Characterization and Comparison of Lipids in Yak Colostrum, Buffalo Colostrum, and Cow Colostrum Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MS Lipidomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Sample Extraction
2.4. UHPLC-QTOF-MS Analysis
2.5. Lipid Annotation and Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
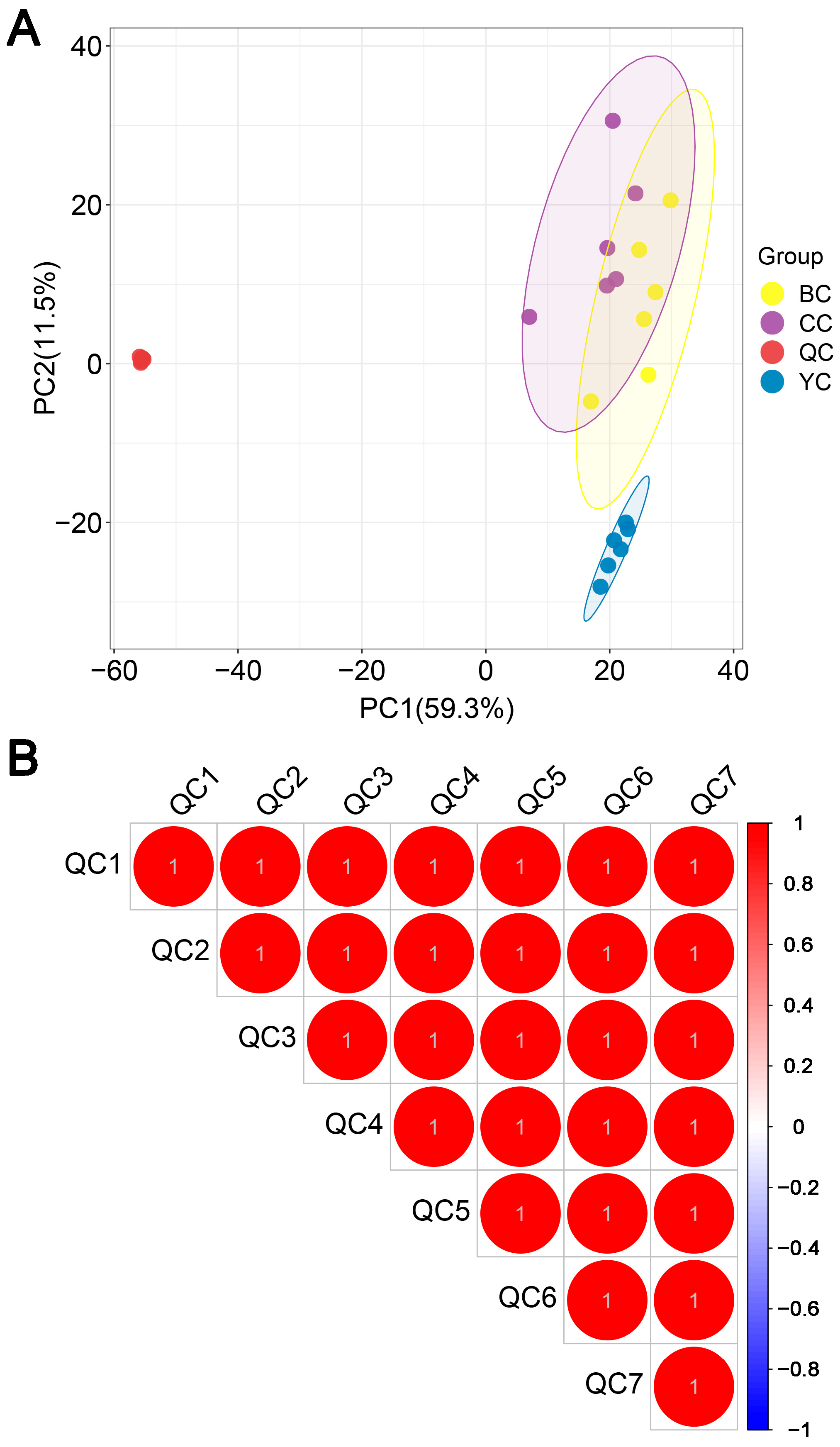
3.1. Feasibility of the Analytical Method
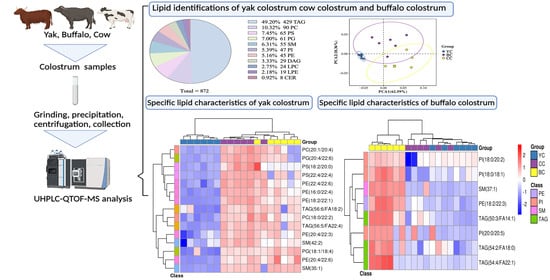
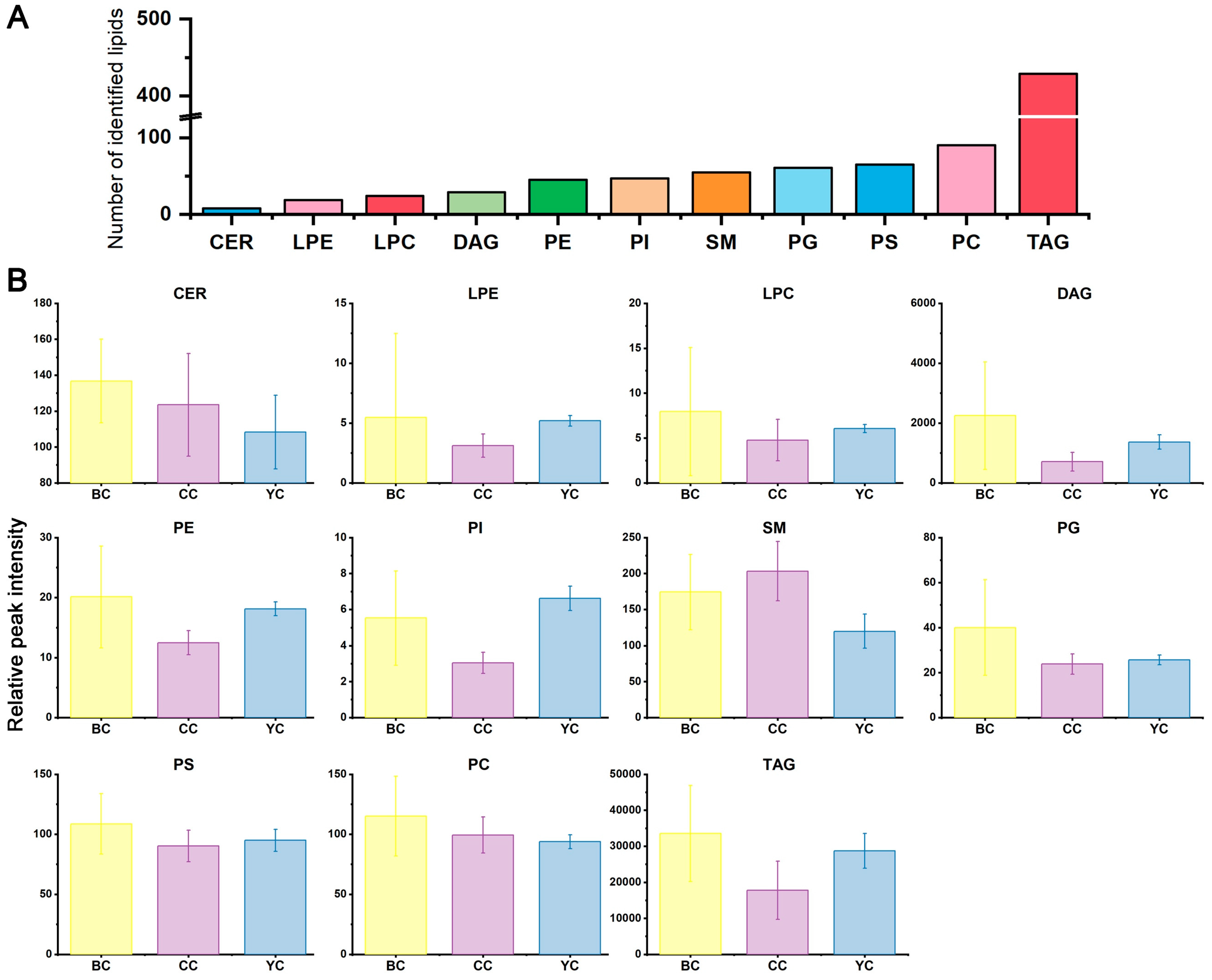
3.2. Lipid Identification of YC, BC, and CC
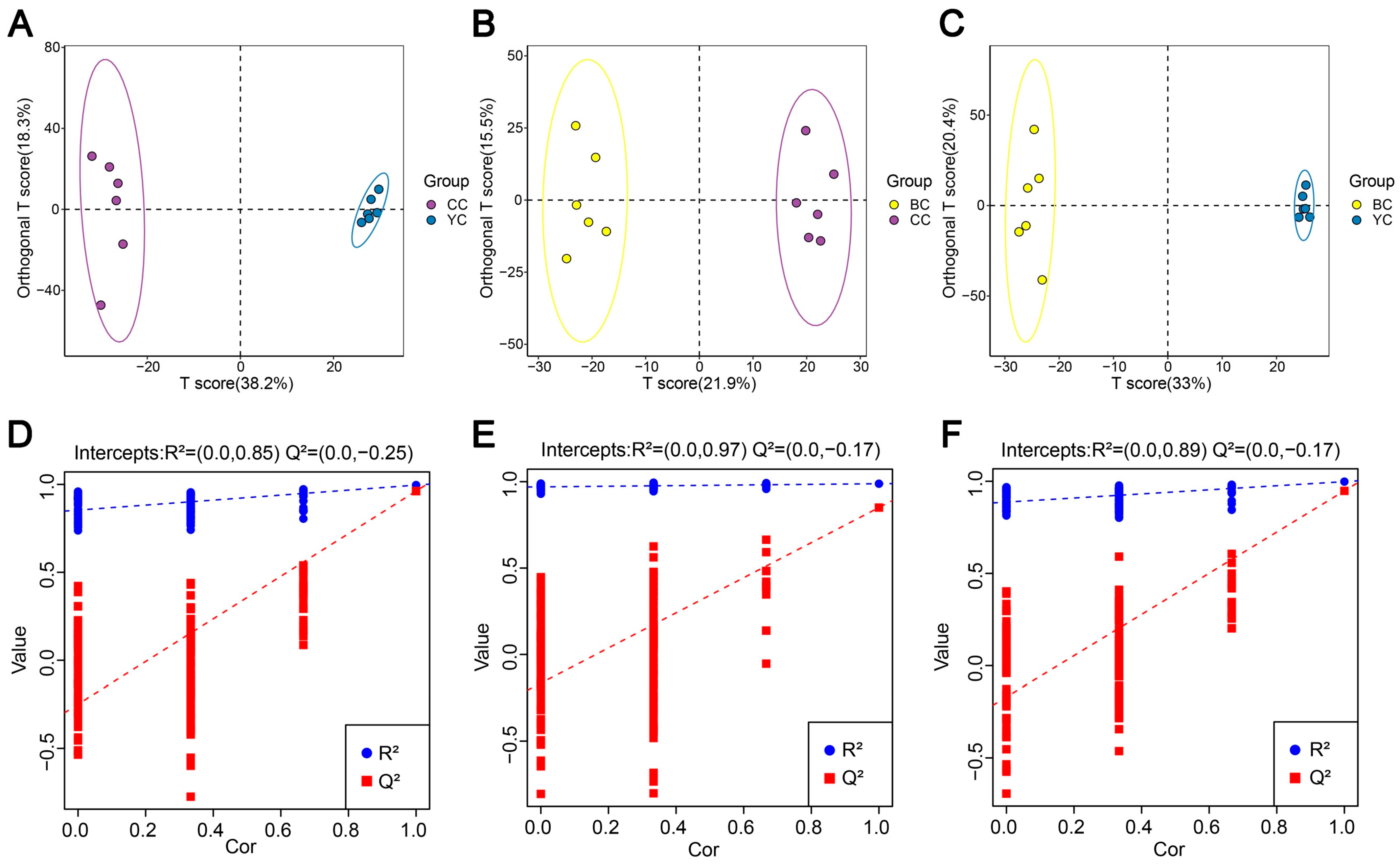
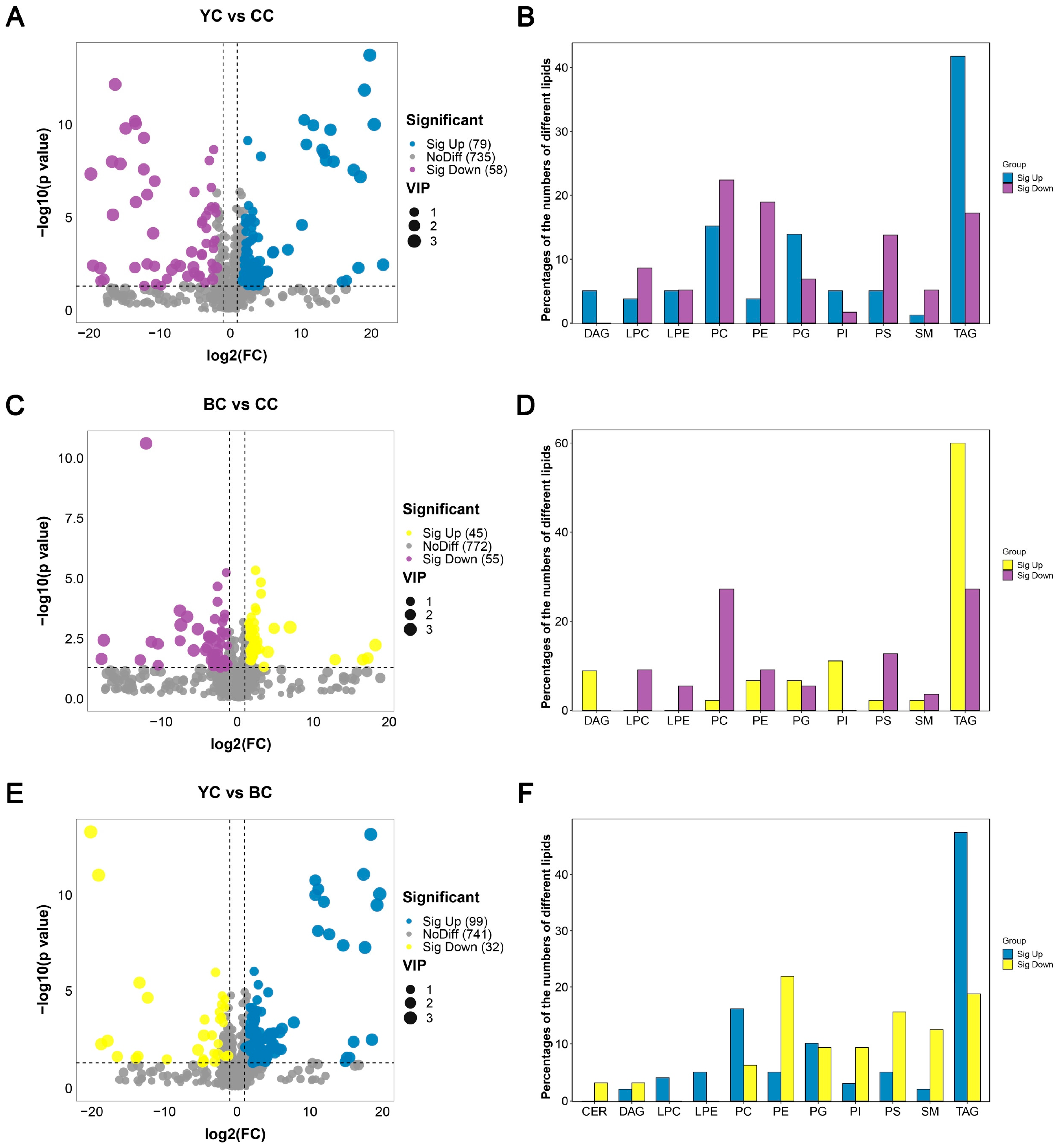
3.3. Multivariate Statistical Comparison of Lipids Between YC, BC, and CC
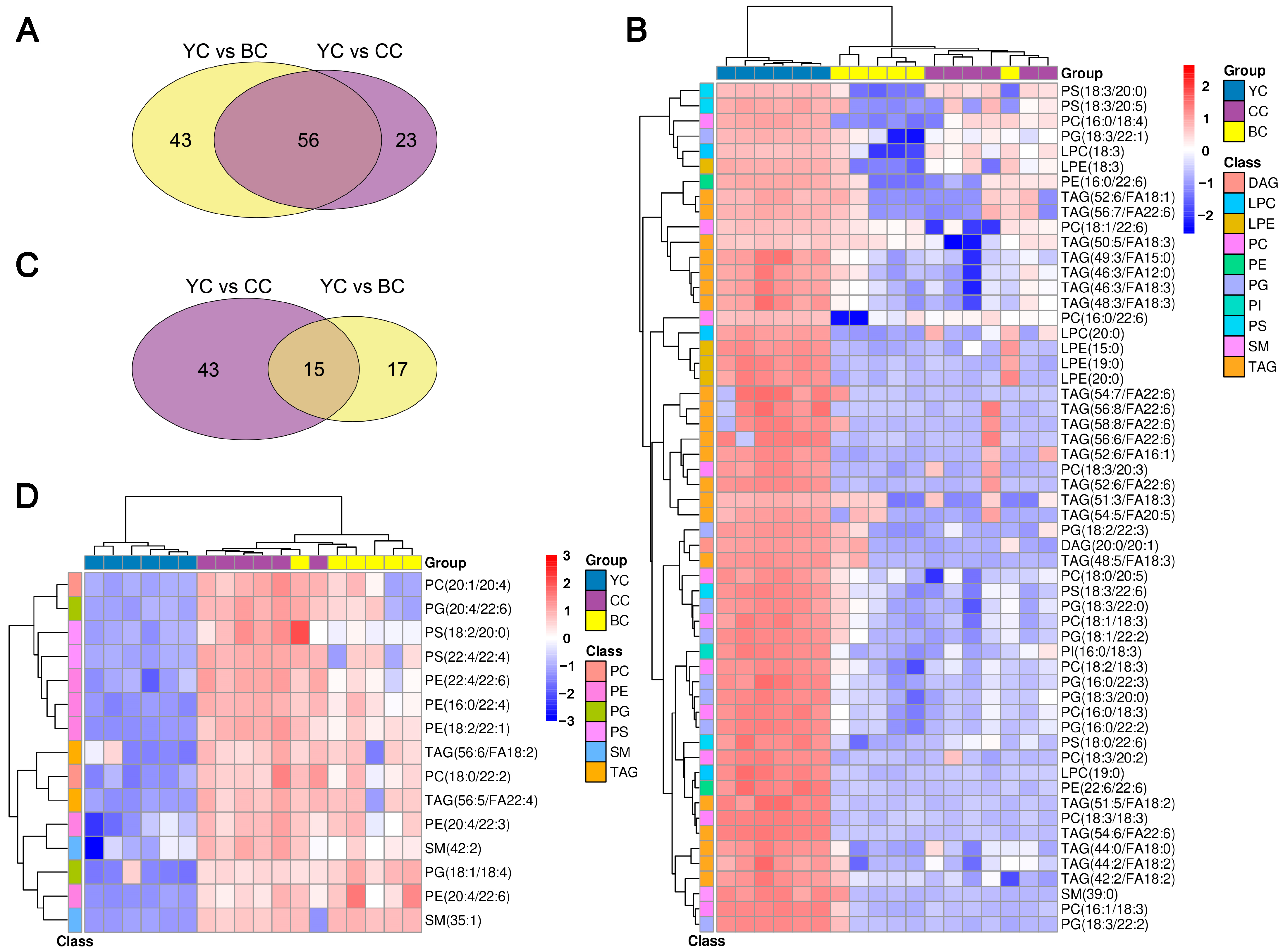
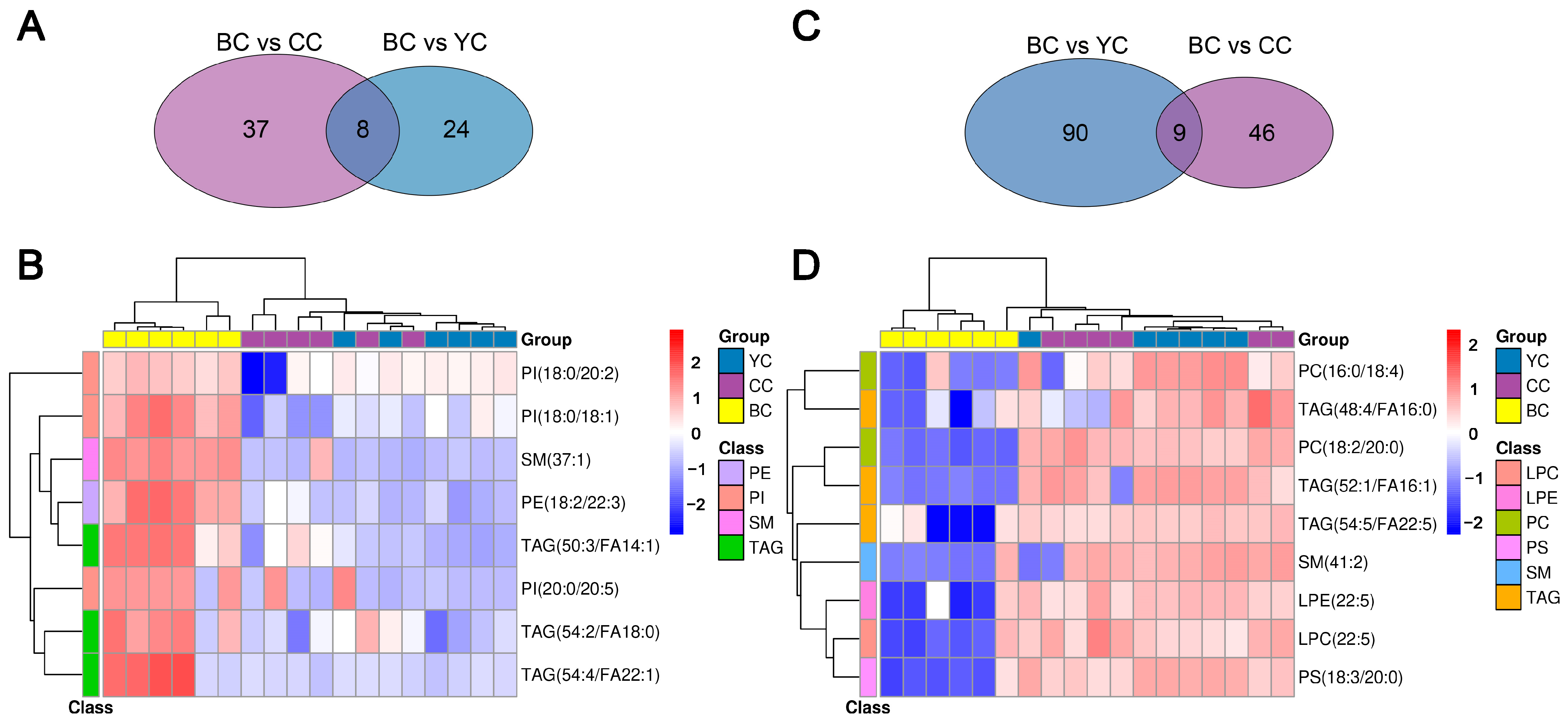
3.4. Identification of DLs Between YC, BC, and CC
3.5. Specific Lipid Characteristics of YC
3.6. Specific Lipid Characteristics of BC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UHPLC-QTOF-MS | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| UPLC-QTOF-MS | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| PLC-QTOF-MS | Performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| YC | Yak colostrum |
| BC | Buffalo colostrum |
| CC | Cow colotrum |
| TAG | Triacylglycerol |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| DLs | Differential lipids |
| QC | Quality control |
