Need for the Scuba Diving Industry to Interface with Science and Policy: A Case of SIDS Blue Workforce
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Conceptual Framework, Materials, and Methods
2.1. Conceptual Framework
2.2. Methods and Materials
3. Results
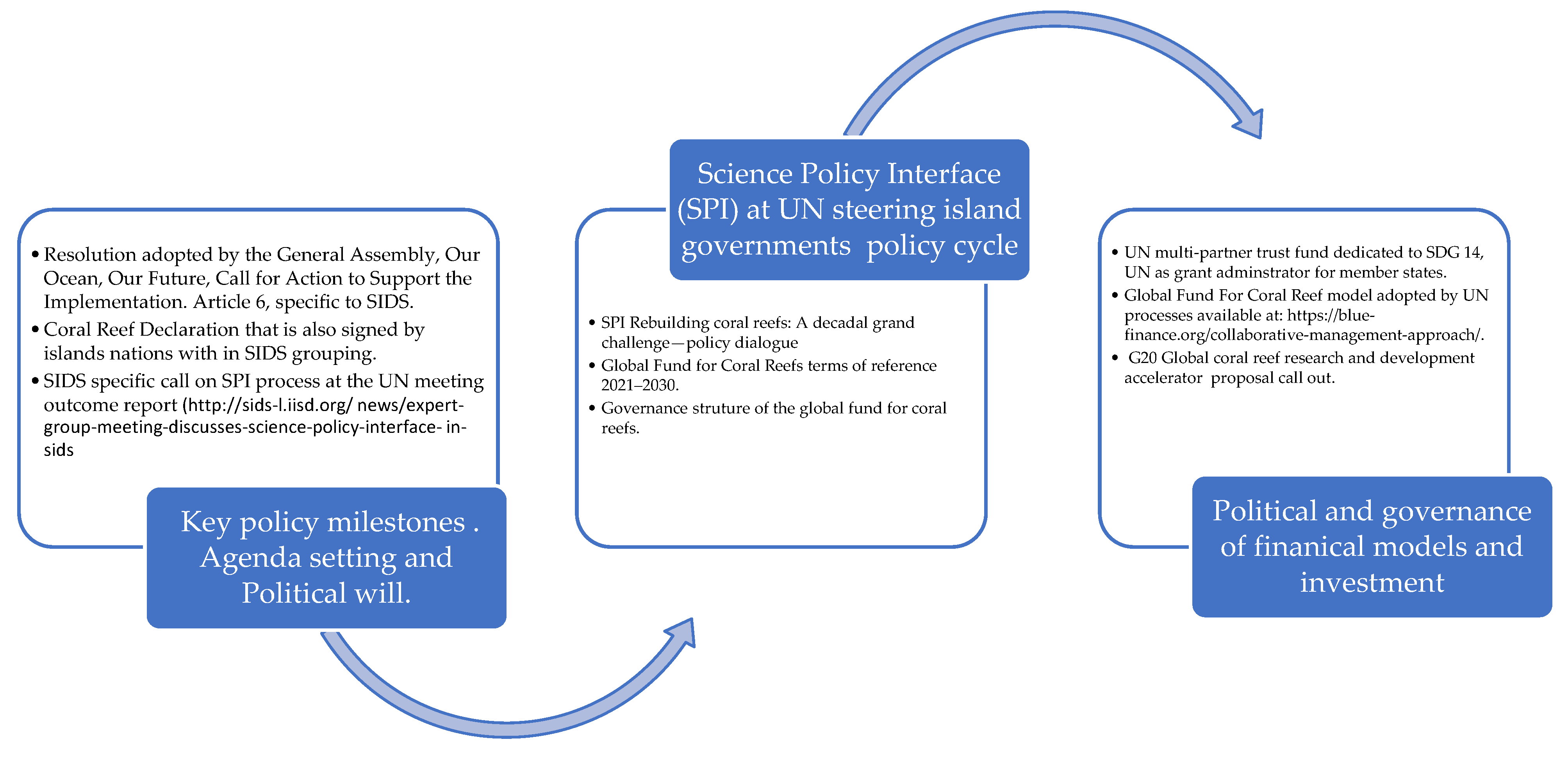
3.1. SIDs Governance Regime Shifts Provide a New Institutional Outlook and Processes for Old Problems
- (a)
- SDG 14.7 is a politically agreed target that positions and provides clear boundaries between industralised and non-industralised nations at the UN and the role of policy evidence to serve the island member states.
