Nitrogen and Phosphorus Discharges from Cargo Ships’ Black and Grey Waters—A Case Study of a Baltic Sea Port
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How much phosphorus and nitrogen (in kilograms) has been generated on board cargo ships (from black and grey water) during their voyages in the Baltic Sea to the designated port?
- What proportion of the wastewater is discharged into the port?
- What are the emission shares from different ship types?
- How significant are these emissions in relation to all sources of nitrogen and phosphorus discharges in the area?
2. Materials and Methods
- Number of vessels and vessel types;
- Distance from the previous port (in the Baltic Sea) to the case port;
- Speed of the vessels;
- Number of crew members on board;
- Daily amount of nitrogen and phosphorus in grey water and black water typically produced per person.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- How much phosphorus and nitrogen (in kilograms) was generated on board of the cargo ships (from black and grey water) during their voyages in the Baltic Sea to the designated port?
- What proportion of the wastewater is discharged into the port?
- What are the emission shares from different ship types?
- How significant are these emissions in relation to all sources of nitrogen and phosphorus discharges in the area?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Review of Maritime Transport 2021; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2021; eISSN: 2225-3459. [Google Scholar]
- Jägerbrand, A.K.; Brutemark, A.; Svedén, J.B.; Gren, I.-M. A review on the environmental impacts of shipping on aquatic and nearshore ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjidian, J. Clean Baltic Sea Shipping; ResearchGate; 2013. