Development and Assessment of a Miniaturized Test Rig for Evaluating Noise Reduction in Serrated Blades Under Turbulent Flow Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
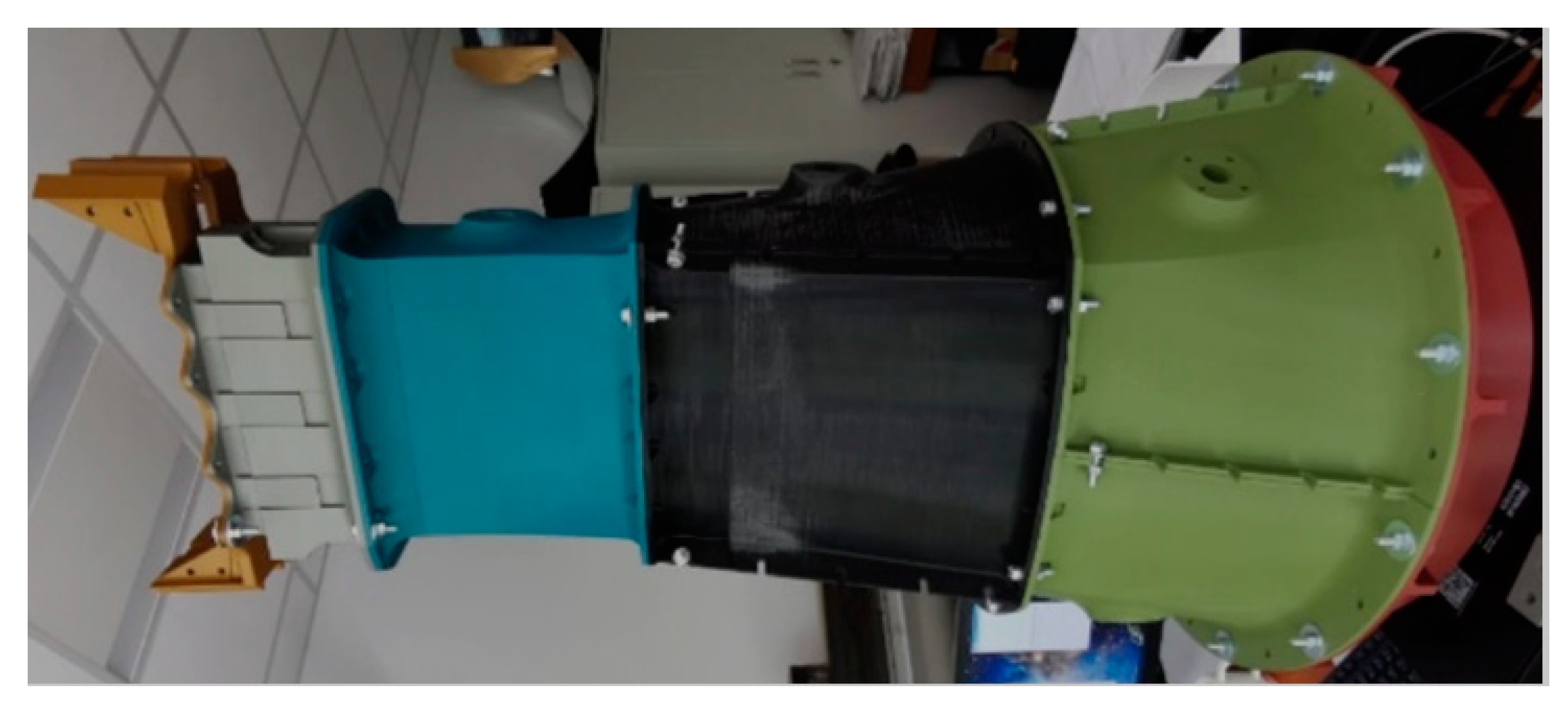
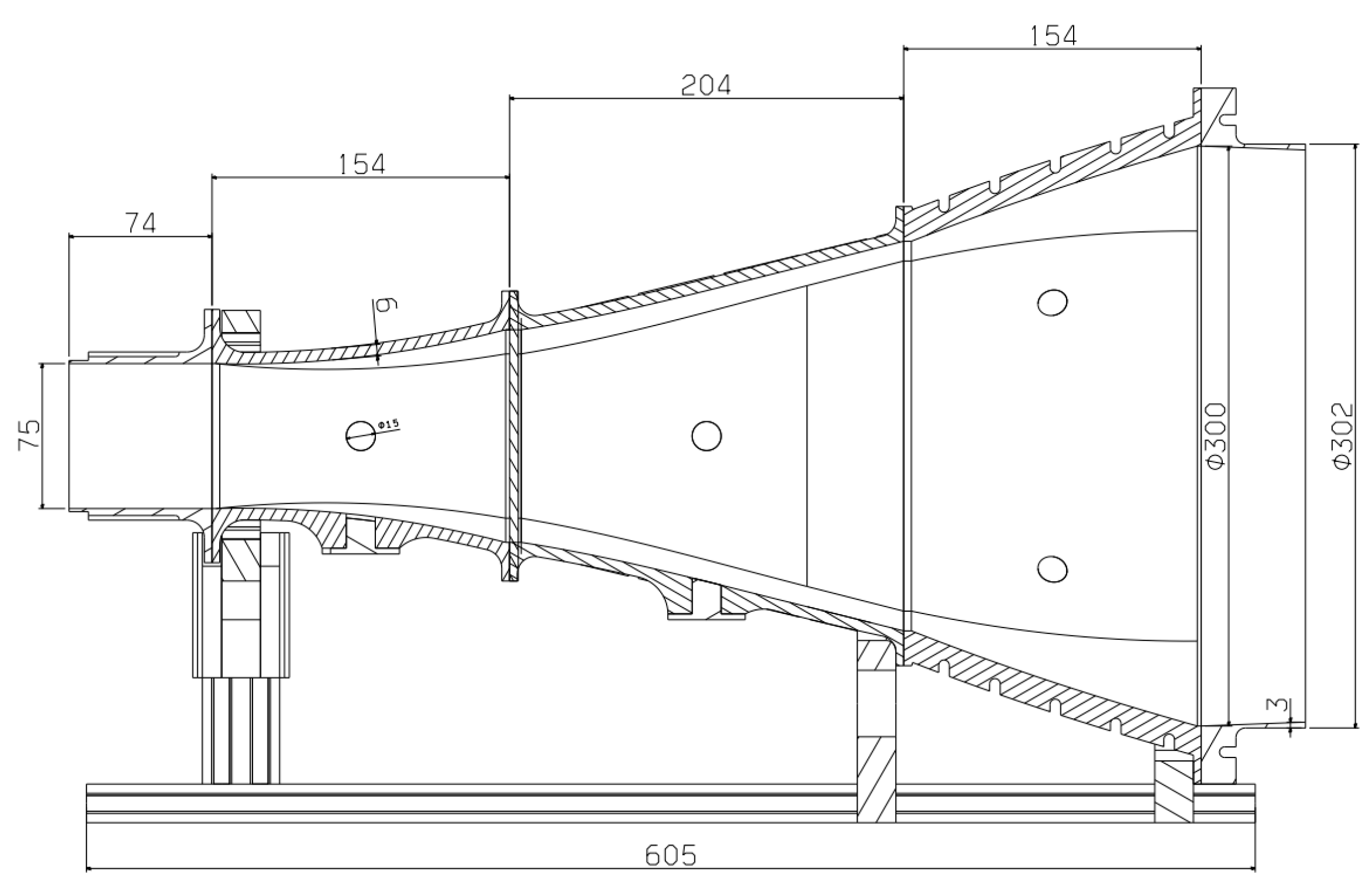
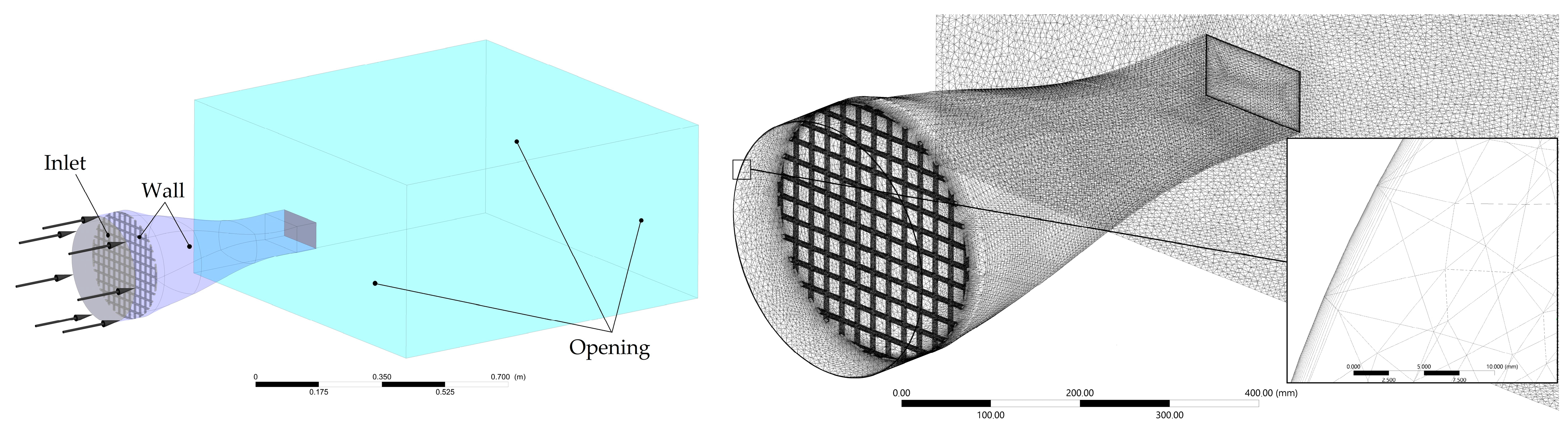
2.1. Experimental Setup
- The transition should not be so abrupt that significant detachments occur.
