Abstract
MXene materials have found emerging applications as catalysts for chemical reactions due to their intriguing physical and chemical applications. In particular, their broad light response and strong photothermal conversion capabilities are likely to render MXenes promising candidates for photothermal catalysis, which is drawing increasing attention in both academic research and industrial applications. MXenes are likely to satisfy all three criteria of a desirable photothermal catalyst: strong light absorption, effective heat management, and versatile surface reactivity. However, their specific functionalities are largely dependent on their structure and composition, which makes understandings of the structure–function relationship of crucial significance. In this review, we mainly focus on the recent progress of MXene–based photothermal catalysts, emphasizing the functionalities and potential applications of MXene materials in fields of photothermal catalysis, and provide insights on design principles of highly efficient MXene–based photothermal catalysts from the atomic scale. This review provides a relatively thorough understanding of MXene–based materials for photothermal catalysis, as well as an in–depth investigation of emerging high-prospect applications in photothermal catalysis.
1. Introduction
Emerging photothermal catalysis, which combines the advantages of both photochemical and thermochemical processes, is drawing increasing attention in both academic research and industrial applications [1,2,3,4]. Compared with conventional thermochemistry process, photothermal catalysis makes use of light energy, particularly the abundant and recyclable solar energy, significantly lowers the energy barrier of a high–temperature reaction, and thus allows for partial or even entire replacement of fossil energy consumption with solar irradiation [5]. Photothermal catalysis has been extensively explored and utilized for various distinct types of reactions, including conversion of CO2 to synthesis gas or hydrocarbons, dry reforming of methane, and reduction of nitrogen to ammonia through the Haber–Bosch process [3,6,7,8]. It is thus a promising strategy to ameliorate the energy and environmental crises faced by human beings nowadays and to diversify the energy structure in industrial catalysis.
Photothermal catalysis functions through the induction of the photothermal effect of catalytic materials upon light irradiation. In this term, nanostructured materials are promising candidates as photothermal catalysts since they have distinct optical and thermal properties from their bulk counterparts [9,10,11]. During the past decades, extensive efforts have been made in discovering nanostructured materials with strong light absorption ability, which is considered one of the key factors in enhancing the photothermal effect. Based on the photothermal effect from local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of catalysts and/or additional inter– or intraband transitions, photothermal catalysts can typically function under the solar spectrum [12,13,14]. The absorption spectra for certain band-engineered catalysts can even cover the entire solar spectrum [15,16], thereby achieving high photothermal conversion efficiencies and reaction rates while operating under moderate conditions. Heating through the photothermal effects of photothermal catalysts is typically highly localized, which can effectively elevate the local temperature at the catalyst-reactant interfaces [17]. This, in turn, leads to a series of consequences, including an increase in the entropy of chemical reactions, modulation of the thermodynamics and kinetics of hot–electron transfer, increase in mass transfer, and enhancement of product selectivity and stability of the catalyst, which collectively contributes to promoting the macroscopic reaction rate in photothermal catalysis [15,18,19,20,21,22].
Based on the three main processes for a typical photothermal catalytic pathway, namely, photothermal conversion, heat management, and surface reactions, it is generally accepted that the rational design of highly efficient photothermal catalysts should satisfy three criteria in photothermal catalysis as follows: (1) excellent sunlight absorption ability, which includes broad absorption range as well as intense light responsivity, and high photothermal conversion efficiency; (2) effective thermal management to prevent heat dissipation at chemical interfaces or losses through ambient conditions; and (3) versatile intrinsic reactivity for efficient catalytic performance [1,23,24,25,26]. Previous studies have laid emphasis on the rational design of highly active photothermal catalysts. However, despite the fact that many efforts have been made in the well–defined design of active photothermal catalysts to boost the solar-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency, it is challenging for the single–component catalyst to meet all the above requirements for the construction of desirable photothermal catalysts [27,28].
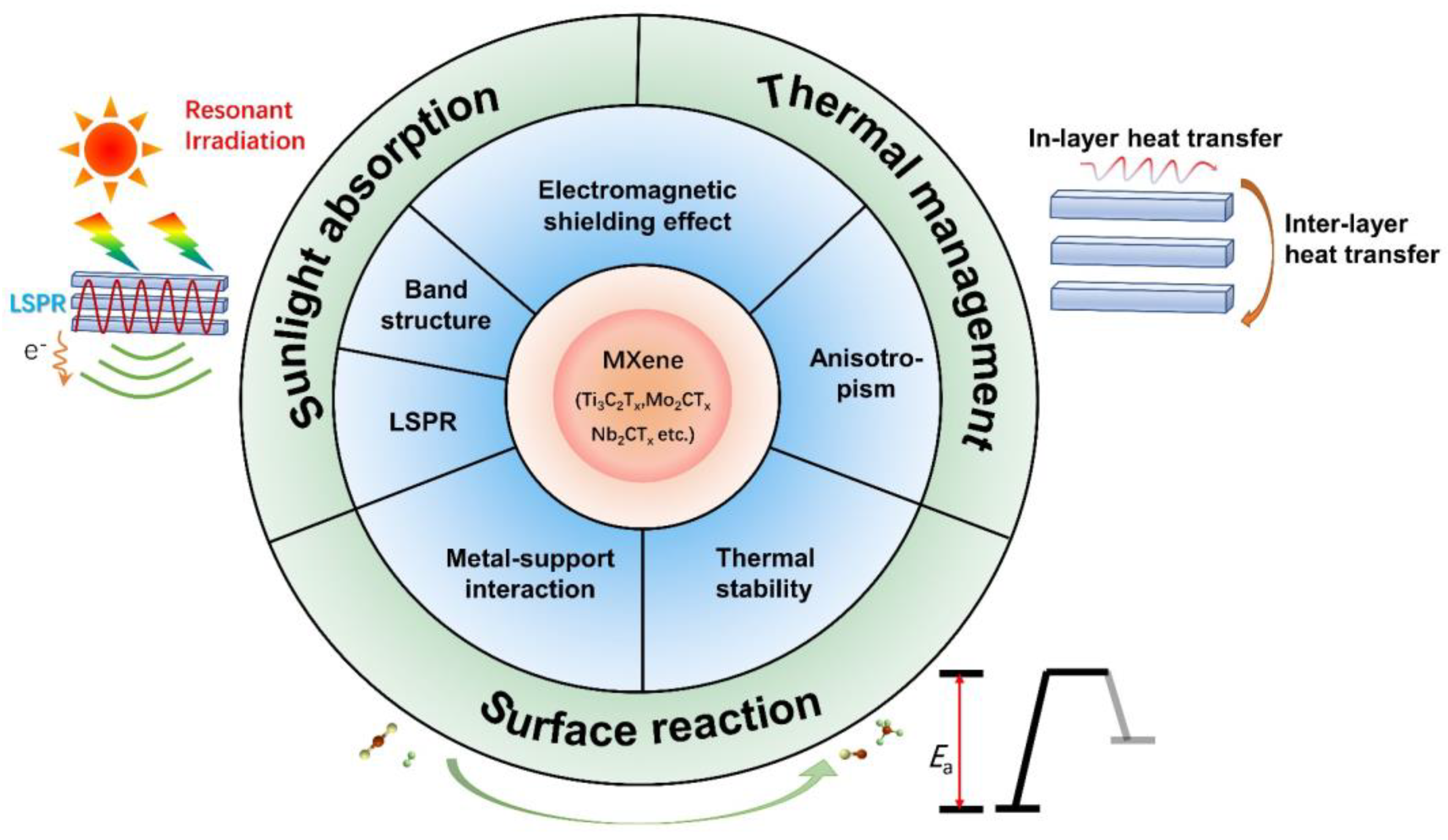
Transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides (denoted MXenes) are likely to satisfy the requirements from all three aspects of the construction of desirable photothermal catalysts and are thus one of the most promising materials in photothermal catalysis. MXenes have become the hotspot of 2–Dimensional (2D) materials since the seminal research by Gogotsi et al. in 2011 [29]. Due to the 2D lamellar structure of MXenes as well as various kinds of surface terminations and exposed transition metal defects, MXenes exhibit distinct intriguing physical and chemical properties, which include tunable work function and band structure, excellent electrical conductivity, great electromagnetic shielding effect, a number of mechanical properties, etc. [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Therefore, MXene–based systems have found numerous applications as anode materials for fuel cells [38,39], in lithium–ion batteries [40,41], in photochemical or photodynamic chemotherapy [42,43], in sensors [44,45], in chemical catalysis and energy and environmental applications [46,47,48], etc. Importantly, MXene materials have been found to sustain broad features of localized surface plasmon resonance in the visible range, which allows them to make full utilization of sunlight by extending the light response to the near–infrared region [49,50,51]. Furthermore, the 2D nature of MXenes, their electromagnetic shield properties, as well as the abundance of vacancies and adsorbents are likely to contribute to the photothermal conversion and surface reactivity, as will be further elaborated in later sections [52,53,54,55]. Consequently, MXene materials may hold promising prospects for photothermal catalysis (Figure 1). However, the specific functionality of MXenes is heavily dependent on their structural properties, including their compositions, layer numbers, etc., which makes investigation and understanding of the structure–function relationship of MXenes of high significance for modulating them towards excellent photothermal catalytic performance. A limited understanding of the advances in fields of MXene–based materials for photothermal catalysis has been cultivated, which has, as of yet, hindered the development of MXene–based photothermal catalysts. Further theoretical and experimental studies are of great necessity to gain insight on the structure–activity relationship of MXene–based photothermal catalysts.
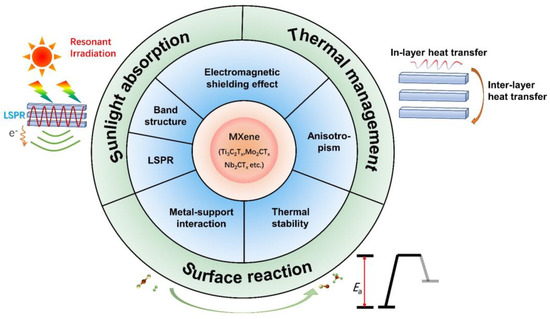
Figure 1.
Properties and functionalities of MXene materials in fields of photothermal catalysis.
In this review, we systematically overview the recent progress of MXene–based photothermal catalysts, emphasizing the functionalities and applications of MXene materials in fields of photothermal catalysis, and providing critical assessments of the construction of active MXene–based photothermal catalysts. The relationship between the fundamental properties of MXene, such as their unique structural, chemical, and electrical properties, and the above-mentioned requirements for the construction of highly efficient photothermal catalysts are proposed. Secondly, current advances within the range of corresponding catalyst design principles are introduced in detail. Finally, the remaining challenges and opportunities for developing MXene–based integrated catalysts for highly efficient photothermal catalysis are provided for further investigation. This review provides a comprehensive understanding and valuable information on MXene–based materials for photothermal catalysis, as well as the in–depth investigation of emerging high–prospect applications in photothermal catalysis. Under a broader context, this review provides guidance for the construction of desirable MXene–based catalytic systems from the atomic scale.
