Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Data-driven reliability modeling outperforms current asset management practices for district heating pipes.
- The relative youth of district heating systems complicates the assessment of failure distribution assumptions.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- District heating operators should focus their efforts on maintenance and operational data collection to further improve and facilitate the transition to data-driven asset management.
- Relatively old district heating systems may provide valuable insights into appropriate failure distribution assumptions. For this reason, inter-utility collaborations are advisable.
Abstract
As district heating networks age, current asset management practices, such as those relying on static life expectancies and age- and rule-based approaches, need to be replaced by data-driven asset management. As an alternative to physics-of-failure models that are typically preferred in the literature, this paper explores the application of more accessible traditional and novel machine learning-enabled reliability models for analyzing the reliability of district heating pipes and demonstrates how common data deficiencies can be accommodated by modifying the models’ likelihood expressions. The tested models comprised the Herz, Weibull, and the Neural Weibull Proportional Hazard models. An assessment of these models on data from an actual district heating network in Funen, Denmark showed that the relative youth of the network complicated the validation of the models’ distributional assumptions. However, a comparative evaluation of the models showed that there is a significant benefit in employing data-driven reliability modeling as they enable pipes to be differentiated based on the their working conditions and intrinsic features. Therefore, it is concluded that data-driven reliability models outperform current asset management practices such as age-based vulnerability ranking.
1. Introduction
District heating systems make up a vital part of the energy infrastructure in many cold-climate countries. With network assets, pipes, and joints specifically being designed to handle the immense mechanical and thermal stress required by their function and the relative youth of many district heating networks, there have been few failure cases historically. In light of this, district heating companies have relied on simple static life expectancies, and rule- and age-based failure probability methods for the long-term management of district heating pipes. Nevertheless, as district heating networks have aged, there has been an increasing focus on developing adequate predictive maintenance tools for these networks to ensure the longevity of their assets and their continued reliable operation.
The approaches to modeling the failure of district heating pipes can broadly be separated into two categories, namely bottom-up and top-down approaches [1]. Bottom-up models may also be referred to as physics-of-failure models. The main benefit of these in relation to district heating pipes is that they are built on established damage-accumulation and aging models, for which empirical data can be and have been obtained in lab environments through accelerated-aging tests and with knowledge transfer from material science in other domains [2,3,4].
For the development of accurate physics-of-failure models, researchers have studied the degradation of the parts constituting district heating pipes, namely the media pipe, the polyurethane (PUR) insulation foam, and the pipe’s outer jacket, related to the failure modes of the different materials. Ref. [5] studied how corrosion in district heating water affects the mechanical properties of welded carbon steel pipes. Vega et. al. investigated how cyclical, mechanical, and thermal loads affect the adhesion strength of PUR foam at the interface with the steel media pipe in [2,6], and further compared the accelerated aging and natural aging of district heating pipes on the adhesion strength of PUR foam in [7]. Leuteritz et. al. studied the degradation of polyethylene jackets of district heating pipes using accelerated-aging tests and the Arrhenius equation [8]. The material properties of naturally aged PUR foam in district heating pipes for different operating temperatures were compared in [9], which confirmed the influence of operating conditions on the degradation of PUR foam. With a basis in damage-accumulation theory, the equivalent full load cycles of district heating pipes were predicted in [10], which is correlated with the life expectancy of district heating pipes. Langroudi and Weidlich presented an overview of suggested physics-of-failure models for different subsystems of district heating pipes in [11].
For predictive maintenance physics-of-failure models, the failure of a material is typically defined as a violation of a design threshold value of one or more material properties, such as the proportion of closed cells and axial shear strength of PUR foam [12]. Using such failure definitions coincidentally results in a situation where a pipe can be faulty while the supply of district heating water remains adequate, and it may even be economically unbeneficial to rehabilitate the failed pipe. It was acknowledged in [1,11] that since district heating pipes are composed of several subsystems of different materials, singular physics-of-failure models are inadequate for the pipes as a whole. Furthermore, physics-of-failure models can have high requirements for data and observability, i.e., the proportion of pipes for which operational data are recorded.
The alternative to physics-of-failure models is top-down modeling. The benefit of top-down reliability models is their accessibility, in that they can be applied for systems with relatively low observability, which has been used to great effect for water distribution systems over the past few decades [13]. Only a few applications of top-down reliability models exist for district heating systems: e.g., in [14], where the failure rate of district heating pipes was modeled based on the Homogeneous and Non-Homogeneous Poisson Processes to identify the most vulnerable components. However, the state of evolution of the application of top-down modeling approaches for district heating pipes is low, with reliability analyses of district heating systems sometimes relying on the static failure rates of the district heating pipes [15,16]. Although the application of data-driven reliability models for district heating pipes is lacking, it is a vital part of the future development of asset management strategies for district heating systems [17]. In water distribution systems, the shift from parametric statistical models that do not consider explanatory features of pipelines [18,19] to those that do [20,21], and even applications of machine learning-based reliability models [22,23], has, however, achieved great results.
The combination of reliability models with machine learning provides a pragmatic approach to comprehending the complex relationships of failure cause–effect chains at a high level and can be carried out for grids with various degrees of observability. In light of this and the scarce literature on the application of reliability models for district heating pipes, we, in this paper, comparatively evaluate traditional reliability models that have obtained good results in water distribution systems and a machine learning-enabled reliability model developed in previous work for analyzing the reliability of power cables [24]. This evaluation is carried out with actual data from the district heating network of Funen, Denmark. Furthermore, we demonstrate how common data deficiencies may be accommodated by modifying the likelihood expression of the models, which is relevant as truncation is typically overlooked in engineering applications [18,20,21,25,26,27].
The contributions of this paper are as follows:
- Assessment of the applicability of traditional reliability models to district heating networks;
- Evaluation of machine learning-enabled reliability models in the context of district heating networks;
- Demonstration of how common data deficiencies can be accommodated in the reliability analysis of district heating networks;
- Comparative evaluation of the models based on data from an actual district heating network.
2. Methods
In the following, three reliability models are introduced alongside information on how they are applied. Additionally, the ways in which common data deficiencies such as right-censoring and left-truncation may be accounted for by modifying the likelihood expression of the models are detailed.
2.1. Herz Failure Distribution
The Herz failure distribution model proposed by Herz [28,29] is designed specifically for the reliability analysis of piping systems. It has seen multiple applications in the water distribution domain. Other researchers have hypothesized that it may be a good distributional choice for analyzing the reliability of district heating pipes. One reason that it may be especially appropriate for piping systems is that it discounts zero-inflated failure data as these are not representative of the aging-related degradation of the piping systems. Zero-inflation is the phenomenon wherein piping systems have relatively high infant-mortality rates due to installation defects [13]. These failures are discounted from the model by setting the hazard rate to zero when the age of the piping system is below a certain resistance time, c. This complements newer district heating systems in which pipes are installed with copper wires for electrical-resistance-based leakage detection as part of warranty control measures from the pipe suppliers. Weidlich and Schuchardt have argued that the Herz model’s asymptotic increase to a constant hazard rate is appropriate for piping systems as this corresponds to a constant rate of deterioration [1].
The hazard rate of the Herz model, i.e., the instantaneous rate of failure, is given as follows:
where a is an aging factor, and b is a failure factor. The reliability and probability density function for the Herz model are given, respectively, by the following:
2.2. Weibull Failure Distribution
The Weibull model is one of the most well-known and renowned reliability models; it has seen many applications in critical infrastructure systems, such as water distribution systems [19,25,30]. One of the key features of the Weibull model is its simplicity and flexibility. In one review of a reliability analysis for water distribution systems, it was reported that good results can be achieved using the Weibull distribution for predicting the time to first failure, while subsequent failures may be better predicted by using an exponential distribution [13].
The hazard rate of the Weibull model can, depending on the parameterization, be described as follows:
where and are the shape and scale parameters, respectively. The reliability, , and probability density function, , of the Weibull model are given by the following:
In the case that , the hazard rate is monotonically decreasing. When , the hazard rate is monotonically increasing, which corresponds to an increase in the instantaneous rate of failure, and when , the hazard rate is constant and the Weibull model reduces to the exponential failure distribution model.
