Abstract
In consideration of the issues of drug delivery systems, the artificial vesicle structures composed of block copolymers called polymersomes recently gained considerable attention. The possibility of tuning the mechanical parameter and increasing the scale-up production of polymersomes led to its wide application in healthcare. Bearing in mind the disease condition, the structure and properties of the polymersomes could be tuned to serve the purpose. Furthermore, specific ligands can be incorporated on the vesicular surface to induce smart polymersomes, thus improving targeted delivery. The synthesis method and surface functionalization are the two key aspects that determine the versatility of biological applications as they account for stability, specific targeting, degradability, biocompatibility, and bioavailability. A perfectly aligned polymer vesicle can mimic the cells/organelles and function by avoiding cytotoxicity. This supramolecular structure can carry and deliver payloads of a wide range, including drugs, proteins, and genes, contributing to the construction of next-generation therapeutics. These aspects promote the potential use of such components as a framework to approach damaged tissue while maintaining healthy environments during circulation. Herein, this article concentrates specifically on the drug delivery applications of polymersomes.
1. Introduction
It is already evident that the delivery carriers are essential to transport the drug without disturbing its stability inside the body. This can be accomplished only when there is a complete understanding of the physiological conditions of disease as well as the features of such drug moieties. The pharmaceutical industry and research institutions spend enormous amounts of money and effort every year on improving therapeutic delivery systems. This involves the development of novel techniques and application of the newer formulation, such as nanostructures at the forefront of creating an efficient drug delivery system [1,2,3]. In recent decades, the field of drug delivery has seen a spectacular leap when nanomaterials have been introduced, which paved a new learning curve compared to bulk materials [4,5]. A nanomaterial has a larger surface area, greater potential, higher chemical reactivity, and conductivity than traditional material. It is possible to encapsulate different therapeutic agents or payloads in nanomaterials and to allow their content to be carried and released at the diseased site having specific physiological environments.
Cancer and bacterial infection pose great threats to the health and well-being of humans. A variety of mechanisms may lead to the ineffectiveness of antibiotics, including the production of enzymes that degrade antimicrobials, changes in target sites or membrane permeability, the transmission of biofilm, and enhanced active efflux mechanisms [6]. Similarly, the treatment relies on chemotherapy and tumor surgery in order to stop the spread of cancer and prevent it from recurrence, and as a result of the resistance to anticancer drugs, cancer chemotherapy faces a number of challenges. In the past few decades, a variety of nanoplatforms including liposomes, hydrogels, niosomes, micelles, emulsions, polymersomes, nanospheres, and nanocomposites have been extensively investigated for targeted drug delivery [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Through endocytosis, these drug-loaded nano-platforms lead to increased drug accumulation in cancer cells by preventing efflux pumps or altered membrane permeabilities. The chemodynamic therapy, photodynamic therapy, and photothermal therapy are some alternative strategies for treating drug-resistant cancers too [15,16,17,18]. Auxiliary reagents, such as a photosensitizer, can sometimes be targeted to cancer tissues and damage the cells by producing ROS (Reactive oxygen species) or heat [19]. Moreover, these alternative techniques have also proven to be very effective in treating infections caused by bacteria. As a result, lipids and copolymers have the end-functional groups responsible for controlling the release of active substances, typically in response to physical and chemical stimuli to reduce potential damage caused to healthy cells around the diseased cell membranes [20].
Self-assembled amphiphilic block copolymers made of polymersome or polymeric vesicles are very promising nanostructures that appear to be highly stable, as biocompatible devices that have been extensively investigated for various biomedical applications including cancer theranostics and antibacterial therapy [21]. In general, polymersomes are composed of hollow membranes, similar to those found in cells or liposomes. The flexibility of polymeric segments, easy modification to attach specific functional groups, controllable particle size, hydrophilic cavities with high capacity, and multifunctional membrane structure make polymersomes ideal for drug delivery [22,23]. Since polymersomes are a membrane that is covered with abundant hydrophilic polymers, they are considered to be more stable than liposomes [24]. As an additional benefit of polymersomes compared to polymeric micelles, they are capable of loading hydrophilic drugs in the lumen at the same time as hydrophobic drugs on the membrane. Other than drug delivery and therapeutic potential, polymersomes also can act as biosensors [25]. Ghorbanizamani et al. were the first to report polymersomes based colorimetric assay for the detection of spike protein (Covid-19). The assay created using polymersomes, composed of poly-caprolactone copolymer and methoxy polyethylene glycol encapsulated with a dye called fuchsine, possessed high reproducibility and sensitivity, which is the major concern of detection techniques [26]. Meanwhile, this review summarizes the principles, synthetic routes, and recent developments of polymersomes for therapeutic applications.
2. Structure and Surface Modification of Polymersomes
The concept of polymeric vesicles was inspired by the phase characteristics of amphiphilic copolymers. There are numerous advanced features of polymersomes that make them the ideal alternative to liposomes, such as higher stability at biological pH, superior functionalization, tunable mechanical properties, the high choice for encapsulation of drugs, and attractive drug release profile, bioavailability, biodegradability, and cargo release through stimuli responsiveness. A polymersome is a hollow sphere with an aqueous core and a polymer shell made of diblock polymers (Figure 1) [27]. An AB type of diblock copolymer can be used to synthesize polymersomes where A is a hydrophobic type of diblock copolymers, and B is the hydrophilic type of diblock copolymers [28]. Additional to the AB types of polymersomes, it can also consist of triblock copolymers, where liner structures are formed from another hydrophobic block. It is possible to form polymersomes based on molecular weights (MWs) and chain length using amphiphilic block copolymers [29]. There is a wide range of controlled membrane thicknesses from 2 nm to 50 nm for polymersomes [30,31]. Compared to polymersomes with a thinner membrane thickness, a thicker membrane has demonstrated greater stability and rigidity, as well as greater efficacy in entrapping hydrophobic drugs. Reports produced by Zheng et al. include synthesis of polymersomes through RAFT polymerization (reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer) technique, crosslinking of pentaflurophenyl groups using diamine linkers, labeling fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate dye on the surface, characterizations, in vitro and in vivo analysis using glioblastoma cells and mice, respectively. The study suggests that the prepared particle was stiff and accumulated well in brain tissues. It is also found that the modification in the crosslinker apparently reflected on the function and characteristics of the particle. Thus, this work intensified the importance of the mechanical properties of a particle in their biological applications [32]. In polymersomes, block copolymers self-assemble to form spheres, vesicles, cylinders, or elongated micelles based on the length distribution. Polymersomes are externally modified to increase their uptake by cell structures by forming selective interaction between the particle and cell membrane. Over the past several decades, it has been a challenging area to design biofunctional polymersomes that can be translated into clinical settings [33]. Nam et al. discovered that lipo-polymersomes (HLPs) could be made by mixing diblock copolymers such as poly(butadiene-b-ethylene oxide) with common natural lipids to form a compositional heterogeneous hybrid lipo-polymersome. Through thermally driven phase separation and cholesterol inclusion, lipid-rich domains are mixed and demixed from polymer-rich matrixes of hybrid vesicles. Cooling rate and lipid composition can control domain size and morphology. In addition to their biocompatible-measuring properties, composite membranes are also structurally stable and can be used for encapsulation-based technologies such as delivery and sensing applications, or the control of biochemical reactions [33].

