Adipokines as Possible Players in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Electrophysiological Evaluation of Their Role in Causing Functional Gastrointestinal Alterations in Murine Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. RES Slightly Affects Gastric Smooth Muscle Cell Membrane Passive Properties in Mice
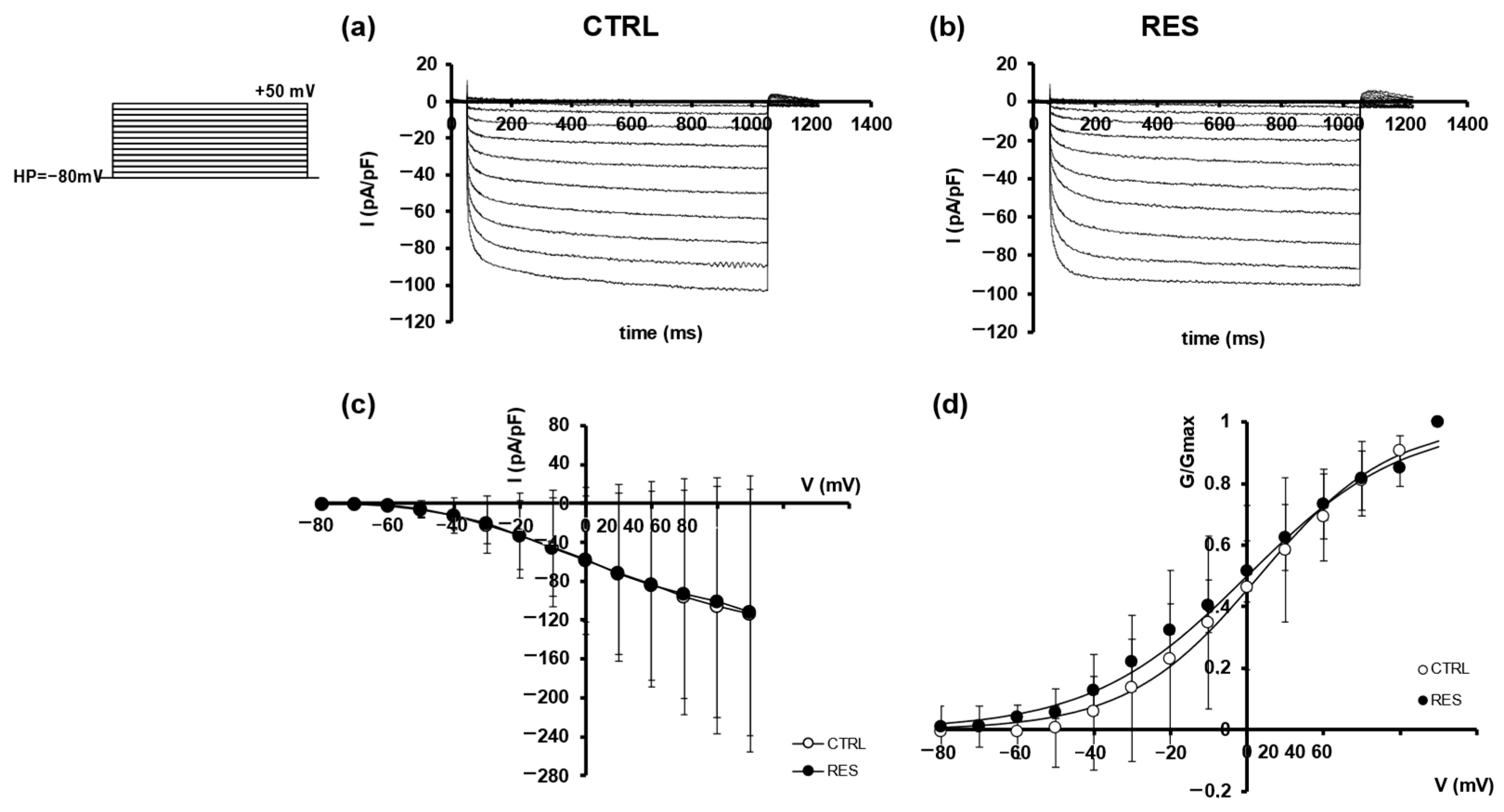
2.2. Effects of RES on SMCs Ion Currents
3. Discussion
3.1. Adipokines and IBD
3.2. Possible Mechanisms of Action of RES
3.3. Significance of RES Functional Effect on Gastric Fundus in IBD
3.4. Limitations of the Study
3.5. Novel Findings
3.6. Concluding Remarks
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Treatments
4.2. Tissue Sample Preparation and Electrophysiological Records
4.3. Data Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moazzami, B.; Moazzami, K.; Rezaei, N. Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Manifestations, genetics and Diagnosis. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2019, 61, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuquteish, D.; Putra, J. Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Involvement of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pathological Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Murad, M.H.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Malekzadeh, R.; Talley, N.J. Meta-analysis: Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, J.B.; Gopal, P.; Greenson, J.K. The Clinical Significance of Focally Enhanced Gastritis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bartee, M.Y.; Yaron, J.R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, D.; Hogue Ian B and Bullard, W.L.; Tibbetts, S.; Lucas, A.R. Mouse Gamma Herpesvirus MHV-68 Induces Severe Gastrointestinal(GI) Dilatation in Interferon Gamma Receptor-Deficient Mice(IFNγR-/-) That Is Blocked by Interleukin-10. Viruses 2018, 10, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Binnewies, U.; Rösch, M.; Juul Holst, J.; Beglinger, C.; Andresen Viola and Layer, P. Gastric Emptying and Disease Activity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigneur, B.; Seksik, P.; Viola, S.; Viala, J.; Beaugerie, L.; Girardet, J.-P.; Ruemmele, F.M.; Cosnes, J. Natural History of Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.B.; Monteiro, I.M. Diagnosis and Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children. BMJ 2017, 357, j2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Ungaro, R.C.; Petrick, L.M.; Chan, A.T.; Porter, C.K.; Khalili, H.; Ananthakrishnan, A.; Balasubramanian, R.; Burke, K.E.; Challa, P.