2.3. Neural Weibull Proportional Hazard Model
The Neural Weibull Proportional Hazard (NWPH) model is an extension of the Weibull model that enables the differentiation of assets’ hazard rates depending on a set of covariates describing the assets. The hazard rate, reliability, and probability density function of the NWPH model are given by the following [24]:
where z is a vector of covariates describing, e.g., environmental factors, operating conditions, material properties, etc. of an asset. represents an arbitrary neural network, whose output may be referred to as the relative risk. The reason for the exponentiation of is that it ensures the positivity of the hazard rate. The benefit of the NWPH model is two-fold, with the flexible modeling of a neural network on the one hand and the fact that it enables data-driven reliability assessment on the other hand when compared to the Weibull and Herz models. While proportional hazard models, such as the Weibull Proportional Hazard model or the Cox Proportional Hazard model, which are characterized by linear relative risk functions, have been applied for reliability analyses, little research has been conducted on this type of combination of machine learning and reliability analysis. The application of the NWPH model in the district heating domain has never been executed before. For the purpose of this paper, the neural network, , is a multi-layer perceptron with hidden layer dimensions [20, 10] and linear activation.
2.4. Incomplete Data and Maximum Likelihood Estimation
For a complete failure dataset, the parameters of a model can be be estimated simply by maximizing the likelihood, given by the following:
where denotes the parameters of a reliability model, d denotes the observed failure data, is the age at failure of the asset, and the function f is the probability density function. Nevertheless, failure data are rarely complete, with right-censoring being perhaps the most common source of incomplete failure data. This is caused by assets such as piping systems not being observed for their entire lifetime. The main reason for this is that the assets are still in operation. In this case, the age at failure for the asset is said to be right-censored. The likelihood expression can be modified to accommodate these incomplete observations as follows [31]:
In Equation (11), I is the set of indices for uncensored observations, i.e., assets for which the age at failure is known, and J is the set of indices for right-censored observations, i.e., assets for which the age at failure is unknown because it has not happened yet. In this case, denotes the censoring time, which is the current age of the asset.
Another common source of incompleteness is left-truncation, which generally happens when a maintenance record is not kept from the time the asset is installed. When observation of the assets then begins, only the failures of those assets with sufficiently long lifetimes will recorded. The non-recorded failures can be a cause of bias for reliability models if unaccounted for. The way to account for this is by using an inverse probability weight, as follows [31]:
Here, and is the age of the and assets when observation began. Older assets will generally have a lower reliability and as such more emphasis is placed on these.
2.4.1. Estimating Parameters for the Weibull Model
Using maximum likelihood estimation, the parameters of the Weibull model can be estimated as follows: Firstly, the likelihood of the Weibull model is given by
and the log-likelihood is
Here, denotes the cardinality of the set I, which is equivalent to the number of uncensored observations. Taking the partial derivatives of the log-likelihood expression gives
Setting Equation (16) to 0 and solving for gives
is found by first substituting Equation (17) into Equation (15) to obtain a univariate function derivative of the log-likelihood as a function of , and then using gradient descent with the following update rule:
Here, is the value of in the iteration, starting with an initial guess of ; is the step size; and the derivative represented with is Equation (17) substituted into Equation (15), evaluated at . After has been determined, is found simply by using Equation (17).
2.4.2. Estimating Parameters for the Neural Weibull Proportional Hazard Model
The likelihood function for the NWPH model under the consideration of right-censoring and left-truncation is as follows:
Here, denotes the parameters of the neural network. The parameters of the NWPH model are found using gradient-based maximum likelihood maximization following the procedure outlined in [24]. The training procedure includes a pre-training step in which the parameters for the baseline hazard rate are found, i.e., and in this case. Subsequently, all parameters, i.e., , , and the weights and biases of the neural network, are optimized jointly to minimize the negative log-likelihood.
2.4.3. Estimating Parameters for the Herz Model
For the Herz model, the likelihood may be expressed as follows:
Here, the assumption is that the age at failure is lower than the resistance time, i.e., . This can easily be enforced by dropping any observations for which , which is aligned with the fact the purpose of the resistance time is to discount these zero-inflated failures that are not due to material degradation but rather are caused by installation or manufacturing defects. Moreover, these observations do by definition not contribute to the likelihood: see Equations (2) and (3).
The parameterization of the Herz model does not easily allow for a parameter estimation procedure that is similar to the one achievable with the Weibull model. Instead, we propose estimating the parameters of the Herz distribution by minimizing the negative log-likelihood using the Nelder–Mead simplex algorithm, with the resistance time, c, set manually to 5 prior to the application of the optimization heuristic.
3. Dataset
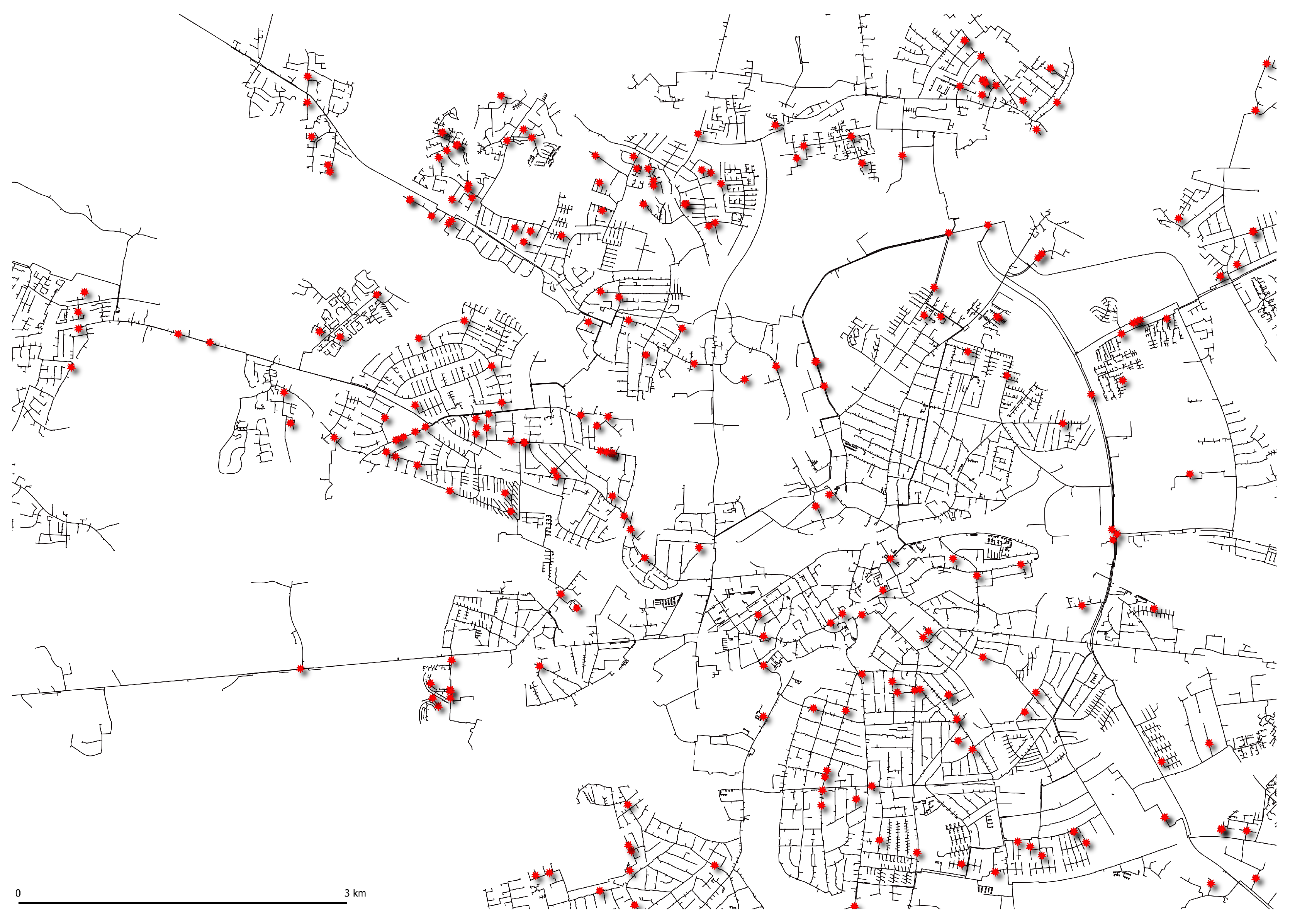
The models were implemented for a Danish district heating system on Funen, Denmark. Its grid consists of more than 1450 km of pipes, not accounting for service pipes; a screenshot of the Geographic Information System (GIS) showing transmission and distribution pipes, along with the location of likely historical failures, can be seen in Figure 1. The GIS contains more than 150,000 pipes currently active and decommissioned, including service pipes. A pipe segment in the GIS can represent multiple pipe segments in the real system, with joints saved in a different layer to be drawn on top.