Figure 1.
General process to obtain polymersomes.
It is necessary to take extra steps in order to form vesicles when polymersomes are conjugated with bulky ligands like antibodies for targeting. Purification, centrifugation, dialysis, and filtration are the most commonly used techniques, all of which have the potential to damage or alter vesicles in some way. Therefore, purifications and surface modifications are always challenging tasks for scientists. For the conjugation of polymersomes with antibodies and ligands, there are several different chemical reactions that have been widely used, such as click chemistry, biotin-streptavidin interactions, Michael addition, and EDC-assisted coupling [34]. The carboxylated polymersomes synthesis often generates intermediates with high hydrolysis affinity causing an issue. An additional amount of carbodiimide must be added to complete the reaction in order to stop the hydrolysis of o-acylisourea as an intermediate in carboxylated polymersomes synthesis [35]. When carbodiimide is present in excess, the colloidal stability of vesicles is altered. The problem can be overcome by using succinimide, which is more stable and has a lower hydrolysis affinity. To attach large biomolecules to polymersomes, amine groups can also be added to the polymersome surface. To accomplish this, bis-aryl-hydrazone bonds have been added to copolymers. As an additional approach to functionalize polymersomes, Michael addition reaction employed a thiol-maleimide coupling strategy. At near-biological pH, thiol-ether bonds are formed due to the stability, greater efficiency, and selectivity of maleimide towards thiol. The synthesis route is one of the important aspects that affect the characteristic potential of a particle. Studies carried out by Travanut et al. studied the biocompatibility of the polymersomes synthesized through a versatile technique called as Passerini 3CR (3 component reaction). The results demonstrated that this technique could provide a facile synthesis of a particle with cytocompatibility and biodegradability, making them a potential drug carrier [36]. Similar work conducted by the same group intensified the importance of the synthesis route in the performance of a particle. The study included the fabrication of polymersomes using the same Passerini chemistry, encapsulating a doxorubicin drug to get an effective treatment against malignant breast cancer. The Passerini polymers synthesized via one-pot reaction featured greater therapeutic efficiency proving that Passerini chemistry allows synthesis for particles with better characteristics [37]. There is another method of modifying the surface of polymersomes by creating an interaction between a copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition and azide using the click chemistry approach. Among the most commonly used methods to target polymersomes is the ligation strategy that involves both biotin and streptavidin. Broz et al. designed polymersomes made up of triblock polymer functionalized with biotin to specifically target the A1 receptor of macrophages. The ligand biotin was functionalized onto the polymer using the coupling agent streptavidin. This particle served diagnostic and therapeutic purposes [38]. There are many advantages associated with this method, including its simplicity, the stability of the bonds, and the compatibility with antibodies and other targeting moieties that can be attached to the modified biotin-streptavidin or biotin-avidin copolymers.
3. Polymersomes as Drug Carrier
The loading of hydrophilic substrates into polymersomes can either be passive or active. A passive loading strategy involves adding the drug to both the aqueous phase and the inner water phase of the polymersomes [39]. This approach involves the diffusion of uncharged drug molecules across the outer structure to reach the core of vesicles. The low or high core pH accounts for the substrate to become charged. With this method, it is possible to achieve high encapsulation efficiency and stable retention of the drug molecules. In remote loading, polymersomes with thicker membranes may prove advantageous since they enable the substrate to diffuse rapidly [40]. Köthe et al. developed a novel method called DAC (Dual asymmetric centrifugation) to prepare polymersomes, where poly caprolactone and polyethylene glycol block copolymers were used as precursor molecules. The particle prepared showed high efficiency in drug loading of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic moieties. The method used no organic solvents and did not involve any post-processing steps, making it a facile process for the fabrication of polymersomes as the best suitable drug carrier [41]. Polymersomes can be encapsulated and decorated with targeting ligands by combining small and large molecules with a block copolymer. It may be possible to extend the release time of drugs when they are incorporated into vesicles by using biodegradable linkers that improve the retention of the drug. Walvekar et al. studied the potential role of polymersomes in the delivery of antibiotics against MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) infections. The particle was synthesized using a self-assembly technique, encapsulated with vancomycin drug, and conjugated with oleylamine- hyaluronic acid ligands. The in vitro study results indicated that this particle would act as a promising drug carrier for the treatment of bacterial infections [42]. Another study by Porges et al. also developed polymersomes for the treatment against antibacterial infections. Block copolymer-based polymersomes were fabricated and encapsulated with antibiotics for the treatment of Burkholderia infections. It was concluded that the developed polymersomes would serve as the best carrier for antibiotics [43]. A transmembrane channel protein can be incorporated into a polymersome membrane to increase its permeability for hydrophilic molecules and ions. It has been shown, for example, that in cascade reactions enzymes encapsulated in membranes containing channel proteins can avoid inhibiting factors and also maintain the ability to access the substrate. This has been demonstrated in the synthesis of polymersomes with cytidine-monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid and OmpF G119D (channel protein) to retain access to the substrate. Alibolandi et al. developed dextran based polymersomes for insulin delivery. The particle was prepared using the hydration method and encapsulated with insulin. The in vivo and in vitro study results demonstrated that the particle loaded with insulin significantly delivered the payload via an oral drug delivery system [44]. As part of more fundamental studies on membrane proteins, polymersome membranes had the ability to be tuned in their mechanical properties by adjusting the chemical composition, allowing for a better insertion of membrane proteins. The functionalization of transmembrane proteins is limited by the thickness of the membrane since most of the channel proteins are designed for only lipid membranes. PMOXA-b-PDMS-b-PMOXA model demonstrates that polymersome membrane conformations adapt to allow biopores smaller than hydrophobic membrane layers [45,46].
When polymersomes are made from long block copolymers, their membranes can have a thickness of up to 50 nanometers. Accordingly, compared to liposomes, polymersomes are theoretically capable of accommodating greater amounts of hydrophobic molecules [47]. Furthermore, thick membranes can lead to a slower release of hydrophobic substrates because the diffusional distances are much higher. When the vesicle is formed, the hydrophobic molecules or drugs occupy the organic part and incorporate it into the membrane. A 47% encapsulation efficiency was achieved by polymersomes made up of poly(trimethylene carbonate) and poly(L-glutamic acid) loaded with doxorubicin by nanoprecipitation at pH 10.5 [48]. A low diffusion distance may result in low drug retention when loading substrates. There is a risk of a high rate of drug release in polymersomes due to the narrow diffusion distance, despite their membrane thickness. A biodegradable polymer might further impair the release profile of the cargo in vivo, as a high polymer degradation rate could result in the destabilization of the membrane and an acceleration of the cargo release process [49]. Table 1 describes some more applications of polymersomes in drug delivery.

Table 1.
Complies with recent advancements in polymersomes for drug delivery applications.