- (b)
- SDG 14.7–also provides direct links to SDG 8 targets pertaining to the International Labor Organisation for fisheries and tourism sectors to reskill and modernise [25,41]. The synergetic nature of SDG 14.7 also links to the ODA partnerships (SDG 17.3), collaboration, and interaction between strategic stakeholders, industry, educational institutions, and government agencies [41].
- (c)
- SDG 14.7–is time-bounded and must be achieved by 2030 hence requires policy mechanisms for building a competent islands’ blue workforce. The target sets the boundaries and differential needs of island nations under climate change and ocean goals.
3.2. Demands to Integrate Blue Skills within Island Coral Reef Economic Sectors and Industry Careers
3.3. Closing the Gap between the Diving Industry and Island Governments in Their Blue Economy Workforce Preparation
4. Discussion: The Role of Island Policymakers
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN-OHRLLS. Small Island Developing States in Numbers: Biodiversity & Oceans. 2019. Available online: http://unohrlls.org (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- UN. Global Sustainable Development Report. 2015. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/publications/global-sustainable-development-report-2015-edition.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- UNDESA. Partnerships for Small Islands Developing States. 2019. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/24591SIDS_Partnerships_May_2019_web.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- UN Environment; ISU; Trucost, I. The Coral Reef Economy: The Business Case for Investment in the Protection, Preservation, and Enhancement of Coral Reef Health. 2018. Available online: www.unenvironment.org (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Watson, C.; Schalatek, L.; Evequoz, A. Accessing Climate Finance: Small Island Developing States; Heinrich Böll Stiftung: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Analysis of Policies Related to the Protection of Coral Reefs-Analysis of Global and Regional Policy Instruments and Governance Mechanisms Related to the Protection and Sustainable Management of Coral Reefs; UN Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sumaila, U.R.; Walsh, M.; Hoareau, K.; Cox, A.; Teh, L.; Abdallah, P.; Akpalu, W.; Anna, Z.; Benzaken, D.; Crona, B.; et al. Financing a sustainable ocean economy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Kennedy, E.V.; Beyer, H.L.; McClennen, C.; Possingham, H.P. Securing a Long-term Future for Coral Reefs. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN Environment and International Coral Reef Initiative UN Environment World Conservation Monitoring Centre. Analysis of International Funding for the Sustainable Management of Coral Reefs and Associated Coastal Ecosystems; UN Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden-kerby, A. Coral-Focused Climate Change Adaptation and Restoration Based on Accelerating Natural Processes: Launching the “Reefs of Hope ’Paradigm”. Oceans 2022, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, E.J.; Pascua, P.; Sigouin, A.; Gazit, N.; Mandle, L.; Betley, E.; Aini, J.; Albert, S.; Caillon, S.; Caselle, J.E.; et al. Creating a space for place and multidimensional well-being: Lessons learned from localizing the SDGs. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 15, 1129–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, P.M. Science-Policy Interfaces: From Warnings to Solutions. 2022. Available online: https://www.iisd.org/articles/science-policy-interfaces (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Polejack, A.; Coelho, L.F. Ocean Science Diplomacy can Be a Game Changer to Promote the Access to Marine Technology in Latin America and the Caribbean. Front. Res. Metrics Anal. 2021, 6, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hove, S.V.D. A rationale for science-policy interfaces. Futures 2007, 39, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConney, P.; Fanning, L.; Mahon, R.; Simmons, B. A first look at the science-policy interface for ocean governance in the Wider Caribbean Region. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UNCTAD. The Oceans Economy: Opportunities and Challenges for Small Island Developing States; UNCTAD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UN-OHRLLS. Small Island Developing States in Numbers: Climate Change Edition 2015. 2015. Available online: http://unohrlls.org/custom-content/uploads/2015/12/SIDS-IN-NUMBERS-CLIMATE-CHANGE-EDITION_2015.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- World Bank and United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. The Potential of the Blue Economy: Increasing Long-Term Benefits of the Sustainable Use of Marine Resources for Small Island Developing States and Coastal Least Developed Countries; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.W.; Forsyth, C. Restoring near-shore marine ecosystems to enhance climate security for island ocean states: Aligning international processes and local practices. Mar. Policy 2018, 93, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. OurCommon Future: Report ofthe 1987 WorldCommission on Environment and Development; United Nations: Oslo, Norway, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- UNCED. United Nations Sustainable Development: United Nations Conference on Environment & Development Rio de Janerio, Brazil, 3 to 14 June 1992 AGENDA 21, United Nations Division for Sustainable Development. 