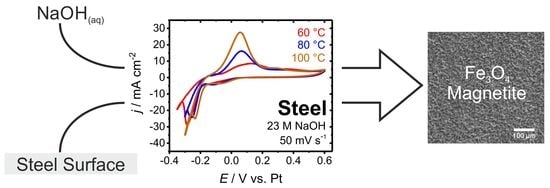
An Electrochemical Route for Hot Alkaline Blackening of Steel: A Nitrite Free Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Blackening
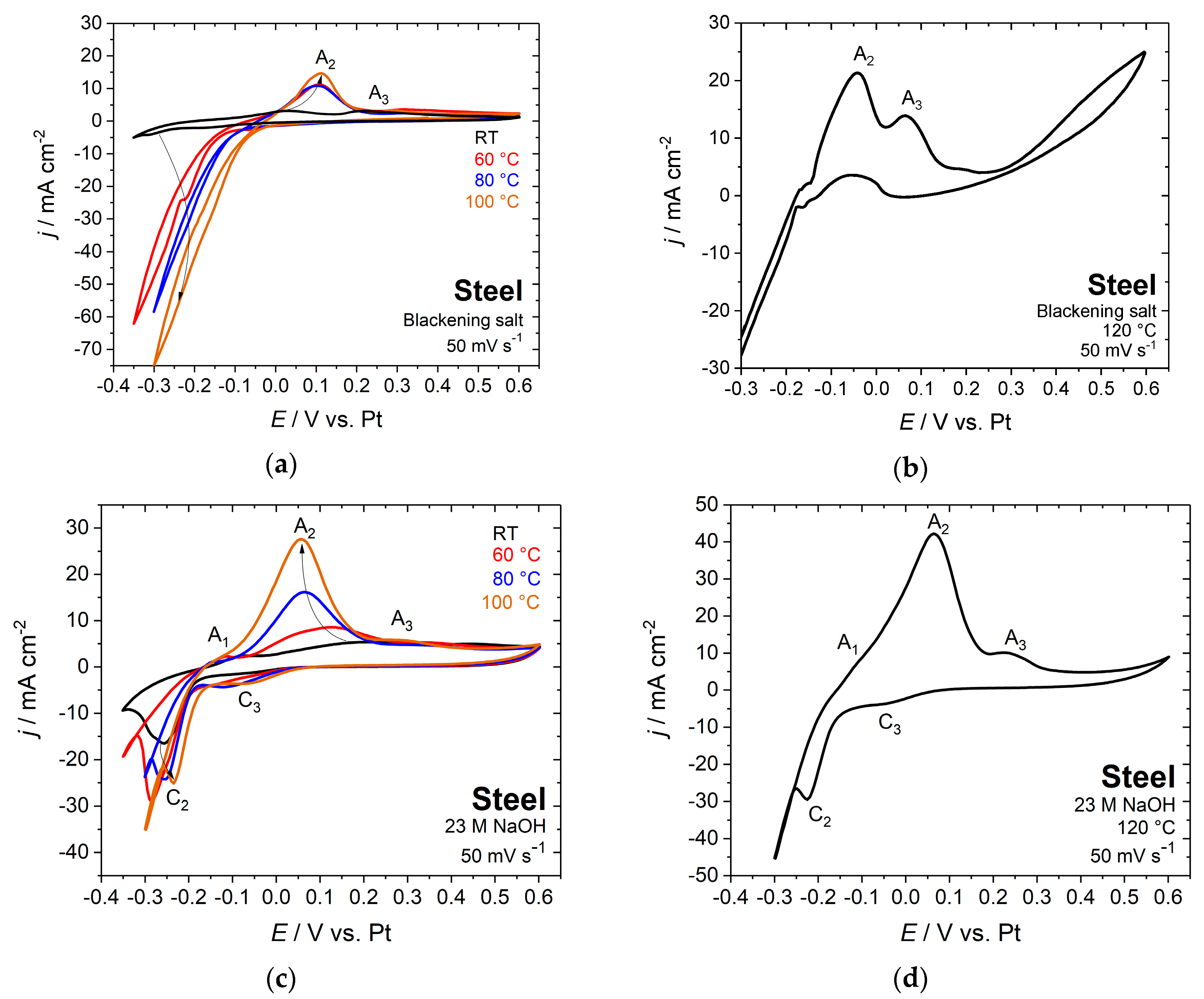
- Blackening solution at 80 °C: E = 0.5 V vs. Pt
- Blackening solution at 100 °C: E = 0 V vs. Pt
- 23 M NaOH at 80 °C: E = 0.6 V vs. Pt
- 23 M NaOH at 100 °C: E = 0.1 V vs. Pt
- 23 M NaOH at 120 °C: E = 0.1 V vs. Pt
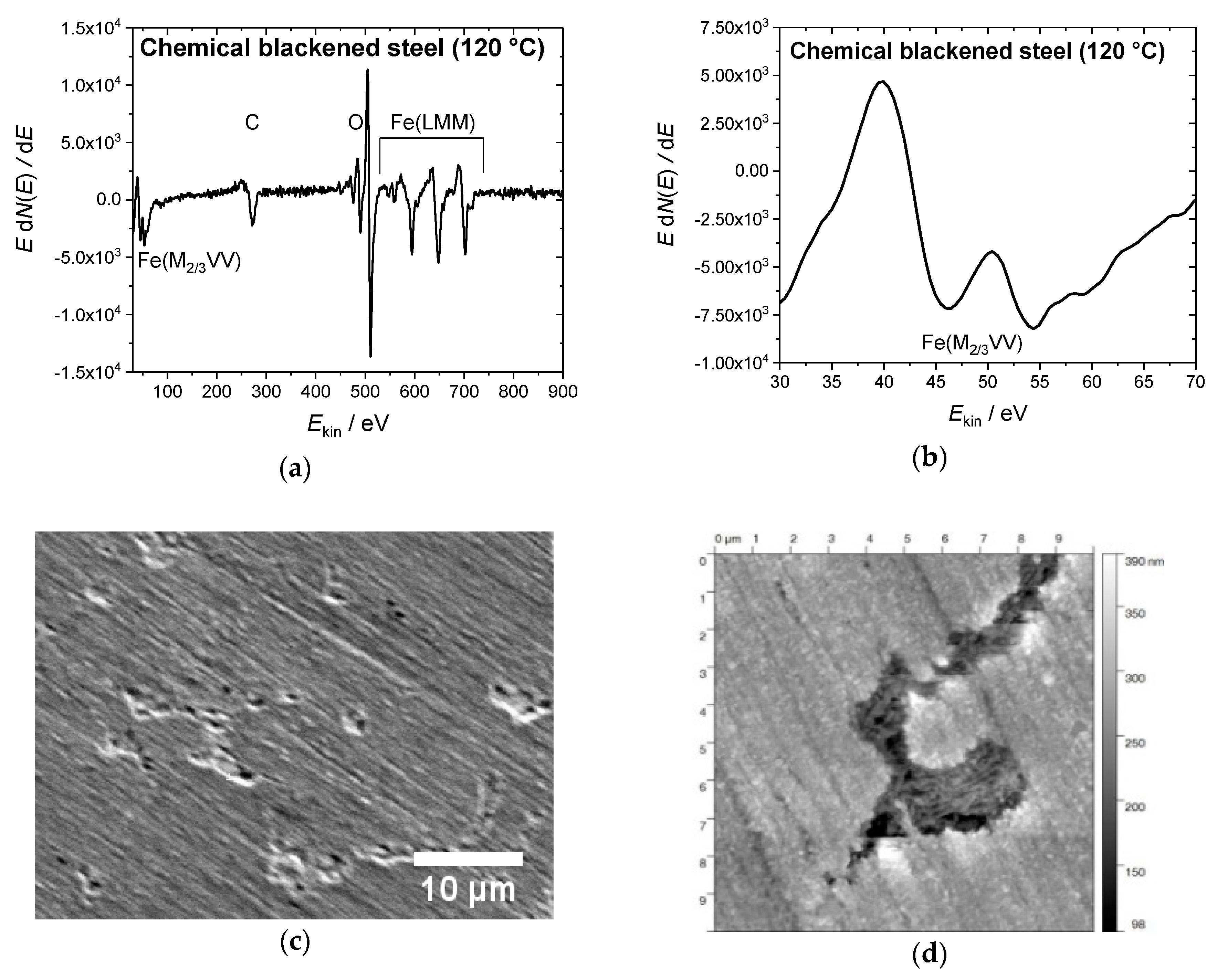
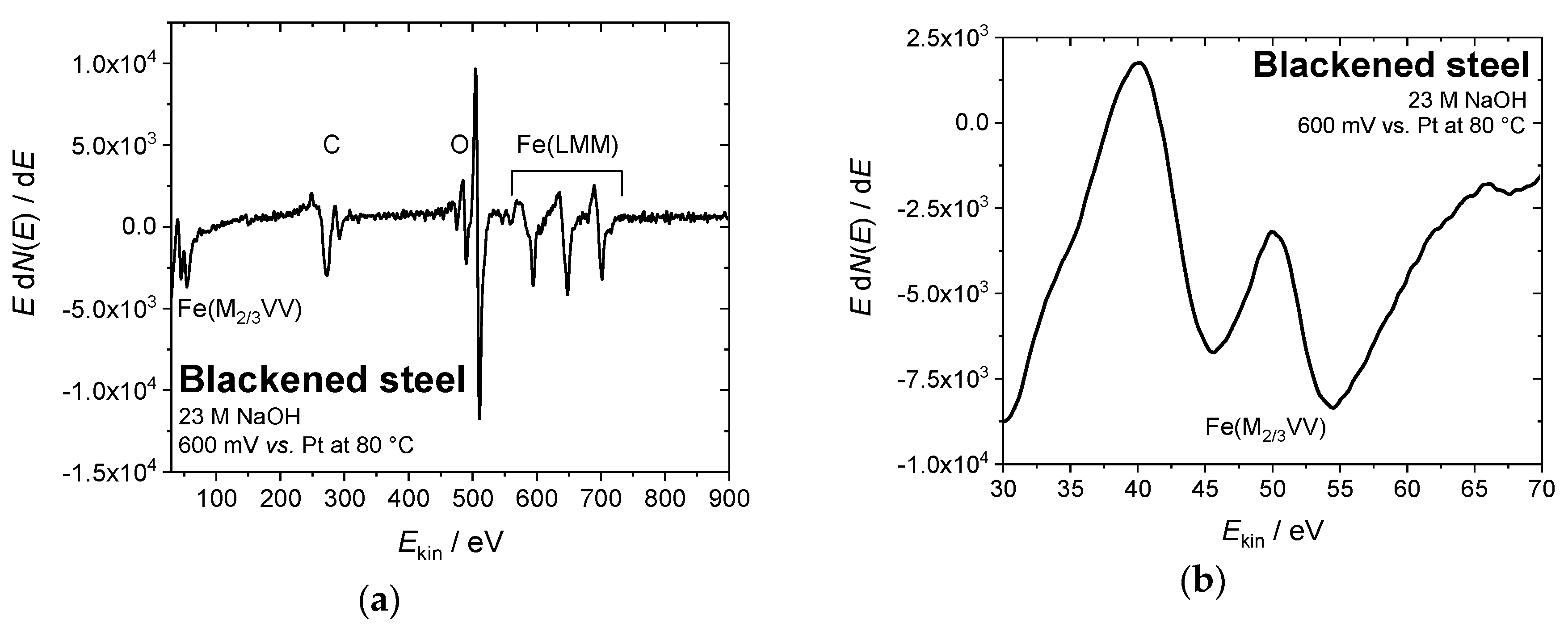
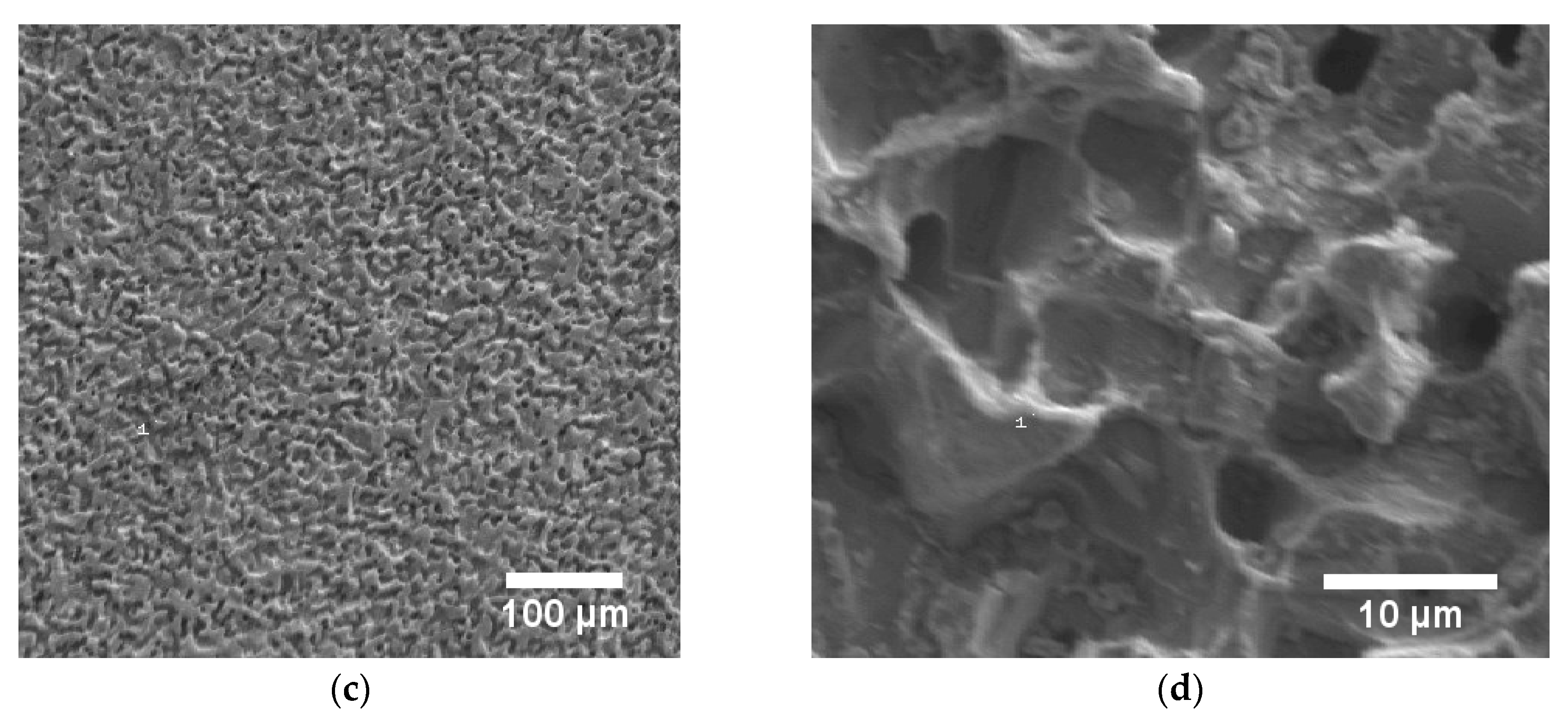
2.3. Characterization of the Blackened Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Blackening
3.2. Electrochemical Blackening
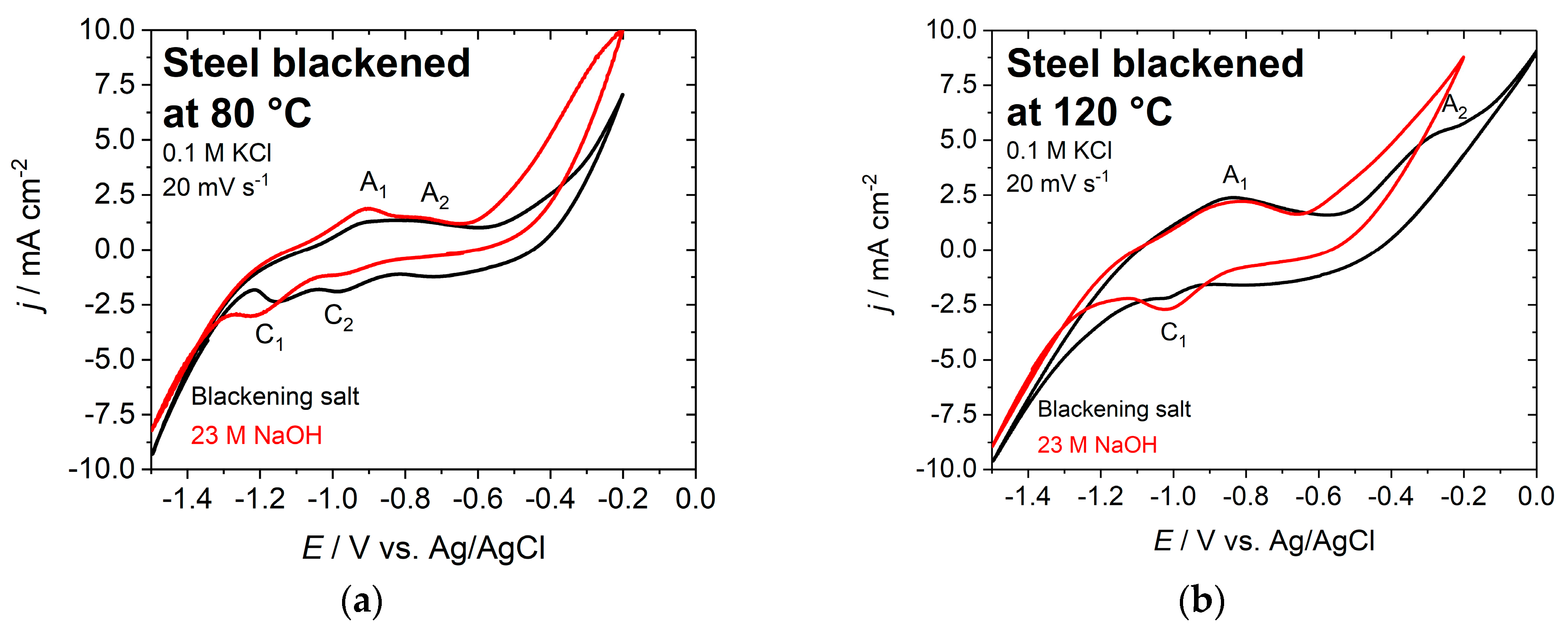
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization
4. Conclusions
- 23 M NaOH, 0.6 V vs. Pt and 80 °C,
- 23 M NaOH, 0.1 V vs. Pt and 120 °C, and
- blackening solution, 0.5 V vs. Pt and 80 °C.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuśmierczak, S.; Makovský, M. Problems of Blackening of Steel Parts in Technical Practice. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 244, 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, R.W. Blackening of Ferrous Metals. Met. Finish. 2007, 105, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machmudah, S.; Zulhijah, R.; Wahyudiono; Setyawan, H.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Magnetite Thin Film on Mild Steel Formed by Hydrothermal Electrolysis for Corrosion Prevention. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 268, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Yazdani Khan, H.; Heidarpour, A. Comparison of Anti-Corrosive Properties between Hot Alkaline Nitrate Blackening and Hydrothermal Blackening Routes. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 676, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, R.M.; Hackerman, N. Kinetic Studies on Formation of Black-Oxide Coatings on Mild Steel in Alkaline Nitrite Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1957, 104, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. The Mechanism of High Temperature Aqueous Corrosion of Stainless Steels. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghuraj, A.R.; Saju, K.K. Black Oxide Conversion Coating on Metals: A Review of Coating Techniques and Adaptation for SAE 420A Surgical Grade Stainless Steel. In Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 4, pp. 9534–9541. [Google Scholar]
- Sankara Narayanan, T.S.N. Phosphate Conversion Coatings—A Metal Pretreatment Process. Corros. Rev. 1994, 12, 201–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofre-Bustamente, E.; Domínguez-Crespo, M.A.; Genescá-Llongueras, J.; Rodríguez-Gómez, F.J. Characteristics of Blueing as an Alternative Chemical Conversion Treatment on Carbon Steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4666–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y. A Point Defect Model for Anodic Passive Films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1981, 128, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, Z.; Noël, J.J.; Wren, J.C. Oxide Growth and Conversion on Carbon Steel as a Function of Temperature over 25 and 80°C under Ambient Pressure. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 6661–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiss, E.; Schikorr, G. Über Das Ferrohydroxyd (Eisen-2-Hydroxyd). Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 1928, 172, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikorr, G. Über Eisen(II)-Hydroxyd Und Ein Ferromagnetisches Eisen(III)-Hydroxyd. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 1933, 212, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vershok, D.B.; Misurkin, P.I.; Timofeeva, V.A.; Solov’eva, A.B.; Kuznetsov, Y.I.; Timashev, S.F. On the Formation of Magnetite Coatings on Low-Carbon Steel in Ammonium Nitrate Solution. Prot. Met. 2008, 44, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.I.; Vershok, D.B.; Timashev, S.F.; Solov’eva, A.B.; Misurkin, P.I.; Timofeeva, V.A.; Lakeev, S.G. Features of Formation of Magnetite Coatings on Low-Carbon Steel in Hot Nitrate Solutions. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2010, 46, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cao, F.; Zuo, D.; Zhu, L.; Jin, D.; Yao, K. A New Hydrothermal Blackening Technology for Fe3O4 Coatings of Carbon Steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 5905–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverskog, B.; Puigdomenech, I. Revised Pourbaix Diagrams for Iron at 25–300 °C. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-Alhosseini, A.; Khan, H.Y. Anodic Oxidation of Carbon Steel at High Current Densities and Investigation of Its Corrosion Behavior. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2017, 48, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, T.D.; Schmuki, P.; Virtanen, S. Properties of the Nanoporous Anodic Oxide Electrochemically Grown on Steel in Hot 50% NaOH. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, C45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, T.D.; Dotson, T.C.; Dotson, K.T.; Gabay, S.J.; Sloan, T.B.; Ferrell, S.G. Anodizing Steel in KOH and NaOH Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, C579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedot’ev, N.P.; Grilikhes, S.Y. Anodizing Cooper, Magnesium, Zinc, Cadmium, Steel and Silver. Electroplat. Met. Finish. 1960, 13, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. Brünieren von Bauteilen Aus Eisenwerkstoffen—Anforderungen Und Prüfverfahren; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Müsig, H.-J.; Arabczyk, W. The Interaction of Oxygen with the Iron (111) Surface, Mainly Studied by AES. Krist. Tech. 1980, 15, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T. The Thermodynamic Consideration for Fe-H2O System at 25 °C. Corros. Sci. 1973, 13, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünnwald, J.; Otto, A. Ramanspektroskopie an Oxidschichten Auf Reineisen Im Elektrolyten. Fresenius’ Zeitschrift für Analytische Chemie 1984, 319, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrebler Guzmán, R.S.; Vilche, J.R.; Arvía, A.J. The Potentiodynamic Behaviour of Iron in Alkaline Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 1979, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Daub, K.; Zhang, X.; Noel, J.J.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Wren, J.C. Oxide Formation and Conversion on Carbon Steel in Mildly Basic Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5727–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekerevac, M.; Nikolic-Bujanovic, L.; Simicic, M. Investigation of Electrochemical Synthesis of Ferrate, Part I: Electrochemical Behavior of Iron and Its Several Alloys in Concentrated Alkaline Solutions. Hem. Ind. 2009, 63, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mácová, Z.; Bouzek, K. The Influence of Electrolyte Composition on Electrochemical Ferrate(VI) Synthesis. Part III: Anodic Dissolution Kinetics of a White Cast Iron Anode Rich in Iron Carbide. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Comins, J.D.; Cukrowski, I. The Growth of the Passive Film on Iron in 0.05 M NaOH Studied in Situ by Raman Microspectroscopy and Electrochemical Polarization. Part II: In Situ Raman Spectra of the Passive Film Surface during Growth by Electrochemical Polarization. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Kaus, R.; Oberst, M. Transpassive Dissolution of Iron to Ferrate(VI) in Concentrated Alkali Hydroxide Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 1985, 30, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidbaur, H. The History and the Current Revival of the Oxo Chemistry of Iron in Its Highest Oxidation States: Fe VI-Fe VIII. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 2018, 644, 536–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfiliev, Y.D.; Benko, E.M.; Pankratov, D.A.; Sharma, V.K.; Dedushenko, S.K. Formation of Iron(VI) in Ozonalysis of Iron(III) in Alkaline Solution. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 2789–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, J.D.; Bielski, B.H.J. Pulse Radiolysis Studies of Alkaline Iron(III) and Iron(VI) Solutions. Observation of Transient Iron Complexes with Intermediate Oxidation States. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, N. Electrochemistry and Corrosion Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]





| Electrolyte | T/°C | E/V vs. Pt | jfinal/mA cm−2 | Ra/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackening salt solution 1 kg·L−1 | 80 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 15 ± 4 |
| 100 | 0 | 0.6 | 38 ± 6 | |
| 130 | −0.05 (EOC) | (0) | 12 ± 1 | |
| NaOH (23 M) | 80 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 30 ± 11 |
| 100 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 59 ± 7 | |
| 120 | 0.1 | 19.5 | 61 ± 11 |
| Sample | Ecorr/V vs. Ag/AgCl | jcorr/µA cm−2 | |βc|/V dec−1 | βa/V dec−1 | RP/kΩ cm−2 | kcorr/mm a−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | −0.67 | 7.1 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 2.7 | 0.082 |