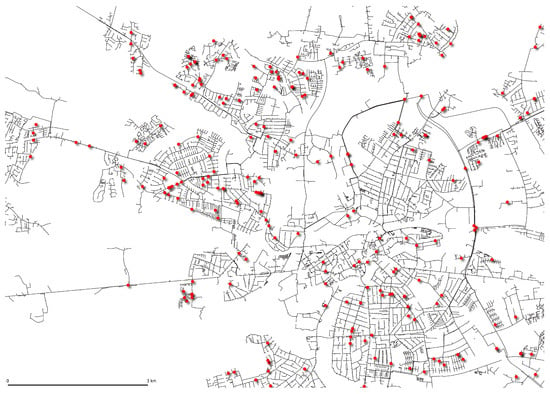
Figure 1.
Example of GIS data of the district heating system, including distribution and transmission pipes, and historical thermography reports indicating failures shown as red stars.
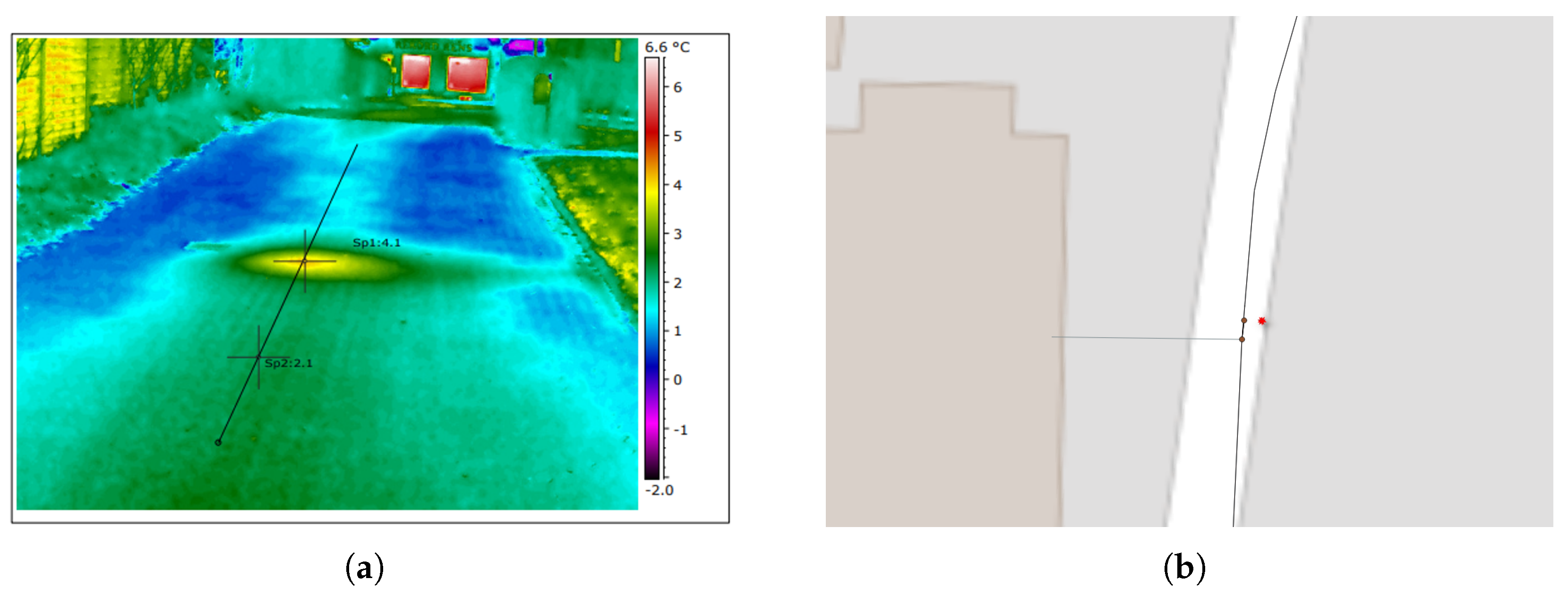
The district heating system’s maintenance record covers the period of 2016–2021, while the eldest pipes are more than 60 years old. This means that the system’s failure data suffer from left-truncation. The maintenance record consists solely of a set of thermography reports, i.e., ground-surface hot spots that are indicative of leakages. There are 474 thermography reports in total. Since the vast majority of the pipes have not failed, the vast majority of the data are right-censored. The thermography reports were associated with specific pipes manually based on the coordinates at which the thermal imaging was performed, Google Maps, and the GIS. An example of a thermal image can be seen in Figure 2. If several hot spots were detected for the same pipe, only 1 failure was associated with it, as the models were employed to predict the time to first failure.
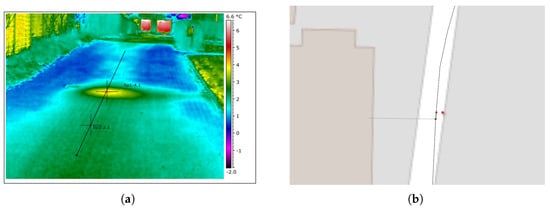
Figure 2.
Example of the link between a thermography report and the GIS. (a) Thermal image from a thermography report showing a ground–surface hot spot, which is indicative of a leakage. (b) GIS at the location of the thermography report. The red star denotes the location of the thermal image, while the brown dots represent joints.
The operators of the district heating network report that based on their experience, the joints of the piping system are especially vulnerable, with the majority of leakages being caused by poor joints. This is likely the case in the example shown in Figure 2, as the hot spot coincides with the location of a joint in the GIS. While reliability analyses of the joints in the network by themselves would be of great interest, this is not possible, as the locations of the majority of joints are unknown to the operators. Reliability models are therefore applied to the combined piping system, consisting of both pipes and joints. In this setting, the joints are seen as attributes of the pipes, with the joints being associated with the upstream connecting pipe. For this reason, the service pipes, i.e., the pipes going from the street into consumers’ properties, were discarded from our analysis.
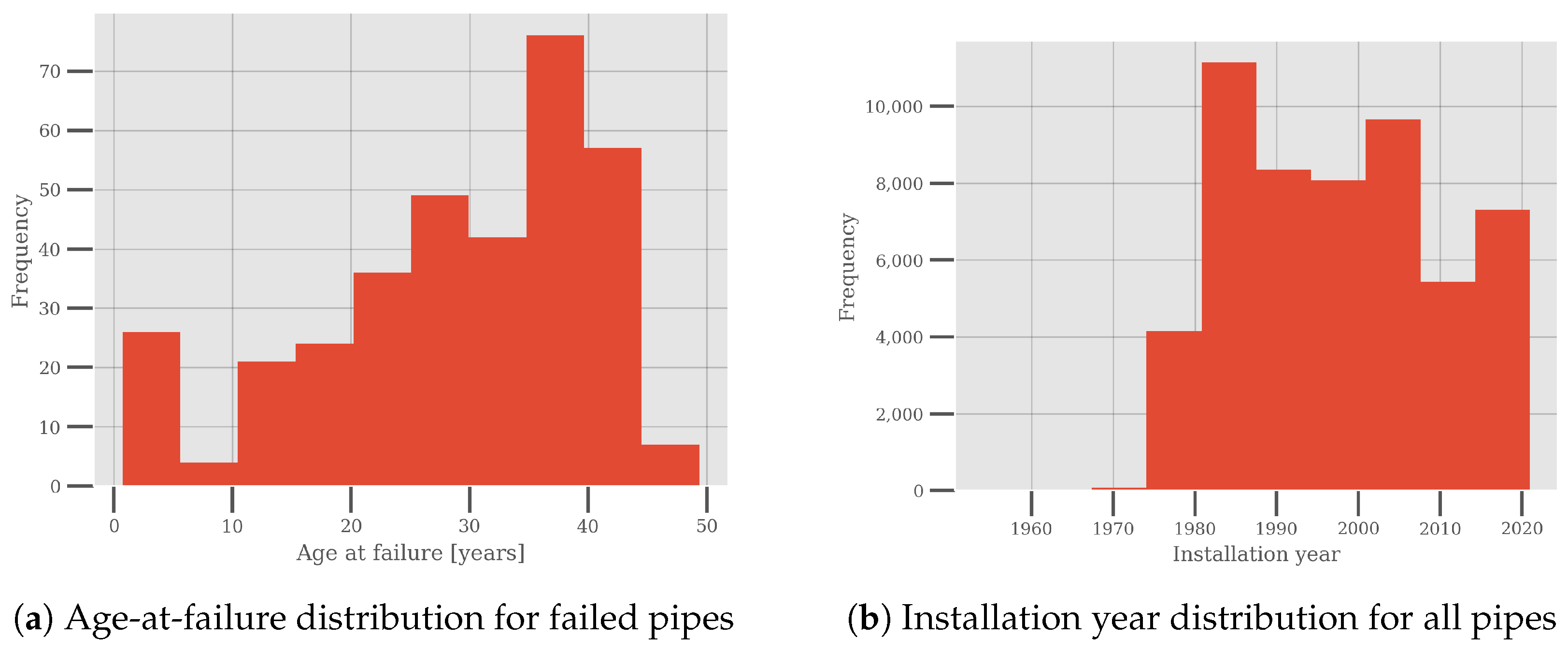
The distribution of the age at failure for the failed pipes is shown in Figure 3 alongside the installation year distribution of the pipes. The age-at-failure distribution indicates that the failure data are zero-inflated and it indicates a growing failure rate.