| NEG | Negative sample |
| POS | Positive sample |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| DAG | Diacylglycerols |
| VIP | Variable importance values |
| PI | Phosphatidylinositol |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| LPC | Lysophosphatidylcholine |
| LPE | Lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
References
- Han, X. Lipidomics for studying metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, M.; Chia, L.W.; Lambers, T.T. Milk polar lipids composition and functionality: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 31–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Logan, A.; Cocks, B.G.; Rochfort, S. Seasonal variation of polar lipid content in bovine milk. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.S.; Akram, N.; Faisal, Z.; Saeed, F.; Rasheed, A.; Ahmed, F.; Afzaal, M. Bovine colostrum: Therapeutic potential and clinical evidence. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 157, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Lopez, E.; Biber, P.; Sener-Aydemir, A.; Hummel, K.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Reisinger, N.; Zebeli, Q.; Kreuzer-Redmer, S.; Hartinger, T. Characterization of the colostrum proteome of Primiparous Holstein cows and its association with colostrum immunoglobulin G concentrations. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, L.; Xin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fan, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. A systemic review of yak milk and its products on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Unique products, chemical composition, biological activities, and microbial composition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 154, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Pan, L.; Li, W.; Peng, X.; Zhang, M.; Dong, L.; Wang, J.; Gu, R. Comparative analysis of whey proteins in yak milk from different breeds in China using a data-independent acquisition proteomics method. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 106, 3791–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Guo, J.; Duan, H.; Zhou, S.; Yan, W. Yak milk: Nutritional value, functional activity, and current applications. Foods 2023, 12, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Salam, M.H.; El-Shibiny, S. A comprehensive review on the composition and properties of buffalo milk. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2011, 91, 663–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Ramella, M.; Pateiro, M.; Maggiolino, A.; Faccia, M.; Franco, D.; De Palo, P.; Lorenzo, J.M. Buffalo Milk as a source of probiotic functional products. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deverao, P.D.; Vinayak, D.V.; Chandran, D.; Radha, R.