Abstract
The technological advancement of software and hardware and the lowering of the prices of instrumentation has made photogrammetry the preferred instrument for surveying activities in archaeological projects. Consequently, archaeological datasets have been enriched with 3D models of archaeological finds and structures. Each project has developed its work pipeline for raw data acquisition and the elaboration of models and their archiving and dissemination. In most cases, the pipeline is the result of empirical experimentation and is designed to act within the specific context of the project. To date, we still lack a shared method for a photogrammetric survey that derives from the specific design and techniques/contexts. This paper aims at proposing an approach for a shared 3D survey workflow for photogrammetry in archaeology. The general approach relies on the digital data curation framework for cultural heritage and encompasses several specialized tasks. We describe the general functions and processes and how they can be implemented in a practical workflow. As a proof of concept, we show how a preliminary release of the workflow has been applied in the context of the BeArchaeo project, for the acquisition, processing, export, modeling, archiving, and indexing of 3D models, resulting from photogrammetric surveys. A long-term aim is a methodological approach for different endeavors of cultural heritage.
1. Introduction
The objective of this contribution is the presentation of an acquisition methodology in the field of cultural heritage that is independent of the use of specific tools or software and compliant with the methods adopted by researchers in humanities and computer science. Over the last few years, numerous approaches have been based on the use of photogrammetry for the acquisition of artifacts and architectural structures both with field applications, as in the case of Catalhoyuk [1], and through the use of drones for overall environmental acquisitions [2]. The photogrammetric technique is also used in similar fields, such as paleontology [3] or geoarchaeology [4]. What is observed is the creation of operational structures and acquisition paths that are limited by a “contextual dependence”, that is, the specific cases for which they were created, i.e., the underlying method relies on the technical tool in use and deploys operational workflows according to the following pipeline: the definition of the tools->preparation of the set->creation of different scenarios->processing of the photos [5]. Although there is a basis to the methodology adopted, it focuses exclusively on the elements of the physical characteristics of the system, such as the management of the lights, the morphological characteristics, and the hardware and software tools to be used [6]
Looking for a repeatable and methodologically corroborated acquisition protocol is a pressing necessity, because of the interoperability of models and the exchange of good practices [7]. Here, we focus on the archaeological context, where photogrammetric acquisition has become of paramount importance. The punctual collection of diverse nature data (such as plans, representation of the found artifacts, stratigraphic sections, excavation diaries, layer files, and technical drawings) is intrinsic to the destructive character of the archaeological excavation. For this reason, with the diffusion of low cost and rapid digital acquisition techniques, the archaeological world immediately took advantage of the potential of the new instrument [8]. Its use impacts every aspect of the multiform typologies of needs expressed by archaeological research both in the relationship between landscape and findings [9] as well as in the support of restoration and conservation activities [10]. However, while in the literature it is possible to trace numerous projects that rely on this technique, there exist very few designs of usage protocols [11]. This descriptive ambiguity derives from the history of the technique, which has exploded in recent years, with behaviors that have adapted to technological development. Paradoxically, the definition of a photogrammetric methodology received more attention in the early stages of this technological revolution when the limits of software and hardware pushed for a collection of photos and reasoned processing of data [12] (also in an attempt to differentiate photogrammetry from laser scanning [13]). This could be defined as methodological anarchy, which mostly manifests itself in a practice that prevents easy communication between different projects (lack of interoperability) and is one of the main concerns of the research field today [14], and many reports and proposals of opted-in standards have been produced in an attempt to establish a European standard [15].
The absence of a shared protocol, in the face of the numerous advantages, leads to the emergence of numerous problems, such as non-traceability, obsolescence [16], data cataloging, and interdisciplinary terminology [17]. In fact, the use of software-specific methodologies makes approaches non-transferrable to other projects (lack of interoperability), generating data transfer problems. These problems, exposed in detail below, can also intertwine with each other, giving rise to complex second-level problems, which, ultimately, can all be traced back to the unique and specific nature that sees the birth of projects in the design contexts of reference [18]. For example, this individualism causes the decay of performances because of the obsolescence of the coding formats, the difficulty of humanities scholars in compiling datasets provided to them by academics from the digital sciences, and the lack of shared digital and methodological protocols for archiving 3D models [19].
The solutions proposed so far have partially focused on the problems that arise from the production of a large number of data, pursuing an intra-disciplinary attitude and centering on certain participating actors or the use of specific software and hardware tools [20]. Even in cases where the methodology is well-defined and comprehensive there is always a strict focus on a specific project and specific development tools [21].
This paper presents an interdisciplinary approach, born from the reflection of the management of cultural heritage digital data, named digital data curation (DDC) [22]. This working hypothesis stems from the shared assumption, as is expressed by the DDC, that data are living entities which change over time, have to be adapted to the context, and, above all, can support the creation of new data when combined with other projects [23]. Since its inception, digital data curation has faced the problem of managing and storing digital data in the long term, from the planning of data acquisition through their creation or reception from external sources to the detailed optimization of digitization practices [24]. We propose the deployment of operational modules defined by the DDC framework for the specific case of photogrammetric acquisition, respecting the assumptions of abstraction to implement interoperability, tracing, and data cataloging.
So, the aim of this article is the definition of a photogrammetric acquisition methodology that is clear and usable for archaeologists in the context of research projects and consistent with DDC framework abstractions.
2. Common Problems Features and the Necessity of Abstraction
There are several inconveniences in carrying out photogrammetry projects without a shared protocol. In this section, we investigate some common problems and show their close interrelationships.
2.1. Classification Types: The Absence of Standards
Data classification concerns the methods used for indexing the digital data that result from a photogrammetric acquisition and the consequent elaboration. The lack of a unified standard from the projects makes inter-communication hard, without considering that the end of a project often represents the loss of the interpretation keys of the classifications. Since attempts at the standardization of the classifications are under debate, we focus on the standardization of the classifications of the elements that produce the metadata (in this case, photographs, point clouds, and 3D models). This problem takes on new applicative aspects when the emphasis is placed on the interdisciplinary nature of a project, which is the case of digital projects involving cultural heritage. Photogrammetry is no exception. Archaeology faces a particular challenge with classification since it involves diverse research interests and record-keeping systems that frequently draw from, or intersect with, other academic fields beyond archaeology. This is partly because archaeological projects tend to be “itinerant,” covering several domains and constantly evolving as research progresses (with the need to use data from different datasets) or short-term collected materials [25]. Added to this is the regulatory issue that although digital recording (often alongside paper recording) is ubiquitous in the discipline, current regulatory practices do not necessarily promote the retention, re-use, or understanding of data, as observed by Huggett when, analyzing the impact of big data in archaeological practice, he speaks of a third revolution in archeology which is not yet able to interpolate the previous techniques of annotation and data collection of a digital nature with the new tools available [26]. Classification in archaeology raises various issues, such as characterizing typologies and arranging artifacts to gain insights into past cultures [27]. A rigorous, consistent, and replicable classification method replaces heterogeneous artifacts with internally homogeneous data classes. This method reflects cultural concepts and ideas implemented by artisans and is analyzed using methods sensitive to the material form of cultural ideas [28].
2.2. Obsolescence
Another problem that has emerged from the use of new technologies in the field of cultural heritage and, in particular, in archeology, is obsolescence, i.e., the progressive aging of machines and software. Obsolescence makes projects unreachable after a short time and irremediably lost after replacements in hardware, software, or in the IT approach. One relevant example of this type is the Electronic Domesday Book, a project initiated by the BBC to celebrate the 900th anniversary of King William’s original inventory of post-conquest Britain. In this specific case, the problems concerned the publication of the project on video discs that could only be read using a specific proprietary player—a software designed for personal computers, BBC Master, adopted at the time by the majority of schools and libraries in the United Kingdom and now hopelessly obsolete [29]. The project, which cost 2.5 million pounds, aimed to establish universally applicable standards and anticipate future technological advancements. However, the long-term forecast proved inaccurate, and the project’s use was limited due to the obsolescence of the interface devices employed [30]. As early as 2013, Italian researchers sought to address device obsolescence by creating a path to insert photogrammetric surveys of selected artifacts from the excavation of Pyrgos Mavroraki in Cyprus into a virtual museum. The surveys were isolated from other 3D elements to recognize their unique nature and the modeling and processing that generated them [31]. What must be taken into consideration is that a three-dimensional model of an archaeological find is substantially different from any other three-dimensional model both from a computer graphics point of view and from its generative path that inextricably links it to the photographs that generated it in a relationship of mutual dependence and validation. Despite numerous attempts to address obsolescence in digital technologies, it is evident that a focus on adaptable methodologies is more effective than software-based approaches. Abstract methodologies are better equipped to adapt to technological advancements, whereas software-based solutions inevitably face obsolescence issues.
2.3. Interdisciplinarity
Interdisciplinarity introduces a linguistic, terminological, and methodological gap between the parties involved (digital sciences and humanities but also archaeometric disciplines), leading to misunderstandings or loss of information. Interdisciplinary research faces not only institutional obstacles but also cognitive constraints and conceptual barriers that limit collaboration across disciplinary boundaries. Lessons from cognitive science and the studies of scientific practices highlight the importance of domain specificity in science, and philosophers of science play a crucial role in understanding and addressing these barriers. Case studies of collaborations between ecologists and economists and between molecular biologists and systems biologists illustrate the cognitive barriers that hinder interdisciplinary work [32]. This issue has become so central as to push scholars to attempt to formalize a language of communication for “changing knowledge and disciplinary boundaries through integrative research methods in the social sciences and humanities”, as established by the STERP project within the Bologna agreements of the 1999 and later described by Ruth Keeling [33]. The identification of communication methods that will be fungible and clear for all the professionals involved from different research fields is not only necessary for correct communication between the parties but also to guarantee the legitimization of the research for the scholars who will verify it. Krebs et al., analyzing the difficulties in interdisciplinary communication, have emphasized the need to identify “quantitative approaches” towards a “scientification of knowledge production” to create a common ground of exchange that does not limit the intrinsic nature of the respective research subjects [34]. Efforts to increase communicability between different domains have in the past caused tension precisely in the attempt to guarantee this legitimacy. On the one hand, the human sciences are considered, in the context of research, to be defined as more reflexive (the concept of reflexivity can be summarized as the tendency to refer internally to the research itself, as opposed to the connection with external elements, characteristic instead of the natural sciences) [35]. On the other hand, however, this has also provoked criticisms of those who observe a dominance of the natural sciences, which push the human sciences to use their methods and languages in an attempt to legitimize themselves [36] or proceeding through some empirical utility testing case by case [37]. What emerges is a need for an upstream adoption of a method that is shared by the entire research community, regardless of individual research areas [38,39]. The idea of abstraction can be useful in indicating formats that are then specialized into different disciplines while keeping a shared core representation.
2.4. Traceability: Relations and Legitimacy Features
Finally, traceability, with particular attention to archaeological data, refers to the necessity of accessibility to the history of the data processes. Since the circulation of the excavation results often takes decades, to which is added the non-compliance of the data released for digital processing, also requiring the entry and adaptation of large and expensive data [40]. Within this process that mixes subjectivity and objectivity, accuracy is measured in the traceability of each step and the richness of the recorded testimonies, but since archaeological excavation is not repeatable, the recording operations must be as accurate as possible. Scientific replicability in this field is uniquely guaranteed by access to primary data [41]. At present, in the context of archaeological projects, data acquisition phases are not fully recorded and primary data are rarely, if ever, published in full [42]. This statement also concerns the excavation reports, which are rarely integral in the conservation of primary information [43]. If we add to this the presence of multidisciplinary research teams (see also above), we can observe the production of highly differentiated datasets (paper files, digital files, databases, etc.), of which only a small part is formally disseminated [44]. Although we observe an attempt to organize the activity of the archaeological field and the consequent interpretations, according to the processes of what Londoño calls “reflexivity” [45] and their subsequent applications with contexts, such as those of Çatalhöyük [46,47], the practice is still substantially dominated by traditional data logging methodologies, generating a mixture of analog and digital techniques strongly influenced by limitations and subjectivity at each stage, as reported by Roosevelt et al. in 2015 [43]. This lack of traceability of the 3D model production process reduces the possibility of their verifiability by researchers external to the project that produced them, negatively influencing the legitimacy of the 3D models. This problem represents a concrete obstacle to the realization of that coincidence, or at least intrinsic dependence, between cultural heritage and its digital representation, as indicated by the 1989 UNESCO convention [48] and restated in 2009 [49]. The abstraction of the method is necessary to ensure that the development of the photo-detected 3D model generation protocol is traceable, and therefore every result produced can be verified, thus giving legitimacy to the work performed.
