Structural and Magnetic Analysis of a Family of Structurally Related Iron(III)-Oxo Clusters of Metal Nuclearity Fe8, Fe12Ca4, and Fe12La4 †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.1.1. (NHEt3)[Fe8O5(OH)5(O2PPh2)10] (1)
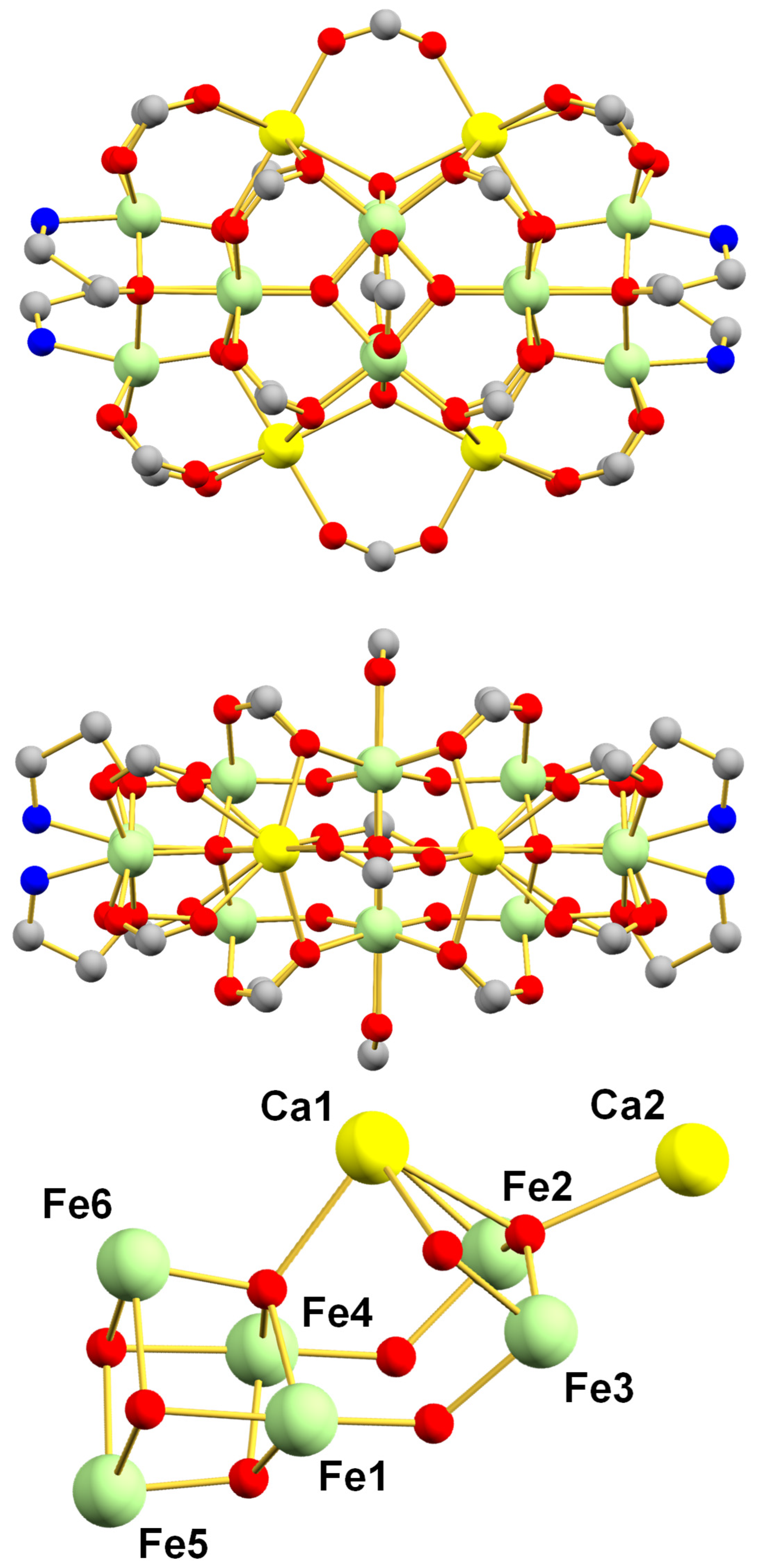
2.1.2. [Fe12Ca4O10(O2CPh)20(hmp)4] (2)
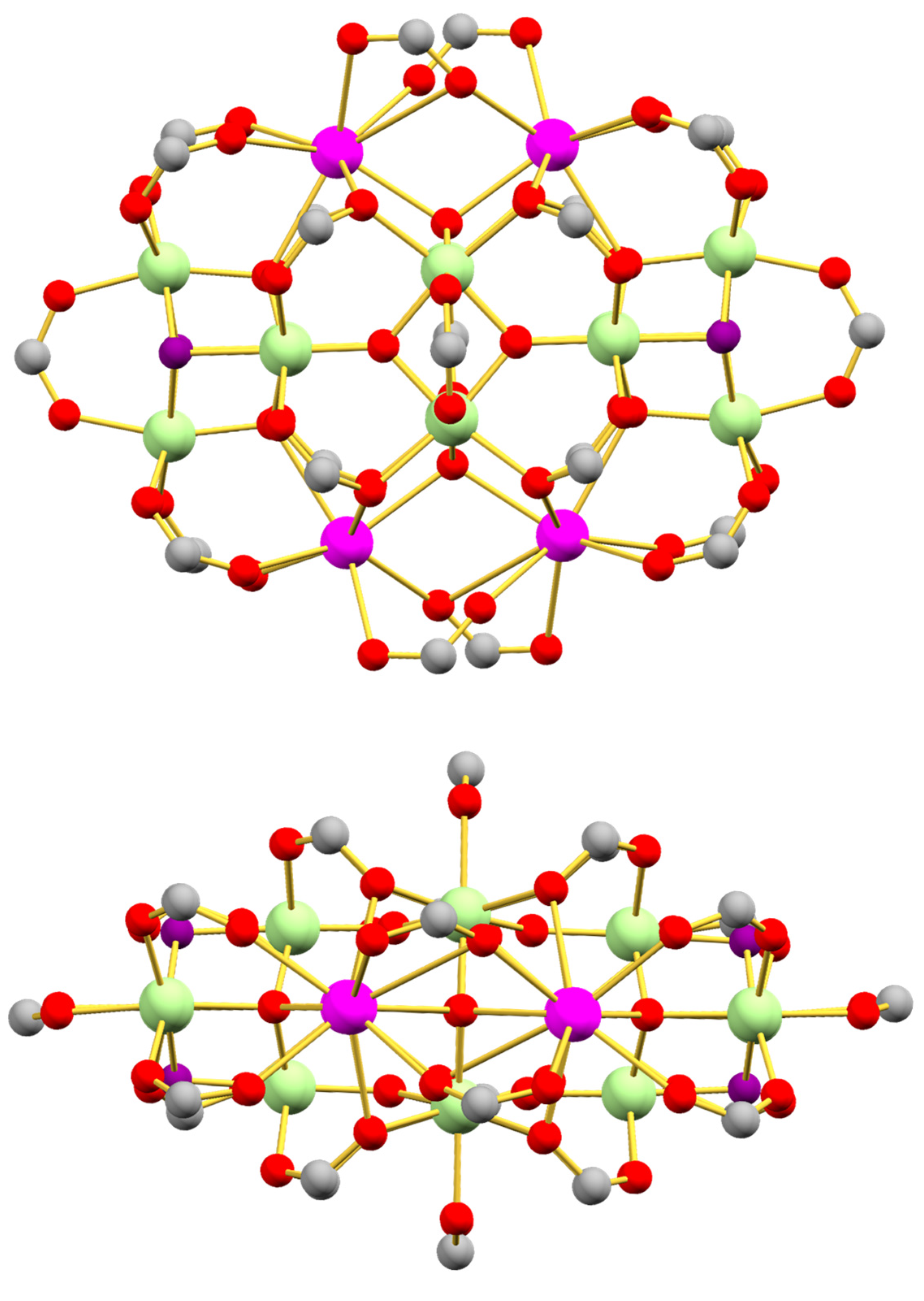
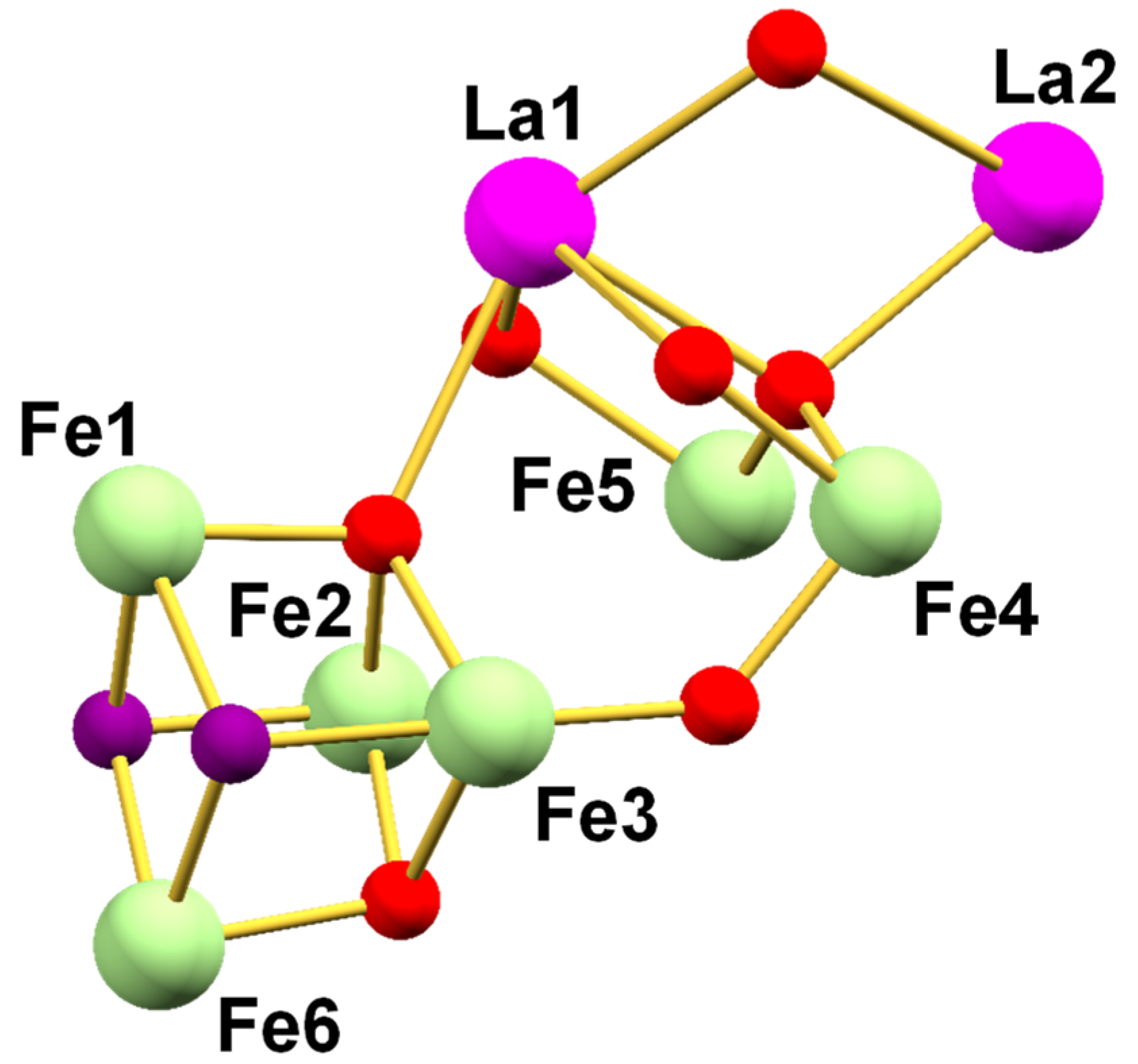
2.1.3. [Fe12La4O10(OH)4(tbb)24] (3)
2.2. X-ray Crystallography
2.3. Physical Measurements
2.4. Theoretical Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
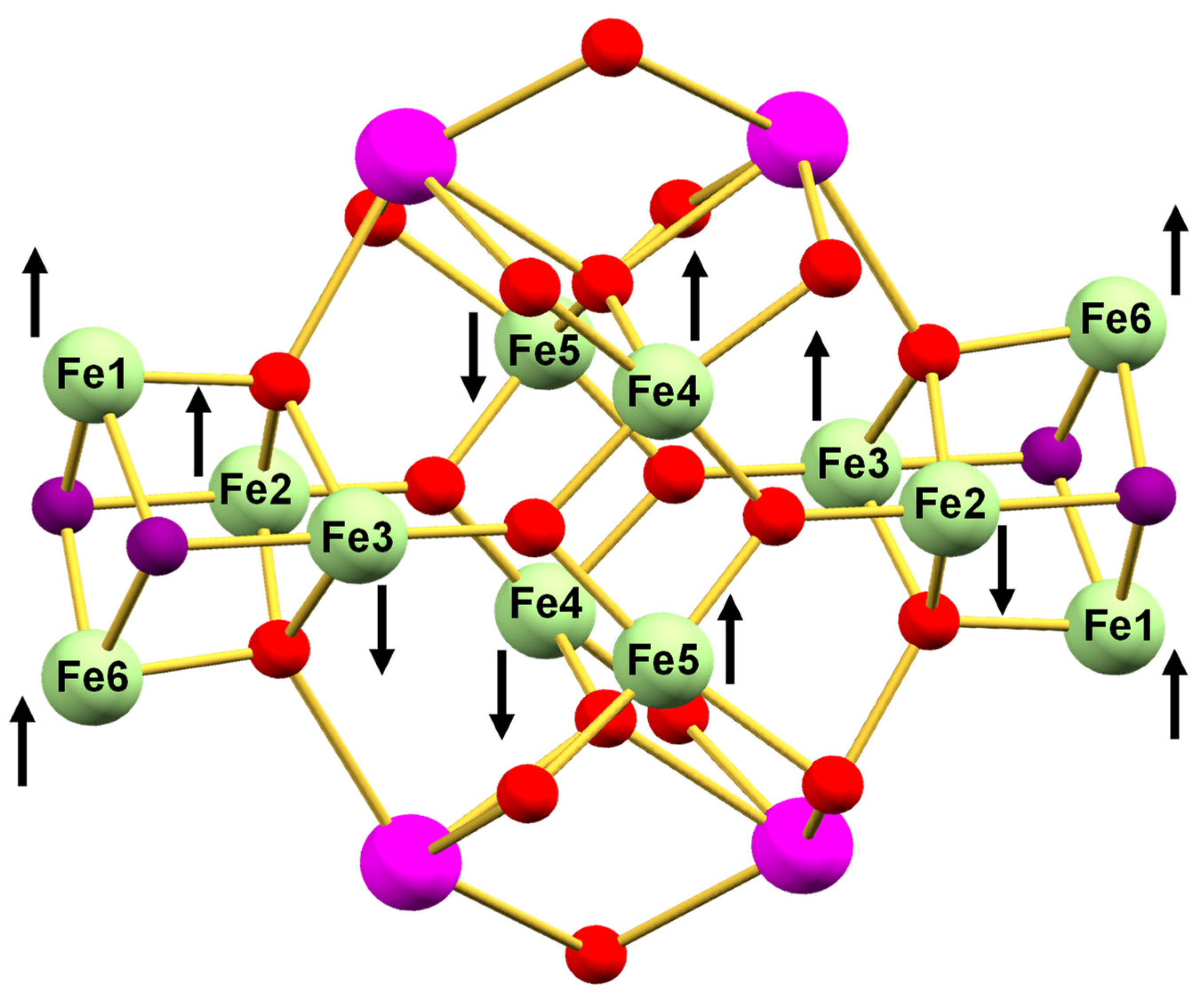
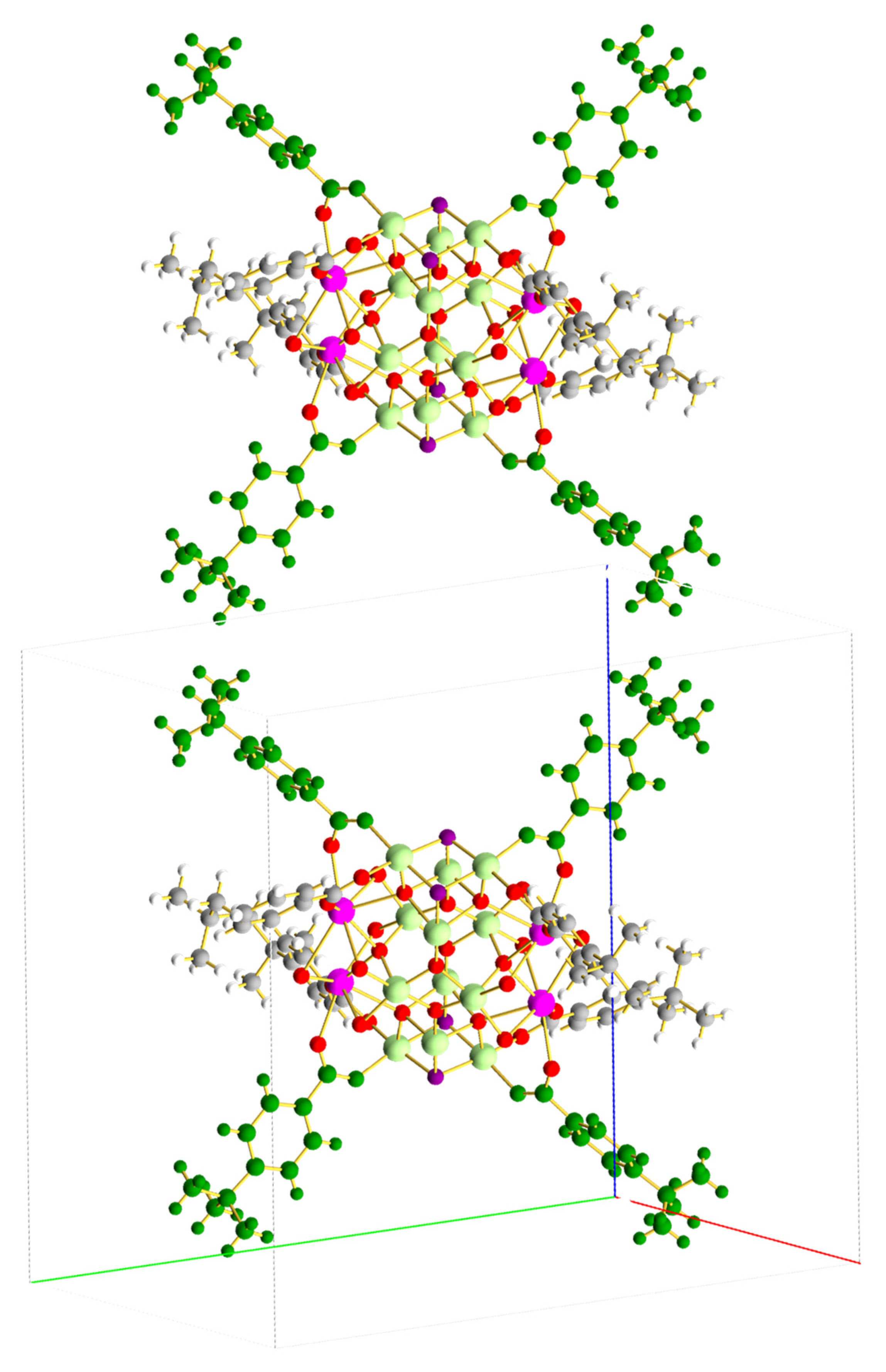
3.2. Description of Structures
3.3. SQUID Magnetometry
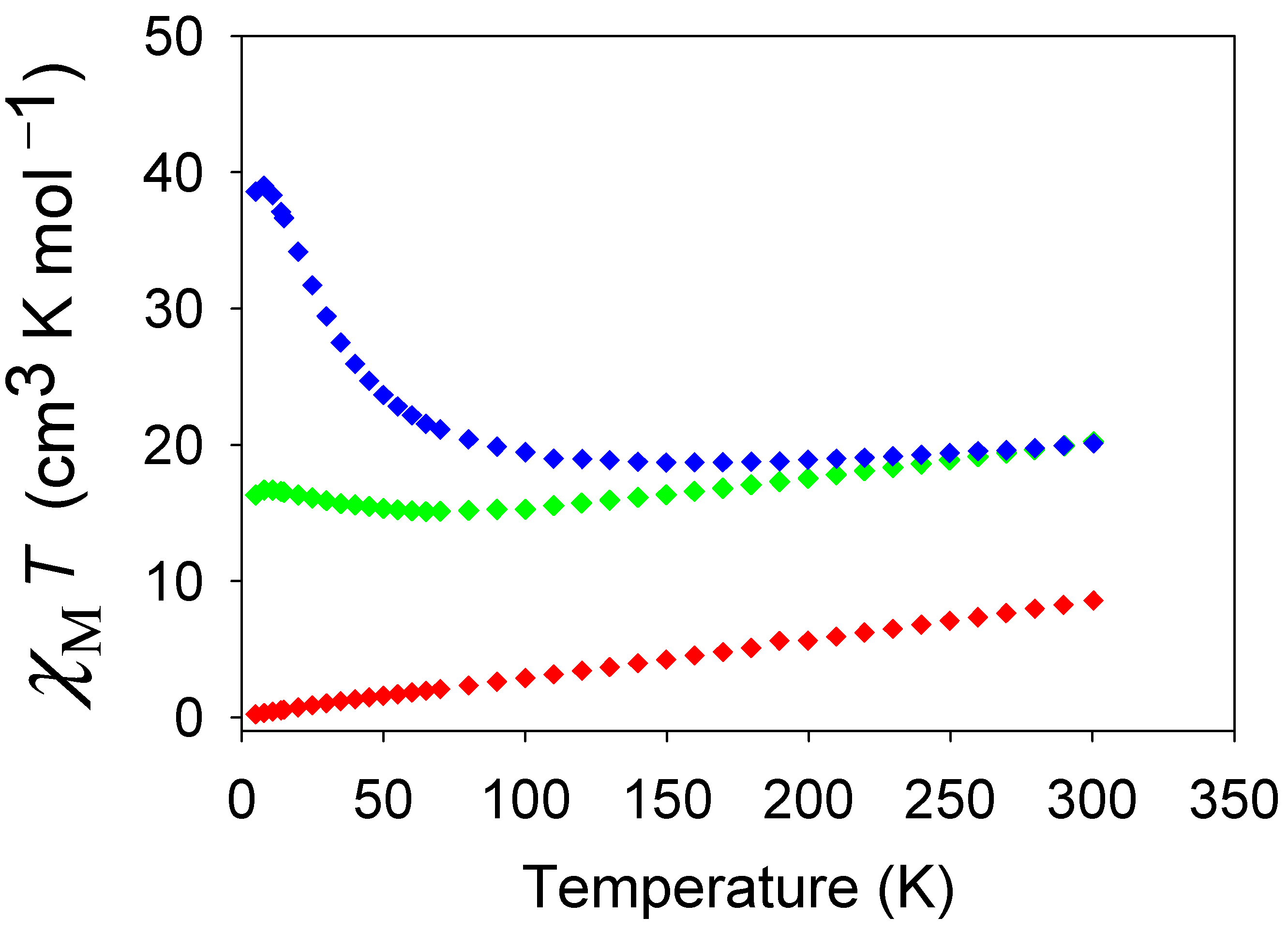
3.3.1. Dc Magnetic Susceptibility Studies
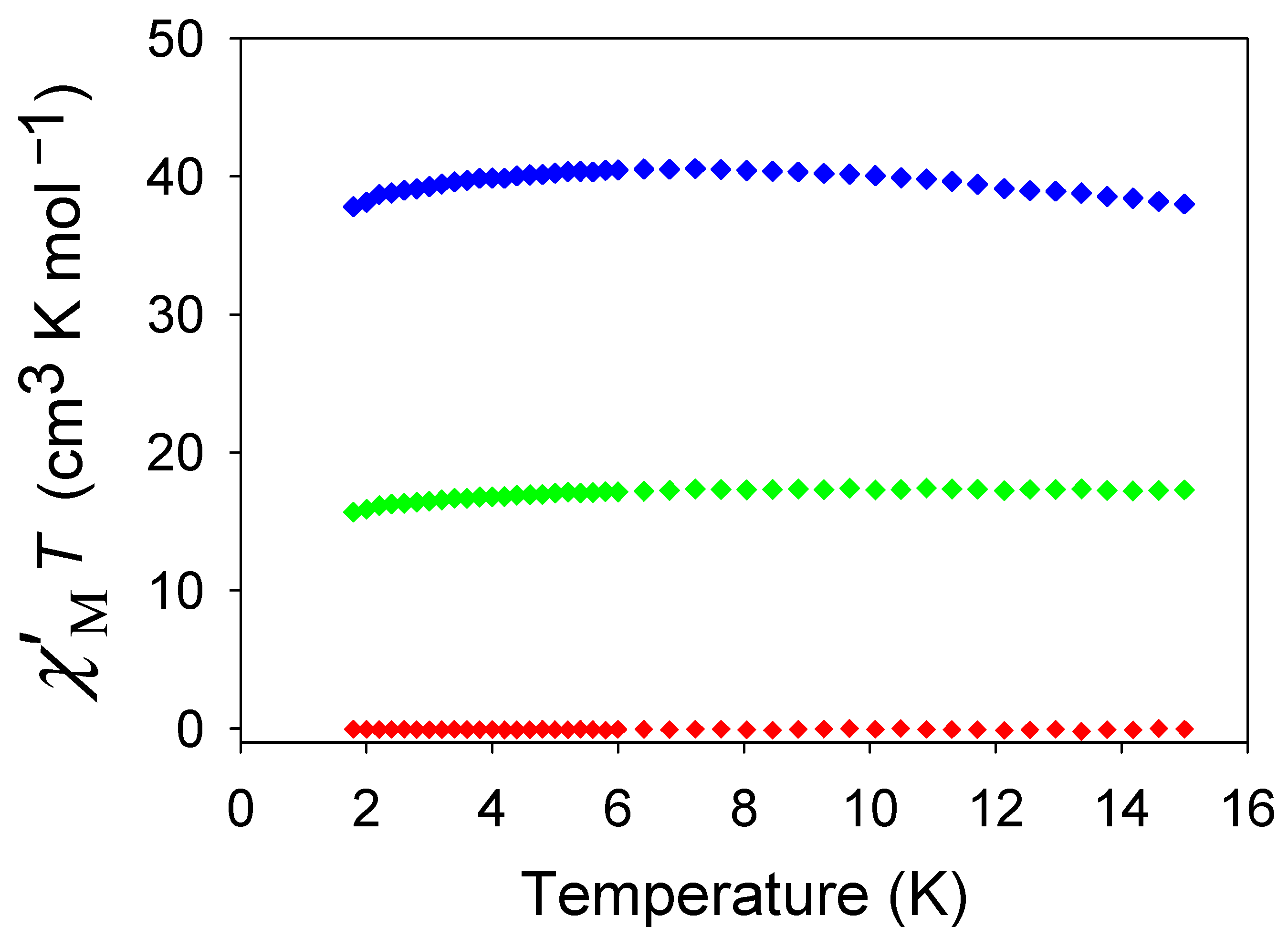
3.3.2. Ac Magnetic Susceptibility Studies
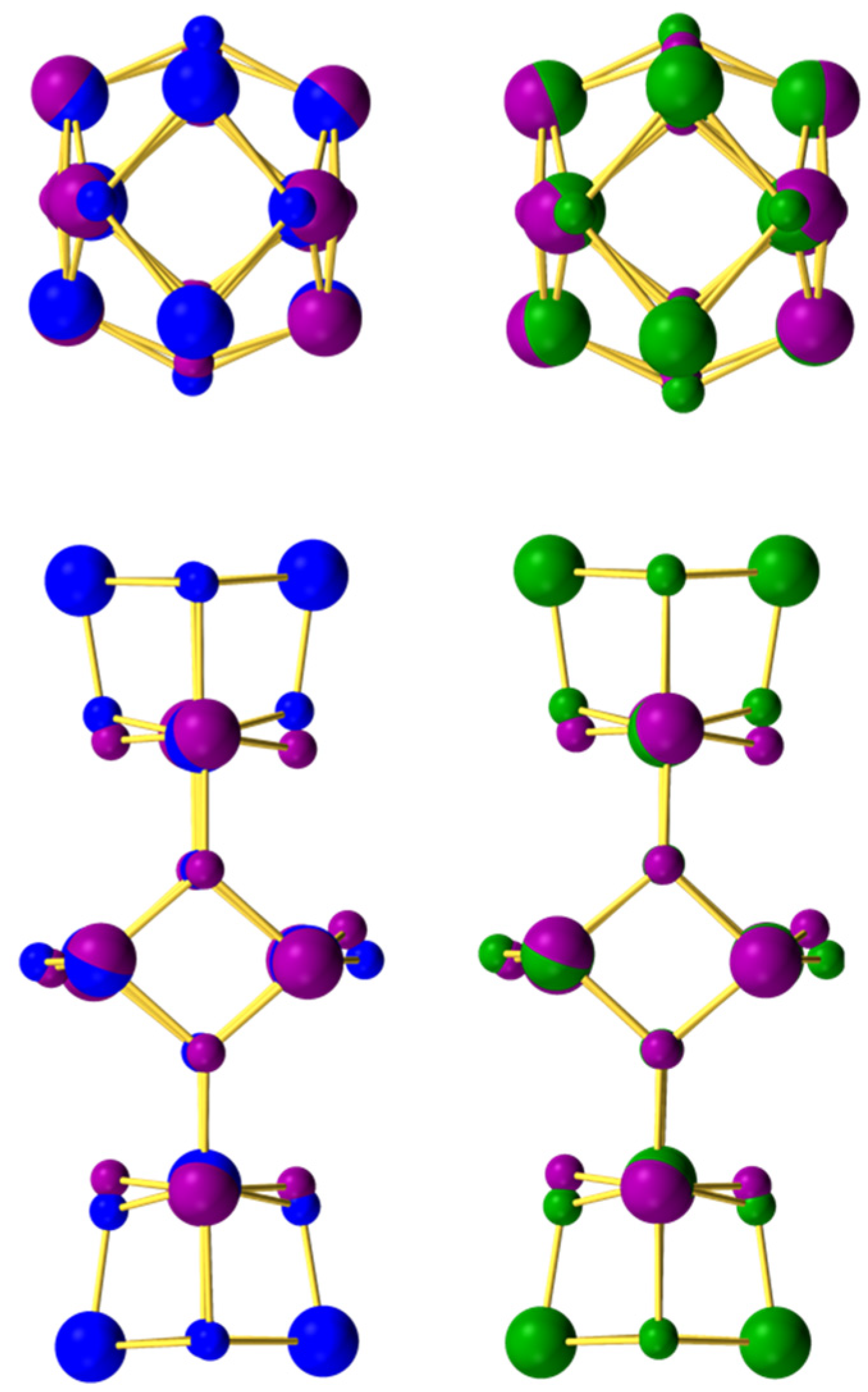
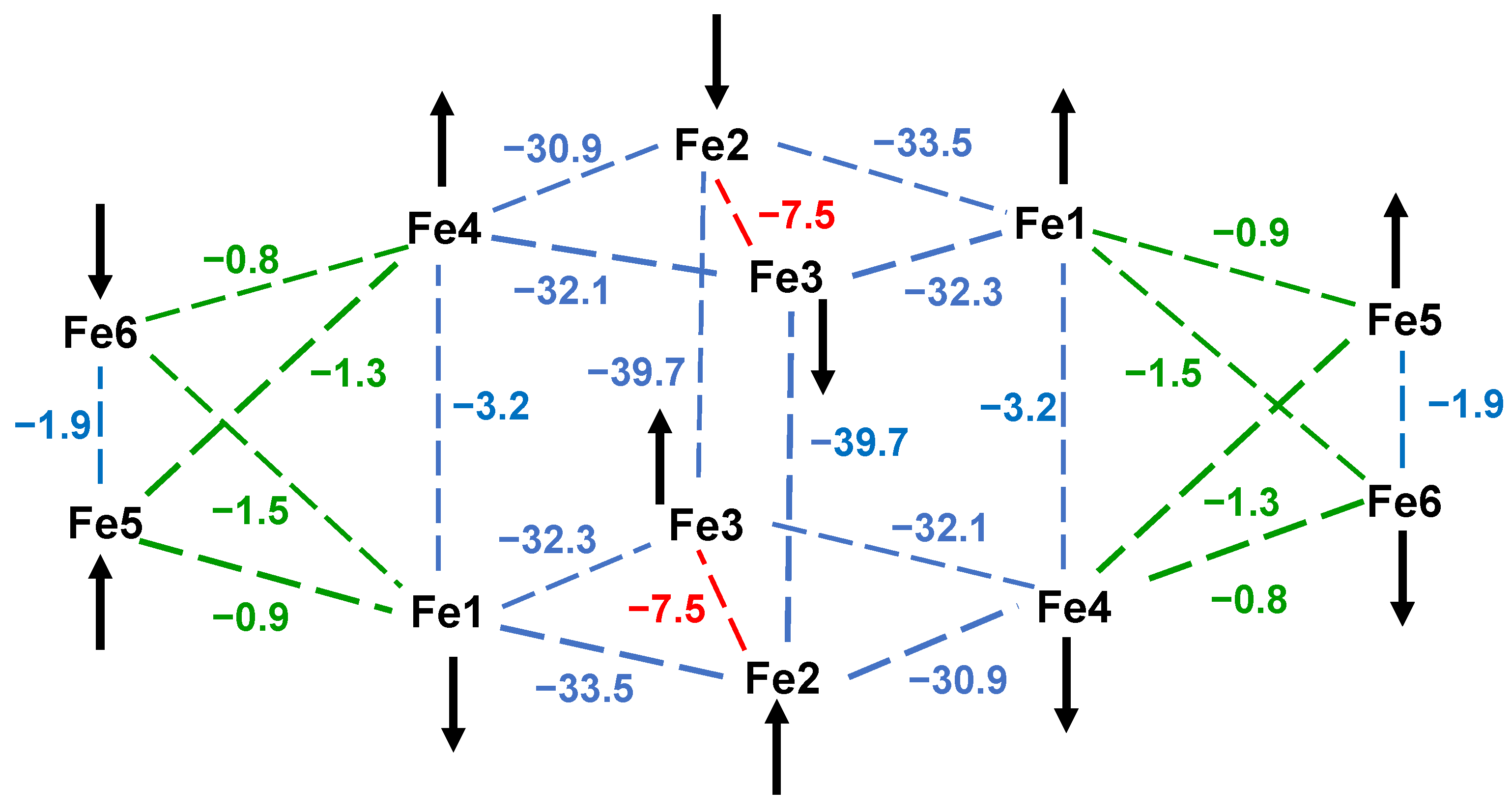
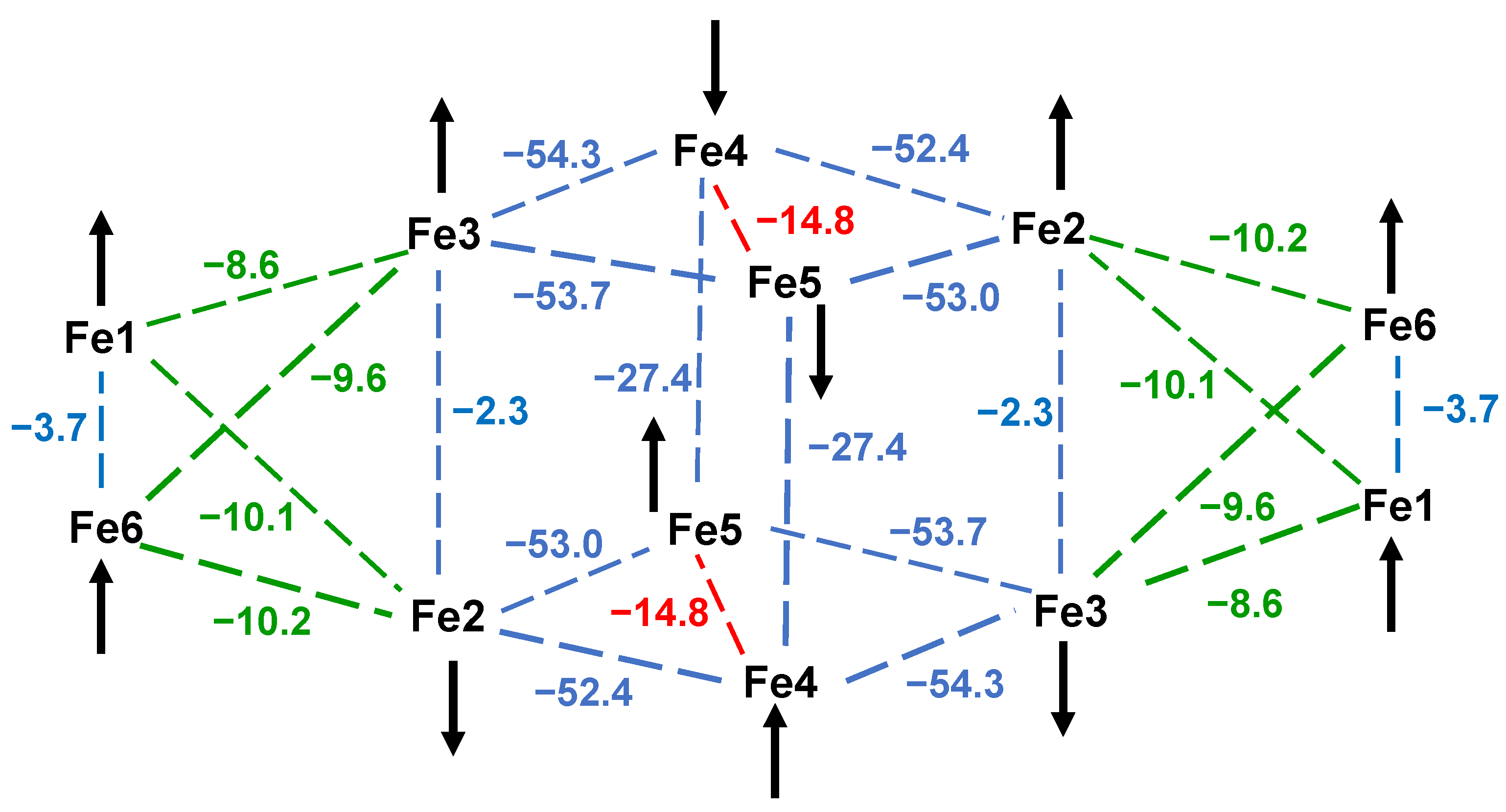
3.3.3. Ground State Spin Rationalization Using a Magnetostructural Correlation (MSC)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagai, R.; Christou, G. The Drosophila of single-molecule magnetism: Mn12O12(O2CR)16(H2O)4. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimblecombe, R.; Swiegers, G.F.; Dismukes, G.C.; Spiccia, L. Sustained water oxidation photocatalysis by a bioinspired manganese cluster. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 7335–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maayan, G.; Gluz, N.; Christou, G. A bioinspired soluble manganese cluster as a water oxidation electrocatalyst with low overpotential. Nat. Cat. 2018, 1, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Das Kumar, B. Cobalt(III)-oxo cubane clusters as catalysts for oxidation of organic substrates. J. Chem. Sci. 2011, 123, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J.B.; Huffman, J.C.; Christou, G.; Li, Q.; Nanny, M.A.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Fong, R.H.; Fish, R.H. Modeling the dinuclear sites of iron biomolecules: Synthesis and properties of Fe2O(OAc)2Cl2(bipy)2 and its use as an alkane activation catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 6898–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, E.J.; Yoo, J.; Folting, K.; Huffman, J.C.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. Dinuclear and hexanuclear iron(III) carboxylate clusters with a bis(bipyridine) ligand: Supramolecular aggregation of [Fe2O2] units to give a [Fe6O6] ladder structure. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 3640–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.M.; Knapp, M.J.; Streib, W.E.; Huffman, J.C.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. Dinuclear and Hexanuclear Iron(III) Oxide Complexes with a Bis(bipyridine) Ligand: A New [Fe6(μ3-O)4]10+ Core. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 6065–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yoo, S.J.; Münck, E.; Que, L. The Flexible Fe2(μ-O)2 Diamond Core: A Terminal Iron(IV)−Oxo Species Generated from the Oxidation of a Bis(μ-oxo)diiron(III) Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3789–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Que, L.; Kauffmann, K.; Muenck, E. The First Bis(.mu.-oxo)diiron(III) Complex. Structure and Magnetic Properties of [Fe2(μ-O)2(6TLA)2](ClO4). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1169–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudalis, A.K.