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Is Associated With Prediagnostic Perturbances in Metabolic Pathways. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 147–150.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Gupta, J.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Gut Biofilm Forming Bacteria in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedzadeh, N.; Rahimlou, M.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Shahrokh, S.; Reza Zali, M.; Mirmiran, P. Association between Adipokines Levels with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Systematic Reviews. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3280–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S.-S. Roles of Adipokines in Digestive Diseases: Markers of Inflammation, Metabolic Alteration and Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmiris, K.; Koutroubakis, I.E. Resistin: Another Rising Biomarker in Inflammatory Bowel? Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 1035–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broedl, U.C.; Schachinger, V.; Lingenhel, A.; Lehrke, M.; Stark, R.; Seibold, F.; Göke, B.; Kronenberg, F.; Parhofer, K.G.; Konrad-Zerna, A. Apolipoprotein A-IV Is an Independent Predictor of Disease Activity in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garella, R.; Cassioli, E.; Chellini, F.; Tani, A.; Rossi, E.; Idrizaj, E.; Guasti, D.; Comeglio, P.; Palmieri, F.; Parigi, M.; et al. Defining the Molecular Mechanisms of the Relaxant Action of adiponectin on Murine Gastric Fundus Smooth Muscle: Potential Perspectives on Eating Disorder Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrizaj, E.; Garella, R.; Nistri, S.; Squecco, R.; Baccari, M.C. Evidence That Resistin Acts on the Mechanical Responses of the Mouse Gastric Fundus. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 930197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrizaj, E.; Garella, R.; Castellini, G.; Francini, F.; Ricca, V.; Baccari, M.C.; Squecco, R. Adiponectin Decreases Gastric Smooth Muscle Cell Excitability in Mice. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garella, R.; Bernacchioni, C.; Chellini, F.; Tani, A.; Palmieri, F.; Parigi, M.; Guasti, D.; Cassioli, E.; Castellini, G.; Ricca, V.; et al. Adiponectin Modulates Smooth Muscle Cell Morpho-Functional in Murine Gastric Fundus via Sphingosine Kinase 2. Life 2023, 13, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Shao, D.; Zhang, R.