Growing Gold Nanostars on SiO2 Nanoparticles: Easily Accessible, NIR Active Core–Shell Nanostructures from PVP/DMF Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of SiO2-NH2
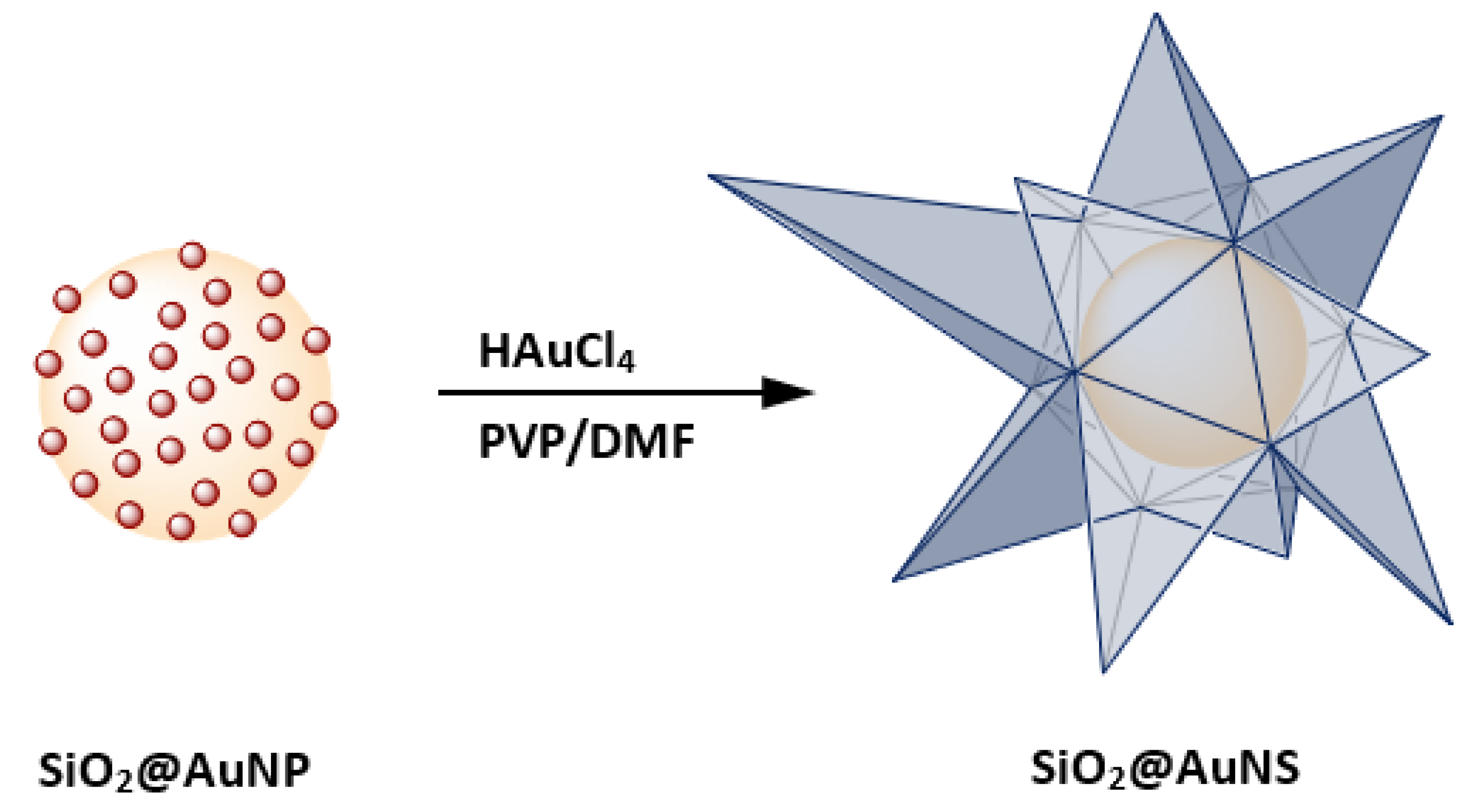
2.2. Synthesis of SiO2@AuNP
2.3. Synthesis of SiO2@AuNS
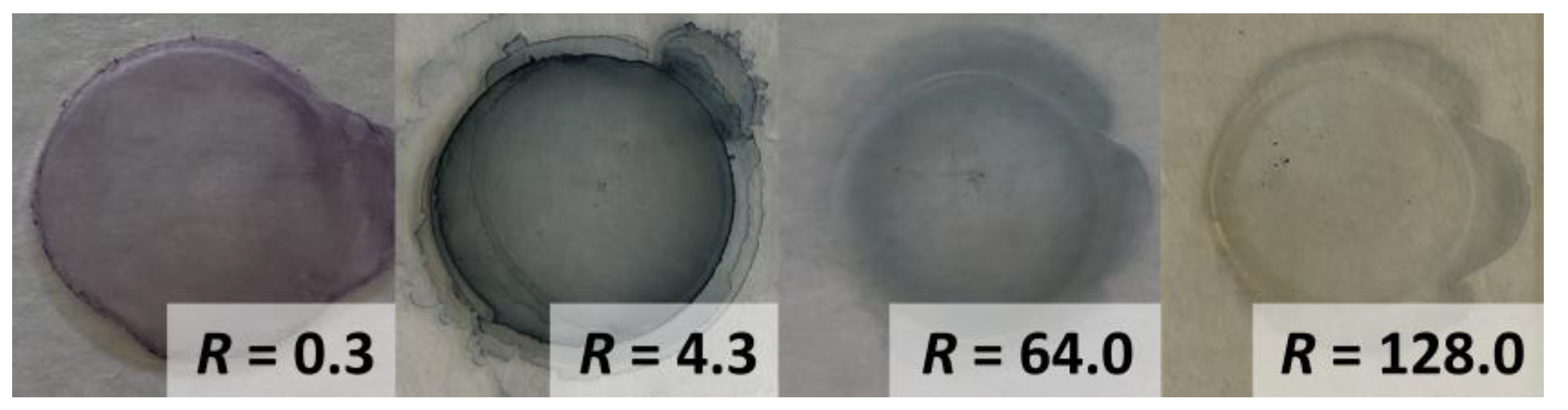
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youn, H.C.; Baral, S.; Fendler, J.H. Dihexadecyl phosphate, vesicle-stabilized and in situ generated mixed cadmium sulfide and zinc sulfide semiconductor particles: Preparation and utilization for photosensitized charge separation and hydrogen generation. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 6320–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, I.; Sano, T.; Komiyama, H. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) for Semiconductor Microcrystallites Observed in Ag-CdS Hybrid Particles. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 6692–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.S.; Sasahara, H.; Honma, I.; Komiyama, H.; Haus, J.W. Coated Semiconductor Nanoparticles: The CdS/PbS System’s Photoluminescence Properties. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Philipse, A.P. Synthesis and Optical Properties of Gold-Labeled Silica Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 176, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dragavon, J.; Cho, S.; Mao, C.; Yildirim, A.; Ma, K.; Chattaraj, R.; Goodwin, A.P.; Park, W.; Cha, J.N. Self-assembled gold nanostar–NaYF4:Yb/Er clusters for multimodal imaging, photothermal and photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4455–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Gutierrez, P.A.; DeWolf, C.; Capobianco, J.A. Upconversion Nanoparticles: Formation of a Supported Lipid Bilayer on Faceted LiYF4 :Tm3+/Yb3+ Upconversion Nanoparticles (Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 12/2016). Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2016, 33, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Ge, X.; Zhao, H.; Shi, L.; Capobianco, J.A.; Jin, D.; Sun, L. Double-Sensitive Drug Release System Based on MnO2 Assembled Upconversion Nanoconstruct for Double-Model Guided Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.R.; Alshamsi, H.A.; Amiri, O.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Synthesis, characterization and application of Co/Co3O4 nanocomposites as an effective photocatalyst for discoloration of organic dye contaminants in wastewater and antibacterial properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.A.; Yousefi, S.R.; Jasim, L.S.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Green synthesis of DyBa2Fe3O7.988/DyFeO3 nanocomposites using almond extract with dual eco-friendly applications: Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 14319–14330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, S.J.; Averitt, R.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Halas, N.J. Nanoengineering of optical resonances. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 288, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinson, B.E.; Lassiter, J.B.; Levin, C.S.; Bardhan, R.; Mirin, N.; Halas, N.J. Nanoshells Made Easy: Improving Au Layer Growth on Nanoparticle Surfaces. Langmuir 2008, 24, 14166–14171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ignacio-De Leon, P.A.A.; Zharov, I. SiO2@Au Core–Shell Nanospheres Self-Assemble To Form Colloidal Crystals That Can Be Sintered and Surface Modified To Produce pH-Controlled Membranes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlather, A.E.; Manjavacas, A.; Lauchner, A.; Marangoni, V.S.; DeSantis, C.J.