Visible/Red/NIR Light-Mediated NO Donors for Biological Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
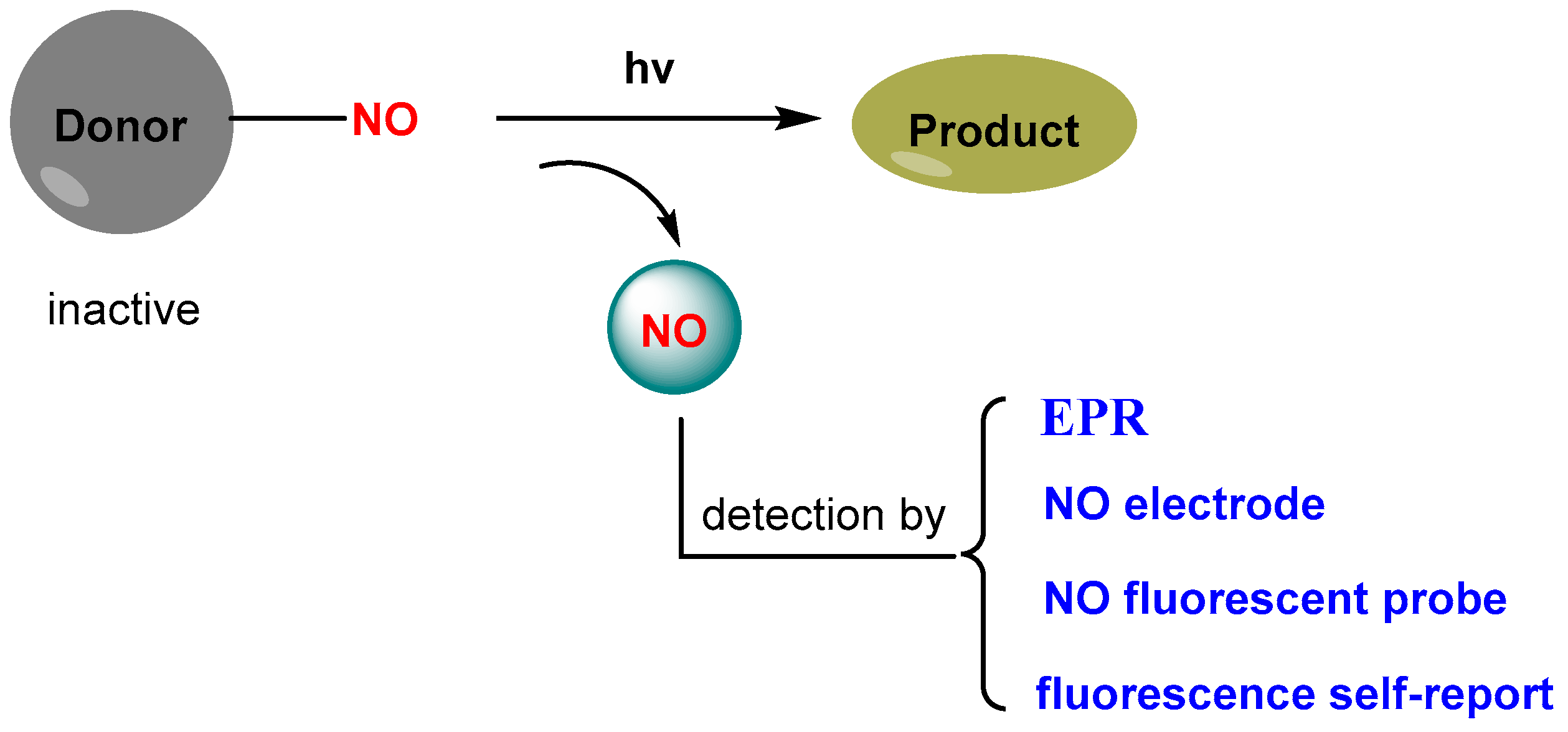
2. Design Strategies for Light-Triggered NO Donors
3. Light-Triggered NO Release and Their Biological Applications
3.1. Single-Function NO Donor
3.2. Dual-Function NO DonorsT
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C.; Calvani, M.; Rizzarelli, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Stella, A.M.G. Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: Neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Higgs, E. The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S193–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garthwaite, J. Concepts of neural nitric oxide-mediated transmission. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 2783–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Loizidou, M.; Ahmed, M.; Charles, I.G. The role of nitric oxide in cancer. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, D.A.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Nitric oxide release: Part I. Macromolecular scaffolds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3731–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, A.B.; Duran, N. Nitric oxide-releasing vehicles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.W.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Nitric oxide release: Part II. Therapeutic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3742–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Saravanakumar, G.; Choi, H.W.; Park, D.; Kim, W.J. A platform for nitric oxide delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.F.; Cai, S.; Yang, Q.H.; Forrest, M.L. Multi-arm polymeric nanocarrier as a nitric oxide delivery platform for chemotherapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3243–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, G.; Yin, W.Y.; Wang, L.M.; Zheng, X.P.; Yan, L.; Li, J.X.; Su, H.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Gu, Z.J.; et al. Controllable generation of nitric oxide by near-infrared-sensitized upconversion nanoparticles for tumor therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.M.; Im, S.; Park, H.; Kim, W.J. Nitric oxide-releasing polymer incorporated ointment for cutaneous wound healing. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Park, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; Yoo, J.C.; Park, C.Y.; Hong, J. Prolonged release period of nitric oxide gas for treatment of bacterial keratitis by amine-rich polymer decoration of nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 8528–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, Y.Q.; Brisbois, E.J.; Bartlett, R.H.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Recent advances in thromboresistant and antimicrobial polymers for biomedical applications: Just say yes to nitric oxide (NO). Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 1161–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schairer, D.O.; Chouake, J.S.