Abstract
Microdebris are nowadays a new emerging threat to marine ecosystems. Estuarine systems are considered sinks of contaminants, retaining these in their sediments. Nevertheless, baseline studies are essential, especially in reference estuarine systems such as the Mira Estuary, in order to establish reference conditions for other ecosystem assessment studies. Microdebris were extracted by density separation with saturated NaCl from sediment samples collected at the bare intertidal area of the lower sector of the Mira Estuary. Sediment vertical profiles showed a high abundance of microdebris, dominated by spherical and fibre-like microdebris, but also presenting metallic and uncategorized items. It was possible to observe that microdebris accumulation had its maximum concentration at a depth of 10 cm, indicating a recent increase in its usage and prevalence on this estuarine system. Comparing the item density from this work with previous studies on other aquatic ecosystems, it was found that the sediments analysed here present a very high concentration of microdebris. Although the Mira Estuary has been considered as a reference condition for the classical chemical contaminant descriptors considered in the Water Framework Directive, the data here presented indicate that this concept should be revisited adding microdebris contamination.
1. Introduction
Microplastics (MP), plastics debris with a diameter smaller than 5 mm, are widely spread throughout the planet. They have been detected in all marine ecosystems, namely surface and deep waters of oceans, beaches and sediments [,,,,], but also in freshwater ecosystems, such as rivers and lakes [,]. These particles are originated for industrial purposes (primary source), where the particles are produced specifically, as resin pellets, ingredients for cosmetics, such as whitening toothbrushes, face scrubs and body washes [,,], or derived from degradation of larger plastic litter (secondary source) [,,,]. The difficulty of developing a suitable infrastructure of waste management for this type of garbage as well as the ubiquity of these small-sized debris with high environmental persistence, are the main problems associated with this type of pollutant [,].
Once in the environment, microdebris are subjected to physical and chemical processes, leading to changes in their surfaces and making these particles suitable to adsorb contaminants, such as heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants, xenoestrogens and microbial pathogens [,,,,]. Additionally, these microdebris can also be ingested by aquatic organisms, with some studies showing that marine species can confuse MPs with food. This is a problem with serious repercussions in marine food webs and human health, since the ingested microdebris can reach other trophic levels due to biomagnification [,,].
Several studies have reported the presence and effects of microdebris in aquatic and terrestrial environments, leading to an increased concern regarding microdebris presence and temporal distribution in brackish and freshwater ecosystems. Previous studies [] observed an increasing trend in the accumulation of MPs in Belgian beaches over 20 years. Moreover, recent studies verified that upper layers of sediment (more recent) in the Derwent estuary (Tasmania, Australia) presented a higher number of MPs than deeper layers (older) []. The increase in the accumulation of microdebris is in accordance with the increase in plastic production [,]. Estuaries are transitory zones between the river and marine environments, and thus prone to several anthropogenic pressures [,]. Previous studies found the presence of MPs in Portuguese rivers that, consequently, reach estuaries, beaches and ultimately the ocean, affecting inhabiting marine species [,,,,,]. Nevertheless, there is still a gap regarding the vertical distribution of MPs in the sediments of Portuguese estuaries, wetlands and mudflats. These ecosystems are known to accumulate and act as sinks for the so-called classic contaminants over time [,], yet the information on MPs accumulation in these areas is still scarce. Moreover, this information acquires even greater importance if the distribution of these contaminants is considered in so-called reference ecosystems, used for baseline comparisons in biological and chemical quality ecosystem assessments, such as the ones undertaken in compliance with the European Water Framework Directive. Within the spirit of this European directive, these baseline studies, particularly in reference systems, are used for comparison in classification studies of other similar transitional systems, thus becoming essential to correctly classify the level of human pressure in non-reference ecosystems []. The Mira Estuary is a transitional water body situated on the southwest of the coast of Portugal and constitutes a part of the Sudoeste Alentejano e Costa Vicentina Natural Park protected area. This estuary is located in a region with relatively low anthropogenic pressure [,]. This fact allows the use of the Mira Estuary as a reference in diversified studies (e.g., [,]). Hence, it is important to ascertain if the Mira Estuary can be used as a reference for studies of MPs presence in sediments. The present work intents to be a first study regarding the vertical distribution of different types of microdebris in the intertidal sediments of a low-impacted estuary in order to establish a first baseline for this type of contaminant.