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Hot Hole Photoelectrochemistry on Au@SiO2@Au Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L. Optical properties of SiO2@M (M = Au, Pd, Pt) core–shell nanoparticles: Material dependence and damping mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2282–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhao, P.; Astruc, D. Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, Applications, and Toxicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1756–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards-Kortum, R.; Sevick-Muraca, E. Quantitative optical spectroscopy for tissue diagnosis. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1996, 47, 555–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, L.R.; Stafford, R.J.; Bankson, J.A.; Sershen, S.R.; Rivera, B.; Price, R.E.; Hazle, J.D.; Halas, N.J.; West, J.L. Nanoshell-mediated near-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13549–13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated Absorption and Scattering Properties of Gold Nanoparticles of Different Size, Shape, and Composition: Applications in Biological Imaging and Biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fales, A.M.; Yuan, H.; Vo-Dinh, T. Silica-Coated Gold Nanostars for Combined Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Detection and Singlet-Oxygen Generation: A Potential Nanoplatform for Theranostics. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12186–12190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Montoto, A.; Gorbe, M.; Llopis-Lorente, A.; Terrés, J.M.; Montes, R.; Cao-Milán, R.; de Greñu, B.D.; Alfonso, M.; Orzaez, M.; Marcos, M.D.; et al. A NIR light-triggered drug delivery system using core–shell gold nanostars–mesoporous silica nanoparticles based on multiphoton absorption photo-dissociation of 2-nitrobenzyl PEG. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9039–9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Grady, N.K.; Kundu, J.; Levin, C.S.; Lassiter, J.B.; Halas, N.J. Tailoring plasmonic substrates for surface enhanced spectroscopies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla, M.; García, I.; de Lázaro, I.; García-Alvarez, R.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Vranic, S.; Kostarelos, K.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Theranostics Thermal Monitoring during Photothermia: Hybrid Probes for Simultaneous Plasmonic Heating and near-Infrared Optical Nanothermometry. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7298–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Chua, Y.A.A.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Lu, X. Highly Symmetric Gold Nanostars: Crystallographic Control and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Property. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10460–10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigari, S.; Rindi, A.; Margheri, G.; Sottini, S.; Dellepiane, G.; Giorgetti, E. Synthesis and modelling of gold nanostars with tunable morphology and extinction spectrum. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6531–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.S.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, B.; De Abajo, F.J.G.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. High-yield synthesis and optical response of gold nanostars. Nanotechnology 2007, 19, 015606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, P.; Osório, I.; Dória, G.; Carvalho, P.A.; Pereira, A.; Langer, J.; Araújo, J.P.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Franco, R.; et al. Star-shaped magnetite@gold nanoparticles for protein magnetic separation and SERS detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3659–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gaytan, B.L.; Park, S.