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Friedman, A.J. The potential of nitric oxide releasing therapies as antimicrobial agents. Virulence 2012, 3, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrearhami, Z.; Nguyen, T.K.; Namivandi-Zangeneh, R.; Jung, K.; Wong, E.H.H.; Boyer, C. Recent advances in nitric oxide delivery for antimicrobial applications using polymer-based systems. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2945–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.-F.; Liu, H.-Y.; Lin, K.-J.; Chia, W.-T.; Sung, H.-W. A pH-responsive carrier system that generates NO bubbles to trigger drug release and reverse P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9890–9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; He, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, N.; Fan, W.; Lin, L.; Niu, G.; et al. Light-responsive biodegradable nanomedicine overcome es multidrug resistance via NO-enhanced chemosensitization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13804–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, A.K. Nitric oxide: Role in tumour biology and iNOS/NO-based anticancer therapies. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, A.J.; Sullivan, F.J.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. The yin and yang of nitric oxide in cancer progression. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, F.; Wu, H.; Hu, C.; Yu, C.; Wu, S. Preparation of a mitochondria-targeted and NO-releasing nanoplatform and its enhanced pro-apoptotic effect on cancer cells. Small 2014, 10, 3750–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, E.S.; Morales, D.P.; Garcia, J.V.; Reich, N.O.; Ford, P.C. Near-IR mediated intracellular uncaging of NO from cell targeted hollow gold nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17692–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.G.; Xian, M.; Tang, X.P.; Wu, X.J.; Wen, Z.; Cai, T.W.; Janczuk, A.J. Nitric oxide donors: Chemical activities and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1091–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Chakrapani, H. Site-directed delivery of nitric oxide to cancers. Nitric Oxide 2014, 43, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroy-Reveles, A.A.; Leung, Y.; Beavers, C.M.; Olmstead, M.M.; Mascharak, P.K. Near-infrared light activated release of nitric oxide from designed photoactive manganese nitrosyls: strategy, design, and potential as NO donors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4447–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortino, S. Light-controlled nitric oxide delivering molecular assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Chen, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Hu, D.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, G. Delivery of small-molecule drugs and protein drugs by injectable acid-responsive self-assembled COF hydrogels for combinatorial lung cancer treatment. ACS App. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 42354–42368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Jia, L. Recent progress in organic small-molecule fluorescent probe detection of hydrogen peroxide. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 15267–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Ni, P. Efficient click synthesis of a protonized and reduction-sensitive amphiphilic small-molecule prodrug containing camptothecin and gemcitabine for a drug self-delivery system. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3770–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Sletten, E.M. Spatiotemporal control of biology: Synthetic photochemistry toolbox with far-red and near-infrared light. ACS Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 3255–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstain, R.; Slanina, T.; Kand, D.; Klán, P. Visible-to-NIR-light activated release: From small molecules to nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 13135–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, F. Nanocrystals for deep-tissue in vivo luminescence imaging in the near-infrared region. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 554–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Cao, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Pan, Y.; Dai, Z.; Xu, N.; Zuo, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Deep red-light-mediated nitric oxide and photodynamic synergistic antibacterial therapy for the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections. Small 2025, 21, e2408759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laneri, F.; Parisi, C.; Seggio, M.; Fraix, A.; Longobardi, G.; Catanzano, O.; Quaglia, F.; Sortino, S. Supramolecular red-light-photosensitized nitric oxide release with fluorescence self-reporting within biocompatible nanocarriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 6500–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yu, J.; Wu, L.; Ji, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Ma, S.; Miao, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; et al. Fluorescent small molecule donors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 6345–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; An, X.; Duan, H. Recent progress on the organic and metal complex-based fluorescent probes for monitoring nitric oxide in living biological systems. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 1522–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, C.; Seggio, M.; Fraix, A.; Sortino, S. A high-performing metal-free photoactivatable nitric oxide donor with a green fluorescent reporter. ChemPhotoChem 2020, 4, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tian, R.; Zeng, Y.; Chu, C.; Liu, G. Activatable fluorescence probes for “turn-on” and ratiometric biosensing and bioimaging: From NIR-I to NIR-II. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, J.; Yung, B.C.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X. Ratiometric optical nanoprobes enable accurate molecular detection and imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2873–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, C.; Emery, B.P.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.-P.; Tian, H.; Yoon, J.; Sessler, J.L.; James, T.D. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based small-molecule sensors and imaging agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5110–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, W. Nitro-glycerine as a remedy for angina pectoris. Lancet 1879, 113, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friederich, J.A.; Butterworth, J.F. Sodium nitroprusside: Twenty years and counting. Anesth. Analg. 1995, 81, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hrabie, J.A.; Keefer, L.K. Chemistry of the nitric oxide-releasing diazeniumdiolate (“nitrosohydroxylamine”) functional group and its oxygen-substituted derivatives. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sadoni, H.; Ferro, A. S-Nitrosothiols: A class of nitric oxide-donor drugs. Clin. Sci. 2000, 98, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fye, W.B.T. Lauder Brunton and amyl nitrite: A Victorian vasodilator. Circulation 1986, 74, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.P.; Tohda, R.; Tsubaki, M.; Hayashi, M.; Matsubara, R. Photosensitization of fluorofuroxans and its application to the development of visible light-triggered nitric oxide donor. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 9647–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, A.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W. Advanced nitric oxide generating nanomedicine for therapeutic applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 8935–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, B.R.; Ferro, A.A.; Tfouni, E.; Bezerra, C.W.B.; Bagatin, I.; Franco, D.W. Detection of the EPR spectra of NO• in ruthenium(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bonoiu, A.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; He, G.S.; Prasad, P.N. Water-soluble two-photon absorbing nitrosyl complex for light-activated therapy through nitric oxide release. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoth, N.; Mosinger, J.; Gref, R.; Sortino, S. A NO photoreleasing supramolecular hydrogel with bactericidal action. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3458–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Li, B.; Wang, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, C.; Mao, L.; Lin, Y. Fabrication of a flexible and stretchable nanostructured gold electrode using a facile ultraviolet-irradiation approach for the detection of nitric oxide released from cells. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7158–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Nakatsubo, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Kawahara, S.; Kirino, Y.; Nagoshi, H.; Hirata, Y.; Nagano, T. Detection and imaging of nitric oxide with novel fluorescent indicators: Diaminofluoresceins. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbie, J.A.; Klose, J.R.; Wink, D.A.; Keefer, L.K. New nitric oxide-releasing zwitterions derived from polyamines. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Shang, Z.; Wang, C.; Cheng, J.; Qian, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y. Photocalibrated NO release from N-nitrosated napthalimides upon one-photon or two-photon irradiation. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7274–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Geng, W.; Mao, Q.; Kitagishi, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Green-light-triggered and self-calibrated cascade release of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide for synergistic glaucoma therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 30361–30371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Z. Light-triggered fluorescence self-reporting nitric oxide release from coumarin analogues for accelerating wound healing and synergistic antimicrobial applications. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissleder, R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.Y.; Knox, H.J.; Reinhardt, C.J.; Partipilo, G.; Nilges, M.J.; Chan, J. Near-infrared photoactivatable nitric oxide donors with integrated photoacoustic monitoring. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11686–11697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, H.J.; Kim, T.W.; Zhu, Z.; Chan, J. Photophysical tuning of N-oxide-based probes enables ratiometric photoacoustic imaging of tumor hypoxia. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1838–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Beard, P.C.; Bohndiek, S.E. Contrast agents for molecular photoacoustic imaging. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zheng, S.; Xiao, S.; Shen, R.; Liu, S.; Hu, J. Red-light-mediated photoredox catalysis enables self-reporting nitric oxide release for efficient antibacterial treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20452–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraix, A.; Parisi, C.; Longobardi, G.; Conte, C.; Pastore, A.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Alberto, M.E.; Francés-Monerris, A.; Quaglia, F.; et al. Red-light-photosensitized NO release and its monitoring in cancer cells with biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 3887–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, H.; Ieda, N.; Hotta, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kimura, K.; Nakagawa, H. A yellowish-green-light-controllable nitric oxide donor based on N-nitrosoaminophenol applicable for photocontrolled vasodilation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiani, P.; Burini, G. Fluorometric determination of nitrite. Talanta 1986, 33, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Buga, G.M.; Wood, K.S.; Byrns, R.E.; Chaudhuri, G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9265–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lin, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, A.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Photo-controlled and photo-calibrated nanoparticle enabled nitric oxide release for antibacterial and anti-biofilm applications. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 33358–33364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Q. A fluorogenic nitric oxide donor induced by yellow LED light for cells proliferation inhibition and imaging. Nitric Oxide 2024, 145, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Nagae, O.; Kato, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Fukuhara, K.; Miyata, N. Photoinduced nitric oxide release from nitrobenzene derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11720–11726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishikawa, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Furuta, T.; Fukuhara, K.; Tsumoto, H.; Suzuki, T.; Miyata, N. Photoinduced nitric oxide release from a hindered nitrobenzene derivative by two-photon excitation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7488–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomski, M.W.; Palmer, R.M.J.; Moncada, S. The role of nitric oxide and cGMP in platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 148, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogo, N.; Magid, K.S.; Shaw, C.A.; Webb, D.J.; Megson, I.L. Inhibition of human platelet aggregation by nitric oxide donor drugs: Relative contribution of cGMP-independent mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xia, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, F.-G.; Wang, H.; Chen, D.; et al. A water-soluble; green-light triggered, and photo-calibrated nitric oxide donor for biological applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraix, A.; Blangetti, M.; Guglielmo, S.; Lazzarato, L.; Marino, N.; Cardile, V.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Manet, I.; Fruttero, R.; Gasco, A.; et al. Light-tunable generation of singlet oxygen and nitric oxide with a bichromophoric molecular hybrid: A bimodal approach to killing cancer cells. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavida, B.; Khineche, S.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Garban, H. Therapeutic potential of nitric oxide in cancer. Drug Resist. Updates 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riganti, C.; Miraglia, E.; Viarisio, D.; Costamagna, C.; Pescarmona, G.; Ghigo, D.; Bosia, A. Nitric oxide reverts the resistance to doxorubicin in human colon cancer cells by inhibiting the drug efflux. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boo, S.; Kopecka, J.; Brusa, D.; Gazzano, E.; Matera, L.; Ghigo, D.; Bosia, A.; Riganti, C. iNOS activity is necessary for the cytotoxic and immunogenic effects of doxorubicin in human colon cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegaev, K.; Riganti, C.; Lazzarato, L.; Rolando, B.; Guglielmo, S.; Campia, I.; Fruttero, R.; Bosia, A.; Gasco, A. Nitric oxide donor doxorubicin conjugates accumulate into doxorubicin resistant human colon cancer cells inducing cytotoxicity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riganti, C.; Rolando, B.; Kopecka, J.; Campia, I.; Chegaev, K.; Lazzarato, L.; Federico, A.; Fruttero, R.; Ghigo, D. Mitochondrialtargeting nitrooxy-doxorubicin: A new approach to overcome drug resistance. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, C.; Moret, F.; Fraix, A.; Menilli, L.; Failla, M.; Sodano, F.; Conte, C.; Quaglia, F.; Reddi, E.; Sortino, S. Doxorubicin–NO releaser molecular hybrid activatable by green light to overcome resistance in breast cancer cells. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapozzi, V.; Ragno, D.; Guerrini, A.; Ferroni, C.; della Pietra, E.; Cesselli, D.; Castoria, G.; Di Donato, M.; Saracino, E.; Benfenati, V.; et al. Androgen receptor targeted conjugate for bimodal photodynamic therapy of prostate cancer in vitro. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Ridnour, L.