The mapping of the problems presented demonstrates the need for a resolution that takes into account these difficulties, aiming at a general approach. In this paper, we envisage a proposal that relies on an encompassing methodology, as already put forward by some works in the literature.
3. Towards an Encompassing Solution: The State of the Art
In recent years, the need to produce an encompassing solution has emerged in several operational pipelines, based on greater abstraction [50].
Remondino and colleagues aimed to identify common patterns in surveying methods across different contexts, with the goal of automating these repetitive tasks. However, they acknowledge that full automation may not currently be feasible [51]. The study addresses traceability and classification but only in a technical context, excluding acquisition stages and interdisciplinary concerns. It focuses on computer science methodology.
De Reu et al. propose a detailed methodology based, however, on a specific software (in this case Agisoft PhotoScan, AgiSoft LLC, 2011b), which focuses on the exclusive context of emergency excavations; moreover, no space is given in this context to a reflection on the fate of 3D models in the subsequent archiving and dissemination phases [52]. The work poses the problem of information classification and was also created as a clear and intelligible operational workflow for cultural heritage scholars. However, the proposal builds its methodology on specific software. There is not even a specific definition of the acquisition method and the fate of the original photographic data being archived.
Deseilligny et al. focus again on the analysis of specific software and develop a path that is, on the one hand, methodologically structured but, on the other hand, does not respond to the needs of the variegated landscape of existing projects that cannot adopt a single tool [53]. The work poses the problem of the need for a punctual acquisition methodology, and it is the only work among those analyzed that addresses the problem of the ultimate fate of the data and metadata in the archiving phase; furthermore, as it does not involve any specific software, it is immune to obsolescence issues. However, the entire method does not go into detail regarding the replicability of the method and is instead closely linked to the specific photographic instrument and does not explain the reasons for the methodological choices made. No indication is given on how to account for the photos underlying the survey.
The work of P. Hallot and M. Gil (2019) poses the problem of the acquisition method and the behavior of the camera, according to a pre-established scheme; however, these observations remain once again limited to a specific field of application and are not placed in a linked relationship with the subsequent stages of data development [54] and other solutions proposed for the photograph acquisition phase remain limited to highly contextual scenarios [55]. In other cases, we observe how instead the search for a shared method focuses on the photo-processing phase. In those cases, research has focused on finding and ranking the best software to use, based on the number of photos required, the image quality, or the algorithm used [56], and the comparison between the different software that perform the processing operations and become the central topic and the procedural pipeline that is built on these comparison considerations [57]. However, by operating in this manner, the 3D model is not managed holistically and the data are not generated with consideration for the project’s overall function. Other projects have instead focused on the subsequent phase in which the 3D model obtained is manipulated and modeled, but even in these cases, rather than proposing an abstract method, in the literature consulted, this phase is also considered to be part of the exclusive remit of the technical, and the focus is on the definition of which software to select [58]. Koutsoudis et al. propose a workflow that, attempting to broaden the spectrum of possibilities, proposes a series of software that can be used but once again does not produce a theory for the final archiving [59]. The final step in which the model is exported from the editing software has also been analyzed, but again, the comparison with the literature places this phase in a purely technical context and the choice of the format is made in this case exclusively taking into account the final needs of the project (such as the preparation for three-dimensional printing [60]). Even where all the necessary steps are considered, as in the case of Ucakar et al. 2022 [61], the resulting pipeline responds to the specific needs of the project presented and does not attempt to make an abstract work for the definition of a general model applicable to different cases.
In general, these project-related approaches do not provide solutions that can be transversal to the needs of archaeological projects, lacking a general solution. We propose the deployment of the methodological workflow from a shared abstraction. Each phase of the digitization process, from the photographic acquisition to the metadata encoding and the consequent dissemination, is properly recorded. We consider the abstraction of the general processes of cultural heritage management by adopting the digital data curation (DDC) framework. The DDC has been developed to implement terminology exchange (overcoming interdisciplinarity barriers), avoid the dependency on specific software or hardware technicalities (addressing the obsolescence failures), and ultimately yield a consistent method of organizing information (shared classification terms).
4. Digital Data Curation as a Theoretical Framework for an Encompassing Method
This section introduce the digital data curation framework. After a historical summary, we address the application of the schema of the photogrammetry process.
4.1. Before Digital Data Curation
Before the advent of digital data curation, attempts to sequence the phases of photogrammetric surveying had been made since the technique’s introduction in the early 2000s [62]. These attempts were particularly prevalent in the archaeological context [63], where photogrammetry’s advantages over analog methods were apparent, and efforts were being made to address associated challenges [64]. Initially, a design was attempted for the cataloging, homologation, and indexing operations of original photographic material and 3D models, without considering the Digital Data Center’s observations. This design had to address the different classification speeds inherent to archaeologists and IT scientists, who are responsible for designing operational workflows and conducting the surveys and subsequent processing, raising classification issues [65,66]. The first solution, therefore, tended to outsource the digital data of the find, placing it back in the debate on the management of additional metadata [67]. In general, in these proposals, one observes a postulation of an ideal working context that does not take into account the horizontal nature in which archaeological projects normally develop. For this reason, proposals aiming at the definition of a complete and comprehensive acquisition work pipeline (such as the inception protocol) depend on the assumption that the entire development path is “supervised” [68]. A more abstract and theoretical approach allows every single party involved in the project to self-determine its position on the pipeline which, referring to the broader definitions of the DDC, does not depend on a “central coordination”.
4.2. Historical Development of DDC
The history of digital curation and the formation of its methodological process are intrinsically linked to the three phases of the Digital Curation Centre. The first phase (2004–2007) focused on the holistic and interdisciplinary transversality of data in order to bring together a research community that is not specific to a single discipline and takes into account a wide range of types of digital data creation methods. The second phase (2007–2010) focused on data care and conservation, developing connection networks between institutes, libraries, and museums for shared and interoperable terminology (e.g., case studies from the Digital Preservation Coalition to the SCARP12 project [69]). The last phase, albeit officially completed in 2016, triggered an abstraction of the processes developed by the individual institutes for the encoding of methods and approaches to be adopted by an international community of professionals. The applications work on data management from the beginning of information collection and ensure effective data validation and active use for the entire lifecycle. Therefore, the major parameters for interpreting the Digital Data Curation universe are interdisciplinary and holistic data representation planned from scratch. Effective methods of data validation, conservation, and access for their active use shared the abstraction of processes, which can be implemented in several ways [70]. To fulfill the purpose of maintaining and preserving and enriching digital data, the DDC and the subsequent reflections of the Digital Curation Center have developed a glossary that defines the lifecycle and curation of digital data, and we refer to this glossary in the exposition of our method. Among these terms, it is necessary to remember some that will be used in the exposition phase of the present method: where the glossary speaks of “Conceptualizing”, it refers to the conception and planning of the digital object, including the data acquisition methods, such as the archiving options. The term “Create” means the production of digital objects and related metadata. The expression “Access and use” refers to the availability of access to digital data; while “Evaluating and selecting” refers to the curation of digital objects as well as the selection of objects that need such attention. The term “Dispose” refers to the disposal of digital objects or parts thereof not included in the previous selection, while the term “Ingest” refers to the transfer of the digital objects to an archive or any other final destination. The “Conservation actions”, as the expression suggests, represents those actions undertaken to guarantee the conservation of the digital object.
4.3. Towards a DDC Scheme for Photogrammetry
Digital data curation refers to the active management and preservation of digital data throughout its lifecycle. The fundamental principles of digital data curation include ensuring the authenticity, integrity, and reliability of the data, as well as its accessibility and usability by future users. The literature recognizes various phases in digital data curation, including the acquisition, appraisal, selection, preservation, maintenance, and dissemination of data. These phases involve a range of activities, such as data identification, documentation, organization, metadata creation, and storage in trusted repositories. The aim of digital data curation is to ensure that valuable digital data is preserved in the long-term and is accessible and usable by future generations of researchers.
Among the objectives of the projects that refer to the observations of the Digital Curation Center, there is not only the schematic systematization of the work phases but also the preservation of the stability of the data by avoiding unwanted transformations to place the active nature of the data at the mercy of the curator [71]. In parallel with the creation of a system of categories aimed at managing and understanding data, digital data curation has set itself the goal of abstracting these concepts to ensure the total transparency of data processing procedures. Transparency is linked to the concept of accessibility (following the principle whereby a structure built on a transparent system produces legible and, therefore, accessible structures) and accessibility is necessary to ensure the scientific validity of the data and the resulting metadata [72]. We can observe that photogrammetric survey projects have already been produced that have taken into account the indications of the Digital Curation Center, such as the work carried out on the Church St. Peter and Paul (Calw, Germany). Although focused exclusively on the conservation and acquisition of archaeological structures in elevation, the project has outlined an acquisition methodology, photogrammetric and via laser scanner, which aims to establish data collection classes to guarantee the conservation of information and its correct curatorship, even if the archaeological asset is ruined or lost [73]. The BeArchaeo project aimed to address the issue of active data management in data archiving by considering the principles of digital data curation. The project aimed to ensure reproducibility, reuse, and proper conservation of data, which would facilitate the generation of new data from existing research. To achieve this, the project implemented institutionalized workflows and utilized IT resources to index information accurately. These precautions are necessary because, in the specific field of archeology, the data acquisition and generation processes are characterized by a tendentially non-linear production for which the abstraction of the archaeological activities is necessary to bring the works together towards a correct form of exhibition curating [74]. In general, it is possible to find approaches in the literature that are inspired by the digital data curation, even if they do not refer to it. However, this lack of “declaration of belonging” represents an obstacle to comparing the established behavioral classes and glossaries and defining to what extent they are attributable to the guidelines established. DDC-compliant projects take into account, in a unitary and continuous way, the management of data-generative processes from the early stages (in this case, photos) to their final use [75] or those projects that involve the needs of cultural heritage with data entries and their use in terms of digital data [76], or in addition, they take into account the fact that errors of an epistemological or compilation nature can only cause cascading error propagation if inserted into technically functional but methodologically inconsistent frameworks [77]. Among these, we can mention the Europeana project [78] or Fernandez’s proposal of 2019 [79].
5. A DDC-Compliant Workflow for Photogrammetry
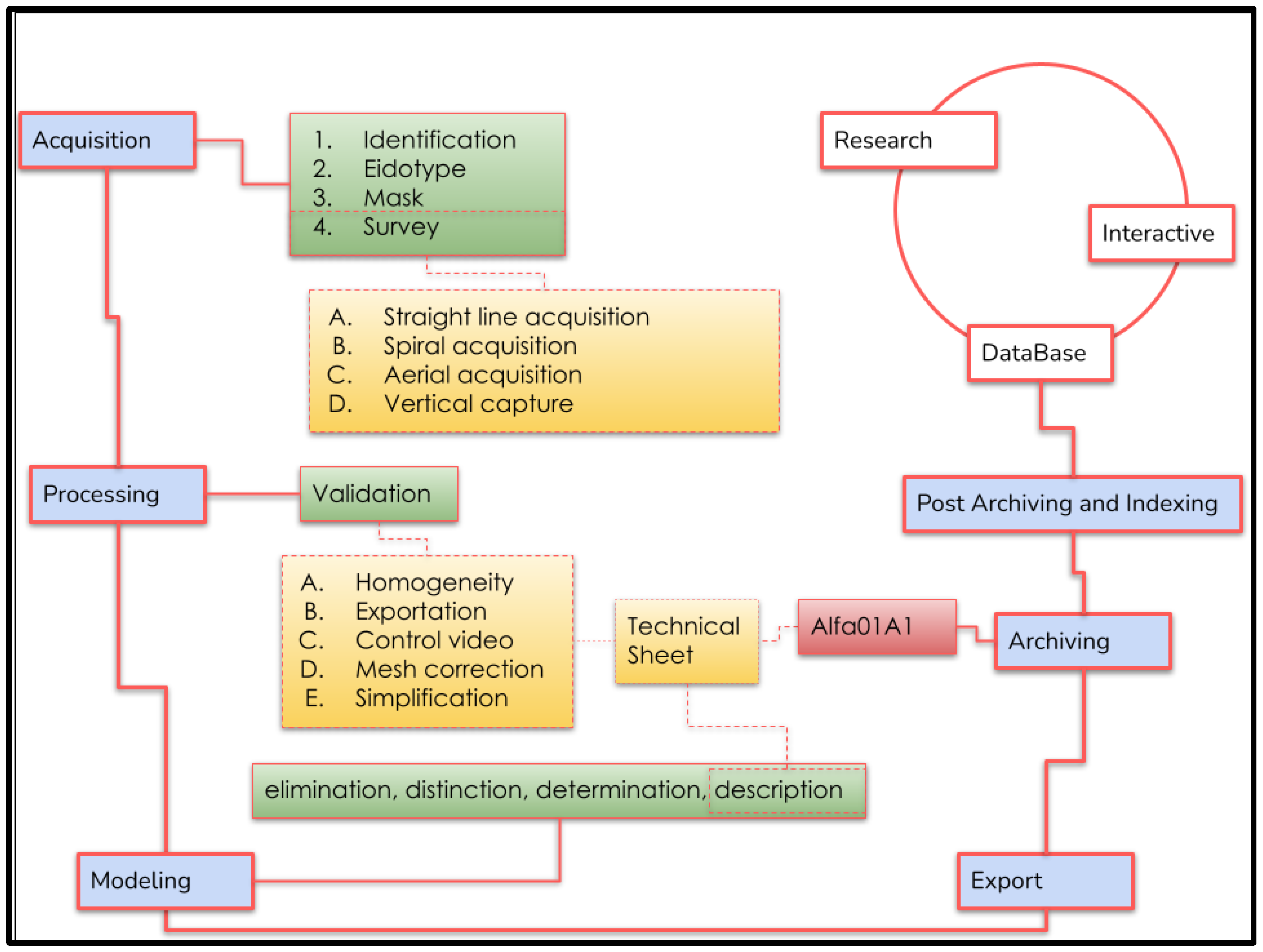
In this section, we address the instantiation of the general digital data curation framework into the photogrammetry workflow. We address a specific workflow, developed for the BeArchaeo project as an instantiation of the DDC schema: each phase is embedded as a component of the high-level DDC operations, adopting a constrained format that descends from the wide design. We proceed by providing a brief description of the project and then analytically on each phase (cf. Figure 1).