4. Polymersome-Based Targeted Anticancer Drug Delivery
It has been over a decade since multiple chemotherapeutics were developed for the treatment of cancer, but in spite of this there are still many challenges in the field of chemotherapeutics like less selectivity, physiological barriers, half-life, and poor bioavailability [60]. Additionally, due to the damage to the liver and kidney caused by cancer therapeutics, chemotherapy may even be discontinued in the course of treatment. Moreover, resistance to anticancer drugs is a major concern because it occurs due to abnormal expression of drug-efflux transporters, which prevents the intracellular transport of cancer therapeutics. This is because drug carriers can improve the bioavailability of anticancer drugs, enhance permeability and retention (EPR) effect, reduce side effects, and provide efficient delivery of chemotherapeutics bypassing the biological barriers [61]. Since polymersome-based drug delivery systems are characterized by a stable structure like a cell with a membrane and lumen that are size-controlled, they have been investigated as smart cancer therapeutics nanocarrier systems [62]. It is possible for polymersomes to encapsulate both hydrophobic and hydrophilic anticancer agents in their lumens or membranes. Furthermore, the polymers can be functionalized with ligands complementary to receptors on the target site as well as with ligands that are sensitive to environmental responsiveness, so that they can deliver drugs precisely and release them in response to stimuli [63]. Polymersomes offer an excellent opportunity to target postsurgical premetastatic niches and microresiduals, resolving the challenges of poor therapeutic delivery [64]. Several studies have demonstrated the synergistic antitumor effect of combination chemotherapy and immunotherapy for cancer. After proper combination with chemotherapy, immunotherapy can significantly improve response rates and efficacy. A study by Japir et al. suggests that tumor-dilatable polymersome nanofactories that are capable of long-term intratumoral retention may represent a promising strategy to enhance enzyme prodrug chemo-immunotherapy using polymersomes [65].
As a result of targeted delivery systems, the target markers in cancer cells that are overexpressed or unique are targeted [66]. A number of cancer targets have been identified, and a number of targeting ligands have been employed in the development of polymersome-based targeted delivery systems, including folate, antibodies, etc. [67]. For example, Polymersomes containing folate are able to target cancer cells by means of endocytosis through the folate receptor. In order to survive a complicated physiological environment and provide efficient targeting capability, these targeted ligands have been conjugated primarily with polymersomes by covalent bonding [68,69]. The folate molecule contains two carboxylic acid groups, which greatly influence polymersome reactivity. In cancer, antibodies may bind specifically to antigens that are over-expressed or those that are cancer-specific. A number of studies had been carried out in the early stages to achieve targeted therapy by conjugating antibodies onto anticancer drugs. Lee et al. conducted in vitro study of anticancer drug delivery to a specific site of breast cancer cells by conjugation of antibodies. Diblock co-polymeric substances containing polyethylene glycol and poly (lactic co-glycolic acid) were synthesized using the solvent evaporation technique. During this fabrication, indocyanine green and doxorubicin were encapsulated in the polymer molecules. Since breast cancer cells overexpress HER2 gene, a complementary binding agent-anti-HER2 antibody was conjugated through the carbodiimide crosslinking method. The experimental results showed that the cell death rate was much higher in the polymersomes encapsulated with the dual drug compared with a single drug dosage. Hence this study indicates that drugs encapsulated in polymeric structure readily reduced the chemotoxicity and increased the therapeutic effect [70]. Clinical trials or even marketing approvals have already begun for several antibody-drug conjugates for cancer treatment. However, there is a low ratio of drug to antibody in the antibody-drug conjugate, which means excessive antibodies are consumed when preparing antibody-drug conjugate, resulting in reduced drug-to-antibody ratios. Alternative options include conjugating antibodies to polymersomes encapsulated with drugs [71,72]. The development of polymersome-based targeted delivery systems has currently been accomplished using several types of antibodies, including anti-EGFR antibodies (cetuximab, trastuzumab), anti-CD44 antibodies, anti-PSCA antibodies, and anti-EpCAM antibodies, among others. The monoclonal antibody AM6 was used to target breast cancer cells. Khanna et al. recently reported that the nanocarrier prepared using poly (lactic co-glycolic acid) encapsulated with paclitaxel drug showed better targeting to breast cancer cells due to the surface functionalization of AM6 antibody. The antibody was conjugated using the reaction chemistry between thiol and maleimide. The results obtained from in vitro and in vivo determine that the antibody-conjugated particle actively targeted perlecan in cancer cells and significantly helped to facilitate the drug release [73].
In cancer cells, short peptides of specific sequences bind to abnormally overexpressed proteins (integrin or transferrin) membrane and enhance their ability to penetrate the cells’ membranes. These peptides were found to have significant abilities to target cancer cells and could be conjugated with polymersomes to provide their ability to target. WREAAYQRFL (tumor-homing peptide) was used by Oz et al. to design an integrin-targeted polymersome [74]. This study showed that the peptide was capable of recognizing and binding to αvβ3 integrin, which is pivotal in tumor growth, spread, and metastasis. Breast cancer cells typically overexpress this integrin. Thiol-ene click chemistry was used to chemically link the targeting peptide to a diblock copolymer. The peptide-conjugated polymers were then assembled to form polymersomes to encapsulate the anticancer drug doxorubicin during the self-assembly process. The use of tetraiodothyroacetic acid, triphenylphosphonium cation, and biotin has also been considered for targeted delivery solutions based on polymersomes [75]. By amination between the amino group and p-anisic acid on polymer chains, anisamide can be incorporated into polymersomes for its affinity to overexpressed sigma receptors in the tumor region. It is also important to note that these polymersome-based targeted delivery systems have the potential to target not only the overexpressed receptors found at tumor sites but also some tissue constituents, like the divalent calcium ions found in hydroxyapatite that accounts for bones formation, which can serve as potential targeting element. Since it was found that folate receptors are abundant in the gastrointestinal tract, oral delivery of anticancer agents is now the best choice of treatment. Hence, Pan et al. worked on the fabrication of polymersome-based carriers suitable for oral drug delivery systems. The polymersomes were prepared with polylactic acid and pluronic F127 and decorated with folic acid ligands. The particle was loaded with paclitaxel and was added to the particle to improve the absorption of the drug Vitamin E TPGS. The in vitro and in vivo results proved that the particle exhibits higher cellular toxicity compared with free drugs. The bioavailability was readily increased due to the specific interaction between the folate receptor and folic acid ligand. Consequently, this particle can be effective in the case of oral delivery [59].
The physiological barriers such as the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and blood–tumor barrier (BTB) remain as major obstacles to the treatment of brain tumors, including gliomas. In order to overcome both the BBB and the BTB, a dual-targeted or multitargeted polymersome delivery system is highly regarded. Research conducted by Figueiredo et al. concluded that overexpression of protein-1 related to low-density lipoprotein in BBB could serve as a target for efficient delivery. The polymersomes were developed with diblock copolymers encapsulated with doxorubicin and conjugated with angiopep-2. The angiopep-2 can actively target the over-expressed protein in BBB. The in vitro study results carried out on glioblastoma cells showed higher cytotoxic effects compared to free drugs. Thus, polymersomes conjugated with angiopep-2 can provide sustained release of the drug at its targeted site [76]. It was discovered by Chen et al. that an efficient polymersome delivery system attaching des-octanoyl ghrelin and folic acid effectively delivers the anticancer drug to brain tumors through dual-targeted polymersomes. The protein des-octanoyl ghrelin travels in the direction of blood to the brain, which may enhance drug-encapsulated polymersome transport across the BBB [77]. Folic acid could directly bind to folate receptors on cancer tissues after traversing the BBB to facilitate receptor-mediated endocytosis for drug concentration enhancement in the cancer cells. Polymersome-based delivery may improve delivery efficacy over conventional delivery systems, but still, there is a requirement to promote rapid drug release within tumor sites to improve therapeutic efficacy. In this regard, stimuli-responsive smart polymersomes can be more effectively used as a means of drug delivery system with controlled release profiles in response to stimulation [78].