-J. Spiky Gold Nanoshells. Langmuir 2010, 26, 19170–19174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Song, H.-M.; Leonov, A.P.; Hale, J.A.; Oh, D.; Ong, Q.K.; Ritchie, K.; Wei, A. Gyromagnetic Imaging: Dynamic Optical Contrast Using Gold Nanostars with Magnetic Cores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Multifunctional Fe3O4 @ Au core/shell nanostars: A unique platform for multimode imaging and photothermal therapy of tumors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, E.E.; Boujday, S.; Pradier, C.-M.; Gu, F.X. Spiky gold shells on magnetic particles for DNA biosensors. Talanta 2018, 182, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Randjelovic, I.; Capek, R.; Gaponik, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Eychmüller, A. Controlled Fabrication of Gold-Coated 3D Ordered Colloidal Crystal Films and Their Application in Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjaguin, B.; Landau, L.D. Theory of the Stability of Strongly Charged Lyophobic Sols and of the Adhesion of Strongly Charged Particles in Solutions of Electrolytes. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1941, 14, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.h.G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids. In The Interaction of Sol Particles Having an Electric Double Layer; Elsevier Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Brandl, D.W.; Le, F.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N. Nanorice: A Hybrid Plasmonic Nanostructure. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Gole, A.M.; Orendorff, C.J.; Gao, J.; Gou, L.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Li, T. Anisotropic Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Assembly, and Optical Applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13857–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Gaytan, B.L.; Qian, Z.; Hastings, S.P.; Reca, M.L.; Fakhraai, Z.; Park, S.-J. Controlling the Topography and Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanoshells by a Templated Surfactant-Assisted Seed Growth Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 8916–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| R | λmax (nm) | dAu (nm) 1 | dhydr(nm) 2 | ζ (mV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2-NH2 | - | - | - | - | +19.8 ± 0.1 |
| SiO2@AuNP | - | 515.0 | 3.9 ± 1.2 | - 4 | −18.0 ± 0.9 |
| SiO2@AuNS | 0.3 | 567.0 | 7.1 ± 0.9 | - 4 | −9.1 ± 2.0 |
| 4.3 | 730.5 | 26.1 ± 6.7 | - 4 | −24.1 ± 1.7 | |
| 64.0 3 | 814.0 | 107.8 ± 12.8 | 112.4 ± 1.1 | −28.2 ± 1.1 | |
| 128.0 | 879.5 | 146.4 ± 17.2 | 147.3 ± 2.7 | −29.4 ± 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Straub, L.C.; Capobianco, J.A.; Wickleder, M.S. Growing Gold Nanostars on SiO2 Nanoparticles: Easily Accessible, NIR Active Core–Shell Nanostructures from PVP/DMF Reduction. Chemistry 2022, 4, 647-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4030046
Straub LC, Capobianco JA, Wickleder MS. Growing Gold Nanostars on SiO2 Nanoparticles: Easily Accessible, NIR Active Core–Shell Nanostructures from PVP/DMF Reduction. Chemistry. 2022; 4(3):647-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleStraub, Laura C., John A. Capobianco, and Mathias S. Wickleder. 2022. "Growing Gold Nanostars on SiO2 Nanoparticles: Easily Accessible, NIR Active Core–Shell Nanostructures from PVP/DMF Reduction" Chemistry 4, no. 3: 647-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4030046
APA StyleStraub, L. C., Capobianco, J. A., & Wickleder, M. S. (2022). Growing Gold Nanostars on SiO2 Nanoparticles: Easily Accessible, NIR Active Core–Shell Nanostructures from PVP/DMF Reduction. Chemistry, 4(3), 647-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4030046