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291338320_Clean_Baltic_Sea_Shipping (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Helsinki Commission (HELCOM). Reinforcing Oil Spill Response Capacity in the Baltic; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Conley, D.J. Save the Baltic Sea. Nature 2012, 486, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellesen, T.; Broeg, K.; Dorgeloh, E.; Joswig, M.; Heitmüller, S. A Technical Guidance for the Handling of Wastewater in Ports of the Baltic Sea Special Area under MARPOL Annex IV; Helsinki Commission—HELCOM, Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Helsinki Commission (HELCOM). Baltic Sea Action Plan 2021 Update; HELCOM: Helsinki, Finland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Savchuk, O.P.; Eilola, K.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Medina, M.R.; Ruoho-Airola, T. Long-Term Reconstruction of Nutrient Loads to the Baltic Sea, 1850–2006; Technical Report No. 6; Baltic Nest Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Raudsepp, U.; Maljutenko, I.; Kõuts, M.; Granhag, L.; Wilewska-Bien, M.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Eriksson, K.M.; Johansson, L.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Karl, M.; et al. Shipborne nutrient dynamics and impact on the eutrophication in the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Wilewska-Bien, M.; Granhag, L.; Ytreberg, E.; Eriksson, K.M.; Yngsell, D.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Magnusson, K.; Raudsepp, U.; et al. Modeling of discharges from Baltic Sea shipping. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency; European Maritime Safety Agency. European Maritime Transport Environmental Report 2021; Publications Office. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/55fefc4e-0ebb-11ec-b771-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Moldanová, J.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Matthias, V.; Fridell, E.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Ytreberg, E.; Quante, M.; Tröltzsch, J.; Maljutenko, I.; Raudsepp, U.; et al. Framework for the environmental impact assessment of operational shipping. Ambio 2022, 51, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, S.