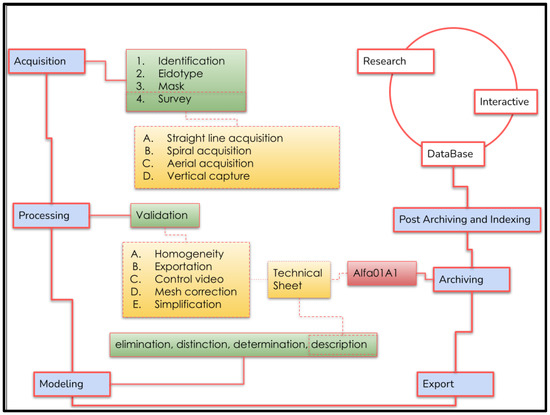
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the BeA-PG protocol for the Photogrammetric Survey for Cultural Heritage. The blue color refers to the main phases of the BeA-PG protocol. The green color refers to the sub-phases. Orange indicates major operating activities. Red indicates the progressive filing system and white refers to the research and development activities that occur following the use of the methodology.
5.1. The BeArchaeo Case Study: Interdisciplinarity and Internationality
The EU H2020 “Beyond Archaeology” (BeArchaeo) project develops interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary methodological models for the study of the historical relationships between the archaeological areas of Okayama and Shimane [80]. The BEA-PG work phases are sequenced as follows: acquisition, processing, modelling, export, archiving, post-archiving, and indexing. The survey activities were carried out from February 2019 to August 2019 and the elaboration processes took place from August 2019 to May 2022, which led to the exhibition phases of the project, first the Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) of the University of Turin (June 2022) and then the creation of BeA-Vir, an interactive system for the Exhibition at Museum of Izumo in Autumn 2022. Considering an average of 50 photos for artifacts and 100 photos for architectural or environmental surveys, we compared a photographic archive of 5850 photographs, which was organized, recovered, and recognized thanks to the specific acquisition methods that we will now illustrate (Figure 1).
5.2. The Conceptualization of Surveys
The process of photogrammetric survey relies on conceptualization as a crucial element throughout its phases, with particular significance during the acquisition phase, where the object of survey is understood and conceptual abstraction begins. Digital data curation outlines six distinct phases for data management—acquisition, appraisal, selection, preservation, maintenance, and dissemination. While these phases may not perfectly align with the proposed phases of the BeA-PG protocol, they serve as an abstract reference for its development, with each phase characterized by the phases of digital data curation. Therefore, these phases should be considered as a defining feature of the BeA-PG protocol. It should be noted that conceptualization is a vital aspect of the entire protocol, as a theoretical and methodological framework. The BeA-PG protocol is composed of several phases, which we will describe in detail. These steps are crucial for producing 3D models of cultural heritage and employing them in archives, exhibitions, and interactive virtual contexts. The phases encompass acquisition, processing, modeling, export, pre-indexing, archiving, and indexing. Although these phases stem from digital data curation, they are not entirely identical.
5.3. Acquisition
The acquisition phase starts with the identification of the object of the acquisition. In the case of an architectural structure, this is identified in an inspection, during which the notable points are identified, i.e., those points which, due to their geometric uniqueness or chromatic discrepancy, can be easily recognized by the software at the time of processing. During these preliminary operations, the recognition of significant points allows the avoidance of the use of targets in the acquisition phase. At this point, an eidotype will be drawn. At the same time as this first phase, a “mask” will be created. With this expression, we refer to a rapid survey of the structure that does not have to coincide with stringent precision parameters but only serves to identify a series of specific problems, such as reflectance, the influence of the sun, the cutting of shadows, and notable points that have escaped the drafting of the eidotype. At this point, we proceed with the photographic acquisition, which must respect the overlapping parameters between one photograph and the next one, at 60/70% [81]. The BeA-PG method enucleates 4 specific acquisition methodologies. The definition of specific categories of acquisition methods is an attempt to summarize the infinite variables that the photogrammetric survey operator normally faces, enclosing the possible acquisition scenarios in a group established based on the context. Furthermore, this approach can guarantee the order in the data collection from the first photographs; in this way, not only will the use of storage space be optimized but future retro-engineering operations will be made much simpler to the extent that it will be possible to repeat the processing of the survey or extrapolate new data as processing technology changes.
- Straight-line acquisition: an acquisition process to be used in the acquisition of large buildings and facades, proceeding parallel to the structure and turning the camera perpendicular to the object of the survey.
- Spiral acquisition: a set of photographs collected by defining an ideal focal point at the center of the object of the survey and pointing the camera towards the center proceed with an overall acquisition of the photographs, first perpendicularly then with an inclination of 45°, and finally with an inclination of 75°. This technique is to be used for single finds and artifacts. However, the spiral acquisition can also be used to collect data on a cavity or a structure with a structure similar to a corridor. In this case, the focal length must be placed at the bottom and one must proceed by placing the base of the spiral perpendicular to the ground and not parallel to it, as in the case of finds and other objects.
- Aerial acquisition: a variant of the straight line acquisition but considering proceeding parallel to the ground and turning the camera downwards. This technique is optimal when used with a drone for the acquisition of a territory and is also perfect for surveying archaeological trenches.
- Vertical capture: a straight line acquisition which is used for elevations that develop in height particularly, and in this case, a drone will most likely have to be used. The acquisition of the photographs can be carried out with cameras and mobile phones and there is no preferential indication for the choice of the instrument [82,83].
More generally, from a purely methodological point of view, one must consider the “rule of opposites”. This process is designed to increase the inclination of the color points in a group of photographs. Photogrammetry processing facilitates the process of recognition of geometries through the inclination of a theoretical polygon identified by the way a specific area of color obstructs the photograph or not and by its transformation from one photograph to another, defining the trend of the surface [84].
The use of such precise terminology and the definition of the various operational sub-phases is aimed at allowing operations carried out on monuments to also be intelligible for photogrammetric operators of the humanities, as it has a basis that allows them to respond to contextual difficulties and thus the problems of the interdisciplinarity of matter. In the same way, a set of documentation made up of an eidotype, a mask, and the collected photographs make it possible to reconstruct, and therefore to trace, all the choices made by the operator and possibly even question them. Furthermore, by keeping detailed information on acquisition procedures, it is possible to repeat the survey to the extent that new software allows for a greater optimization of the inferable data, thus opposing obsolescence processes. From the point of view of classification, already in this first phase, the nature of the object of the survey is clearly distinguished based on its geometric characterizations.
5.4. Processing
Although, as stated, the conceptualization underlies each phase, here we propose that there is a profound link between the processing phase and the term “Create” in the DDC glossary. Processing is when the photographs are processed to give life to the point cloud and subsequently to the three-dimensional model. The choice of a specific software or photographic acquisition tool would seem decisive, but studies on main parameters, such as views/ease of use, primitives/polygon creation tools, editing polygons, complex surface and volume operations, texture maps and materials, and export [85]; the process of structure for motion [86]; the accuracy of return [87]; processing algorithms [88]; or the efficient scalability of the models produced [89], on the other hand, show us how difficult it is to determine a definitive processing software. In the context of also illustrating the operations to be carried out in the point cloud to non-experts, an attempt was made to describe a method that could be applied to any cloud editing software (thus obviating the dependence on specific software and thus curbing the problems inherent in obsolescence). This phase is also used to skim the data, in fact, in the context of the BeArchaeo project, the BeA-PG method required all the operators involved to check the following:
- The homogeneity of the point cloud, with a consistent average density.
- For all surveys, it was necessary to produce a control video in AVI format showing the survey in its entirety for a maximum duration of 1 min, with a black background and double lighting, one fixed and one mobile.
- The mesh correction of the part where the deformations of the texture coincidence must be eliminated.
- All the surveys must be known and exposed at the time of loading on the database in the form of a technical sheet whose structure is illustrated below.
Once again, the decision to provide the verification indications of the point cloud status was made in order not to exclude any of the researchers involved from the job evaluation processes, providing general indications to be able to recognize the qualitative status of the job. Naturally, numerous variables in the context of processing are purely technical, but for this very reason, they are not the object of this abstract analysis and which, if placed as a central topic, as we have seen in previous case studies, risk moving toward software-based paths.
5.5. Modeling
Modeling can be defined, from an operational point of view, as a set of operations that are carried out on the obtained three-dimensional model. Modeling is a process that here is distinguished both from processing and from exporting as the conceptual independence of both the phase and the existence of the 3D model, which is claimed in the context of editors (Blender, Maya, Rhino, 3D Studio Max) and detached from the photos that generated it and from the inert model after export. Once again, if one observes the literature consulted, this phase too is considered to be within the exclusive remit of the technical and the focus is on the definition of which software to select [58]; however, even in this phase, we have limited ourselves to providing indications of the verification and cleaning operations to be carried out regardless of the software used to oppose its obsolescence processes as its potential and tools change considerably over the years. Even when a workflow is proposed, if it is built starting from the centrality of this phase over other phases, it is structured by imagining only one possible sequence of technical choices (type of camera, type of processing software, type of software modeling process) and omitting the subsequent data archiving phases [59]. This choice was made to guarantee the traceability of the phases carried out and the modeling, isolated in this specific context, becomes the only manipulative part of the 3D model, thus isolating any actions that need to be traced in a specific moment that is easily recognizable. Yet, the fact that this phase requires speculative processes becomes more and more evident and is compared with the characteristic operations of design. Since the operations carried out in the 3D model point to a specific selection of the contents which are preserved or eliminated (regarding which we can speak of “Selection” and “Dispose” in the context of the DDC) [90]. In light of the aforementioned and remaining faithful to the principles of interdisciplinarity, the activities to be carried out in the context of modeling, proposed here, are as follows: eliminate the areas in which textures and polygons do not coincide, then proceed with the distinction between the shadows due to the absence of data (such as objects that may have stood in the way at the time of acquisition) and shadows generated from processing errors. Then, the average detail trend of the point cloud needs to be determined. A quick method to achieve this is to evaluate the density of the cloud, ensuring that it is consistent throughout the model. Another important aspect is the identification of the object of the work, that is, the element that represents the concrete object of study, in order to proceed with the elimination of non-inherent or misleading aspects. This must also be performed to try to gain storage space and stay within the parameters established in the previous steps. Naturally, the original processing data must be kept in rigid archives that will be part of the project’s warehouse material. In any case, each modeling operation carried out must be reported in the notes of the final sheet. Yet, the fact that this phase requires speculative processes becomes more and more evident and is compared with the characteristic operations of “Design” as defined by DDC. Since the operations carried out in the 3D model point to a specific selection of the contents, which are preserved or eliminated [91]. All the manipulation operations carried out on the 3D model must be shown and must be able to fall into one of the exposed categories which serve to justify the actions carried out and thus trace the work activities.