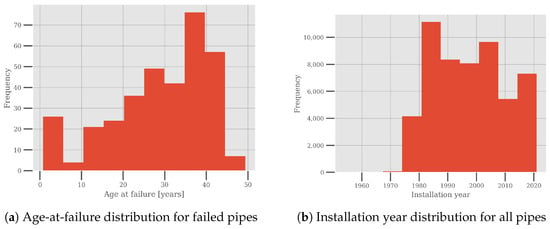
Figure 3.
Age-at-failure distribution for failed pipes and installation year distribution for all pipes within the dataset.
For the application of the NWPH model, the pipes were described according to a set a covariates or features. Reports by several engineering firms for the Danish district heating association, Dansk Fjernvarme, highlight that the risk of external corrosion of poor joints could be impacted by soil and groundwater conditions, and that road classifications for nearby roads are correlated with the pipe conditions [32,33]. There is also an emphasis on soil conditions in research papers that report reliability analyses of pipes in water distribution systems [21,27,34]. Therefore, the features of the dataset were selected to represent the environmental conditions that the pipes lie in, but also the estimated number of joints on the pipes, alongside information about the pipes, such as their nominal diameter. The estimation of the number of joints and the processing of the remaining features followed the strategy outlined in a previous work by the authors [35].
The pipes’ operational data were not included in the analysis as the grid has limited observability, meaning that, e.g., the pipes’ pressure and temperature are not monitored. Generally, the system is monitored at decentral heating plants and pump stations, typically located at the intersection between the transmission and distribution grid, and at the locations of individual consumers.
4. Results
To comparatively evaluate the models, repeated cross-validation was applied. In each iteration, the data were randomly partitioned into 80% training and 20% testing data in a stratified way (equal ratios between uncensored and right-censored observations in each dataset), with the model parameters being determined based on the training data and the performance metrics being calculated based on the testing data. The number of iterations was set to 20. We report the average performance metrics here.
4.1. Brier Score
The models are compared firstly according to the Inverse Probability of Censoring Weighted Brier Score [36,37] (referred to as the Brier Score in this paper), , which can be thought of as a mean squared error for probabilistic predictions. The Brier Score spans the range [0, 1], with 0.25 being indicative of a naïve prediction of 50 % reliability. The inverse probability weighting accounts for the fact that right-censored observations become increasingly under-represented with time.
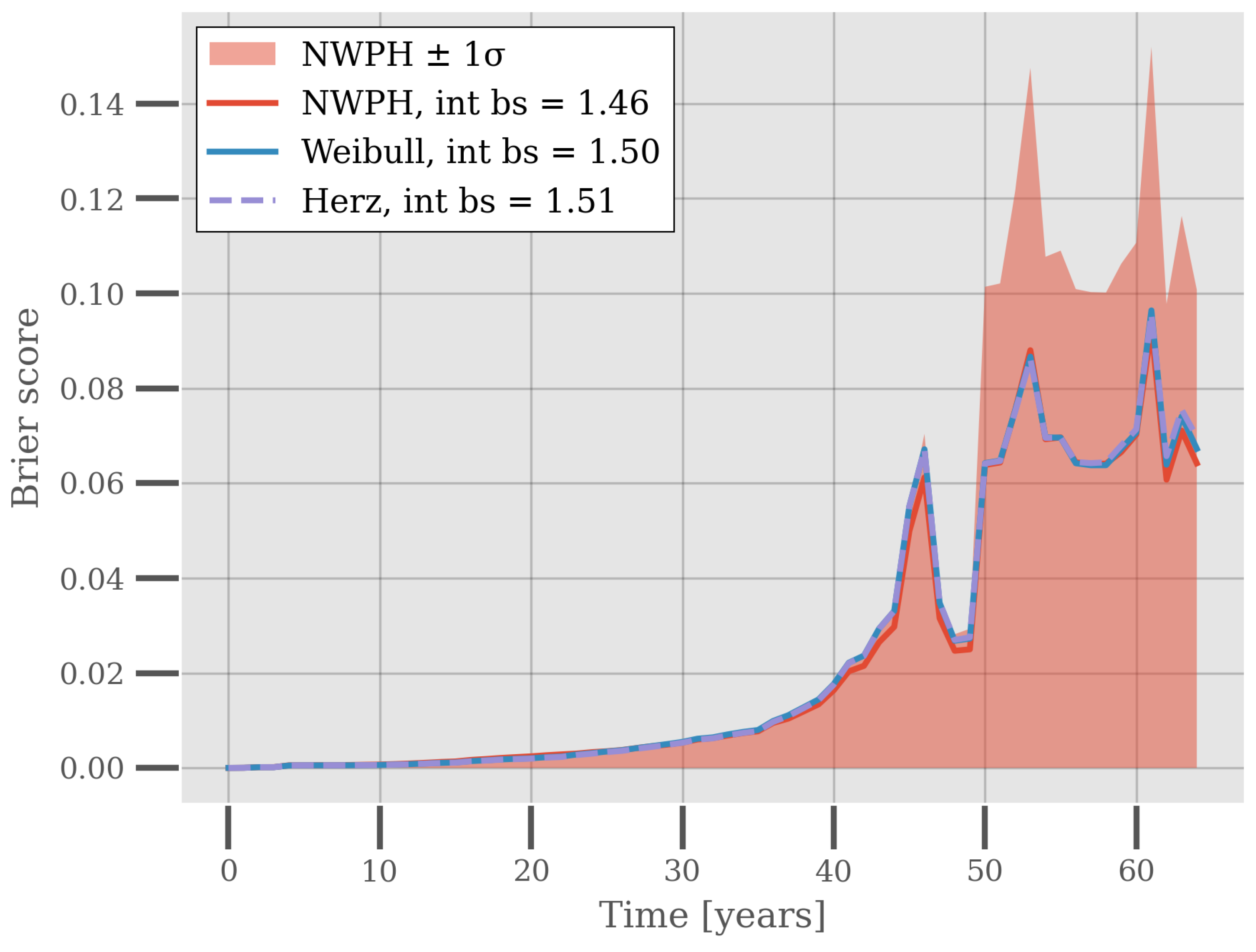
The Brier Scores for the models are shown in Figure 4. Evidently, the Brier Scores are very similar across the models, slight favoring the NWPH. However, the Brier Scores have a high standard deviation across the cross-validation experiment for all of the models. The figure shows this for the NWPH model as an example. This means that on a population basis and within the time domain currently covered by the data, the models performed equally well. It may be a testimony to the flexibility of the reliability models that they fit the data equally well, but also it may be a consequence of the relatively young population of the piping system that it is hard to discern the distributional properties of the population.
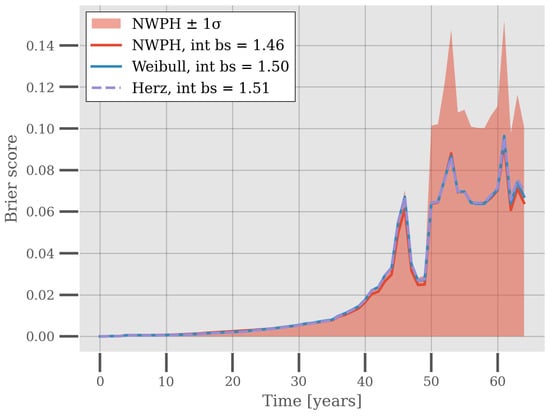
Figure 4.
Inverse Probability of Censoring Weighted Brier Score for the Weibull, Herz, and NWPH models. Each Brier Score is the average across 20 iterations of repeated stratified cross-validation. The integrated Brier Score, i.e., the area under the curve, is reported in the legend for each model. The figure also shows the Brier Scores for the NWPH model ± 1 standard deviation.