2. Functionalities and Applications of MXenes in Photothermal Catalysis
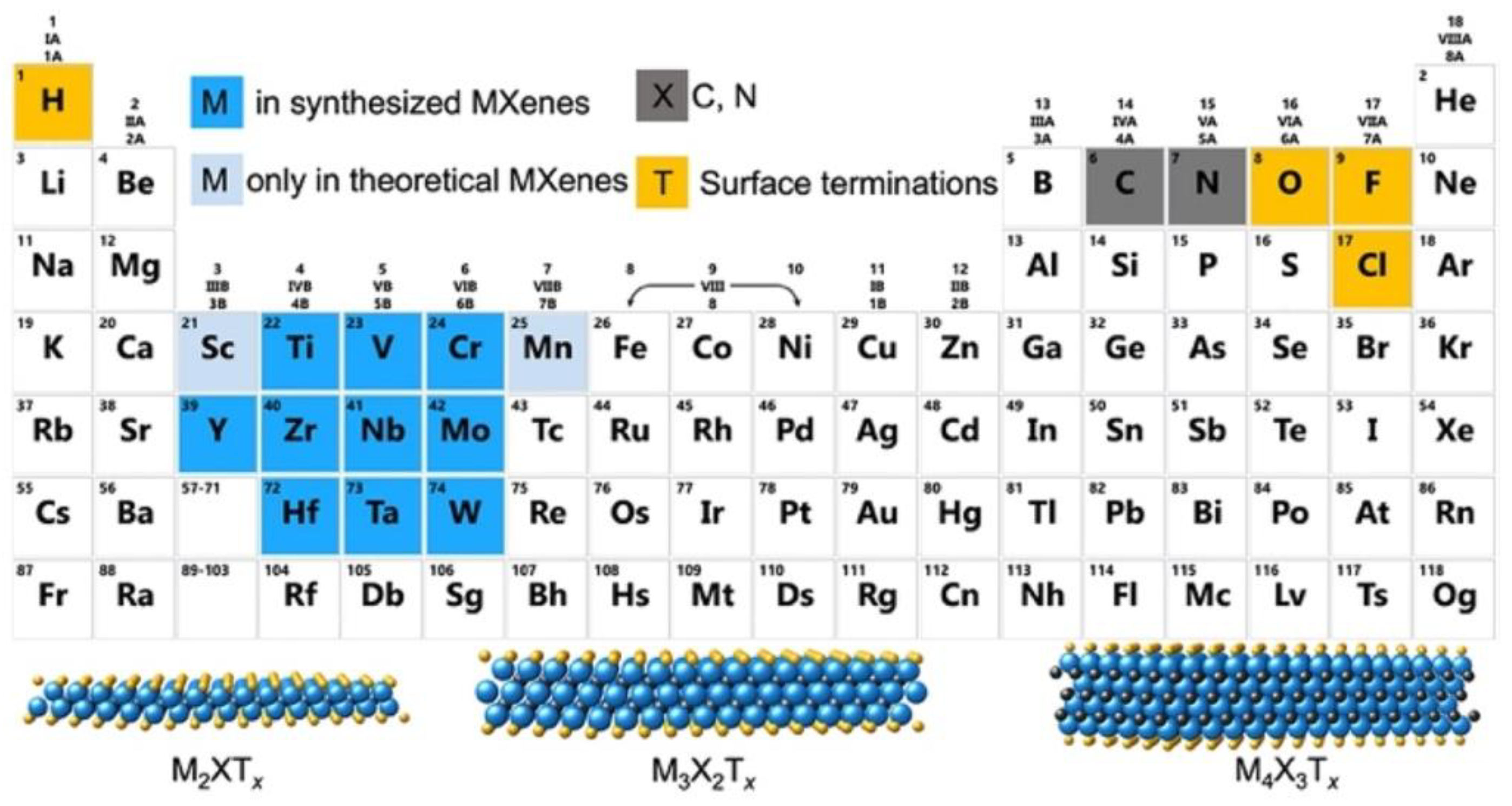
The general formula of MXenes is Mn+1XnTx, where M represents a transition metal, X represents carbon or nitrogen, and Tx refers to surface terminations resulting from synthetic processes [56,57]. The structure of MXenes contains the Mn+1Xn unit from the corresponding MAX precursors and the tunable surface termination groups from the etching and delamination process [58]. The MAX phases are layered ternary carbides and nitrides with the general formula of Mn+1AXn, where A represents Al and Si mainly from groups 13 and 14 of the periodic table. As shown in Figure 2, MXenes demonstrated the same hexagonal atomic lattice P63/mmc as MAX phases after the etching process, in which the M atoms are hexagonally closed packed and X atoms fill the octahedral interstitial sites. In MAX phases, the “M–X” interactions are mainly covalent and ionic bonds, whereas “M–A” bonds are metallic [59]. It is noticeable that the “M–X” interactions are less active than metallic bonds of “M–A”; thus, MXenes can be typically synthesized by selective etching of A layers from MAX precursors. After etching, various surface terminations, such as –O, –OH, and/or –F, are bonded to multi–layer MXenes, which are connected by van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding characteristics of traditional kinds of 2D materials. Then, the effective delamination process, mainly achieved by organic intercalators, was developed to synthesize few–/single–layer MXenes. Moreover, delamination is necessary to obtain few–/single–layer MXenes with high surface area, good hydrophilicity, and rich surface terminations. Based on these structural factors, MXenes therefore possess many interesting physical, chemical and electrical properties.
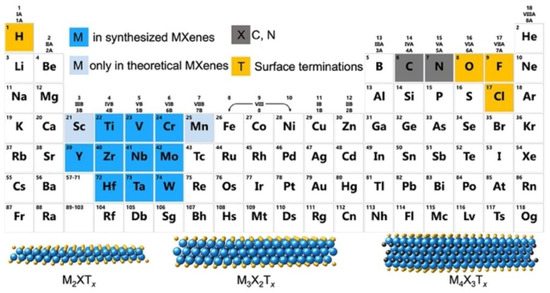
Figure 2.
Periodic table showing compositions of MXenes, MAX phases, and corresponding elements used to build MXenes. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [34]. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society).
Notably, there are specific kinds of properties that correspond well to the criteria for the construction of desirable photothermal catalysts. Firstly, the LSPR effect of MXene materials makes a great contribution to sunlight absorption and photothermal conversion processes [49,60]. Secondly, due to the special interlayer structure of MXenes, excellent electromagnetic shielding properties, and low mid–IR emissivity, MXene materials are of great benefit in preventing heat dissipation by effective heat management based on anisotropic heat transfer efficacy [30,61]. Thirdly, the unique strong metal–support interaction (SMSI) and tunable surface terminations of MXenes contribute to the favorable tunability of the dispersity and stability of catalysts, thus enhancing the intrinsic catalytic activity [62,63]. Therefore, by means of structural, compositional, and additional engineering strategies, it is likely that certain MXene–based systems can satisfy all three prerequisites for the construction of a desirable photothermal catalyst. This is extremely rare in previous studies. For example, a few works have demonstrated the efficacy of enhanced absorption and heat management processes towards augmented photothermal catalytic performance, while unfortunately neglecting surface reactivity engineering. Feng et al. achieved photon–efficient photocatalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation over a cobalt plasmonic superstructure with a nearly 100% light absorption efficiency across the entire solar spectrum [27]. Additionally, due to the heat insulation and infrared shielding effect, the outer SiO2 shell confined the photothermal energy of the cobalt core, enabling an enhanced photothermal effect. Therefore, the plasmonic superstructure catalyzed photothermal hydrogenation of carbon dioxide more efficiently than their counterparts. However, this work focused on light absorption, light–to–heat conversion, and thermal management process, neglecting the surface reactions in photothermal catalysis. Similarly, Kong et al. demonstrated the preparation of strongly light-absorptive and highly dispersed Ru nanocatalysts that exhibit enhanced activity and relatively good stability in the photothermal hydrogenation of CO2 [28]. The ability to improve sunlight absorption without sacrificing the metal dispersity would be beneficial to the design of highly efficient photothermal catalysts, which has, as of yet, been a crucial challenge in the designs of photothermal catalytic systems.
Although MXene–based systems are likely to serve as a promising candidate to meet all three prerequisites for photothermal catalysis, not all kinds of MXene materials can simultaneously sustain the above–mentioned properties. It is therefore important to make further investigations and to obtain deeper understandings of the effect that the composition and surface structure of MXene materials can have on their photophysical properties and catalytic performance. For instance, for sunlight absorption and photothermal conversion processes, the LSPR effect of MXene materials may play a decisive role. It has been shown that Ti–based MXene materials (Ti2C, Ti3C2) exhibited much higher intensity of surface plasmon resonance than other kinds of MXene materials, which may probably be responsible for their better LSPR effect [64]. The evident LSPR response can not only broaden the spectral response range of materials but also improve the dynamics and kinetics of photothermal catalytic reactions through local field enhancement, hot–electron injection, and photothermal effect. In addition, for the process of surface reactions, benefiting from their various element compositions, adjustable surface terminations, and enriched transition metal vacancy sites, MXenes can be used as efficient catalysts in many typical reactions, including hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, CO oxidation, and N2 fixation [65,66,67,68]. Among all kinds of MXenes, Ti3C2Tx, Mo2CTx, and V2CTx are applied extensively. For example, Zhou et al. developed a layered TiO2 (noted as M–TiO2) catalyst, which is evolved in situ from a Ti3C2Tx MXene material, as a new type of efficient metal-oxide catalyst for the oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of ethane. The M–TiO2 catalyst exhibited much better ethane conversion, ethylene selectivity, and stability than their counterparts. Combined with experimental and theoretical results, it is clearly demonstrated that the Ti vacancy sites, derived from an effective etching process, can not only increase the reducibility of the lattice oxygen in M–TiO2 but also stabilize the defective structure to improve the catalytic performance of oxidative dehydrogenation [69]. Based on the examples above, the adjustable element composition and surface structure of MXene materials is a prerequisite for the construction of highly efficient MXene–based photothermal catalysts (Figure 2). The specific requirements for each criterion are elaborated in the following sections.
2.1. Sunlight Absorption and Photothermal Conversion Process
According to previous studies, the spatially confined free electrons of MXene materials are likely to provide enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance effect, which is mainly attributed to the high density of states (DOS) at the Fermi level, excellent electrical conductivity driven by higher carrier concentration, and their metallic character. In detail, Gogotsi and co–workers demonstrated that due to excellent conductivities and more pronounced metallic character, Ti-based MXene materials (Ti2C, Ti3C2) exhibited much higher free carrier density and mobility than other kinds of MXene materials, which may be responsible for their better LSPR [64]. In contrast, the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) intensity of V2C is an order of magnitude smaller compared to Ti3C2 and Ti2C, which could result from more structural defects inherited from a harsher synthesis method. Additionally, Mo– and Nb–based MXene materials showed lower SPR intensity owing to much lower carrier concentrations and less metallic character.
