Abstract
In an effort to reduce the occurrence of chlorine derived residues such as chlorate and trichloromethane (TCM) in milk and ultimately in dairy products, ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning of milking equipment became compulsory in the Republic of Ireland (ROI) from January 2021. While data exists on TCM levels in bulk tank milk, little is known about the prominence and typical levels (mg/kg) of chlorate residue in bulk tank milk. To address this, 3625 bulk milk samples were collected from six milk processors and were analysed for chlorate and TCM residues across 2020 and 2021, with 2020 representing a period before chlorine-free cleaning was introduced and 2021 being the period after chlorine removal. In 2020, 15% of the samples analysed had detectable levels of chlorate (0.0020–1.6 mg/kg), but this reduced to 8% in 2021 (0.0020–3.9 mg/kg), following the introduction of ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning. Chlorate and TCM residues have not been totally eliminated because sources of residue other than cleaning chemicals exist, i.e., chlorinated water.
1. Introduction
Chlorine has formed the basis of cleaning routines across the dairy industry for decades due to its excellent bactericidal and peptising properties [1]. However, chlorine has negative aspects as well, such as the occurrence of disinfectant by-product residues that are deleterious to human health. Chlorate and trichloromethane (TCM) are examples of such residues. At high concentrations, chlorate is a significant threat to human health due to its capacity to inhibit the function of the thyroid gland, particularly that of infants and young children [2], and it is a regulated residue in the European Union (EU) [3]. A maximum residue limit (MRL) of 0.10 mg/kg is imposed for chlorate in milk in its ‘ready to use form’ [3].
Chlorate has previously been detected in both staple dairy products and dried dairy ingredients produced in Ireland [4,5,6]. Chlorate is of particular pertinence to products that are destined for consumption by infants and young children, i.e., infant milk formula (IMF) [7]. A specific MRL of 0.01 mg/kg is in place for such specialist nutrition products [8]. Approximately 13% of the world’s IMF is produced in the ROI [9], earning approximately one billion euros on an annual basis [7]. Butter is of similar economic importance to the ROI, with an export value of 1.3 billion euros in 2023 [10].
In contrast to chlorate, TCM is not a product of chlorine degradation. Instead, it forms as a result of the ‘haloform reaction’ which occurs when chlorine combines with a substance that contains methyl ketones, i.e., milk [11]. As opposed to targeting the thyroid gland, TCM has carcinogenic properties [12]. TCM is a lipophilic residue and therefore, most likely to be present and concentrate in fat rich products such as butter [1,12]. There are no statutory limits in place for TCM in milk or butter, but milk processors in the ROI observe industry-imposed limits. Milk destined for use in butter manufacture must have a TCM content of <0.00124 mg/kg to yield butter with a TCM level of <0.0248 mg/kg [13].
In an effort to minimise the incidence of chlorate and TCM in farm bulk milk and subsequently in manufactured milk products such as IMF and butter, dairy processors in the ROI made the collective decision to prohibit the use of chlorine-based chemicals for cleaning and disinfection on both dairy farms and in dairy processing plants. This came into effect on 1 January 2021 [14]. The introduction of alternative ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning protocols, which predominantly consist of sodium hydroxide detergents, phosphoric/nitric acid descalers and peracetic acid (for disinfection), were introduced to the industry in advance of January 2021, i.e., over 2019 and 2020 [14,15].
Despite the dairy industry’s commitment to the removal of chlorine from cleaning protocols, there was a paucity of data regarding chlorate levels in milk produced on commercial dairy farms in the ROI. Moreover, little was known about the effect that the prohibition of chlorine would have on TCM levels in milk, which were already being monitored in conjunction with strategies focusing on the cognisant use of chlorine to minimise TCM incidence in bulk tank milk [12,13]. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to ascertain the baseline levels of chlorate and TCM in bulk tank milk produced in the ROI when chlorine was still in use on the majority of farms (2020), to ascertain if the use of chlorine-free cleaning led to a reduction in chlorate and TCM levels in bulk tank milk, relative to when chlorine was still in use, and to determine if there were any seasonal trends with regard to chlorate and TCM levels in milk.
