Network Security Challenges and Countermeasures for Software-Defined Smart Grids: A Survey
Highlights
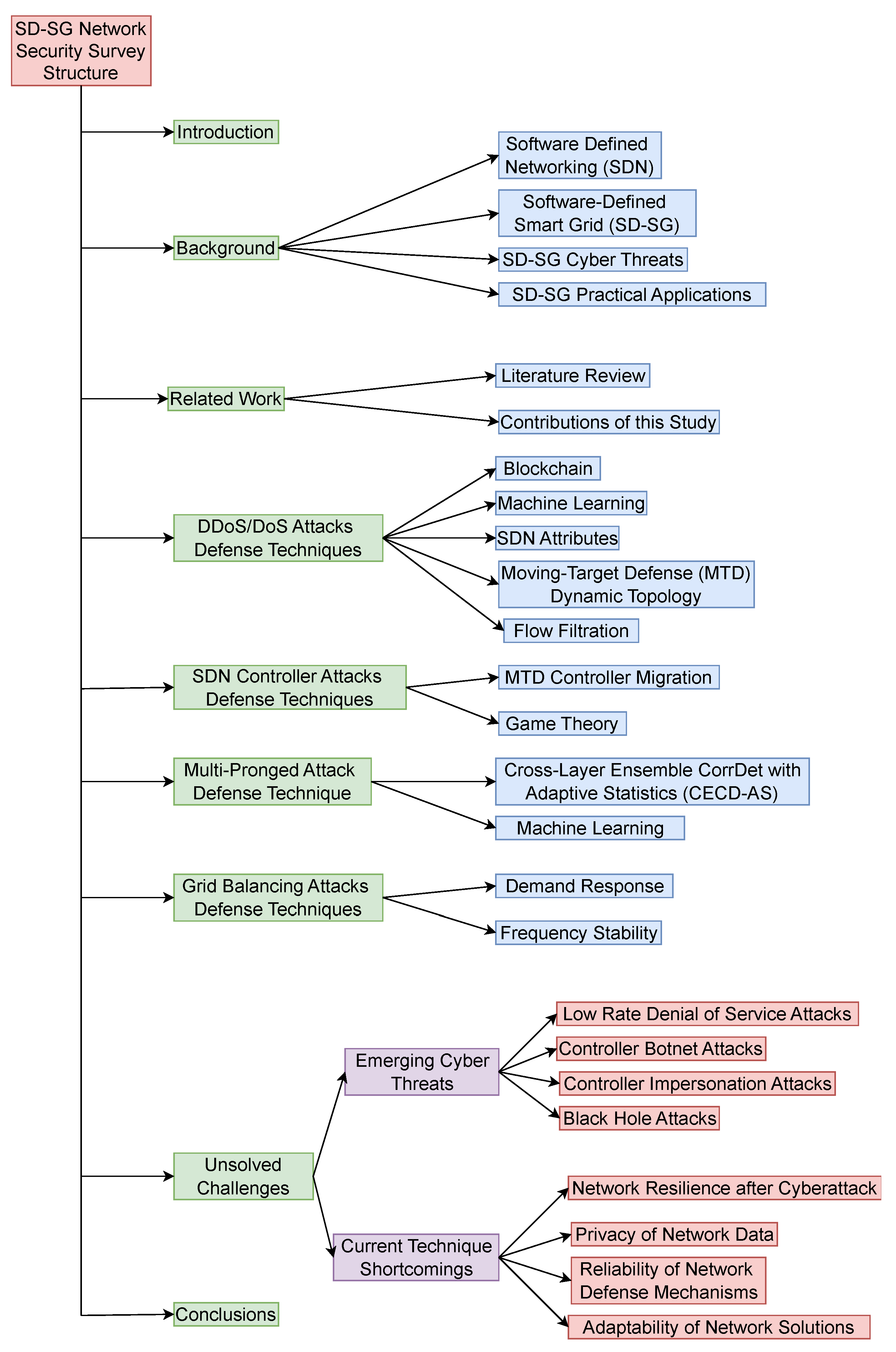
- We have reviewed previous related work for software-defined smart grid (SD-SG) network cybersecurity and have determined that previous efforts have primarily concentrated on denialof- service (DoS)/distributed the denial-of-service (DDoS), software-defined controller, multipronged, and grid balancing attacks and defense techniques that consist of blockchain, machine learning, moving target defense, game theory, software-defined networking attributes, demand response, and frequency stability.
- Unresolved challenges of SD-SG network cybersecurity research include SD-SG security against emerging threats, namely low-rate DoS, controller botnet, controller impersonation, and black hole attacks, and current technique shortcomings include network resilience following a cyberattack, network data privacy, network defensive mechanism reliability, and network solution adaptability.
- Previous SD-SG network cybersecurity research has primarily focused on these attacks, which demonstrates that a greater attack landscape has yet to be investigated and realized in current research efforts.
- Researchers have not yet examined these potential risks that could cause severe damage, and the existing cybersecurity solutions for SD-SG have shortcomings that must be addressed in future research.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- It is an up-to-date study on cyberattacks targeting SD-SG and the latest methods used to mitigate them.
- It provides a contemporary discussion of defense systems that consider multi-pronged cyberattacks and defenses that can be applied to various types of SD-SG networks.
- It involves a review of open challenges of SD-SG cybersecurity and potential mitigation techniques for emerging cyberattacks such as low-rate denial of service, controller botnet attacks, and black hole attacks for SD-SG network security.
2. Background
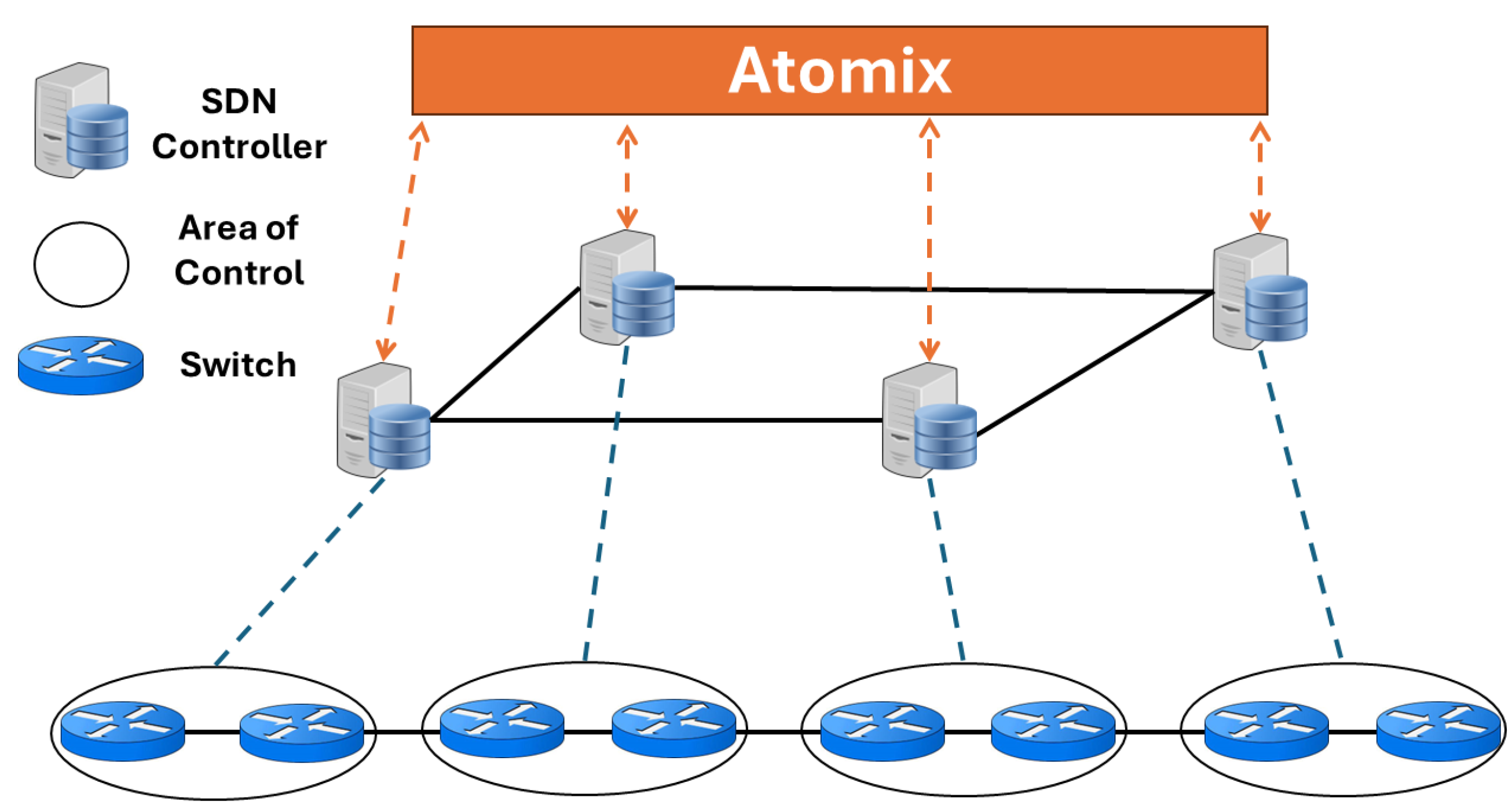
2.1. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
- The control plane and data plane are independent of one another.
