Interaction Between Iso-α-Acid Extracted from Hops and Protein Z Improves Beer Foam Quality and Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of PZ and Iso-α-Acids
2.3. Fluorescence Titration
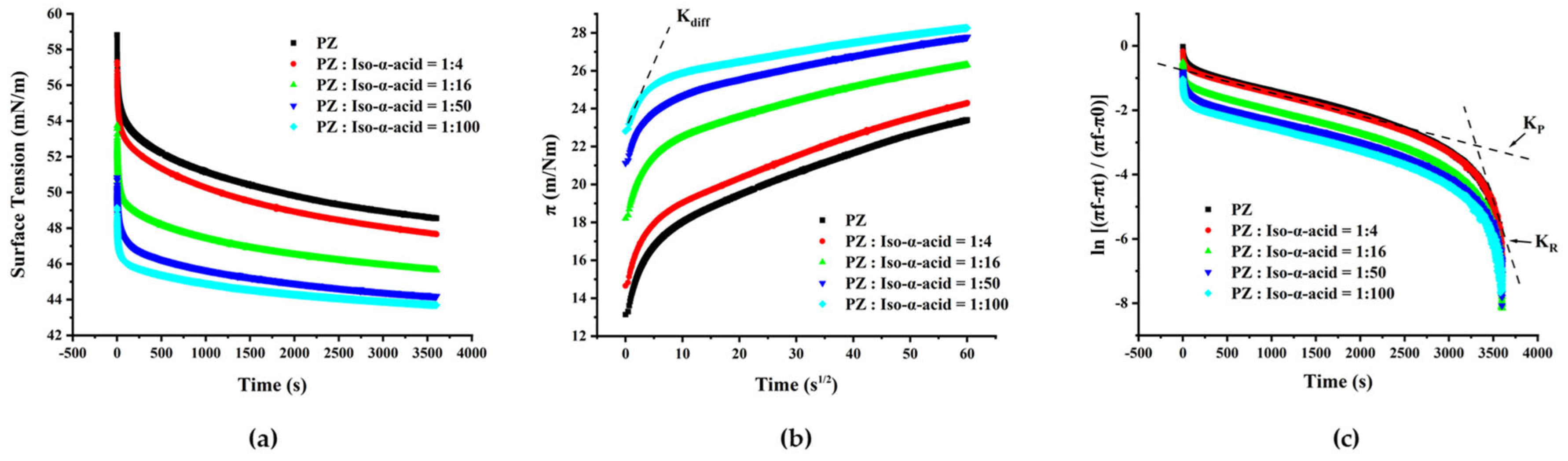
2.4. Dynamic Surface Tension
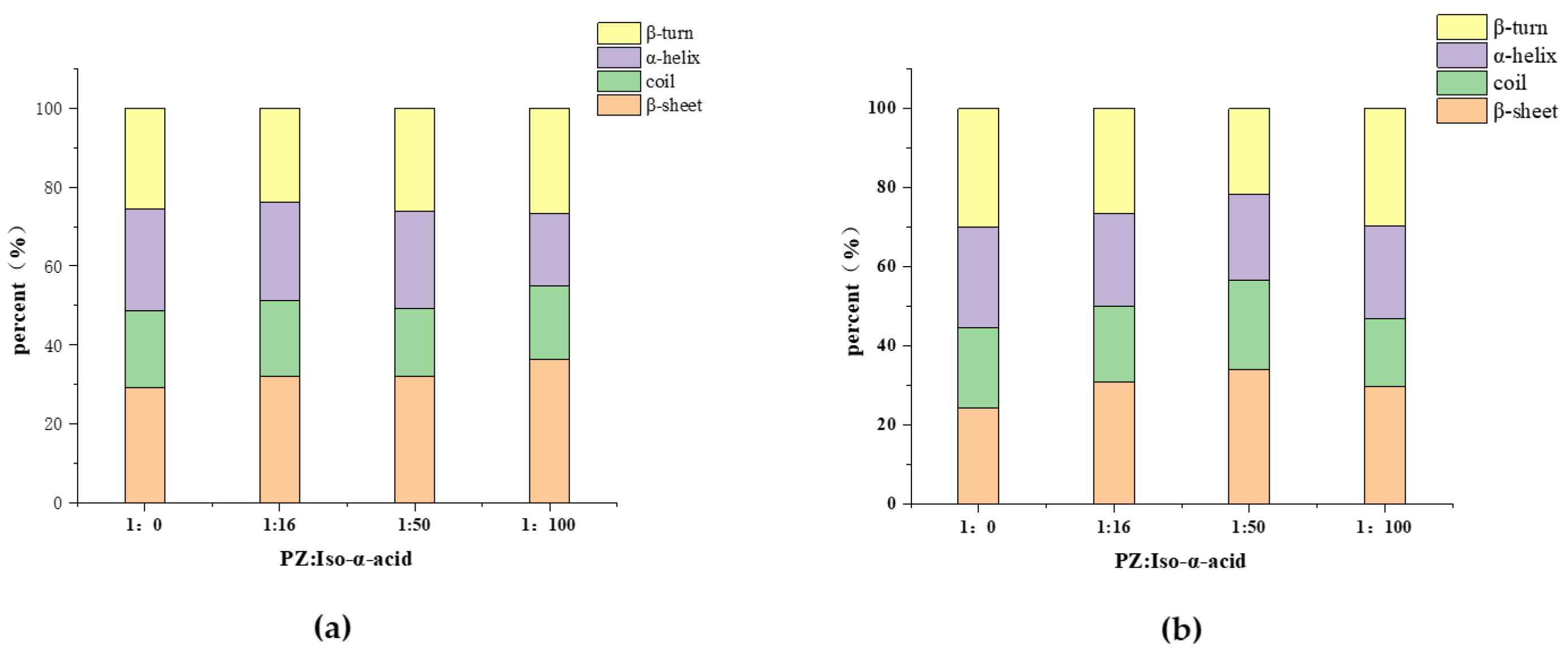
2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
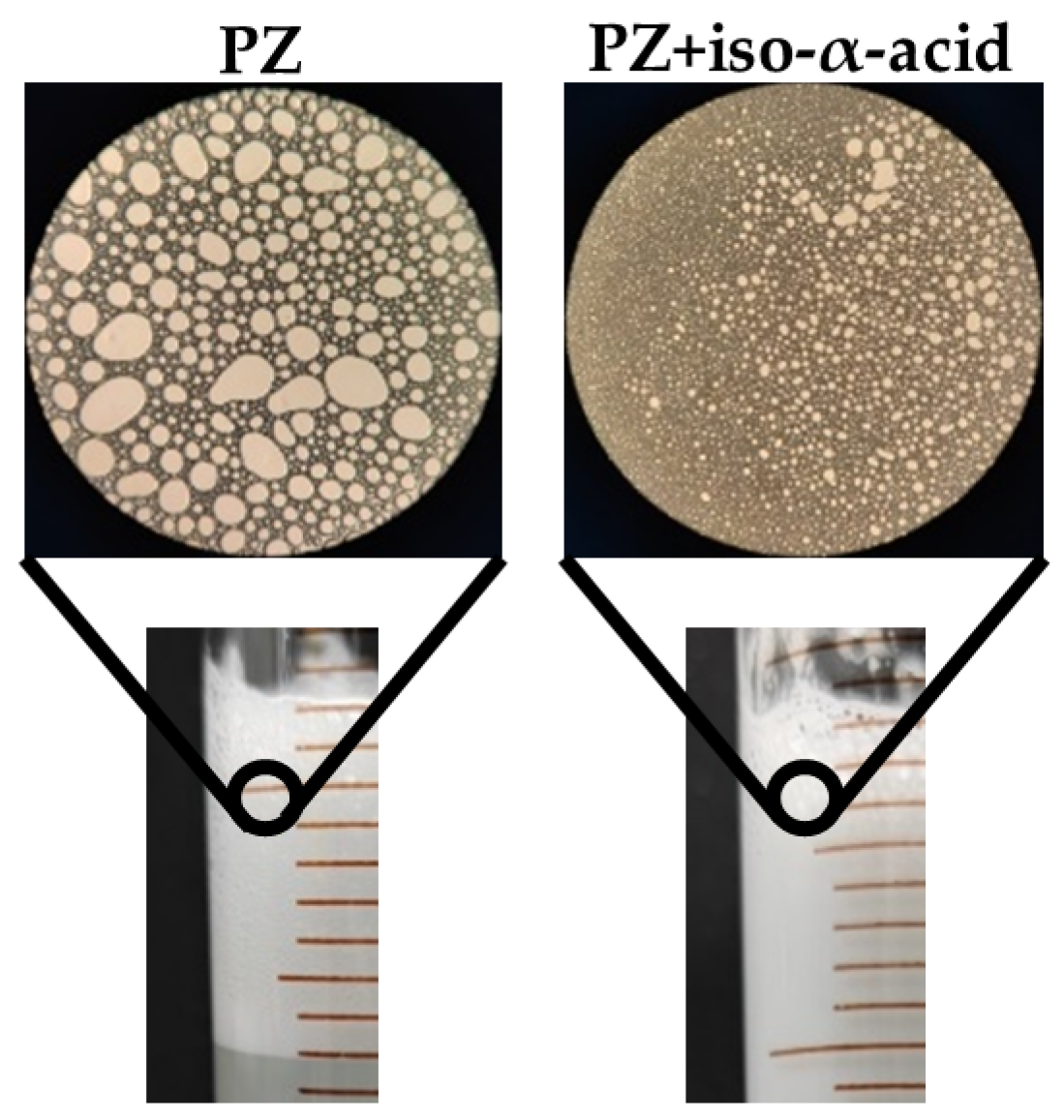
2.6. Foaming Performance
2.7. Surface Pressure and Surface Tension
2.8. Protein Penetration and Molecular Reorganization
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of PZ and Iso-α-Acid
3.2. Interaction Between PZ and Iso-α-Acid
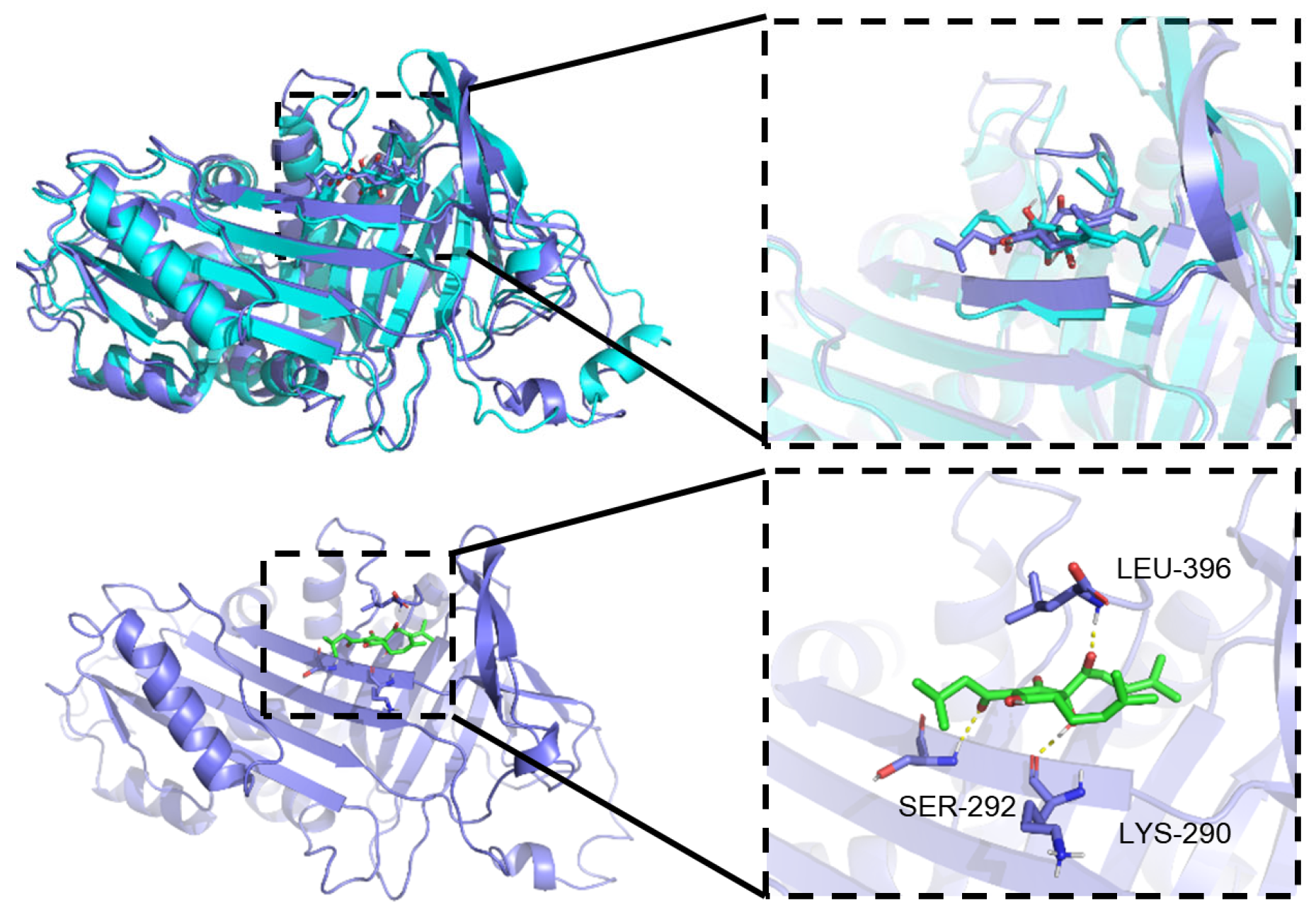
3.2.1. Molecular Interactions and Stoichiometric Correspondence Between PZ and Iso-α-Acid
3.2.2. Effect of Iso-α-Acid Binding to PZ on Its Structure
3.3. Influence of Iso-α-Acid on PZ Foaming Properties
3.4. Effect of the Interaction of Iso-α-Acid with PZ on the Stability of Beer Foam
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kosin, P.; Savel, J.; Evans, D.E.; Broz, A. Relationship between Matrix Foaming Potential, Beer Composition, and Foam Stability. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2010, 68, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.E.; Surrel, A.; Sheehy, M.; Stewart, D.C.; Robinson, L.H. Comparison of Foam Quality and the Influence of Hop α-Acids and Proteins Using Five Foam Analysis Methods. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2008, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandigunta, B.; Karthick, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Dhoble, A.S. Impact of temperature and surfactant addition on milk foams. J. Food Eng. 2021, 299, 