- It must be modular so turbulence-generating elements can be introduced between these sections (axial sectioning is also relatively uniform).
- To be able to incorporate measuring instruments (it is possible to provide at certain instrumentation points/areas for mounting pressure/temperature probes).
- Can be easy to manufacture (3D-printable).
- Have good mechanical strength (both the section and the turbulence-generating elements to be inserted in the flow path).
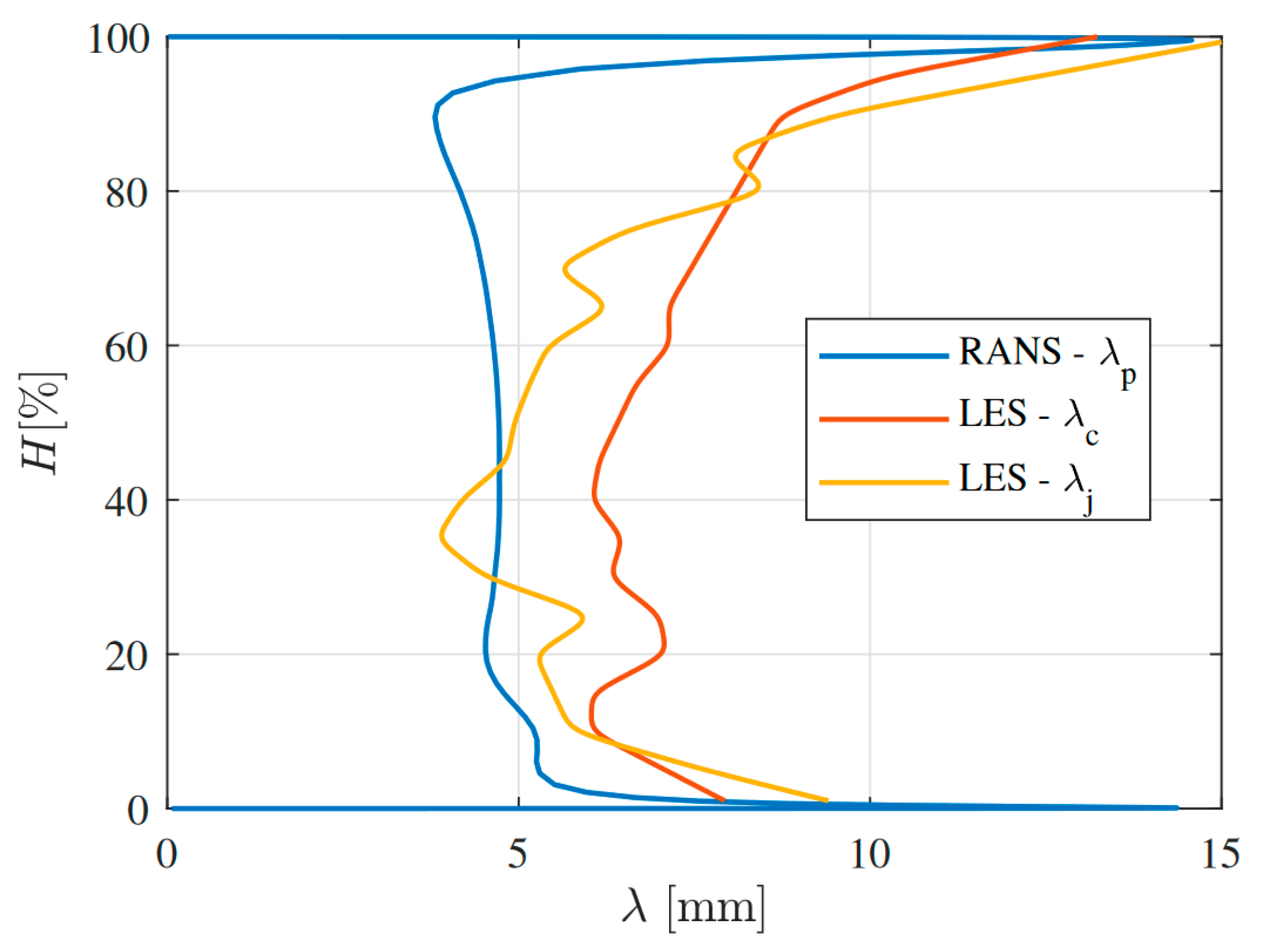
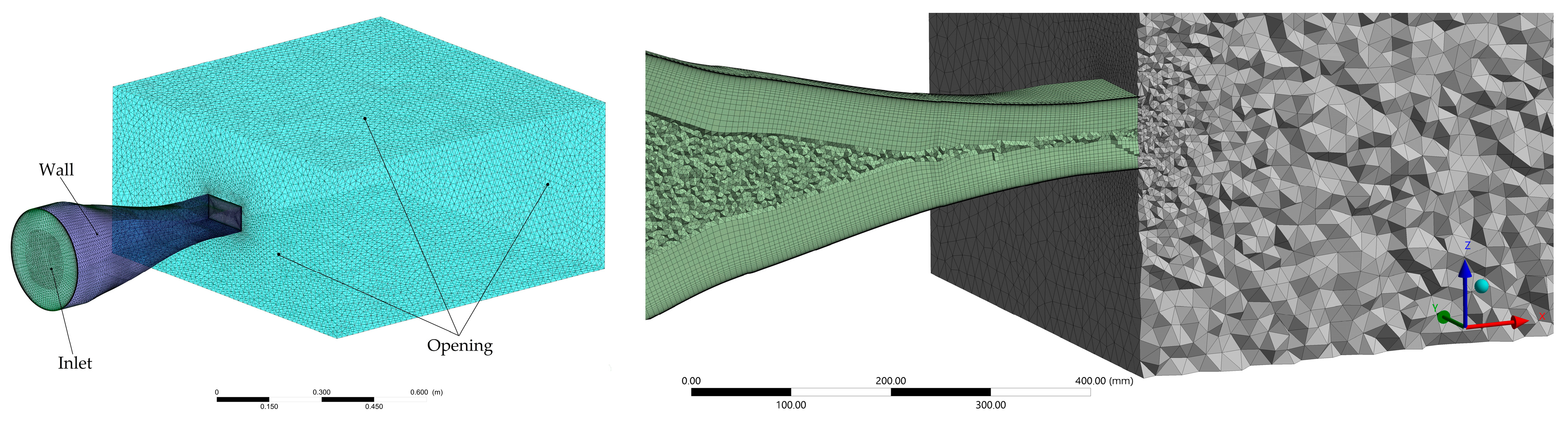
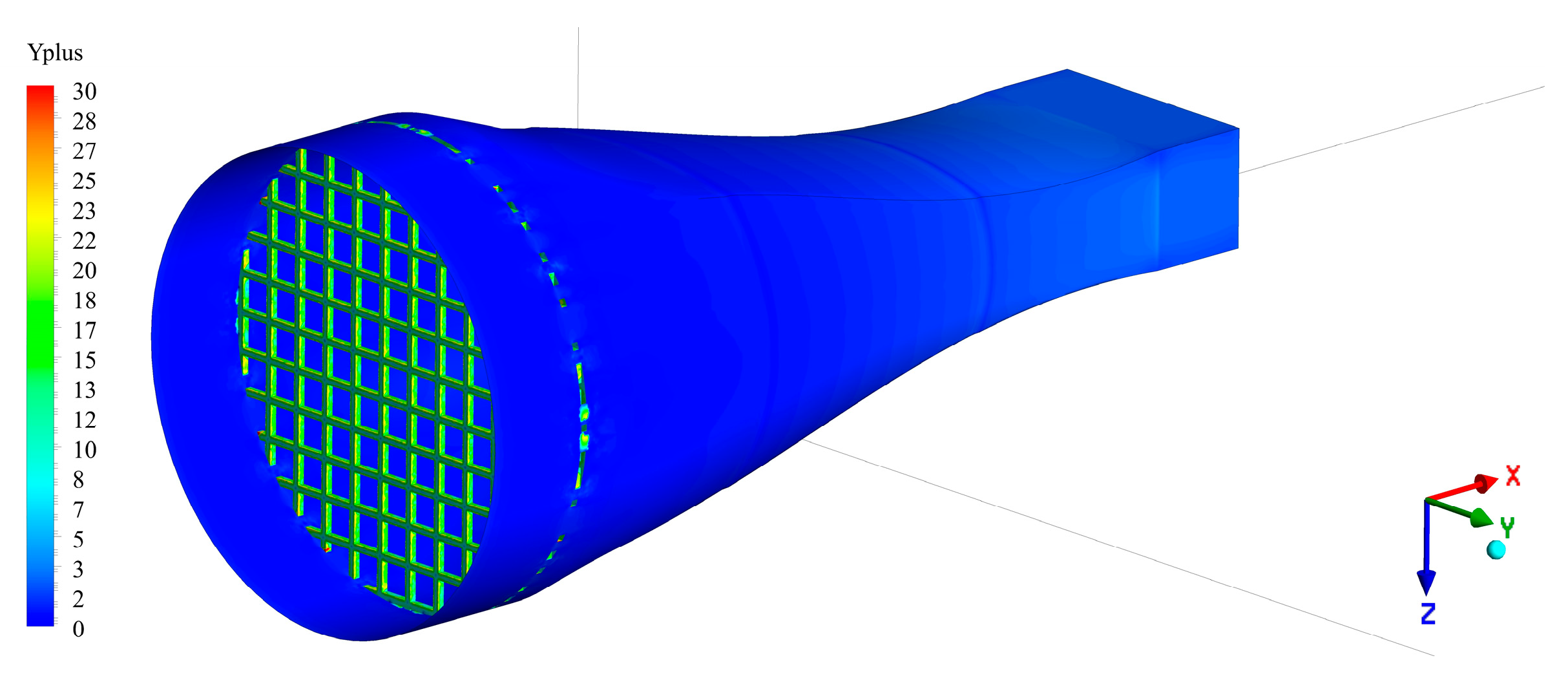
2.2. Mathematical Methods and Numerical Simulation
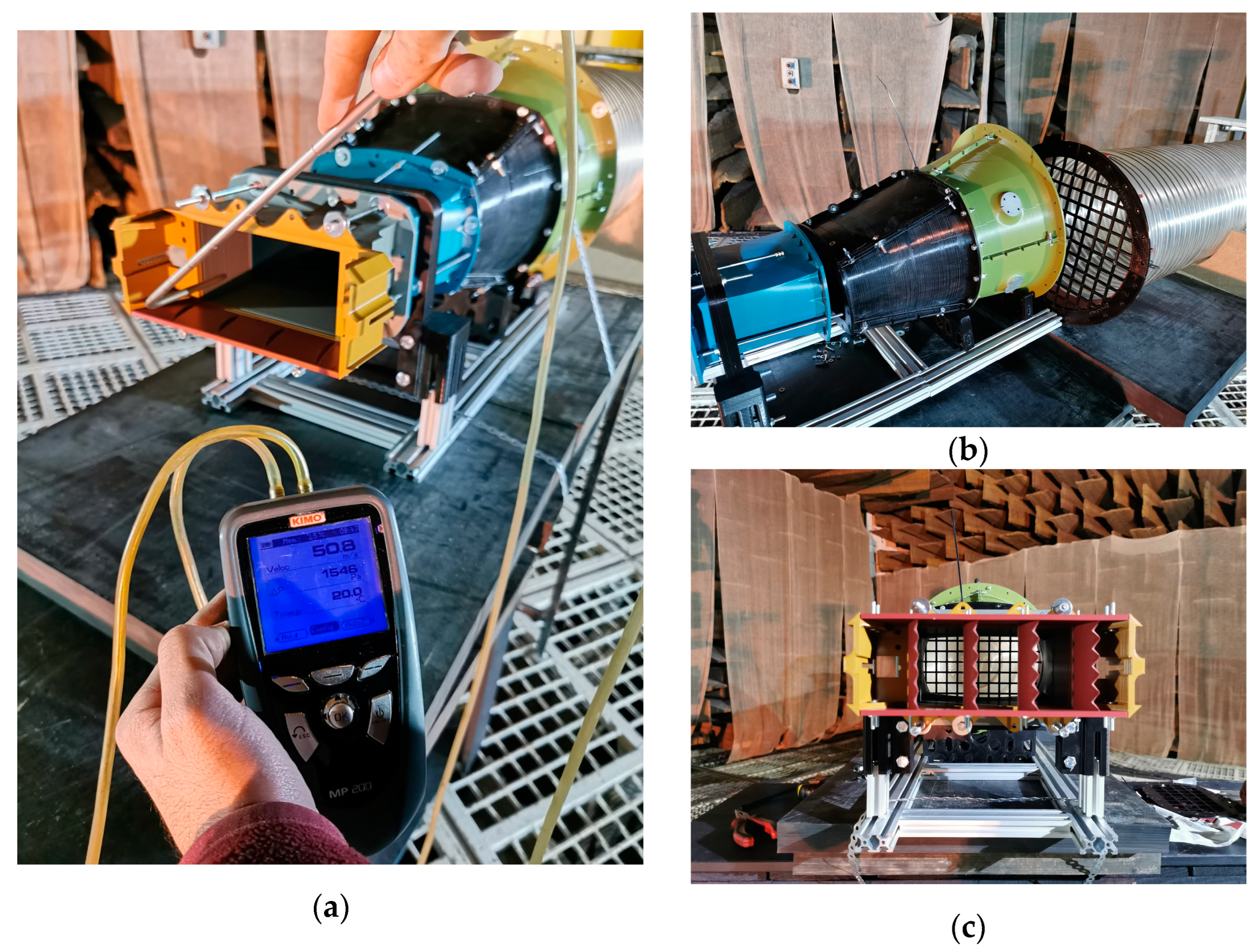
2.3. Manufacturing
2.4. Experimental Test Bench
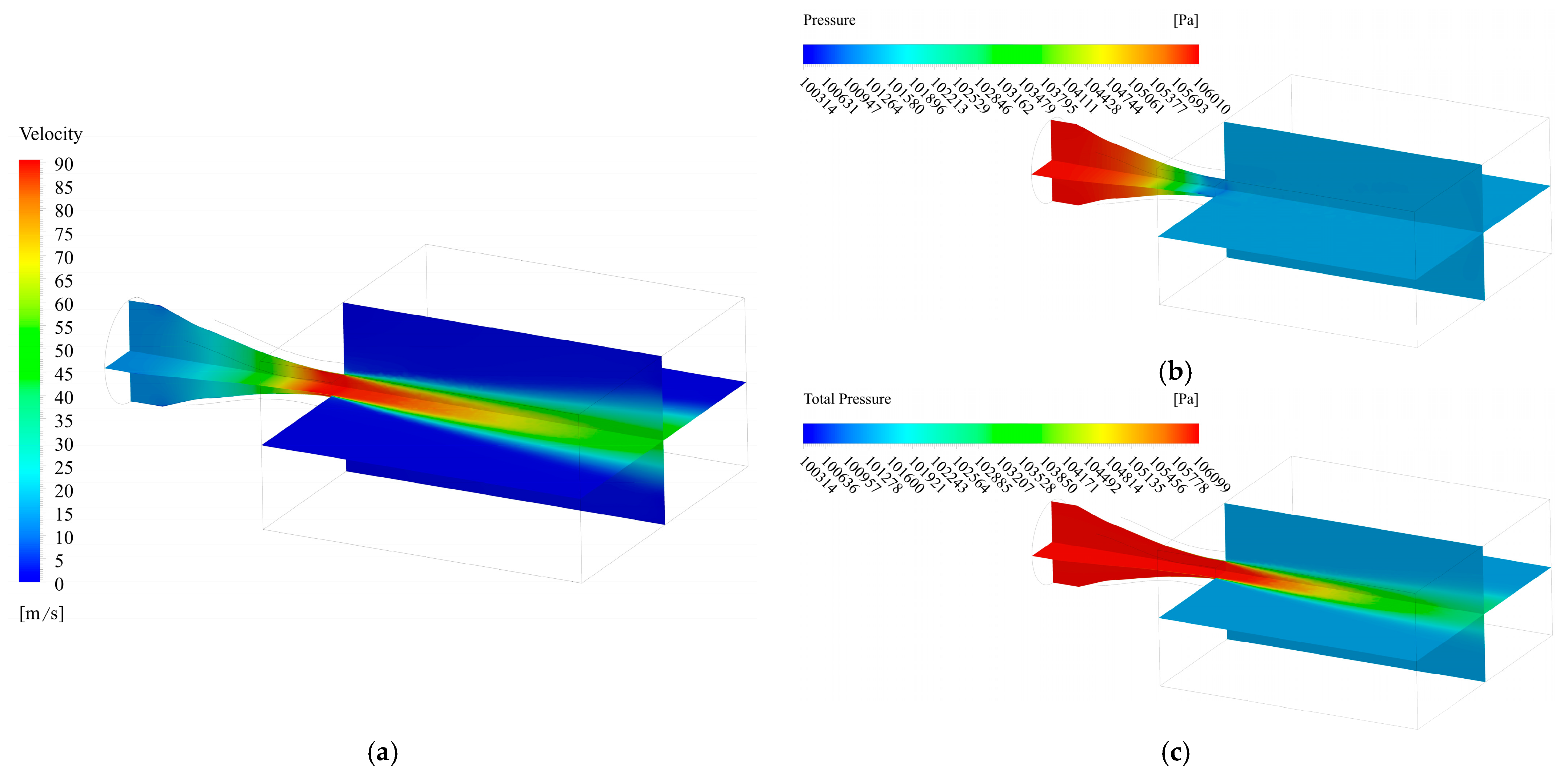
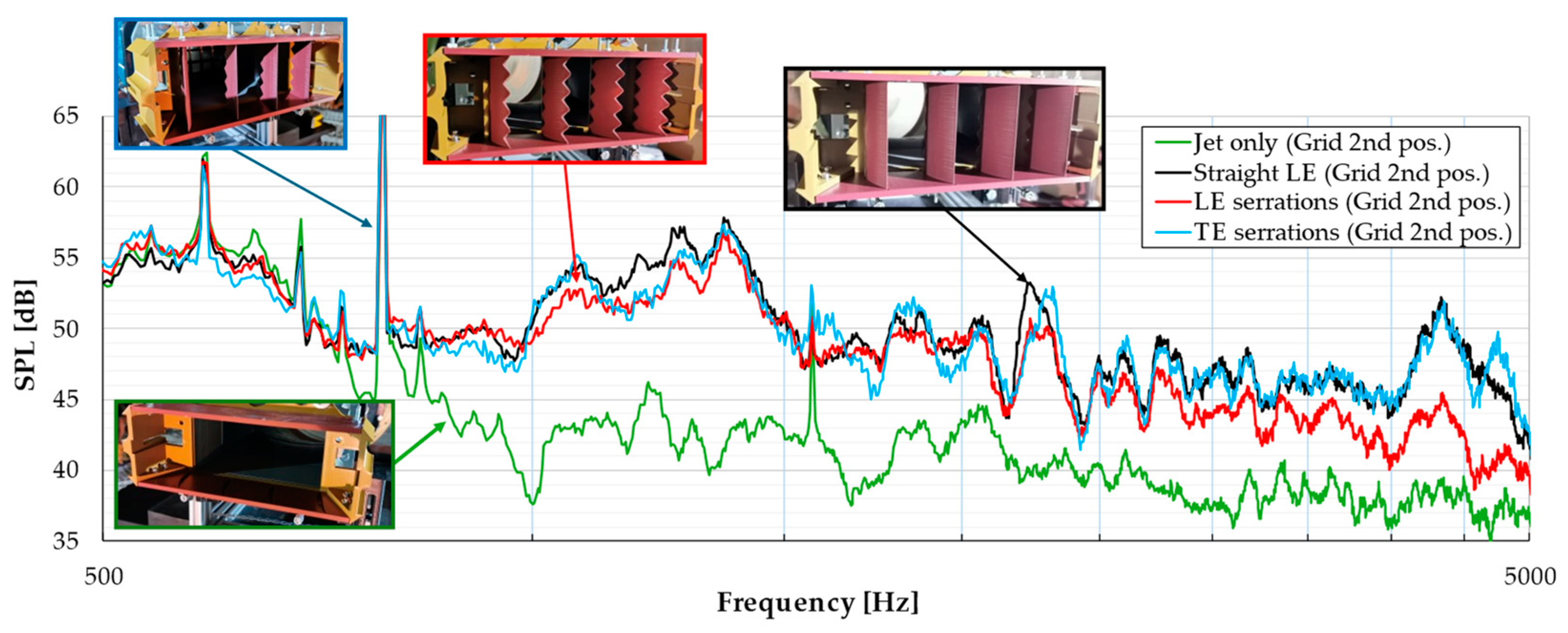
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| a | grid bars thickness |
| h | serration amplitude |
| k | turbulent kinetic energy |
| l | grid bars width |
| h/δ | dimensionless serration amplitude parameter |
| h/λ | dimensionless parameter associated with the serration angle |
| A | grid frontal area |
| coefficient (0.45) | |
| coefficient (0.09) | |
| L | grid square side |
| Lw | Gaussian wake width |
| ,W0 | jet velocity (averaged) |
| ε | energy dissipation rate |
| λ | serration pitch |
| σ | blade solidity |
| ω | specific dissipation rate |
| Λ | turbulence length scale |
| BPF | blade passing frequency |
| ILS | integral length scale |
References
- Arunvinthan, S.; Pillai, S.N.; Cao, S. Aerodynamic characteristics of variously modified leading-edge protuberanced (LEP) wind turbine blades under various turbulent intensities. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 202, 104188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovych, V.; Duda, D.; Uruba, V.; Tomášková, T. Hot-Wire Investigation of Turbulence Topology behind Blades at Different Shape Qualities. Processes 2022, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, J.; Lee, H.M. Noise Attenuation by Half Flat tip Serrated Trailing Edge in Rotating Blades. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2489, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce-León, C.A. Modelling of Serrated Trailing Edges to Reduce Aerodynamic Noise in Wind Turbines Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Master’s Thesis, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, A.; Sun, B.; Bei, B. Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise in Axial Fan Using Serration Edge Blades. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2020, 13, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jawahar, H.K.; Azarpeyvand, M.; Theunissen, R. Wake Development of Airfoils with Serrated Trailing Edges. In Proceedings of the 22nd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Lyon, France, 30 May–1 June 2016; AIAA 2016-2817. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc. (AIAA): Reston, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacsek, C.; Cader, A.; Barrier, R.; de Laborderie, H.; Gea-Aguilera, F. Aeroacoustic Design and Broadband Noise Predictions of a Turbofan Stage with Serrated Outlet Guide Vanes. In Proceedings of the 26th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Montreal, Canada, 7–11 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhalifa, A.S.; Uddin, M.N.; Atkinson, M. Aerodynamic Performance Analysis of Trailing Edge Serrations on a Wells Turbine. Energies 2022, 15, 9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Bertagnolio, F.; Shen, W.Z.; Madsen, J. Noise model for serrated trailing edges compared to wind tunnel measurements. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 753, 022053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ishibashi, K.; Ikeda, T.; Fujii, T.; Nakata, T.; Liu, H. Morphological effects of leading-edge serrations on the acoustic signatures of mixed flow fan. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 041909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruna, C.; Avallone, F.; Casalino, D.; Ragni, D. Numerical investigation of leading edge noise reduction on a rod-airfoil configuration using porous materials and serrations. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 494, 115880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Chen, B.; Aecom, P. Numerical and Experimental Studies on Grid-Generated Turbulence in Wind Tunnel. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacsek, C.; Cader, A.; Buszyk, M.; Barrier, R.; Gea-Aguilera, F.; Posson, H. Aeroacoustic design and broadband noise predictions of a fan stage with serrated outlet guide vanes. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.S.; Haeri, S.; Kim, J.W. The effect of wavy leading edges on aerofoil–gust interaction noise. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 6234–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaron, R.; Herthum, H.; Franke, M.; Moreau, A.; Guérin, S. Impact of Turbulence Models on RANS-Informed Prediction of Fan Broadband Interaction Noise. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Stockholm, Sweden, 3–7 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaron, R.; Moreau, A.; Guérin, S.; Schnell, R. Optimization of Trailing-Edge Serrations to Reduce Open-Rotor Tonal Interaction Noise. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery, Honolulu, HI, USA, 10–15 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dicholkar, A.; Zahle, F.; Sørensen, N.N. Convergence enhancement of SIMPLE-like steady-state RANS solvers applied to airfoil and cylinder flows. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2022, 220, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacsek, C.; Barrier, R.; Kohlhaas, M.; Carolus, T.; Kausche, P.; Moreau, A.; Kennepohl, F. Turbofan Interaction Noise reduction Using Trailing Edge Blowing: Numerical Design and Assessment and Comparison with Experiments.V2. Aerosp. Lab 2014, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, E.; Ragni, D. Trailing edge serrations effects on the aerodynamic performance of a NACA 643418. Wind. Energy 2019, 22, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Cao, H.; Zhang, M.; Liao, C. Performance simulation of wind turbine with optimal designed trailing-edge serrations. Energy 2022, 243, 122998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Joseph, P.; Haeri, S.; Kim, J.W. Noise Reduction Studies from the Leading Edge of Serrated Flat Plates. In Proceedings of the 20th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, M. Airfoil Noise Reduction by Edge Treatments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Li, X.