2. Materials and Methods
Sampling was carried out at the Mira Estuary (southwest coast of Portugal) in February 2015. Located on the south-western coast of Portugal (37°40′ N, 8°40′ W), the Mira Estuary is a small mesotidal system with a semidiurnal tidal regime (Figure 1). It is formed by a single channel, 5–10 m deep and up to 400 m wide, where the saline tide propagates 40 km upstream. This estuarine system presents a low seasonal and limited freshwater input, with riverine discharges estimates varying from 0 to 500 m3 s−1 during rainy periods in winter and spring []. Mira Estuary tidal ranges vary from 1.0 m at neap tide to 8.9 m at spring tide []. A high degree of asymmetry is evident in the channel currents, with maximum tidal currents speeds varying from 0.3 m s−1 to 1.0 m s−1, presenting a high degree of spatial and fortnightly variability []. Its lower sector presents extensive Zostera noltii meadows, bare sandy areas and muddy substrates, with saltmarshes occurring as far as 20 km upstream []. This system is included within the Natural Park of ‘Sudoeste Alentejano e Costa Vicentina’ and is considered relatively undisturbed and free from industrial pollution [,,]. One sampling site was chosen in the lower estuarine system, in the vicinity of an intertidal area mostly colonized by seagrass meadows (Figure 1). Considering the urbanized (north) side of the estuarine system without natural ecosystems, the south side was chosen to evaluate the levels of microdebris that settle at the mouth of the estuary, aiming to reflect in this way the possible downflow inputs form the river catchment and also the input from the human activities more evident at the lower estuary mouth. Although sampling in only one site is a potential limitation of the present study, this choice was taken considering its location in the vicinity of the largest urban settlement in the estuarine system, in order to understand its effect on the surrounding estuarine ecosystems.
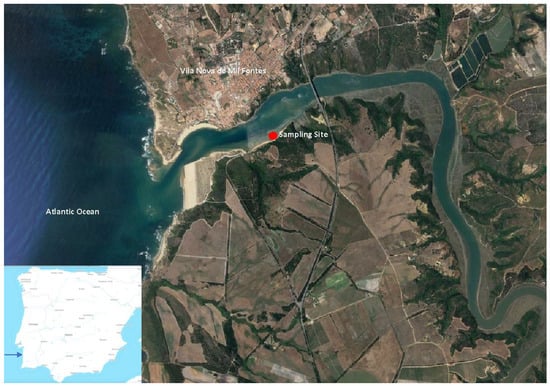
Figure 1.
Mira estuary location and overview and sampling site (∙).
Sediments were sampled at the non-colonized area (bare sediments) using tubular 30 cm polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cores (20 cm diameter, n = 5). The cores were capped to avoid sediment losses and transported back to the laboratory in refrigerated containers. At the laboratory, cores were sliced in 3-cm intervals, and sediment slices were placed in clean glass dishes covered with aluminium foil and oven-dried at 60 °C to a constant weight.
Microdebris were extracted from the sediment samples following the method described by []. All material used for microdebris extraction was pre-soaked in HNO3 10% for 24 h to remove contaminants, fibres and particles, as advised by standardized methods for monitoring microplastics in sediments []. Fifty grams of dried sediment was weighed into a 250 mL glass beaker. Sediment was added with 200 mL of a saturated NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) salt solution (density = 1.20 g/cm3) and stirred using a magnetic stirrer for 5 min. The sediment–water mixture was allowed to settle for 24 h. The supernatant was then carefully filtered through a Whatman GF/F filter (pore size = 0.7 μm) and the extraction procedure repeated until no floating debris were found. Approximately 10 mL of 30% H2O2 (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) was added to the filter to degrade organic matter. Microdebris trapped in the filter were enumerated in a stereoscopic magnifying glass and grouped into morphologically defined categories (spherical pellets, fibres, metallic particles and unclassified). Sodium chloride solution blanks were also performed in order to discard possible contaminations from the extraction solution. All microdebris were expressed as number of particles per sediment dry weight (DW).