5.6. Exporting
An often overlooked problem is the file export format. This phase represents the “point of no return”, beyond which the 3D model is “closed” and becomes a defined object [92], and for this reason, in this proposal, we match the export with the “Ingest” and “Preservation Action” of the digital data curation glossary. This is because the 3D model, as long as it is located in the editor for manipulation, is an “open project” and is therefore susceptible not only to modifications but also to problems related to its placement in a specific hard drive. The editors make references to elements external to the software itself and it is often impossible to export the open project to new locations related to the specific use that the project foresees. Since it is not the object of this paper to analyze in detail the advantages and disadvantages of the different formats, we deem it crucial here to emphasize the methodological importance of distinguishing this phase from the previous manipulation phase. Assuming that the user of this methodology retains all the raw data, which are still traceable and classifiable, in this phase, it is necessary to add a note indicating the reason that prompted the use of a specific export format.
5.7. Pre-Indexing
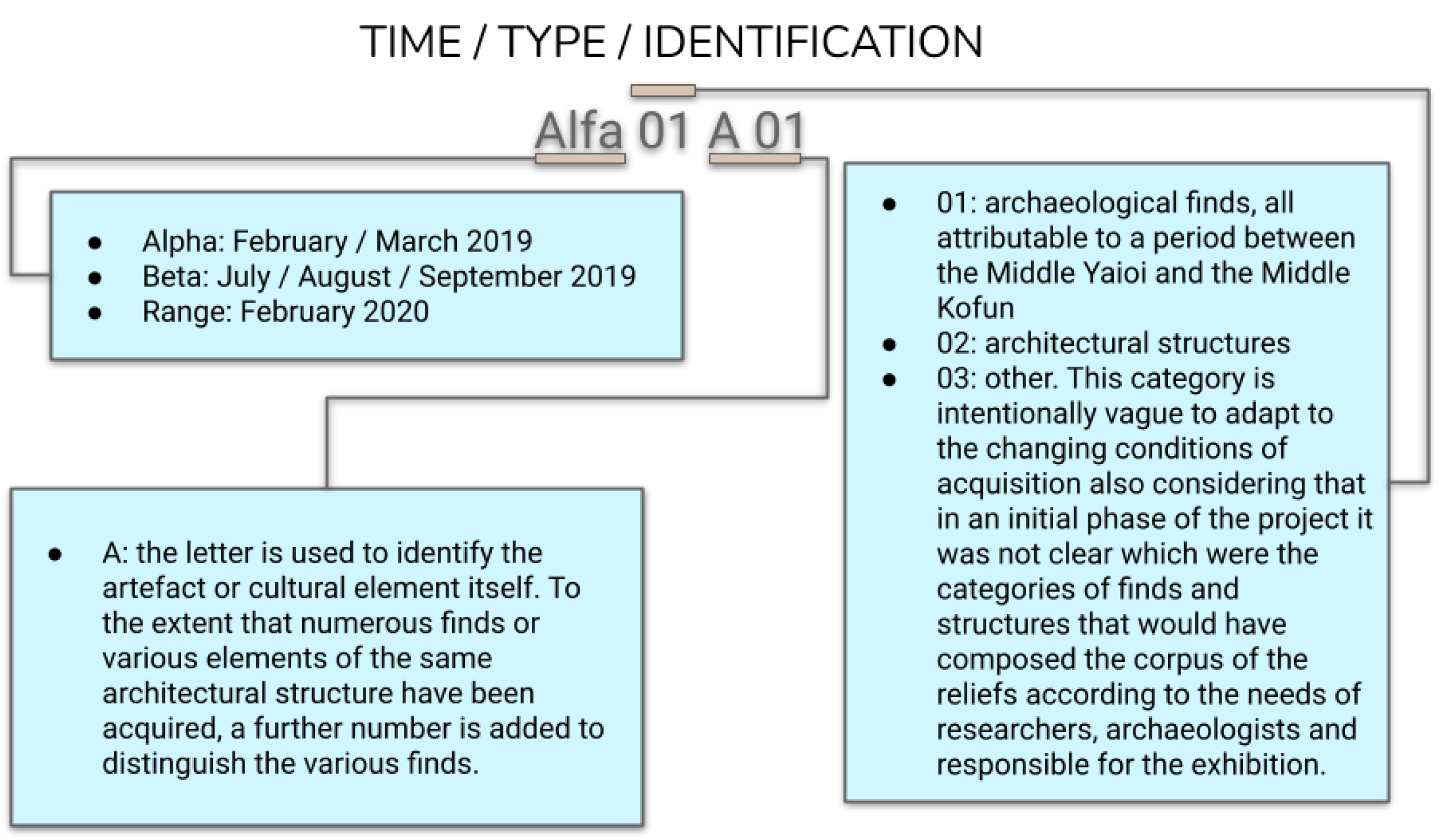
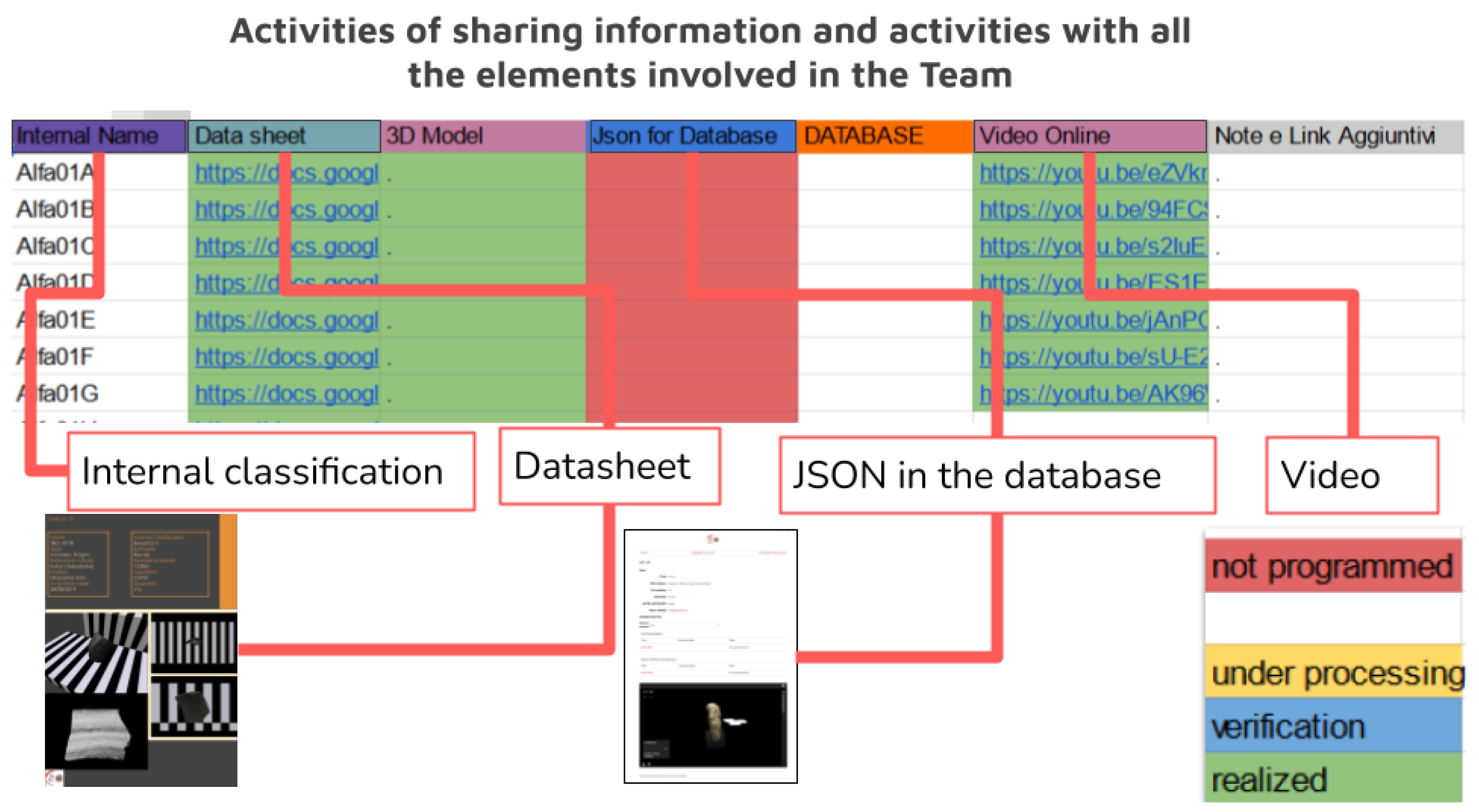
From a purely operational point of view, archiving is the process by which data are collected, categorized, indexed, and entered into a database from which they can be easily retrieved. For 3D models, this phase is often transient, as they are often placed in query software, such as virtual interactives, presentations, museum exhibits, and videos, but this would not be possible without the proper archiving of the models. For these reasons, “Archiving”, in the digital data curation terminology, coincides both with the “Store”, “Access Use”, and “Reuse”, and due to its fundamental function of not dispersing data, it has probably been the most analyzed phase in the scientific literature, much often to the detriment of the other phases. Having the DDC as its main objective, along with the archiving and management of digital data, and considering the number of studies that are concerned with the specific area of this paper, it would be misleading to delve too far into this topic. What is important here is to represent this phase in the context of the DDC applied to the photogrammetric acquisition, in other words, how the archiving of the 3D models is the result of a reasoned process which respects the parameters set out and which allows for a second phase of the easy reuse of data. Such “second access” to information must meet the content quality verification metrics, as outlined by the DDC. The need for this preliminary pre-indexing step is linked to the consideration that in this phase a considerable amount of data has already been produced for this reason and it becomes essential to carry out the preventive cataloging of the material [93]. This cataloging is not a substitute for the final one, which will compose the database, but is an obligatory step to be able to trace the data at a later time, carry out checks, or submit the three-dimensional models to reverse engineering processes. For this reason, every time the three-dimensional model is exported, a form is filled in and associated with the model. Additionally, for this reason, cataloging follows the elaboration processes, the classification parameters are progressive, and the definition of the categories is clear. The classification of digital materials takes place by indicating the following: the time at which the acquisition was made, the macro-category of reference, and an alphanumeric list that makes the identification code unique.
This method allows the creation of reference tables for which data can be easily recovered even in the measure in which, as occurred during the case study, there is a long time between the first acquisition and the first insertion of the data in the database. Furthermore, this leads to the creation of a table in which to communicate the data created up to that point and as the elements that are inserted into the database it is connected with. This intermediate step is meant to eventually be buried as a junction part of the manufacturing process when the database becomes fully operational. This ensures complete traceability of the work (Figure 2) carried out not only from the point of view of the 3D model alone but also from a temporal point of view. Pre-indexing provides all the information on the period in which the survey was carried out, to which category the find belongs, and to which subgroup it has been assigned (Figure 3). This categorization is free from the use of a specific database and is the basis on which digital archives must also be built. As we will also observe, in the practical example reported in the conclusion, this allows not only the traceability and classification of the find, but since it does not depend on any specific database, it allows adaptability and transfer to other contexts as well (thus opposing the problems of obsolescence). Furthermore, this system traces the digital object without requiring the help of specific database glossaries which, although shared, can isolate scholars belonging to disciplinary areas that do not use them.
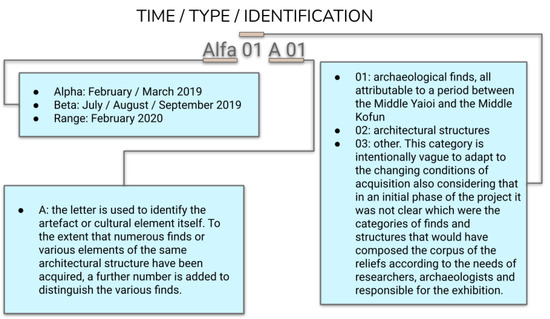
Figure 2.
The pre-indexing of the finds and the generation of an alphanumeric procedural code.