110509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Shinagawa, K.; Hashimoto, N. Characterization of Haze-Forming Proteins of Beer and Their Roles in Chill Haze Formation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1982, 40, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, C.W. The foaming properties of beer. J. Inst. Brew. 1985, 91, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Dohata, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Hoshi, A.; Uchida, K.; Takashima, A.; Nakayama, H. Iso-α-acids, Bitter Components of Beer, Prevent Inflammation and Cognitive Decline Induced in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3720–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hong, K.; I Agbaka, J.; Song, Y.; Lv, C.; Ma, C. Characterization of bitter-tasting and antioxidant activity of dry-hopped beers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 4843–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, K.; Gao, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhao, G.; Lv, C. Comparison of recombinant protein Z with natural protein Z derived from malt: From structure to functional properties. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. Malt derived proteins: Effect of protein Z on beer foam stability. Food Biosci. 2018, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Hang, Y.; Yin, X.; Li, Q. Circular dichroism and infrared spectroscopic characterization of secondary structure components of protein Z during mashing and boiling processes. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunimune, T.; Shellhammer, T.H. Foam-stabilizing effects and cling formation patterns of iso-α-acids and reduced iso-α-acids in lager beer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8629–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Bergenståhl, B.; Nilsson, L. Interfacial properties and interaction between beer wort protein fractions and iso-humulone. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Osmark, P.; Bergenståhl, B.; Nilsson, L. Vesicular structures formed from barley wort proteins and iso-humulone. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Lv, C. Interactions between humulinone derived from aged hops and protein Z enhance the foamability and foam stability. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Gan, J.; Wang, L.; Lv, C. Binding of curcumin to barley protein Z improves its solubility, stability and bioavailability. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Matsukura, Y.; Ozaki, H.; Nishimura, K.; Shindo, K. Identification and quantification of the oxidation products derived from α-acids and β-acids during storage of hops (Humulus lupulus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3121–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, T.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, J. Improving foam performance using colloidal protein–polyphenol complexes: Lactoferrin and tannic acid. Food Chemistry 2022, 377, 131950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Bai, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhao, G.; Chen, B. NADH induces iron release from pea seed ferritin: A model for interaction between coenzyme and protein components in foodstuffs. Food Chemistry 2013, 141, 3851–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Yokoi, S.; Kamada, K.; Kamimura, M. Foam stability and physicochemical properties of beer. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1991, 49, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Li, C. Conformational changes and functional properties of whey protein isolate-polyphenol complexes formed by non-covalent interaction. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 129622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Sun, H.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Functional and conformational changes to soy proteins accompanying anthocyanins: Focus on covalent and non-covalent interactions. Food Chem. 2017, 245, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zou, L.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Tang, J.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, W. Plant-based nanoparticles prepared from proteins and phospholipids consisting of a core multilayer-shell structure: Fabrication, stability, and foamability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6574–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. Mechanism of sodium alginate synergistically improving foaming properties of pea protein isolate: Air/water interface microstructure and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Phillips, M. Proteins at liquid interfaces: III. Molecular structures of adsorbed films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 70, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Johnpaul, I.A.; Hong, K.; Gao, H.; Song, Y.; Lv, C.; Ma, C. Protein Z-based promising carriers for enhancing solubility and bioaccessibility of Xanthohumol. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmeni, I.; Karoui, R.; Blecker, C. Impact of pH on the structure, interfacial and foaming properties of pea protein isolate: Investigation of the structure—Function relationship. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ding, L.; Xia, M.; Huang, X.; Isobe, K.; Handa, A.; Cai, Z. Role of lysozyme on liquid egg white foaming properties: Interface behavior, physicochemical characteristics and protein structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, Z.; Gao, F.; Lu, J.; Cai, G.; Dong, J.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Characterization of Barley Serpin Z7 That Plays Multiple Roles in Malt and Beer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5643–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, E.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Protein changes during malting and brewing with focus on haze and foam formation: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 232, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Lv, C. Interaction Between Iso-α-Acid Extracted from Hops and Protein Z Improves Beer Foam Quality and Stability. Chemistry 2025, 7, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7020065
Chen C, Lv C. Interaction Between Iso-α-Acid Extracted from Hops and Protein Z Improves Beer Foam Quality and Stability. Chemistry. 2025; 7(2):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7020065
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Canyan, and Chenyan Lv. 2025. "Interaction Between Iso-α-Acid Extracted from Hops and Protein Z Improves Beer Foam Quality and Stability" Chemistry 7, no. 2: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7020065
APA StyleChen, C., & Lv, C. (2025). Interaction Between Iso-α-Acid Extracted from Hops and Protein Z Improves Beer Foam Quality and Stability. Chemistry, 7(2), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7020065