- The controller functions as the primary decision-making and external component. Its primary function is to manage the flow of traffic throughout the network and ensure the network’s operational status.
- Forwarding decisions are based on flow policies and not the destination. A flow represents a common set of instructions for the exchange of packets between a source and a destination. SDN controllers provide policies that are used to establish flow tables. The flow tables are then implemented by forwarding devices.
- The network can be configured using software programs that operate on top of the SDN controller.
- Application programming interfaces (APIs) facilitate the transfer of data between the different layers of the SDN system.
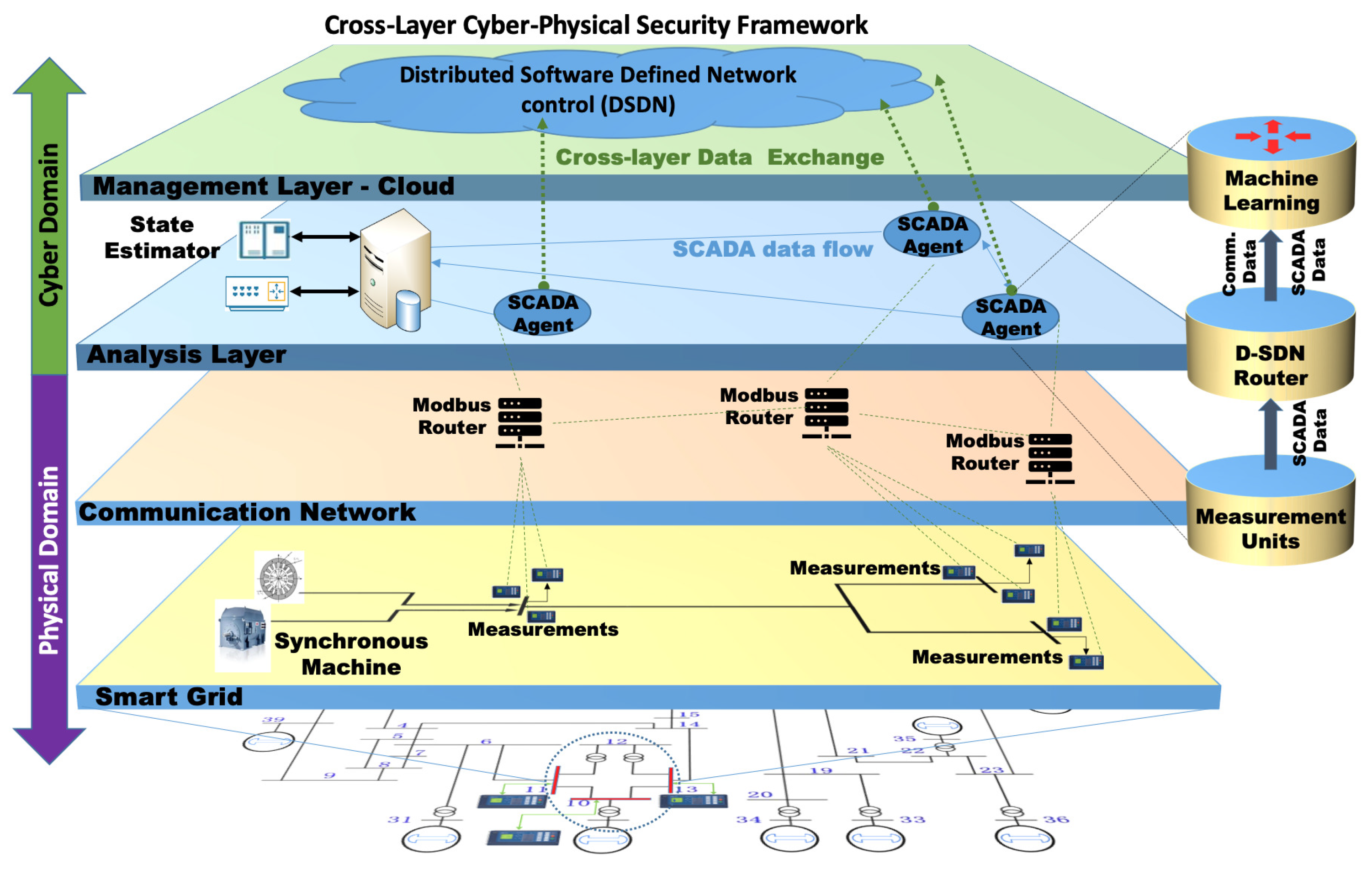
2.2. Software-Defined Smart Grid (SD-SG)
- Infrastructure/Data Layer: The data layer facilitates the movement of data amongst SG entities, including energy producers, servers, power transmission lines, and private/commercial users. The data are sent to programmable SDN-based switches and routers to be directed to the desired destination. The control layer enforces routing decisions through its policies.
- Control Layer: The advanced distribution management system (ADMS) and the SDN controller(s) make up the control layer. The ADMS includes supplementary control and data acquisition (SCADA), distributed energy resource management (DERMS), and a distribution management system (DMS) to monitor the smart grid system. Receiving system data from the application layer and returning those data to it is the role of this layer.
- Application Layer: The application layer receives data from the lower two tiers of the system to verify that the system is functioning in line with the policies set by the control layer. It carries out statistical analysis, load balancing, mobility management, flow filtration, security monitoring, and real-time system monitoring and analysis.
2.3. SD-SG Cyber Threats
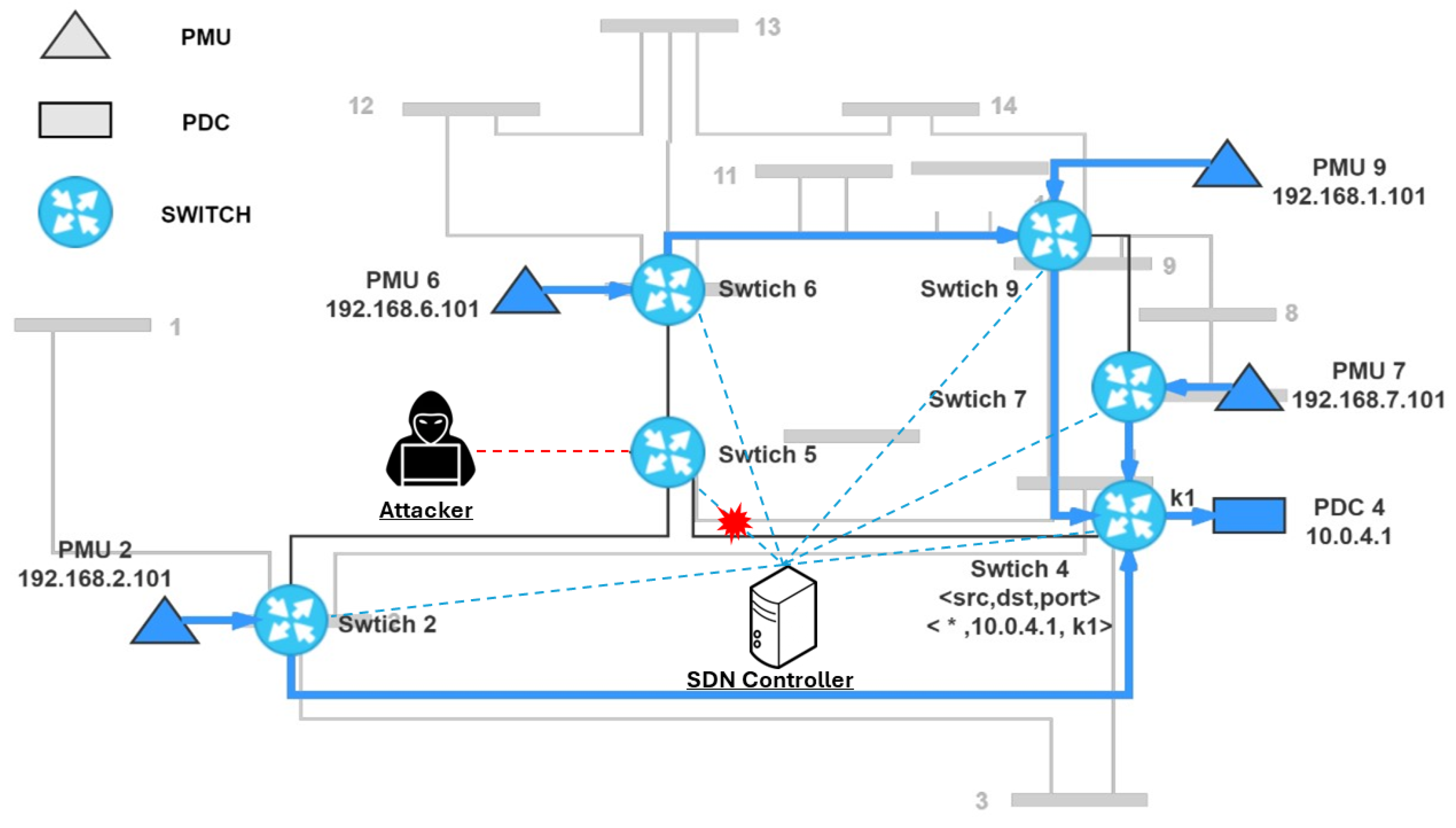
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): A DDoS/DoS attack involves launching a coordinated attack from multiple nodes on a target with the aim of overwhelming the server’s resources, rendering it incapable of responding to valid requests [34].
