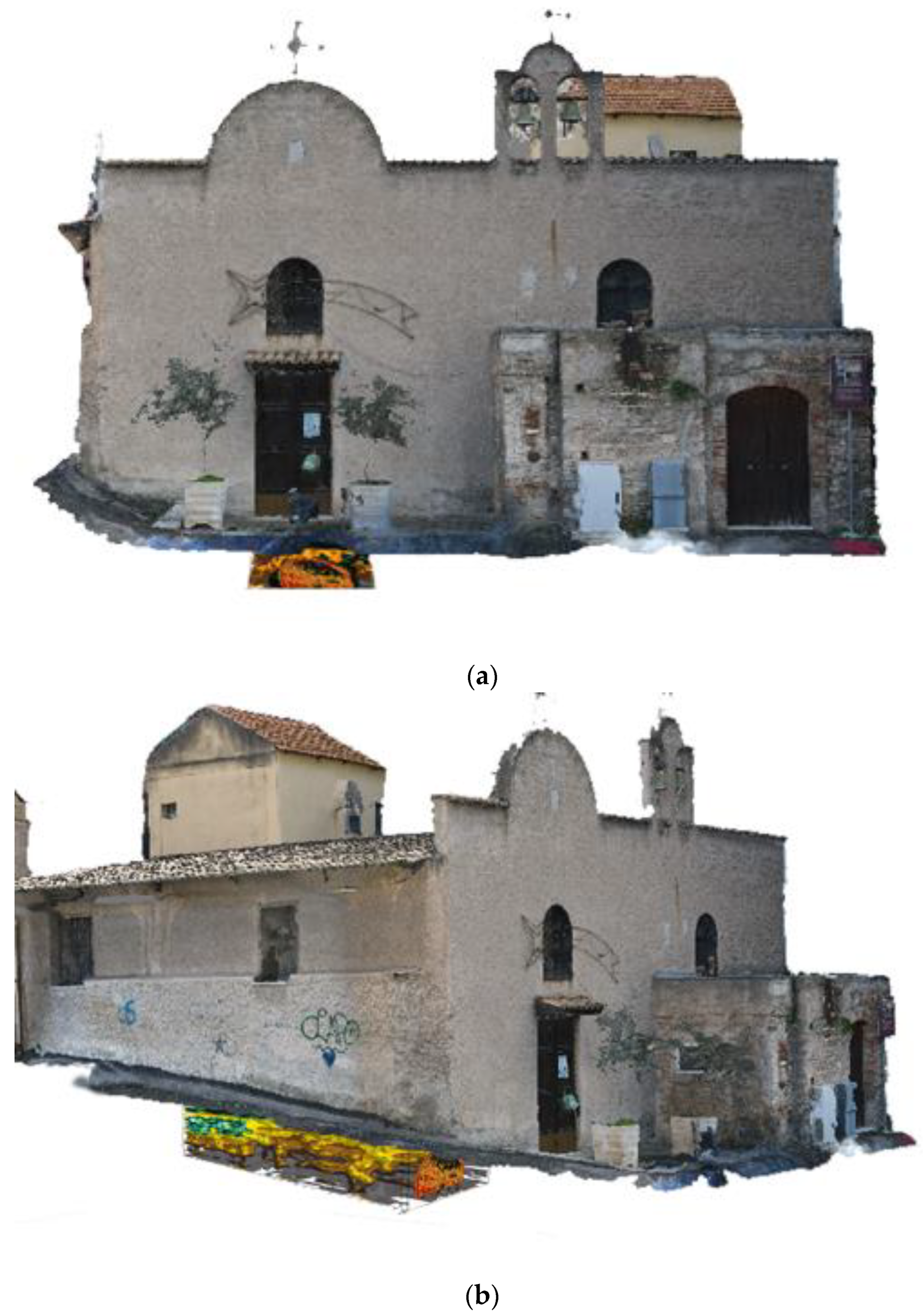
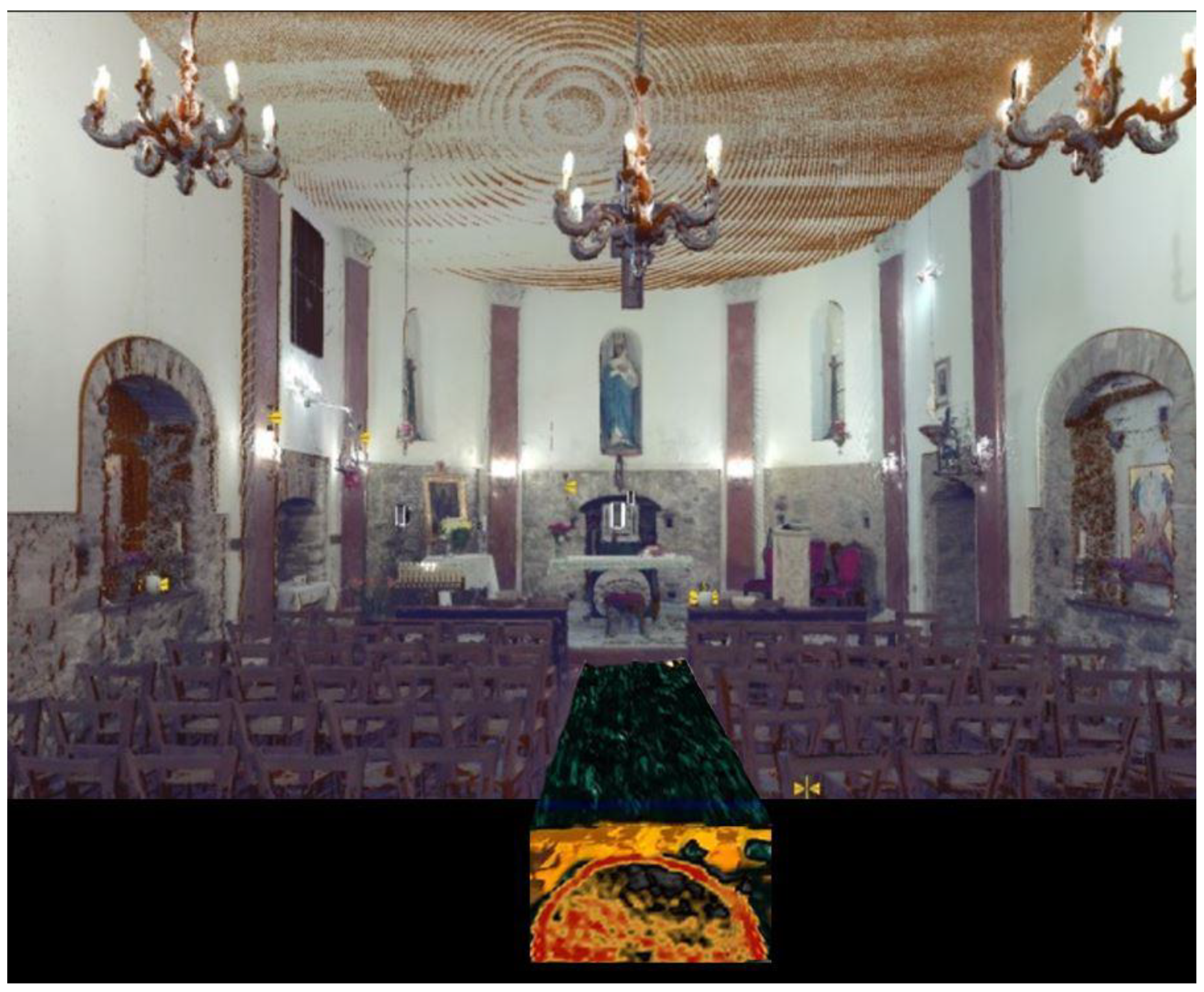






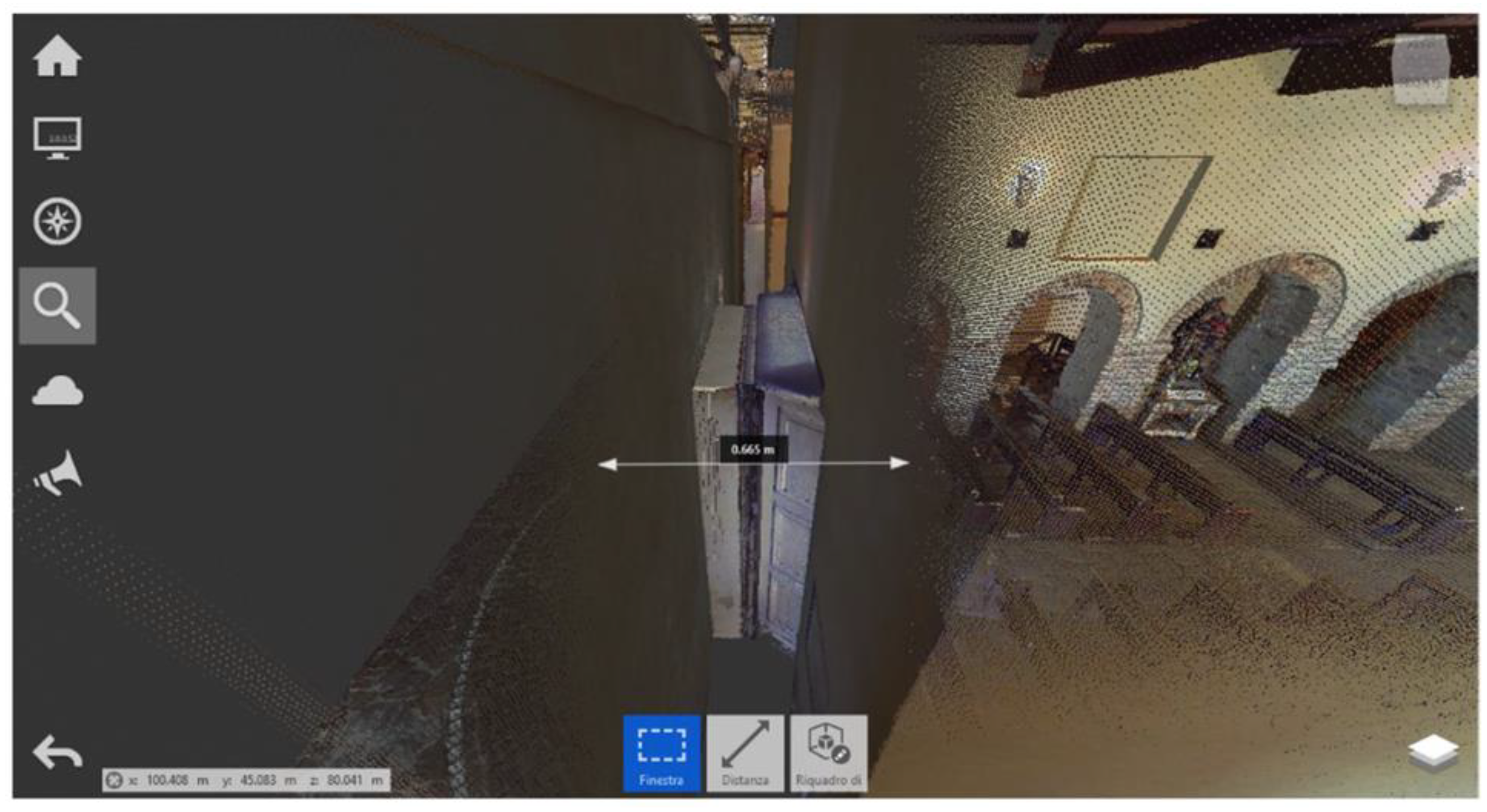






| Element | Real Measurement | Photogrammetry 3D Model Measurement | TLS 3D Model Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| External door 1 width | 84 | 85.2 | 84 |
| External door 1 height (z) | 240 | 240.9 | 240.5 |
| Window | 60 | 60.4 | 60 |
| Window height | 60 | 61 | 62 |
| Stlwrite (FILE, FACES, VERTICES) | Takes Faces and Vertices Separately, Rather Than in an FV Structure |
|---|---|
| stlwrite (FILE, X, Y, Z) | Creates an STL file from surface data in X, Y and Z |
| stlwrite | Triangulates these gridded data into a triangulated surface using triangulation options, as specified below. X, Y and Z can be two-dimensional arrays with the same size. If X and Y are vectors with a length equal to SIZE(Z,2) and