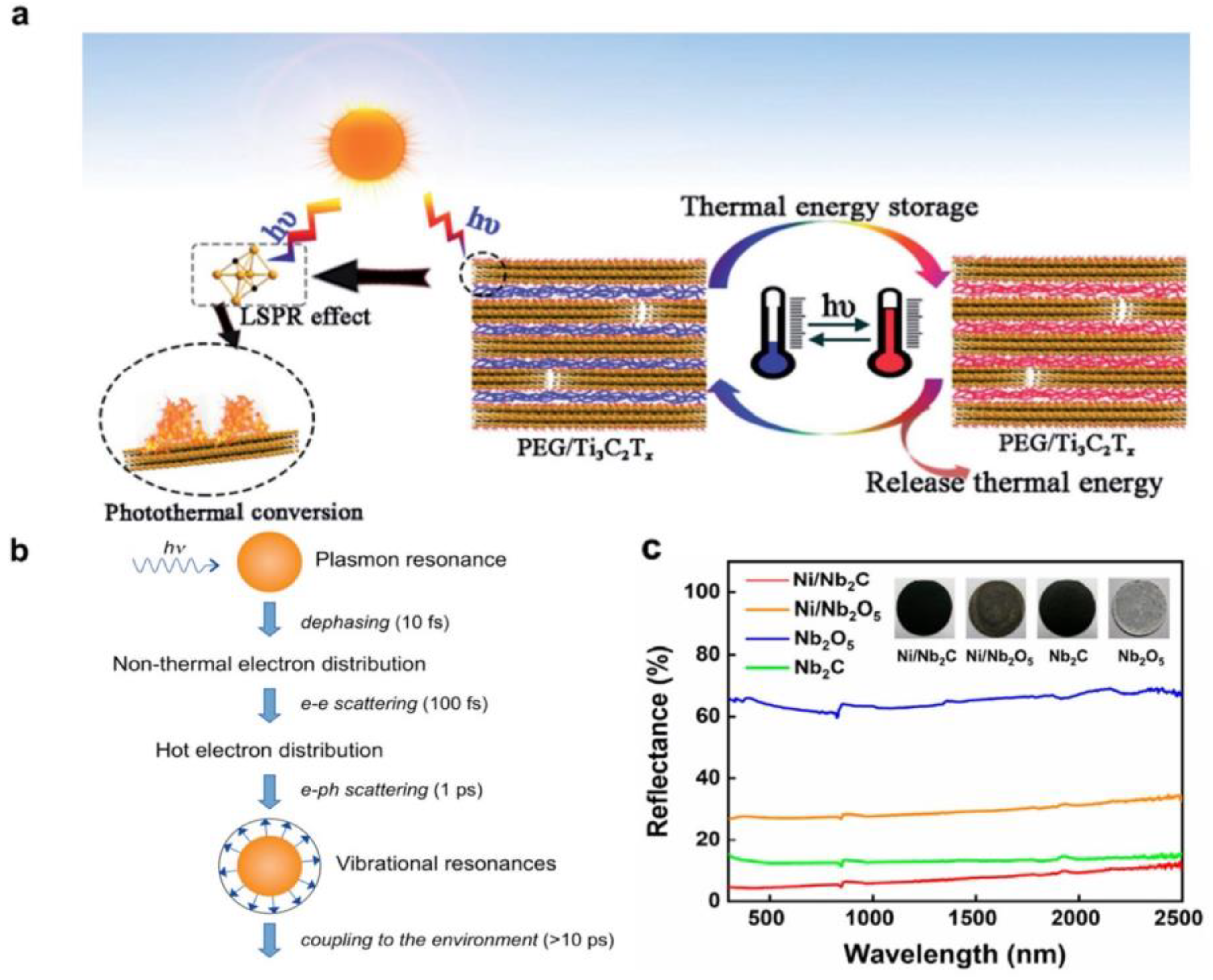
For the specific processes of sunlight absorption and photothermal conversion, the surface LSPR effect plays a vital role (Figure 3). As shown in Figure 3a,b, after resonant excitation of the LSPR in MXenes, the photoexcited carriers could go through non–radiative relaxation, generating charge carriers at higher energy levels. This could be followed by electron–electron scattering, where energy transfer amongst the electron clouds can happen through collisions between electrons, creating a Fermi–Dirac distribution at higher temperatures. Subsequently, the high–energy “hot” electrons can interact with phonons, converting kinetic energy into vibrational energy of the lattice, and subsequently into heat [70,71]. The subsequent incidence of electron–phonon scattering further elevates the lattice vibration of MXene, leading to rapid surface temperature increases.
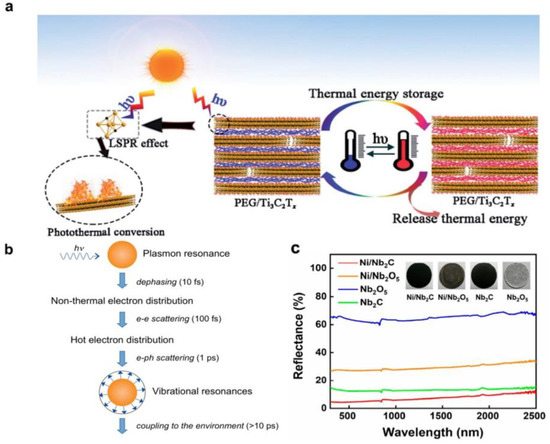
Figure 3.
Absorption and photothermal conversion properties of MXenes. (a) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of photothermal energy conversion and storage of MXene–based materials. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [50]. 2019 Royal Society of Chemistry); (b) Sequence of events and approximate time scales following absorption of photons. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [72]. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society); (c) Diffuse reflectance spectra of MXene–based photothermal catalysts. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [73]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society).
In order to ensure high photothermal conversion efficiencies in MXene photothermal catalysts, it is presumable that the photothermal catalyst possesses not only broad absorption features in the UV–Vis–NIR range to ensure efficient harvesting of the solar spectrum, but also high absorption intensity to guarantee high photothermal heat generation. On the one hand, in terms of absorption width, MXenes, owing to their abundant surface functional groups, demonstrate a typical semiconductor behavior with a narrow band gap, which enables a broad absorption in the solar spectrum [29,53]. This is an evident advantage over conventional wide-bandgap semiconductors in terms of photothermal conversion efficiencies, as the absorption ranges of the latter are typically confined to the UV, which accounts for only a small portion of the solar spectrum. On the other hand, the LSPR effect of MXenes enables high light responsivity in the UV–visible–NIR range. This is extremely beneficial for photothermal conversion efficiency. It has been established in prior works that for the photothermal effect induced by hot carriers, namely through the electron-electron and electron–phonon scatterings introduced above, the local temperature increase at the nanoparticle (NP) surface can be calculated based on Equation (1), where Q is the absorbed light power, and can be further extended to the product of the absorption cross-section (σabs) and incident irradiance (I), as expressed in Equation (2) [71]. β is a geometrical correction factor; κs is the thermal conductivity of the surrounding medium, which accounts for heat losses to the ambient medium or environment; and Req is the equivalent nanoparticle radius. At the resonant wavelengths, the LSPR effect significantly increases the absorption cross-section (σabs) of MXenes, thus facilitating the photothermal conversion efficiencies.
Based on the discussions above, it is likely that MXenes can sustain both broad absorption width in the solar spectrum and high absorption efficiencies, which could collectively contribute to the photothermal conversion processes. These possibilities have been implemented in some prior research. For example, our group first reported the discovery of MXene materials as superior photothermal supports for metal nanoparticles. We demonstrated that MXene materials can enhance the photothermal effect and thus boost the photothermal catalytic performance of metal nanoparticles (Figure 3c) [73]. Our research also confirmed the excellent sunlight absorption ability and light-to-heat conversion property of MXene in the UV–Vis–NIR region.
Although the LSPR responses of MXenes have been relatively widely explored, understanding of the specific source of the LSPR of MXenes as well as its specific role in enhancement mechanisms and catalytic pathways is still pending. In addition, the LSPR intensity of MXenes and its enhancement of optical cross–sections are still relatively weak compared to conventional plasmonic metals, such as Au and Ag, which presents large room for further improvement of the light responsivity and photothermal conversion efficiencies of MXenes [74,75,76,77]. This is essentially due to limited charge carrier density and mobility. This can be further evidenced by the Clausius–Mossotti relation and the classic Drude model. For metals or more expressed metallic character systems, when the particle sizes are much smaller than the incident wavelength, according to the classic Drude model, the dipolar polarizability α can be described by the Clausius–Mossotti relation in Equation (3), where V is the volume of the nanoparticle and εm and ε0 are the medium dielectric constant and permittivity of vacuum, respectively. κ is a shape factor that is subject to the geometry of the surface. Furthermore, in order to derive the value of the dielectric function of the metal, the classic Drude model is used in Equation (4), where ω is the angular frequency of the excitation source, γ is the electron collision frequency in the bulk, and ωp is the bulk plasma frequency of the free electrons. ωp is determined by the density of free electrons n and the effective mass me of the electrons, as shown in Equation (5).
Henceforth, it can be established that the charge carrier density in the catalytic system is directly related to the dipolar polarizability α, which is a clear indicator of the light response and the LSPR intensity. Further amelioration of the charge carrier density and mobility in MXene–based photocatalysts could prove beneficial to induce improved light response as well as reactivity through enhanced LSPR.
2.2. Thermal Management
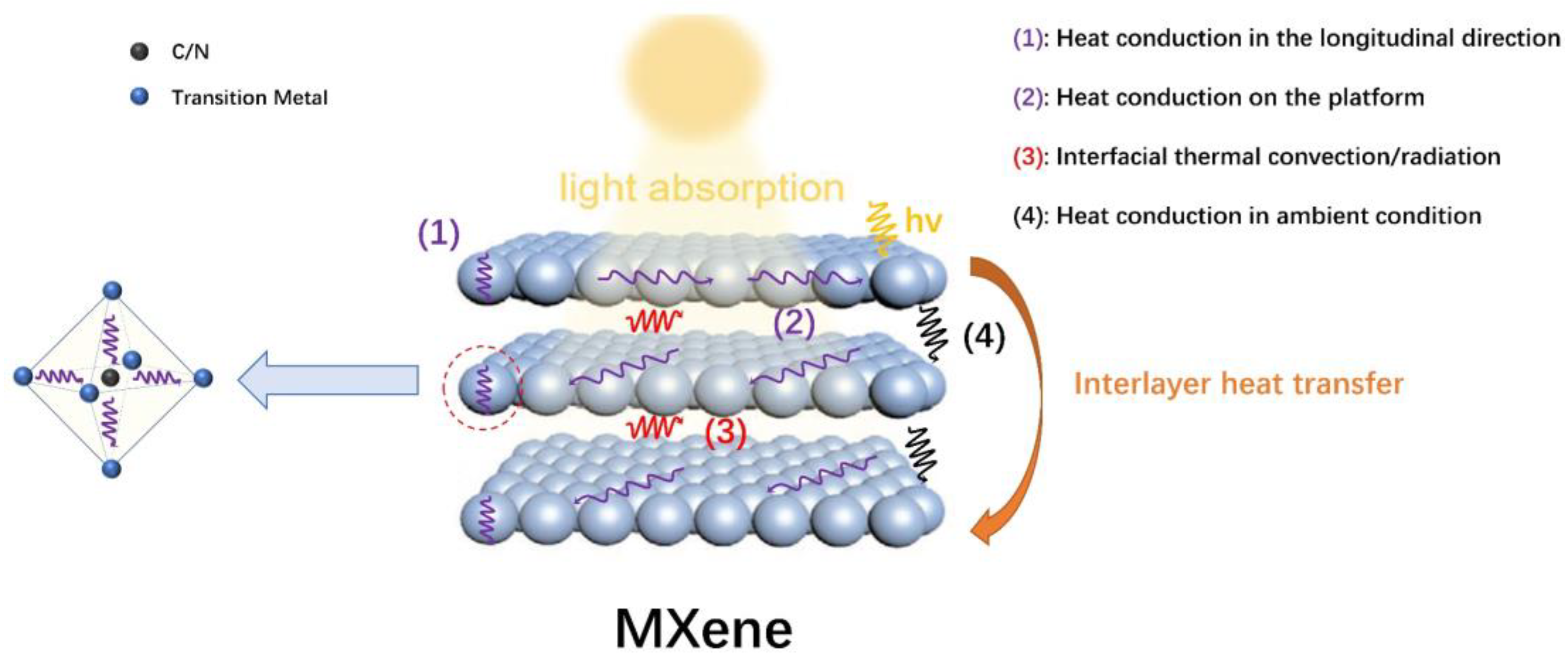
Besides the light absorption and light–to–heat conversion process, ideal heat management to prevent heat dissipation is also a key step in photothermal catalysis. Based on its 2D and lamellar structure, the heat transfer process in MXenes is highly anisotropic. It is generally conceived that MXenes possess larger thermal resistance for interlayer heat transfer processes than in–layer transfers, as the latter only involves heat conduction with the crystal lattices, whereas the former involves much more complicated transfer pathways. Overall, the interlayer heat transfer processes of MXenes are illustrated in Figure 4. When MXene nanosheets are irradiated, localized heating leads to an evident temperature increase on the exposed surface. In–layer heat conduction rapidly disperses the generated heat throughout the first (exposed) layer of MXenes (processes (1), (2)). When the conducted heat reaches the interface between crystal lattice layers and ambient medium, interfacial thermal convection and/or radiation (process (3)), as well as heat conduction in the ambient atmospheric or medium environment between layers (process (4)), could occur in order for interlayer heat conversion to happen. This is followed by an almost identical heat conduction process on the next layer as compared to the illuminated layer immediately after illumination and heat production. The presence of (3) and (4) could significantly increase the interlayer heat transfer resistance, which grants it better thermal insulation properties than conventional bulk materials.
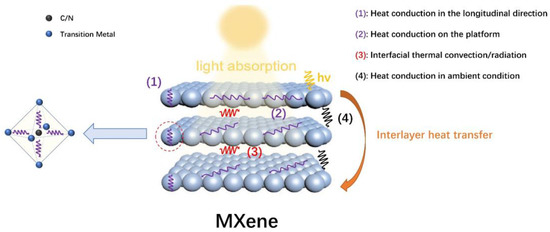
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of the structure and the mechanism of heat transfer process of MXenes.