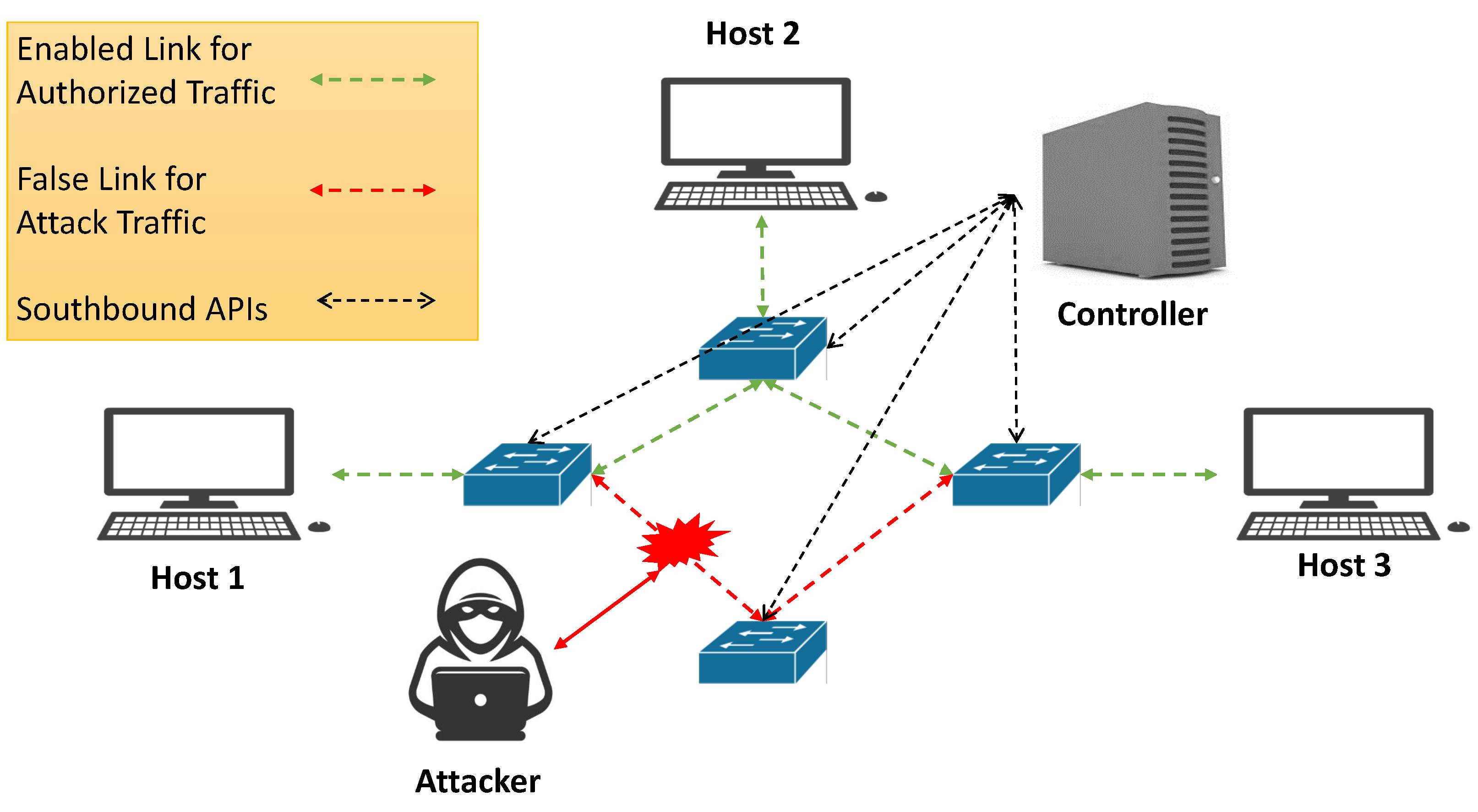
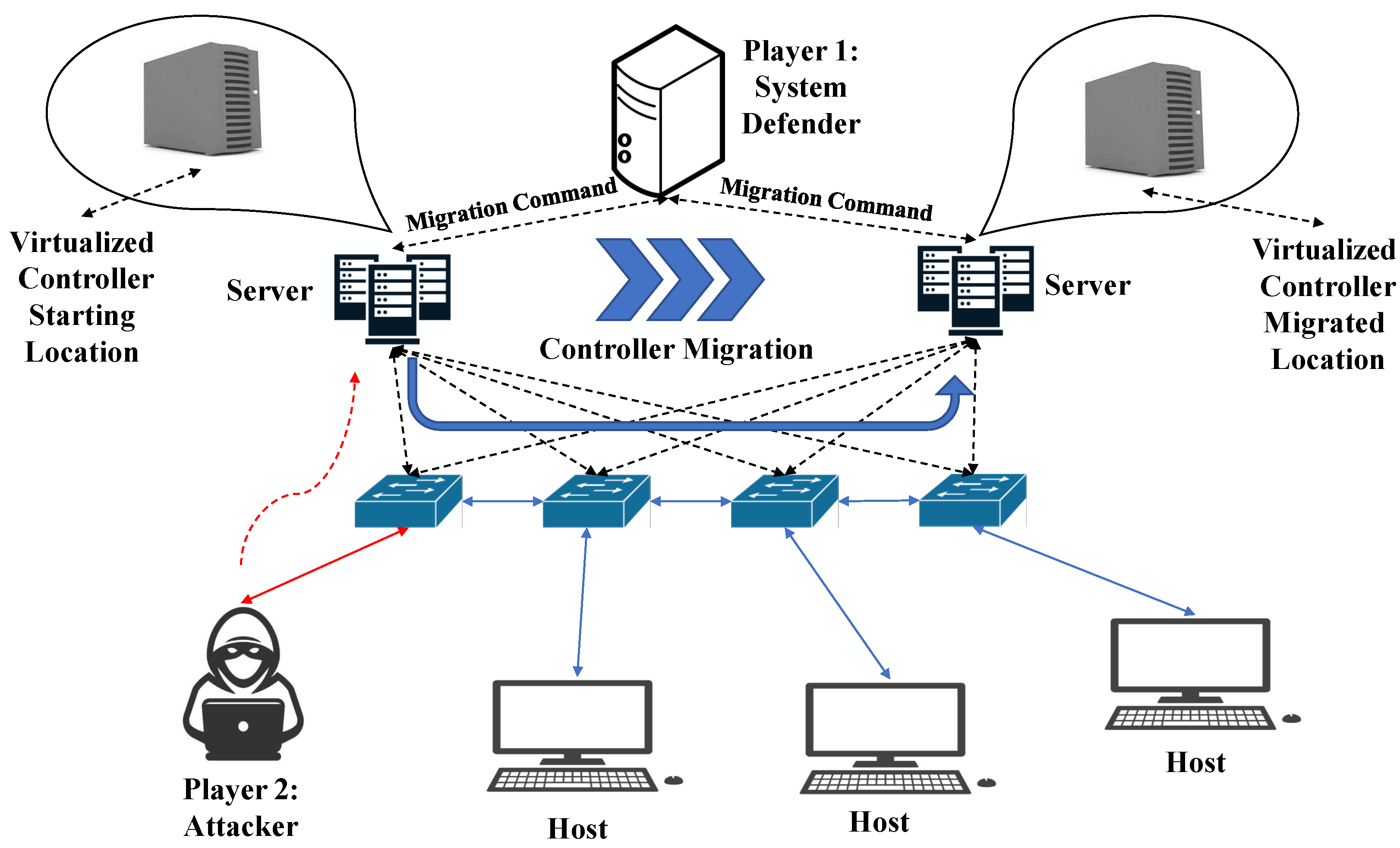
- Controller Attacks: SDN networks’ controllers are susceptible to many threats, such as DoS, hijacking, and illegal access [3,35]. These attacks seek to exploit the centralized nature of SDN controllers, which creates a single point of failure. Thus, for simple, centralized, SDN controller architectures, these attacks can disrupt the entire network by attacking the controller.
- Multi-Pronged Attacks: Multi-pronged attacks involve multiple cyberattacks of different types. An attacker can launch cyberattacks (e.g., DDoS/DoS and controller attacks) on a network without authorization. Very few researchers have investigated multi-pronged attacks against SD-SGs [36].