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Flores-Santana, W.; Switzer, C.H.; Donzelli, S.; Hussain, P.; Vecoli, C.; Paolocci, N.; Ambs, S.; et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: Implications in cellular signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Silverman, R.B. Revisiting heme mechanisms. A perspective on the mechanisms of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), heme oxygenase (HO), and cytochrome P450s (CYP450s). Biochemistry 2008, 47, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiburcio-Félix, R.; Cisneros, B.; Hernández-Kelly, L.C.R.; Hernández-Contreras, M.A.; Luna-Herrera, J.; Rea-Hernández, I.; Jiménez-Aguilar, R.; Olivares-Bañuelos, T.N.; Ortega, A. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase in cultured cerebellar bergmann glia: Glutamate-dependent regulation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, J.K.Y. Gut microbiota; nitric oxide, and microglia as prerequisites for neurodegenerative disorders. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D.P.; Hossain, S.; Xu, Y.; Boon, E.M. Nitric oxide regulation of bacterial biofilms. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3717–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chug, M.K.; Feit, C.; Brisbois, E.J. Increasing the Lifetime of Insulin Cannula with Antifouling and Nitric Oxide Releasing Properties. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5965–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Espey, M.G.; Ridnour, L.A.; Hofseth, L.J.; Mancardi, D.; Harris, C.C.; Wink, D.A. Hypoxic inducible factor 1α, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and p53 are regulated by distinct threshold concentrations of nitric oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8894–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Ridnour, L.A.; Espey, M.G.; Donzelli, S.; Ambs, S.; Hussain, S.P.; Harris, C.C.; DeGraff, W.; Roberts, D.D.; Mitchell, J.B.; et al. Superoxide fluxes limit nitric oxide-induced signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25984–25993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, S.; Singh, R.; Hernandez, E.; Wu, G.; Chaudhuri, G. Nitric oxide in physiologic concentrations targets the translational machinery to increase the proliferation of human breast cancer cells: Involvement of mammalian target of rapamycin/eIF4E pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, S.; Singh, R.; Freije, W.A.; Chaudhuri, G. MKP-1-induced dephosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase is essential for triggering nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8853–8860. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.A.; Simons, J.W.; Mabjeesh, N.J. HIF at the crossroads between ischemia and carcinogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 200, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borutaite, V.; Brown, G.C. S-nitrosothiol inhibition of mitochondrial complex I causes a reversible increase in mitochondrial hydrogen peroxide production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2006, 1757, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hetrick, E.M.