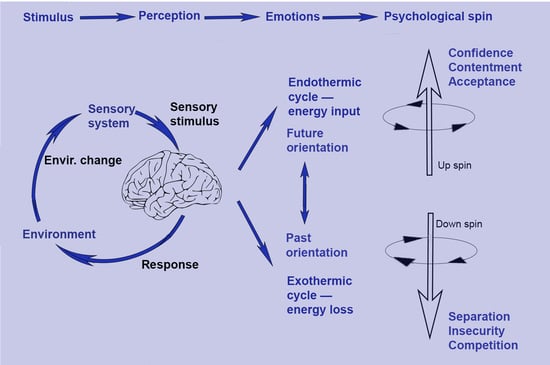
What Is Psychological Spin? A Thermodynamic Framework for Emotions and Social Behavior
Abstract
Share and Cite
Deli, E.K. What Is Psychological Spin? A Thermodynamic Framework for Emotions and Social Behavior. Psych 2023, 5, 1224-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych5040081
Deli EK. What Is Psychological Spin? A Thermodynamic Framework for Emotions and Social Behavior. Psych. 2023; 5(4):1224-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych5040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeli, Eva K. 2023. "What Is Psychological Spin? A Thermodynamic Framework for Emotions and Social Behavior" Psych 5, no. 4: 1224-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych5040081
APA StyleDeli, E. K. (2023). What Is Psychological Spin? A Thermodynamic Framework for Emotions and Social Behavior. Psych, 5(4), 1224-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych5040081