Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco
Abstract
1. Introduction
Background
2. Modeling Methods
2.1. Model Inputs
2.2. Modeling Steps
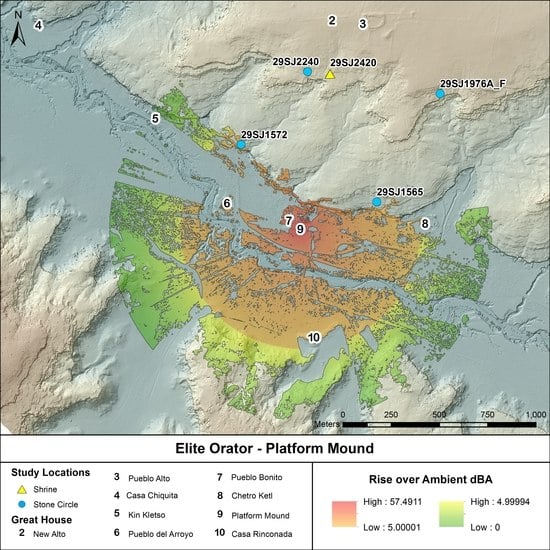
3. Modeling Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes in the Past: Towards a Phenomenology of Sound at the Landscape Level. Presented at the 81st Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–10 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes in the Past: A GIS Approach to Landscape Scale Archaeoacoustics. Presented at the Frontiers in Archaeological Sciences Symposium, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 23–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Witt, D.E.; Primeau, K.E. Soundscapes in the Past: Interaudibility in the Chacoan Built Landscape. Presented at the 82nd Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29 March–2 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes in the Past: Investigating Sound at the Landscape Level. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 19, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, T.; Coben, L.S. Overture: An Invitation to the Archaeological Theater. In Archaeology of Performance: Theaters of Power, Community, and Politics; Inomata, T., Coben, L.S., Eds.; Altamira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2006; pp. 11–44. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.C. Domination and the Arts of Resistance: Hidden Transcripts; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, I.; Zubrow, E.B.W.; Cowan, F. Musical behaviours and the archaeological record: A preliminary study. In Experimental Archaeology; Mathieu, J., Ed.; British Archaeological Reports: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, I.; Watson, A. Acoustics and the human experience of socially-organized sound. In Archaeoacoustics; Scarre, C., Lawson, G., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- D’Errico, F.; Lawson, G. The sound paradox: How to assess the acoustic significance of archaeological evidence? In Archaeoacoustics; Scarre, C., Lawson, G., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Devereux, P. Stone Age Soundtracks: The Acoustic Archaeology of Ancient Sites; Vega: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Eneix, L.C. (Ed.) Archaeoacoustics: The Archaeology of Sound; The OTS Foundation: Myakka City, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, R.; Till, R.; Howell, M. (Eds.) Music & Ritual: Bridging Material & Living Cultures; Ekho Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scarre, C. Sound, place and space: Towards an archaeology of acoustics. In Archaeoacoustics; Scarre, C., Lawson, G., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, A.; Keating, D. Architecture and sound: An acoustic analysis of megalithic monuments in prehistoric Britain. Antiquity 1999, 73, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, M.A. Sensing sonically at Andean Formative Chavín de Huántar, Perú. Time Mind 2017, 10, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.; Markham, B.; Wall, J.N. Acoustical archaeology—Recreating the soundscape of John Donne’s 1622 gunpowder plot sermon at Paul’s Cross. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2013, 19, 015133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, B.; Azevedo, M.; Wall, J.N. Recreating the soundscape of John Donne’s 1622 gunpowder plot sermon at Paul’s Cross. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.N. Transforming the Object of our Study: The Early Modern Sermon and the Virtual Paul’s Cross Project. Available online: http://journalofdigitalhumanities.org/3-1/transforming-the-object-of-our-study-by-john-n-wall/ (accessed on 24 December 2018).