1992. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/Agenda21.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Griggs, D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Gaffney, O.; Rockström, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Shyamsundar, P.; Steffen, W.; Glaser, G.; Kanie, N.; Noble, I. Sustainable Development Goals for People and Planet. Nature 2013, 495, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, S.; Dalal-Clayton, B. Small Island States and Sustainable Development: Strategic Issues and Experience; International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED): London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal-Clayton, B.; Bass, S. The challenges of environmental mainstreaming. In Experience of Integrating Environment into Development Institutions and Decisions; International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED): London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nisa, Z.A. The role of marine and diving authorities in workforce development in the blue economy. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-DESA. Review of Partnerships for Small Island Developing States; UN-DESA: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zitoun, R.; Sander, S.; Masque, P.; Pijuan, S.; Swarzenski, P.W. Review of the Scientific and Institutional Capacity of Small Island Developing States in Support of a Bottom-up Approach to Achieve Sustainable Development Goal 14 Targets. Oceans 2020, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. UNEP: A Global Venture to Make Green Fins Standards on Sustainable Diving the Social Norm. 2018. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/press-release/global-venture-make-green-fins-standards-sustainable-diving-social (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Morrison, T.H.; Adger, N.; Barnett, J.; Brown, K.; Possingham, H.; Hughes, T. Advancing Coral Reef Governance into the Anthropocene. One Earth 2020, 2, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, A.M.; Moncada, S.; Mycoo, M.; Nunn, P.; Tandrayen-Ragoobur, V.; Evans, C. Small Island Developing States in a post-pandemic world: Challenges and opportunities for climate action. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, M.; Olsen, S.H. The Design of Environmental Priorities in the SDGs. Glob. Policy 2019, 10, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Institute for Global Environmental Strategies. Realising the Transformative Potential of the SDGs; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Kanagawa, Japan, 2018; Available online: https://pub.iges.or.jp/pub/realising-transformative-potential-sdgs (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Osiecka, A.N.; Quer, S.; Wróbel, A.; Osiecka-Brzeska, K. Unpaid Work in Marine Science: A Snapshot of the Early-Career Job Market. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Putten, I.; Cvitanovic, C.; Fulton, E.A. A changing marine sector in Australian coastal communities: An analysis of inter and intra sectoral industry connections and employment. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 131, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, N.; Grottoli, A.G.; Kleypas, J.; Obura, D.; Corcoran, E.; de Goeij, J.M.; Felis, T.; Harding, S.; Mayfield, A.; Miller, M.; et al. Rebuilding Coral Reefs: A Decadal Grand Challenge; International Coral Reef Society and Future Earth Coasts: Glasgow, Scotland, 2021; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Von Schuckmann, K.; Holland, E.; Haugan, P.; Thomson, P. Ocean science, data, and services for the UN 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. Mar. Policy 2020, 121, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.T.; Gibbs, B.L.; Newlands, M.; Ivey, J. Scaling up the global reef restoration activity: Avoiding ecological imperialism and ongoing colonialism. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNGA. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 25th Semptember 2015. A/RES/70/1. Available online: https://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/70/1&Lang=E (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- UNCTAD. Advancing Sustainable Development Goal 14: Sustainable Fish, Seafood Value Chains, Trade and Climate. 2019. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/ditcted2019d3_en.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Le Blanc, D. Towards Integration at Last? The Sustainable Development Goals as a Network of Targets. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, Z.A.; Schofield, C.; Neat, F.C. Work Below Water: The role of scuba industry in realising sustainable development goals in small island developing states. Mar. Policy 2022, 136, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, D.; Freire, C.; Vierros, M. Mapping the Linkages between Oceans and Other Sustainable Development Goals: A preliminary exploration. DESA Working Paper No. 149. 