2. Materials and Methods
Bulk milk samples analysed as part of this study were supplied by six individual milk processing companies from across the ROI, hereafter referred to as processors A–F. Milk production in the ROI predominantly occurs between March and November because the majority of dairy farms operate spring calving dairy herds in order to align milk production with grass growth [16]. Therefore, sampling spanned the main milk producing months (March to November) of 2020 and 2021. Across 2020 and 2021, a total of 3625 bulk milk samples were analysed for chlorate, of which 3117 samples were also analysed for TCM. Five of the six collaborating milk processors (processors A–E) were already submitting samples on a monthly basis for TCM analysis as part of an industry-led TCM monitoring programme based at Teagasc, Moorepark, Cork, Ireland [13]. Therefore, the samples used for this study were a randomly selected subset of each milk processor’s monthly submission of bulk milk samples. This random subset was retained for chlorate analysis following TCM analysis (TCM status unknown at this time). Processor F selected bulk milk samples at random at their own premises before transporting them to Teagasc, Moorepark, Cork, Ireland where they were retained for chlorate analysis only. The samples procured during each month of both 2020 and 2021 were not from the same farms, and no background information, such as detail on cleaning procedures, was available for any of the farms. If the same farms were sampled more than once during the study, it was coincidence. The number of samples that were selected at random from each processor was equivalent to 2.5% of the total number of milk suppliers that each had. Therefore, the number of samples retained from each processor depended on the number of milk suppliers that each had.
2.1. TCM Analysis
Upon arrival at the Milk Quality laboratory in Moorepark, samples were logged and stored in a −20 °C freezer. In advance of TCM analysis, samples were removed from the freezer and defrosted overnight (16 h) at room temperature. Once defrosted, 2 mL of milk was removed from each sample and used for TCM analysis (remainder of the sample remaining in the original sample bottle). TCM was analysed using head space gas chromatography coupled with electron capture detection (HS-GC-ECD) in accordance with the method outlined by Resch and Guthy [17]. The minimum level of TCM that could be reliably detected using this method was 0.00010 mg/kg. Once TCM analysis was complete, the subset of samples randomly chosen for inclusion in this study were retained for chlorate analysis in a −20 °C freezer.
2.2. Chlorate Analysis
On a monthly basis, bulk milk samples were transported in their frozen state (on ice and in insulated containers) to the Food Safety laboratory at Teagasc, Ashtown, Dublin, Ireland for chlorate analysis. This analysis was conducted using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) in accordance with methods described by [18].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA, 2016). The generalized linear model (GLM) procedure was used for the comparison of both TCM and chlorate levels (where detected) in milk across spring, summer and autumn (spring = March/April/May; summer = June/July/August; autumn = September/October/November) and entire milk production seasons (2020/2021). Means were compared using the Tukey–Kramer test. All tests of difference were at a statistical significance level α = 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chlorate
When results are examined at a fundamental level, the majority (85% in 2020 and 92% in 2021) of samples analysed displayed non-detectable levels of chlorate (<0.0020 mg/kg). Only 15% of the samples analysed in 2020 contained detectable levels of chlorate (≥0.0020 mg/kg), with the chlorate detection rate reducing to 8% in 2021 (Table 1). This significant reduction (p < 0.01) in chlorate occurrence is indicative of the benefits of removing chlorine from the cleaning process. Previous research found that even where chlorinated chemicals were removed from the bulk tank wash protocol alone, reductions in chlorate occurrence were found relative to total chlorine-based cleaning, with further reductions observed when chlorine-free cleaning of both the plant and bulk tank were implemented [19].

Table 1.
Chlorate levels in bulk tank milk sampled in 2020 and 2021.