4.2. Ranking Performance
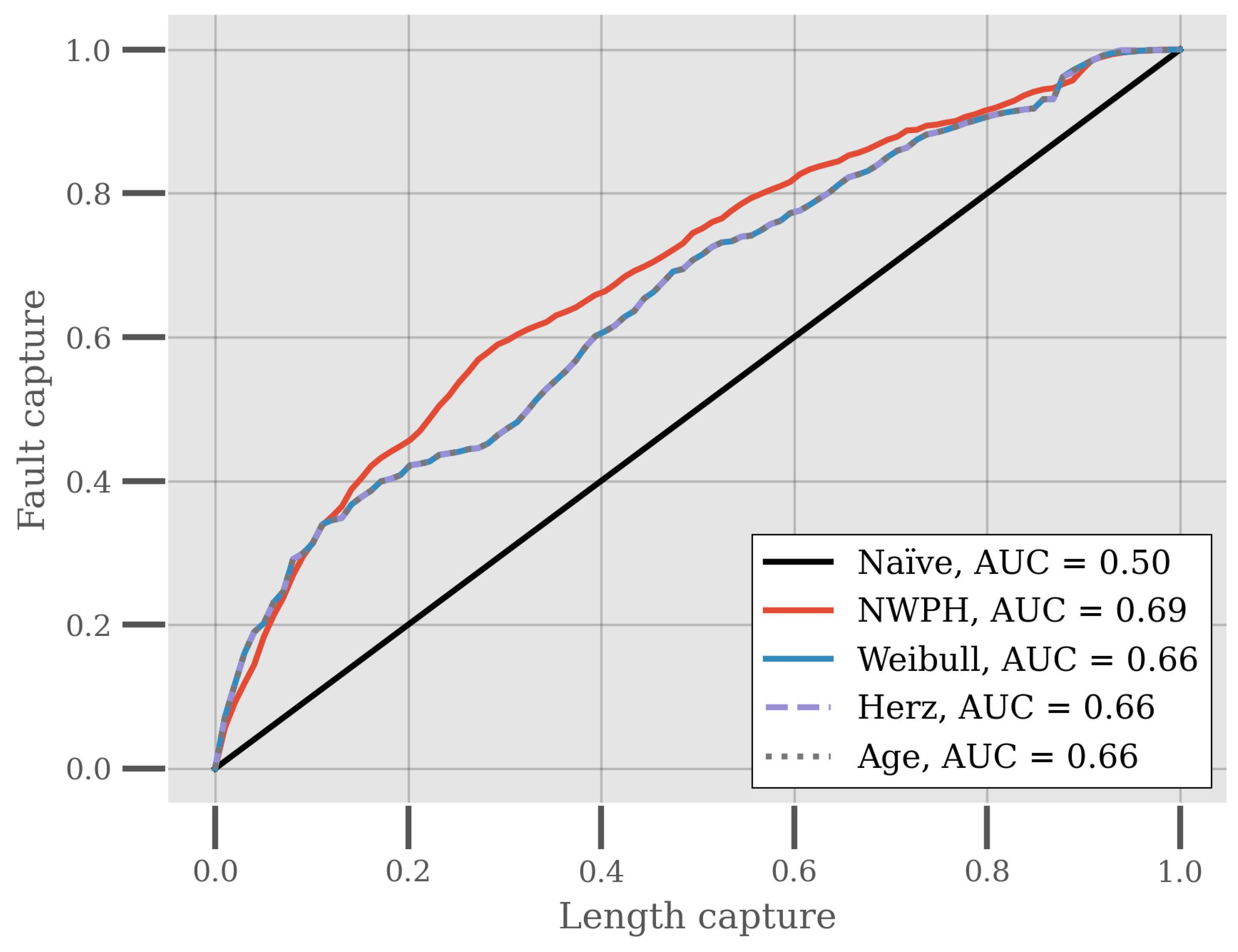
Another important characteristic of these reliability models is their ability to differentiate between the reliability or hazard rates of assets, which is important for asset maintenance decision-making and renovation planning. For this reason, the models are compared based on their fault capture length capture [35,38] (FCLC), which is a measure of the relation between the normalized cumulative sum of actual historical faults and the normalized cumulative sum of pipe length. As an example, the (0.2, 0.3) point on the FCLC curve would be interpreted as the 20% of the pipes length-wise that are identified as the most vulnerable being responsible for 30% percent of the failures. The larger the area under the curve (AUC), the better the result, with a naïve ranking of the pipes having an AUC of 0.5 on average.
Figure 5 shows the average FCLC for each of the reliability models and a ranking based entirely on the age of the piping system. All of the models achieve a better ranking than a naïve ranking, with the average performance of the Weibull and Herz models and the age-based ranking being identical. The NWPH on the other hand outperforms the Weibull and Herz models and age-based ranking in terms of this relative fault vulnerability ranking.
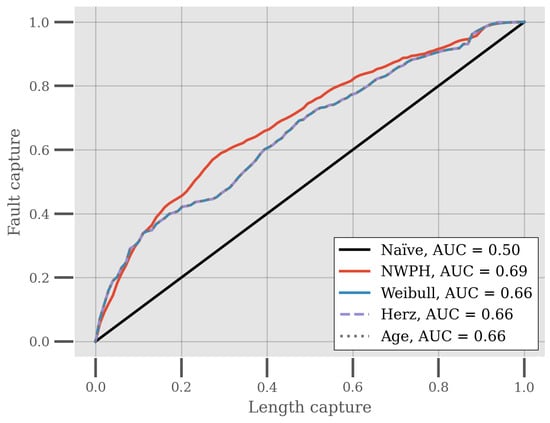
Figure 5.
Fault capture length capture curves for the Weibull, Herz, and NWPH models. The curves represent averages across 20 iterations of repeated stratified cross-validation. The area under the curve (AUC) is noted in the legend for each of the model.
To determine whether the ranking performance of the NWPH model was statistically significantly better than the age-based ranking, we performed a series of tests. These non-parametric statistical tests for differences in the distribution and pairwise distributions of the NWPH model’s AUC and the age-based ranking’s AUC are presented in Table 1. The Wilcoxon two-sample statistic test was firstly employed to test whether the pairwise differences in the AUC for the NWPH model and the age-based ranking were zero-centered. The p-value of 1.91 × 10−5, with a significance level of 5%, confirms that this is not the case. Therefore, the alternative hypothesis is accepted. Subsequently, we tested whether the pairwise differences between the AUC for the NWPH model and the AUC for the age-based ranking were greater than zero, which is confirmed. It can therefore be concluded that the AUC of the NWPH model is significantly greater than that of the age-based ranking when compared pairwise on the repeated cross-validation samples.

Table 1.
Non-parametric statistical tests for assessing differences in the distributions and pairwise distributions of the NWPH model’s AUC and the age-based ranking’s AUC.
To further substantiate this result, the non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to test the alternative hypothesis that the samples in one distribution are likely to be bigger than the other. For this test, the p-value is 0.0019. With the 5% significance level, this test therefore confirms that the AUC for the NWPH is larger than that of the age-based ranking. Since the age-based ranking is identical to the Weibull and Herz model in terms of the FCLC, the NWPH model also outperforms these models. These results therefore show that a contextual understanding of how the piping systems’ features impact its reliability is useful for ranking.