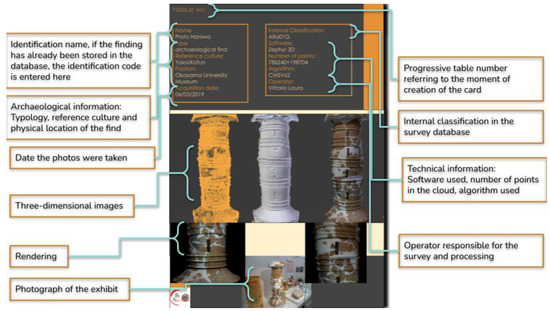
Figure 3.
Pre-indexing form of the BeArchaeo project with the information taken from the previous phases.
5.8. Archiving and Final Indexing
This phase closes the cycle of creating the 3D model by photogrammetry, according to the BeA-PG protocol, and represents the delicate keystone of the entire process as poor data management practices (how data are created and maintained), which can lead to information loss, and undetected errors in data can cause confusion and lead to misinterpretations [94]. The post-archiving and indexing phase is perhaps the most nuanced of the entire process and coincides with “Transformation”, according to the DDC glossary. Concretely, it is the moment in which the 3D models collected are finalized for a specific case study. The models can be extracted from the archive to be subjected to new analyzes, or they can be transmitted via a virtual or real exhibition model (utilizing 3D prints). In any case, whatever the final destination, it is at this moment that a second indexing of the models to adapt their wording to the new reception environment often occurs. This last phase as described here as the most speculative and is derived from the assumption that the whole process of coincidence between DDC and the photogrammetric acquisition pipeline is taken for granted. For this reason, any in-depth analysis and methodological comparison is entrusted to the presentation of the method, where reference is made to the following paragraphs. After the temporary pre-organization based on progressive classification notes, which are also useful later when accessing the repository of intermediate forms, from the photos to the 3D model, one can proceed with the insertion of the data in the final database of the project to the extent that one has foreseen. In this phase, all the finds are reclassified to adapt to the new tool aimed at the work of archaeologists or for dissemination purposes, so a database entry that integrates the digital twin metadata with the data input from archaeometry and archaeologists, reporting the global project identifier.
Observing these works, one realizes that attempts at abstraction and theoretical definition, if deduced from a purely technical and non-methodological reflection, risk forcing the method towards the idea of an ideal workspace where specific technologies, generous funds, and ample timescales are available [95].
6. Final Observations and Conclusions
6.1. Verification and Legitimacy: The Case Study
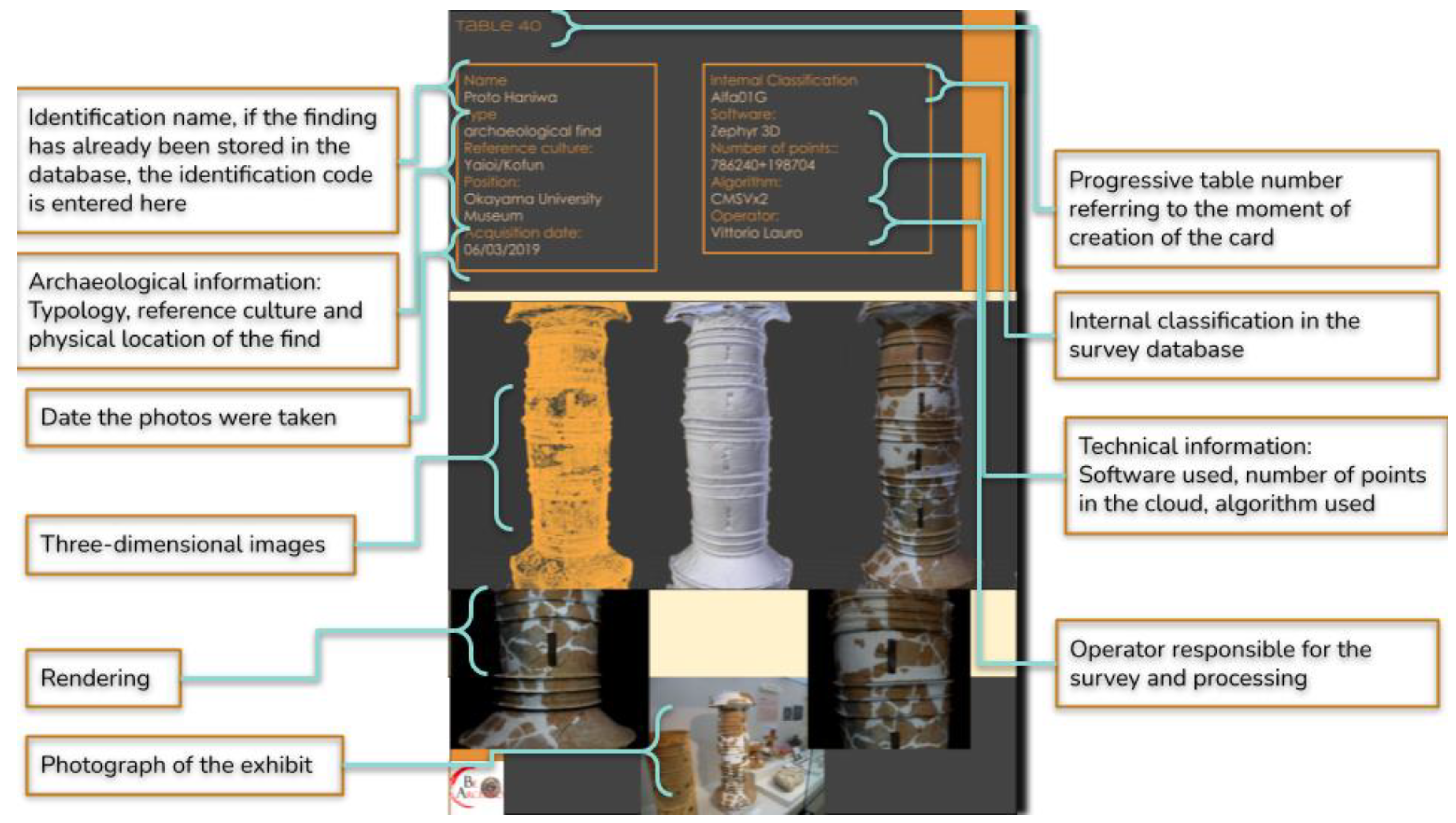
The advantages of having been able to experiment and use the BeA-PG method in a real project has allowed the verification of its ongoing functioning, demonstrating, above all, the main nature of this process, which can be defined as a palindrome, in the sense that it can be utilized in both directions, either starting from the database card with any final destination up to the original photos or starting from the surveys, following its natural process of creating the template. Taking, for example, the pre-indexed exhibit, Alfa01E, as shown in the interdisciplinary workshop on 17 July 2020 for researchers, starting from the simple initials, it was possible to trace the name, the type, the reference culture, the current positioning of the find, the date on which it was found, with which software it was processed, following which algorithm, and how many points the cloud was made up of, as well as accessing a large number of images that perfectly frame the find. Furthermore, by breaking down the identification code and having access to the project hard drives, since the raw data folders are built according to the same methodology, we will know the exact position of the original photos of the survey, i.e., C: Alfa\01\E, and in it we will find the original photos, including those discarded from the survey. All this additional information then flows into the “Database” tab in which the reference code to the survey tab will be queued in order to be able to carry out the reverse path again, from which researchers will be able to access all the existing details on the find, including carrying out a cross-check with the database files relating to the stratigraphic units to which the find is associated and verify which other finds have the same origin. The database in question was created according to the principles of the Semantic Web—this means that a stringent categorization based on known archives has been created, taken from the documentation registers of the Italian Central Institute for Cataloging and Documentation, Getty AAT9 and CIDOC-CRM, and the main semantic properties taken were directly from Web Omeka-S11 [96].
The definitive verification, the so-called litmus test regarding the functioning of this dual-direction system, took place in February 2022 after a long operational pause imposed on the project by the COVID-19 pandemic, when in the archiving phase of the 3D finds, it was possible to recover the original photos, following the classifications indicated by the survey and to be able to repeat the surveys, thus overcoming some problems that had occurred in the first iterations, but above all, it was possible to easily search thousands of photos, recovering exact image required, and, in this way, repeat the surveys of an excavation activity carried out 4 years earlier, obtaining new information on the stratigraphic units and the distribution of the finds in the excavation.
6.2. Detailed Case Study
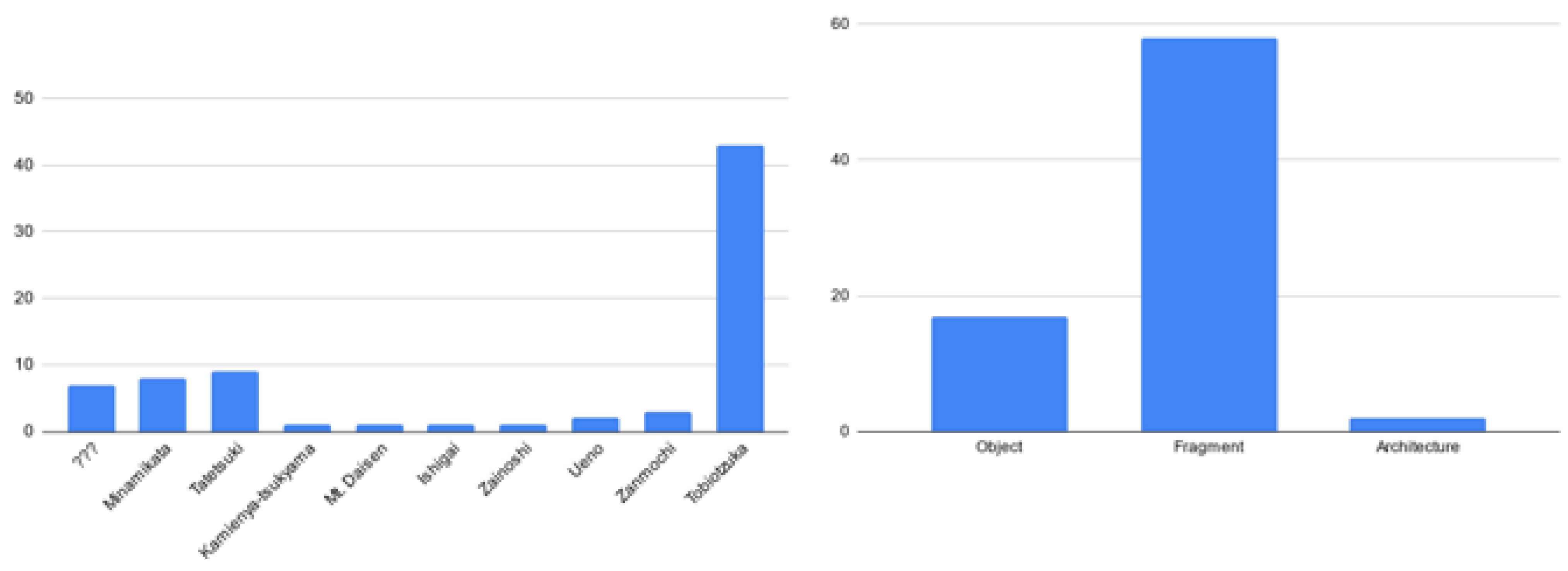
The method described so far, applied in the context of the BeArchaeo project using the times and methods described, has led to the survey of 80 elements, including archaeological finds, architectural structures, and archeozoological finds. To these must be added the survey of the burial chamber of Tobiotsuka Kofun and the survey of the excavation trenches for a total number of further 20 three-dimensional models. Considering an average of 50 photos for artifacts and 100 photos for architectural or environmental surveys, we were confronted with a photographic archive of 5850 photographs, which could be organized, recovered, and recognized thanks to the specific acquisition methods that have been illustrated in the previous paragraphs. The photographs, therefore, led to the elaborations, and even in this phase, for each element, the reference sheet was drawn up with information on the reconstructive algorithm used, the software used, the number of points that make up the surface of the model, and the images of comparison between the 3D model obtained and the original object. In some cases, it was also possible to insert in the cards the three-dimensional model of the find at the time of its discovery, from the excavation directly, allowing it to be associated with the reference stratigraphic unit (this was valid for 29 finds found in the excavations carried out in the Sepulchral Chamber of Tobiotsuka Kofun). This allowed an initial classification by observing the sites of origin of the finds and identifying the most represented morphological categories (Figure 4).
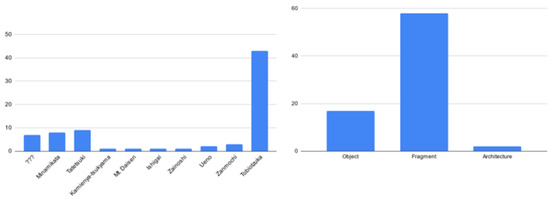
Figure 4.