- Reznikoff, I. Sound resonance in prehistoric times: A study of Paleolithic painted caves and rocks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, R.G.; Devereux, P.; Ibison, M. Acoustical resonances of assorted ancient structures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Trematerra, A.; Qandil, A. The Acoustics of the Catacombs. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 39, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Berardi, U. The Acoustic of Cumaean Sibyl. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2017, 30, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Marletta, L.; Sicurella, F.; Ianniello, E. Acoustic measurements in the Ear of Dionysius at Syracuse (Italy). In Proceedings of the 39th International Congress on Noise Control Engineering 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–16 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kolar, M.A. Archaeological Psychoacoustics at Chavín de Huántar, Perú. Ph.D. Dissertation, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M.; de Smet, T. Chacoan Soundscapes. Archaeol. Southwest Mag. 2018, 32, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Andreu, M.; García Benito, C. Acoustics and Levantine rock art: Auditory perceptions in La Valltorta Gorge (Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 3591–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, T.; Farina, A.; Armelloni, E.; Hameau, P.; Díaz-Andreu, M. Echoing landscapes: Echolocation and the placement of rock art in the Central Mediterranean. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 83, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Andreu, M.; Atiénzar, G.G.; Benito, C.G.; Mattioli, T. Do You Hear What I See? Analyzing Visibility and Audibility in the Rock Art Landscape of the Alicante Mountains of Spain. J. Anthropol. Res. 2017, 73, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileson, S. Sound and Landscape. In The Oxford Handbook of Later Medieval Archaeology in Britain; Christopher, G., Alejandra, G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 713–727. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuz, D. Listening to landscapes: Modelling past soundscapes in GIS. Internet Archaeol. 2004, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwosz, C.R. Benchmarks: Ontological Considerations at Two Mojave Desert Petroglyph Labyrinths. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli, T.; Díaz-Andreu, M. Hearing rock art landscapes: A survey of the acoustical perception in the Sierra de San Serván area in Extremadura (Spain). Time Mind 2017, 10, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, J. Experiencing the past? The development of a phenomenological archaeology in British prehistory. Archaeol. Dialogues 2005, 12, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, V.; Whittle, A. Places of Special Virtue: Megaliths in the Neolithic Landscape of Wales; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.H. Phenomenological Approaches in Landscape Archaeology. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2012, 41, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, C. A Phenomenology of Landscape; Routledge: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C. The Materiality of Stone: Explorations in Landscape Phenomenology; Berg: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C. Body and Image: Explorations in Landscape Phenomenology 2; Left Coast Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C. Interpreting Landscapes: Geologies, Topographies, Identities; Explorations in Landscape Phenomenology 3; Left Coast Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M. Phenomenology in archaeology. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology; Smith, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 5909–5917. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilakis, Y. Archaeology and the Senses: Human Experience, Memory, and Affect; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Merleau-Ponty, M. Phenomenology of Perception; Routledge: London, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.; Whitehouse, R.; Brown, K.; Combes, P.; Herring, E.; Thomas, M.S. Phenomenology in practice: Towards a methodology for a ‘subjective’ approach. Eur. J. Archaeol. 2006, 9, 31–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eve, S. Augmenting Phenomenology: Using Augmented Reality to Aid Archaeological Phenomenology in the Landscape. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M. Landscape Phenomenology, GIS and the Role of Affordance. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobera, M. Life on a Pixel: Challenges in the Development of Digital Methods Within an “Interpretive” Landscape Archaeology Framework. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennell, R. Experience and GIS: Exploring the Potential for Methodological Dialogue. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigg, D. Place and Non-place: A Phenomenological Perspective. In Place, Space, and Hermeneutics; Janz, B.B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Trigger, B.G. A History of Archaeological Thought, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hacigüzeller, P. GIS, critique, representation and beyond. J. Soc. Archaeol. 2012, 12, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, D.Z. GIS and Urban Studies: Positivism, Post-Positivism, and Beyond. Urban Geogr. 1994, 15, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingold, T. The Perception of the Environment; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bunzel, R.L. Zuni Ceremonialism; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.N. The Distribution of Sound Instruments in the Prehistoric Southwestern United States. Ethnomusicology 1967, 11, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E. Instruments of Power: Musical Performance in Rituals of the Ancestral Puebloans of the American Southwest. Ph.D. Dissertation, Columbia University, University Microfilms, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E. Musical instruments in the pre-hispanic southwest. Park Sci. 2009, 26, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E. Music of the center place: The instruments of Chaco Canyon. In Flower World: Music Archaeology of the Americas; Stöckli, M., Howell, M., Eds.; Ekho Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.N. Ethnomusicology and the prehistoric southwest. Ethnomusicology 1971, 15, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, B.J.; Ferguson, T.J. Animate objects: Shell trumpets and ritual networks in the greater southwest. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2008, 15, 338–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, K. Gateways to Another World: The Symbolism of Supernatural Passageways in the Art and Ritual of Mesoamerican and the American Southwest. In Painting the Cosmos: Metaphor and Worldview in Images from the Southwest Pueblos and Mexico; Hays-Gilpin, K., Schaafsma, P., Eds.; Museum of Northern Arizona: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2010; pp. 73–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hays-Gilpin, K.; Sekaquaptewa, E.; Newsome, E.A. Sìitalpuva, “through the land brightened with flowers”: Ecology and cosmology in mural and pottery painting, Hopi and beyond. In Painting the Cosmos: Metaphor and Worldview in Images From the Southwest Pueblos and Mexico; Hays-Gilpin, K., Schaafsma, P., Eds.; Museum of Northern Arizona: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2010; pp. 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, R.S. A Sensory Approach to Exotica, Ritual Practice, and Cosmology at Chaco Canyon. Kiva 2015, 81, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, R.M. The Chacoan past: Creative representations and sensory engagements. In Subjects and Narratives in Archaeology; Dyke, R.M.V., Bernbeck, R., Eds.; University Press of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015; pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Akins, N.J. The burials of Pueblo Bonito. In Pueblo Bonito: Center of the Chacoan World; Neitzel, J.E., Ed.; Smithsonian Books: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. Tse’Biinaholts’a Yalti (Curved Rock That Speaks). Time Mind 2008, 1, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loose, R.W. That old music: Reproduction of a shell trumpet from Pueblo Bonito. Pap. Archaeol. Soc. N. M. 2012, 38, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. Archaeoacoustics: Adding a Sound Track to Site Descriptions. Pap. Archaeol. Soc. N. M. 2010, 36, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. A Report on Tse Biinaholtsa’a Yałti (Curved Rock that Speaks): An Open-Air Public Performance Theater at Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Manuscript on File; Chaco Culture National Historical Park: New Mexico, NM, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. Computer Analysis of Sound Recordings from Two Anasazi Sites in Northwestern New Mexico. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.R.; Friedman, R.; Blackhorse, T.; Loose, R. Revisiting Downtown Chaco. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 199–223. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.E.; Mann, J.P.; Boggs, J.L. SPreAD-GIS: An ArcGIS Toolbox for Modeling the Propagation of Engine Noise in a Wildland Setting, version 1.2; The Wilderness Society: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.E.; Boggs, J.L.; Mann, J.P. SPreAD-GIS: An ArcGIS Toolbox for Modeling the Propagation of Engine Noise in a Wildland Setting, version 2.0; The Wilderness Society: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, G.; Richards-Rissetto, H.; Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Bringing Sound into the Picture: Experiencing Ancient Maya Landscapes with GIS and 3D Modeling. Presented at the Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology (CAA) International Conference, Tübingen, Germany, 19–23 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, G.; Richards-Rissetto, H.; Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes and Visionscapes: Investigating Ancient Maya Cities with GIS and 3D Modeling. Presented at the 83rd Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Western Regional Climate Center. Chaco Canyon National Monument [sic], New Mexico, Monthly Climate Summary. Available online: http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?nm1647 (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Ambrose, S. Sound Levels in the Primary Vegetation Types in Grand Canyon National Park, July 2005; NPS Report No. GRCA-05-02; Sandhill Company: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hayne, M.J.; Rumble, R.H.; Mee, D.J. Prediction of crowd noise. In Proceedings of the Acoustics 2006, Christchurch, New Zealand, 20–22 November 2006; pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Van Heusden, E.; Plomp, R.; Pols, L.C.W. Effect of ambient noise on the vocal output and the preferred listening level of conversational speech. Appl. Acoust. 1979, 12, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organización Internacional de Normalización. ISO 9613-2:1996, Acoustics: Attenuation of Sound during Propagation Outdors. General Method of Calculation; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI). ANSI S1.26-1995 Method for Calculation of the Absorption of Sound by the Atmosphere; Acoustical Society of America: New York City, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa, Z. Noise reduction by screens. Appl. Acoust. 1968, 1, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamancusa, J.S. Outdoor sound propagation. In Noise Control, ME 458 Engineering Noise Control; Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Primeau, K.E. Methodological Improvements in Landscape Archaeoacoustics: Exploring the Effects of Vegetation and Ground Cover. Presented at the 84th Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 10–14 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, N.M. The Architecture of Pueblo Bonito; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; Volume 147. [Google Scholar]
- Windes, T.C. Investigations at the Pueblo Alto Complex, Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, 1975–1979; National Park Service: Sante Fe, NM, USA, 1987; Volume II, Pt. 2: Architecture and Stratigraphy. [Google Scholar]