-T.; Kotta, J.; Tombak, M.-L.; Tapaninen, U. Using Machine Learning Methodology to Model Nutrient Discharges from Ports: A Case Study of a Fertilizer Terminal. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StatFin. International Sea Transport by Port and Commodity Group by Commodity Group. Statistics Finland’s Free-of-Charge Statistical Database. Available online: https://pxdata.stat.fi/PxWeb/pxweb/en/StatFin/ (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- HaminaKotka. The Biggest Universal Port in Finland. Available online: https://www.haminakotka.com/about-port/biggest-universal-port-finland (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Finnish Transport Infrastructure Agency. Trans-European Transport Network TEN-T; 11 August 2020. Available online: https://vayla.fi/en/transport-network/transport-system/ten-t (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- HELCOM Map and Data Service. Available online: https://maps.helcom.fi/website/mapservice/index.html (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Anttila-Huhtinen, M. Water Monitoring in Kotka Port Areas in 2020; Research Report No. 514/2021; Water and Environment Association of the River Kymijoki: Tampere, Finland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nakari, H.; Anttila-Huhtinen, M. Monitoring Report of Waters at Pyhtää-Kotka-Hamina Sea Area; Report No. 311/2022; Water and Environment Association of the River Kymijoki: Tampere, Finland, 2022; ISSN 2670-2177. [Google Scholar]
- Helsinki Commission (HELCOM). Copenhagen Ministerial Declaration, Taking Further Action to Implement the Baltic Sea Action Plan—Reaching Good Environmental Status for a Healthy Baltic Sea; 3 October 2013. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/2013-Copenhagen-Ministerial-Declaration-w-cover-1.