-D.; Zhou, J.-J. Experimental and numerical investigation on sound generation from airfoil-flow interaction. Appl. Math. Mech. 2011, 32, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampanis, G.; Roger, M.; Moreau, S. On a three-dimensional investigation of airfoil turbulence-impingement noise and its reduction by leading-edge tubercles. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 520, 116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgios, B.; Michel, R. Three-dimensional effects in the reduction of turbulence-impingement noise of aerofoils by wavy leading edges. In Proceedings of the Euronoise 2018, Crete, Greece, 27–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marc, J. Introduction to experimental aeroacoustics, Lecture 1. In Design and Operation of Aeroacoustic Wind Tunnels for Ground and Air Vehicles; Von Karman Institute: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Clair, V.; Salze, E.; Souchotte, P.; Jondeau, E. Turbulence interaction noise from a rectilinear cascade of airfoils and effects of porous material inclusions. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2023 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S. Aerodynamic Influence of Leading-Edge Serrations on an Airfoil in a Low Reynolds Number. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2009, 4, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldahl, R.E.; Klimas, P.C. Aerodynamic Characteristics of Seven Symmetrical Airfoil Sections through 180-Degree Angle of Attack for Use in Aerodynamic Analysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbines; Technical Report No. SAND80-2114; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger, R.A. Low Speed Aerodynamics for Ultra-Quiet Flight; Technical Report; DTIC Document: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, D.; Brooks, L.; Doolan, C. On the noise reduction mechanism of a flat plate serrated trailing edge at low-to-moderate Reynolds number. In Proceedings of the 18th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (33rd AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, M. A noise reduction study on flow-permeable trailing-edges. In Proceedings of the Eighth ONERA-DLR Aerospace Symposium (ODAS), Göttingen, France, 17–19 October 2007; Volume 17, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Anyoji, M.; Wakui, S.; Hamada, D.; Aono, H. Experimental Study of Owl-Like Airfoil Aerodynamics at Low Reynolds Numbers. J. Flow Control. Meas. Vis. 2018, 6, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Martínez, R.; Carpio, A.R.; Pereira, L.T.L.; van Herk, S.; Avallone, F.; Ragni, D.; Kotsonis, M. Aeroacoustic design and characterization of the 3D-printed, open-jet, anechoic wind tunnel of Delft University of Technology. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 170, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totu, A.-G.; Cican, G.; Crunțeanu, D.