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Comparative effect of cooling on the physico-chemical-sensory properties of ghee from cow and buffalo milk, and evaluation of the low-fat spread prepared from cow and buffalo milk ghee. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Mass spectrometry-based lipidomics in food science and nutritional health: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2530–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhu, Q. Comparative lipidomics analysis of human, bovine and Caprine milk by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Leng, Y.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, S. Comparative lipidomic analysis of human, bovine, and caprine milk. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furse, S.; Watkins, A.J.; Koulman, A. Extraction of lipids from liquid biological samples for high-throughput lipidomics. Molecules 2020, 25, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafian, M.H.; Gaudin, M.; Lewis, M.R.; Martin, F.P.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumans, M.E. Objective set of criteria for optimization of sample preparation procedures for ultra-high throughput untargeted blood plasma lipid profiling by ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5766–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wen, B.; Hou, G.; Lei, L.; Mei, Z.; Jia, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Lipidomics profiling reveals the role of glycerophospholipid metabolism in psoriasis. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Comparative lipidomics analysis of human colostrum, mature milk and yak mature milk. Food Chem. 2025, 476, 143396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhu, S.; Weiser, M.; Mao, X. Research advances in the nutrient composition and functional characteristics of bovine colostrum. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Multi-Omics analysis of five species of milk and specific composition links within each species. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, S.S.; Krieger, I.V.; Ann, J.; Lee, J.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Igumenova, T.I. Structural anatomy of protein kinase C C1 domain interactions with diacylglycerol and other agonists. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiowetz, A.J.; Olzmann, J.A. Lipid droplets and cellular lipid flux. Nat. Cell Biol. 2024, 26, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2012, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aralan, A.; Kaplan, M.; Duman, H.; Bayraktar, A.; Erturk, M.; Henrick, B.M.; Frese, S.A.; Karav, S. Bovine colostrum and its potential for human health and nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 651721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, X. Lipid