4.3. Distributions
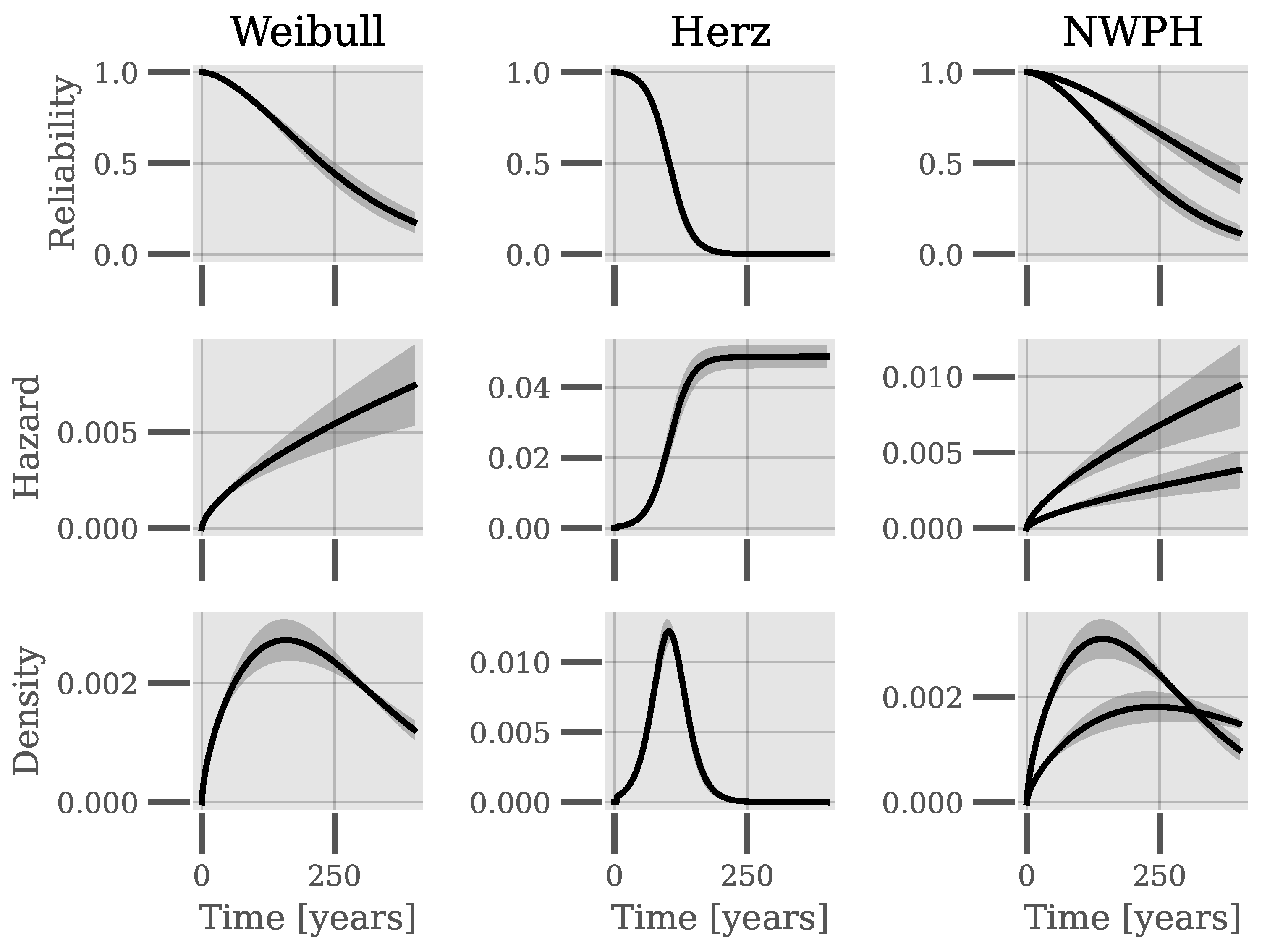
Figure 6 shows the reliability, hazard rates, and probability density functions for the Weibull, NWPH, and Herz models based on the parameters estimated during cross-validation. For the NWPH mode, every unique covariate vector has its own unique functions, for which reason examples from two piping systems are shown in the figure. It is clear that there appears a great disparity between the reliability and hazard rates of the Weibull and Herz models as time increases. For t < 50, where the majority of the data reside, the reliability according to the two models is very similar, which is likely why the Brier Scores are almost identical. To further substantiate the disparity between models, consider that the expected lifetimes on average of the cross-validation for the Weibull and Herz models, respectively, are 256 years and 104 years.
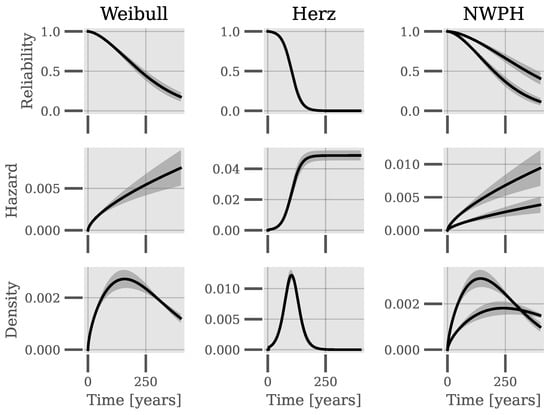
Figure 6.
Reliability, hazard rate, and probability density function data for the Weibull, NWPH, and Herz models based on the parameters estimated during cross-validation. For the NWPH model, examples from two piping systems are shown. The shaded areas show the mean ± 1 standard deviation.
Although the Herz model imposes an asymptotic limit for the hazard rate, the Weibull model does not come anywhere near this limit of about 0.05 for the first hundred years. Without failure data covering a longer period of the lifetime of the piping systems, determining which distributional assumption fits the population best in the long term is not possible.
4.4. Feature Importance
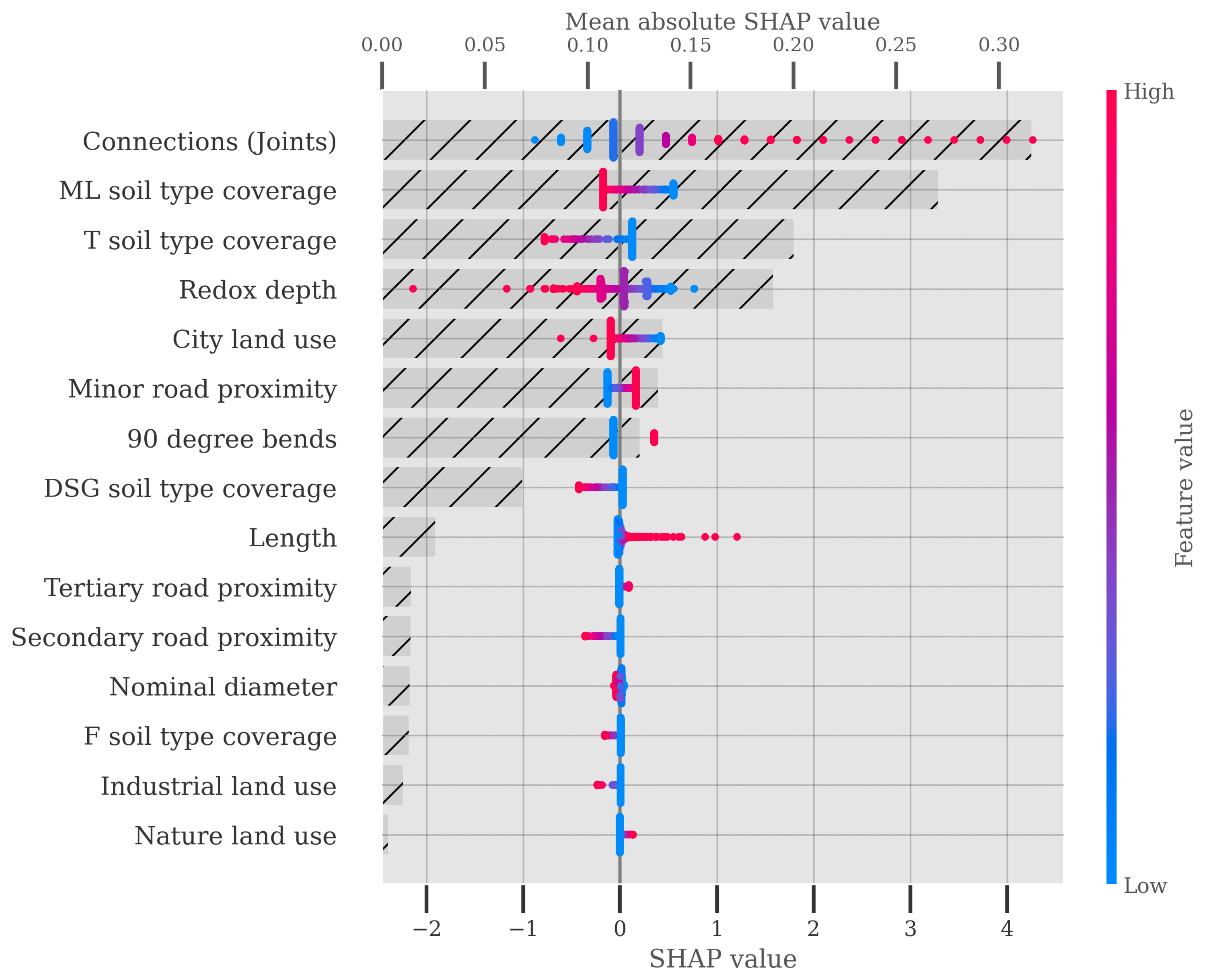
The importance that the neural network of the NWPH model puts on the features of the piping system is shown in Figure 7 using Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP) values. To produce this plot, the NWPH model was trained on all data. The figure shows both the distribution of the SHAP values for each feature (primary x-axis) and the mean absolute SHAP value or model impact (secondary x-axis). The number of connections each pipe has, each being representative of a joint, is the most important feature, which is consistent with the operators’ experience regarding the failures being typically caused by poor joints. The degree of coverage of different soil types and the redox depth, which is the depth to the anaerobic boundary, also show a relatively high correlation with relative risk according to the NWPH model. The length of the pipe, while positively correlated with the relative risk, has a relatively low impact on the model’s predictions.