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Drinking Water Fluorosis on L-Type Calcium Channel of hippocampal Neurons in Mice. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Shi, Y.L. Characterization of an Inward-Rectifying Potassium Current in NG108-15 Neuroblastoma Glioma Cells. Pflug. Arch. 1997, 433, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, T.; Karnup, S.; Shimizu, N.; Ni, J.; de Groat, W.C.; Yoshimura, N. Therapeutic Effects of P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibition on Hyperexcitability of Capsaicin Sensitive Bladder Afferent Neurons in Mice with Spinal Cord Injury. Life Sci. 2023, 325, 121738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, C.; Kasirer, M.Y.; Pan, J.; Shifrin, Y.; Belik, J. Pantoprazole Decreases Gastroesophageal Muscle Tone in Newborn Rats via Rho-Kinase Inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G390–G396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Cheon, J.H. Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Recent advances in Biologic Therapies. Immune Netw. 2017, 17, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasant, D.H.; Ford, A.C. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Inflammatory Bowel: Time for a Paradigm Shift? World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3712–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracie, D.J.; Williams, C.J.M.; Sood, R.; Mumtaz, S.; Bholah, H.M.; Hamlin, J.P.; Ford, A.C. Poor Correlation between Clinical Disease Activity and Mucosal, and the Role of Psychological Comorbidity, in inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Johnson, A.C.; Grundy, D. Gastrointestinal Physiology and Function. In Gastrointestinal Pharmacology; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin as an Anti-Inflammatory Factor. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 380, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnoush, A.H.; Maroufi, S.P.; Reshadmanesh, T.; Kia, Y.M.; Norouzi, M.; Mohammadi, S.M.; Klisic, A.; Khalaji, A. Circulatory Resistin Levels in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kim, S.-O.; Marshall, H.E.; Stamler, J.S. Protein S-Nitrosylation: Purview and Parameters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Snyder, S.H.; Zweier, J.L. Nitric Oxide Synthase Generates Superoxide and Nitric Oxide In Arginine-Depleted Cells Leading to Peroxynitrite-Mediated Cellular Injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6770–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.-L.R.; Ye, J.