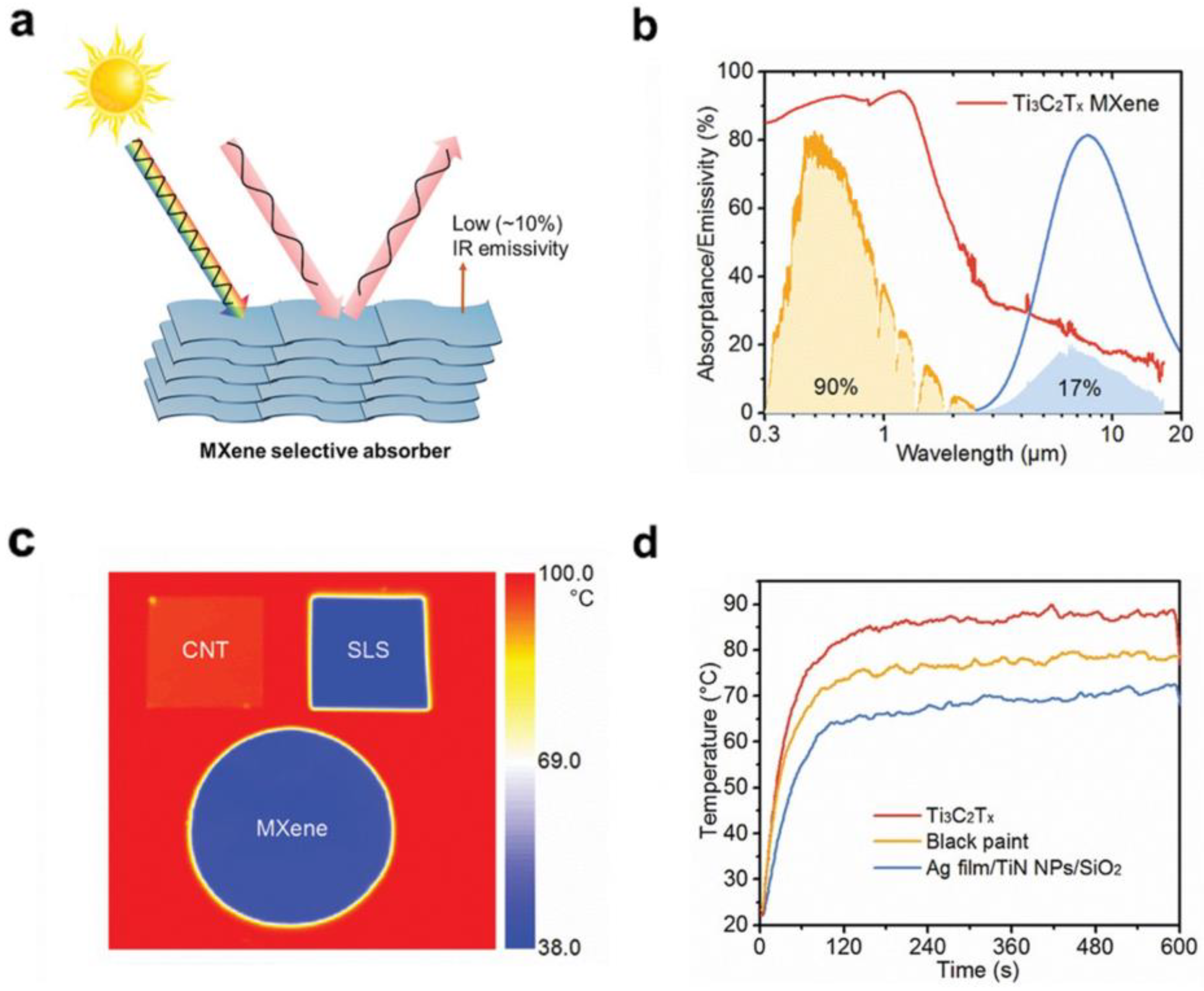
In addition to the interlayer thermal insulating properties of MXenes based on their 2D lamellar structure, another factor that distinguishes MXenes from other 2D materials systems in terms of heat management is their electromagnetic interference shielding effect, which has been investigated and reported in several works [78]. More specifically, Gogotsi and co-workers also demonstrated the potential of several MXenes and their polymer composites for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding [30]. A 45–micrometer–thick Ti3C2Tx film exhibited an EMI shielding effectiveness of 92 decibels, which is the highest among synthetic materials of comparable thickness produced to date. The excellent performance is attributed to the excellent electrical conductivity and multiple internal reflections from Ti3C2Tx MXenes. Despite strong absorption in the UV–Vis–NIR range, MXenes typically possess low mid-IR emissivity. This essentially cuts off interlayer heat transfer through radiation at the interfaces between layers (process (3)), which further enhances its thermal insulating performance and macro heat management. Li and co–workers reported the intrinsically low mid–IR emissivity (down to 10%) of the 2D Ti3C2, as shown in Figure 5 [79]. This is one crucial advantage for MXenes as photothermal catalysts over other 2D materials, such as graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). In general, the above-mentioned properties allow MXenes to be a promising new type of heat management material towards photothermal catalytic applications.
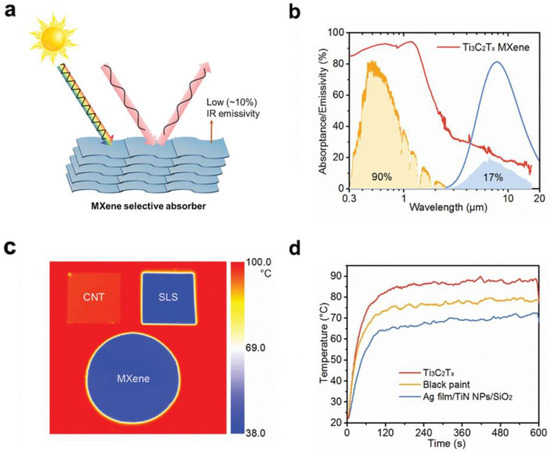
Figure 5.
Light–matter interaction of MXene materials. (a) The high solar absorptance, high mid–IR reflectance, and low IR emissivity of MXenes; (b) Absorptance/emissivity spectra of a Ti3C2Tx film; (c) IR photographs of the SLS, CNT, and MXene on a hot plate with a constant temperature of 100 °C; (d) Temperature versus time of Nylon 66 membranes coated with Ti3C2Tx and metamaterial absorbers under 1 sun. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [79]. 2021 John Wiley and Sons).
2.3. Surface Reaction
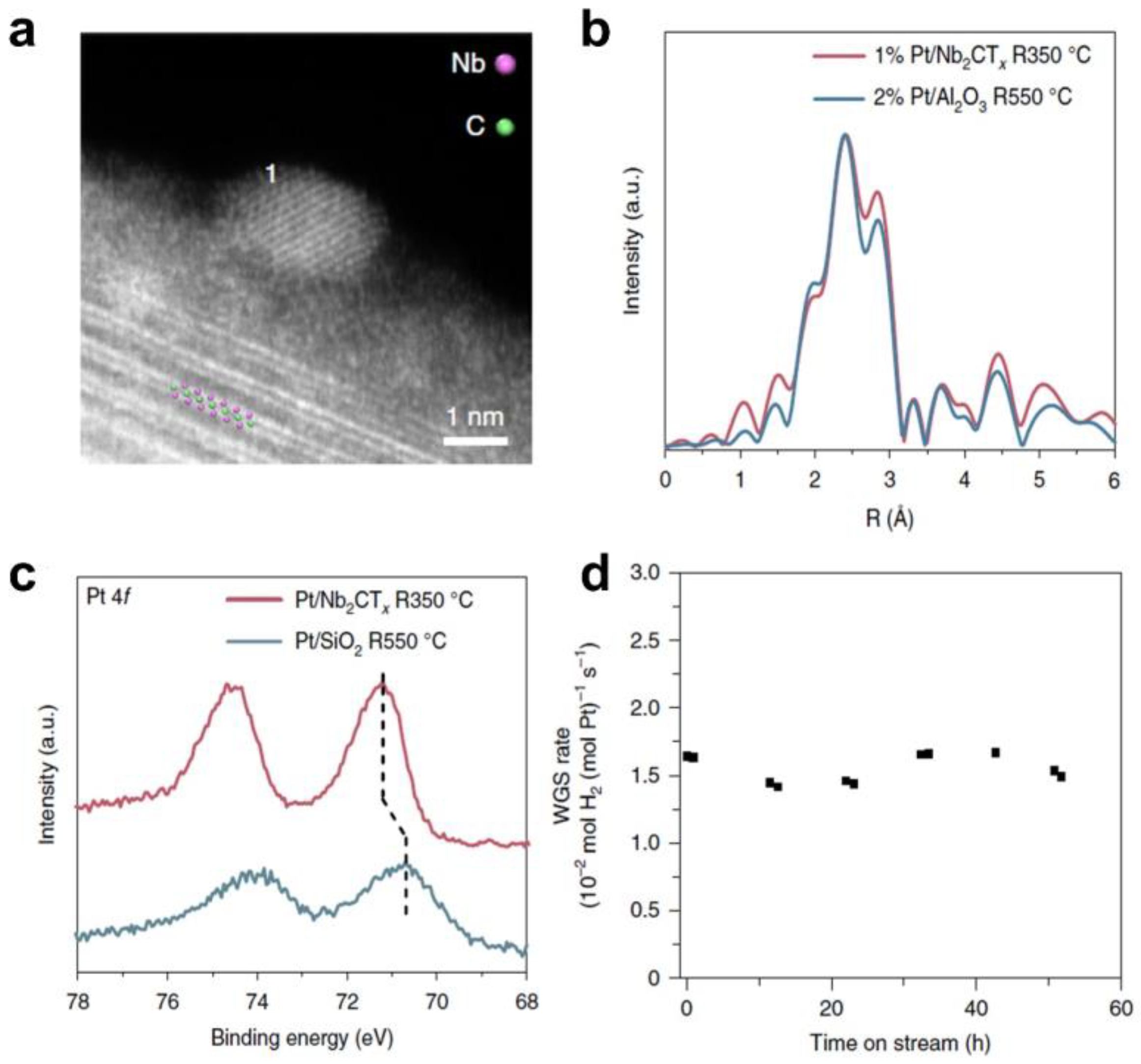
The utilization of MXene–based materials for the construction of efficient photothermal catalysts holds great promise. Although researchers have begun to investigate the construction of MXene photothermal catalysts, the specific role of MXene materials in photothermal catalysis has not been clearly elaborated. In fact, various works have classified photothermal catalysis as a special type of thermal catalysis. In heterogeneous thermal catalysis, loaded metal catalysts are the most widely explored catalysts, which is also often the case with MXene–based photothermal catalysis. Through the modulation of the active site, the kinetic factors of the reaction can be controlled and thus the catalytic reaction can be regulated. Due to the presence of transition metal defects and the tunability of the surface groups, the unique metal–support interaction formed by MXene materials constitutes enriched active sites that allow for a wide range of modulation of catalytic activity and selectivity. For example, Wu and co–workers first reported the non–oxide–based reactive metal–interaction effect (RMSI) between platinum and Nb2CTx (Pt/Nb2CTx) (Figure 6) [80]. The formation of Pt-Nb alloying, verified by electron energy–loss spectroscopy (EELS) and in situ X–ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), promoted dissociation of H2O and desorption of H2, resulting in outstanding WGS catalytic performance.