- Grid Balancing Attacks: Grid balancing attacks refer to the various techniques employed by adversaries to disrupt the demand response (DR) and frequency stability (FS) of SD-SG by initiating cyberattacks, including deception cyberattacks (DCAs), DoS attacks, delay attacks, and replay attacks.

2.4. SD-SG Practical Applications
3. Related Work
Specific Contributions of This Study
4. DDoS/DoS Attacks
4.1. Blockchain
4.2. Machine Learning
4.3. SDN Attributes
4.4. Moving Target Defense—Dynamic Topology
4.5. Flow Filtration
4.6. Summary and Lessons Learned
5. SDN Controller Attacks
5.1. Moving Target Defense for Controller Attacks: Controller Migration
5.2. Game Theory
5.3. Summary and Lessons Learned
6. Multi-Pronged Attacks
6.1. Cross-Layered Machine Learning Approach
| Algorithm 1: Cross-Layer Ensemble CorrDet with Adaptive Statistics (CECD-AS) Algorithm from Aljohani et al. [17] |
|
6.2. Machine Learning
6.3. Summary and Lessons Learned
7. Grid Balancing Attacks
7.1. Demand Response
7.2. Frequency Stability
7.3. Summary and Lessons Learned
8. Emerging Security Threats to SD-SG
8.1. Low-Rate Denial-of-Service (LDoS) Attacks
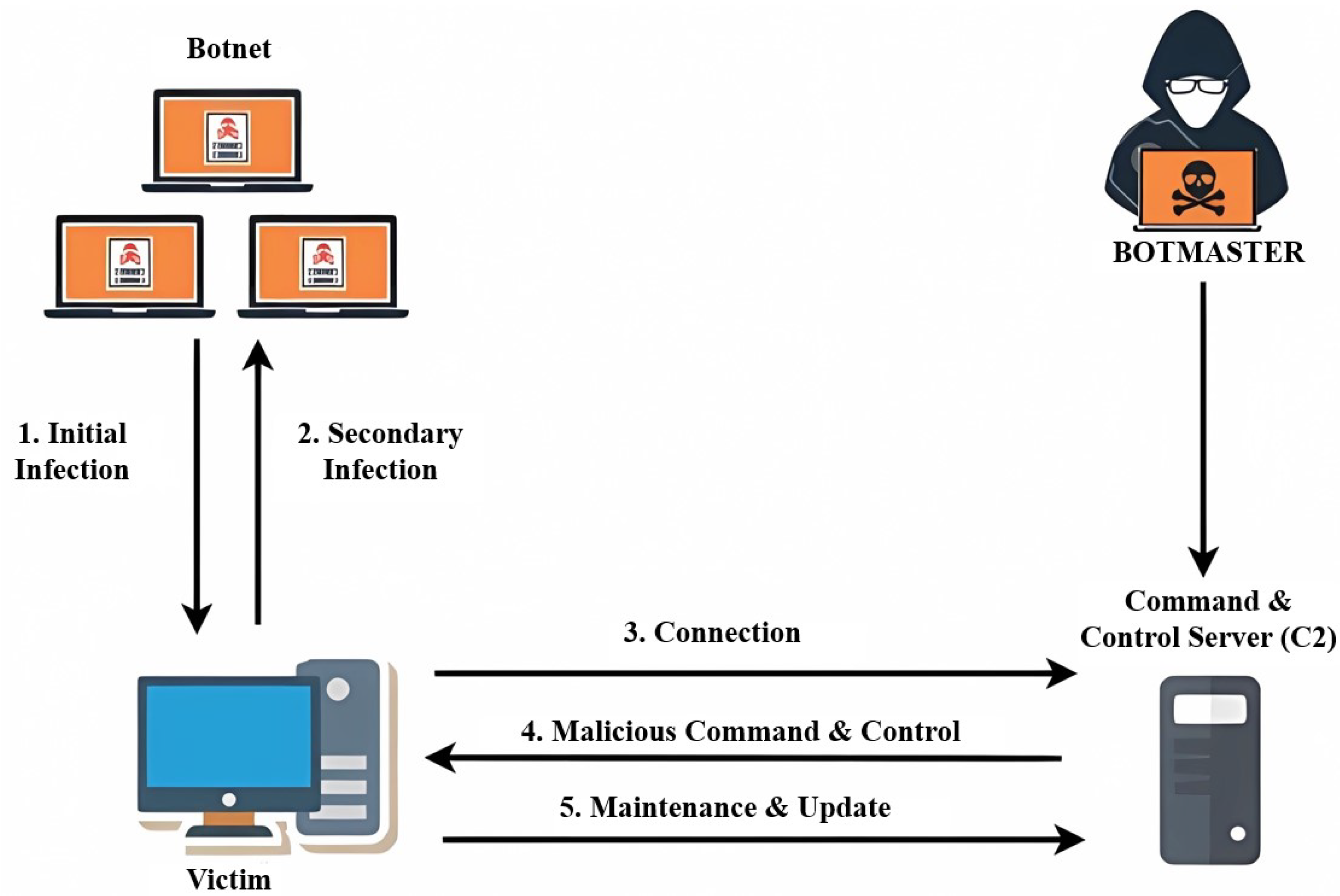
8.2. Controller Botnet Attacks
8.3. Controller Impersonation Attacks
8.4. Black Hole Attacks
8.5. Summary and Lessons Learned
9. Open Challenges
9.1. Network Resilience after Cyberattack
9.2. Privacy of Network Data
9.3. Reliability of Network Defense Mechanisms
9.4. Adaptability of Network Solutions
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehmani, M.H.; Davy, A.; Jennings, B.; Assi, C. Software defined networks-based smart grid communication: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2637–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Kumar, N.; Tanwar, S.; Alazab, M. A survey on energy trading in the smart grid: Taxonomy, research challenges and solutions. IEEE Access 2022, 9, 116231–116253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleh, Y.; Qasmaoui, Y.; El Gholami, K.; Sadqi, Y.; Mounir, S. A comprehensive survey on SDN security: Threats, mitigations, and future directions. J. Reliab. Intell. Environ. 2023, 9, 201–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbara, N.; Nait Belaid, M.O.; Gibescu, M.; Camargo, L.R.; Cantenot, J.; Coste, T.; Audebert, V.; Morais, H. Towards Software-Defined Protection, Automation, and Control in Power Systems: Concepts, State of the Art, and Future Challenges. Energies 2022, 15, 9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.; Aljohani, N.; Mathieu, R.; Boamah, S.; Nagaraj, K.; McNair, J.; Bretas, A. Implementation Aspects of Smart Grids Cyber-Security Cross-Layered Framework for Critical Infrastructure Operation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Bose, R.; Joshi, A. Entropy-based electricity theft detection in AMI network. IET Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2018, 3, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibdah, D.; Kanani, M.; Lachtar, N.; Allan, N.; Al-Duwairi, B. On the security of SDN-enabled smartgrid systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical and Computing Technologies and Applications (ICECTA), Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, 21–23 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Akkaya, K.; Uluagac, A.S.; Aydeger, A. Software defined networking for wireless local networks in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 40th Local Computer Networks Conference Workshops (LCN Workshops), Clearwater Beach, FL, USA, 26–29 October 2015; pp. 826–831. [Google Scholar]
- Abujubbeh, M.; Al-Turjman, F.; Fahrioglu, M. Software-defined wireless sensor networks in smart grids: An overview. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Sagiroglu, S. Software-defined networking for improving security in smart grid systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), Paris, France, 14–17 October 2018; pp. 1021–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Filali, F.; Ko, Y.B. Trends and potentials of the smart grid infrastructure: From ICT sub-system to SDN-enabled smart grid architecture. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 706–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, I.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, R.; Singh, P.K.; Satapathy, S.C. Identifying cyber insecurities in trustworthy space and energy sector for smart grids. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.Y. A review of quantum key distribution protocols in the perspective of smart grid communication security. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 16, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, O.M.; Zulqarnain, M.; Butt, T.M. Recent advancement in smart grid technology: Future prospects in the electrical power network. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirojan, T.; Lu, S.; Phung, B.T.; Ambikairajah, E. Embedded edge computing for real-time smart meter data analytics. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Porto, Portugal, 9–11 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, P.Y. Routing in communication networks with interdependent power grid. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2020, 28, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, N.; Agnew, D.; Nagaraj, K.; Boamah, S.A.; Mathieu, R.; Bretas, A.S.; McNair, J.; Zare, A. Cross-Layered Cyber-Physical Power System State Estimation towards a Secure Grid Operation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Denver, CO, USA, 17–21 July 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Ren, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. Restoration of smart grids: Current status, challenges, and opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Tanwar, S.; Tyagi, S.; Kumar, N.; Obaidat, M.S.; Rodrigues, J.J. Fog computing for smart grid systems in the 5G environment: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Fu, X.; Luo, B.; Du, X. Detecting and mitigating ARP attacks in SDN-based cloud environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 659–664. [Google Scholar]
- McKeown, N.; Anderson, T.; Balakrishnan, H.; Parulkar, G.; Peterson, L.; Rexford, J.; Shenker, S.; Turner, J. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks. ACM Sigcomm Comput. Commun. Rev. 2008, 38, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, K.; Jimson, E.R.; Hijazi, M.; Memon, S.K. A survey: Architecture, security threats and application of SDN. J. Ind. Electron. Technol. Appl. 2019, 2, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M. Performance evaluation of Software-Defined Network (SDN) controllers using Dijkstra’s algorithm. Wirel. Netw. 2022, 28, 3787–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, D.; Ramos, F.M.; Verissimo, P.E.; Rothenberg, C.E.; Azodolmolky, S.; Uhlig, S. Software-defined networking: A comprehensive survey. Proc. IEEE 2014, 103, 14–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleplidis, E.; Salim, J.H.; Halpern, J.M.; Hares, S.; Pentikousis, K.; Ogawa, K.; Wang, W.; Denazis, S.; Koufopavlou, O. Network programmability with ForCES. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, J.P.; Le Roux, J.L. Path Computation Element (PCE) Communication Protocol (PCEP); Technical Report; Cisco Systems, France Telecom, Paris, France, 2009.