- Lekson, S.H. Great House Form. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 7–44. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.R.; Lekson, S.H. Anasazi Ritual Landscapes. In Anasazi Regional Organization and the Chaco System; Doyel, D.E., Ed.; University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1992; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Crown, P.L. (Ed.) The Pueblo Bonito Mounds of Chaco Canyon; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Toll, H.W. Making and Breaking Pots in the Chaco World. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, C.M. Pink Chert, Projectile Points, and the Chacoan Regional System. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, W. Building Social History at Pueblo Bonito: Footnotes to a Biography of Place. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, M.P. The Chacoan Roads: A Cosmological Interpretation. In Anasazi Architecture and American Design; Morrow, B.H., Price, V.B., Eds.; University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1997; pp. 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sofaer, A. The Primary Architecture of the Chacoan Culture: A Cosmological Expression. In Anasazi Architecture and American Design; Morrow, B.H., Price, V.B., Eds.; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1997; pp. 88–132. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M. Sacred Landscapes: The Chaco-Totah Connection. In Chaco’s Northern Prodigies: Salmon, Aztec, and the Ascendancy of the Middle San Juan Region after AD 1100; Reed, P.F., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2008; pp. 334–348. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, W.H. Ritual and Mound Formation during the Bonito Phase in Chaco Canyon. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windes, T.C. Gearing Up and Piling On: Early Great Houses in the Interior San Juan Basin. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 45–92. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M. The Chaco Experience: Landscape and Ideology at the Center Place; School for Advanced Research Press: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, C.M. Sacred Earthen Architecture in the Northern Southwest: The Bluff Great House Berm. Am. Antiq. 2002, 67, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekson, S.H. A History of the Ancient Southwest; School for Advanced Research Press: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin, M.A. Plazas, Performance, and Symbolic Power in Ancestral Pueblo Religion. In Religious Transformation in the Late Pre-Hispanic Pueblo World; Glowacki, D.M., Keuren, S.V., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, ZA, USA, 2012; pp. 130–152. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarsson, J.J.; Nordström, H.; Lundén, P.; Nilsson, M.E. Aircraft noise and speech intelligibility in an outdoor living space. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boren, B. Whitefield’s Voice. In George Whitefield; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 167–189. [Google Scholar]
- Boren, B. The Maximum Intelligible Range of the Human Voice. Ph.D. Dissertation, New York University, New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boren, B.; Roginska, A.; Gill, B. Maximum Averaged and Peak Levels of Vocal Sound Pressure. In Proceedings of the 135th Audio Engineering Society Convention, New York, NY, USA, 17–20 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Larm, P.; Hongisto, V. Experimental comparison between speech transmission index, rapid speech transmission index, and speech intelligibility index. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, H. Prediction of Verbal Communication is Noise—A review: Part 1. Appl. Acoust. 1986, 19, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovičić, S.T. A relation between speech intelligibility and distribution of speech pressure about the head. Appl. Acoust. 1991, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, N.M. The Material Culture of Pueblo Bonito; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 124. [Google Scholar]
- Luckman, T. Comments on Legitimation. Curr. Sociol. 1987, 35, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, R. Legitimating Identities: The Self-Presentations of Rulers and Subjects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Elliot, J.H. A Palace for a King: The Buen Retiro and the Court of Philip IV; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley, P.M. Deliberate Acts: Changing Hopi Culture through the Oraibi Split; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yoffee, N. The Chaco “Rituality” Revisited. In Chaco Society and Polity: Papers from the 1999 Conference; Cordell, L.S., Judge, W.J., Piper, J.-E., Eds.; New Mexico Archaeological Council: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2001; pp. 63–78. [Google Scholar]





| Environmental Inputs | Cultural Inputs |
|---|---|
| Percentage of Relative Humidity | Location of Sound Source |
| Air Temperature (°F) | Height of Sound Source (ft) |
| Ambient Sound Pressure Level (dB(A)) | Sound Pressure Level of Source (dB(A)) |
| LiDAR-based DEM | Measurement Distance of Source (ft) |
| Frequency of Source (Hz) |
| Modeling Inputs | Elite Orator with a Raised Voice: Afternoon in June | Conch Shell Trumpet: Dawn in June | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Inputs | Percentage of Relative Humidity | 30% | 30% |
| Air Temperature | 89.6 °F (32 °C) | 55.4 °F (13 °C) | |
| Ambient Sound Pressure Level | 20.7 dB(A) | 20.7 dB(A) | |
| Cultural Inputs | Height of Sound Source | 5 ft (1.5 m) | 6 ft (1.8 m) |
| Sound Pressure Level of Source | 84 dB(A) | 96 dB(A) | |
| Measurement Distance of Source | 3 ft (0.9 m) | 4 ft (1.2 m) | |
| Frequency of Source | 325 Hz | 330 Hz | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Witt, D.E.; Primeau, K.E. Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco. Acoustics 2019, 1, 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007
Witt DE, Primeau KE. Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco. Acoustics. 2019; 1(1):78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleWitt, David E., and Kristy E. Primeau. 2019. "Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco" Acoustics 1, no. 1: 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007
APA StyleWitt, D. E., & Primeau, K. E. (2019). Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco. Acoustics, 1(1), 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007