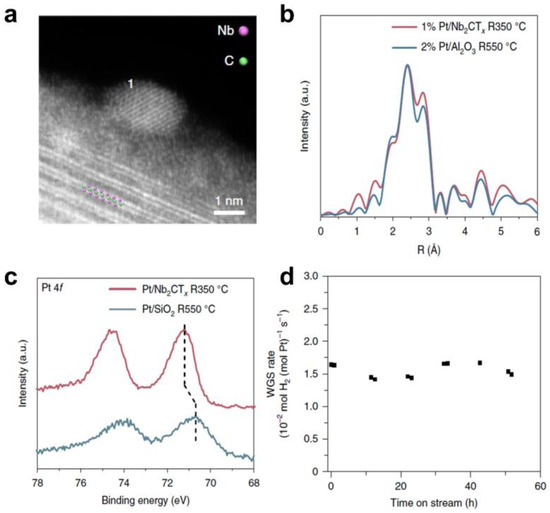
Figure 6.
The reactive metal–support interaction of MXene–based catalysts. (a) HAADF–STEM images of typical nanoparticles supported by Nb2CTx MXene. The majority of each particle is hanging over the vacuum to avoid niobium interference from the support; (b) Fourier transform magnitude of the k2–EXAFS of the 2% Pt/Al2O3 sample treated at 550 °C and fresh 1% Pt/Nb2CTx treated at 350 °C in 3% H2/He; (c) Quasi in situ XPS spectra of platinum 4f of Pt/SiO2 reduced at 550 °C and 1% Pt/Nb2CTx reduced at 350 °C; (d) WGS rates normalized by the amount of platinum in the 1% Pt/Nb2CTx catalyst. The rates were measured at 300 °C. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [80]. 2018 Springer Nature).
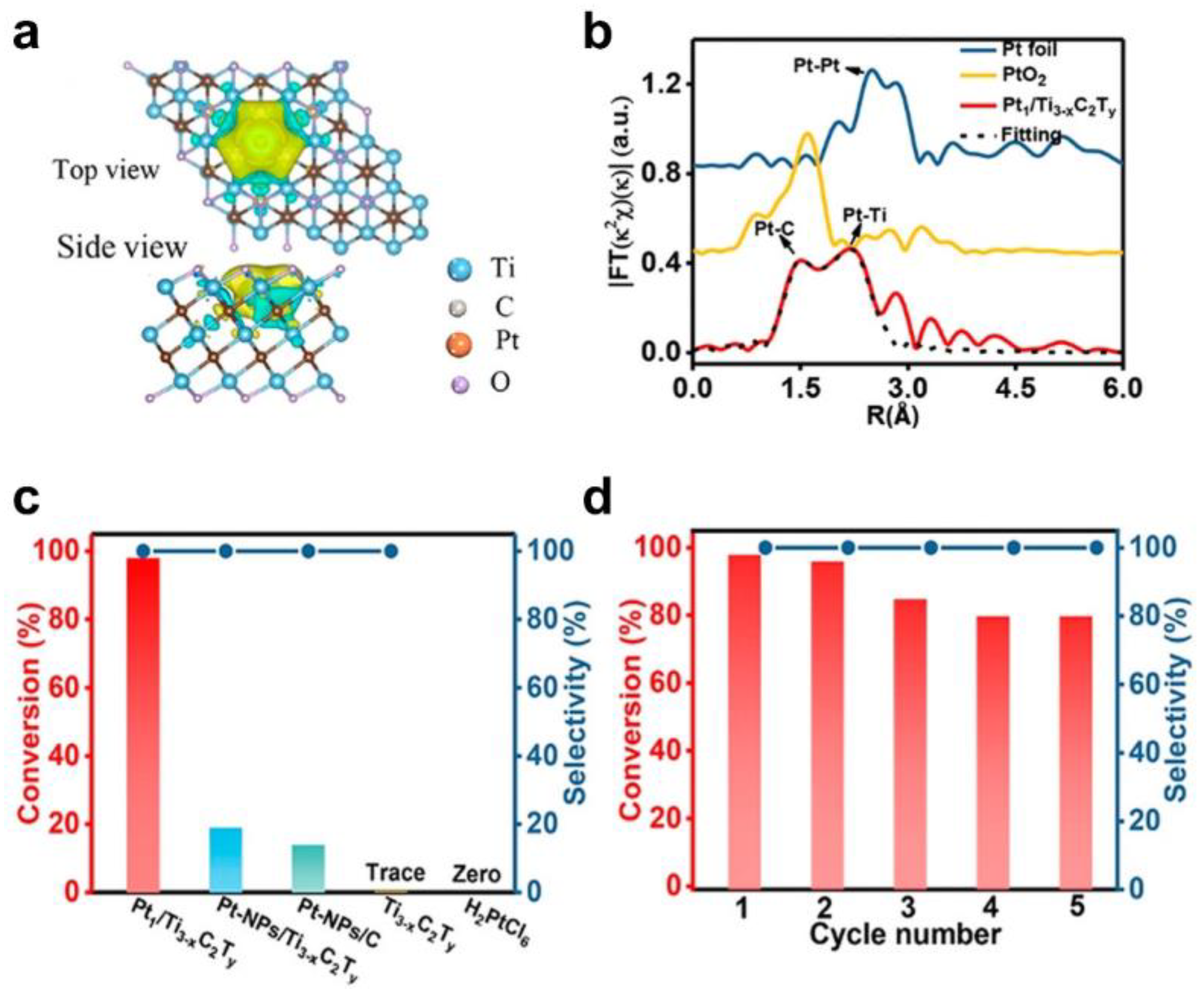
Zhao et al. reported the preparation of single–atom catalysts by self–reduction stabilization process using Ti3-xC2Ty MXene materials (Figure 7) [81]. Abundant Ti vacancies on Ti3-xC2Ty are provided to anchor Pt single atoms. The special coordination environment of Pt-C was then formed in situ. Combined with extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), X–ray diffraction (XRD), X–ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS), and DFT calculations, the single Pt atoms featuring the strong metal–carbon binding (Pt–C) exhibited partial positive charges, which helped to decrease the adsorption energy and activation energy of reactants.
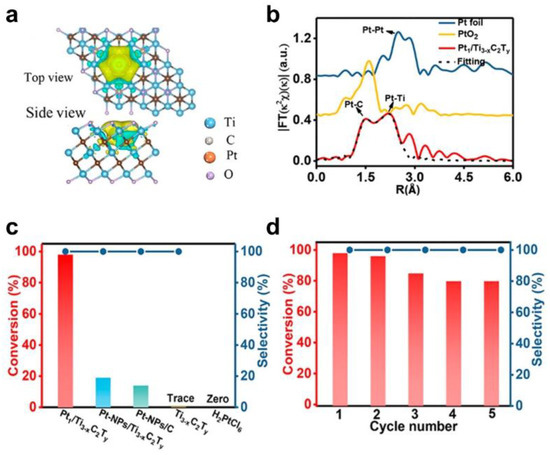
Figure 7.
Identification of active sites and catalytic performance of MXene–based catalysts. (a) Charge density difference of Pt1/Ti3−xC2Ty with a plain view (upper image) and a side–on view (lower image); (b) EXAFS FT k2–weighted χ(k) function spectra of Pt1/Ti3−xC2Ty and a reference; (c) Catalytic performance of the N–formylation of aniline using different catalysts; (d) Recycling test of Pt1/Ti3−xC2Ty for the catalytic N–formylation of aniline. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [81]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society).
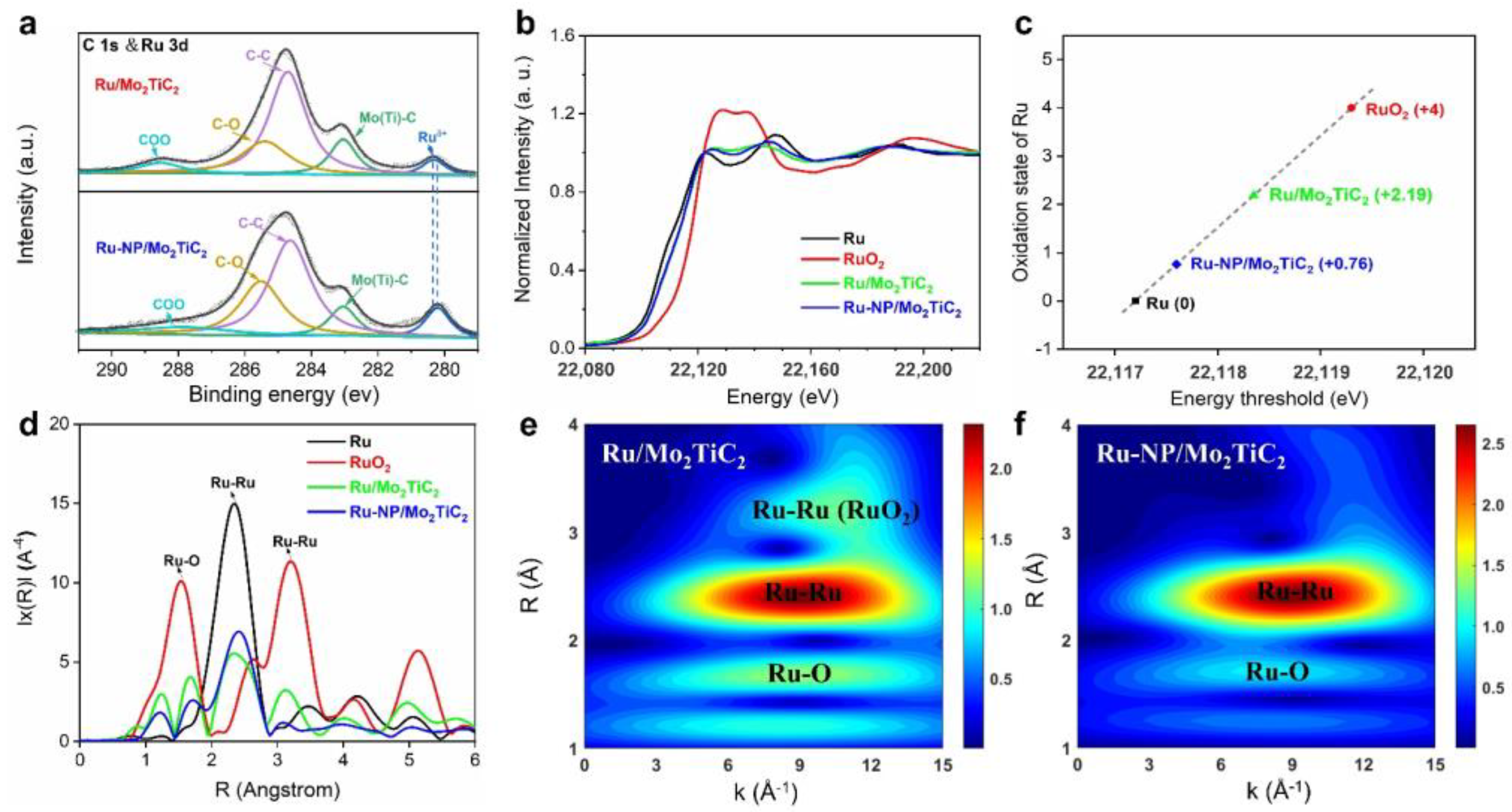
Additionally, our group reported the preparation of Mo2TiC2 MXene–supported Ru clusters (Ru/Mo2TiC2) with pronounced broadband sunlight absorption ability and high sintering resistance. Under the illumination of focused sunlight, Ru/Mo2TiC2 can catalyze the reverse water–gas shift (RWGS) reaction to produce carbon monoxide with enhanced activity, selectivity, and stability [82]. As shown in Figure 8, XPS and XAS analysis of Ru/Mo2TiC2 demonstrated that the oxidation state of Ru is higher than conventional Ru/SiO2 catalysts, which provides a stable interface of Ru/RuOx/MoOx/Mo2TiC2 between MXene materials and Ru clusters.
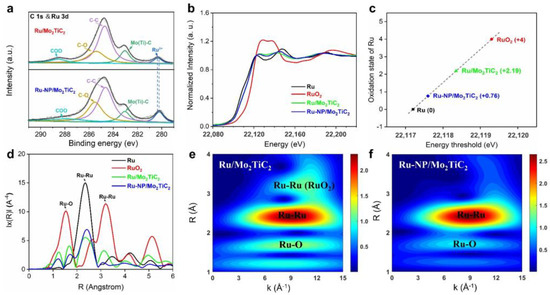
Figure 8.