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Terzis, A.; Perlepes, S.P. 2,2′-Bipyrimidine (bpym) in iron(III) carboxylate chemistry: Preparation and characterization of [Fe2O(O2CMe)2 (bpym)2(H2O)2](ClO4)2, and the influence of weak interactions in the formation of metal clusters. Polyhedron 2004, 23, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-T.; Su, X.-J.; Xie, F.; Liao, R.-Z.; Zhang, M.-T. Iron-Catalyzed Water Oxidation: O–O Bond Formation via Intramolecular Oxo–Oxo Interaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12467–12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-M.; Yao, S.; Li, Y.-G.; Clérac, R.; Lu, Y.; Su, Z.-M.; Wang, E.-B. Protein-Sized Chiral Fe168 Cages with NbO-Type Topology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14600–14601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, A.R.; Lott, M.E.; Peralta, J.E.; Foguet-Albiol, D.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Magnetic Properties of High-Nuclearity Fex-oxo (x = 7, 22, 24) Clusters Analyzed by a Multipronged Experimental, Computational, and Magnetostructural Correlation Approach. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 11261–11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Lippard, S.J. Carboxylate-bridged diiron(II) complexes: Synthesis characterization, and O2-reactivity of models for the reduced diiron centers in methane monooxygenase and ribonucleotide reductase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lippard, S.J. Structural and functional models of the dioxygen-activating centers of non-heme diiron enzymes ribonucleotide reductase and soluble methane monooxygenase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12153–12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menage, S.; Zang, Y.; Hendrich, M.P.; Que, L. Structure and reactivity of a bis(.mu.-acetato-O,O′)diiron(II) complex, [Fe2(O2CCH3)2(TPA)2](BPh4)2. A model for the diferrous core of ribonucleotide reductase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7786–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, M.; Itoh, M.; Kano, K.; Funabiki, T.; Reglier, M. A Diiron Center Stabilized by a Bis-TPA Ligand as a Model of Soluble Methane Monooxygenase: Predominant Alkene Epoxidation with H2O2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7104–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Wang, D.; De Hont, R.; Fiedler, A.T.; Shan, X.; Münck, E.; Que, L. A synthetic precedent for the [FeIV2(μ-O)2] diamond core proposed for methane monooxygenase intermediate Q. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20713–20718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas, M.; Rohde, J.U.; Stubna, A.; Ho, R.Y.N.; Quaroni, L.; Münck, E.; Que, L., Jr. A synthetic model for the putative FeIV2O2 diamond core of methane monooxygenase intermediate Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12931–12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaralingam, M.; Palaniandavar, M. Diiron(III) complexes of tridentate 3N ligands as functional models for methane monooxygenases: Effect of the capping ligand on hydroxylation of alkanes. Polyhedron 2014, 67, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, H.; Nagatomo, S.; Kitagawa, T.; Miwa, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Einaga, H.; Masuda, H. A novel diiron complex as a functional model for hemerythrin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2000, 82, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, T.J.; Kuzelka, J.; Spingler, B.; DuBois, J.L.; Davydov, R.M.; Hedman, B.; Hodgson, K.O.; Lippard, S.J. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of non-heme diiron(III) species with a terminal hydroperoxide ligand: Models for hemerythrin. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 4662–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Mishina, Y. Modeling non-heme iron proteins. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tshuva, E.Y.; Lippard, S.J. Synthetic Models for Non-Heme Carboxylate-Bridged Diiron Metalloproteins: Strategies and Tactics. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 987–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, L. The Road to Non-Heme Oxoferryls and Beyond. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Furutachi, H.; Fujinami, S.; Nagatomo, S.; Maeda, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kitagawa, T.; Suzuki, M. Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization of (μ-Hydroxo or μ-Oxo)(μ-peroxo)diiron(III) Complexes: Models for Peroxo Intermediates of Non-Heme Diiron Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 826–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foguet-Albiol, D.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. High-nuclearity homometallic iron and nickel clusters: Fe22 and Ni24 complexes from the use of N-methyldiethanolamine. Chem. Commun. 2005, 4282–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, J.K.; Vincent, J.B.; Schmitt, E.A.; Mino, M.L.; Shin, K.; Coggin, D.K.; Hagen, P.M.; Huffman, J.C.; Christou, G.; Hendrickson, D.N. Molecular spin frustration in the [Fe4O2]8+ core: Synthesis, structure, and magnetochemistry of tetranuclear iron-oxo complex [Fe4O2(O2CR)7(bpy)2](C1O4) (R = Me, Ph). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O. Competing spin interactions and degenerate frustration for discrete molecular species. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 265, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatteschi, D.; Caneschi, A.; Sessoli, R.; Cornia, A. Magnetism of large iron-oxo clusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1996, 25, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murch, B.P.; Boyle, P.D.; Que, L. Structures of binuclear and tetranuclear iron(III) complexes as models for ferritin core formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 6728–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.N.; Thompson, C.; Theil, E.C.; Chasteen, N.D.; Sayers, D.E. Fe(III).ATP complexes. Models for ferritin and other polynuclear iron complexes with phosphate. J. Bio. Chem. 1985, 260, 7975–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Q.T.; Sayers, D.E.; Theil, E.C.; Gorun, S.M. A comparison of an undecairon(III) complex with the ferritin iron core. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1989, 36, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, K.L.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Lippard, S.J. Synthesis, Structure, and Electronic Properties of a Mixed-Valent Dodecairon Oxo Complex, a Model for the Biomineralization of Ferritin. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachicotte, R.J.; Hagen, K.S. Synthesis and structures of trinuclear and μ-hydroxo pentanuclear iron(II) carboxylates as models of reduced ferritin and white rust. Inorg. Chimi. Acta 1997, 263, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Thompson, M.S.