metabolism at membrane contacts: Dynamics and functions beyond lipid homeostasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 615856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, P.; Wang, P.; Chu, M.; Luo, J.; Ren, F.; et al. Untargeted metabolomics reveals key differences between yak, buffalo, and cow colostrum based on UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Foods 2025, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppel, K.; Gołębiewski, M.; Grodkowski, G.; Slósarz, J.; Kunowska-Slósarz, M.; Solarczyk, P.; Łukasiewicz, M.; Balcerak, M.; Przysucha, T. Composition and factors affecting quality of bovine colostrum: A Review. Animals 2019, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, J.B.; Dillard, C.J. Composition, Structure and absorption of milk lipids: A source of energy, fat-soluble nutrients, and bioactive molecules. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 57–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.A.; Golfetto, I.; Ghebremeskel, K.; Min, Y.; Moodley, T.; Poston, L.; Phylactos, A.; Cunnane, S.; Schmidt, W. The potential role for arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids in protection against some central nervous system injuries in preterm infants. Lipids 2003, 38, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. The role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in infant brain development. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 28, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Ye, D.; Yu, R.; Yang, Q. Comprehensive lipidomic profiling of human milk from lactating women across varying lactation stages and gestational ages. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, A.M.; German, J.B.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Mills, D.A. Human milk glycobiome and its impact on the infant gastrointestinal microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4653–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, S.; Ikeda, Y. Regulation of membrane phospholipid biosynthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.N.; Ren, F.Z.; Jiang, L.; Ma, Z.L.; Qiao, H.J.; Zeng, S.S.; Gan, B.Z.; Guo, H.Y. Short communication: Fatty acid profile of yak milk from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in different seasons and for different parities. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabutzki, P.; Schiller, J.; Engel, K.M. Phospholipid-derived lysophospholipids in (patho)physiology. Atherosclerosis 2024, 398, 118569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, B.; Miao, Z. Phosphatidylserine, inflammation, and central nervous system diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 