Chemical state analysis of the Ru/Mo2TiC2 catalysts. (a) C 1s and Ru 3d core–level XPS spectra of Ru/Mo2TiC2 and Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2. Ru/Mo2TiC2 exhibited a higher Ru oxidation state than Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2; (b) Normalized XANES spectra at the Ru K–edge of Ru, RuO2, Ru/Mo2TiC2, and Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2; (c) Oxidation states of Ru for reference and synthesized materials as determined from the edge positions in the Ru K–edge XANES spectra; (d) Corresponding FT–EXAFS spectra derived from the Ru K–edge of Ru, RuO2, Ru/Mo2TiC2 and Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2; (e,f) Wavelet transformation for the Ru K–edge EXAFS signals of Ru/Mo2TiC2 and Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [82], Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society).
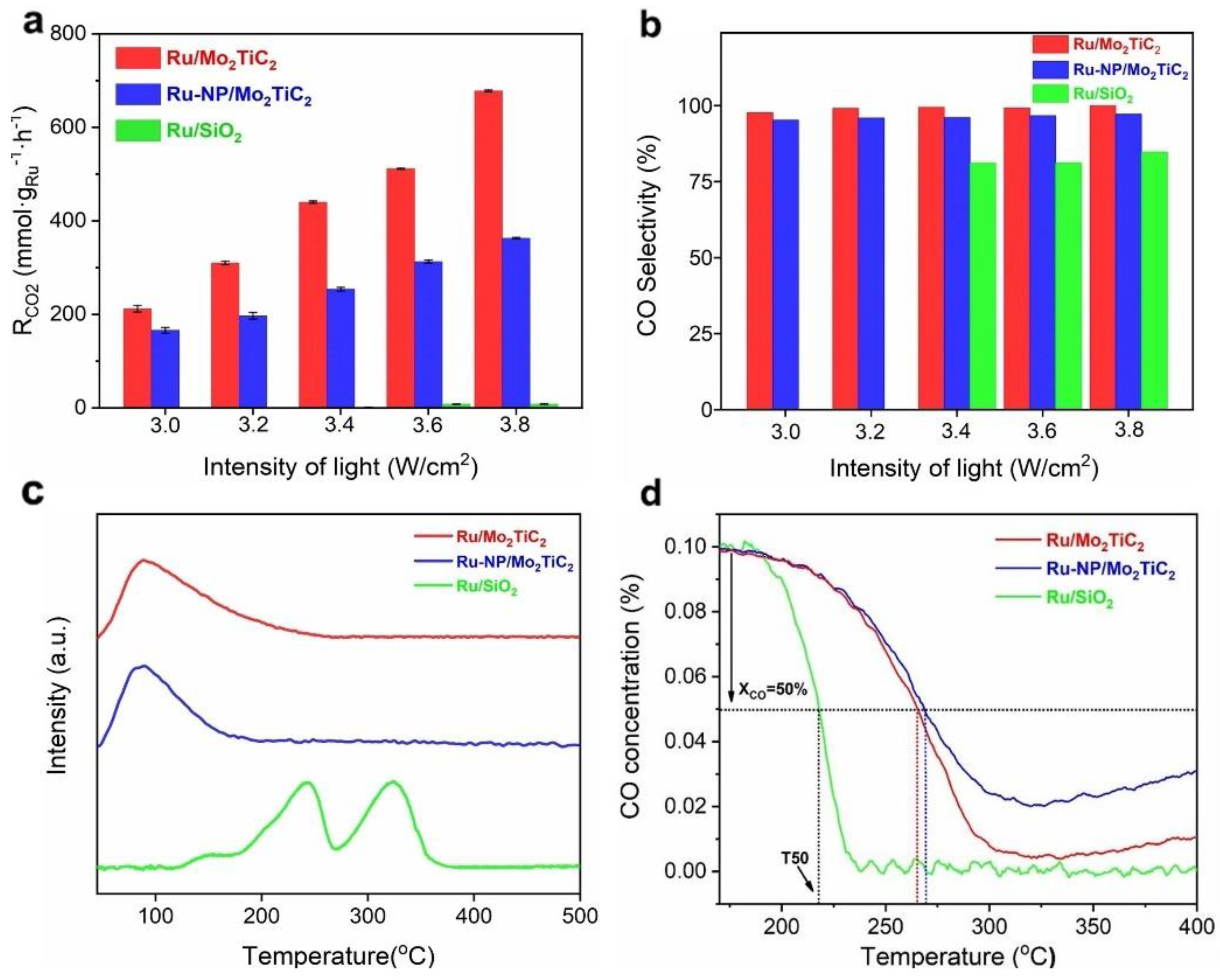
MXene–supported Ru clusters with a higher oxidation state of Ru exhibited a slightly lower activation temperature and thus a stronger ability for H2–assisted CO dissociation than Ru nanoparticles, while CO temperature–programmed desorption experiments suggested that CO desorption from Ru/Mo2TiC2 occurs at a lower temperature than from Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2. Thus, the special metal–support interaction of MXene–supported Ru cluster catalysts is favorable for the minor dissociation of H2 and kinetic desorption of CO, leading to the near–unity CO selectivity (Figure 9). Our research indicates that MXenes can not only stabilize the active metal center but also serve as superior photothermal supports for photothermal catalysis [82]. The rational construction of MXene–based photothermal catalysts is expected to reduce the energy consumption of the reaction and thus achieve better conversion efficiency under milder conditions.
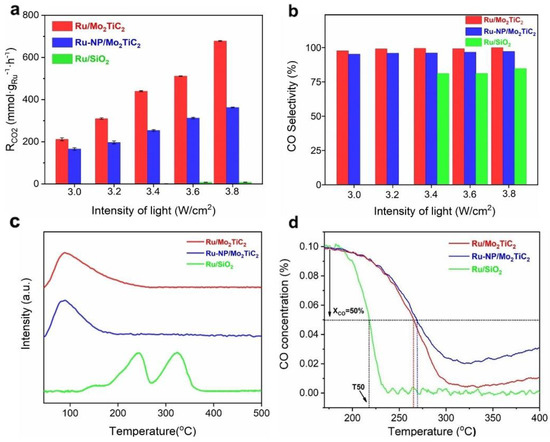
Figure 9.
Photothermal catalytic performance and reaction mechanism of Ru/Mo2TiC2. (a,b) Photothermal catalytic activity and CO selectivity of Ru/Mo2TiC2, Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2, and Ru/SiO2 under different illumination conditions; (c) H2–TPD profiles of Ru/Mo2TiC2, Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2 and Ru/SiO2 catalysts; (d) CO signal of H2–assisted CO hydrogenation TPSR for Ru/Mo2TiC2, Ru–NP/Mo2TiC2 and Ru/SiO2 catalysts. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [82], Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society).
Unfortunately, the current works on MXene have only focused on thermal effects in photothermal catalysis. Although some researchers have found that MXene catalysts can significantly enhance catalytic activity through the LSPR effect, the principles of the light response mechanism in MXene–based catalysts are still in their infancy. In–depth understanding of the specific light response mechanisms in MXene is also likely to provide new possibilities for synergistic photochemistry–thermochemistry-driven catalysis [83]. The development of synergistic catalytic pathways can prove beneficial for further improving the catalytic performance as well as reaction onset conditions, which may still appear rigorous. The realization of synergistic photothermal catalysis, though, is challenged by a few additional factors, such as difficulties in deconvoluting the reaction mechanisms of photochemistry, the identification of the dominant contribution of light and heat, and the accurate measurement of nanoscale local temperature of catalysts. Subsequent research could also be performed on how light is involved in the reaction and the charge transport on the MXene surface by various kinds of in situ characterization techniques, as is elaborated in Section 3.
3. Summary and Outlook
As discussed in previous sections, MXenes have exhibited preliminary potentials in all three required fields for a desirable photothermal catalyst: light absorption and photothermal conversion, heat management, and surface reactivity. For the light absorption and photothermal conversion process, MXene materials with narrow band gaps exhibited excellent LSPR properties, which accounted for enhanced light absorption capability and light–to–heat conversion properties. For the heat management process, it is the special interlayer structure, excellent electromagnetic wave shielding properties, and low mid–infrared emissivity of MXene materials that contributed to optimizing the heat management process. For surface reactivity, the unique metal–support interaction between MXene materials and the active metal helps to improve the dispersion and stability of the catalyst and promote the surface reaction process. Corresponding representative works for each requirement have also been elaborated.
In order to compare the effect of distinct MXene–based photocatalytic systems, we have summarized the catalyst composition, reaction conditions, and catalytic performance of some reported systems (Table 1). A few works have attempted to exploit MXenes for photochemical or photothermal HER, N2 fixation, and CO2 reduction reactions. Decent catalytic performance has been recorded for distinct types of reactions, particularly for Ni and Ru–loaded MXene photothermal catalysts towards CO2 hydrogenation, as elaborated in Section 2.3.

Table 1.
Summary of the MXene–based materials in photocatalytic/photothermal catalysis.
Despite current achievements, in order for MXenes to meet the requirements of large-scale catalytic applications and achieve comparable reactivity to conventional thermal catalysis, improvements still await for all three aspects of photothermal catalysis, and there is still plenty of room to explore for MXene–based photothermal catalysts. Firstly, in order to further enhance the conversion efficiency of MXene in photothermal catalysis, it is of primary importance to further improve the light absorption properties. Considering that the superior light absorption performance of MXene is due to the LSPR effect on its surface, the design and modification of the MXene surface in combination with the plasmonic antenna-reactor (AR) catalytic systems implemented by Halas et al. or with some other super-structured catalysts with excellent light absorption performance, is expected to produce a next-generation plasmonic catalyst to further enhance its light absorption performance [8]. However, this relies on the acquisition of a deeper understanding of the fundamental properties of MXene LSPR, such as its origin, enhancement mechanisms, modulation strategies, etc., in order to harvest it for both enhancements of optical cross–sections and catalytic pathways. As mentioned earlier, another crucial challenge for MXenes is that the LSPR intensity as well as enhancement factors of the optical cross–sections of MXenes are relatively low compared to conventional plasmonic metals, which impedes their specific applications in photothermal catalysis. Future research could focus on the effective tuning of free carrier concentration as well as carrier mobility, for instance, through defect engineering, to enhance the charge carrier collective oscillation amplitude, and thus the LSPR effect of MXene materials. Additionally, it is also of great significance to obtain in-depth understandings of the construction of MXene–based photothermal catalysts.
Secondly, in order to further augment the heat management performance of MXenes in photothermal catalysis, confinement of in-layer heat conduction could be a prominent strategy. As introduced in Section 2.2, interlayer heat conduction is well–confined based on the 2D lamellar structure and EMI shielding effect, which makes in–layer heat conduction a non–negligible source of heat losses. It is possible that through the optimization of surface defect engineering and the design of a more electromagnetic interlayer absorbing high–entropy MXene is expected to be a proven method to further reduce the thermal conductivity within the layers. Further, thermal management can be optimized in terms of structural design. The further increase in the fate of photogenerated carriers (or hot electrons) through photochemical effects may also reduce the activation energy of the reaction, thus allowing the reaction to proceed under milder conditions. Combining the above three points, a thorough study of the structure–function conformational relationship of MXene will allow further improvement of the MXene catalyst into a better photothermal catalyst in all aspects.