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Unusual Fe9 and Fe18 structural types from the use of 2,6-pyridinedimethanol in FeIII cluster chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 9131–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, I.A.; Milios, C.J.; Evangelisti, M.; Heath, S.L.; Collison, D.; Parsons, S.; Brechin, E.K. Synthesis and magnetic properties of heptadecametallic Fe(III) clusters. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada-Vilalta, C.; O’Brien, T.A.; Brechin, E.K.; Pink, M.; Davidson, E.R.; Christou, G. Large spin differences in structurally related Fe6 molecular clusters and their magnetostructural explanation. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 5505–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Joshi, R.P.; Abboud, K.A.; Peralta, J.E.; Christou, G. Molecular spin frustration in mixed-chelate Fe5 and Fe6 oxo clusters with high ground state spin values. Polyhedron 2020, 176, 114182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.; Stamatatos, T.C.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Reversible Size Modification of Iron and Gallium Molecular Wheels: A Ga10 “Gallic Wheel” and Large Ga18 and Fe18 Wheels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7379–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artus, P.; Boskovic, C.; Yoo, J.; Streib, W.E.; Brunel, L.C.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. Single-molecule magnets: Site-specific ligand abstraction from [Mn12O12(O2CR)16(H2O)4] and the preparation and properties of [Mn12O12(NO3)4(O2CCH2Bu(t))12(H2O)4]. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 4199–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boskovic, C.; Pink, M.; Huffman, J.C.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. Single-molecule magnets: Ligand-induced core distortion and multiple Jahn-Teller isomerism in Mn12O12(O2CMe)8(O2PPh2)8(H2O)4. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9914–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brockman, J.T.; Abboud, K.A.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. A new family of Mn12 single-molecule magnets: Replacement of carboxylate ligands with diphenylphosphinates. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakov, N.E.; Abboud, K.A.; Zakharov, L.N.; Rheingold, A.L.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. Reaction of Mn12O12(O2CR)16(H2O)4 single-molecule magnets with non-carboxylate ligands. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakov, N.E.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Abboud, K.A.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Christou, G. Single-molecule magnets. A Mn12 complex with mixed carboxylate-sulfonate ligation: Mn12O12(O2CMe)8(O3SPh)8(H2O)4. Dalt. Trans. 2003, 2243–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakov, N.E.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Mixed-valence (MnMnIV)-Mn-III clusters Mn7O8(O2SePh)8(O2CMe)(H2O) and Mn7O8(O2SePh)9(H2O): Single-chain magnets exhibiting quantum tunneling of magnetization. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 5919–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakov, N.E.; Thuijs, A.E.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Rheingold, A.L.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Unusual Mn(III/IV)4 Cubane and MnIII16M4 (M = Ca, Sr) Looplike Clusters from the Use of Dimethylarsinic Acid. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 8468–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, S.; Clearfield, A. Synthesis and Characterization of High Nuclearity Iron(III) Phosphonate Molecular Clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 5573–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.-C.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zheng, L.-M.; Xin, X.-Q. Syntheses, structures and magnetic properties of tetra- and heptanuclear iron(III) clusters incorporating phosphonate ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2005, 358, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolis, E.I.; Helliwell, M.; Langley, S.; Raftery, J.; Winpenny, R.E.P. Synthesis and Characterization of Iron(III) Phosphonate Cage Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3804–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.K.; Peralta, J.E.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Iron(III)–Oxo Cluster Chemistry with Dimethylarsinate Ligands: Structures, Magnetic Properties, and Computational Studies. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 18090–18101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.K.; Aebersold, L.; Peralta, J.E.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetic Properties of an Fe36 Dimethylarsinate Cluster: The Largest “Ferric Wheel”. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 17256–17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, I.; Healy, M.R.; Doidge, E.D.; Love, J.B.; Morrison, C.A.; Tasker, P.A. Metal-binding motifs of alkyl and aryl phosphinates; versatile mono and polynucleating ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 335, 150–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.F.; Xu, G.C.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Bu, X.H.; Gao, S.; Sanudo, E.C. Single-Molecule-Magnet Behavior in a Fe12Sm4 Cluster. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9734–9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Zeng, Y.F.; Xue, L.; Han, S.D.; Jia, J.M.; Hu, T.L.; Bu, X.H. Tuning the magnetic behaviors in FeIII12LnIII4 clusters with aromatic carboxylate ligands. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, P.X.; Du, M.H.; Han, Y.Z.; Wei, R.J.; Ouyang, Z.W.; Kong, X.J.; Zhuang, G.L.; et al. Insights into Magnetic Interactions in a Monodisperse Gd12Fe14 Metal Cluster. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11475–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Du, M.H.; Amiri, M.; Nyman, M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T.; Kong, X.J.; Long, L.S.; Zheng, L.S. Atomically Precise Lanthanide-Iron-Oxo Clusters Featuring the epsilon-Keggin Ion. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Chen, M.T.; Du, M.H.; Wei, R.J.; Kong, X.J.; Long, L.S.; Zheng, L.S. Capturing Lacunary Iron-Oxo Keggin Clusters and Insight Into the Keggin-Fe-13 Cluster Rotational Isomerization. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 11985–11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumousi, E.S.; Mukherjee, S.; Beavers, C.M.; Teat, S.J.; Christou, G.; Stamatatos, T.C. Towards models of the oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) of photosystem II: A Mn4Ca cluster of relevance to low oxidation states of the OEC. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 11128–11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, A.A.; Takahashi, D.