-E. Serrations as a Passive Solution for Turbomachinery Noise Reduction. Aerospace 2024, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.G.; Sowers, H.D. Cascade Tests of Serrated Leading Edge Blading at High Subsonic Speeds. 1974; NASA CR-2472. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19750003911/downloads/19750003911.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Howe, M.S. Noise Produced by a Sawtooth Trailing Edge. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Ji, L.; Tong, W.; Chen, W. Application of Phased Array în the Study of Linear Cascade Noise Reduction on the Indoor Test Bed. In Proceedings of the 5th Berlin Beamforming Conference, Berlin, Germany, 19–20 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitanya, P.; Joseph, P.; Narayanan, S.; Vanderwel, C.; Turner, J.; Kim, J.W.; Ganapathisubramani, B. Performance and mechanism of sinusoidal leading edge serrations for the reduction of turbulence–aerofoil interaction noise. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 818, 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, B.R. Modeling Fan Broadband Noise from Jet Engines and Rod-Airfoil Benchmark Case for Broadband Noise Prediction. Master’s Thesis, Iowa State University of Science and Technology, Ames, IA, USA, 1 January 2015. p. 14326. Available online: https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd/14326 (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Jacob, M.C.; Boudet, J.; Casalino, D.; Michard, M. A rod-airfoil experiment as a benchmark for broadband noise modeling. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2005, 19, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Am, J.; Clair, V.; Giauque, A.; Boudet, J.; Gea-Aguilera, F. Direct noise predictions of fan broadband noise using LES and analytical models. In Proceedings of the 28th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics 2022 Conference, Southampton, UK, 14–17 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, S.; Kissner, C.; Seeler, P.; Blázquez, R.; Laraña, P.C.; de Laborderie, H.; Lewis, D.; Chaitanya, P.; Polacsek, C.; Thisse, J. ACAT1 Benchmark of RANS-Informed Analytical Methods for Fan Broadband Noise Prediction: Part II—Influence of the Acoustic Models. Acoustics 2020, 2, 617–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, L.; Kissner, C.; Behn, M.; Tapken, U.; Meyer, R. Comparison of Techniques for the Estimation of Flow Parameters of Fan Inflow Turbulence from Noisy Hot-Wire Data. Fluids 2021, 6, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys. Best Practice: Scale-Resolving Simulations in Ansys CFD. v2.00, Technical Paper. 2015. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/content/dam/product/fluids/cfd/tb-best-practices-scale-resolving-models.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Filamentive Limited. PLA/rPLA, Datasheet. Available online: https://www.farnell.com/datasheets/2913593.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- ASRO, SR EN ISO 3745: 2012; Acoustics-Determination of Sound Power Levels and Sound Energy Levels of Noise Sources Using Sound Pressure-Precision Methods for Anechoic Rooms and Semi-Anechoic Rooms. ISO: Bucuresti, Romania, 2012.