2017. Available online: http://www.un.org/en/development/desa/papers/ (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Stockholm Environment Institute. Sustainable Development Goal Interactions through a Climate Lens: A Global Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://www.sei.org/publications/sdg-interactions-climate-global/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI). ICRI Forum 2017: SDG 14; Coral Reef Life Declaration 2017. Available online: https://www.icriforum.org/document-types/coral-reefs-and-international-agreements/ (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- UNDESA. In-Depth Analysis of Ocean Conference Voluntary Commitments to Support and Monitor Their Implementation SDG 14. 2017. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/17193OCVC_in_depth_analysis.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- UNDP. Global Fund for Coral Reefs Terms of Reference 2020–2030. 2020. Available online: https://globalfundcoralreefs.org (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Österblom, H.; Cvitanovic, C.; van Putten, I.; Addison, P.; Blasiak, R.; Jouffray, J.-B.; Bebbington, J.; Hall, J.; Ison, S.; LeBris, A.; et al. Science-Industry Collaboration: Sideways or Highways to Ocean Sustainability? One Earth 2020, 3, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österblom, H.; Jouffray, J.-B.; Folke, C.; Crona, B.; Troell, M.; Merrie, A.; Rockström, J. Transnational corporations as ‘keystone actors’ in marine ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.K.; Kim, K.; Choi, H.Y. A Research on safety rules for safe scuba diving. Rev. Int. Geogr. Educ. Online 2021, 11, 365–376. [Google Scholar]
- Divers Alert Network. Annual Diving Report 2019 Edition—A Report on 2017 Diving Fatalities, Injuries and Incidents; Divers Alert Network: Durham, NC, USA, 2019; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Diver Accreditation Scheme (ADAS). Career Opportunities | Occupational Diver Certification. 2021. Available online: https://adas.org.au/careers/ (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- EDA. Divers for the Environment Magazine; Emirates Diving Assoication (EDA): Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2019; Available online: https://issuu.com/allylandes/docs/eda_march_issue_2019_issuu (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Roberts, J.; Ali, A.; The Blue Economy and Small States. Commonwealth Blue Economy Series, No. 1. 2016. Available online: http://www.jgme.org/doi/10.4300/JGME-D-15-00414.1 (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Hawke, C. Oceans and small island states: First think opportunity, then think blue. In UNDP: Our Perspectives; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/blog/2017/2/22/Oceans-and-small-island-states-First-think-opportunity-then-think-blue.html (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Odume, O.N.; Amaka-Otchere, A.B.; Onyima, B.N.; Aziz, F.; Kushitor, S.B.; Thiam, S. Pathways, contextual and cross-scale dynamics of science-policy-society interactions in transdisciplinary research in African cities. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 125, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, D.B.; Cvitanovic, C.; van Putten, I.E.; Colvin, R.M.; Armitage, D.; Aswani, S.; Ballesteros, M.; Ban, N.C.; Barragán-Paladines, M.J.; Bednarek, A.; et al. Lessons from bright-spots for advancing knowledge exchange at the interface of marine science and policy. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 114994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J. Qualitative inquiry and research design. In Choosing among Five Approaches; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bardach, E.; Patashnik, E.M. A Practical Guide for Policy Analysis Fifth Edition; CQ Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods, 6th ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, N. SDG Synergies: An Approach for Coherent 2030 Agenda Implementation; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Weitz, N.; Carlsen, H.; Nilsson, M.; Skånberg, K. Towards systemic and contextual priority setting for implementing the 2030 agenda. Sustain. Sci. 2017, 13, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, M.; Griggs, D.; Visbeck, M. Policy: Map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature 2016, 534, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blythe, J.L.; Armitage, D.; Bennett, N.J.; Silver, J.J.; Song, A.M. The Politics of Ocean Governance Transformations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNGA. Our Oceans, Our Future: Call for Actions, Resolution Adopted by the General Assesmbly on 6 July 2017, A/RES/71/312; UNGA: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 11370, pp. 1–6. Available online: https://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/71/312&Lang=E (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- United National Development Programme (UNDP). SDG Accelerator and Bottleneck Assessment. 2017. Available online: https://www.undp.org/content/dam/undp/library/SDGs/English/SDG_Accelerator_and_Bottleneck_Assessment_Tool.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2022).