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Christou, G.; Stamatatos, T.C. Emissive {MnIII4Ca} Clusters with Square Pyramidal Topologies: Syntheses and Structural, Spectroscopic, and Physicochemical Characterization. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 2137–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Stull, J.A.; Yano, J.; Stamatatos, T.C.; Pringouri, K.; Stich, T.A.; Abboud, K.A.; Britt, R.D.; Yachandra, V.K.; Christou, G. Synthetic model of the asymmetric [Mn3CaO4] cubane core of the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2257–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.E. Structure and mechanism of alkaline phosphatase. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1992, 21, 441–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassila, J.K.; Zalatan, J.G.; Herschlag, D. Biological phosphoryl-transfer reactions: Understanding mechanism and catalysis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 669–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamerlin, S.C.; Sharma, P.K.; Prasad, R.B.; Warshel, A. Why nature really chose phosphate. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 46, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.C.; Roversi, P.; Lillington, J.; Rodriguez, F.; Krehenbrink, M.; Zeldin, O.B.; Garman, E.F.; Lea, S.M.; Berks, B.C. A complex iron-calcium cofactor catalyzing phosphotransfer chemistry. Science 2014, 345, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, D.E.; Lionetti, D.; Rittle, J.; Agapie, T. Heterometallic Triiron-Oxo/Hydroxo Clusters: Effect of Redox-Inactive Metals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 19075–19078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prodius, D.; Turta, C.; Mereacre, V.; Shova, S.; Gdaniec, M.; Simonov, Y.; Lipkowski, J.; Kuncser, V.; Filoti, G.; Caneschi, A. Synthesis, structure and properties of heterotrinuclear carboxylate complexes [Fe2M(Ca, Sr, Ba)O(CCl3COO)6(THF)n]. Polyhedron 2006, 25, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Klüfers, P. Stabilization of Iron Clusters by Polyolato Ligands and Calcium Ions: An Fe14 Oxocluster from Aqueous Alkaline Solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Saalfrank, R.W.; Maid, H.; Scheurer, A.; Heinemann, F.W.; Trautwein, A.X.; Böttger, L.H. Synthesis and Redox Properties of Mixed-Valent Octanuclear Iron Defective Hexacubanes and a (CaCl)-Capped Body-Centered Six-Sided Iron(III) Polyhedron. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5885–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, A.; Figgis, B.N.; Lewis, J. Chemistry of polynuclear compounds. Part VI. Magnetic properties of trimeric chromium and iron carboxylates. J. Chem. Soc. A 1966, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spek, A. PLATON SQUEEZE: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Cryst. Sec. C 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spek, A. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. Sec. D 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gagne, O.C.; Hawthorne, F.C. Comprehensive derivation of bond-valence parameters for ion pairs involving oxygen. Acta Cryst. Sec. B Struc. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mat. 2015, 71, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, I.D.; Altermatt, D. Bond-Valence Parameters Obtained from a Systematic Analysis of the Inorganic Crystal-Structure Database. Acta Cryst. Sec. B Struc. Sci. 1985, 41, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bain, G.A.; Berry, J.F. Diamagnetic corrections and Pascal’s constants. J. Chem. Edu. 2008, 85, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wullen, C. Broken Symmetry Approach to Density Functional Calculation of Magnetic Anisotropy or Zero Field Splittings for Multinuclear Complexes with Antiferromagnetic Coupling. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 11535–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencini, A.; Totti, F.; Daul, C.A.; Doclo, K.; Fantucci, P.; Barone, V. Density functional calculations of magnetic exchange interactions in polynuclear transition metal complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 5022–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.; Rodriguez-Fortea, A.; Cano, J.; Alvarez, S.; Alemany, P. About the calculation of exchange coupling constants in polynuclear transition metal complexes. J. Comp. Chem. 2003, 24, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, R.; Costa, R.; Moreira, I.; Truhlar, D.G.; Illas, F. Performance of the M06 family of exchange-correlation functionals for predicting magnetic coupling in organic and inorganic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comba, P.; Hausberg, S.; Martin, B. Calculation of Exchange Coupling Constants of Transition Metal Complexes with DFT. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 6751–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.J.; Peralta, J.E. Magnetic Exchange Couplings from Semilocal Functionals Evaluated Nonself-Consistently on Hybrid Densities: Insights on Relative Importance of Exchange, Correlation, and Delocalization. J. Chem. Theory Comp. 2012, 8, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.P.; Phillips, J.J.; Mitchell, K.J.; Christou, G.; Jackson, K.A.; Peralta, J.E. Accuracy of density functional theory methods for the calculation of magnetic exchange couplings in binuclear iron(III) complexes. Polyhedron 2020, 176, 114194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Ditchfield, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular-orbital methods.12. further extensions of gaussian-type basis sets for use in molecular-orbital studies of organic-molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Binkley, J.S.; Seeger, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular-orbital methods.20. basis set for correlated wave-functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaudeau, J.P.; McGrath, M.P.; Curtiss, L.A.; Radom, L. Extension of Gaussian-2 (G2) theory to molecules containing third-row atoms K and Ca. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 5016–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazis, D.A.; Neese, F. All-Electron Scalar Relativistic Basis Sets for the Lanthanides. J. Chem. Theory Comp. 2009, 5, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, M.; Kroll, N.M. Quantum electrodynamical corrections to the fine structure of helium. Ann. Phys. 1974, 82, 89–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.A. Applicability of the no-pair equation with free-particle projection operators to atomic and molecular-structure calculations. Phys. Rev. 1985, 32, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.A. Relativistic electronic-structure calculations employing a two-component no-pair formalism with external-field projection operators. Phys. Rev. 1986, 33, 3742–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision B.01, Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016.