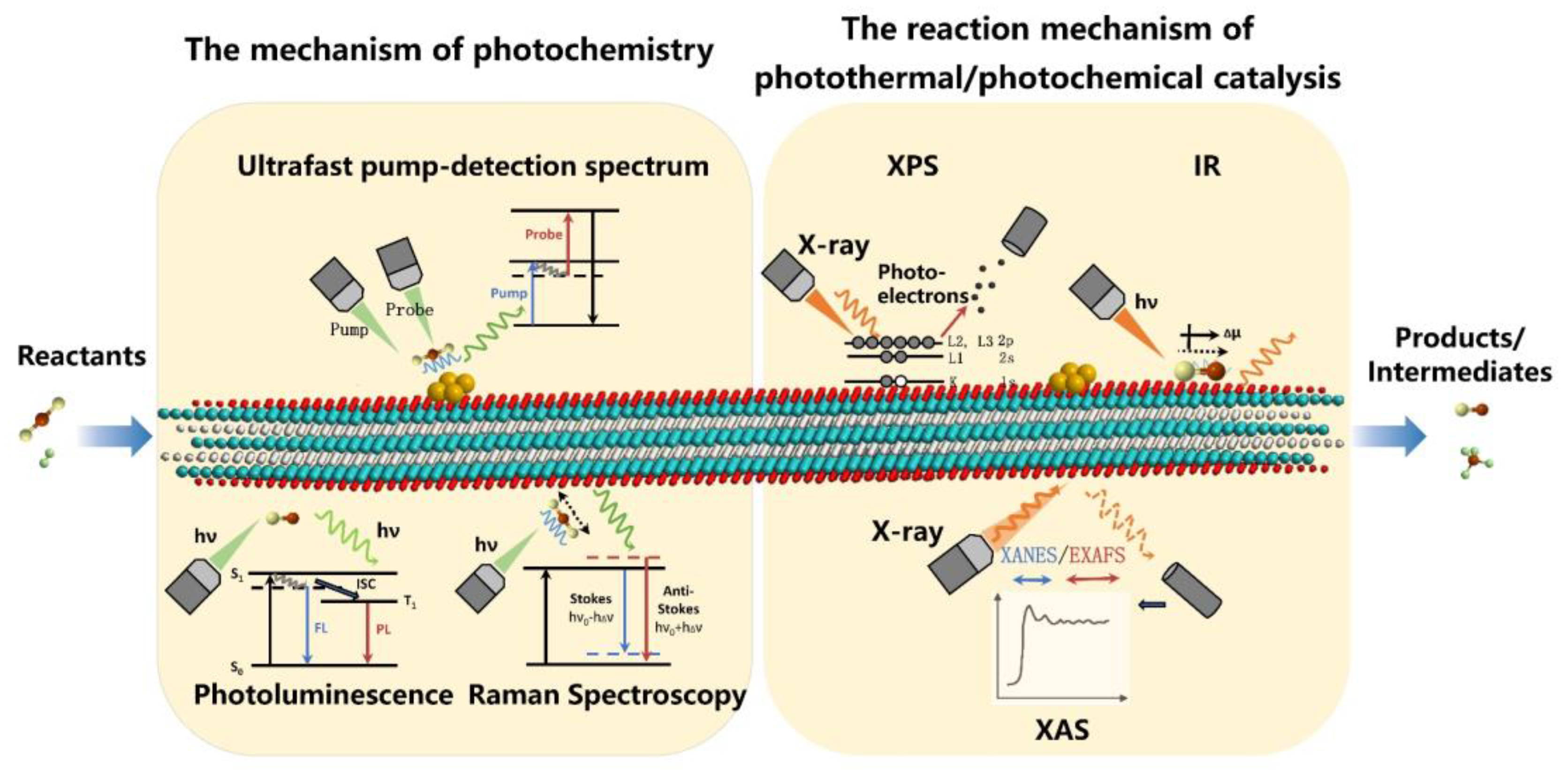
Thirdly, one fundamental issue in catalysis remains the understanding of the kinetic behavior of intermediates in the reaction process and thus the design of efficient catalysts from the most fundamental electronic structures. However, MXene–based catalysts are unable to reflect their original properties under catalytic conditions in many characterizations due to their active surface groups and their high oxyphilicity. At the same time, excellent light absorption and electromagnetic shielding limit its optical characterizations. This represents yet another important challenge for studies of MXenes in photothermal catalysis. As a possible solution, in situ or operando characterization techniques could prove extremely useful [93] (Figure 10). In situ X–ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X–ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) can accurately indicate the electron transfer and structural changes of MXene under catalytic conditions. Taking Diffuse Reflaxions Infrared Fourier Transformations Spectroscopy (DRIFTS) as an example, the excellent IR light absorption of MXene makes it difficult to collect signals from adsorbed intermediates on the surface under in situ catalytic reactions. Thus, the combination of various characterization tools and novel techniques is therefore crucial in the characterization of MXene and the structure-activity relationships of MXene–based photothermal catalysts.
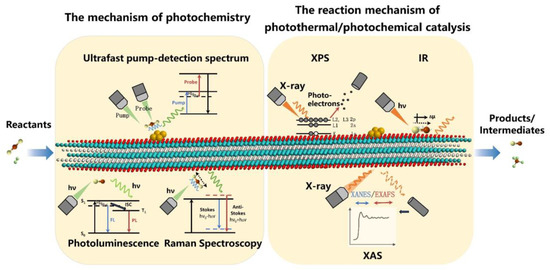
Figure 10.
In situ characterization techniques of MXene–based photothermal catalysts.
Furthermore, optimizing the cost efficiency of MXene–based catalysts is essential for their provisional large–scale applications, particularly in industrial catalysis. For more practical catalytic reactions, higher catalytic benefits depend on the cost of producing the catalyst. Therefore, despite the initial exploration by Gogotsi and co–workers, the large-scale industrial production of MXene still needs to be improved. Under a broader context, precise regulation of the intraband or interband transitions to achieve efficient use of sunlight from the perspective of electronic structures is not only applicable to MXenes but also be further extended to other kinds of ideal photothermal catalysts. In combination with the latest photothermal reactor designs, photothermal catalysis is expected to hold great prospects for further industrialization.
In summary, this review describes the functionality of MXenes in photothermal catalysis by considering the three processes of photothermal catalysis in relation to specific applications. It is possible to combine all three aspects to form a highly efficient photothermal catalyst with excellent performance compared to other photothermal catalysts. At the same time, this review offers constructive ideas and suggestions for the respective process of photothermal catalysis, which are expected to further improve the characterization and commercialization of MXene–based catalysts. Our insights into the construction principles of photothermal catalysts can be further extended to other kinds of photothermal catalytic materials, enabling the commercialization of photothermal catalysis.
Author Contributions
Z.W. and J.S. contributed equally to this work. Z.W., J.S., C.W., C.Z. and Z.L. wrote and edited the manuscript. C.L., X.A. and L.H. made comprehensive revision and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52172221, 51920105005, 52272229), the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFF0502000), the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX20220222), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M702388), Jiangsu Funding Program for Excellent Postdoctoral Talent (2022ZB564), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20200101), Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials and Devices (ZZ2103), Suzhou Key Laboratory of Functional Nano & Soft Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science & Technology, the 111 Project, Soochow University-Western University Centre for Synchrotron Radiation Research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cai, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Tountas, A.A.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Feng, K.; Xu, A.-B.; et al. Greenhouse-inspired Supra-photothermal CO2 Catalysis. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Yan, T.; Hu, Z.; Jelle, A.A.; Meira, D.M.; Duchesne, P.N.; Loh, J.Y.Y.; Qiu, C.; Storey, E.E.; et al. Black Indium Oxide a Photothermal CO2 Hydrogenation Catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Chen, G.; Shi, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, Y.; Wen, X.D.; et al. Co-based Catalysts Derived from Layered-double-hydroxide Nanosheets for the Photothermal Production of Light Olefins. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1800527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wen, X.D.; Zhang, T. Titania-supported Ni2P/Ni Catalysts for Selective Solar-driven CO Hydrogenation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2103248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linic, S.; Christopher, P.; Ingram, D.B. Plasmonic-metal Nanostructures for Efficient Conversion of Solar to Chemical Energy. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Xu, H.; Qi, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ouyang, S.; Ye, J. Microstructure Induced Thermodynamic and Kinetic Modulation to Enhance CO2 Photothermal Reduction: A Case of Atomic-scale Dispersed Co–N Species Anchored Co@C Hybrid. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 4726–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Shi, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Shang, L.; Sheng, G.; et al. Alumina-supported CoFe Alloy Catalysts Derived from Layered-double-hydroxide Nanosheets for Efficient Photothermal CO2 Hydrogenation to Hydrocarbons. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Martirez, J.M.P.; Finzel, J.; Zhang, C.; Swearer, D.F.; Tian, S.; Robatjazi, H.; Lou, M.; Dong, L.; Henderson, L.; et al. Light-driven Methane Dry Reforming with Single Atomic Site Antenna-reactor Plasmonic Photocatalysts. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.G.; Sandhel, A.; Wood, T.E.; Jelle, A.A.; Hoch, L.B.; Perovic, D.D.; Mims, C.A.; Ozin, G.A. Photomethanation of Gaseous CO2 over Ru/Silicon Nanowire Catalysts with Visible and Near-infrared Photons. Adv. Sci. 2014, 1, 1400001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, L.B.; O’Brien, P.G.; Jelle, A.; Sandhel, A.; Perovic, D.D.; Mims, C.A.; Ozin, G.A. Nanostructured Indium Oxide Coated Silicon Nanowire Arrays: A Hybrid Photothermal/photochemical Approach to Solar Fuels. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9017–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; O’Brien, P.G.; He, L.; Qiao, Q.; Fei, T.; Reyes, L.M.; Burrow, T.E.; Dong, Y.; Liao, K.; Varela, M.; et al. Visible and Near-infrared Photothermal Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Gaseous CO2 over Nanostructured Pd@Nb2O5. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1600189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wong, R.J.; Tan, T.H.; Higham, M.; Gibson, E.K.; Decarolis, D.; Callison, J.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F.; Bowker, M.; Catlow, C.R.A.; et al. Synergistic Ultraviolet and Visible Light Photo-activation Enables Intensified Low-temperature Methanol Synthesis over Copper/zinc oxide/alumina. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, D.; Cerrillo, J.L.; Durini, S.; Gascon, J. Fundamentals and Applications of Photo-thermal Catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 50, 2173–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, U.; Rao, V.G.; Chavez, S.; Linic, S. Catalytic Conversion of Solar to Chemical Energy on Plasmonic Metal Nanostructures. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Song, L.; Jia, G.; Huang, H.; Ouyang, S.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Zou, Z. Cooperative Catalysis Coupling Photo-/photothermal Effect to Drive Sabatier Reaction with Unprecedented Conversion and Selectivity. Joule 2021, 5, 3235–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. 3D Self-assembly of Aluminium Nanoparticles for Plasmon-enhanced Solar Desalination. Nat. Photon. 2016, 10, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gao, M.; Peh, C.K.N.; Ho, G.W. Solar-driven Photothermal Nanostructured Materials Designs and Prerequisites for Evaporation and Catalysis Applications. Mater. Horiz. 2018, 5, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Xu, C.; Deng, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Photothermal Chemistry Based on Solar Energy: From Synergistic Effects to Practical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, S.; Li, P.; Hu, H.; Kako, T.; Iwai, H.; Tanaka, A.; Ye, J. Photothermal Conversion of CO2 into CH4 with H2 over Group VIII Nanocatalysts: An Alternative Approach for Solar Fuel Production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11478–11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, N.; Ye, J. Nanometals for Solar-to-chemical Energy Conversion: From Semiconductor-based Photocatalysis to Plasmon-mediated Photocatalysis and Photo-thermocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6781–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoussoub, M.; Xia, M.; Duchesne, P.N.; Segal, D.; Ozin, G. Principles of Photothermal Gas-phase Heterogeneous CO2 Catalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1122–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, S.; Williams, G.R.; Mahadi, A.H.; Ma, D. Solar-versus Thermal-driven Catalysis for Energy Conversion. Joule 2019, 3, 920–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tang, R.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chu, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yin, K.; He, L.; et al. Integrated Photothermal Nanoreactors for Efficient Hydrogenation of CO2. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2022, 28, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Tang, R.; Shen, J.; Chu, M.; Xu, A.B.; Zhang, B.; He, L.; Zhang, X. Rationally Designed Nanoarray Catalysts for Boosted Photothermal CO2 Hydrogenation. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11568–11574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.-J.; Li, C.-R.; He, L. Enhancing Photothermal CO2 Catalysis by Thermal Insulating Substrates. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L. Fe3Si Assisted Co3O4 Nanorods: A Case Study of Photothermal Catalytic CO Oxidation under Ambient Solar Irradiation. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Feng, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; Cai, M.; et al. Cobalt Plasmonic Superstructures Enable almost 100% Broadband Photon Efficient CO2 Photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2000014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Han, B.; Li, Z.; Fang, Y.; Feng, K.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, A.-B.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Ruthenium Nanoparticles Supported on Mg(OH)2 Microflowers as Catalysts for Photothermal Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, F.; Alhabeb, M.; Hatter, C.B.; Anasori, B.; Man Hong, S.; Koo, C.M.; Gogotsi, Y. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with 2D Transition Metal Carbides (MXenes). Science 2016, 353, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.L.; Zhang, X.T.; Abdolhosseinzadeh, S.; Sheng, H.W.; Lan, W.; Pakdel, A.; Heier, J.; Nuesch, F. Two-dimensional Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides (MXenes): Synthesis, Properties, and Electrochemical Energy Storage Applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2020, 3, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Mochalin, V.N.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. 25th Anniversary Article: MXenes: A New Family of Two-dimensional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukatskaya, M.R.; Mashtalir, O.; Ren, C.E.; Dall’Agnese, Y.; Rozier, P.; Taberna, P.L.; Naguib, M.; Simon, P.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Cation Intercalation and High Volumetric Capacitance of Two-dimensional Titanium Carbide. Science 2013, 341, 1502–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Anasori, B. The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8491–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafie, N.; Zulfiqar, M.; Samsudin, M.F.R.; Sufian, S. Current Scenario of MXene-based Nanomaterials for Wastewater Remediation: A Review. Chemistry 2022, 4, 1576–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Liang, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. 2D Carbide MXene Ti2CTX as a Novel High-performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Material. Carbon 2019, 146, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Genest, A.; Rupprechter, G.; He, L. Emerging Applications of MXene Materials in CO2 Photocatalysis. FlatChem 2021, 28, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, R.; Chang, W.; Zhang, L.; Peng, B.