Reorganization and recognition of the morphology and of the main sites of origin of the finds inferred from the application of the BeA-PG method.
6.3. Overcoming the Paradigm of the Absolute Standard
In conclusion, the proposed methodological protocol does not claim to be revolutionary or resolutive in its entirety but tries to shift the object of the problem from a purely technical to a purely humanities-based methodology, attempting to bring the two visions together. It is the opinion of the authors that many of the problems inherent in the realization of concretely interdisciplinary projects are the difficulties arising from the various parties involved in abandoning their approaches; nevertheless, the increasingly intensive use of technologies in the field of cultural heritage pushes more and more archaeologists to deal with tools such as databases, laser scanners, and photogrammetry and more and more computer scientists to have to apply their techniques and methodologies to the infinite and unique complexities characteristics of archaeological finds and ancient structures. The method has a specific and characterizing focus: to not disperse data. The most dangerous feature of an interdisciplinary system that fails to involve all the various researchers from different subjects is that the data quickly becomes unobtainable, and an archaeological excavation for which concrete and measurable data does not exist may as well have never existed. Furthermore, this method also allows an external observer to verify the data very easily, how they were produced, and if necessary, repeat the operations that led to the specific product line of three-dimensional materials, making the entire structure of the project available for de facto a peer review that is not limited exclusively to final data of the searches but also to all the intermediate steps. With the publication of the BeArchaeo project database, it will be possible to verify the method and how functional it was in the production of data, and since it is open, anyone can repeat the various operations, even to the extent that if they want to request the raw data, they will always be easily recoverable, thanks to the organization of the folders, which, as already noted, follows the order of the entire structure. In addition, the suggestion of acquisition methodologies can prove to be a very efficient tool to bring even archaeologists closer to a more technical photogrammetric survey methodology and, above all, also adaptable to new software that may become available. Creating a perfect model is impossible due to the very nature of technological development; therefore, our aspiration was not to create a perfect model.
All the activities carried out were made available in real-time by the research team by sharing an Excel file (Figure 5), where each step was updated and gradually associated with the official classifications that the archaeologists provided for the finds.
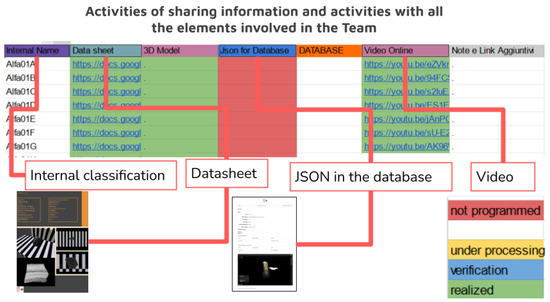
Figure 5.
The classification of information within the BeArchaeo project in the context of the transfer from the pre-indexing files to the final database files.
At this point, the material was sorted by the various intended uses, including the Interactive Model for CAVE, presentations and conferences, and, above all, the database.
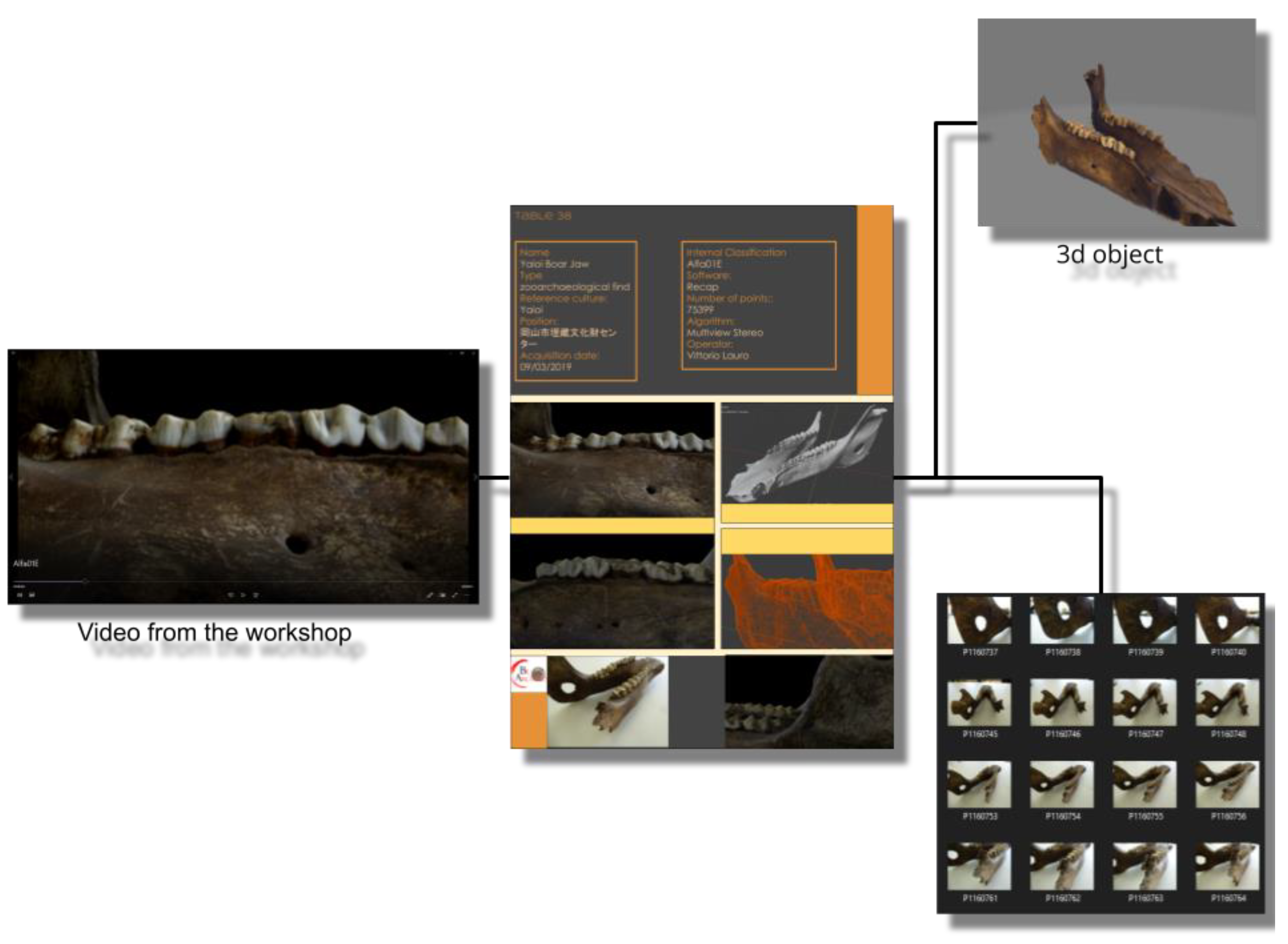
To show the operations carried out in detail, let us take an artifact as an example and observe all the steps that led it from its acquisition to its final results. This process is a true palindrome, in the sense that it can be followed in both directions, either starting from the database card or any final results and moving backwards, up to tracing the original photos, or starting from the initial finds and following the natural process of creating the template. So let us perform both processes. During the interdisciplinary workshop on 17 July 2020, a wild boar jaw was shown in an illustrative video as an example of the three-dimensional surveys carried out in high definition (Figure 6). The video, according to the archiving procedure provided by the methodology, depicted the wording Alfa01E at the bottom left. This is a very interesting example, as we are not starting from the official database of the project, but from a video that has as its object a find that, not being the result of an excavation activity, will be documented by archaeologists. Anyone who was part of the project, even with these data only, could access the file on the storage drive. From this, they would learn the name, the type, the reference culture, the current location of the find, the date on which it was detected, with which software it was processed, following which algorithm, and how many points the cloud is made up of, as well as accessing a large number of images that perfectly frame the find. However, let us imagine that anyone who is following this reverse path requires the original data of the find, perhaps in order to carry out new processing. First of all, the same code that allows access to the card also allows the identification the object model of the find within the 3D archive always present in the shared project drive. Furthermore, by breaking down the identification code and having access to the project hard drives, since the raw data folders are built according to the same methodology, we will know the exact position of the original photos of the survey; therefore, C: Alfa\01\E, and through this we would find the original photos, including those discarded from the presentation.
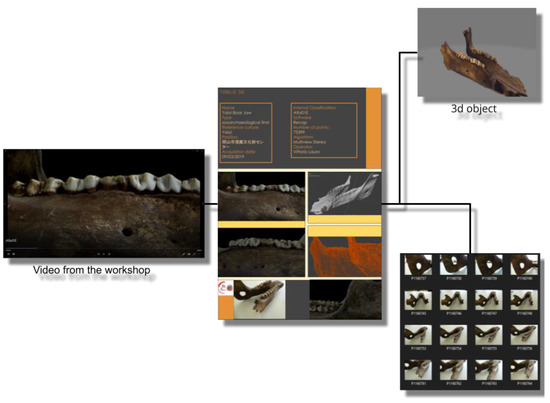
Figure 6.
The example of exhibit ALFA01E in the context of retrieving information from the identification label.
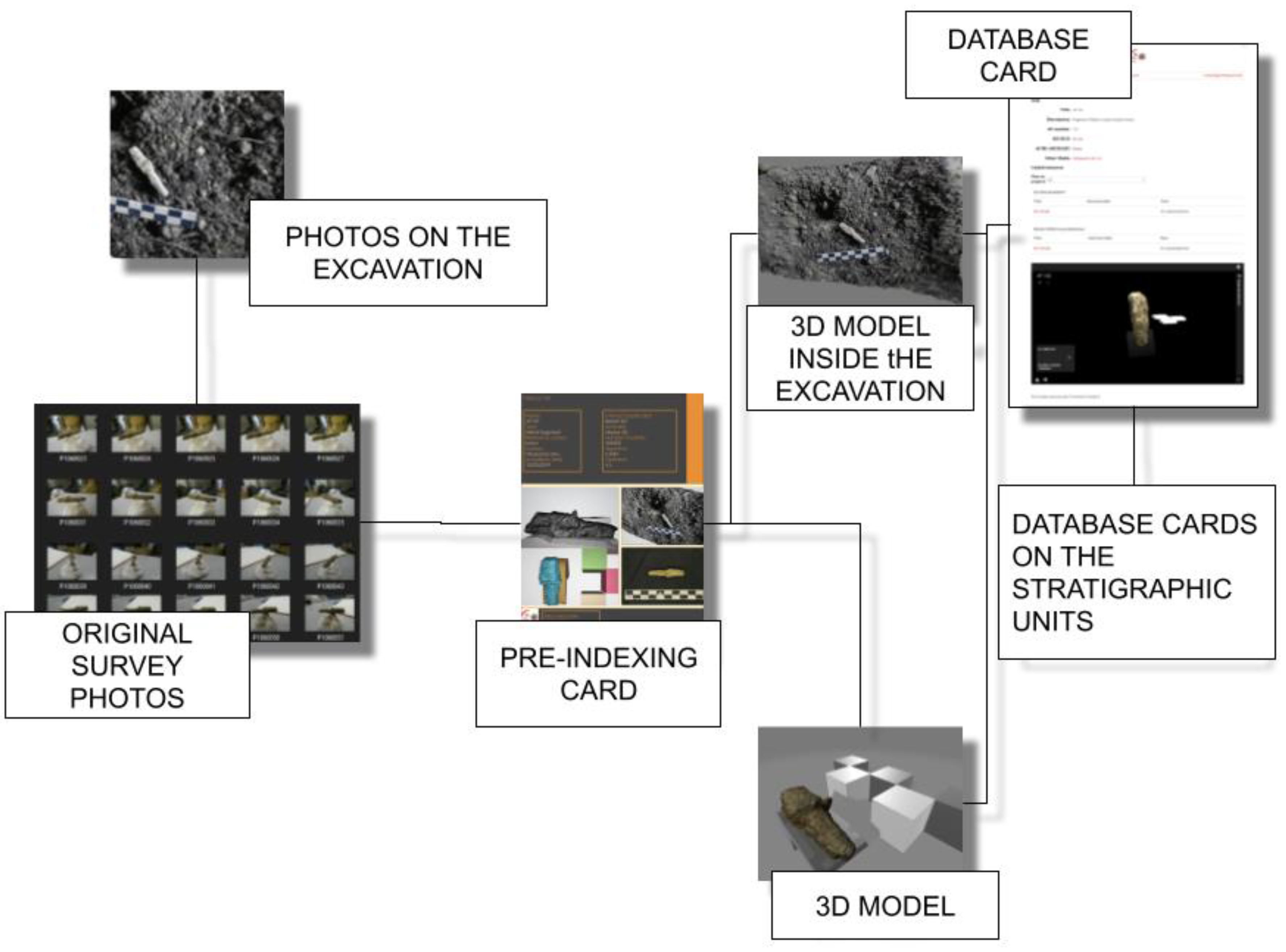
Let us now observe how the same structure is conventionally used to move from the survey to the “Database” tab. Let us take as an example a metal fragment found during the funerary excavation of the Tobiotsuka Kofun burial chamber on 3 September 2019 (Figure 7), which, on 7 September 2019, was brought to the excavation laboratory. At this point, the find was assigned the acronym AF137. On 12 September 2019, the find was detected. The photos were saved in the C: \\Beta\01\S\22 folders, from which the three-dimensional model saved as Beta01S22, which was obtained, and the reference card was associated with it. Subsequently, the data from the excavation directly were processed, from which the data of the find were obtained at the time of its discovery in association with its reference “Stratigraphic Unit”. All this additional information then flows into the “Database” tab, in which the reference code to the survey tab will be saved in order to be able to carry out the reverse path again, and from which researchers will be able to access all the existing details on the find, including carrying out a cross-check with the database files relating to the stratigraphic units to which the find is associated and verify which other finds have the same origin.