-S.; Yu, A.C.H.; Sheu, F.-S. Differential Mechanisms Underlying the Modulation of Delayed-Rectifier K+channel in Mouse Neocortical neurons by Nitric Oxide. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 2167–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.G. Oxidants in Physiological Processes. In Reactive Oxygen Species; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Máthé, C.; Beyer, D.; M-Hamvas, M.; Vasas, G. The Effects of Microcystins (Cyanobacterial Heptapeptides) on the Eukaryotic Cytoskeletal System. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.A.; de Andrade, K.Q.; Dos Santos, J.C.F.; Araújo, O.R.P.; Goulart, M.O.F. Antioxidant Therapy for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Does It Work? Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrizaj, E.; Garella, R.; Squecco, R.; Baccari, M.C. Can Adiponectin Have an Additional Effect on the Regulation of Food Intake by Inducing Gastric Motor Changes? World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.; He, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, L.; Fan, N.; Liu, X. C3 Transferase-Expressing ScAAV2 Transduces Ocular Anterior Segment Tissues and Lowers Intraocular Pressure in Mouse and Monkey. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemanyi, F.; Baidouri, H.; Burns, A.R.; Raghunathan, V. Dexamethasone and Glucocorticoid-Induced Matrix Temporally Modulate Key Integrins, Caveolins, Contractility, and Stiffness in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Qian, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. RhoA/ROCK-YAP/TAZ Axis Regulates the Fibrotic Activity in Dexamethasone-Treated Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 728932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gang, X.; Zhou, T.; Han, J.; Cao, Y.; Qi, B.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Metformin Protects Trabecular Meshwork against Oxidative injury via Activating Integrin/ROCK Signals. eLife 2023, 12, e81198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrizaj, E.; Nistri, S.; Zizi, V.; Baccari, M.C. Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase as a Shared Target for the effects of Adiponectin and Resistin on the Mechanical responses of the Mouse Gastric Fundus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squecco, R.; Garella, R.; Luciani, G.; Francini, F.; Baccari, M.C. Muscular Effects of Orexin A on the Mouse Duodenum: Mechanical and Electrophysiological Studies. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 5231–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacchioni, C.; Squecco, R.; Gamberi, T.; Ghini, V.; Schumacher, F.; Mannelli, M.; Garella, R.; Idrizaj, E.; Cencetti, F.; Puliti, E.; et al. S1P Signalling Axis Is Necessary for Adiponectin-Directed Regulation of Electrophysiological Properties and Oxidative Metabolism in C2C12 Myotubes. Cells 2022, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