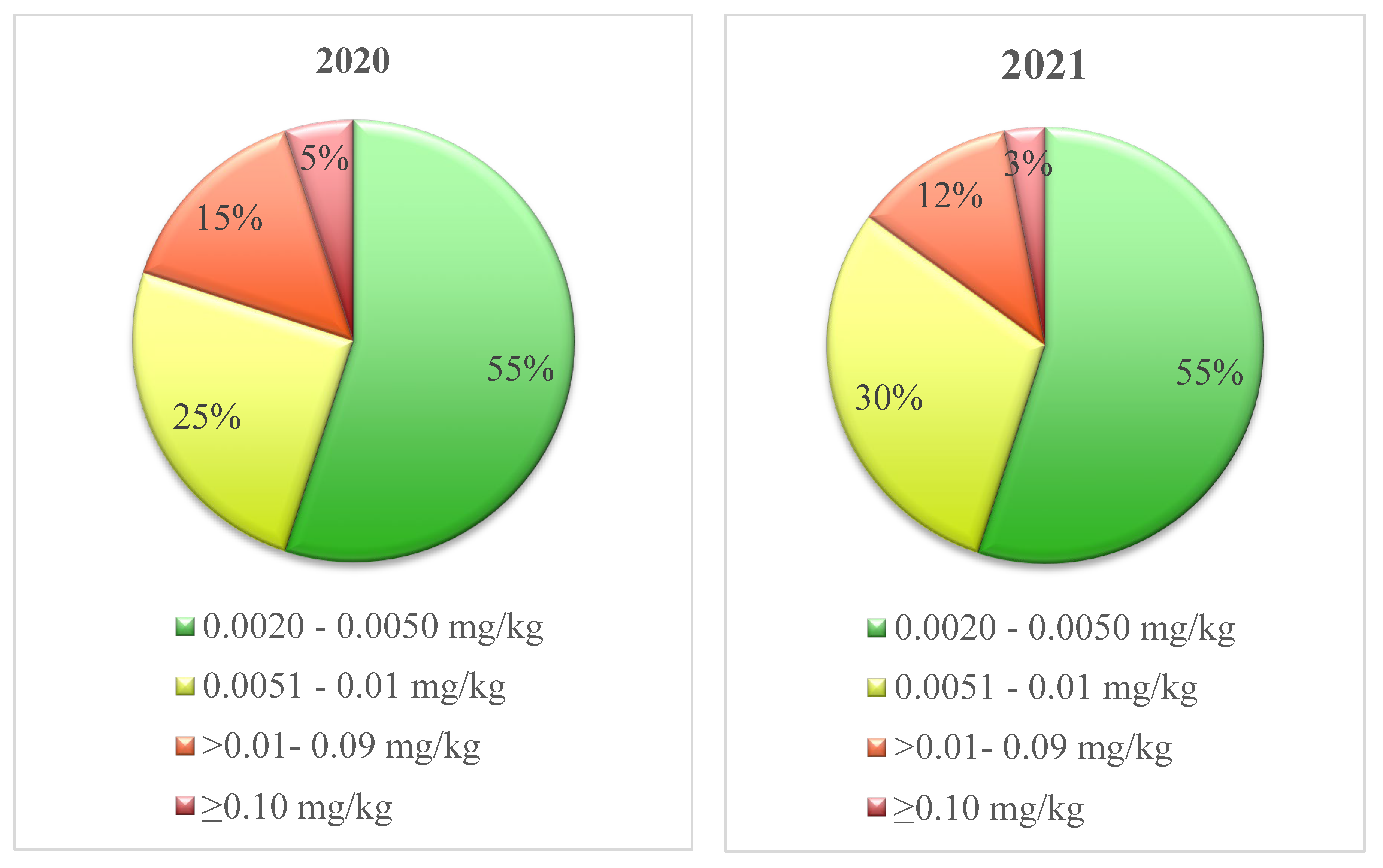
Aside from occurrence rate, the actual levels (mg/kg) of chlorate detected in milk must also be considered. Mean chlorate levels in 2020 and 2021 were not significantly different (p > 0.05). Unexpectedly, the mean level of chlorate in bulk tank milk (where detected) in 2020 (0.0275 mg/kg) was actually lower than the mean level (where detected) in 2021 (0.040 mg/kg). This higher mean chlorate level in 2021 may be the attributed to a minority of milk suppliers who did not correctly employ ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning, consequently had hygiene problems in the milking system and then resorted to intense ‘chlorine cleaning’ to address these problems. Notwithstanding the higher mean chlorate level in 2021, the adoption of ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning had a positive impact on chlorate levels in bulk tank milk. As indicated in Figure 1, the percentage of samples with higher levels of chlorate in 2021 was lower (relative to 2020). For example, in 2020, 25% of samples with detected levels of chlorate had levels between 0.0051 and 0.01 mg/kg, with a further 15% of samples with chlorate levels between 0.01 mg/kg and 0.09 mg/kg. In 2021, a greater percentage (30%) of samples were in the 0.0051 to 0.01 mg/kg category as a result of fewer samples being in the >0.01–0.09 mg/kg and ≥0.10 mg/kg categories. This clearly demonstrates a reduction in the number of samples with high levels of chlorate. In both 2020 (95% of samples < 0.10 mg/kg) and 2021 (97% of samples < 0.10 mg/kg), a minority of samples analysed displayed levels of chlorate that were in excess of the EU MRL (0.10 mg/kg). Therefore, it is clear that even when chlorinated chemicals were still in use (2020), the chlorate burden in bulk tank milk was low and statutory compliance was high.