SIZE(Z,1), respectively, they are passed through MESHGRID to create gridded data. If X or Y are scalar values, they are used to specify the X and Y spacing between grid points. |
| Stlwrite (..., ’PropertyName’, VALUE, ’PropetyName’, VALUE,...) | Writes an STL file using the following property values:
|
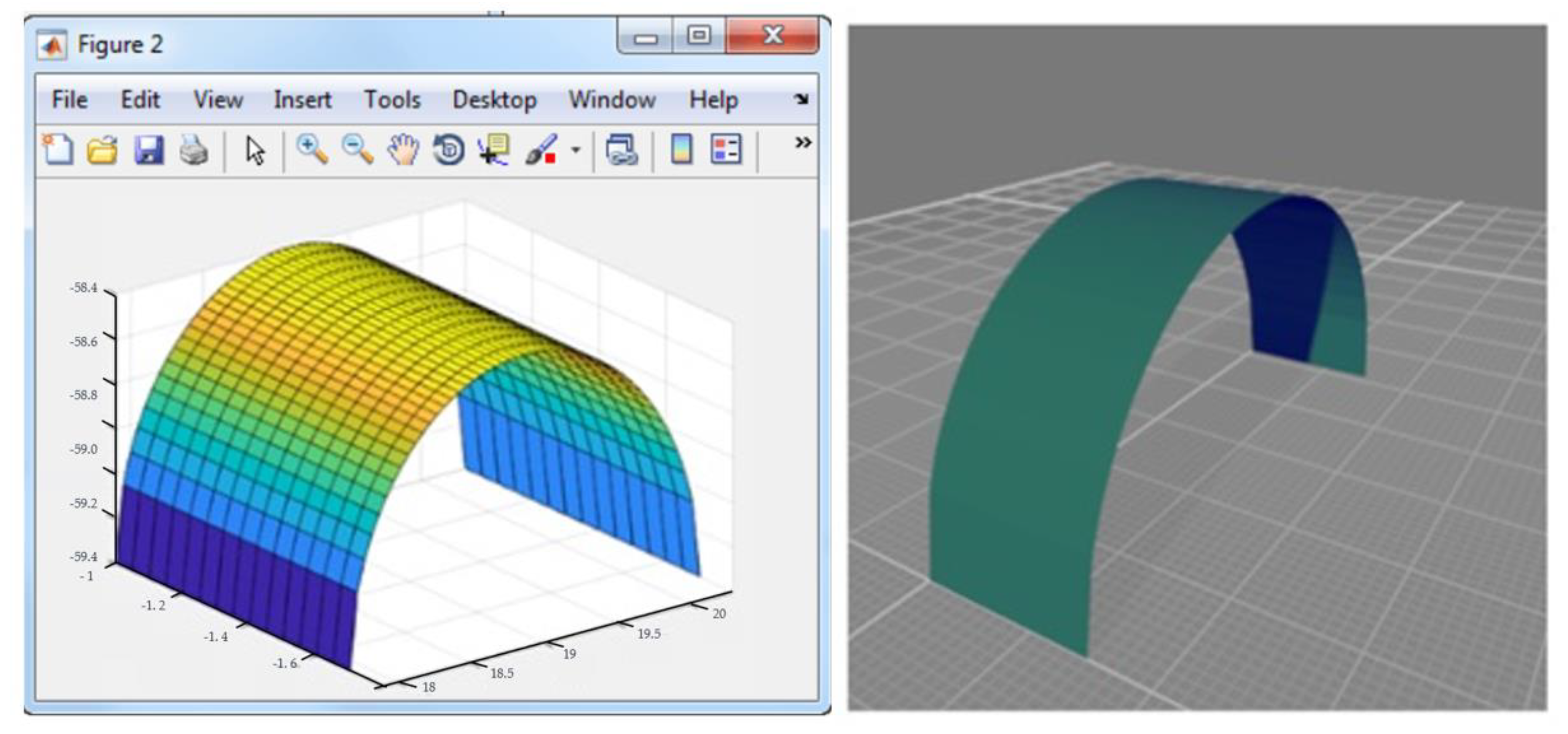
| - To draw the surface, we used “mesh” and “surf” instructions. |
| - By first constructing matrices for node coordinates on which to evaluate the function z = f(x,y) on the rectangle [a,b] × [c,d], we obtained: >> [x,y] = meshgrid(a:stepx:b,c:stepy:d) (it builds the matrices x and y, where x is equal to [a:stepx:b] and y is equal to [c:stepy:d]). |
| - Then, the heights matrix z_ij = f(x_i,y_j) was calculated. >> z = f(x,y); |
| - For the 3D-perspective plot of the Z values, we used the mesh command. >> mesh (x,y,z) |