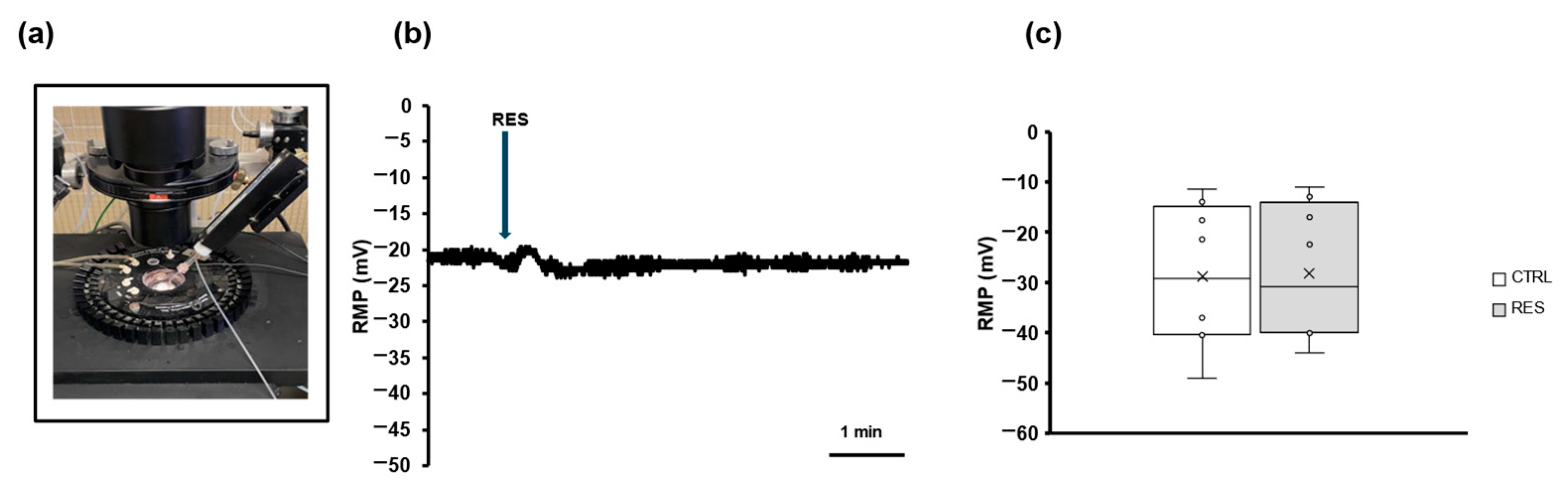
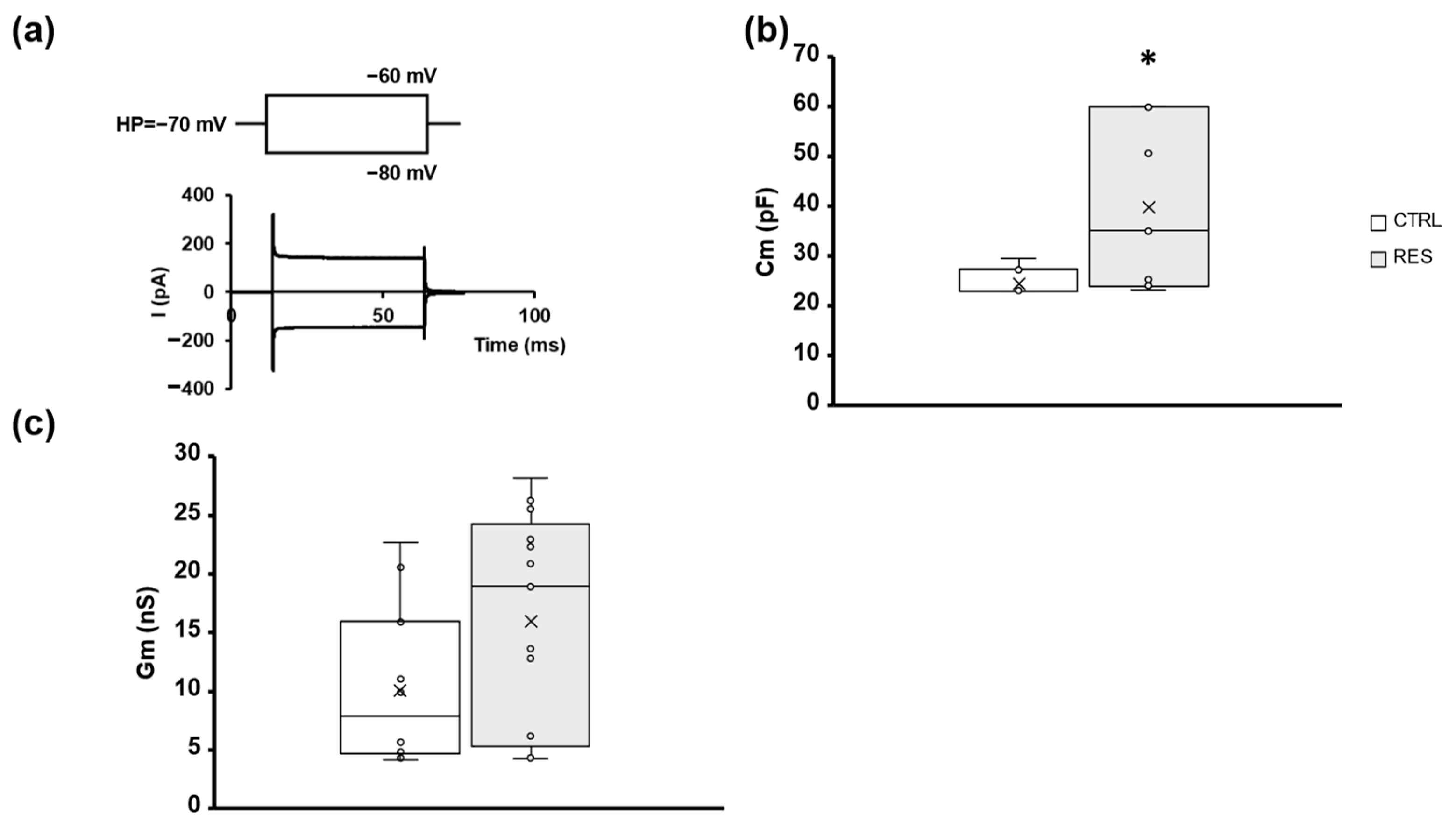

| CTRL | RES | |
|---|---|---|
| RMP (mV) | −28.87 ± 14.32 n = 8 | −28.25 ± 13.7 n = 8 |
| Cm (pF) | 24.54 ± 2.7 n = 7 | 39.77 ± 16.78 * n = 7 |
| Gm (nS) | 10.06 ± 6.41 n = 14 | 15.91 ± 9.23 n = 17 |
| Outward Current | Inward Current | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | RES | CTRL | RES | |
| V0.5 (mV) | 4.50 ± 23.01 n = 3 | 18.04 ± 7.96 n = 3 | 3.09 ± 7.17 n = 3 | 0.00 ± 0.21 n = 3 |
| k (mV) | 20.00 ± 4.61 n = 3 | 14.55 ± 3.84 n = 3 | 17.24 ± 2.04 n = 3 | 20.47 ± 3.45 n = 3 |
| R2 | 0.991 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.992 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garella, R.; Palmieri, F.; Squecco, R. Adipokines as Possible Players in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Electrophysiological Evaluation of Their Role in Causing Functional Gastrointestinal Alterations in Murine Tissue. Gastrointest. Disord. 2024, 6, 513-525. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020035
Garella R, Palmieri F, Squecco R. Adipokines as Possible Players in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Electrophysiological Evaluation of Their Role in Causing Functional Gastrointestinal Alterations in Murine Tissue. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2024; 6(2):513-525. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarella, Rachele, Francesco Palmieri, and Roberta Squecco. 2024. "Adipokines as Possible Players in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Electrophysiological Evaluation of Their Role in Causing Functional Gastrointestinal Alterations in Murine Tissue" Gastrointestinal Disorders 6, no. 2: 513-525. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020035
APA StyleGarella, R., Palmieri, F., & Squecco, R. (2024). Adipokines as Possible Players in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Electrophysiological Evaluation of Their Role in Causing Functional Gastrointestinal Alterations in Murine Tissue. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 6(2), 513-525. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020035


.png)