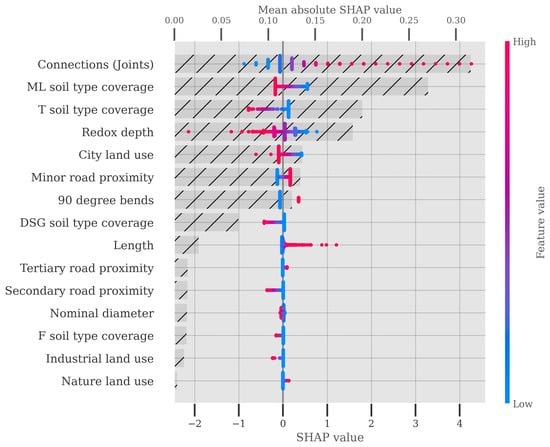
Figure 7.
SHAP values for the features of the NWPH model (primary x-axis). The features are presented in descending order according to their mean absolute SHAP values, i.e., the most impactful features come first. The underlying horizontal bar chart shows the mean absolute model impact for each feature on the secondary x-axis.
5. Discussion
Both the Weibull and Herz distributions are flexible enough to fit the data well within the first 50 years of operation. However, it proves impossible to discern between the Herz and Weibull failure distribution as the district heating system is relatively young. The fact that the models differ greatly in their long-term predictions of the hazard rate and reliability means that caution should be exercised when using these models to forecast failure rates and plan maintenance interventions. Forecasting failure rates only a few years into the future combined with continuous retraining and comparative evaluation of the models could be part of the solution to this challenge. More importantly, the comparative evaluation of the models for district heating systems that are relatively older should be prioritized in future research to validate the parametric assumptions of the models.
5.1. Estimation Techniques
In this work, the parameter estimation of the models was performed using maximum likelihood estimation. While this enabled a good fit on the current failure data, it does not guarantee good extrapolations. In [28], the use of ’soft’ estimation techniques is suggested for the Herz model, relying on the experience of experts such as maintenance personnel, operators, and pipe suppliers, determining the distributional parameters based on expected lifetime and lifetime variance. In this setting, the Danish district heating association, Dansk Fjernvarme, expects district heating pipes to have lifetimes of upwards of 100 years [39], which is consistent with the expected lifetime of the Herz model. On the other hand, the Weibull distribution has been used to good effect for modeling the reliability of water pipes using likelihood estimation techniques [20,26]. Using the existing literature to validate the distributional assumptions is therefore not straightforward. This is further complicated by the historic changes in the manufacturing and installation paradigms for piping systems, which likely incur changes in the failure distribution of the piping systems, forcing young district heating systems to largely navigate uncharted territory.
Another consideration regarding the expected lifetime based on the Herz and Weibull models is that of the definition of failure. While in this paper a failure refers to the leakage or degradation of insulation with enough severity to produce a ground-surface hot spot, in other contemporary work in the literature, a failure is considered to be the degradation of the material properties of a pipe or its components beyond a predefined threshold value, e.g., the percentage of closed cells in the insulating PUR foam exceeding 88% [12]. The traditional lifetime estimates of a minimum of 30 to 50 years [2,12], and expected lifetimes of upwards of 100 years, are therefore not directly relatable to the lifetime estimates based on the Herz and Weibull models in this paper.
5.2. Multi-Component Systems
The failure distribution of joints and pipes likely differ, with joints having a lower expected lifetime than district heating pipes. The failure distribution of the combined system is therefore likely to be different from that of any of its constituent parts. The Weibull and Herz distribution assumptions applied in this paper, based on their merits in the reliability modeling of water pipes, are therefore challenged by the multi-component application of the models. Without longer-spanning failure data, it is not possible to ascertain whether these are appropriate. The immediate solution is the disaggregation of the modeling of the joints and pipes, which is also not possible without precise information about all pipes and joints and a more detailed maintenance record that associates failures to specific components based on maintenance personnel’s investigations.
5.3. Repairs
Maintenance interventions following the failure of piping systems are typically decided upon based on the extent of the damage and the age of the asset. In some cases, a spot repair is carried out, after which the pipe system continues to be in operation. The models in this paper have been applied to predict the apparent time to first failure, but predicting any subsequent failures should be considered as well. This is a complex undertaking for several reasons. Firstly, the distribution of time to first failure and time to subsequent failures may follow different trends, as evidence has shown is the case for water distribution pipes [18,25]. In this case, several reliability models could be applied depending on the failure history of the piping system. In [18], it is found that the time to first failure follows a Weibull distribution, while the time to subsequent failures follows an exponential distribution, showing monotonically increasing and constant hazard rates, respectively. While the Weibull model can fit either setting, the Herz model has both an initial period of an increasing failure rate and a subsequent period of a near-constant failure rate.
A generalized renewal formulation, such as that proposed by Kijima and Sumita [40], of the Herz model could therefore be appropriate for having a single model that accommodates both settings. In either case, a generalized Herz renewal model or several Weibull models, determining the renewal parameter and the parameters of the distribution, requires statistics on the time to subsequent failures. Although the case dataset contains multiple thermography reports for the same pipe in a handful of cases, these are not necessarily detections of subsequent failures but are likely means to monitor the evolution of a hot spot before any maintenance intervention is carried out. The point is that the case dataset does not provide sufficient statistics to properly explore the modeling of repairable systems.
5.4. Data-Driven Reliability
Our comparison of the ranking performance of the NWPH approach and the Herz, Weibull, and age-based ranking approaches showed that there was a significant advantage to using data-driven reliability modeling compared to standard population-scoped reliability models and age-based ranking. The feature-importance investigation in Section 4.4 showed that the number of joints is the most important feature for determining the relative risk of the pipes, which is well aligned with the experience of operators. During the process of associating likely faults to pipes, it was noticed that the location of the detected hot spots typically coincided with the apparent location of joints, either those drawn into the GIS or branched connections.
As for the majority of other correlations found with the model between the relative risk and the remaining features, it showed that soil and conditions had a high influence on the model’s predictions. These cannot be guaranteed to be cause–effect correlations. Had there, however, been a record of the maintenance personnel’s evaluations of failure causes, it would provide a valuable tool in evaluating these correlations. A record of failure causes could also inform the initial feature selection, for which reason keeping such a record should be a focus point for future asset management efforts. Given that such a record does not exist, we primarily relied on our experience from other studies and research from similar domains for the feature selection.
District heating pipes are subject to cyclical loads due to temperature variations. Over time, these loads degrade the material properties of the pipe, effectively weakening the pipe and making it more prone to failure. District heating pipes are designed for a specific number of temperature cycles [41]. For this reason, the number of equivalent temperature cycles a pipe has been subjected to could be a valuable input for reliability models. Equivalent temperature cycles can be calculated using the Rainflow counting method [42]. It has been noted by several researchers that this calculation depends on the frequency of temperature measurements [43,44], with there being a positive correlation between measurement frequency and equivalent temperature cycles, which adds requirements to the data collection practices of district heating operators.
The intrinsic operational conditions of the pipes, such as temperature and pressure, were not included in this study due to the low observability of the pipes. Even though these data are not directly measured currently, they can be estimated. For this purpose, there exist commercial data-driven tools such as Heat Intelligence [45]. The intrinsic operating conditions of district heating pipes, should they be available, can be represented as static summary statistics or as time-dependent variables in the reliability model. Representing these conditions as time-dependent variables can be achieved, e.g., by dividing the hazard rate formulation into periods where the otherwise time-dependent covariates are constant [46].
6. Conclusions
This paper assessed the applicability of traditional and machine learning-enabled reliability models for district heating pipes, and comparatively evaluated them using data from an actual district heating network. The data-driven approach to reliability analysis using the NWPH model showed a significant benefit in comprehending the relationship between the working conditions and intrinsic features of the pipes and their relative risk. This paper also demonstrates how common data deficiencies from incomplete failure data can be accommodated by modifying the likelihood expression of the models. Although operational data were not available for our case system, several approaches to incorporate operational data are suggested here based on the literature. Discerning between the distributional assumptions of the models was not possible, with the relative youth of the network being identified as the likely reason for this. Nevertheless, it was found that all models performed better than a naïve prediction according to their Brier Scores. Future research should aim to validate failure distribution assumption by investigating old district heating networks and aggregating data from multiple networks.