- Enns, R. NETCONF Configuration Protocol; Technical Report; Juniper Networks, Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2006.
- Hares, S.; White, R. Software-defined networks and the interface to the routing system (I2RS). IEEE Internet Comput. 2013, 17, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Luo, M.; Chou, W. REST API design patterns for SDN northbound API. In Proceedings of the 2014 28th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Victoria, BC, Canada, 13–16 May 2014; pp. 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Tootoonchian, A.; Ganjali, Y. Hyperflow: A distributed control plane for openflow. In Proceedings of the 2010 Internet Network Management Conference on Research on Enterprise Networking, San Jose, CA, USA, 27 April 2010; Volume 3, pp. 10–5555. [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs, T.L.; Gude, N.S.; Casado, M.; Mitchell, J.C.; Shenker, S. Practical declarative network management. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on Research on Enterprise Networking, Barcelona, Spain, 21 August 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy, A.; Kim, H.; Feamster, N. Procera: A language for high-level reactive network control. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networks, Helsinki, Finland, 13 August 2012; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, N.; Harrison, R.; Freedman, M.J.; Monsanto, C.; Rexford, J.; Story, A.; Walker, D. Frenetic: A network programming language. ACM Sigplan Not. 2011, 46, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Afaqui, N.; Humayan, O. Detection and prevention of DDoS attacks on software defined networks controllers for smart grid. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2019, 975, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Souza, D.; Santo, W.; Ribeiro, A.; Moreno, E. Machine learning algorithms to detect DDoS attacks in SDN. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5402. [Google Scholar]
- Starke, A.; Nagaraj, K.; Ruben, C.; Aljohani, N.; Zou, S.; Bretas, A.; McNair, J.; Zare, A. Cross-layered distributed data-driven framework for enhanced smart grid cyber-physical security. IET Smart Grid 2022, 5, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, A.; Tian, H.; He, W.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Kadoch, M. A distributed security SDN cluster architecture for smart grid based on blockchain technology. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, H.; Türkoğlu, M.; Polat, O.; Şengür, A. A novel approach for accurate detection of the DDoS attacks in SDN-based SCADA systems based on deep recurrent neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 116748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, K.; Starke, A.; McNair, J. GLASS: A Graph Learning Approach for Software Defined Network Based Smart Grid DDoS Security. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, O.; Smith, P.; Magin, J.; Reuter, L. Anomaly Detection in Smart Grids based on Software Defined Networks. In Proceedings of the SMARTGREENS, Heraklion, Greece, 3–5 May 2019; pp. 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Starke, A.; McNair, J.; Trevizan, R.; Bretas, A.; Peeples, J.; Zare, A. Toward Resilient Smart Grid Communications Using Distributed SDN with ML-Based Anomaly Detection. In Proceedings of the Wired/Wireless Internet Communications; Chowdhury, K.R., Di Felice, M., Matta, I., Sheng, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Presekal, A.; Ştefanov, A.; Rajkumar, V.S.; Palensky, P. Attack Graph Model for Cyber-Physical Power Systems using Hybrid Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 4007–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Mahmood, D.; Shaheen, Q.; Akhtar, R.; Changda, W. S-DPs: An SDN-based DDoS protection system for smart grids. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalek, M.; Hyder, B.; Govindarasu, M.; Rieger, C.G. Moving target defense routing for SDN-enabled smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR), Rhodes, Greece, 27–29 July 2022; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Gómez-Expósito, A.; Netto, M.; Mili, L.; Abur, A.; Terzija, V.; Kamwa, I.; Pal, B.; Singh, A.K.; Qi, J.; et al. Power System Dynamic State Estimation: Motivations, Definitions, Methodologies, and Future Work. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 3188–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Singh, A.K.; Mir, A.S.; Taha, A.; Rouhani, A.; Gomez-Exposito, A.; Meliopoulos, A.; Pal, B.; Kamwa, I.; Qi, J.; et al. Power System Dynamic State and Parameter Estimation-Transition to Power Electronics-Dominated Clean Energy Systems: IEEE Task Force on Power System Dynamic State and Parameter Estimation; IEEE Power and Energy Society Resource Center: New Yor, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Singh, A.K.; Zhao, J.; Meliopoulos, A.P.S.; Pal, B.; Ariff, M.A.b.M.; Van Cutsem, T.; Glavic, M.; Huang, Z.; Kamwa, I.; et al. Dynamic State Estimation for Power System Control and Protection. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 5909–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, N. An iterative dynamic state estimation and bad data processing. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 1989, 11, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, A.S.; Bretas, N.G.; Massignan, J.A.D.; London Junior, J.B.A. Hybrid Physics-Based Adaptive Kalman Filter State Estimation Framework. Energies 2021, 14, 6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ding, L.; Chakrabarti, S.; Gryazina, E.; Terzija, V. Power system anomaly detection using innovation reduction properties of iterated extended kalman filter. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 136, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Dong, M.; Ota, K.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Wu, J. Security function virtualization based moving target defense of SDN-enabled smart grid. In Proceedings of the ICC 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Azab, M.; Samir, M.; Samir, E. “MystifY”: A proactive Moving-Target Defense for a resilient SDN controller in Software Defined CPS. Comput. Commun. 2022, 189, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, V.; Sikdar, B. A game-theoretic approach for enhancing data privacy in sdn-based smart grids. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 10583–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, M.; Azab, M.; Samir, E. SD-CPC: SDN controller placement camouflage based on stochastic game for moving-target defense. Comput. Commun. 2021, 168, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, R.A.; Faheem, Y. A Bayesian Game-Theoretic Intrusion Detection System for Hypervisor-Based Software Defined Networks in Smart Grids. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 88656–88672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, K.; Zou, S.; Ruben, C.; Dhulipala, S.; Starke, A.; Bretas, A.; Zare, A.; McNair, J. Ensemble CorrDet with adaptive statistics for bad data detection. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevizan, R.D.; Ruben, C.; Nagaraj, K.; Ibukun, L.L.; Starke, A.C.; Bretas, A.S.; McNair, J.; Zare, A. Data-driven physics-based solution for false data injection diagnosis in smart grids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM, Denver, CO, USA, 17–21 July 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ruben, C.; Dhulipala, S.; Nagaraj, K.; Zou, S.; Starke, A.; Bretas, A.; Zare, A.; McNair, J. Hybrid data-driven physics model-based framework for enhanced cyber-physical smart grid security. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Houda, Z.A.; Brik, B.; Khoukhi, L. Ensemble Learning for Intrusion Detection in SDN-Based Zero Touch Smart Grid Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 47th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 26–29 September 2022; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengpeng, D.; Jinguo, L.; Liangliang, W.; Mi Wen, Y.G. HYBRID-CNN: An Efficient Scheme for Abnormal Flow Detection in the SDN-Based Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the Security and Communication Networks, Xi’an, China, 21–23 August 2020; p. 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lao, K.W.; Hui, H.; Chen, Y. Secure distributed control for demand response in power systems against deception cyber-attacks with arbitrary patterns. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lao, K.W.; Chen, Y.; Hui, H. Resilient distributed control against false data injection attacks for demand response. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 39, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Tan, Z. Membership-function-based secondary frequency regulation for distributed energy resources in islanded microgrids with communication delay compensation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 39, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lao, K.W.; Hui, H.; Chen, Y. A robustness-enhanced frequency regulation scheme for power system against multiple cyber and physical emergency events. Appl. Energy 2023, 350, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, C.K.; Yu, L.; Tan, Z. Hierarchical Control of Inverter Air Conditioners for Frequency Regulation Service of Islanded Microgrids With Fair Power Participation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, A.; Hoyos, J.; Hulse, M.; Keller, E. Software-defined energy communication networks: From substation automation to future smart grids. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 558–563. [Google Scholar]