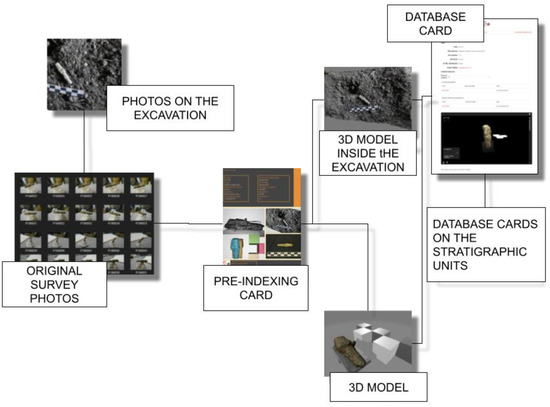
Figure 7.
The example of exhibit BETA01S22 in the context of retrieving information from the database card.
6.4. Towards the Evolution of Bea-PG: Application of the Method on Another Project
The main strength of the BEA-PG method is the fact that it is completely independent of specific software or technical tools, aiming instead at being a behavioral handbook while remaining faithful to the dictates of digital data curation. Another key advantage is the fact that this method has been actively tested within the BeArchaeo project. What was perhaps the most successful was the possibility of verifying the interdisciplinary breadth of the methodology, which was intelligible for all its users. Even more important was the verification of the palindrome nature of the project. In fact, because of an interruption due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the project was paused for almost two years, at the end of which, there was considerable difficulty in recovering the data; this obstacle, however, did not concern the 3D models of the various finds, which were not only easily recoverable but, in some cases, completely reworked. In fact, at the time of verification, before being included in the exhibition held at the Izumo Museum, during which the models were presented in a virtual interactive environment, by exploiting the production methodology, it was possible to recover the original photos, rework and optimize the exhibits, and reintroduce them into the work pipeline without any problems. On the other hand, the limits of this methodology are evident: desiring to be a bridge between the needs of the field of cultural heritage and the technical requirements of the world of computer sciences, the BEA-PG method lacks the technical specificities of either area. With its high level of abstraction, on the one hand, it aims to be adaptable to multiple different scenarios, even fields external to cultural heritage; however, on the other hand, this risks making the project superficial. For this reason, in order to achieve a concrete evaluation of the method, it must be also applied to other contexts, archaeological or otherwise, and this will be one of the objectives of our work in the coming years.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization; methodology; writing—original draft preparation; data curation, V.L. (Vittorio Lauro); validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, supervision, V.L. (Vincenzo Lombardo). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Project Beyond Archaeology (BeArchaeo), was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie, Grant Agreement No 823826.
Data Availability Statement
The data relating to the BeArchaeo project database can be consulted at the link https://bearchaeo.unito.it/omeka-s/s/bea_resources_site_ja/page/welcome_bearchaeo-resources-site.
Acknowledgments
This research is also related to a project called. The photogrammetric survey activities were carried out within The Work Package WP4: Database and its software tools, led by prof. Vincenzo Lombardo of the University of Turin. The surveys were carried out and coordinated by the task leader of the Surveys Vittorio Lauro (University of Turin) during the 2019/2020 excavation campaigns of Tobiotsuka Kofun and on the most representative archaeological materials from the museum of the University of the Okayama and Okayama Prefecture, as well as some museums in the Izumo area in Shimane Prefecture, with the support of Rosaria Vitolo (I.R.I.A.E.), Nicolò Masturzo (University of Turin) and Giorgia Greco (I.R.I.A.E.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Forte, M. 3D Archaeology. New Perspectives and Challenges. The example of Catalhoyuk. Near East. Archaeol. 2014, 2, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiz, J.I.; Martín, P.M.; Cuesta, R.; Subías, E.; Codina, D.; Cartes, A. Examples and Results of Aerial Photogrammetry in Archeology with UAV: Geometric Documentation, High Resolution Multispectral Analysis, Models and 3D Printing. Drones 2022, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkingham, P.L. Acquisition of high resolution three-dimensional models using free, open-source, photogrammetric software. Palaeontol. Electron. 2011, 15, 15.1.1T. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchiaro, S.; Fallu, D.J.; Zhao, P.; Waddington, C.; Cockcroft, D.; Tarolli, P.; Brown, A.G. SfM photogrammetry for Geoarchaeology. Dev. Earth Surf. Process. 2020, 23, 183–205. [Google Scholar]
- Aicardi, I.; Chiabrando, F.; Lingua, A.M.; Noardo, F. Recent trends in cultural heritage 3D survey: The photogrammetric computer vision approach. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 32, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deli, R.; Galantucci, L.M.; Laino, A.; D’Alessio, R.; Di Gioia, E.; Savastano, C.; Lavecchia, F.; Percoco, G. Three-dimensional methodology for photogrammetric acquisition of the soft tissues of the face: A new clinical-instrumental protocol. Prog. Orthod. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faniel, I.; Kansa, E.; Kansa, S.W.; Barrera-Gomez, J.; Yakel, E. The Challenges of Digging Data: A Study of Context in Archaeological Data Reuse. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM/IEEE-CS Joint Conference on Digital Libraries, New York, NY, USA, 22–26 July 2013; pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, D.; Frischer, B.; Humphreys, G. Research challenges for digital archives of 3D cultural heritage models. J. Comput. Cult. Heritage 2009, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Črešnar, M.; Mele, M. Early Iron Age Landscapes of the Danube Region; Archaeolingua for the Iron-Age-Danube: Graz, Austria; Budapest, Hungary, 2019; p. 19. ISBN 978-615-5766-33-6. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, D.; Hermon, S.; Eliades, I. Virtual and physical re-composition of fragmented ecclesiastical frescoes using a photogrammetric approach. In Proceedings of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Commission VI, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–19 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giulio, R. Integrated data capturing requirements for 3d semantic modelling of cultural heritage: The Inception Protocol. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W3, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechala, P.; Mahoney, J.; Farkas, L.G. Digital two-dimensional photogrammetry: A comparison of three techniques of obtaining digital photographs. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 103, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltsavias, E.P. A comparison between photogrammetry and laser scanning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülch, E. PHOTOGRAMMETRIC MEASUREMENTS IN FIXED WING UAV IMAGERY. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2012, XXXIX-B1, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Communications Networks, Content and Technology. Study on Quality in 3D Digitisation of Tangible Cultural Heritage: Mapping Parameters, Formats, Standards, Benchmarks, Methodologies, and Guidelines: Executive Summary; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2759/581678 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Documentary Heritage at Risk: Policy Gaps in Digital Preservation, Outcomes of UNESCO Policy Dialogue, Prepared by the Preservation Sub-Committee of the International Advisory Committee of the UNESCO Memory of the World Programme 5 September 2021. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/sites/default/files/documentary_heritage_at_risk_policy_gaps_in_digital_preservation_en.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Sobotkova, A. Sociotechnical Obstacles to Archaeological Data Reuse. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2018, 6, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodoronek, M. The Use and Application of Photogrammetry for the In-Field Documentation of Archaeological Features: Three Case Studies from the Great Plains and Southeastern Alaska. Master’s Thesis, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, Nebraska, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Douglass, M.; Lin, S.; Chodoronek, M. The Application of 3D Photogrammetry for In-Field Documentation of Archaeological Features; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gattiglie, G. Classificare le ceramiche: Dai metodi tradizionali all’intelligenza artificiale. In L’esperienza del progetto europeo ArchAIDE. In Proceedings of the ARCHEOLOGIA QUO VADIS? Catania, Italy, 18–19 January 2018; pp. 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, A.; Ioannidis, C. Photogrammetric and Surveying Methods for the Geometric Recording of Archaeological Monuments in “Archaeological Surveys. FIG Work. Week 2004, 22, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S. The DCC Curation Lifecycle Model. Int. J. Digit. Curation 2008, 3, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, T. Data Curation: An opportunity for the libraries. In Proceedings of the MANLIBNET 2018: International Conference on Emerging Trends in Librarianship: Role of Libraries in Learning Environment, Indian Institute of Management Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India, 10–12 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, D. What is Digital Curation? DCC Briefing Papers: Introduction to Curation. Edinburgh: Digital Curation Centre. Handle: 1842/3362. 2008. Available online: https://www.dcc.ac.uk/guidance/briefing-papers/introduction-curation (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Kansa, E.C.; Kansa, S.W. Promoting data quality and reuse in archaeology through collaborative identifier practices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2109313118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, J. Is big digital data different? Towards a new archaeological paradigm. J. Field Archaeol. 2020, 45 (Suppl. S1), S8–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, A.P., III; Rozen, K.C. Debitage Analysis and Archaeological Interpretation in American Antiquity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, CA, USA, 1985; Volume 50, pp. 755–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Readt, D.W. Archaeological Classification. In The Encyclopedia of Archaeological Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Available online: https://www.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781119188230 (accessed on 14 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.P. Disciplinary Impact and Technological Obsolescence in Digital Medieval Studies; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.P. Cædmon’s Hymn: A Multimedia Study, Archive and Edition. Society for Early English and Norse Electronic Texts A.7; D. S. Brewer in association with SEENET and the Medieval Academy: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lauro, V. A hypothesis for the Pyrgos Virtual Museum from Relief to Virtual Museum New technological proposals applied to cultural goods. In Proceedings of the Archaeometry and Charm, Gender Copper and Music of Silk, Archaeological Research Unit, University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus, 11–12 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, M. What makes interdisciplinarity difficult? Some consequences of domain specificity in interdisciplinary practice. Synthese 2018, 195, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, R. The Bologna Process and the Lisbon Research Agenda: The European Commission’s expanding role in higher education discourse. Eur. J. Educ. 2006, 41, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, R.; Wenk, S. Disciplinary Barriers between the Social Sciences and Humanities, Current Debates about the Construction of Knowledge in the Social Sciences and Humanities and the Impact of These on Disciplinization in Eight European Countries; Carl von Ossietzky Universität: Oldenburg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny, H.; Scott, P.; Gibbons, M. Re-Thinking Science: Mode 2 in Societal Context. (This article is based on a revised version of Helga Nowotny, Peter Scott and Michael Gibbons, Mode 2 Revisited: The New Production of Knowledge, forthcoming in Minerva (2003)). In Knowledge Creation, Diffusion, and Use in Innovation Networks and Knowledge Clusters: A Comparative Systems Approach across the United States, Europe and Asia; Greenwood Publishing Group: Westport, CT, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zarka, Yves Charles La Crise des Science Humaines et Sociales au CNRS (First Published as “Dérive des Sciences Humaines et Sociales au CNRS” Libération 27 July 2004) 21 March. 2005. Available online: http://recherche-en-shs.apinc.org/article.php3?id_article=80 (accessed on 11 July 2015).