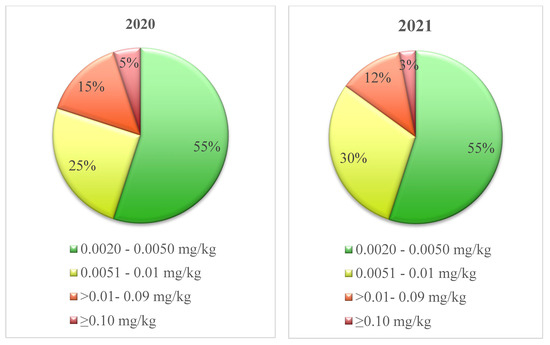
Figure 1.
Breakdown of chlorate levels in bulk tank milk samples in which chlorate was detected in 2020 and 2021.
In both 2020 and 2021, mean chlorate levels were lowest in summer (June, July and August) relative to levels detected in both spring (March, April and May) and autumn (September, October and November) (Table 2). Similar trends have previously been observed and have been attributed to the dilution of chlorate residue in larger quantities of milk in summer (mid-lactation) relative to autumn (late lactation) [4].

Table 2.
Mean chlorate levels in bulk tank milk sampled in spring, summer and autumn of 2020 and 2021.
When studied at milk processor level, it is clear that the incidence of chlorate at detectable levels varies between milk processors (Figures S1 and S2; Supplementary Materials). For example, in 2020, 62%, 71%, 84% and 87% of samples from processors A, E, D and F, respectively, did not have chlorate detected (<0.0020 mg/kg). This is in contrast to processors B and C who had no detectable level of chlorate (<0.0020 mg/kg) in 92% of samples analysed in 2020. In 2021, following the mandatory uptake of chlorine-free cleaning on the majority of farms, all processors with the exception of processors D (87%) and E (78%) had <0.0020 mg/kg of chlorate in ≥90% of samples analysed. This is evidence of progress on the part of all processors, but particularly processor A, who increased the percentage of samples with non-detectable levels of chlorate by 28% in 2021 relative to 2020.
The presence of chlorate in some milk produced in 2021 is testament to the fact that implementing ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning alone will not eliminate chlorate residue in milk. Other than the continued use of chlorinated chemicals on some farms in 2021, a further reason for the remaining chlorate is the use of chlorinated water for washing milking equipment [20]. Chlorinated water (water treated with sodium hypochlorite) can cause chlorate contamination of milk where it has not been drained away properly pre-milking. Improper drainage leads to milk and chlorinated water mixing, thereby resulting in chlorate residue in milk [20]. The presence of residual chlorate in sodium hydroxide detergent is another possible cause of chlorate in bulk tank milk where ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning is employed [21]. As a consequence of its manufacture alongside chlorine during the ‘chlor-alkali’ process, sodium hydroxide contains chlorate, albeit at levels that are approximately 140 times lower [21,22]
3.2. Trichloromethane
Relative to 2020 (n = 356), there was a reduction in the number of samples analysed in 2021 (n = 88) that were in excess of the industry limit of 0.00124 mg/kg for TCM in milk (Table 3). Moreover, the mean level of TCM detected in milk samples was also significantly lower (p <0.001) in 2021 relative to 2020 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Trichloromethane (TCM) levels in bulk tank milk in 2020 and 2021.