- Goodney, A.; Kumar, S.; Ravi, A.; Cho, Y.H. Efficient PMU networking with software defined networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 378–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; He, K.; Thottan, M.; Deshpande, J.G. Virtualized and self-configurable utility communications enabled by software-defined networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Venice, Italy, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, E.; Jacob, E.; Matias, J.; Moreira, N.; Astarloa, A. Using software defined networking to manage and control IEC 61850-based systems. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 43, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Seet, B.C.; Lie, T.T.; Foh, C.H. Opportunities for software-defined networking in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing, Tainan, Taiwan, 10–13 December 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Lin, H.; Tan, R.; Iyer, R.K.; Kalbarczyk, Z. Software-defined networking for smart grid resilience: Opportunities and challenges. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on Cyber-Physical System Security, Singapore, 14–17 April 2015; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jakaria, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Gokhale, A. Resiliency-aware deployment of SDN in smart grid SCADA: A formal synthesis model. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021, 18, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, U.; Chatterjee, P.; Shetty, S. A security framework for SDN-enabled smart power grids. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW), Atlanta, GA, USA, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sydney, A.; Nutaro, J.; Scoglio, C.; Gruenbacher, D.; Schulz, N. Simulative comparison of multiprotocol label switching and openflow network technologies for transmission operations. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmani, M.H.; Akhtar, F.; Davy, A.; Jennings, B. Achieving resilience in sdn-based smart grid: A multi-armed bandit approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th IEEE Conference on Network Softwarization and Workshops (NetSoft), Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–29 June 2018; pp. 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Agnew, D.; Boamah, S.; Mathieu, R.; Cooper, A.; McNair, J.; Bretas, A. Distributed software-defined network architecture for smart grid resilience to denial-of-service attacks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 July 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Chen, B.; Jin, D. Cyber-resilience enhancement of PMU networks using software-defined networking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Tempe, AZ, USA, 11–13 November 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chica, J.C.C.; Imbachi, J.C.; Vega, J.F.B. Security in SDN: A comprehensive survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 159, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Khorsandroo, S.; Sánchez, A.G.; Tosun, A.S.; Arco, J.M.; Doriguzzi-Corin, R. Hybrid SDN evolution: A comprehensive survey of the state-of-the-art. Comput. Netw. 2021, 192, 107981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsch, N.; Kurtz, F.; Georg, H.; Hägerling, C.; Wietfeld, C. Software-defined networking for smart grid communications: Applications, challenges and advantages. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Venice, Italy, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Nafi, N.S.; Ahmed, K.; Gregory, M.A.; Datta, M. Software defined neighborhood area network for smart grid applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 79, 500–513. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, A.; Govindarasu, M. Cyber attack exposure evaluation framework for the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedramnia, K.; Rahmani, M. Survey of DoS Attacks on LTE infrastructure used in AMI System and Countermeasures. In Proceedings of the 2018 Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Sanandaj, Iran, 28–29 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Shin, M.; Jang, H.s. A Study on the Application of Cross-Certification Technology for the Automatic Authentication of Charging Users in ISO 15118 Standard. J. Soc. -Bus. Stud. 2020, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fehér, M.; Yazdani, N.; Hansen, M.T.; Vester, F.E.; Lucani, D.E. Smart meter data compression using generalized deduplication. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2020–2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ruan, D.; Gu, D.; Gao, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Dai, F.; Yang, J. Analysis of smart grid security standards. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering, Shanghai, China, 10–12 June 2011; Volume 4, pp. 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.Q.; Al-Shaer, E.; Duan, Q. Randomizing AMI configuration for proactive defense in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, V.S.; Tealane, M.; Ştefanov, A.; Presekal, A.; Palensky, P. Cyber attacks on power system automation and protection and impact analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT-Europe), The Hague, The Netherlands, 26–28 October 2020; pp. 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, S.N.; Ravikumar, G.; Govindarasu, M. Distributed intrusion detection system using semantic-based rules for SCADA in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition (T&D), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, Z.A.; Amoudi, A.R. An Analysis of Smart Grid Attacks and Countermeasures. J. Commun. 2013, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.J.; Sagisi, J.; James, J.; Leger, A.S.; King, K.; Duncan, K.J. Simulation of man in the middle attack on smart grid testbed. In Proceedings of the 2019 SoutheastCon, Huntsville, AL, USA, 11–14 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wlazlo, P.; Sahu, A.; Mao, Z.; Huang, H.; Goulart, A.; Davis, K.; Zonouz, S. Man-in-the-middle attacks and defence in a power system cyber-physical testbed. IET Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2021, 6, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Kumar, V.; Ahmad, M. An elliptic curve cryptography based mutual authentication scheme for smart grid communications using biometric approach. J. King Saud-Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 698–705. [Google Scholar]
- El Mrabet, Z.; Kaabouch, N.; El Ghazi, H.; El Ghazi, H. Cyber-security in smart grid: Survey and challenges. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 67, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, F. Review of results on smart-meter privacy by data manipulation, demand shaping, and load scheduling. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Hwang, Y.M.; Sun, Y.G.; Sim, I.; Kim, D.I.; Wang, X. Detection for non-technical loss by smart energy theft with intermediate monitor meter in smart grid. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129043–129053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Masud, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Kaur, A. Blockchain and homomorphic encryption-based privacy-preserving data aggregation model in smart grid. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Xiao, Y. FNFD: A fast scheme to detect and verify non-technical loss fraud in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International on Workshop on Traffic Measurements for Cybersecurity, Xi’an, China, 30 May 2016; pp. 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Musleh, A.S.; Chen, G.; Dong, Z.Y. A survey on the detection algorithms for false data injection attacks in smart grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 11, 2218–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zeng, W.; Chow, M.Y. Resilient distributed DC optimal power flow against data integrity attack. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 9, 3543–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.M.; Li, W.T.; Yuen, C.; Chung, W.H.; Wen, C.K. Local cyber-physical attack with leveraging detection in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Dresden, Germany, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, K. Real-time detection of false data injection attack using residual prewhitening in smart grid network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Dresden, Germany, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Agarwal, A. Emerging technology IoT and OT: Overview, security threats, attacks and countermeasures. IJERT 2021, 10, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Zeadally, S.; He, D. Anonymous and efficient message authentication scheme for smart grid. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.A.; Yahya, K.; Garg, S.; Kaddoum, G.; Hassan, M.M.; Zikria, Y.B. LAS-SG: An Elliptic Curve-Based Lightweight Authentication Scheme for Smart Grid Environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimabadi, M.; Younis, M.; Karimi, N. Hardware assisted smart grid authentication. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Cheng, Q.; Li, X. An anonymous key agreement protocol with robust authentication for smart grid infrastructure. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shereen, E.; Dán, G. Model-based and data-driven detectors for time synchronization attacks against PMUs. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 38, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanoski, M.; Suminoski, T.; Risteski, A. Analysis of the SYN flood DoS attack. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Inf. Secur. (IJCNIS) 2013, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holik, F.; Flå, L.H.; Jaatun, M.G.; Yayilgan, S.Y.; Foros, J. Threat modeling of a smart grid secondary substation. Electronics 2022, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansilla, J.; Vasudevan, N.; JayachandraBensam, J.; Anunciya, J. Data security in Smart Grid with hardware implementation against DoS attacks. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Circuits, Power and Computing Technologies [ICCPCT-2015], Nagercoil, India, 19–20 March 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.; Kim, H.K.; Lim, Y.H.; Lim, J.I. A behavior-based intrusion detection technique for smart grid infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gunduz, M.Z.; Das, R. Cyber-security on smart grid: Threats and potential solutions. Comput. Netw. 2020, 169, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, K.; Qiu, M.; Ming, Z.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, L. Spoofing-jamming attack strategy using optimal power distributions in wireless smart grid networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, L.; Han, Z. Multiact dynamic game strategy for jamming attack in electricity market. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. Camouflage traffic: Minimizing message delay for smart grid applications under jamming. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2014, 12, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ji, X.; Xu, W. Jamming-resilient backup nodes selection for RPL-based routing in smart grid AMI networks. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2022, 27, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jin, X.; Jin, Q.; Luo, K.; Han, W. Cooperative Jamming Attack Strategy against Power Balance of Wireless Smart Grid Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 22nd IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Valencia, Spain, 10–12 March 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1042–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.Y.; Cheng, S.M.; Chen, K.C. Smart attacks in smart grid communication networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Cardenas, D.J.S.; Hahn, A.; Liu, C.C. Intrusion detection for cybersecurity of smart meters. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 12, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlullah, Z.M.; Fouda, M.M.; Kato, N.; Shen, X.; Nozaki, Y. An early warning system against malicious activities for smart grid communications. IEEE Netw. 2011, 25, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, K.; Hauser, C.; Gamage, T. Flexible data authentication evaluated for the smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Nge, C.L.; Ranaweera, I.U.; Midtgård, O.M.; Norum, L. A real-time energy management system for smart grid integrated photovoltaic generation with battery storage. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicanfar, H.; Jokar, P.; Leung, V.C. Smart grid authentication and key management for unicast and multicast communications. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Perth, Australia, 13–16 November 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, K.; Alatrash, N.; Wang, Z. A secure and efficient framework to read isolated smart grid devices. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 8, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Shin, O.S.; Lee, J.H. Detection of replay attacks in smart grid systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Computing, Management and Telecommunications (ComManTel), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 21–24 January 2013; pp. 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Farraj, A.; Hammad, E.; Kundur, D. A distributed control paradigm for smart grid to address attacks on data integrity and availability. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Netw. 2017, 4, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, L.; Rekha, D. Prevention of replay attack for isolated smart grid. In Proceedings of the Next Generation Information Processing System: Proceedings of ICCET 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lu, R.; Zhou, L.; Yang, B.; Shen, X. An efficient merkle-tree-based authentication scheme for smart grid. IEEE Syst. J. 2013, 8, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Kumar, N.; Naushad, A.; Chaudhry, S.A. A robust access control protocol for the smart grid systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 6855–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Lee, Y.; Hyun, S.H.; Koo, I. Feature selection–based detection of covert cyber deception assaults in smart grid communications networks using machine learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 27518–27529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Lu, Y.; Jafari, M.; Skare, P.M.; Rohde, K. Protecting smart grid automation systems against cyberattacks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, S.G.; Naji, H.R.; Mahani, A. Sybil attack Detection: Improving security of WSNs for smart power grid application. In Proceedings of the 2013 Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Tehran, Iran, 17–18 December 2013; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sriranjani, R.; Hemavathi, N.; Parvathy, A.; Salini, B.; Nandhini, L. Received Signal Strength and Optimized Support Vector Machine based Sybil Attack Detection Scheme in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Communication and Computational Techniques (ICCT), Jaipur, India, 19–20 January 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, D.; Singh, K.; Matnjul, M. Performance evaluation of sybil attack in cyber physical system. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, M.; Yazdani, N.; Aranha, D.F.; Lucani, D.E.; Hansen, M.T.; Vester, F.E. Side channel security of smart meter data compression techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Tempe, AZ, USA, 11–13 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.Q.; Yousefian, R.; Al-Shaer, E.; Kamalasadan, S.; Zhu, Q. Two-tier data-driven intrusion detection for automatic generation control in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29–31 October 2014; pp. 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathri, B.; Yammani, C. Multi-Attacking Strategy on Smart Grid with Incomplete Network Information. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Power Systems (ICPS), Jaipur, India, 20–22 December 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sakhnini, J.; Karimipour, H.; Dehghantanha, A.; Parizi, R.M. Physical layer attack identification and localization in cyber–physical grid: An ensemble deep learning based approach. Phys. Commun. 2021, 47, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, G.F.; Henderson, T.R. The ns-3 network simulator. In Modeling and Tools for Network Simulation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, R.L.S.; Schweitzer, C.M.; Shinoda, A.A.; Prete, L.R. Using mininet for emulation and prototyping software-defined networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Colombian Conference on Communications and Computing (COLCOM), Bogota, Colombia, 4–6 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas Silva, F.S.; Silva, E.; Neto, E.P.; Lemos, M.; Venancio Neto, A.J.; Esposito, F. A taxonomy of DDoS attack mitigation approaches featured by SDN technologies in IoT scenarios. Sensors 2020, 20, 3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Montieri, A.; Kundu, D.; Karim, M.R.; Islam, M.J.; Umme, S.; Nascita, A.; Pescapé, A. On the Integration of Blockchain and SDN: Overview, Applications, and Future Perspectives. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2022, 30, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.B.; Zhao, J.; Niyato, D.; Lam, K.Y.; Zhang, X.; Ghias, A.M.; Koh, L.H.; Yang, L. Blockchain for future smart grid: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yu, F.R.; Huang, T.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. A survey of machine learning techniques applied to software defined networking (SDN): Research issues and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 21, 393–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chai, S.; Zhang, B.; Xia, Y. Research about DoS Attack against ICPS. Sensors 2019, 19, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, A.; Erdem, H. A Review of KDD99 Dataset Usage in Intrusion Detection and Machine Learning between 2010 and 2015; Baskent University: Ankara, Türkiye, 2016; Available online: https://peerj.com/preprints/1954/ (accessed on 1 March 2024)Technical Report.
- Rohith, R.; Moharir, M.; Shobha, G. SCAPY-A powerful interactive packet manipulation program. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Networking, Embedded and Wireless Systems (ICNEWS), Bangalore, India, 27–28 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.H.; Sharma, D.P.; Alavizadeh, H.; Yoon, S.; Ben-Asher, N.; Moore, T.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lim, H.; Nelson, F.F. Toward proactive, adaptive defense: A survey on moving target defense. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 709–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E.; Bucy, R.S. New Results in Linear Filtering and Prediction Theory. J. Basic Eng. 1961, 83, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A. Synchronized phasor measurements-a historical overview. In Proceedings of the IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exhibition, Yokohama, Japan, 6–10 October 2002; Volume 1, pp. 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debs, A.S.; Larson, R.E. A Dynamic Estimator for Tracking the State of a Power System. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1970, PAS-89, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiya, K.I.; Takagi, H.; Hasegawa, J.; Koike, T. Dynamic state estimation for electric power systems—introduction of a trend factor and detection of innovation processes. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 1976, 96, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiya, K.; Hasegawa, J.; Koike, T. Dynamic state estimation including anomaly detection and identification for power systems. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1982, 129, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, A.; Akter, R.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.M. Towards Lightweight Intrusion Identification in SDN-based Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 27th Asia Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 19–21 October 2022; pp. 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Samir, M.; Azab, M.; Rizk, M.R.; Sadek, N. PYGRID: A software development and assessment framework for grid-aware software defined networking. Int. J. Netw. Manag. 2018, 28, e2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverty, D.M.; O’Raw, J.; Morrow, D.J.; Cregan, M.; Best, R. Practical evaluation of telecoms for smart grid measurements, control and protection. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd IEEE PES International Conference and Exhibition on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Manchester, UK, 5–7 December 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore, S.; Bhandari, A. Review of game theory approaches for DDoS mitigation by SDN. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2022, 88, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalakis, C.; Goldberg, P.W.; Papadimitriou, C.H. The complexity of computing a Nash equilibrium. Commun. ACM 2009, 52, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power Systems Test Case Archive. 2018. Available online: http://labs.ece.uw.edu/pstca/ (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Alvey, B.; Zare, A.; Cook, M.; Ho, D.K. Adaptive coherence estimator (ace) for explosive hazard detection using wideband electromagnetic induction (wemi). In Proceedings of the Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XXI. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–21 April 2016; Volume 9823, p. 982309. [Google Scholar]
- Dabbagchi, I.; Christie, R. Power Systems Test Case Archive; University of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Berde, P.; Gerola, M.; Hart, J.; Higuchi, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Koide, T.; Lantz, B.; O’Connor, B.; Radoslavov, P.; Snow, W.; et al. ONOS: Towards an open, distributed SDN OS. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networking, Chicago, IL, USA, 22 August 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, J.; Ghumman, N.S. Network programmability using POX controller. In Proceedings of the ICCCS International Conference on Communication, Computing & Systems, Punjab, India, 8–9 August 2014; Volume 138, p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Cokic, M.; Seskar, I. Software defined network management for dynamic smart GRID traffic. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijun, W.; Wenjing, L.; Liang, L.; Meng, Y. Low-rate DoS attacks, detection, defense, and challenges: A survey. IEEE access 2020, 8, 43920–43943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Tang, L.; Dai, R.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Rodrigues, J.J. MF-Adaboost: LDoS attack detection based on multi-features and improved Adaboost. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 106, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, S.; Ahmed Khan, H. SDN based collaborative scheme for mitigation of DDoS attacks. Future Internet 2018, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Yan, C.; Yue, M. Low-rate DoS attack flows filtering based on frequency spectral analysis. China Commun. 2017, 14, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yin, J.; Cai, Z.; Chen, W. RRED: Robust RED algorithm to counter low-rate denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2010, 14, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanovic, A.; Knightly, E.W. Low-rate TCP-targeted denial of service attacks: The shrew vs. the mice and elephants. In Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communications, Karlsruhe, Germany, 25–29 August 2003; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; He, Y.; Xiong, Q. A Q-learning based real-time mitigating mechanism against LDoS attack and its modeling and simulation with CPN. J. Comput. Res. Develop. 2011, 48, 432–439. [Google Scholar]