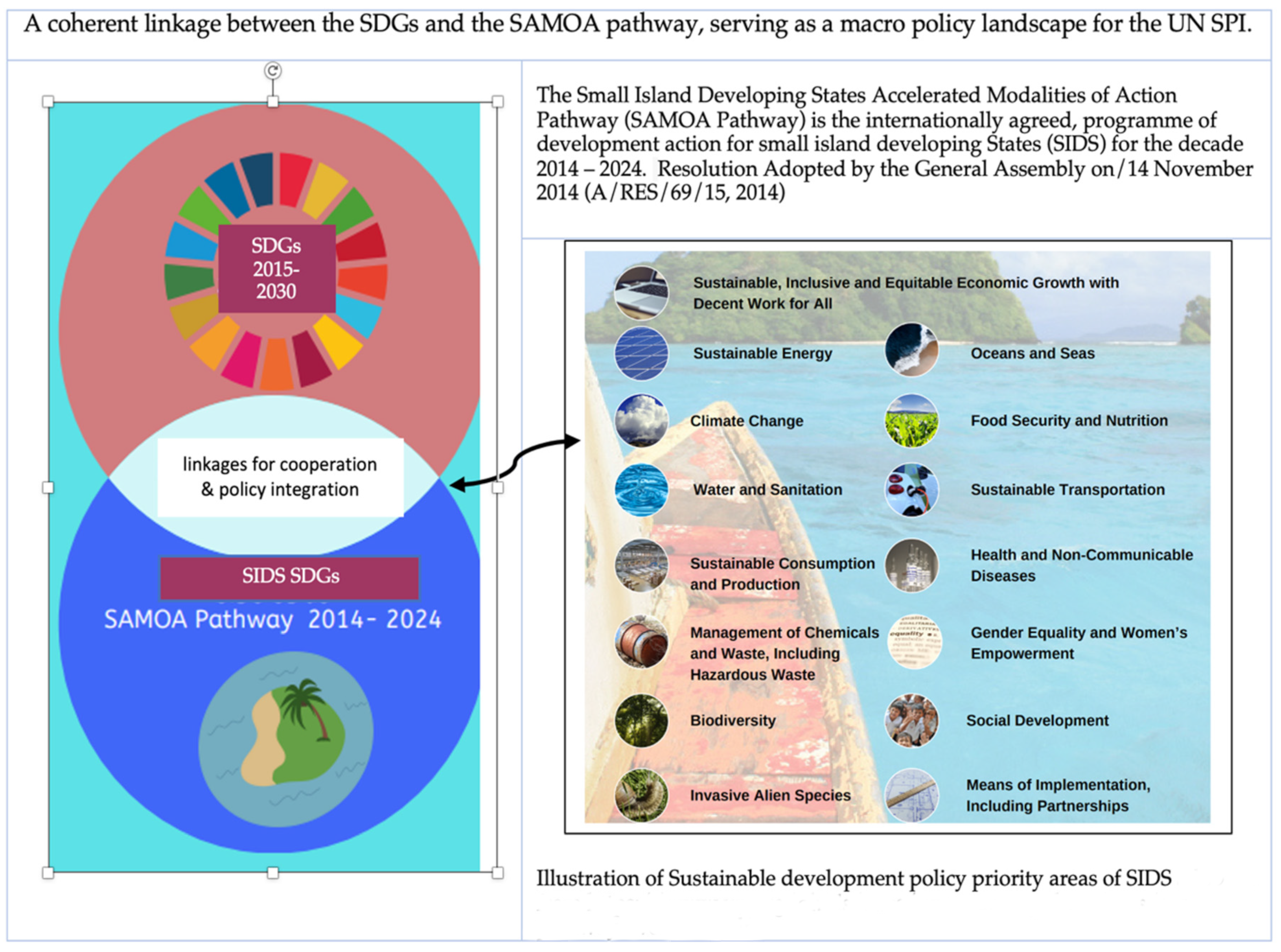
- UNGA. SIDS Accelerated Modalities of Action (SAMOA) Pathway, Resolution Adopted by the General Assesmbly on/14 November 2014. A/RES/69/15. 2014. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/ares69d15_en.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Global Ocean Commisson (GOC). From Decline to Recovery: A Rescue Package for the Global Ocean; Global Ocean Commisson (GOC): Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chasek, P.S.; Wagner, L.M.; Leone, F.; Lebada, A.; Risse, N. Getting to 2030: Negotiating the Post-2015 Sustainable Development Agenda. ev. Eur. Comp. Int. Environ. Law 2016, 25, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Neumann, B.; Waweru, Y.; Durussel, C.; Unger, S.; Visbeck, M. SDG 14 conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development. In A Guide to SDG Interactions: From Science to Implementation, International Council for Science; Nilsson, M.D., Griggs, A.-S., Stevance, D., McCollum, Eds.; ICSU: Paris, France, 2017; pp. 174–218. [Google Scholar]
- ESCAP. Leveraging Ocean Resources for Sustainable Development of Small Island Developing States.Asia-Pacific Countries with Special Needs Development Report; ESCAP: Bangkok, Thailand, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Conservation Finance Alliance, Global Fund for Coral Reefs Investment Plan 2021. Available online: https://www.conservationfinancealliance.org/gfcrhttps (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- UN General Assembly. Global Indicator Framework for the Sustainable Development Goals and Targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/indicators/database/archive (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Bautista-Puig, N.; Aleixo, A.; Leal, S.; Azeiteiro, U.; Costas, R. Unveiling the Research Landscape of Sustainable Development Goals and Their Inclusion in Higher Education Institutions and Research Centers: Major Trends in 2000–2017. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Secchi, M.; Corrado, S.; Beylot, A.; Sala, S. Assessing the decoupling of economic growth from environmental impacts in the European Union: A consumption-based approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheel, C.; Aguiñaga, E.; Bello, B. Decoupling economic development from the consumption of finite resources using circular economy. A model for developing countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UNCTAD. Achieving the Targets of Sustainable Development Goal 14: Sustainable Fish and Seafood Value Chains and Trade for the Second Oceans Forum; UNCTAD/DITC/TED/MISC/2018/2; UNCTAD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Quirk, G.; Hanich, Q.A. Ocean Diplomacy: The Pacific Island Countries’ Campaign to the UN for an Ocean Sustainable Development Goal. Asia-Pacific J. Ocean Law Policy 2016, 1, 68–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ILO. Decent Work in Caribbean Small Island Developing States; ILO Publications: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ILO. Decent Work and Social Justice in Pacific Small Island Developing States. Challenges, Opportunities and Policy Responses. ILO Publications: Geneva, Switzerland. 