| Blackening salt solution 80 °C | −0.74 | 1.2 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 6.6 | 0.014 |
| Blackening salt solution 130 °C | −0.57 | 2.0 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 5.6 | 0.023 |
| NaOH 80 °C | −0.84 | 4.4 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 3.0 | 0.051 |
| NaOH 120 °C | −0.75 | 2.8 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 3.7 | 0.033 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eckl, M.; Zaubitzer, S.; Köntje, C.; Farkas, A.; Kibler, L.A.; Jacob, T. An Electrochemical Route for Hot Alkaline Blackening of Steel: A Nitrite Free Approach. Surfaces 2019, 2, 216-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020017
Eckl M, Zaubitzer S, Köntje C, Farkas A, Kibler LA, Jacob T. An Electrochemical Route for Hot Alkaline Blackening of Steel: A Nitrite Free Approach. Surfaces. 2019; 2(2):216-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleEckl, Maximilian, Steve Zaubitzer, Carsten Köntje, Attila Farkas, Ludwig A. Kibler, and Timo Jacob. 2019. "An Electrochemical Route for Hot Alkaline Blackening of Steel: A Nitrite Free Approach" Surfaces 2, no. 2: 216-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020017
APA StyleEckl, M., Zaubitzer, S., Köntje, C., Farkas, A., Kibler, L. A., & Jacob, T. (2019). An Electrochemical Route for Hot Alkaline Blackening of Steel: A Nitrite Free Approach. Surfaces, 2(2), 216-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020017