- Walter, S. ‘Über das Verhältnis der Soziologie zu den Geisteswissenschaften’. In Wozu Geisteswissenschaften? Kontroverse Argumente für eine überfällige Debatte; Institut für Hochschulforschung (HoF) an der Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg: Wittenberg, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3-593-37336-X. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, P.; Goodsite, M.E.; Cloetingh, S.; Agnoletti, M.; Moldan, B.; Lang, D.J.; Leemans, R.; Moeller, J.O.; Buendía, M.P.; Pohl, W.; et al. Collaboration between the natural, social and human sciences in Global Change Research. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 28, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, A.; Lyall, C.; Tait, J.; Williams, R. Interdisciplinary integration in Europe: The case of the Fifth Framework programme. Futures 2004, 36, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, N.; Angelini, I.; Artioli, G.; Benati, G.; Bitelli, G.; Curci, A.; Marfia, G.; Roccetti, M. NEARCHOS. Networked Archaeological Open Science: Advances in Archaeology Through Field Analytics and Scientific Community Sharing. J. Archaeol. Res. 2018, 26, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, L.; Kansa, S.W.; Lev-Tov, J.; Kansa, E.C. Other People’s Data: A Demonstration of the Imperative of Publishing Primary Data. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 20, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintigh, K.W.; Altschul, J.H.; Kinzig, A.P.; Limp, W.; Michener, W.K.; Sabloff, J.A.; Hackett, E.J.; Kohler, T.A.; Ludäscher, B.; Lynch, C.A. Cultural Dynamics, Deep Time, and Data: Planning cyberinfrastructure investments for archaeology. Adv. Archaeol. Pr. 2015, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosevelt, C.H.; Cobb, P.; Moss, E.; Olson, B.R.; Ünlüsoy, S. Excavation is Destruction Digitization: Advances in Archaeological Practice. J. Field Archaeol. 2015, 40, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansa, E.C.; Whitcher-Kansa, S.; Watrall, E. (Eds.) Archaeology 2.0: New Approaches to Communication and Collaboration; Cotsen Digital Archaeology Series 1; Cotsen Institute of Archaeology Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://escholarship.org/uc/item/1r6137tb (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Londoño, W. Reflexivity in archaeology. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology; Smith, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 6258–6261. [Google Scholar]
- Berggren, Å. Reflexivitet inom arkeologin. In Reflexiv fältarkeologi? Återsken av ett Seminarium; Berggren, Å., Burström, M., Eds.; Malmö Kulturmiljö & Riksantikvarieämbetet: Stockholm, Sweden; Malmö, Sweden, 2002; Volume 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Berggren, Å. Reflexive approaches in archaeology, development of. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology; Smith, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 6249–6257. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Draft Medium Term Plan 1990–1995; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Charter on the Preservation of the Digital Heritage; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization Organisation des Nations Unies pour l’éducation, la Science et la Culture: Paris, France, 2009; Document Code: CL/3865. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.; Remondino, F.; Guidi, G. Principali tecniche e strumenti per il rilievo tridimensionale in ambito archeologico. Archeol. Calc. 2011, 22, 169–198. [Google Scholar]
- Remondino, F.; Pizzo, S.D.; Kersten, T.; Troisi, S. Low-Cost and Open-Source Solutions for Automated Image Orientation—A Critical Overview. In Proceedings of the Progress in Cultural Heritage Preservation, Limassol, Cyprus, 29 October–3 November 2012; pp. 40–54. [Google Scholar]
- De Reu, J.; Plets, G.; Verhoeven, G.; de Smedt, P.; Bats, M.; Cherretté, B.; de Maeyer, W.; Deconynck, J.; Herremans, D.; Laloo, P.; et al. Towards a three-dimensional cost-effective registration of the archaeological heritage. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 40, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deseilligny, M.P.; Luca, L.D.; Remondino, F. Automated image-based procedures for accurate artifacts 3D modeling and orthoimage generation. Geoinf. FCE CTU 2011, 6, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallot, P.; Gil, M. Methodology for 3d acquisition of highly reflective goldsmithing artefacts. In The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop LowCost 3D—Sensors, Algorithms, Applications, Strasbourg, France, 2–3 December 2019; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Leibniz University Hannover Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation Nienburger Str. 1 D-30167: Hannover, Germany, 2019; Volume XLII-2/W17, pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, M.; Moreno-Escribano, J.C.; Monterroso-Checa, A. Photogrammetric Acquisitions in Diverse Archaeological Contexts Using Drones: Background of the Ager Mellariensis Project (North of Córdoba-Spain). Drones 2020, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, M.; Berger, L.; Mathelier, R.; Agrafiotis, P.; Skarlatos, D. Software comparison for underwater archaeological photogrammetric applications. In The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Proceedings of the 27th CIPA International Symposium “Documenting the Past for a Better Future”, Ávila, Spain, 1–5 September 2019; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Leibniz University Hannover Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation Nienburger Str. 1 D-30167: Hannover, Germany, 2019; Volume XLII-2/W15. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, H.; Champion, E. To 3D or Not 3D: Choosing a Photogrammetry Workflow for Cultural Heritage Groups. Heritage 2019, 2, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, G.; Beraldin, J.A.; Atzeni, C. High-Accuracy 3-D Modeling of Cultural Heritage: The Digitizing of Donatello’s “Maddalena”. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoudis, A.; Arnaoutoglou, F.; Pavlidis, G.; Tsiafakis, D.; Chamzas, C. A versatile workflow for 3D reconstructions and modelling of cultural heritage sites based on open source software. In Proceedings of the Virtual Systems and Multimedia Dedicated to Digital Heritage Conference, Limassol, Cyprus, 20–26 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barszcz, M.; Montusiewicz, J.; Paśnikowska-Łukaszuk, M.; Sałamacha, A. Comparative Analysis of Digital Models of Objects of Cultural Heritage Obtained by the “3D SLS” and “SfM” Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Učakar, A.; Sterle, A.; Vuga, M.; Pečak, T.T.; Trček, D.; Ahtik, J.; Košak, K.; Muck, D.; Tomc, H.G.; Kočevar, T.N. 3D Digital Preservation, Presentation, and Interpretation of Wooden Cultural Heritage on the Example of Sculptures of the FormaViva Kostanjevica Na Krki Collection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwan, Y.D. Current Situation and Prospect of Digital Heritage Study. J. Cult. Contents 2013, 3, 95–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hahulina, N.; Maslikhova, L.; Akimova, S. Modern Technologies Applied to Archaeological Research in Voronezh Region. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 272, p. 032037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Petrovic, V.; Meyer, D.; Rissolo, D.; Kuester, F. Fusion of multimodal three-dimensional data for comprehensive digital documentation of cultural heritage sites. Digit. Herit. 2015, 2, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maietti, F.; Di Giulio, R.; Balzani, M.; Piaia, E.; Medici, M.; Ferrari, F. 3D Data Acquisition and Modelling of Complex Heritage Buildings. In Proceedings of the Digital Cultural Heritage Final Conference of the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Initial Training Network for Digital Cultural Heritage, ITN-DCH 2017 Olimje, Slovenia, May 23–25 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Coburn, E.; Lanzi, E.; O’Keefe, E.; Stein, R.; Whiteside, A. The Cataloging Cultural Objects experience: Codifying practice for the cultural heritage community. IFLA J. 2010, 36, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, M. Practical Issues in Applying Metadata Schemas and Controlled Vocabularies to Cultural Heritage Information. Cat. Classif. Q. 2003, 36, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maietti, F.; Di Giulio, R.; Piaia, E.; Medici, M.; Ferrari, F. Enhancing Heritage fruition through 3D semantic modelling and digital tools: The INCEPTION project. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Volume 364, Florence Heri-Tech—The Future of Heritage Science and Technologies, Florence, Italy, 16–18 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, M.; Jones, S. DCC Data Management Plan Content Checklist; Digital Curation Centre: Scotland, UK, 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S. Digital Curation: The development of a discipline within information science. J. Doc. 2018, 74, 1318–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragin, M.H.; Heidorn, P.B.; Palmer, C.L.; Smith, L.C. An Educational Program on Data Curation; Institute of Museum and Library Services RE-05-06-0036-06; Illinois Library: Springfield, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S. Digital Curation: The Emergence of a New Discipline. Int. J. Digit. Curation 2011, 6, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owda, A.; Balsa-Barreiro, J.; Fritsch, D. Methodology for digital preservation of the cultural and patrimonial heritage: Generation of a 3D model of the Church St. Peter and Paul (Calw, Germany) by using Laser scanning and digital photogrammetry. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, V.; Karatas, T.; Damiano, R.; Mattutino, C.; Sasakura, M. Bringing Digital Curation to Archaeological Projects: Evidence from the BeArchaeo Project. In Proceedings of the AVI2CH Workshop on Advanced Visual Interfaces and Interactions in Cultural Heritage co-located with 2020 International Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI 2020), Isola d’Ischia, Naples, Italy, 29 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Benardou, A.; Champion, E.; Dallas, C.; Hughes, L.M. (Eds.) Cultural Heritage Infrastructures in Digital Humanities; Series: Digital Research in the Arts and Humanities; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2018; ISBN 9781472447128. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.; Weller, K.; Foster, A.; Rafferty, P. Managing Digital Cultural Objects; Facet: Online, 2018; ISBN 9781783301539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantopoulos, P.; Dallas, C. Aspects of a digital curation agenda for cultural heritage. In IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilis, D.; Dallas, C.; Angelis, S. A curation-oriented thematic aggregator. In International Conference on Theory and Practice of Digital Libraries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R. Digital Curation of Photogrammetric Data. In Proceedings of the 84th Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 10–14 April 2019. tDAR id: 451423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L. 3D reconstruction methods for digital preservation of cultural heritage: A survey. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 50, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Russo, M.; Guidi, G. Main techniques and tools for three-dimensional survey in the archaeological field. Archeol. Calc. 2011, 22, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Khalloufi, H.; Azough, A.; Ennahnahi, N.; Kaghat, F.Z. Low-cost terrestrial photogrammetry for 3d modeling of historic sites: A case study of the marinids’ royal necropolis city of Fez, Morocco. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2020, 20, 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, F.M.; Mohammed, M.U.; Kadhim, S.J. Architectural and cultural heritage conservation using low-cost cameras. Appl. Res. J. 2017, 3, 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Denmark, E.L. A Technical Analysis of Photogrammetry with Reality Capture. Ph.D. Thesis, Computer Science and Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, H.; Engberg, A.; Pope, S.T. A Comparison of 3d Modeling Programs; ATON Project/CREATE; D.o.M, University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-F. A Comparison Study of Five 3D Modeling Systems Based on the SfM Principles; Technical Report 2011–01; Visualize Inc.: Goleta, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi, M.; Furini, A.; Russo, V.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Russo, P. Accuracy of cultural heritage 3D models byRPAS and terrestrial photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapitsch, A.; Park, J.; Zhou, Q.-Y.; Koltun, V. Tanks and Temples: Benchmarking Large-Scale Scene Reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagati, C.; Inzerillo, L.; Di Paola, F. Image based modeling techniques for architectural heritage 3d Digitalization: Limits and potentialities. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XXIV International CIPA Symposium, Strasbourg, France, 2–6 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Montusiewicz, J.; Barszcz, M.; Korga, S. Preparation of 3D Models of Cultural Heritage Objects to Be Recognised by Touch by the Blind—Case Studies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopigno, R.; Callieri, M.; Cignoni, P.; Corsini, M.; Dellepiane, M.; Ponchio, F.; Ranzuglia, G. 3D Models for Cultural Heritage: Beyond Plain Visualization. Computer 2011, 44, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, H.; Champion, E.; Bekele, M. From photo to 3D to mixed reality: A complete workflow for cultural heritage visualisation and experience. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Heritage 2019, 13, e00102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ştefan, R.-M. A Comparison of Data Classification Methods. Procedia Econ. Finance 2012, 3, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintigh, K.W. The promise and challenge of archaeological data integration. Am. Antiq. 2006, 71, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadanza, E.; Maietti, F.; Ziri, A.E.; Di Giulio, R.; Medici, M.; Ferrari, F.; Bonsma, P.; Turillazzi, B. Semantic Web Technologies Meet Bim for Accessing and Understanding Cultural Heritage. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330771926_SEMANTIC_WEB_TECHNOLOGIES_MEET_BIM_FOR_ACCESSING_AND_UNDERSTANDING_CULTURAL_HERITAGE (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Karatas, T.; Lombardo, V. A Multiple Perspective Account of Digital Curation for Cultural Heritage: Tasks, Disciplines and Institutions. In Proceedings of the Adjunct Publication of the 28th ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization (UMAP ‘20 Adjunct), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 14–17 July 2020; pp. 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).