5. Smart Polymersomes-Based Delivery Systems
There are many advantages to the intelligent delivery system, such as the delivery of the drugs effectively with rapid release at the tumor site reducing the probability of drug release in the bloodstream or surrounding healthy tissues [17,79]. The microenvironment of tumor tissues differs quite a bit from that of normal tissues, including pH, hypoxia, and overexpression of enzymes (Figure 2) [80,81,82]. To construct polymersome-based smart delivery systems, it is necessary to take advantage of the specificity of the microenvironment in tumor tissues to design and build environment-responsive polymers (Table 2). The response to external stimuli, such as ultrasound, light, or magnetic fields, can also be used. The smart polymersome-based delivery is classified into three categories depending on their source of stimulation and function. The chemical stimuli include the pH of the microenvironment, redox, reactive oxygen species, and ions, whereas the physical stimuli include temperature, heat, light, magnetic field, and ultrasound. Ultrasound waves will help to improve the release of the drug from the carrier into the target cell efficiently. Zhong et al. fabricated nanobubble carrier system using poly (lactic co-glycolic acid). The carrier was loaded with paclitaxel drug via double emulsion and conjugated with herceptin antibody via carbodiimide coupling reaction. The in vitro and in vivo study experiments showed that the herceptin decorated nanobubble reacted well to the ultrasound and promoted the targeting and release. This study concluded that this particle, when combined with ultrasound, could function as theranostic agent in image-guided therapy [83]. Other than these two, there are some biological stimuli like proteins, enzymes, and bioactive molecules like ATP. It has been reported that polymersomes that are pH- and redox-sensitive are most commonly found.
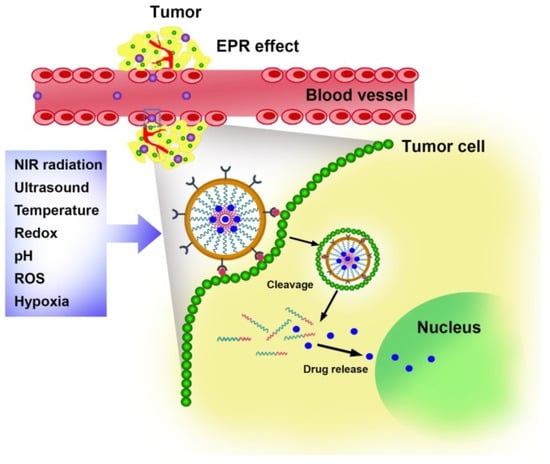
Figure 2.
Stimuli responsive characteristics of polymersomes.
Changes in pH can affect the structure or properties of pH reactive polymersomes. The introduction of pH-responsive groups is one way to achieve pH-responsive ionizability. Under alternant change in pH, the polymers can reversibly modify their pH-responsive properties, which can influence the accelerated release of the drug encapsulated within [84]. In addition to this approach, it is also possible to attach pH-sensitive bonds into polymer, after which the release of drugs in polymer chains can be accomplished by cleavage in chemical bonds or by pH-induced degradation of main chains and side chains. Therefore, polymersomes are stable at physiological pH; hence the structure or properties of polymersome can be altered to trigger the release of drugs in the pH of the microenvironment, which is lowered (acidic conditions). Albuquerque et al. developed block copolymer encapsulated with doxorubicin via microfluidic technology. This method produced monodispersed polymer and was further characterized using hi-end photophysical tools. The in vitro results showed that doxorubicin-encapsulated polymer possessed pH responsiveness towards tumor microenvironment and delivered the drug precisely [85].
For cells to proliferate and function properly, glutathione plays a critical role, and due to the rapid proliferation of cancer cells glutathione concentrations are at least four times higher in cancer cells than in those of healthy tissues [86]. During exposure to a reductive condition like a high glutathione environment, the disulfide bond cleaves to produce free thiol. In order to trigger glutathione-induced drug release, redox-responsive polymersomes were developed [87]. Therefore, through disulfide bonds, anticancer drugs can be covalently conjugated to amphiphilic polymers. Upon delivery to cancer cells, glutathione cleaves the disulfide bonds to release the anticancer drugs to the cancer cells. As a result of this method, we are able to produce polymersomes containing anticancer drugs that have a high drug loading capacity to avoid the release of drugs in circulation. In addition, another approach is to design amphiphilic polymers that are composed of disulfide bonds along their main chains or on their side chains [88]. The cleavage of disulfide bonds in an environment with high glutathione concentrations produces alterations in hydrophobicity or dismantling of polymer structures, which results in the rapid release of payload as a result of the cleavage of disulfide bonds. Additionally, external physical stimuli can be precisely applied to specific tumor sites to minimize unnecessary side effects [89]. As a result of temperature-sensitive polymersomes, the chemical properties and morphology respond to it and release the drug rapidly. Polymersomes that respond to temperature have been developed using a variety of temperature-sensitive polymers [90]. As a noninvasive stimulus, ultrasound and magnetic fields have also been considered as promising possibilities.
Polymersomes that respond to biological stimuli have also been developed using enzymes and ATP. Taking advantage of the microenvironment, the particle can be designed in a way to respond to the condition. The hypoxic surrounding is one of the common characteristics possessed by tumor cells that will contribute to the growth and relapse of tumors. This condition also limits the entry of drug carriers into solid tumor tissues. Designing a carrier, which could respond to hypoxia, will facilitate the entry and delivery. According to this hypothesis, Kulkarni et al. designed an echogenic particle that can respond to hypoxic stimuli. Polymersomes were fabricated with polyethylene glycol and poly lactic acid. The particle was then functionalized with azobenzene and peptide- iRGD for hypoxia responsiveness and tissue penetration, respectively, also encapsulating gemcitabine for treating pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The in vitro and in vivo results demonstrated that the polymersomes penetrated well into the solid tumor and delivered the drug efficiently. The echogenicity of the particle helped in imaging the study model under the ultrasound technique. Thus, it is concluded that the polymersomes designed above served as drug carriers and monitored the delivery simultaneously [50].

Table 2.
Recent research evidence based on the development of stimuli-responsive polymersomes.
Table 2.