Data analysis and visualization were performed using SigmaPlot 12 software (Systat Software, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
Overall, the number of microdebris in the assessed profile ranged from 8.0 to 37.1 particles g−1 DW. About 83%–94% of all the particles detected were found to be spherical plastic pellets (Figure 2). This type of microdebris showed a density range from 6.8 to 33.3 particles per gram of sediment DW. This type of particle showed a more uneven distribution along the analysed profile (variance = 61.6 particles g−1 DW). Fibre-like microdebris were found to be the second most abundant group, accounting for about 3%–8% of all the particles enumerated, ranging from 0.3 to 2.0 particles g−1 DW. Regarding metallic particles, these were found to range from 0 to 0.3 particles g−1 DW, being homogenously distributed along the sediment profile (variance = 0.0 particles g−1 DW). Unclassified microdebris showed a minimum value of 0.2 particles g−1 DW and a maximum value of 1.7 particles g−1 DW, representing 1%–9% of the total microdebris found in the sediment profile. It is interesting to notice that the peak of the abundance of all microdebris types was observed in the layers corresponding to 3–6 cm (metallic particles) and 9–12 cm (spherical and fibre-like particles).
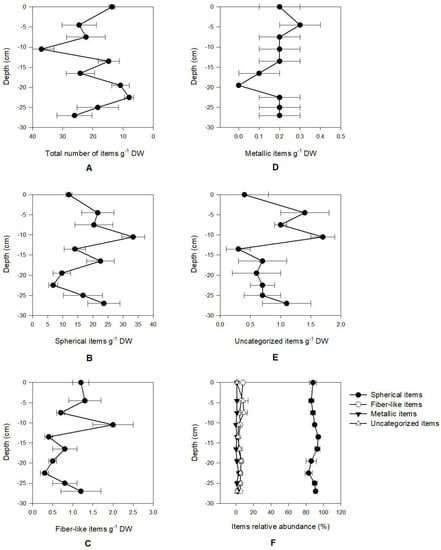
Figure 2.
Microdebris concentration vertical profiles (A—Total; B—Spherical items; C—Fiber-like items; D—Metallic items; E—Unclassified items; average ± standard error, n = 5) and relative abundance by category (F; average ± standard error, n = 5).
Observing the land cover and occupation map of the Mira Estuary (Figure 3), it is possible to observe that the reference/pristine status of this transitional system derives from the reduced urban fabric together with the absence of industrial sites. Nevertheless, the mouth of the estuary harbours a significant port area. This land cover assessment is important to disclose possible microdebris sources. According to previous studies [], the Mira Estuary is under major anthropogenic pressure from wastewater treatment discharges, aquaculture and agriculture activities. Although the port activity does not appear as a major anthropogenic pressure in former studies [], the fishery activities are the major source of fibres alongside with urban wastewater discharges []. Regarding spherical items, these particles are small plastic spheres, manufactured and deliberately included in a number of personal care products, particularly toothpaste and face washes, where particles act as exfoliators [], and thus derive from urban activity, being introduced in the estuarine system urban wastewater discharges. Additionally, some Styrofoam spherical microparticles could be detected, with a probable origin in Styrofoam fish transport boxes (personal observation). Metallic particles may originate from the degradation of marine structures such as pears and harbours, but also from vessels, boats and fishing gear. Nevertheless, although metallic debris are more resistant to mechanical (e.g., wave action) and chemical weathering processes, which largely contribute to the breakage and degradation of plastic debris [], these items were found in small amounts in the surveyed sediment samples.
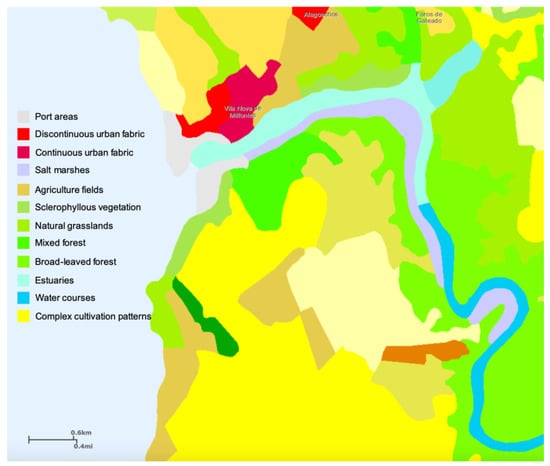
Figure 3.
CORINE Land Cover 2017–2018 (Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 for gap filling) map of the Mira Estuary, with a geometric accuracy ≤ 10 m (Sentinel-2) and thematic accuracy ≥ 85% (https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover) [].