- Armstrong, W.H.; Roth, M.E.; Lippard, S.J. Tetranuclear iron-oxo complexes. Synthesis, structure, and properties of species containing the nonplanar {Fe4O2}8+ core and seven bridging carboxylate ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6318–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudalis, A.K.; Lalioti, N.; Spyroulias, G.A.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Terzis, A.; Bousseksou, A.; Tangoulis, V.; Tuchagues, J.-P.; Perlepes, S.P. Novel Rectangular [Fe4(μ4-OHO)(μ-OH)2]7+ versus “Butterfly” [Fe4(μ3-O)2]8+ Core Topology in the FeIII/RCO2−/phen Reaction Systems (R = Me, Ph; phen = 1,10-Phenanthroline): Preparation and Properties of [Fe4(OHO)(OH)2(O2CMe)4(phen)4](ClO4)3, [Fe4O2(O2CPh)7(phen)2](ClO4), and [Fe4O2(O2CPh)8(phen)]. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 6474–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizaga, L.; Gancheff, J.S.; Faccio, R.; Cañón-Mancisidor, W.; González, R.; Kremer, C.; Chiozzone, R. Synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties of a novel tetranuclear oxo-bridged iron(III) butterfly. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1058, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagai, R.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. A New N,N,O Chelate for Transition Metal Chemistry: Fe5 and Fe6 Clusters from the Use of 6-Hydroxymethyl-2,2‘-bipyridine (hmbpH). Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 5567–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagai, R.; Datta, S.; Betancur-Rodriguez, A.; Abboud, K.A.; Hill, S.; Christou, G. Diversity of New Structural Types in Polynuclear Iron Chemistry with a Tridentate N,N,O Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 4535–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, P.; Winter, M.; Fleischhauer, P.; Haase, W.; Flörke, U.; Haupt, H.-J. Synthesis, structure and magnetism of a tetranuclear Fe(III) complex containing an [Fe4(μ3-O)2]8+ core. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1993, 212, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammala, P.; Cashion, J.D.; Kepert, C.M.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S.; Spiccia, L.; West, B.O. An Octanuclear FeIII Compound Featuring a New Type of Double Butterfly Iron–Oxo Core. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1688–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchy, T.; Ruiz, E.; Alvarez, S. Magnetostructural Correlations in Polynuclear Complexes: The Fe4 Butterflies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15722–15727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, J.; Hibbs, D.E.; Rentschler, E.; Timco, G.A.; Larsen, F.K. Experimental and Theoretical Electron Density Distribution and Magnetic Properties of the Butterfly-like Complex [Fe4O2(O2CCMe3)8(NC5H4Me)2]·2CH3CN. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 7593–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.J.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Magnetostructural Correlation for High-Nuclearity Iron(III)/Oxo Complexes and Application to Fe5, Fe6, and Fe8 Clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 6597–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, A.R.; Aebersold, L.E.; Peralta, J.E.; Foguet-Albiol, D.; Abboud, K.A.; Christou, G. Analysis of spin frustration in an FeIII7 cluster using a combination of computational, experimental, and magnetostructural correlation methods. Polyhedron 2022, 225, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskovic, C.; Bircher, R.; Tregenna-Piggott, P.L.W.; Gudel, H.U.; Paulsen, C.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Barra, A.L.; Khatsko, E.; Neels, A.; Stoeckli-Evans, H. Ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic intermolecular interactions in a new family of Mn4 complexes with an energy barrier to magnetization reversal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14046–14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula a | C126H115Fe8NO30.50P10 | C163.6H122.4Fe12Ca4N3.6O55.6 | C161.76H177.25Fe6La2N4.25O31 |
| Fw, g/mol | 2887.68 | 3858.76 | 3289.74 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic | Monoclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | Pbca | P21/c | P |
| a, Å | 25.7321(8) | 18.4877(16) | 19.6897(9) |
| b, Å | 29.8328(9) | 23.1092(19) | 21.5274(10) |
| c, Å | 37.9740(12) | 23.7055(19) | 24.0099(11) |
| α, ° | 90 | 90 | 97.3530(10) |
| β, ° | 90 | 112.917(2) | 111.5360(10) |
| γ, ° | 90 | 90 | 115.5490(10) |
| Volume, Å3 | 29,151.1(16) | 9328.4(13) | 8028.5(6) |
| Z | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| T, K | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) |
| λ, Å a | 0.71073 | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| ρcalc, Mg/m3 | 1.316 | 1.374 | 1.361 |
| R1 b, d | 4.49 | 5.89 | 4.72 |
| wR2 c, e | 9.90 | 15.00 | 11.52 |
| Complex | Atom | BVS | Assignment a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | O1 | 1.86 | O2− |
| O2 | 1.86 | O2− | |
| O3 | 1.87 | O2− | |
| O4 | 1.91 | O2− | |
| O5 | 0.98 | OH− | |
| O6 | 1.00 | OH− | |
| O7 | 1.02 | OH− | |
| O8 | 0.81 | OH− | |
| O111 | 1.24 | OH− | |
| O112 | 1.55 b | O2− b | |
| 3 | O1 | 1.72 | O2− |
| O2 | 1.73 | O2− | |
| O3 | 1.83 | O2− | |
| O4 | 2.07 | O2− | |
| O5 | 1.14 | OH− | |
| O6 | 2.01 | O2− | |
| O7 | 1.15 | OH− |
| Pair | JMSC 1 a | Pair | JMSC 2 a | Pair | JMSC 3 a | JDFT 3 a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe1–Fe2 | −26.9 | Fe1–Fe2 | −33.5 | Fe2–Fe4 | −52.4 | −44.9 |
| Fe1–Fe4 | −20.9 | Fe1–Fe3 | −32.3 | Fe2–Fe5 | −53.0 | −44.3 |
| Fe2–Fe3 | −26.2 | Fe2–Fe4 | −28.1 | Fe3–Fe4 | −54.3 | −46.3 |
| Fe3–Fe4 | −25.4 | Fe3–Fe4 | −29.3 | Fe3–Fe5 | −53.7 | −44.2 |
| Fe2–Fe4 | −8.8 b | Fe2–Fe3 | −7.6 b | Fe4–Fe5 | −14.8 | +0.8 b |
| Fe5–Fe6 | −29.4 | Fe1–Fe4 | −3.2 | Fe4–Fe5′ | −27.4 | −27.4 |
| Fe5–Fe8 | −20.5 | Fe1–Fe5 | −0.9 | Fe1–Fe6 | −3.7 | −0.1 d |
| Fe6–Fe7 | −25.7 | Fe1–Fe6 | −1.5 | Fe3–Fe6 | −9.6 | −7.5 |
| Fe7–Fe8 | −29.4 | Fe2–Fe3′ | −36.3 | Fe2–Fe6 | −10.2 | −7.8 |
| Fe6–Fe8 | −9.9 b | Fe4–Fe5 | −1.3 | Fe2–Fe3 | −2.3 | +2.0 |
| Fe1–Fe5 | −5.4 | Fe4–Fe6 | −0.8 | Fe1–Fe2 | −10.1 | −8.0 |
| Fe3–Fe7 | −2.3 | Fe5–Fe6 | −1.9 d | Fe1–Fe3 | −8.6 | −5.1 |
| Fe2–Fe6 | −24.7 | |||||
| Fe4–Fe8 | −51.7 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.P.; Brantley, C.L.; Lee, K.H.K.; Abboud, K.A.; Peralta, J.E.; Christou, G. Structural and Magnetic Analysis of a Family of Structurally Related Iron(III)-Oxo Clusters of Metal Nuclearity Fe8, Fe12Ca4, and Fe12La4. Chemistry 2023, 5, 1599-1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5030110
Singh AP, Brantley CL, Lee KHK, Abboud KA, Peralta JE, Christou G. Structural and Magnetic Analysis of a Family of Structurally Related Iron(III)-Oxo Clusters of Metal Nuclearity Fe8, Fe12Ca4, and Fe12La4. Chemistry. 2023; 5(3):1599-1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Alok P., ChristiAnna L. Brantley, Kenneth Hong Kit Lee, Khalil A. Abboud, Juan E. Peralta, and George Christou. 2023. "Structural and Magnetic Analysis of a Family of Structurally Related Iron(III)-Oxo Clusters of Metal Nuclearity Fe8, Fe12Ca4, and Fe12La4" Chemistry 5, no. 3: 1599-1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5030110
APA StyleSingh, A. P., Brantley, C. L., Lee, K. H. K., Abboud, K. A., Peralta, J. E., & Christou, G. (2023). Structural and Magnetic Analysis of a Family of Structurally Related Iron(III)-Oxo Clusters of Metal Nuclearity Fe8, Fe12Ca4, and Fe12La4. Chemistry, 5(3), 1599-1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5030110