2014. Available online: www.ilo.org/publns (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- Greenhill, L.; Hughes, A.; Day, J.; Stanley, M.S. Blue Knowledge—Developing knowledge to support transition to a Blue Economy: A strategic approach. Isl. Stud. 2015, 3, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Blue Ribbon Panel to the Global Partnership for Oceans. Indespensible Ocean: Aligning Ocean Health and Human Well-Being. 2013. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/2013/10/18516203/indispensable-ocean-aligning-ocean-health-human-well-being-guidance-blue-ribbon-panel-global-partnerships-oceans (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Grégoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garçon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Isensee, K.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spalding, M.; Burke, L.; Wood, S.A.; Ashpole, J.; Hutchison, J.; zu Ermgassen, P. Mapping the global value and distribution of coral reef tourism. Mar. Policy 2017, 82, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, M.; Longley-wood, K.; Cole, A.; Wood, S.; Christopher, H.; Zach, F. Estimating Reef-Adjacent Tourism Value in the Caribbean. 2018. Available online: https://oceanwealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Reef-Adjacent-Tourism-Value-Caribbean-Study.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Peterson, R.R.; DiPietro, R.; Harrill, R. In search of inclusive tourism in the Caribbean: Insights from Aruba. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. Themes 2020, 12, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Business of Diving Institute (BDI). Analysing the SCUBA Diving Industry for the Purpose of Developing Strategies. 2018. Available online: https://www.scubanomics.com/dive-industry/business-marketing-analysis/ (accessed on 16 March 2020).
- UNCTAD. Sustainable Fisheries: International Trade, Trade Policy and Regulatory Issues; UNCTAD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- UNWTO. Tourism in Small Island Developing States (SIDS) Tourism—Fostering Growth and Development; UNWTO: Madrid, Spain, 2014; p. 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Business of Diving Institute (BDI). The Lack of Scuba Diving Industry Statistics & Market Data. 2019. Available online: https://medium.com/scubanomics/the-lack-of-scuba-diving-industry-statistics-market-data-bd0e409256da (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Musa, G.; Dimmock, K. The Business of SCUBA Diving. In Scuba Diving Tourism; Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lucrezi, S.; Egi, S.M.; Pieri, M.; Burman, F.; Ozyigit, T.; Cialoni, D.; Thomas, G.; Marroni, A.; Saayman, M. Safety priorities and underestimations in recreational scuba diving operations: A European study supporting the implementation of new risk management programmes. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tourtas, A.; Papadimitriou, K.; Karadimou, E.; Schill, R.O. Diving as a Scientist: Training, Recognition, Occupation—The ‘Science Diver’ Project. In Underwater Work, Edited by Sérgio António Neves Lousada; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanoudis, P.V.; Licuanan, W.; Morrison, T.; Talma, S.; Veitayaki, J.; Woodall, L.C. Turning the tide of parachute science. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R184–R185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafford-Smith, M.; Griggs, D.; Gaffney, O.; Ullah, F.; Reyers, B.; Kanie, N.; Stigson, B.; Shrivastava, P.; Leach, M.; O’Connell, D. Integration: The key to implementing the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Sci. 2016, 12, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orecchini, F.; Valitutti, V.; Vitali, G. Industry and academia for a transition towards sustainability: Advancing sustainability science through university-business collaborations. Sustain. Sci. 2012, 7, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNIDO. UNIDO’s Small Island Developing States Strategy, 2019–2025; UNIDO: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.unido.org/sids (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- NOAA. Diving Manual, Dving for Science and Technology, 6th ed.; NOAA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- PADI. Worldwide Corporate Statistics; PADI: Rancho Santa Margarita, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. Available online: https://www.padi.com/sites/default/files/documents/2019-02/2019PADIWorldwideStatistics.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- CMAS. CMAS International Diver Training Standards and Procedures Manual; CMAS: Frisco, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]

| SAMOA Pathway: Oceans and Seas Policy Priorities in Parallel with SDG 14, Life Below Water. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SIDS Oceans and Seas section Para 58 a- p SIDS Accelerated Modalities of Action (SAMOA) Pathway, Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on/14 November 2014. A/RES/69/15, 2014) | Corresponding SDG 14 targets | ||
| a | Sustainably use the oceans, seas and their resources by supporting research and the implementation of strategies on coastal zone management and ecosystem-based management. | 14.7 | Sustainable use of marine resources, including through sustainable management of fisheries, aquaculture, and tourism. |
| b | Engage in national and regional efforts to sustainably develop the ocean resources of small island developing states and generate increasing returns for their peoples. | 14.7 | Increase the economic benefits to small island developing states and least developed countries from the sustainable use of marine resources. |
| c | Protection of regional seas | 14.2 | Sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems to avoid significant adverse impacts, including by strengthening their resilience and acting for their restoration to achieve healthy and productive oceans. |
| d | Mitigate marine pollution | 14.1 | Prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution. |
| e | To undertake urgent action to protect coral reefs and other vulnerable marine ecosystems through the development and implementation of comprehensive and integrated approaches for managing and enhancing their resilience to withstand pressures. | 14.2 | Sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems to avoid significant adverse impacts, including by strengthening their resilience and acting for their restoration to achieve healthy and productive oceans. |
| f | Marine scientific research | 14. a | Increase scientific knowledge, develop research capacity and transfer marine technology. |