- Shinan, K.; Alsubhi, K.; Alzahrani, A.; Ashraf, M.U. Machine Learning-Based Botnet Detection in Software-Defined Network: A Systematic Review. Symmetry 2021, 13, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yan, Q.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. Using MTD and SDN-based honeypots to defend DDoS attacks in IoT. In Proceedings of the 2019 Computing, Communications and IoT Applications (ComComAp), Shenzhen, China, 26–28 October 2019; pp. 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ja’fari, F.; Mostafavi, S.; Mizanian, K.; Jafari, E. An intelligent botnet blocking approach in software defined networks using honeypots. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 2993–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, Q.; Basit, A. DDoS botnet prevention using blockchain in software defined internet of things. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 8–12 January 2019; pp. 624–628. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, B. SDN-based hybrid honeypot for attack capture. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chengdu, China, 15–17 March 2019; pp. 1602–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjeetha, R.; Raj, A.; Saivenu, K.; Ahmed, M.I.; Sathvik, B.; Kanavalli, A. Detection and mitigation of botnet based DDoS attacks using catboost machine learning algorithm in SDN environment. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Explor. 2021, 8, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.J.; Zubair, M. Botnet Detection and Prevention in Software Defined Networks (SDN) using DNS Protocol. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. (IJCSIS) 2019, 17, 23–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Z.; Wang, A.; Guo, Y.; Montgomery, D.; Chen, S. BotSifter: An SDN-based online bot detection framework in data centers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 June 2019; pp. 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ieracitano, C.; Adeel, A.; Morabito, F.C.; Hussain, A. A novel statistical analysis and autoencoder driven intelligent intrusion detection approach. Neurocomputing 2020, 387, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Kim, K. Genetic convolutional neural network for intrusion detection systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 113, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.; Moustafa, N.; Bukhshi, A.D.; Javed, A. Intrusion Detection System for SDN-enabled IoT Networks using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 25th International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Workshop (EDOCW), Gold Coast, Australia, 25–29 October 2021; pp. 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mutaher, H.; Kumar, P. Security-enhanced SDN controller based Kerberos authentication protocol. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 28–29 January 2021; pp. 672–677. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Meng, W.; Kwok, L.F. A survey on OpenFlow-based Software Defined Networks: Security challenges and countermeasures. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 68, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derhab, A.; Guerroumi, M.; Gumaei, A.; Maglaras, L.; Ferrag, M.A.; Mukherjee, M.; Khan, F.A. Blockchain and random subspace learning-based IDS for SDN-enabled industrial IoT security. Sensors 2019, 19, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.T.; Ku, C.Y. Detection of gray hole attack in software defined networks. In Proceedings of the ICEB 2018 Proceedings, Guilin, China, 2–6 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gurung, S.; Chauhan, S. A survey of black-hole attack mitigation techniques in MANET: Merits, drawbacks, and suitability. Wirel. Netw. 2020, 26, 1981–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkha, H.; Satori, H.; Satori, K. Preventing black hole attack in wireless sensor network using HMM. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 148, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruebler, A.; McDonald-Maier, K.D.; Alheeti, K.M.A. An intrusion detection system against black hole attacks on the communication network of self-driving cars. In Proceedings of the 2015 Sixth International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies (EST), Braunschweig, Germany, 3–5 September 2015; pp. 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Gite, P.; Chouhan, K.; Krishna, K.M.; Nayak, C.K.; Soni, M.; Shrivastava, A. ML Based Intrusion Detection Scheme for various types of attacks in a WSN using C4. 5 and CART classifiers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 80, 3769–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, W.; Jin, D.; Song, J. A cluster-based countermeasure against blackhole attacks in MANETs. Telecommun. Syst. 2014, 57, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katal, A.; Wazid, M.; Goudar, R.; Singh, D. A cluster based detection and prevention mechanism against novel datagram chunk dropping attack in MANET multimedia transmission. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Information & Communication Technologies, Thuckalay, India, 11–12 April 2013; pp. 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, M.; Joshi, B.K.; Singh, U. Mitigate wormhole attack and blackhole attack using elliptic curve cryptography in MANET. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 121, 503–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Varadarajan, V.; Kumar, A.; Dadheech, P.; Choudhary, S.S.; Kumar, V.A.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Veluvolu, K.C. Black hole attack detection in vehicular ad-hoc network using secure AODV routing algorithm. Microprocess. Microsystems 2021, 80, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthika, V.; Malarvizhi, N. Mitigate black hole attack using hybrid bee optimized weighted trust with 2-Opt AODV in MANET. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 106, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveena, S.; Senthilkumar, C.; Manikandan, T. Analysis and countermeasures of black-hole attack in manet by employing trust-based routing. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 6–7 March 2020; pp. 1222–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Galasso, C.; McNair, J.; Fujii, M.; Dong, Z. Resilient infrastructure. Commun. Eng. 2022, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, R.; Boamah, S.; Cooper, A.; Agnew, D.; Mcnair, J.; Bretas, A. Communication Network Layer State Estimation Measurement Model for a Cyber-Secure Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the ISGT NA 2024, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2024. [Google Scholar]




| Acronyms | Definitions |
|---|---|
| SG | Smart Grid |
| SD-SG | Software-Defined Smart Grid |
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| LDoS | Low-Rate Denial of Service |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technologies |
| SDWSNs | Software-Defined Wireless Sensor Networks |
| HANs | Home Area Networks |
| NANs | Neighborhood Area Networks |
| WANs | Wide Area Networks |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| ForCES | Forwarding and Control Element Separation |
| PCEP | Path Computation Element Communication Protocol |
| NetConf | Network Configuration Protocol |
| I2RS | Interface to Routing System |
| FML | Flow-Based Management Language |
| RESTful | Representational State Transfer |
| ALTO | Application-Layer Traffic Optimization |
| NVP | Nicira Network Virtualization Platform |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| OVSDB | Open vSwitch Database Management |
| BC | Blockchain |
| POF | Protocol Oblivious Forwarding |
| P2P | Peer-to-Peer Communication |
| RNNs | Deep Recurrent Neural Networks |
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional Long Short RNN |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| MTD | Moving Target Defense |
| IDS | Intrusion Detection System |
| HIDS | Host IDS |
| SIDS | Signature-Based IDS |
| AIDS | Anomaly-Based IDS |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| SD-CPC | Software-Defined Controller Placement Camouflage |
| VSFs | Virtual Security Functions |
| RED | Random Early Detection |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| AQM | Active Queue Management |
| C&C | Command and Control Channel |
| DNS | Domain Name System |
| DDNS | Dynamic DNS |
| WSNs | Wireless Sensor Networks |
| MANETs | Mobile Ad Hoc Networks |
| SDDCs | Software-Defined Data Centers |
| CECD-AS | Cross-Layer Ensemble CorrDet with Adaptive Statistics |
| FDI | False Data Injection |
| TCP-SYN | Transmission Control Protocol—Synchronize |
| TSA | Time Synchronization Attack |
| MITM | Man in the Middle |
| DR | Demand Response |
| FS | Frequency Stability |
| References | Publication Year | DDoS/DoS Attacks | Controller Attacks | Defense Techniques for Each Cyberattack | Defense System Considers Multi-Pronged Attacks | Emerging Threats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | 2019 | — | * | * | — | — |
| [7] | 2017 | * | — | — | — | — |
| [8] | 2015 | — | * | * | — | — |
| [9] | 2019 | * | — | * | — | — |
| [10] | 2018 | ✓ | — | * | — | — |
| [11] | 2015 | — | —- | * | — | — |
| This Survey | 2023 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Main Domain | Sub-Topic: Cyberattack | References |
|---|---|---|
| DDoS/DoS | [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50] | |
| SD-Smart Grid Security | SDN Controller | [51,52,53,54,55] |
| Multi-Attack | [5,17,36,56,57,58,59,60] | |
| Grid Balancing | [61,62,63,64,65] | |
| DDoS/DoS/PhysicalDoS (PDoS) | [82,83,84,85] | |
| Spoofing, Sniffing, and Message Relay | [86,87,88,89] | |
| MITM, Eavesdropping, and Homograph | [90,91,92,93,94] | |
| Meter Manipulation and Theft | [95,96,97,98] | |
| FDI | [99,100,101,102] | |
| Impersonation, Session Key Exposure, and TSA | [103,104,105,106,107,108] | |
| Smart Grid Security | TCP-SYN Flooding | [109,110,111,112] |
| Jamming | [113,114,115,116,117,118] | |
| RAM Exhaustion/CPU Overload | [119,120,121] | |
| Brute Force | [122,123,124,125] | |
| Message Replay, Covert | [126,127,128,129,130,131] | |
| Sybil | [132,133,134,135] | |
| Multi-Attack | [136,137,138,139] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agnew, D.; Boamah, S.; Bretas, A.; McNair, J. Network Security Challenges and Countermeasures for Software-Defined Smart Grids: A Survey. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 2131-2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040085
Agnew D, Boamah S, Bretas A, McNair J. Network Security Challenges and Countermeasures for Software-Defined Smart Grids: A Survey. Smart Cities. 2024; 7(4):2131-2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgnew, Dennis, Sharon Boamah, Arturo Bretas, and Janise McNair. 2024. "Network Security Challenges and Countermeasures for Software-Defined Smart Grids: A Survey" Smart Cities 7, no. 4: 2131-2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040085
APA StyleAgnew, D., Boamah, S., Bretas, A., & McNair, J. (2024). Network Security Challenges and Countermeasures for Software-Defined Smart Grids: A Survey. Smart Cities, 7(4), 2131-2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040085