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Analytical chemistry of nitric oxide. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.N. Nitric oxide measurement by chemiluminescence detection. Neuroprotocols 1992, 1, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedioui, F.; Villeneuve, N. Electrochemical nitric oxide sensors for biological samples–principle, selected examples and applications. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privett, B.J.; Shin, J.H.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Electrochemical nitric oxide sensors for physiological measurements. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T. Nitric oxide and tumors: From small-molecule donor to combination therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkovics, G.; Perez-Lloret, M.; Afonso, D.; Darcsi, A.; Béni, S.; Fenyvesi, É.; Malanga, M.; Sortino, S. A multifunctional β-cyclodextrin-conjugate photodelivering nitric oxide with fluorescence reporting. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraix, A.; Manet, I.; Ballestri, M.; Guerrini, A.; Dambruoso, P.; Sotgiu, G.; Varchi, G.; Camerin, M.; Coppellotti, O.; Sortino, S. Polymer nanoparticles with electrostatically loaded multicargo for combined cancer phototherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








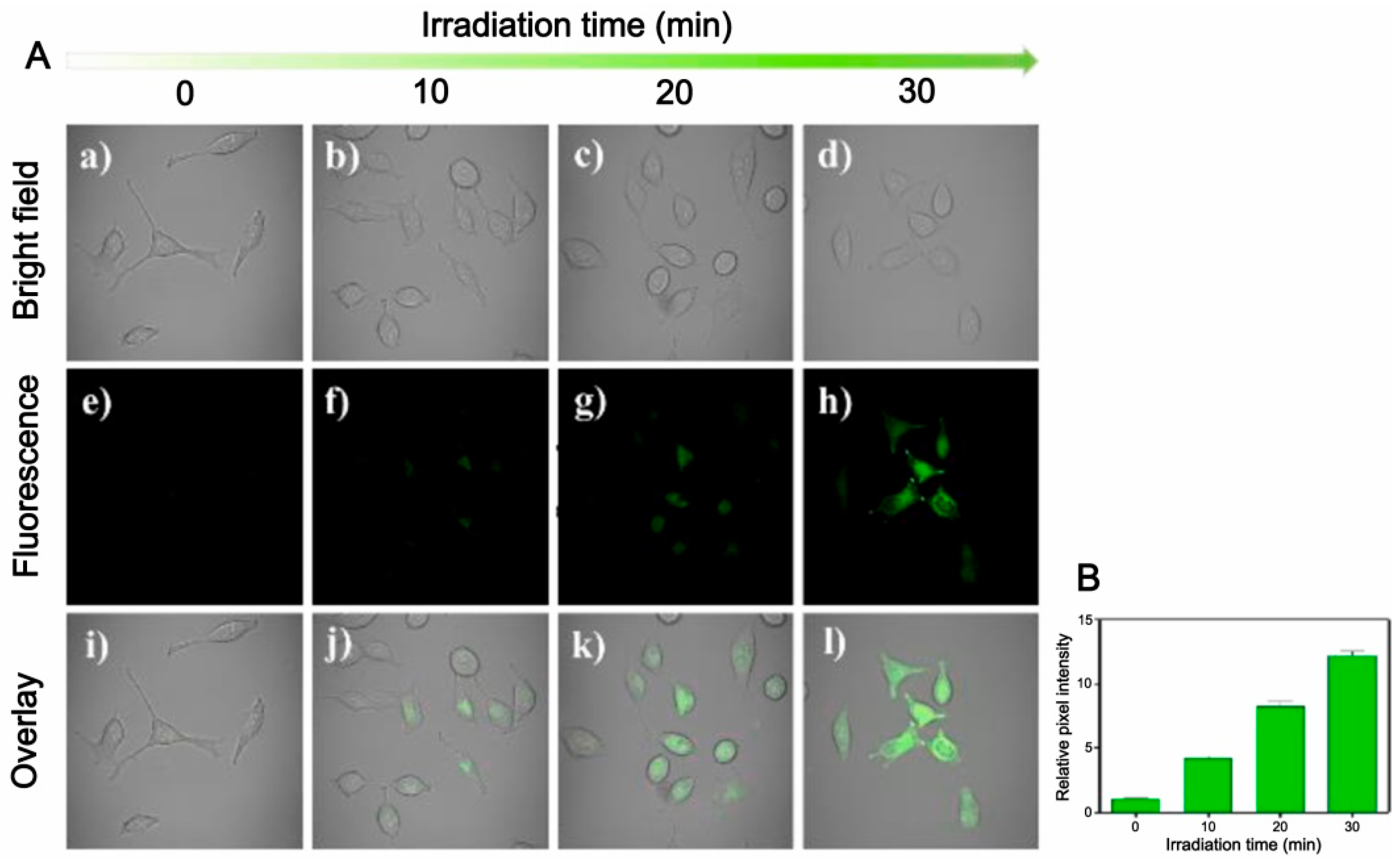
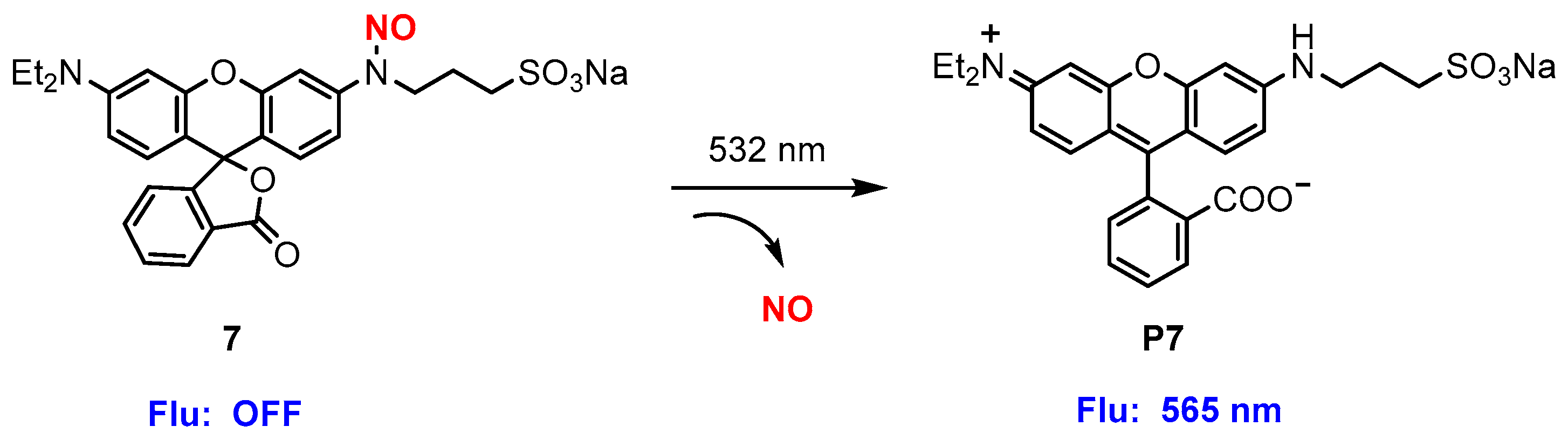

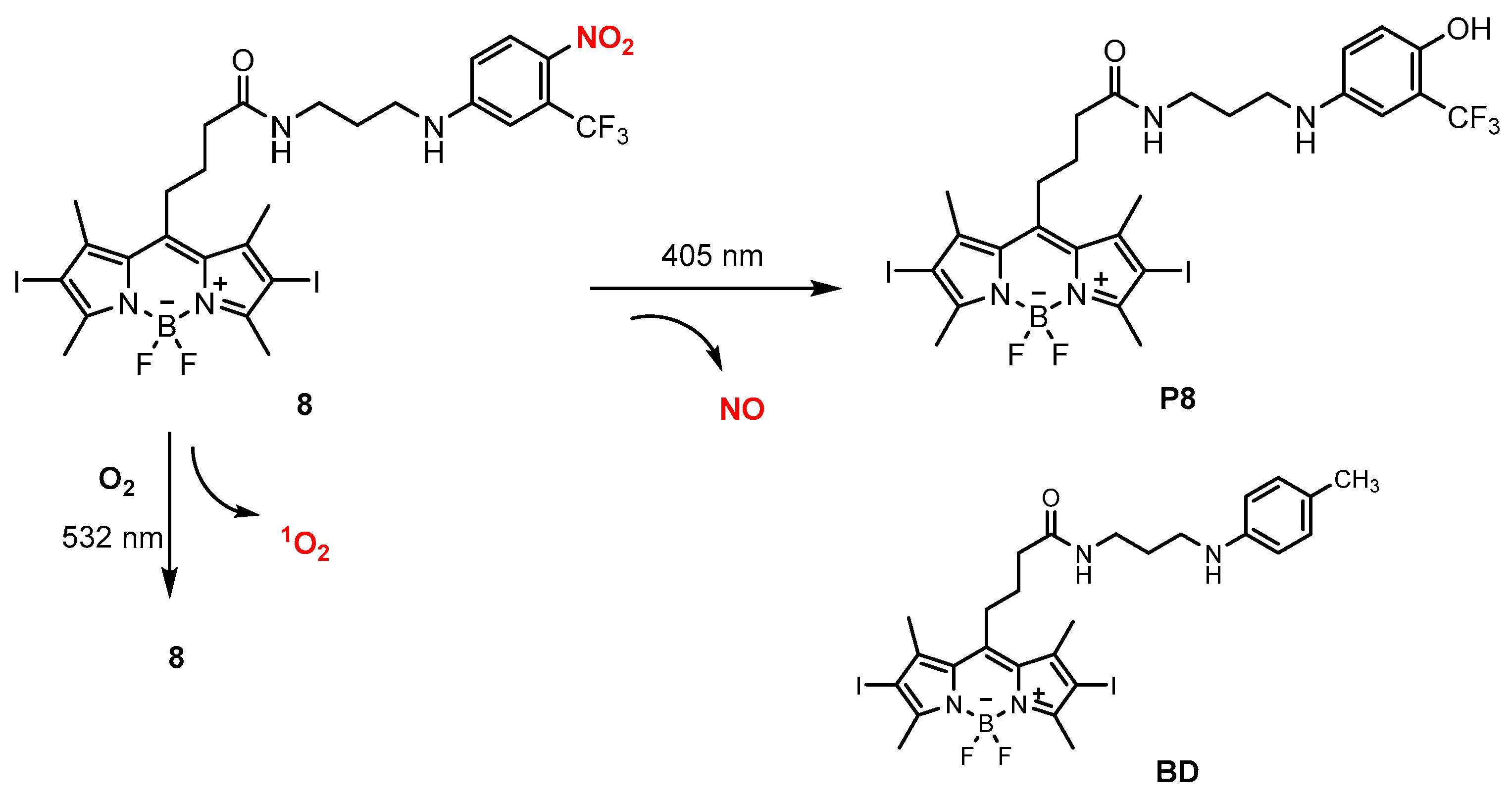

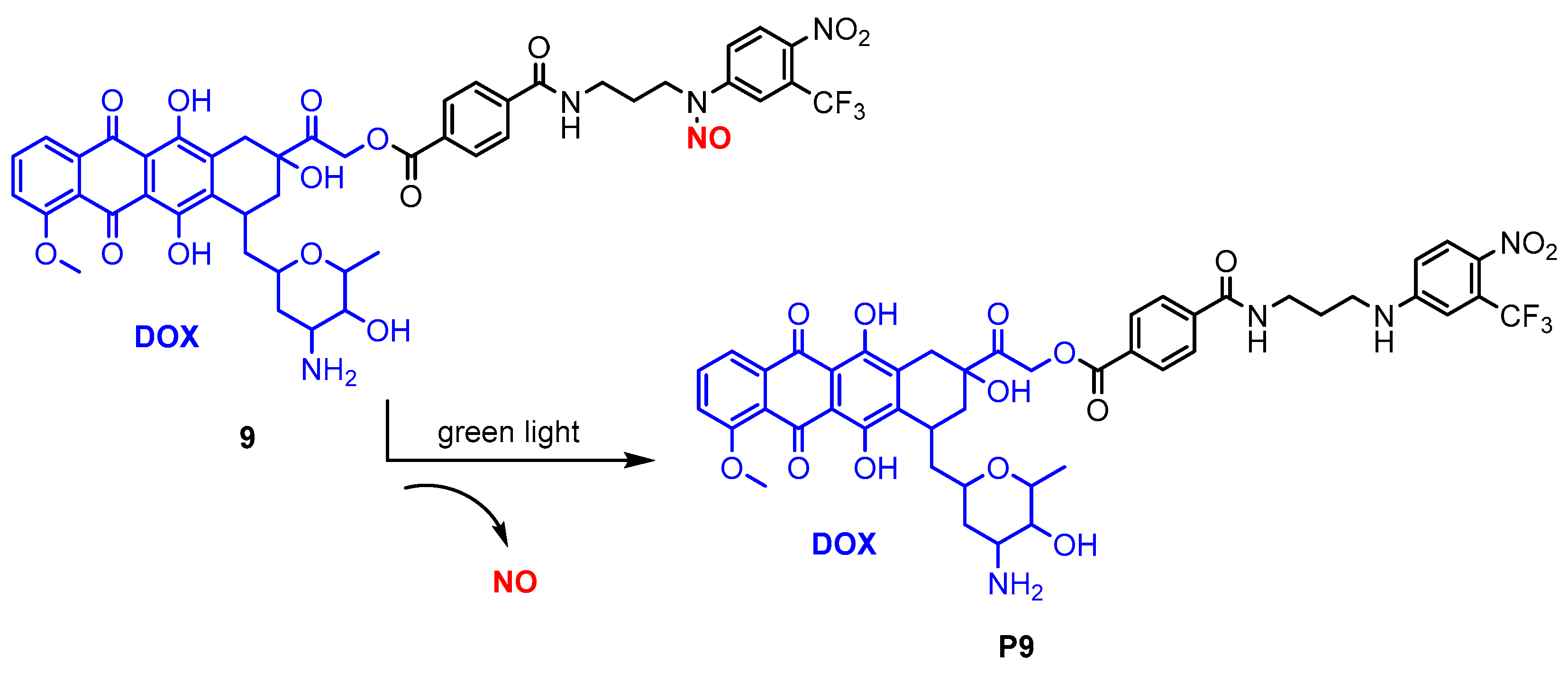


| Donor | Chemical Structure | Class a | Irradiation | Testing Mode | Biological Application | Ref b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
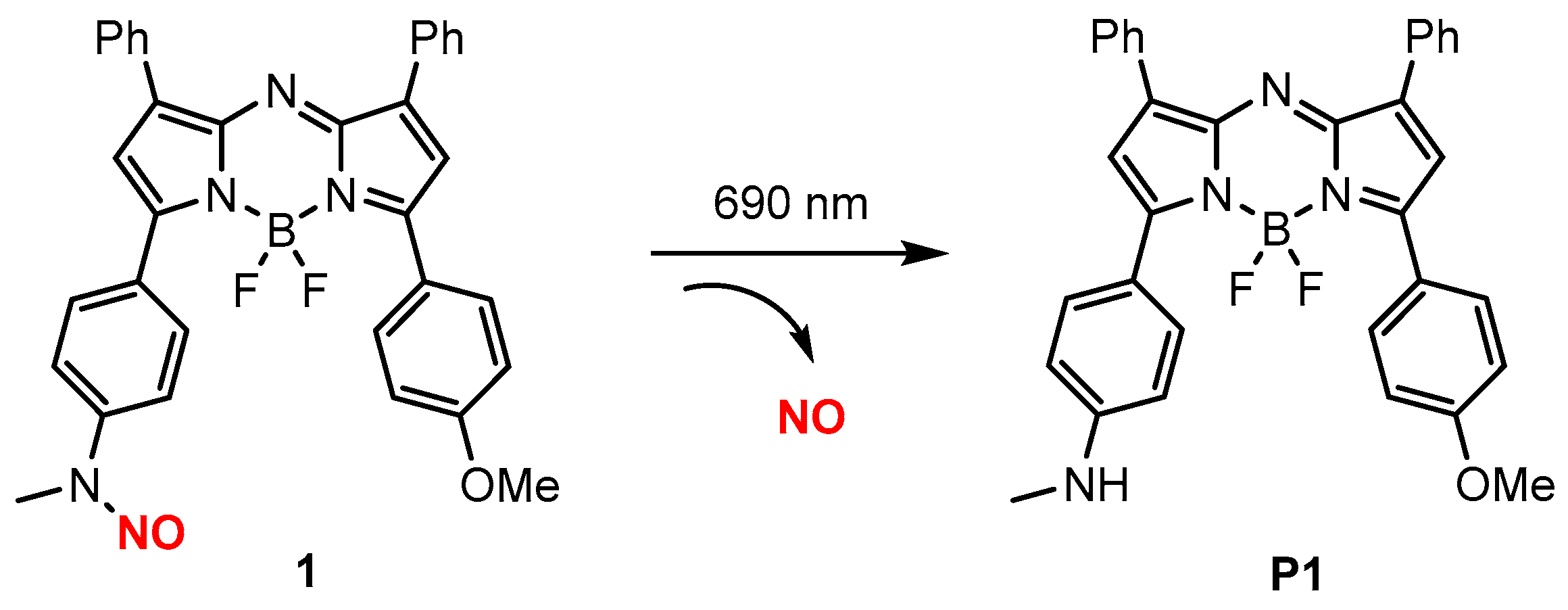
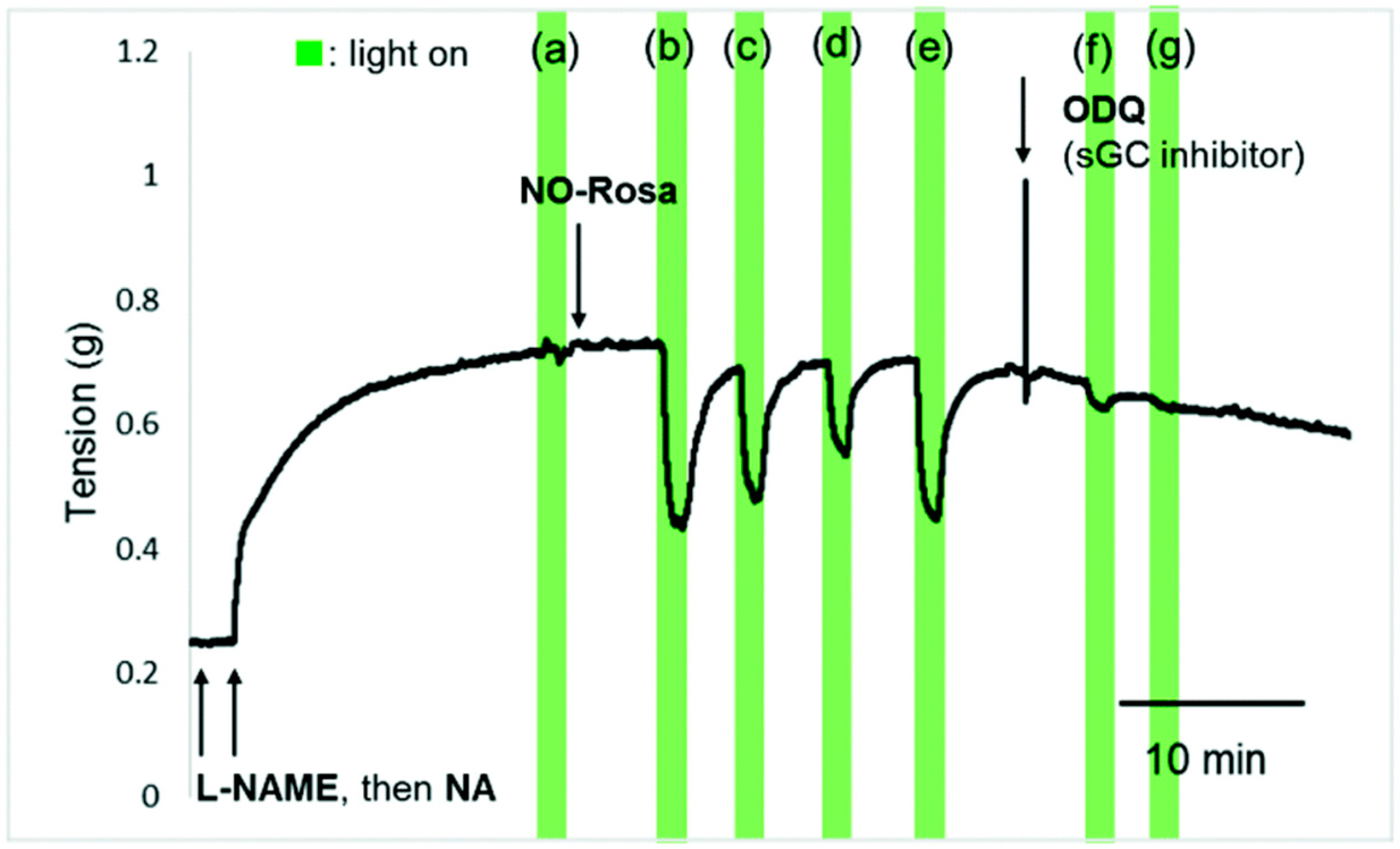
| 1 |  | A | 690 nm | In vivo | Antitumor | [58] |
| 2 | 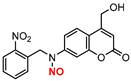 | A | 630 nm | In vivo | Antimicrobial | [61] |
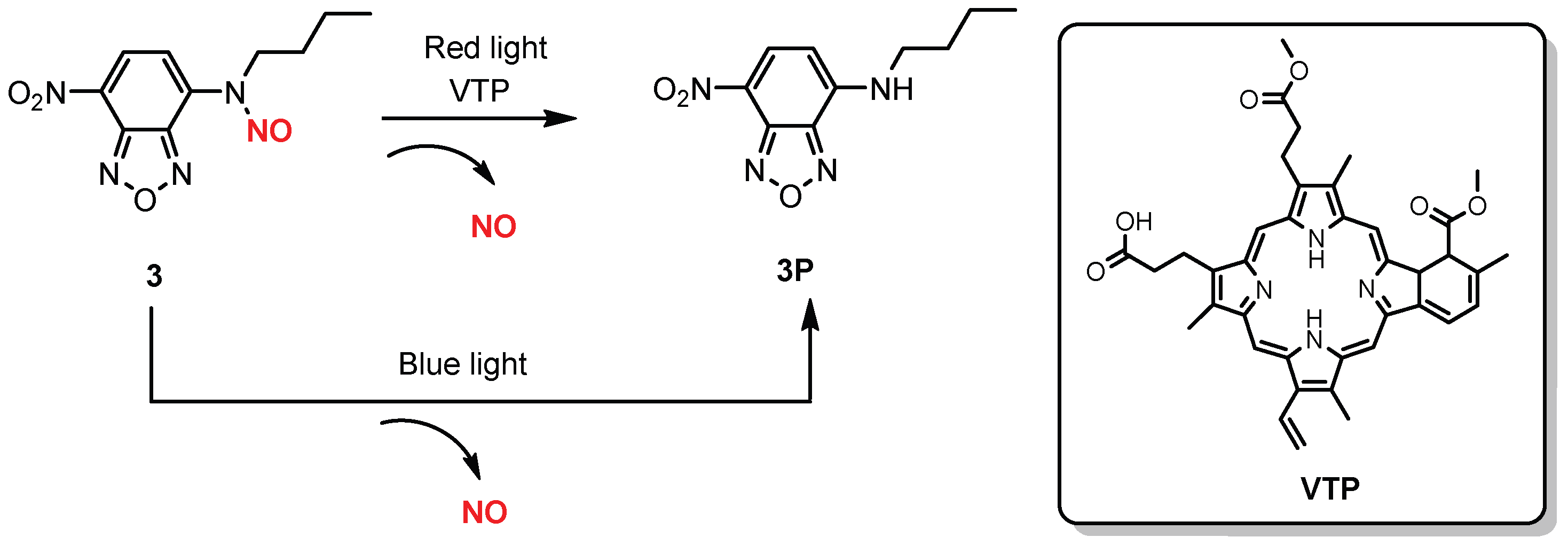
| 3 |  | A | 620–630 nm | In vitro | Antitumor | [62] |
| 4 |  | A | 530–590 nm | Ex vivo | Vasodilation | [63] |
| 5 |  | A | 450 nm | In vitro | Antimicrobial | [66] |
| 6 | 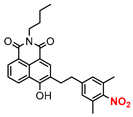 | A | Yellow LED | In vitro | Antitumor | [67] |
| 7 |  | A | 532 nm | In vitro | Platelet aggregation | [72] |
| 8 |  | B | 405 and 532 nm | In vitro | Antitumor | [73] |
| 9 | 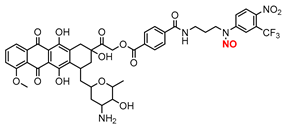 | B | Green light | In vitro | Antitumor | [79] |
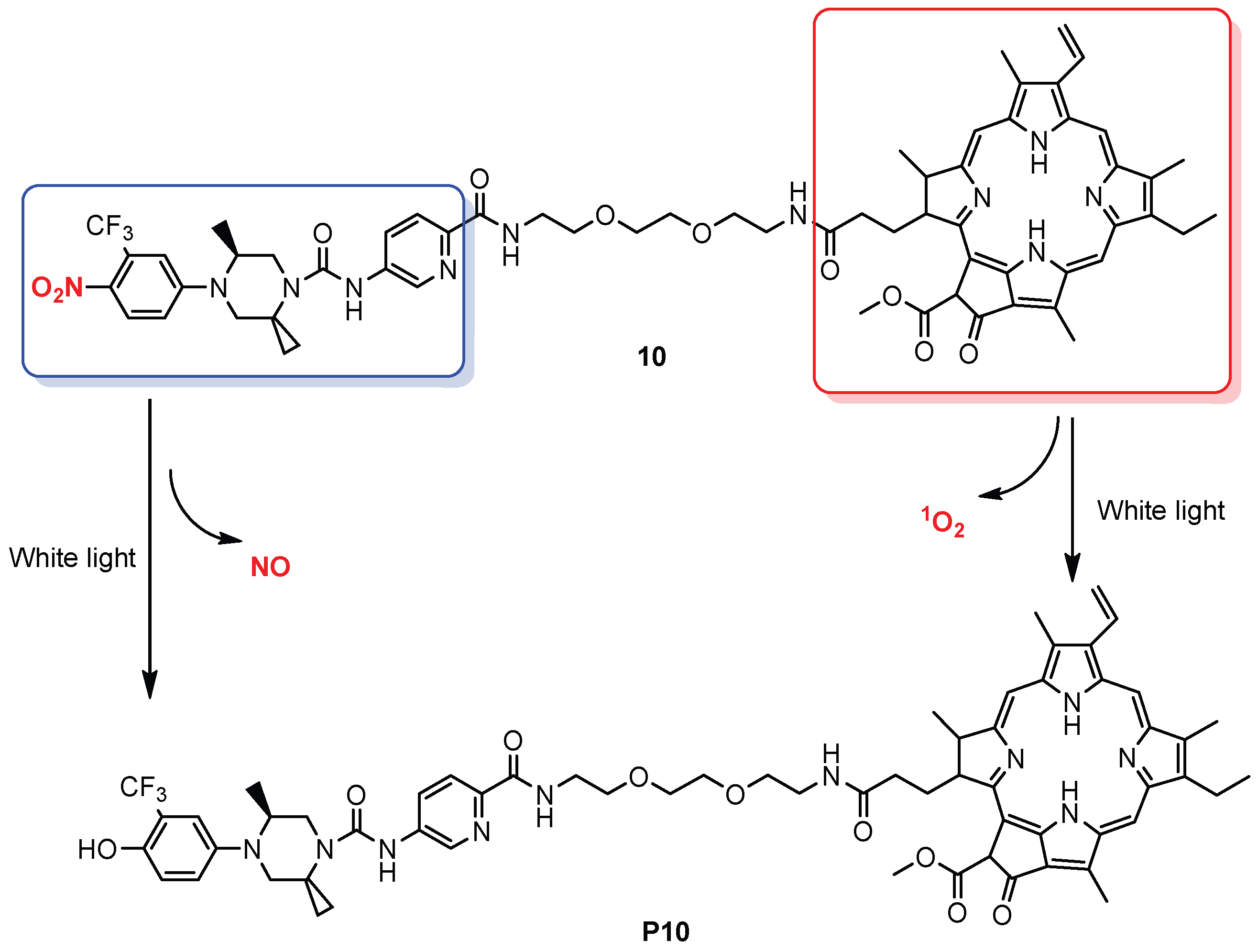
| 10 |  | B | White light | In vitro | Antitumor | [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y. Visible/Red/NIR Light-Mediated NO Donors for Biological Applications. Chemistry 2025, 7, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030066
Chen Y. Visible/Red/NIR Light-Mediated NO Donors for Biological Applications. Chemistry. 2025; 7(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi. 2025. "Visible/Red/NIR Light-Mediated NO Donors for Biological Applications" Chemistry 7, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030066
APA StyleChen, Y. (2025). Visible/Red/NIR Light-Mediated NO Donors for Biological Applications. Chemistry, 7(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030066