| g | To enhance and implement the monitoring, control and surveillance of fishing vessels to effectively prevent, deter and eliminate illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, including through institutional capacity-building at the appropriate levels. | 14. a | transfer marine technology to improve ocean health and to enhance the contribution of marine biodiversity to the development of developing countries, |
| h | To support the sustainable development of small-scale fisheries, improved mechanisms for resource assessment and management and enhanced facilities for fisheries workers, as well as initiatives that add value to outputs from small-scale fisheries and to enhance access. | 14. b | Provide access for small-scale artisanal fishers to marine resources and markets. |
| i | Reform fishery subsidies | 14.6 | Prohibit certain forms of fisheries subsidies which contribute to overcapacity and overfishing, and eliminate subsidies that contribute to illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing. |
| j | Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage | No correlating targets. | |
| k | promote the conservation, sustainable use and management of straddling and highly migratory fish stocks, including through measures that benefit Small Island Developing States. | 14.4 | Effectively regulate harvesting and end overfishing, illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing and destructive fishing practices and implement science-based management plans, |
| l | Enhance the capacity for SIDS to use their fisheries resources and develop fisheries-related industries, enabling them to maximise benefits from their fisheries resources and ensure that the burden of conservation and management of ocean resources is not disproportionately transferred to Small Island Developing States. | 14.7 | By 2030, increase the economic benefits to small island developing States and least developed countries from the sustainable use of marine resources, including through sustainable management of fisheries, aquaculture and tourism. |
| m | Cooperation of the international community in implementing shared responsibilities under regional fisheries management organisations | No correlating targets. | |
| N | Mitigate ocean acidification | 14.3 | Minimise and address the impacts of ocean acidification. |
| O | To protect 10 per cent of coastal and marine areas | 14.5 | By 2020, conserve at least 10 per cent of coastal and marine areas. |
| p | To prevent toxic waste disposal | 14.1 | By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nisa, Z.A. Need for the Scuba Diving Industry to Interface with Science and Policy: A Case of SIDS Blue Workforce. Oceans 2023, 4, 132-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4020010
Nisa ZA. Need for the Scuba Diving Industry to Interface with Science and Policy: A Case of SIDS Blue Workforce. Oceans. 2023; 4(2):132-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNisa, Zahidah Afrin. 2023. "Need for the Scuba Diving Industry to Interface with Science and Policy: A Case of SIDS Blue Workforce" Oceans 4, no. 2: 132-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4020010
APA StyleNisa, Z. A. (2023). Need for the Scuba Diving Industry to Interface with Science and Policy: A Case of SIDS Blue Workforce. Oceans, 4(2), 132-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4020010