- Acoustics and Vibrations Laboratory, COMOTI. Available online: http://ftp.comoti.ro/en/laboratoare_experimentari_4_2.htm (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Tyacke, J.; Vadlamani, N.; Trojak, W.; Watson, R.; Ma, Y.; Tucker, P. Turbomachinery simulation challenges and the future. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2019, 110, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedevergne, F. Analytical wall function including roughness corrections. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 73, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedevergne, F.; Aupoix, B. Accounting for wall roughness effects in turbulence models: A wall function approach. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference for Aeronautics And Aerospace Sciences (EUCASS), Milan, Italy, 3–6 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Laurendeau, E. Consistent surface roughness extension for wall functions. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2020, 82, 108552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

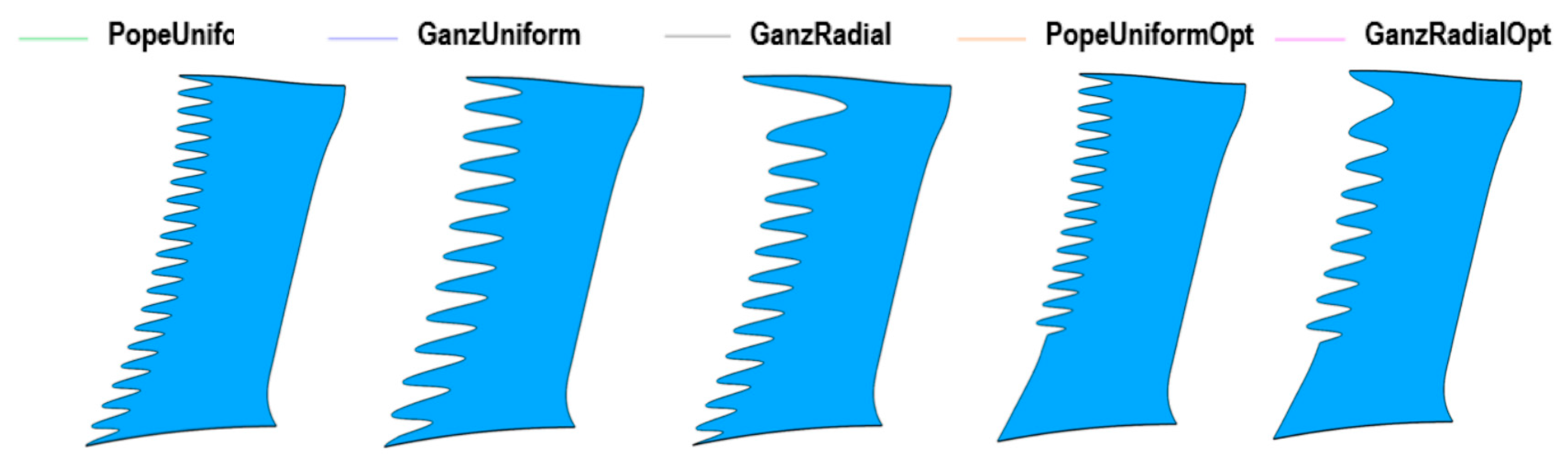



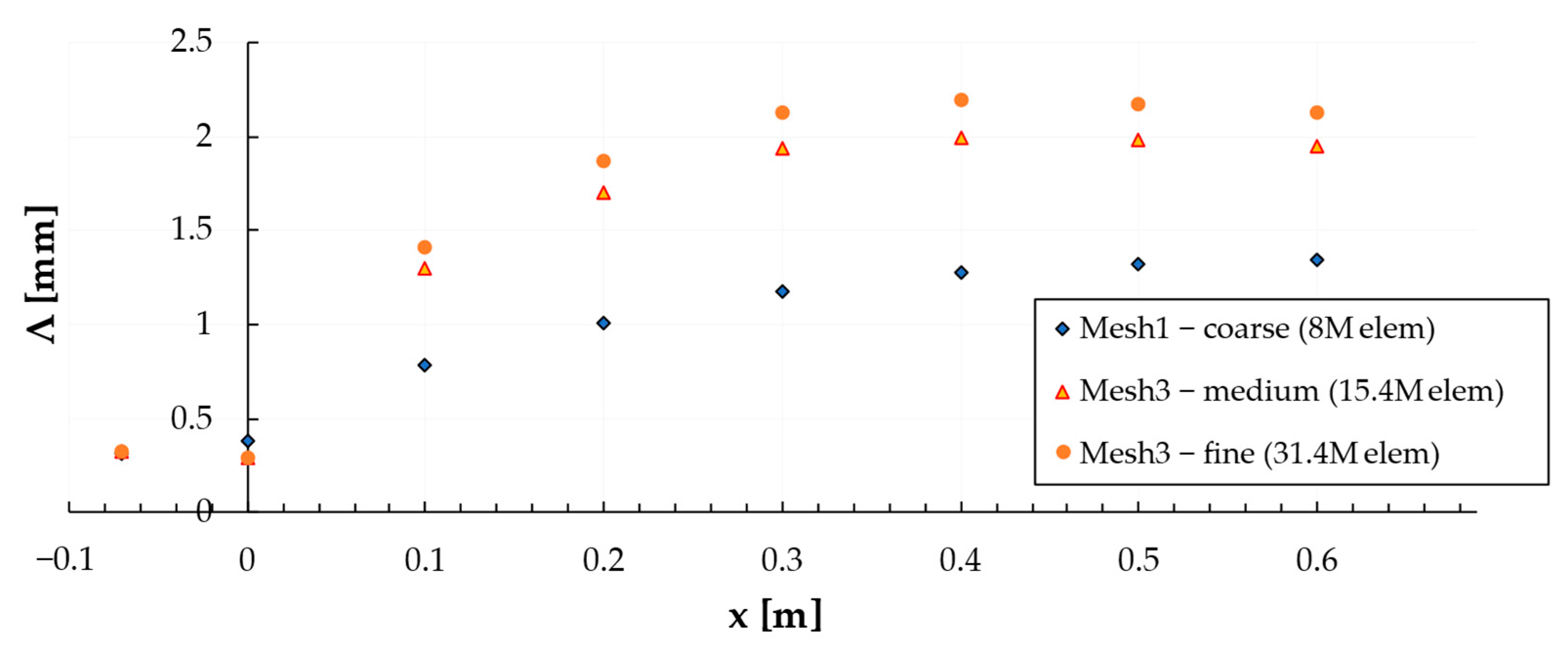
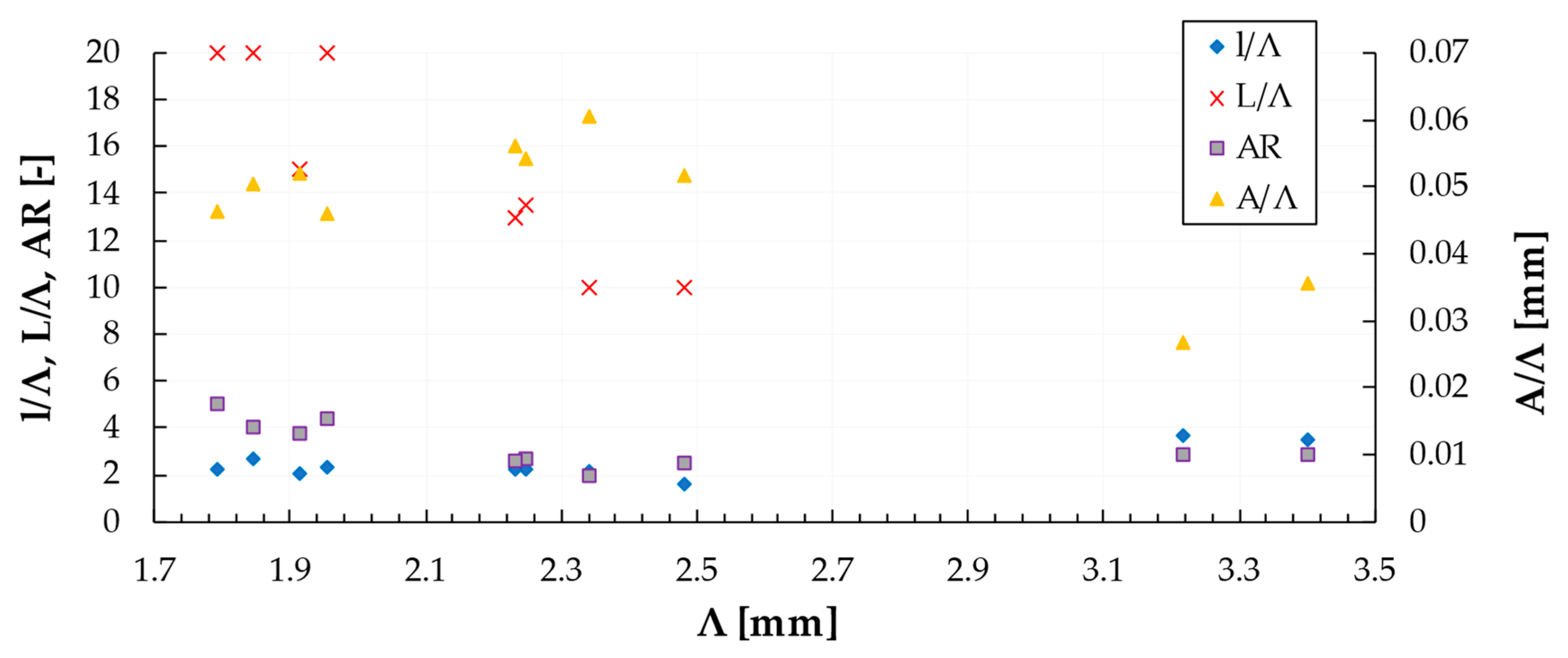
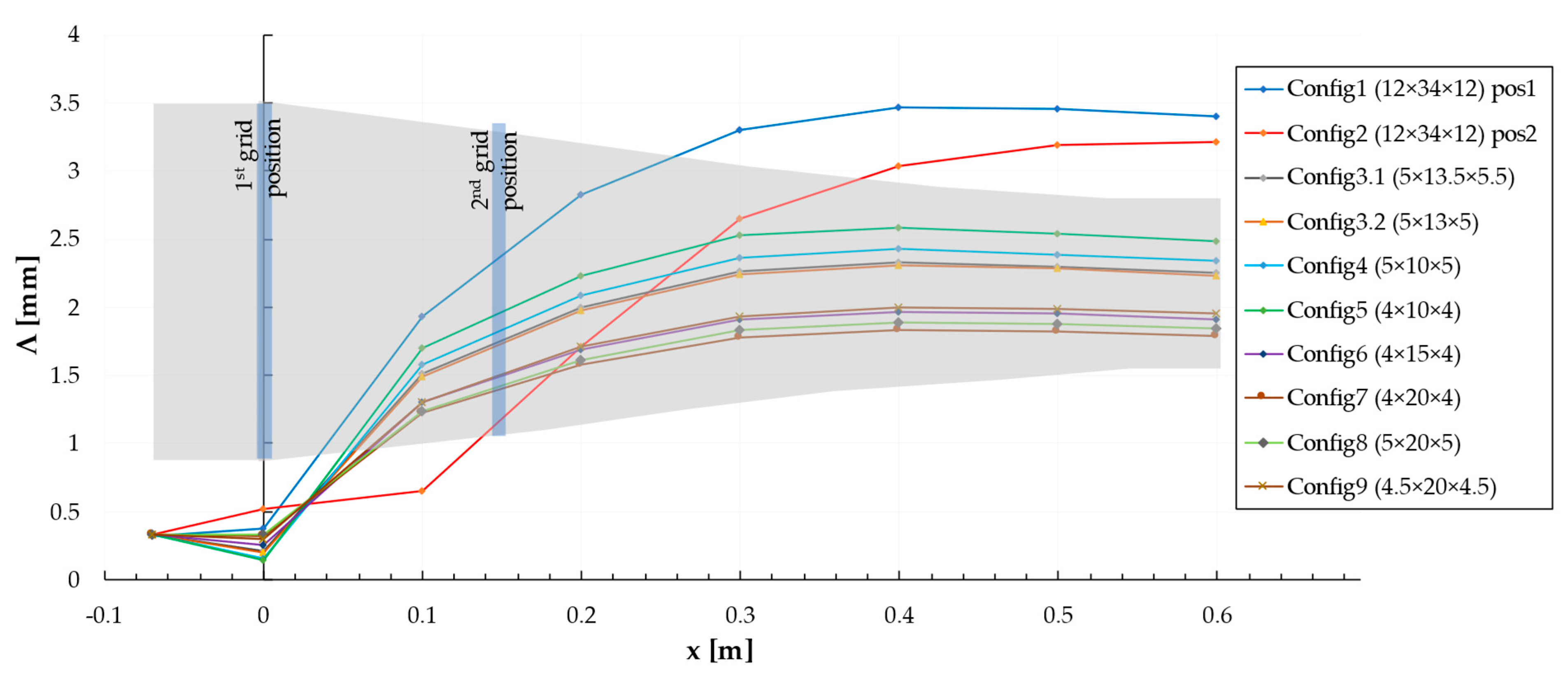
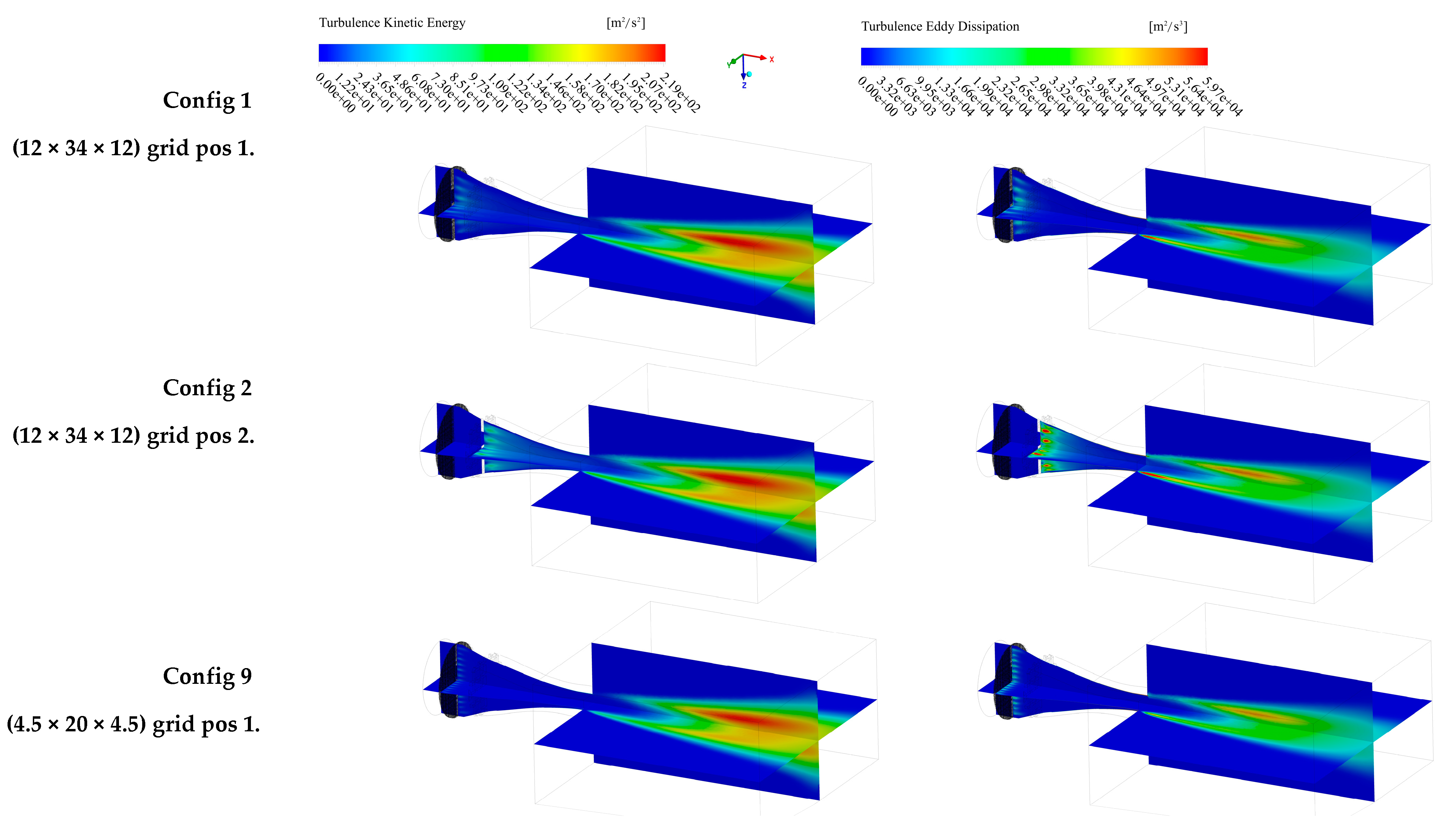
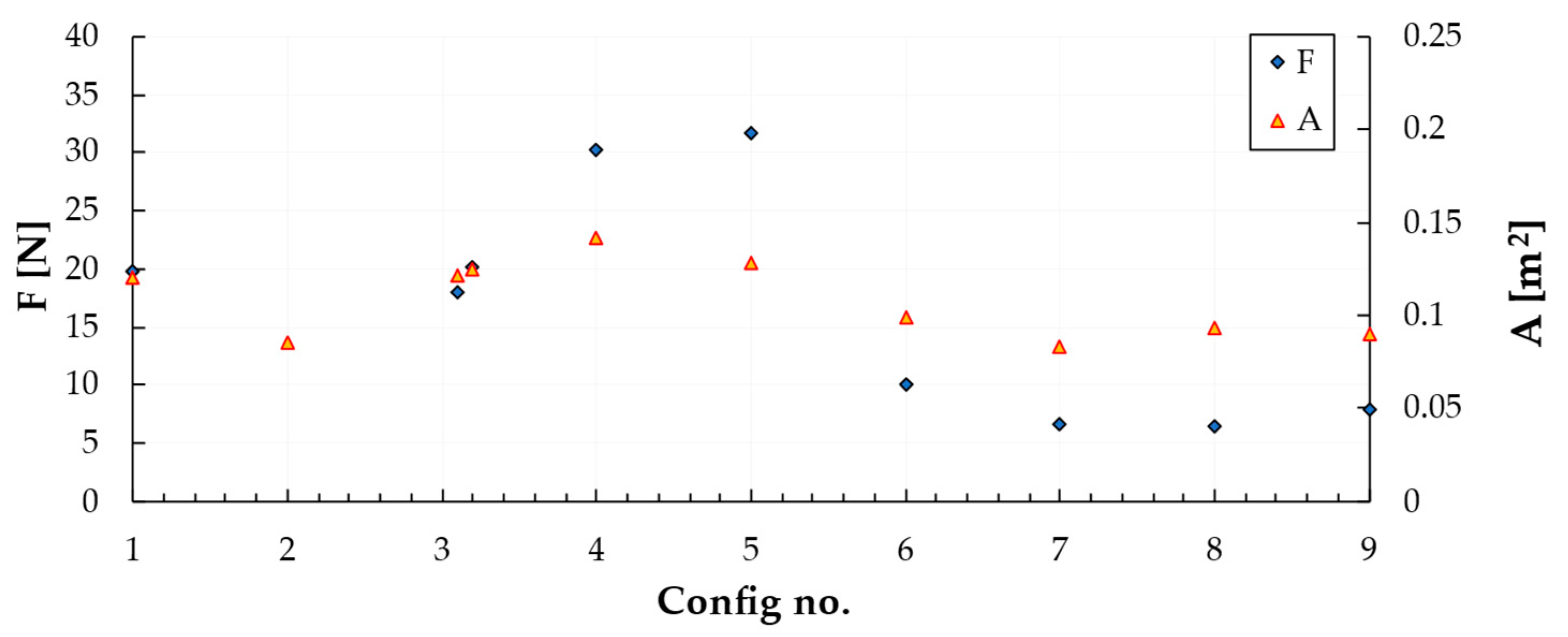

| Relation | Reference |
|---|---|
| Smith, 1974 [36] | |
| Howe, 1991 [37] | |
| Howe, 1991 [37] | |
| Qiao, 2014 [38] | |
| Chaytanya, 2017 [39] | |
| Gruber, 2012 [22] | |
| Lau, 2013 [14] |
| Grid No. | 1 | 2 (Grid 1 2nd Pos) | 3.1 | 3.2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L [mm] | 34 | 34 | 13.5 | 13 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| l [mm] | 12 | 12 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4.5 |
| a [mm] | 12 | 12 | 8.5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Totu, A.-G.; Olariu, C.-T.; Trifu, A.-T.; Totu, A.-C.; Cican, G. Development and Assessment of a Miniaturized Test Rig for Evaluating Noise Reduction in Serrated Blades Under Turbulent Flow Conditions. Acoustics 2024, 6, 978-996. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6040054
Totu A-G, Olariu C-T, Trifu A-T, Totu A-C, Cican G. Development and Assessment of a Miniaturized Test Rig for Evaluating Noise Reduction in Serrated Blades Under Turbulent Flow Conditions. Acoustics. 2024; 6(4):978-996. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleTotu, Andrei-George, Cristian-Teodor Olariu, Andrei-Tudor Trifu, Andreea-Cătălina Totu, and Grigore Cican. 2024. "Development and Assessment of a Miniaturized Test Rig for Evaluating Noise Reduction in Serrated Blades Under Turbulent Flow Conditions" Acoustics 6, no. 4: 978-996. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6040054
APA StyleTotu, A.-G., Olariu, C.-T., Trifu, A.-T., Totu, A.-C., & Cican, G. (2024). Development and Assessment of a Miniaturized Test Rig for Evaluating Noise Reduction in Serrated Blades Under Turbulent Flow Conditions. Acoustics, 6(4), 978-996. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6040054