Recent research evidence based on the development of stimuli-responsive polymersomes.
| Scheme No. | Polymer | Payload | Stimuli Response | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PEO-b-PCSSMA copolymer | Doxorubicin | Dual responsive (Light and reduction) | Synergistic loading and programmed release of therapeutics | [91] |
| 2 | Poly (ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether-b-methyl methacrylate-ran-2-(dimethyl amino) ethyl methacrylate mPEG-b-(PMMA-ran-PDMAEMA) | Curcumin, 2-naphthole, paclitaxel, and ampicillin sodium salt | pH-responsive | Intermolecular drug release interactions | [92] |
| 3 | Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(2-((((5-methyl-2-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)amino)ethyl methacrylate) (PEO-b-PTTAMA) | Nile red Doxorubicin | pH-responsive | Targeted combinational therapeutic drugs | [93] |
| 4 | Poly(2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl choline phosphate)-b-poly(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PMCP-b-PDPA) | Doxorubicin | pH-responsive | Targeted intracellular delivery system | [94] |
| 5 | Methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly[2-(diethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-co-2-hydroxy-4-(methacryloyloxy)benzophenone] | Doxorubicin, paclitaxel | pH-responsive Temperature | Promising drug carriers for tumor combination chemotherapy | [95] |
| 6 | Poly(3-methyl-N-vinylcaprolactam)-block-poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) (PMVC-PVPON) | Doxorubicin | Temperature | Tumor targeting and next-generation drug carriers | [96] |
| 7 | Poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(N,N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate) (PEG-b-PDEAEM) | Gold nanorods, doxorubicin | pH-responsive, NIR-irradiation | Photothermal therapy and targeted drug delivery vehicles | [97] |
| 8 | Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-(diethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)-stat-poly(methoxyethyl methacrylate) [PEO-b-P(DEA-stat-MEMA)] | Doxorubicin | Ultrasound | Chemotherapeutic efficiency | [98] |
| 9 | Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-dox-polyethylene glycol)-2,4,6-trimethoxy benzylidene pentaerythritol carbonate (PNIPAM-DOX-PEG-PTMBPEC) | Doxorubicin | pH-responsive, Temperature | Development of Cancer Therapy | [99] |
| 10 | Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam)10-b-poly(dimethylsiloxane)65-b-poly(N-vinylcaprolactam)10 | Doxorubicin | pH-responsive, temperature | Delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic anticancer therapeutics and controlled drug delivery system | [100] |
| 11 | Poly[2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate]-block-polystyrene (PDMAEMA-b-PS) | Ascorbic acid, cationic EPR probe CAT1 | Ph-responsive, Temperature | Gene delivery and Nanoreactors | [101] |
| 12 | Amphiphlic poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(β-aminoacrylate)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) | Doxorubicin and photosensitizer IR-780 | NIR responsive | Chemotherapy, Photothermal, and photodynamic therapy | [102] |
| 13 | poly(ethylene glycol)113-b-P-(CPT methacrylate monomer0.48-co-2-(pentamethyleneimino) ethyl methacrylate0.52)92 PEG113-b-P(CPTKMA0.48-co-PEMA0.52)92 | Camptothecin | ROS-responsive pH-responsive | Starving therapy, chemodynamic therapy, and chemotherapy | [103] |
| 14 | Poly(propylene sulfide)20-bl-poly(ethylene glycol)12 (PPS20-b-PEG12) | Zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc), Doxorubicin | ROS NIR irradiation | Chemo-photodynamic therapy | [104] |
It is possible for polymersomes with dual responses to more complex intracellular environments. To demonstrate the concept of dual-responsive polymersomes, a series of polymersomes with dual-triggered release capability has been developed. Through reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT), Zhou et al. have constructed dual, thermo-, and pH-responsive polymersomes containing a self-assembled triblock polymer. A layered membrane was present in the dual-responsive polymersomes, allowing the permeability of the membrane to be adjusted. Additionally, it was demonstrated that the polymersomes responded to temperature changes based on pH. In the fabricated polymersomes, doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) and paclitaxel (PTX) had the potential to be encapsulated in a hydrophilic-hydrophobic pair. In order to independently control the release of DOX and PTX, the membrane permeability was triggered by temperature and pH changes. The polymersomes encapsulated with DOX and PTX could work synergistically in simulated tumor microenvironments [95]. With the same RAFT technique, Rodriguez et al. developed polymersomes using amphiphilic block copolymers. The particle was encapsulated with an anticancer drug, doxorubicin, and gold nanorods. The particle possessed dual stimuli responsiveness of pH and NIR irradiation. This resulted in higher cytotoxicity due to an increased release rate at the site [97]. Khan and the others synthesized three types of polymers that were both reductive and acidic using poly(mPEG-SS amino) (N,N-diisopropylethylenediamino)phosphazenes] (PPDPs). Thereafter, the PPDPs were allowed to self-assemble into polymersomes loaded with hydrophilic or hydrophobic anticancer drugs in high loading content with higher encapsulation efficiency. As a result of the polymersomes made of PPDPs, an anticancer drug was released in response to reductive/acidic stimuli [105].
6. Engineering of Large-Scale Production of Polymersomes
In medical and biotechnological applications, polymersomes are expected to be acceptable carriers and universal reaction compartments due to their increased stability. In order to put polymersome technology into practice at the industrial level, it is imperative to develop controlled and cost-effective methods to produce large quantities of vesicles [106]. There are a couple of basic requirements that must be met as part of a scale-up strategy, among them the use of the same material for both the model scale and the larger scale processes. Therefore, it is critical to maintain physicochemical parameters influencing crucial material characteristics at both scales. Additionally, the process equipment needs to be linearly scaled up to maintain geometrical similarity. Finally, scale transfer criteria specific to a given process need to be identified and maintained. Poschenrieder et al. have reported the production of polymersomes using an amphiphilic triblock copolymer from 12 mL to 1.5 L controlling the process engineering parameters. The produced polymeric vesicles showed monodispersity with a hydrodynamic diameter of 180 nm, and the polydispersity index was maintained at <0.2 [106]. Rameez et al. have reported on the low-pressure extrusion procedure for the synthesis of polymersomes on a large scale. By continuously extruding hollow fiber membranes with pore diameters of 200 nm, vesicles were produced. A monodisperse empty polymersome with a particle diameter of less than 200 nm was formed [107]. It can be stated that polymersomes offer an additional advantage over liposomes due to their large-scale production.
7. Conclusions and Future Perspective
The progress in the development of polymersomes as nanotherapeutic platforms implies their importance in future pharmaceuticals. The attractive characteristics of polymersomes enabled the researchers to work with them in all possible ways, including drug delivery and imaging. This review, with special attention, described the potential application of polymersomes in the delivery of chemotherapeutics. The microenvironmental condition can be taken advantage of by fabricating particles that could specifically target the tumor tissues and release the drug in a slow and sustained manner. Ligands complementary to the receptors in the cancer cells are designed and decorated on the polymersome to enable site-specific drug delivery. In-depth knowledge on the biological interactions between the particle and cellular targets needs to be gained to advance in medical applications. However, recent reports suggest that they possess minimal toxicity as they enter the distribution step. A comprehensive and systematic study is strongly recommended to further minimize the adverse effects and thereby broaden the application of this technique by comparing it against liposomal or other stable vesicle models.
Undeniably, the design and development of new copolymers will show the way for the fabrication or engineering of polymersomes with the desired properties for integrating a variety of payloads into them. Clinical trials have actually been conducted with very few polymersome-based systems so far. Upscaling most polymersome preparation techniques is difficult and reproducible, which limits their application in clinical practice. For the evaluation of the biosafety of nanocarriers, it is essential to understand the pharmacokinetic and biodistribution parameters in vivo. Until now, little research has been done on the pharmacokinetics of polymersomes, as well as on their biodistribution. A primary consideration for practical applications of polymersomes should be their safety, and it must be evaluated whether polymersomes are safe on a long-term basis and if they are immunogenic in order to enhance this strategy further. There is a need for more research comparing polymersomes with therapeutic liposome controls, whose clinical safety profile is well established. This would help determine how effective polymersomes are in loading drugs, therapeutic efficacy, and pharmacokinetics, as well as biodistribution of drugs. Novel strategies for delivering therapeutic loads into tumor cells could be delivered by developing highly stable polymersomes with efficacies.