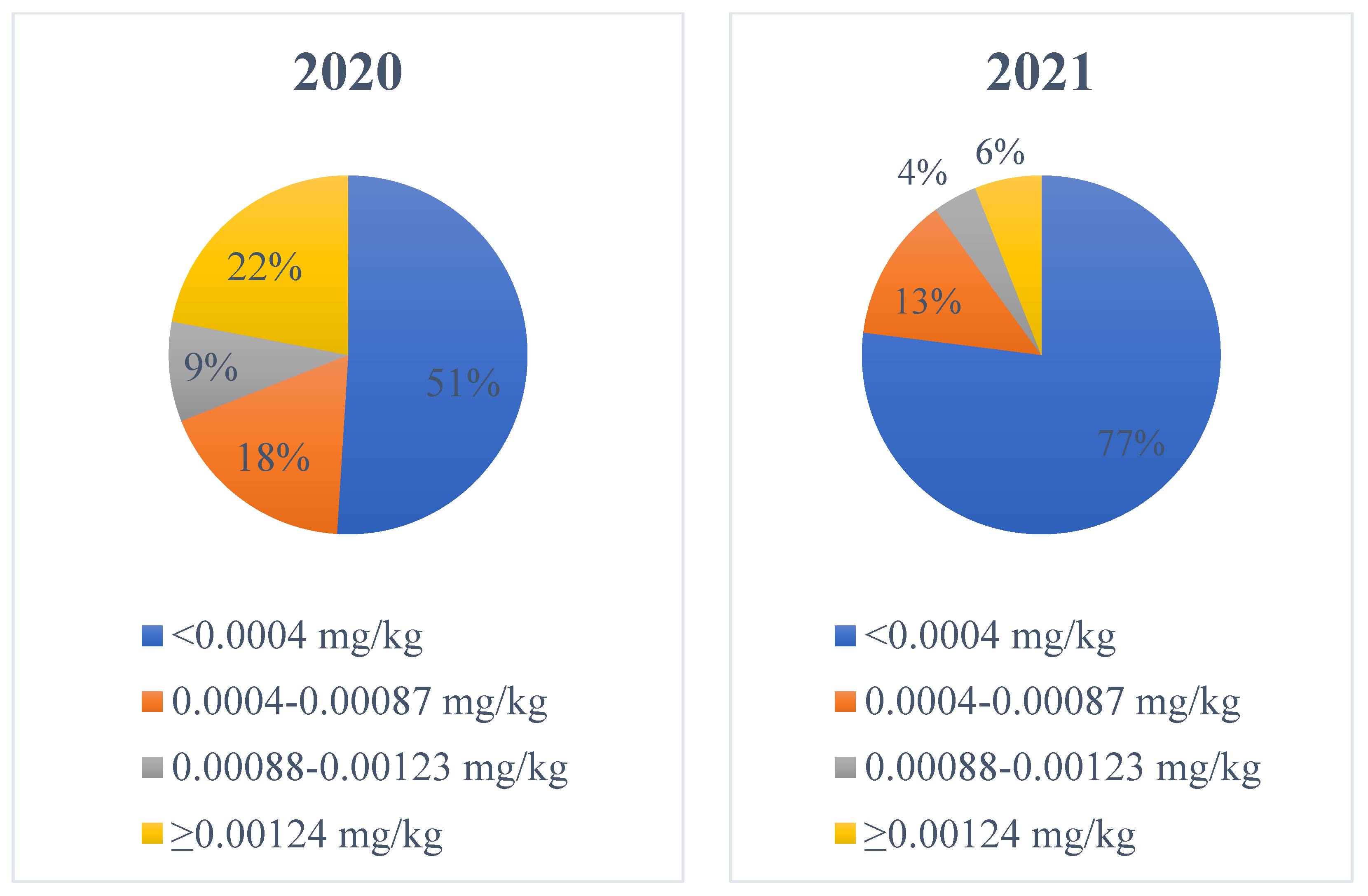
At individual processor level, this trend is also apparent. The percentage of samples in excess of the industry limit (0.00124 mg/kg) in 2021 relative to 2020 decreased from 25% to 8% for processor A, from 15% to 4% for processor B, from 24% to 4% for processor C, from 33% to 16% for processor D and from 18% to 6% for processor E. The levels of TCM detected in milk in 2021 (<0.00010–0.02300 mg/kg) were far lower than those detected in 2020 (<0.00010–0.08100 mg/kg) (Figure 2) (Figures S3 and S4; Supplementary Materials).