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- International Maritime Organization (IMO). MARPOL Annex IV, Regulations for the Prevention of Pollution by Sewage from Ships, 2022th ed.; International Maritime Organization (IMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization (IMO). MEPC.227(64) Resolution, 2012 Guidelines on Implementation of Effluent Standards and Performance Tests for Sewage Treatment Plants; International Maritime Organization (IMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wilewska-Bien, M.; Anderberg, S. Reception of sewage in the Baltic Sea—The port´s role in the sustainable management of ship wastes. Mar. Policy 2018, 93, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT). Policy Update; International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT): Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Port of HaminaKotka, Kotka, Finland. Unpublished work. 2021.
- MarineTraffic. Distance Calculation Tool. Available online: www.marinetraffic.com (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Agarwal, M. What Is The Speed of a Ship at Sea? Marine Insight, 26 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, J. Study of Grey Water Samples from Cargo and Passenger Ships and an Assessment of the Impacts of Wastewater on the Marine Environment; Research Report No. 519/2021; Water and Environment Association of the River Kymijoki: Tampere, Finland, 2021; ISSN 2670-2185. [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson, H.; Baky, A.; Jeppsson, U.; Hellström, D.; Kärrman, E. Composition of Urine, Feaces, Greywater and Bio-Waste for Utilisation in the URWARE Model. 2005. Available online: https://www.iea.lth.se/publications/Reports/LTH-IEA-7222.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Baltic Sea Action Group (BSAG). Available online: https://www.bsag.fi/ajankohtaista/rahtialusten-jatevedet-kertovat/ (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- HaminaKotka. Sewage from Cargo Ships Turned into Biogas. News from the Port. Available online: https://www.haminakotka.com/news-from-the-port/sewage-cargo-ships-turned-biogas (accessed on 13 April 2024).
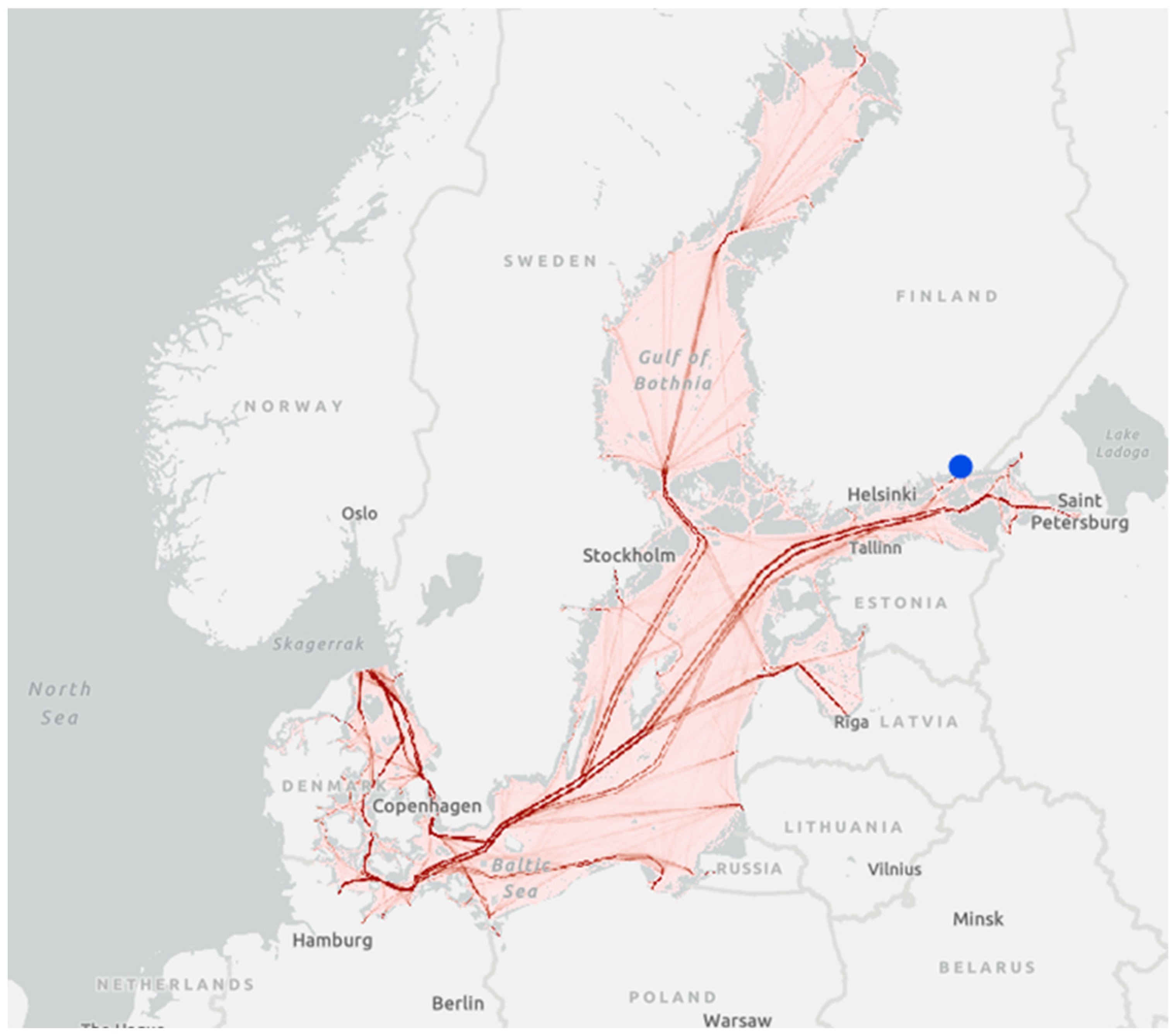
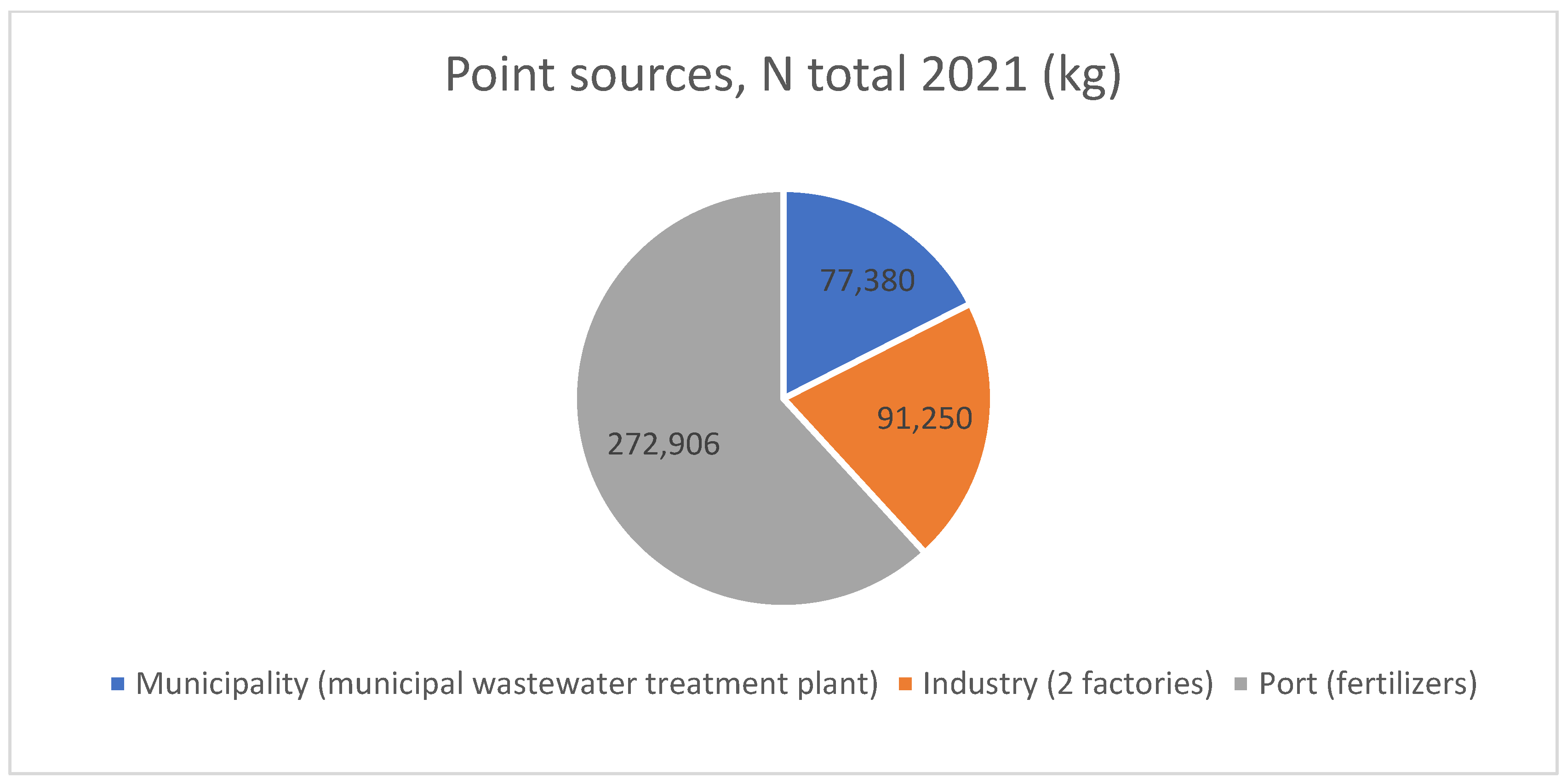