Author Contributions
P.P. and K.H. collected all required data and wrote the initial draft. P.G. and K.G. compiled it with additional data. The concept, overall representation, and the final version were prepared by A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge CARE for financial and infrastructural support. P.P., K.H. and P.G. acknowledge CARE for fellowships too.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Agnihotri, S.A.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances on chitosan-based micro-and nanoparticles in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, S.; Rathore, A.; Dave, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Chouhan, R.S.; Sadhu, V. Recent developments in functionalized polymer nanoparticles for efficient drug delivery system. Nano-Struct. Nano Objects 2019, 20, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmiladevi, P.; Breghatha, M.; Dhanavardhini, K.; Priya, R.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Efficient Wormlike Micelles for the Controlled Delivery of Anticancer Drugs. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 11, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsaveni, G.; Farook, A.S.; Haribabu, V.; Murugesan, R.; Girigoswami, A. Engineered multifunctional nanoparticles for DLA cancer cells targeting, sorting, MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2013, 5, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Gopikrishna, A.; Keerthana, V.; Girigoswami, A.; Girigoswami, K. An Overview of Nanoformulated Nutraceuticals and their Therapeutic Approaches. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 17, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: Mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimaladevi, M.; Divya, K.C.; Girigoswami, A. Liposomal nanoformulations of rhodamine for targeted photodynamic inactivation of multidrug resistant gram negative bacteria in sewage treatment plant. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, R.; Girigoswami, K.; Murugesan, R.; Girigoswami, A. Influence of divalent cation on morphology and drug delivery efficiency of mixed polymer nanoparticles. Curr. Drug Del. 2018, 15, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.S.; Okano, T. Polymeric micelles as new drug carriers. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1996, 21, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-P.; Ji, J.; Chen, W.-D.; Shen, J.-C. Novel biomimetic polymersomes as polymer therapeutics for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 107, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.A.; Yousefi, S.R.; Jasim, L.S.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Green synthesis of DyBa2Fe3O7. 988/DyFeO3 nanocomposites using almond extract with dual eco-friendly applications: Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 14319–14330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.R.; Alshamsi, H.A.; Amiri, O.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Synthesis, characterization and application of Co/Co3O4 nanocomposites as an effective photocatalyst for discoloration of organic dye contaminants in wastewater and antibacterial properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramita, P.; Subramaniam, V.D.; Murugesan, R.; Gopinath, M.; Ramachandran, I.; Ramalingam, S.; Sun, X.F.; Banerjee, A.; Marotta, F.; Pathak, S. Evaluation of potential anti-cancer activity of cationic liposomal nanoformulated Lycopodium clavatum in colon cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girigoswami, A.; Das, S.; De, S. Fluorescence and dynamic light scattering studies of niosomes-membrane mimetic systems. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2006, 64, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavi, P.; Girigoswami, A.; Girigoswami, K.; Hansda, S.; Ghosh, R. Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer. In Handbook of Oxidative Stress in Cancer: Therapeutic Aspects; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavi, P.; Sharmiladevi, P.; Haribabu, V.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. A Nano Approach to Formulate Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Curr. Nanosci. 2022, 18, 675–689. [Google Scholar]
- Harini, K.; Pallavi, P.; Gowtham, P.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Smart Polymer-Based Reduction Responsive Therapeutic Delivery to Cancer Cells. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 8, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, K.; Girigoswami, K.; Ghosh, D.; Pallavi, P.; Gowtham, P.; Girigoswami, A. Architectural fabrication of multifunctional janus nanostructures for biomedical applications. Nanomed. J. 2022, 9, 180–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Song, J.; Nie, L.; Chen, X. Reactive oxygen species generating systems meeting challenges of photodynamic cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6597–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasir, J.K.; Reddy, M.K.; Labhasetwar, V.D. Nanosystems in drug targeting: Opportunities and challenges. Curr. Nanosci. 2005, 1, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Ji, J. Biocompatible and biodegradable polymersomes as delivery vehicles in biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 8811–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, M.; Trewyn, B.G. Polymer-based stimuli-responsive nanosystems for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araste, F.; Aliabadi, A.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Self-assembled polymeric vesicles: Focus on polymersomes in cancer treatment. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 502–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rideau, E.; Dimova, R.; Schwille, P.; Wurm, F.R.; Landfester, K. Liposomes and polymersomes: A comparative review towards cell mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8572–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zartner, L.; Muthwill, M.S.; Dinu, I.A.; Schoenenberger, C.-A.; Palivan, C.G. The rise of bio-inspired polymer compartments responding to pathology-related signals. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6252–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Zihnioglu, F.; Evran, S.; Cicek, C.; Sertoz, R.; Arda, B.; Goksel, T.; Turhan, K.; Timur, S. Quantitative paper-based dot blot assay for spike protein detection using fuchsine dye-loaded polymersomes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, A.; Kishimura, A.; Osada, K.; Jang, W.-D.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Semipermeable polymer vesicle (PICsome) self-assembled in aqueous medium from a pair of oppositely charged block copolymers: Physiologically stable micro-/nanocontainers of water-soluble macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5988–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, B.M.; Won, Y.-Y.; Ege, D.S.; Lee, J.C.; Bates, F.S.; Discher, D.E.; Hammer, D.A. Polymersomes: Tough vesicles made from diblock copolymers. Science 1999, 284, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferji, K.; Nouvel, C.; Babin, J.; Li, M.-H.; Gaillard, C.; Nicol, E.; Chassenieux, C.; Six, J.-L. Polymersomes from amphiphilic glycopolymers containing polymeric liquid crystal grafts. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Huang, Y.; Prasad, V.; Baumgartner, R.; Zhang, S.; Harris, K.; Katz, J.S.; Cheng, J. Preparation of surfactant-resistant polymersomes with ultrathick Membranes through RAFT dispersion polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17033–17037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoPresti, C.; Massignani, M.; Fernyhough, C.; Blanazs, A.; Ryan, A.J.; Madsen, J.; Warren, N.J.; Armes, S.P.; Lewis, A.L.; Chirasatitsin, S. Controlling polymersome surface topology at the nanoscale by membrane confined polymer/polymer phase separation. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Du, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, X.; Lu, Y.; Yin, J.; Zou, Y.; Park, J.B. Tuning the elasticity of polymersomes for brain tumor targeting. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.; Vanderlick, T.K.; Beales, P.A. Formation and dissolution of phospholipid domains with varying textures in hybrid lipo-polymersomes. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7982–7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulahoum, H.; Ghorbanizamani, F.; Zihnioglu, F.; Timur, S. Surface biomodification of liposomes and polymersomes for efficient targeted drug delivery. Bioconj. Chem. 2021, 32, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Mura, S.; Brambilla, D.; Mackiewicz, N.; Couvreur, P. Design, functionalization strategies and biomedical applications of targeted biodegradable/biocompatible polymer-based nanocarriers for drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1147–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travanut, A.; Monteiro, P.F.; Oelmann, S.; Howdle, S.M.; Grabowska, A.M.; Clarke, P.A.; Ritchie, A.A.; Meier, M.A.; Alexander, C. Synthesis of Passerini-3CR Polymers and Assembly into Cytocompatible Polymersomes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travanut, A.; Monteiro, P.F.; Smith, S.; Howdle, S.M.; Grabowska, A.M.; Kellam, B.; Meier, M.A.; Alexander, C. Passerini chemistries for synthesis of polymer pro-drug and polymersome drug delivery nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brož, P.; Benito, S.M.; Saw, C.; Burger, P.; Heider, H.; Pfisterer, M.; Marsch, S.; Meier, W.; Hunziker, P. Cell targeting by a generic receptor-targeted polymer nanocontainer platform. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Alibolandi, M. Biocompatible polymersomes-based cancer theranostics: Towards multifunctional nanomedicine. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombek, F.; Castiglione, K. Polymersomes as Nanoreactors Enabling the Application of Solvent-Sensitive Enzymes in Different Biphasic Reaction Setups. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 1900561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köthe, T.; Martin, S.; Reich, G.; Fricker, G. Dual asymmetric centrifugation as a novel method to prepare highly concentrated dispersions of PEG-b-PCL polymersomes as drug carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvekar, P.; Gannimani, R.; Salih, M.; Makhathini, S.; Mocktar, C.; Govender, T. Self-assembled oleylamine grafted hyaluronic acid polymersomes for delivery of vancomycin against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2019, 182, 110388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porges, E.; Jenner, D.; Taylor, A.W.; Harrison, J.S.; De Grazia, A.; Hailes, A.R.; Wright, K.M.; Whelan, A.O.; Norville, I.H.; Prior, J.L. Antibiotic-Loaded Polymersomes for Clearance of Intracellular Burkholderia thailandensis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 19284–19297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibolandi, M.; Alabdollah, F.; Sadeghi, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Hadizadeh, F. Dextran-b-poly (lactide-co-glycolide) polymersome for oral delivery of insulin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2016, 227, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garni, M.; Thamboo, S.; Schoenenberger, C.-A.; Palivan, C.G. Biopores/membrane proteins in synthetic polymer membranes. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 619–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoori, S.; Leroux, J.-C. Twenty-five years of polymersomes: Lost in translation? Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, D.E.; Ortiz, V.; Srinivas, G.; Klein, M.L.; Kim, Y.; Christian, D.; Cai, S.; Photos, P.; Ahmed, F. Emerging applications of polymersomes in delivery: From molecular dynamics to shrinkage of tumors. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 838–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanson, C.; Schatz, C.; Le Meins, J.-F.; Soum, A.; Thévenot, J.; Garanger, E.; Lecommandoux, S. A simple method to achieve high doxorubicin loading in biodegradable polymersomes. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, G.; Marchessault, R.H.; Leroux, J.-C. Polyester-based micelles and nanoparticles for the parenteral delivery of taxanes. J. Control. Release 2010, 143, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Haldar, M.K.; Karandish, F.; Confeld, M.; Hossain, R.; Borowicz, P.; Gange, K.; Xia, L.; Sarkar, K.; Mallik, S. Tissue-Penetrating, Hypoxia-Responsive Echogenic Polymersomes for Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 12490–12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besada, L.N.; Peruzzo, P.; Cortizo, A.M.; Cortizo, M.S. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro activity evaluation of triblock copolymer-based polymersomes for drugs delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, G.P.; Saunders, R.L.; Haun, J.B.; Rawson, J.; Therien, M.J.; Hammer, D.A. Tunable leuko-polymersomes that adhere specifically to inflammatory markers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14089–14096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. Reversibly crosslinked temperature-responsive nano-sized polymersomes: Synthesis and triggered drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Liu, R.; Bi, S.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Gu, J. Photo-Responsive Polymersomes as Drug Delivery System for Potential Medical Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yang, H.; Bao, C.; Fan, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L. Light-responsive polymersomes with a charge-switch for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, M.; Fischer, K.; Depoix, F.; Fritz, T.; Thiermann, R.; Mohr, K.; Zentel, R. Pentafluorophenyl ester-based polymersomes as nanosized drug-delivery vehicles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Haldar, M.; Confeld, M.; Langaas, C.; Yang, X.; Qian, S.; Mallik, S. Mitochondria-targeted fluorescent polymersomes for drug delivery to cancer cells. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 4151–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.L.; Gong, Y.C.; Xiong, X.Y. Transferrin/folate dual-targeting Pluronic F127/poly (lactic acid) polymersomes for effective anticancer drug delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 33, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Q.; Gong, Y.C.; Li, Z.L.; Li, Y.P.; Xiong, X.Y. Folate-conjugated pluronic/polylactic acid polymersomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilangala, A.B.; Lechanteur, A.; Fillet, M.; Piel, G. Therapeutic peptides for chemotherapy: Trends and challenges for advanced delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 167, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadwal, A.; Baldi, A.; Kumar Narang, R. Nanoparticles as carriers for drug delivery in cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Prasher, P.; Aljabali, A.A.; Mishra, V.; Gandhi, H.; Kumar, S.; Mutalik, S.; Chellappan, D.K.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Dua, K. Emerging era of “somes”: Polymersomes as versatile drug delivery carrier for cancer diagnostics and therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1171–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.; Sun, H.; Zhong, Z. Smart polymersomes dually functionalized with cRGD and fusogenic GALA peptides enable specific and high-efficiency cytosolic delivery of apoptotic proteins. Biomacromolecules 2018, 20, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ge, Z.; Toh, K.; Liu, X.; Dirisala, A.; Ke, W.; Wen, P.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, S. Enzymatically Transformable Polymersome-Based Nanotherapeutics to Eliminate Minimal Relapsable Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japir, A.A.-W.M.M.; Ke, W.; Li, J.; Mukerabigwi, J.F.; Ibrahim, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Mohammed, F.; Ge, Z. Tumor-dilated polymersome nanofactories for enhanced enzyme prodrug chemo-immunotherapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kataoka, K. Chemo-physical strategies to advance the in vivo functionality of targeted nanomedicine: The next generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 143, 538–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anajafi, T.; Mallik, S. Polymersome-based drug-delivery strategies for cancer therapeutics. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, R.H.; Patravale, V.B.; Joshi, M.D. Polymeric nanoparticles for targeted treatment in oncology: Current insights. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Schlich, M.; Cryan, J.F.; O′Driscoll, C.M. Targeted drug delivery via folate receptors for the treatment of brain cancer: Can the promise deliver? J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3413–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Chang, D.-S. Fabrication, characterization, and biological evaluation of anti-HER2 indocyanine green-doxorubicin-encapsulated PEG-b-PLGA copolymeric nanoparticles for targeted photochemotherapy of breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.V.; Gohil, S.V.; Jain, J.P.; Kumar, N. Functionalized polymersomes for biomedical applications. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 3160–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Qin, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, C.; Du, J. Intelligent design of polymersomes for antibacterial and anticancer applications. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology 2022, e1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, V.; Kalscheuer, S.; Kirtane, A.; Zhang, W.; Panyam, J. Perlecan-targeted nanoparticles for drug delivery to triple-negative breast cancer. Future Drug Discov. 