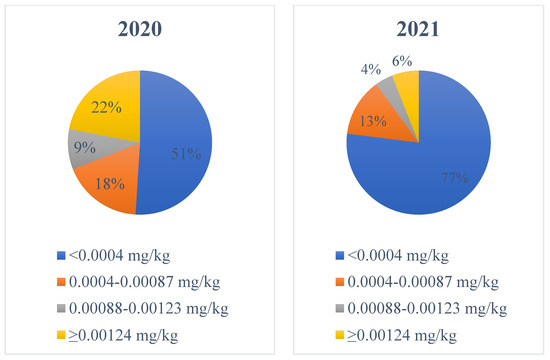
Figure 2.
Breakdown of trichloromethane levels detected in bulk tank milk sampled in 2020 and 2021.
The levels of TCM detected in 2021 were significantly lower than those detected in 2020 in each season, with TCM reducing incrementally between spring 2020 and autumn 2021 (Table 4). This is in contrast to research conducted by [4] where TCM levels in autumn (late lactation) milk were higher than those found in summer (mid-lactation) milk. The trends displayed in this current study are most likely the consequence of the continuous and systematic removal of chlorine from on-farm cleaning. The occurrence of TCM in a minority of milk samples at levels >0.00124 mg/kg in 2021 is likely attributable to the continued use of chlorine on some farms.

Table 4.
Mean trichloromethane (TCM) levels detected in bulk tank milk sampled in spring, summer and autumn of 2020 and 2021.
4. Conclusions
The adoption of ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning on dairy farms in the ROI has led to a reduction in both the levels (mg/kg) and occurrence of both chlorate and TCM residues in bulk tank milk. This is beneficial from a milk processing perspective as it lowers the risk of residues being present in all types of manufactured dairy products, but especially in milk powders (chlorate) and butter (TCM). However, using ‘chlorine-free’ cleaning protocols alone will not totally mitigate against chlorate occurrence because other sources of contamination exist.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/dairy5020023/s1, Figure S1: Chlorate occurrence in milk from each participating processor in 2020; Figure S2: Chlorate occurrence in milk from each participating processor in 2021; Figure S3: Trichloromethane (TCM) occurrence in milk from each participating processor in 2020; Figure S4: Trichloromethane (TCM) occurrence in milk from each participating processor in 2021.