Comparing the total values observed integrating all the particles present in the core volume, and using a sediment density of 1.2 g cm−3 [], it was possible to calculate the microdebris density on a mass and area basis, providing comparable data to previous studies (Table 1). Comparing the total number of items assessed in this study with previous studies, it was possible to observe that the sediments surveyed here presented a very high content in total microdebris. Considering the so-called classical contaminants and ecological quality biotic indexes, this estuarine system is considered as a reference system [,,]. Nevertheless, if the data presented here is taken into account, the same cannot be said in terms of marine litter, as the Mira Estuary sediments present a very high concentration of microdebris when compared to other transitional systems.

Table 1.
Microdebris abundance in the sediments of several aquatic ecosystems.
This high accumulation has serious impacts on estuarine communities, not only directly due to the accumulation and magnification of these microdebris throughout the trophic webs [] but also indirectly affecting other contaminants’ biogeochemistry, availability and transport in the estuarine system [,], with serious implication for the transfer of other contaminants along the trophic segments.
Although very little information exists on the hydrodynamic features that regulate estuarine transport for the Mira system, previous studies [] showed that this system presents lower export rates. These authors point to a low hydrodynamic force with a single outwelling period during the winter season. Thus, the Mira estuary particle transport is ebb-dominated, leading to conservation of the particles generated within its system inside the estuarine system. Considering this and the only urban area present in the Mira estuarine system, the microdebris found in the present study are likely to have originated in this urban settlement, with low transport rates to other areas of the estuary. This reinforces the role of the intertidal areas in the vicinity of the anthropogenic settlements of the Mira Estuary as potentially good areas for monitoring the presence of microdebris.
4. Conclusions
The results presented here show that this estuarine system has a concentration of microdebris items stored in its sediments, which have serious impacts on biological quality elements (BQEs) such as invertebrates and fishes. With the present work, it is possible to observe that there is a chronological deposition of microdebris in this estuarine system, with a particular emphasis on the period 1990–2004. Although the Mira Estuary is considered a reference condition for the classical chemical contaminant descriptors considered in the Water Framework Directive, this concept should be revisited, adding microdebris contamination to this classification scheme, in order to better understand how these emerging contaminants will impact the ecological quality status (EQS) established by the application of the BQEs biotic indexes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.D.; methodology, E.M.; validation, B.D., I.C.; formal analysis, B.D.; investigation, E.M.; data curation, B.D.; writing—original draft preparation, B.D.; writing—review and editing, E.M., I.C.; supervision, I.C.; project administration, I.C.; funding acquisition, B.D., I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) for funding the research via project grants PTDC/CTA-AMB/30056/2017 (OPTOX) and UIDB/04292/2020. B. Duarte was supported by an investigation contract (CEECIND/00511/2017).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, A.M. Organic pollutants in microplastics from two beaches of the Portuguese coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1988–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Gago, J.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P. Microplastics in coastal sediments from Southern Portuguese shelf waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 114, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP Sources. Fate and effects of MP in the marine environment. J. Ser. GESAMP Rep. Stud. 2015, 90, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Officer, R.; Lyashevska, O.; Thompson, R.C.; O’Connor, I. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition along a latitudinal gradient in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D.; Smit, A.J. Plastic pollution in five urban estuaries of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Plastic Waste: Ecological and Human Health Impacts. Sci. Environ. Policy 2011, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhomme, S.; Cuer, A.; Delort, A.M.; Lemaire, J.; Sancelme, M.; Scott, G. Environmental biodegradation of polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 81, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M. Leaching of plastic additives to marine organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chatterjee, S. Microplastic pollution, a threat to marine ecosystem and human health: A short review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21530–21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; De Meester, S.; Van Landuyt, L.; De Clerck, K.; Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K.A.; Eriksen, R.; Wilcox, C.; Hardesty, B.D. Microplastic distribution at different sediment depths in an urban estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Neto, J.M.; Marques, J.C.; Adams, J.B.; Caçador, I. Marine angiosperm indices used to assess ecological status within the Water Framework Directive and South African National Water Act: Learning from differences and common issues. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Caçador, I. Particulate metal distribution in Tagus estuary (Portugal) during a flood episode. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, F.; Barría, P.; Neto, J.M.; Frias, J.P.G.L.