975176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, P.; Wang, P.; Chu, M.; Luo, J.; et al. Characterization and Comparison of Lipids in Yak Colostrum, Buffalo Colostrum, and Cow Colostrum Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MS Lipidomics. Dairy 2025, 6, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy6020014
Li R, Wang Y, Li C, Huang J, Zeng Q, Li L, Yang P, Wang P, Chu M, Luo J, et al. Characterization and Comparison of Lipids in Yak Colostrum, Buffalo Colostrum, and Cow Colostrum Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MS Lipidomics. Dairy. 2025; 6(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy6020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruohan, Yuzhuo Wang, Changhui Li, Jiaxiang Huang, Qingkun Zeng, Ling Li, Pan Yang, Pengjie Wang, Min Chu, Jie Luo, and et al. 2025. "Characterization and Comparison of Lipids in Yak Colostrum, Buffalo Colostrum, and Cow Colostrum Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MS Lipidomics" Dairy 6, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy6020014
APA StyleLi, R., Wang, Y., Li, C., Huang, J., Zeng, Q., Li, L., Yang, P., Wang, P., Chu, M., Luo, J., Ren, F., & Zhang, H. (2025). Characterization and Comparison of Lipids in Yak Colostrum, Buffalo Colostrum, and Cow Colostrum Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MS Lipidomics. Dairy, 6(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy6020014