2019, 1, FDD8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, U.C.; Bolat, Z.B.; Ozkose, U.U.; Gulyuz, S.; Kucukturkmen, B.; Khalily, M.P.; Ozcubukcu, S.; Yilmaz, O.; Telci, D.; Esendagli, G. A robust optimization approach for the breast cancer targeted design of PEtOx-b-PLA polymersomes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 111929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. Dual-targeted nanomedicines for enhanced tumor treatment. Nano Today 2018, 18, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, P.; Balasubramanian, V.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Correia, A.; Wu, D.; Palivan, C.G.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Santos, H.A. Angiopep2-functionalized polymersomes for targeted doxorubicin delivery to glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chiang, C.-F.; Chen, L.-F.; Liang, P.-C.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Lin, W.-L. Polymersomes conjugated with des-octanoyl ghrelin and folate as a BBB-penetrating cancer cell-targeting delivery system. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4066–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qin, Y.; Lee, J.; Liao, H.; Wang, N.; Davis, T.P.; Qiao, R.; Ling, D. Stimuli-responsive nano-assemblies for remotely controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 566–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmiladevi, P.; Akhtar, N.; Haribabu, V.; Girigoswami, K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Girigoswami, A. Excitation wavelength independent carbon-decorated ferrite nanodots for multimodal diagnosis and stimuli responsive therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.G.; Surendran, S.P.; Jeong, Y.Y. Tumor Microenvironment-Stimuli Responsive Nanoparticles for Anticancer Therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girigoswami, A.; Yassine, W.; Sharmiladevi, P.; Haribabu, V.; Girigoswami, K. Camouflaged nanosilver with excitation wavelength dependent high quantum yield for targeted theranostic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haribabu, V.; Sharmiladevi, P.; Akhtar, N.; Farook, A.S.; Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. Label free ultrasmall fluoromagnetic ferrite-clusters for targeted cancer imaging and drug delivery. Curr. Drug Del. 2019, 16, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Ling, Z.; Zhou, Z.; He, J.; Ran, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J. Herceptin-decorated paclitaxel-loaded poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanobubbles: Ultrasound-facilitated release and targeted accumulation in breast cancers. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, W.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C. Recent development of pH-responsive polymers for cancer nanomedicine. Molecules 2018, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, L.J.; Sincari, V.; Jager, A.; Konefal, R.; Panek, J.; Cernoch, P.; Pavlova, E.; Stepanek, P.; Giacomelli, F.C.; Jager, E. Microfluidic-assisted engineering of quasi-monodisperse pH-responsive polymersomes toward advanced platforms for the intracellular delivery of hydrophilic therapeutics. Langmuir 2019, 35, 8363–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, G.; Galeotti, T.; Chiarugi, P. Metastasis: Cancer cell’s escape from oxidative stress. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.J.; Gibson, M.I. Redox-sensitive materials for drug delivery: Targeting the correct intracellular environment, tuning release rates, and appropriate predictive systems. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 786–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, P. Synthesis strategies for disulfide bond-containing polymer-based drug delivery system for reduction-responsive controlled release. Front. Mater. Sci. 2015, 9, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, K.; Yang, D.; Li, P.; Qian, Z. Physical-, chemical-, and biological-responsive nanomedicine for cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 12, e1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kozlovskaya, V.; Medipelli, S.; Xue, B.; Ahmad, F.; Saeed, M.; Cropek, D.; Kharlampieva, E. Temperature-sensitive polymersomes for controlled delivery of anticancer drugs. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7945–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, J.; Liu, S. Photo-and reduction-responsive polymersomes for programmed release of small and macromolecular payloads. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrella, M.C.; Di Capua, A.; Adami, R.; Reverchon, E.; Mella, M.; Izzo, L. Impact of intermolecular drug-copolymer interactions on size and drug release kinetics from pH-responsive polymersomes. Supramol. Chem. 2017, 29, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S. Acid-disintegratable polymersomes of pH-responsive amphiphilic diblock copolymers for intracellular drug delivery. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7262–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-l.; Ma, X.-j.; Yu, X.-f. pH-responsive polymersome based on PMCP-b-PDPA as a drug delivery system to enhance cellular internalization and intracellular drug release. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Fei, Z.; Jin, L.; Zhou, P.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C. Dual-responsive polymersomes as anticancer drug carriers for the co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Ingle, K.; Qian, S.; Halade, G.V.; Urban, V.S.; Kharlampieva, E. Temperature-responsive polymersomes of poly (3-methyl-N-vinylcaprolactam)-block-poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) to decrease doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3989–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiazDuarte-Rodriguez, M.; Cortez-Lemus, N.A.; Licea-Claverie, A.; Licea-Rodriguez, J.; Méndez, E.R. Dual responsive polymersomes for gold nanorod and doxorubicin encapsulation: Nanomaterials with potential use as smart drug delivery systems. Polymers 2019, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Sun, M.; Yang, B.; Xiao, J.; Du, J. Ultrasound-responsive polymersomes capable of endosomal escape for efficient cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroojalian, F.; Babaei, M.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Encapsulation of thermo-responsive gel in pH-sensitive polymersomes as dual-responsive smart carriers for controlled release of doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2018, 288, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Ingle, K.; Ahmad, A.; Halade, G.V.; Kharlampieva, E. Dually Responsive Poly (N-vinylcaprolactam)-b-poly (dimethylsiloxane)-b-poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) Polymersomes for Controlled Delivery. Molecules 2022, 27, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, V.V.; Carretero, G.P.; Vitale, P.A.; Todeschini, Í.; Kotani, P.O.; Saraiva, G.K.; Guzzo, C.R.; Chaimovich, H.; Florenzano, F.H.; Cuccovia, I.M. Stimuli-responsive polymersomes of poly [2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate]-b-polystyrene. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Park, D.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.J. Polymersomes with singlet oxygen-labile poly (β-aminoacrylate) membrane for NIR light-controlled combined chemo-phototherapy. J. Controlled Release 2020, 327, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.; Li, J.; Mohammed, F.; Wang, Y.; Tou, K.; Liu, X.; Wen, P.; Kinoh, H.; Anraku, Y.; Chen, H. Therapeutic polymersome nanoreactors with tumor-specific activable cascade reactions for cooperative cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Hu, P.; Peng, H.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, Q.; He, Y. Near-infrared laser-triggered, self-immolative smart polymersomes for in vivo cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.U.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, W.; Nazir, A.; Fahad, S.; Chen, X.; Elsharaarani, T. Synthesis of polyorganophosphazenes and preparation of their polymersomes for reductive/acidic dual-responsive anticancer drugs release. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 8264–8284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poschenrieder, S.T.; Schiebel, S.K.; Castiglione, K. Polymersomes for biotechnological applications: Large-scale production of nano-scale vesicles. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameez, S.; Bamba, I.; Palmer, A.F. Large scale production of vesicles by hollow fiber extrusion: A novel method for generating polymersome encapsulated hemoglobin dispersions. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5279–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).