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P.; Marques, J.C. Occurrence of microplastics in commercial fish from a natural estuarine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, P.M.; Serra-Gonçalves, C.; Ferreira, J.L.; Catry, T.; Granadeiro, J.P. Plastic and other microfibers in sediments, macroinvertebrates and shorebirds from three intertidal wetlands of southern Europe and west Africa. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.; Sobral, P. Plastic marine debris on the Portuguese coastline: A matter of size? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, B.; Caetano, M.; Almeida, P.R.; Vale, C.; Caçador, I. Accumulation and biological cycling of heavy metal in four salt marsh species, from Tagus estuary (Portugal). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Caçador, I.; Marques, J.C.; Croudace, I.W. Tagus estuary salt marshes feedback to sea level rise over a 40-year period: Insights from the application of geochemical indices. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Valiela, I.; Freitas, H. Eutrophication in Portuguese estuaries evidenced by δ15N of macrophytes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 351, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duarte, B.; Pedro, S.; Marques, J.C.; Adão, H.; Caçador, I. Zostera noltii development probing using chlorophyll a transient analysis (JIP-test) under field conditions: Integrating physiological insights into a photochemical stress index. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caçador, I.; Neto, J.M.; Duarte, B.; Barroso, D.V.; Pinto, M.; Marques, J.C. Development of an Angiosperm Quality Assessment Index (AQuA-Index) for ecological quality evaluation of Portuguese water bodies—A multi-metric approach. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 25, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.P.; Reis-Santos, P.; Tanner, S.; Fonseca, V.; Latkoczy, C.; Günther, D.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H. Discriminating estuarine nurseries for five fish species through otolith elemental fingerprints. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 350, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, J.O.; Ferreira, M.A.; Andrade, F.A. Effect of a broad shallow sill on tidal circulation and salt transport in the entrance to a coastal plain estuary (Mira—Vila Nova de Milfontes, Portugal). Estuaries 2000, 23, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, V.; Paula, J. Carcinus maenas (Crustacea: Brachyura): Influence of artificial substrate type and patchiness on estimation of megalopae settlement. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2007, 346, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Catarino, F.; Bettencourt, A. The role of salt marshes in the mira estuary (portugal). Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 9, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Pagter, E.; Nash, R.; O’Connor, I.; Carretero, O.; Filgueiras, A.; Viñas, L.; Gago, J.; Antunes, J.; Bessa, F.; et al. Standardised protocol for monitoring microplastics in sediments. JPI Ocean. BASEMAN Proj. 2018, 33. [Google Scholar]
- CORINE Land Cover 2017–2018. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Vasconcelos, R.P.; Reis-Santos, P.; Fonseca, V.; Maia, A.; Ruano, M.; França, S.; Vinagre, C.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H. Assessing anthropogenic pressures on estuarine fish nurseries along the Portuguese coast: A multi-metric index and conceptual approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmão, F.; Di Domenico, M.; Amaral, A.C.Z.; Martínez, A.; Gonzalez, B.C.; Worsaae, K.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Cunha Lana, P. In situ ingestion of microfibres by meiofauna from sandy beaches. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Qiao, F.; Liu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Qi, H.; Cui, S.; Yue, X.; Deng, Y.; An, L. Microplastics releasing from personal care and cosmetic products in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viehman, S.; Vander Pluym, J.L.; Schellinger, J. Characterization of marine debris in North Carolina salt marshes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olson, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Ivleva, N.P.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Laforsch, C. Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R867–R868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L. Distribution and degradation of fresh water plastic particles along the beaches of Lake Huron, Canada. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, L.; Cheung, P.K. Hong Kong at the Pearl River Estuary: A hotspot of microplastic pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Su, J.; Xiong, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, J. Microplastic pollution of lakeshore sediments from remote lakes in Tibet plateau, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, C.C.; Lockridge, G.R.; Battiste, D.; Cebrian, J. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in beach sediments: Insights into microplastic accumulation in northern Gulf of Mexico estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, J.C.; Frias, J.G.L.; Micaelo, A.C.; Sobral, P. Resin pellets from beaches of the Portuguese coast and adsorbed persistent organic pollutants. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthy, S.; Ramasamy, E.V. Microplastic pollution in Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: The first report of microplastics in lake and estuarine sediments in India. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbery, M.; O’Connor, W.; Palanisami, T. Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.M.R.; Manjate, E.; Ramos, S. Adsorption of Cd and Cu to different types of microplastics in estuarine salt marsh medium. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, A.M.M.; Neves, R.J.J.; Lanca, M.J.; Batista, P.J.; Alves, M.J. Uncertainties in import/export studies and the outwelling theory. An analysis with the support of hydrodynamic modelling. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1995, 42, 734–735. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).