Author Contributions
L.T.—data curation, writing original draft, review and editing; A.F.—review and editing; B.O.—funding acquisition, conceptualisation, administration, review and editing; T.B.—conceptualisation, review and editing; P.R.—statistical analysis, review and editing, M.D.—analysis, review and editing; and D.G.—funding acquisition, conceptualisation, administration, review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by both the Irish Department of Agriculture, Food and Marine (DAFM) as part of the Food Institutional Research Measure (FIRM), Grant number 2019R555, and through Dairy Research Ireland (Project number 1163).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because this research was conducted in conjunction with private companies. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to bernadette.obrien@teagasc.ie.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Aoife McDonald and Rachel Holmes for coordinating samples and TCM analysis and Mary Moloney and Moses Madende for the quantification of chlorate. Lorna Twomey is also in receipt of a Teagasc Walsh Scholarship funded by the DAFM (FIRM) grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ryan, S.; Gleeson, D.; Jordan, K.; Furey, A.; Brien, B.O. Evaluation of trichloromethane formation from chlorine-based cleaning and disinfection agents in cow’s milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2012, 65, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, W.P.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; Danahar, M.; Gleeson, D.; O’Connor, C.; Fenelon, M.A.; Tobin, J.T. Chlorate and other oxychlorine contaminants within the dairy supply chain. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/749 of 4 June 2020 amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for chlorate in or on certain products. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, 63, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Paludetti, L.F.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Brien, B.; Gleeson, D. Monitoring residue concentrations in milk from farm and throughout a milk powder manufacturing process. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, L.; Furey, A.; O’Brien, B.; Beresford, T.P.; Reid, P.; Danaher, M.; Moloney, M.; Madende, M.; Gleeson, D. Chlorate Levels in Dairy Products Produced and Consumed in Ireland. Foods 2023, 12, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, L.; Furey, A.; O’Brien, T.; Beresford, T.; O’Brien, B.; Gleeson, D. An evaluation of dairy product quality where chlorine-free cleaning is employed across the dairy processing chain from bacterial and chemical residue perspectives. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 146, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.; Jordan, S.; Danaher, M. A Winning Formula. TResearch Spring 2023 Edition. 2023. Available online: https://www.teagasc.ie/news--events/daily/food/a-winning-formula.php (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- European Commission. Chlorate. 2024. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/maximum-residue-levels/chlorate_en (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Bord Bia. Dairy from Ireland: Where We Work in Harmony with Nature. Dublin: Bord Bia—Irish Food Bord. 2020. Available online: www.bordbia.info/dairy/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Bord Bia. Trends in the Industry: Butter. 2024. Available online: https://www.bordbia.ie/industry/irish-sector-profiles/dairy-sector-profile/ (accessed on 19 February 2024).
- Fuson, R.C.; Bull, B.A. The haloform reaction. Chem. Rev. 1934, 15, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Gleeson, D.; Jordan, K.; Furey, A.; O’Sullivan, K.; O’Brien, B. Strategy for the reduction of Trichloromethane residue levels in farm bulk milk. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, B. Residues in Milk—An Update on Progress and Ongoing Challenges. Teagasc Milk Quality Webinar. 2021. Available online: https://www.teagasc.ie/media/website/about/research-and-innovation/Residues-in-milk_BOBrien.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Phelan, S. ‘Ornua Moves to Phase out Chlorine-Based Detergents’. Agriland, 1 February 2019. Available online: https://www.agriland.ie/farming-news/ornua-moves-to-phase-out-chlorine-based-detergents/ (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Gleeson, D.; O’Brien, B.; Jordan, K. The effect of using nonchlorine products for cleaning and sanitising milking equipment on bacterial numbers and residues in milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2013, 66, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.; Hennessy, D. Scientific appraisal of the Irish grass-based milk production system as a sustainable source of premium quality milk and dairy products. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2017, 56, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, P.; Guthy, K. Chloroform in milk and dairy products. Part A: Analyzis of chloroform using static headspace gaschromatography. Dtsch. Lebensm.-Rundsch. 1999, 95, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Moloney, M.; Hossain, M.; Danaher, M. Teagasc Accredited Method SOP FADM 530: Determination of Oxyanion Residues in Dairy Products by UHPLC-MS/MS, version 3.0; Teagasc Food Research Centre: Dublin, Irland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, D.; Paludetti, L.; O’Brien, B.; Beresford, T. Effect of chlorine-free cleaning of milking equipment on the microbiological quality and chlorine-related residues in bulk tank milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2022, 75, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, L.; Furey, A.; O’Brien, B.; Beresford, T.; Gleeson, D. Chlorinated water as a source of chlorate contamination in farm bulk milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 77, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, D. Chlorates in Milk—Sample Results to Date [Presentation]. 2023. Available online: https://www.teagasc.ie/media/website/animals/dairy/Chlorates-in-Milk-David-Gleeson.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Lakshmanan, S.; Murugesan, T. The chlor-alkali process: Work in progress. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).