The results regarding the features’ impacts on the model outputs show that out of the environmental features, those representing the soil types and the conditions that the pipes lie in have the highest impact on reliability. Moreover, the vicinity of the pipes to some road types also has a high impact on predictions of their reliability. It is therefore encouraged that practitioners and researchers improve and standardize their collection of failure data. Specifically, the collection of data on the failure modes, root causes, and material properties of failed and decommissioned pipes can help validate data-driven reliability models and provide insights into how they can be improved. In line with this, better management of GIS data, such that multi-component systems, i.e., joint–pipe systems, can be disaggregated, is advisable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.K.M. and H.R.S.; methodology, L.K.M.; software, L.K.M.; validation, L.K.M.; formal analysis, L.K.M.; investigation, L.K.M.; data curation, L.K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.K.M.; writing—review and editing, H.R.S.; visualization, L.K.M.; supervision, H.R.S.; project administration, L.K.M. and H.R.S.; funding acquisition, H.R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Danish Energy Agency under the Energy Technology Development and Demonstration program (project number: 134241-521237) as part of the IEA DHC Annex TS6 on the status assessment, aging, lifetime prediction, and asset management of district heating (DH) pipes.
Data Availability Statement
The authors do not have permission to share the data of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| NWPH | Neural Weibull Proportional Hazard |
| FCLC | fault capture length capture |
| PUR | polyurethane |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanation |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| BSIPCW | Inverse Probability of Censoring Weighted Brier Score |
References
- Weidlich, I.; Schuchardt, G.K. New Approach for Asset Management in District Heating (DH) Networks. Energy Procedia 2017, 113, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.; Yarahmadi, N.; Sällström, J.H.; Jakubowicz, I. Effects of cyclic mechanical loads and thermal ageing on district heating pipes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 182, 109385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, G.I.; Kim, K.M.; Ko, S.J.; Kim, W.C.; Kim, J.G. Localized Corrosion Occurrence in Low-Carbon Steel Pipe Caused by Microstructural Inhomogeneity. Materials 2022, 15, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, E.A.; Al-Moubaraki, A.H.; Al-Masoudi, D.I.; Chafiq, M.; Chaouiki, A.; Ko, Y.G. Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel X36 in Solutions of Soils Collected from Different Areas Linked to the Main Pipe Network of a Water Distribution System in Jeddah City. Metals 2023, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.J.; An, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, W.C.; Kim, J.G. Effects of corrosion on mechanical properties of welded carbon steel pipe in district heating water. Materials 2019, 12, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.; Weidlich, I. Effects of thermal and mechanical cyclic loads on polyurethane pre-insulated pipes. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2021, 44, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.; Yarahmadi, N.; Jakubowicz, I. Determining the useful life of district heating pipes: Correlation between natural and accelerated ageing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 175, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuteritz, A.; Döring, K.D.; Lampke, T.; Kuehnert, I. Accelerated ageing of plastic jacket pipes for district heating. Polym. Test. 2016, 51, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.g.; Yoon, J. Effect of operating temperature conditions in 21-year-old insulated pipe for a district heating network. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Weidlich, I. Identification of Individual District Heating Network Conditions using Equivalent Full Load Cycles. Energy Procedia 2017, 116, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langroudi, P.P.; Weidlich, I. Applicable Predictive Maintenance Diagnosis Methods in Service-Life Prediction of District Heating Pipes. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2020, 24, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, S.; Leuteritz, A.; Morgenthum, M. Remaining service life of preinsulated bonded pipes—A key element of transformation strategies and future district heating systems in Germany. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.A.; Hallett, S.H.; Jude, S.R.; Tran, T.H. An evolution of statistical pipe failure models for drinking water networks: A targeted review. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3784–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimkevicius, S.; Kaliatka, A.; Valincius, M.; Dundulis, G.; Janulionis, R.; Grybenas, A.; Zutautaite, I. Development of approach for reliability assessment of pipeline network systems. Appl. Energy 2012, 94, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.; Wang, P.; Lu, W. The reliability and availability evaluation of repairable district heating networks under changeable external conditions. Appl. Energy 2017, 203, 686–695. [Google Scholar]
- Postnikov, I. Application of the Methods for Comprehensive Reliability Analysis of District Heating Systems. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2020, 24, 145–162. [Google Scholar]
- DHC; Euro Heat and Power. Digital Roadmap for District Heating and Cooling—v.2.; DHC+ Technology Platform: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mailhot, A.; Pelletier, G.; Noël, J.; Villeneuve, J. Modeling the evolution of the structural state of water pipe networks with brief recorded pipe break histories: Methodology and application. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3053–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Scholten, L.; Scheidegger, A.; Reichert, P.; Maurer, M. Combining expert knowledge and local data for improved service life modeling of water supply networks. Environ. Model. Softw. Environ. Data News 2013, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kimutai, E.; Betrie, G.; Sadiq, R.; Tesfamariam, S. Comparison of statistical models for prediction pipe failures: Illustrative example with the city of Calgary water main failure. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2015, 6, 04015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debón, A.; Carrión, A.; Cabrera, E.; Solano, H. Comparing risk of failure models in water supply networks using ROC curves. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2010, 95, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.M.A.; Ertuğrul, Ö.F.; Gharabaghi, B.; McBean, E.A.; Cao, J. Extreme learning machine model for water network management. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoudakis, K.; Behzadian, K.; Farmani, R.; Butler, D. Pipeline failure prediction in water distribution networks using evolutionary polynomial regression combined with K-means clustering. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, L.K.; Shaker, H.R. A Neural Weibull Proportional Hazard Model for Reliability Prediction of Underground Power Cables Considering Common Data Deficiencies. Results Eng. 2024. under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvisi, S.; Franchini, M. Comparative analysis of two probabilistic pipe breakage models applied to a real water distribution system. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2010, 27, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajani, B.; Kleiner, Y.; Sink, J.E. Exploration of the relationship between water main breaks and temperature covariates. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, G.; Tesfamariam, S.; Loeppky, J.; Sadiq, R. Predicting water main failures: A Bayesian model updating approach. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 110, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, R. Alterung und erneuerung von infrastrukturbeständen - ein kohortenüberlebensmodell. Jahrb. Reg. 1993, 14, 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Herz, R. Alterungsprozesse in Wasserrohrnetzen und daraus resultierender erneuerungsbedarf. In Sonderdruck: Sichere Ver-und Entsorgung durch Rohrleitungen; Schriftenreihe aus dem Institut für Rohrleitungsbau an der Fachhochschule: Oldenburg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gat, Y.; Eisenbeis, P. Using maintenance records to forecast failures in water networks. Urban Water 2000, 2, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.P.; Moeschberger, M.L.; SpringerLink (Online Service). Survival Analysis: Techniques for Censored and Truncated Data, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.E.; Fafner, K. Værktøjer til Renoverinsplanlægning; Technical Report; Rambøll: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, A.H. SmartRenovering; Technical Report; Niras: Aarhus, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, R.A.; Guikema, S.D.; Henneman, L. Bayesian Belief Networks for predicting drinking water distribution system pipe breaks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 130, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, L.K.; Shaker, H.R.; Veje, C.T. Relative fault vulnerability prediction for energy distribution networks. Appl. Energy 2022, 322, 119449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, E.; Schmoor, C.; Sauerbrei, W.; Schumacher, M. Assessment and comparison of prognostic classification schemes for survival data. Stat. Med. 1999, 18, 2529–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerds, T.A.; Schumacher, M. Consistent Estimation of the Expected Brier Score in General Survival Models with Right-Censored Event Times. Biom. J. 2006, 48, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.Y.J.; Guikema, S.D. Prediction of water main failures with the spatial clustering of breaks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 203, 107108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjernvarme, D. Levetid for Ledninger. 2022. Available online: https://danskfjernvarme.dk/viden-og-v%C3%A6rkt%C3%B8jer/ledningsnet-og-lagring/levetid-for-ledninger (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Kijima, M.; Sumita, U. A useful generalization of renewal theory: Counting processes governed by non-negative Markovian increments. J. Appl. Probab. 1986, 23, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13941-1; District Heating Pipes—Design and Installation of Thermal Insulated Bonded Single and Twin Pipe Systems for Directly Buried Hot Water Networks: Part 1: Design. European CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
- AGFW FW 401; Installation and Calculation of Preinsulated Bonded Pipes for District Heating Networks. Part 10: Static Design; Basics of Stress Analysis. AGFW: Franfur am Main, Germany, 2007.
- Christensen, R.; Hansen, K.E.; Neergaard, L.B.; Randløv, P.; Olsson, N. Temperature Variations in Preinsulated District Heating Pipes, Low Cycle Fatigue; International Energy Agency, IEA District Heating and Cooling: Sittard, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Banushi, G. Performance of Operating District Heating Pipelines Subjected to Thermal Aging and Fatigue; Universitätsbibliothek der HafenCity Universität Hamburg (HCU): Hamburg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kamstrup. Heat Intelligence; Kamstrup: Skanderborg, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sparling, Y.H.; Younes, N.; Lachin, J.M.; Bautista, O.M. Parametric survival models for interval-censored data with time-dependent covariates. Biostatistics 2006, 7, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).