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Yan, M.; Guo, C. Ti3C2 MXene as an Excellent Anode Material for High-performance Microbial Fuel Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 20887–20895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Gu, J.; Du, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, S. Single-Atom Sites on MXenes for Energy Conversion and Storage. Small Sci. 2021, 1, 2100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Qu, J.; Lai, C. Ti3C2Tx MXene Interface Layer Driving Ultra-Stable Lithium-Iodine Batteries with Both High Iodine Content and Mass Loading. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-T.; Kan, X.; Yang, F.; Gan, L.-Y.; Schwingenschlögl, U. MXene/Graphene Heterostructures as High-Performance Electrodes for Li-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32867–32873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Gao, S.; Dai, C.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. A Two-Dimensional Biodegradable Niobium Carbide (MXene) for Photothermal Tumor Eradication in NIR-I and NIR-II Biowindows. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16235–16247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Lin, H.; Xu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y. Biocompatible 2D Titanium Carbide (MXenes) Composite Nanosheets for pH-Responsive MRI-Guided Tumor Hyperthermia. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 8637–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Topographic Design in Wearable MXene Sensors with in-sensor machine Learning for Full-body Avatar Reconstruction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5311–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ha, E.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, D.; Yue, G.; Hu, L.; Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Lee, L.Y.S.; et al. Recent Advance in MXenes: A Promising 2D Material for Catalysis, Sensor and Chemical Adsorption. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 352, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. 2D MXene-based Materials for Electrocatalysis. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2020, 26, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-Hui, Y.; Shao-Zheng, Z.; Jia-Lin, J.I.; Shi-Hao, W.E.I. Adsorption Activities of O, OH, F and Au on Two-dimensional Ti2C and Ti3C2 Surfaces. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Song, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. In2O3 Nanocubes/Ti3C2Tx MXene Composites for Enhanced Methanol Gas Sensing Properties at Room Temperature. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 23028–23037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, P. MXene Ti3C2: An Effective 2D Light-to-heat Conversion Material. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B. MXene Ti3C2Tx for Phase Change Composite with Superior Photothermal Storage Capability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 14319–14327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Insights into the Photothermal Conversion of 2D MXene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Mechanism, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Shuck, C.E.; Rakhmanov, R.; Parchment, D.; Anasori, B.; Koo, C.M.; Friedman, G.; Gogotsi, Y. Beyond Ti3C2Tx: MXenes for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5008–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei, M.; Arai, M.; Sasaki, T.; Ranjbar, A.; Liang, Y.; Yunoki, S. OH-terminated Two-dimensional Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides as Ultralow Work Function Materials. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 075411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimova, R.; Rinke, P.; Komsa, H.-P. Native Vacancy Defects in MXenes at Etching Conditions. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 2896–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.-L.; Wei, J.-X.; Liu, Y.; Zaman, F.U.; Rehman, W.; Hou, L.-R.; Yuan, C.-Z. V2CTx MXene and its Derivatives: Synthesis and Recent Progress in Electrochemical Energy Storage Applications. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamysbayev, V.; Filatov, A.S.; Hu, H.; Rui, X.; Lagunas, F.; Wang, D.; Klie, R.F.; Talapin, D.V. Covalent Surface Modifications and Superconductivity of Two-dimensional Metal Carbide MXenes. Science 2020, 369, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D Metal Carbides and Nitrides (MXenes) for Energy Storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16098–16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H. Two-dimensional Carbide/nitride (MXene) Materials in Thermal Catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 19444–19465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, H.; Lin, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Duployer, B.; Persson, P.O.Å.; Eklund, P.; Hultman, L.; Li, M.; et al. A General Lewis Acidic Etching Route for Preparing MXenes with Enhanced Electrochemical Performance in Non-aqueous Electrolyte. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Two-Dimensional Ultrathin MXene Ceramic Nanosheets for Photothermal Conversion. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Shahzad, F.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, J.; Hong, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Gogotsi, Y.; Koo, C.M. Anomalous Absorption of Electromagnetic Waves by 2D Transition Metal Carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene). Science 2020, 369, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Milligan, C.; Ma, T.; Zhou, L.; Cui, Y.; Qi, Z.; Libretto, N.; Xu, B.; Luo, J.; et al. Two-dimensional Transition Metal Carbides as Supports for Tuning the Chemistry of Catalytic Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5258–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, C.; Dong, C.-L.; Liu, R.-S.; Han, C.-P.; Li, Y.; Gogotsi, Y.; Wang, G. Single Platinum Atoms Immobilized on an MXene as an Efficient Catalyst for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, K.; Sarycheva, A.; Gogotsi, Y. Evaluation of Two-dimensional Transition-metal Carbides and Carbonitrides (MXenes) for SERS Substrates. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Shen, B.; Tong, T.; Fu, J.; Yu, J. 2D/2D Heterojunction of Ultrathin MXene/Bi2WO6 Nanosheets for Improved Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Hu, M.; Lian, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Su, D.S.; Liu, H. Ti3C2Tx MXene Catalyzed Ethylbenzene Dehydrogenation: Active Sites and Mechanism Exploration from both Experimental and Theoretical Aspects. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10051–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-García, Á.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Illas, F. MXenes: New Horizons in Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 13487–13503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, J.D.; Morales-García, Á.; Viñes, F.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Illas, F. Facile Heterogeneously Catalyzed Nitrogen Fixation by MXenes. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5049–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chai, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Lin, J.; Han, Y.; Li, L.; Qi, H.; Gu, Y.; Kang, L.; et al. Defect-Rich TiO2 in situ Evolved from MXene for the Enhanced Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethane to Ethylene. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 15223–15233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Erramilli, S.; Reinhard, B.M. Plasmonic Nano-antimicrobials: Properties, Mechanisms and Applications in Microbe Inactivation and Sensing. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3374–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffou, G.; Quidant, R. Thermo-plasmonics: Using Metallic Nanostructures as Nano-sources of Heat. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartland, G.V. Optical Studies of Dynamics in Noble Metal Nanostructures. Chem. Rev 2011, 111, 3858–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Feng, K.; Cai, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Chu, M.; Zhang, C.; Shen, J.; et al. Niobium and Titanium Carbides (MXenes) as Superior Photothermal Supports for CO2 Photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5696–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, P.; Xin, H.; Linic, S. Visible-light-enhanced Catalytic Oxidation Reactions on Plasmonic Silver Nanostructures. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Meng, X.; Qiu, J. Boosting the Electrocatalysis of MXenes by Plasmon-induced Thermalization and Hot-electron Injection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9416–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Kays, J.C.; Lightcap, I.V.; Ouyang, T.; Dennis, A.M.; Reinhard, B.M. Wavelength-dependent Bifunctional Plasmonic Photocatalysis in Au/chalcopyrite Hybrid Nanostructures. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6813–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Stelter, D.; Keyes, T.; Reinhard, B.M. Plasmonic Photocatalysis of Urea Oxidation and Visible-light Fuel Cells. Chem 2019, 5, 2228–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W. MXene Materials for Advanced Thermal Management and Thermal Energy Utilization. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, C.; Huang, H.; Peng, X.; Mei, D.; Li, M.; Liu, G.; Wu, M.; Zhao, T.; Huang, B. 2D Ti3C2Tx MXenes: Visible Black but Infrared White Materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2103054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cui, Y.; Wu, Z.; Milligan, C.; Zhou, L.; Mitchell, G.; Xu, B.; Shi, E.; Miller, J.T.; Ribeiro, F.H.; et al. Reactive Metal–support Interactions at Moderate Temperature in Two-dimensional Niobium-carbide-supported Platinum Catalysts. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Cheong, W.C.; Zheng, L.; Ren, F.; Ying, G.; et al. MXene (Ti3C2) Vacancy-confined Single-atom Catalyst for Efficient Functionalization of CO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4086–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Feng, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Meira, D.M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, D.; et al. Mo2TiC2 MXene-supported Ru Clusters for Efficient Photothermal Reverse Water-gas Shift. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, T.; Ho, G.W. Advances of Photothermal Chemistry in Photocatalysis, Thermocatalysis, and Synergetic Photothermocatalysis for Solar-to-fuel Generation. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9985–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zhao, C.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tian, L.; Xu, H.; Tang, H.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Yang, X. In Situ Fabrication of 1D CdS Nanorod/2D Ti3C2 MXene Nanosheet Schottky Heterojunction toward Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 268, 118382–118392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, L.; Guo, Y.; Liang, Z.; Cui, H.; Tian, J. Boosting the Photocatalytic Ability of g-C3N4 for Hydrogen Production by Ti3C2 MXene Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 41440–41447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Liao, Y.; Wu, Y.; An, Y.; Lin, J.; Gu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, X. RuO2-loaded TiO2–MXene as a High Performance Photocatalyst for Nitrogen Fixation. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 136, 109141–109146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Han, B.; Xie, Y.; Liang, S.; Deng, H.; Lin, Z. Ultrathin Co-Co LDHs Nanosheets Assembled Vertically on MXene: 3D Nanoarrays for Boosted Visible-light-driven CO2 Reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123519–123526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.; Zhang, L.; Tong, T.; Shen, B.; Yu, J. TiO2/MXene Ti3C2 Composite with Excellent Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Activity. J. Catal. 2018, 361, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Ma, X.; Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Jia, M.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wangyang, P.; He, L.; Liu, Y. CsPbBr3 Perovskite Nanocrystal Grown on MXene Nanosheets for Enhanced Photoelectric Detection and Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 6590–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, E.; Ye, J.; Wang, D. Boosting the Photocatalytic Activity of P25 for Carbon Dioxide Reduction by Using a Surface-Alkalinized Titanium Carbide MXene as Cocatalyst. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Deng, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Decorating g-C3N4 with Alkalinized Ti3C2 MXene for Promoted Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 564, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tan, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; Lv, K. 2D/2D Ti3C2 MXene/g-C3N4 Nanosheets Heterojunction for High Efficient CO2 Reduction Photocatalyst: Dual Effects of Urea. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 268, 118738–118746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, E.; Grzeschik, R.; Maier, S.A.; Schlücker, S. Experimental Characterization Techniques for Plasmon-assisted Chemistry. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).