| - To see the surface from another angle, we used the function >> view (angle, elevation), where angle represents the angle between the y-axis and the point of view measured on the x–y coordinate plane, and elevation is the angle between the x–y coordinate plane and the point of view). |
| - To interactively rotate the surface on the current window using the mouse, we used “rotate3d on” command (Sigurdsson and Overgaard, 1998). |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrile, V.; Bernardo, E.; Fotia, A.; Bilotta, G. Integration of Laser Scanner, Ground-Penetrating Radar, 3D Models and Mixed Reality for Artistic, Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Dissemination. Heritage 2022, 5, 1529-1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030080
Barrile V, Bernardo E, Fotia A, Bilotta G. Integration of Laser Scanner, Ground-Penetrating Radar, 3D Models and Mixed Reality for Artistic, Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Dissemination. Heritage. 2022; 5(3):1529-1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030080
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrile, Vincenzo, Ernesto Bernardo, Antonino Fotia, and Giuliana Bilotta. 2022. "Integration of Laser Scanner, Ground-Penetrating Radar, 3D Models and Mixed Reality for Artistic, Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Dissemination" Heritage 5, no. 3: 1529-1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030080
APA StyleBarrile, V., Bernardo, E., Fotia, A., & Bilotta, G. (2022). Integration of Laser Scanner, Ground-Penetrating Radar, 3D Models and Mixed Reality for Artistic, Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Dissemination. Heritage, 5(3), 1529-1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030080