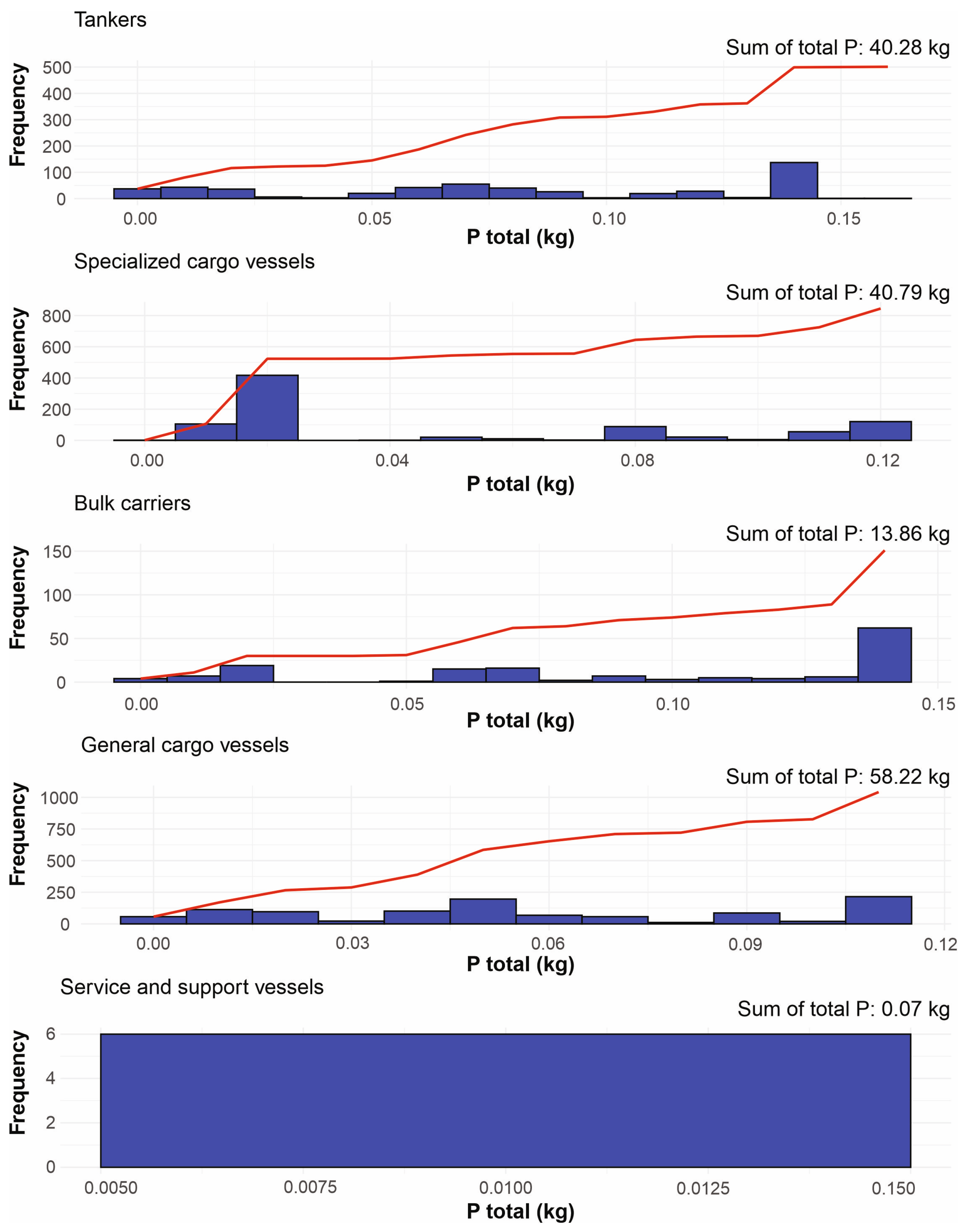
| Ship Type | Number of Ships [25] | Ships’ Speed [27] | Persons On Board [28] | P in GW [10] | P in BW [10] | N in GW [10] | N in BW [10] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Container | 431 | 20 | 19 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 16 |
| Tanker | 501 | 15 | 17 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 16 |
| Bulk carrier | 151 | 14 | 15 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 16 |
| Tug | 6 | 10 | 4 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 16 |
| General cargo | 1042 | 12 | 10 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 16 |
| Roro | 414 | 19 | 17 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 16 |
| 2021 | Nitrogen (kg) | Phosphorus (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Black water (sewage) | 612.9 | 61.3 |
| Grey water | 168.5 | 72.8 |
| TOTAL | 781.4 | 134.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lappalainen, S.-T.; Tapaninen, U.; Kotta, J. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Discharges from Cargo Ships’ Black and Grey Waters—A Case Study of a Baltic Sea Port. Oceans 2024, 5, 560-570. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5030032
Lappalainen S-T, Tapaninen U, Kotta J. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Discharges from Cargo Ships’ Black and Grey Waters—A Case Study of a Baltic Sea Port. Oceans. 2024; 5(3):560-570. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleLappalainen, Suvi-Tuuli, Ulla Tapaninen, and Jonne Kotta. 2024. "Nitrogen and Phosphorus Discharges from Cargo Ships’ Black and Grey Waters—A Case Study of a Baltic Sea Port" Oceans 5, no. 3: 560-570. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5030032
APA StyleLappalainen, S.-T., Tapaninen, U., & Kotta, J. (2024). Nitrogen and Phosphorus Discharges from Cargo Ships’ Black and Grey Waters—A Case Study of a Baltic Sea Port. Oceans, 5(3), 560-570. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5030032








